by Scott Muniz | May 10, 2021 | Security, Technology
This article is contributed. See the original author and article here.
| amazon — freertos |
The kernel in Amazon Web Services FreeRTOS before 10.4.3 has insufficient bounds checking during management of heap memory. |
2021-05-03 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-32020
MISC |
| apache — airflow |
The “origin” parameter passed to some of the endpoints like ‘/trigger’ was vulnerable to XSS exploit. This issue affects Apache Airflow versions <1.10.15 in 1.x series and affects 2.0.0 and 2.0.1 and 2.x series. This is the same as CVE-2020-13944 & CVE-2020-17515 but the implemented fix did not fix the issue completely. Update to Airflow 1.10.15 or 2.0.2. Please also update your Python version to the latest available PATCH releases of the installed MINOR versions, example update to Python 3.6.13 if you are on Python 3.6. (Those contain the fix for CVE-2021-23336 https://nvd.nist.gov/vuln/detail/CVE-2021-23336). |
2021-05-02 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-28359
MISC
MLIST |
| apache — unomi |
Apache Unomi prior to version 1.5.5 allows CRLF log injection because of the lack of escaping in the log statements. |
2021-05-04 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-31164
MISC |
| artica — pandora_fms_742 |
A remote file inclusion vulnerability exists in Artica Pandora FMS 742, exploitable by the lowest privileged user. |
2021-05-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-32100
MISC
MISC
MISC |
| artica — pandora_fms_742 |
Artica Pandora FMS 742 allows unauthenticated attackers to perform Phar deserialization. |
2021-05-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-32098
MISC
MISC
MISC |
| artica — pandora_fms_742 |
A SQL injection vulnerability in the pandora_console component of Artica Pandora FMS 742 allows an unauthenticated attacker to upgrade his unprivileged session via the /include/chart_generator.php session_id parameter, leading to a login bypass. |
2021-05-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-32099
MISC
MISC
MISC |
asus — gt-ac2900_devices
|
The administrator application on ASUS GT-AC2900 devices before 3.0.0.4.386.42643 allows authentication bypass when processing remote input from an unauthenticated user, leading to unauthorized access to the administrator interface. This relates to handle_request in router/httpd/httpd.c and auth_check in web_hook.o. An attacker-supplied value of ” matches the device’s default value of ” in some situations. |
2021-05-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-32030
MISC
MISC |
| avahi — avahi |
A flaw was found in avahi 0.8-5. A reachable assertion is present in avahi_s_host_name_resolver_start function allowing a local attacker to crash the avahi service by requesting hostname resolutions through the avahi socket or dbus methods for invalid hostnames. The highest threat from this vulnerability is to the service availability. |
2021-05-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-3502
MISC
MISC |
| btcpay_server — btcpay_server |
BTCPay Server through 1.0.7.0 suffers from directory traversal, which allows an attacker with admin privileges to achieve code execution. The attacker must craft a malicious plugin file with special characters to upload the file outside of the restricted directory. |
2021-05-05 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-29246
MISC
MISC |
| btcpay_server — btcpay_server |
BTCPay Server through 1.0.7.0 uses a weak method Next to produce pseudo-random values to generate a legacy API key. |
2021-05-05 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-29245
MISC
MISC |
| btcpay_server — btcpay_server |
BTCPay Server through 1.0.7.0 suffers from a Stored Cross Site Scripting (XSS) vulnerability within the POS Add Products functionality. This enables cookie stealing. |
2021-05-05 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-29250
MISC
MISC |
| btcpay_server — btcpay_server |
BTCPay Server through 1.0.7.0 could allow a remote attacker to obtain sensitive information, caused by failure to set the Secure flag for a cookie. |
2021-05-05 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-29248
MISC
MISC |
| btcpay_server — btcpay_server |
BTCPay Server through 1.0.7.0 could allow a remote attacker to obtain sensitive information, caused by failure to set the HTTPOnly flag for a cookie. |
2021-05-05 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-29247
MISC
MISC |
| centreon_web — centreon_web |
Insecure Permissions in Centreon Web versions 19.10.18, 20.04.8, and 20.10.2 allows remote attackers to bypass validation by changing any file extension to “.gif”, then uploading it in the “Administration/ Parameters/ Images” section of the application. |
2021-05-04 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-26804
MISC |
| chamilo — chamilo |
Chamilo LMS 1.11.10 does not properly manage privileges which could allow a user with Sessions administrator privilege to create a new user then use the edit user function to change this new user to administrator privilege. |
2021-05-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-23128
CONFIRM
MISC |
cisco — broadworks_messaging_server_software
|
A vulnerability in the web-based management interface of Cisco BroadWorks Messaging Server Software could allow an authenticated, remote attacker to access sensitive information or cause a partial denial of service (DoS) condition on an affected system. This vulnerability is due to improper handling of XML External Entity (XXE) entries when parsing certain XML files. An attacker could exploit this vulnerability by uploading a crafted XML file that contains references to external entities. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to retrieve files from the local system, resulting in the disclosure of sensitive information, or cause the application to consume available resources, resulting in a partial DoS condition on an affected system. There are workarounds that address this vulnerability. |
2021-05-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1530
CISCO |
| cisco — content_security_management_appliance |
A vulnerability in the web-based management interface of Cisco AsyncOS Software for Cisco Content Security Management Appliance (SMA), Cisco Email Security Appliance (ESA), and Cisco Web Security Appliance (WSA) could allow an authenticated, remote attacker to access sensitive information on an affected device. The vulnerability exists because confidential information is included in HTTP requests that are exchanged between the user and the device. An attacker could exploit this vulnerability by looking at the raw HTTP requests that are sent to the interface. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to obtain some of the passwords that are configured throughout the interface. |
2021-05-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1516
CISCO |
| cisco — content_security_management_applicance |
A vulnerability in the user account management system of Cisco AsyncOS for Cisco Content Security Management Appliance (SMA) could allow an authenticated, local attacker to elevate their privileges to root. This vulnerability is due to a procedural flaw in the password generation algorithm. An attacker could exploit this vulnerability by enabling specific Administrator-only features and connecting to the appliance through the CLI with elevated privileges. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to execute arbitrary commands as root and access the underlying operating system. To exploit this vulnerability, the attacker must have valid Administrator credentials. |
2021-05-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1447
CISCO |
| cisco — enterprise_nfv_infrastructure_software |
A vulnerability in Cisco Enterprise NFV Infrastructure Software (NFVIS) could allow an authenticated, local attacker to perform a command injection attack on an affected device. The vulnerability is due to insufficient validation of user-supplied input to a configuration command. An attacker could exploit this vulnerability by including malicious input during the execution of this command. A successful exploit could allow a non-privileged attacker authenticated in the restricted CLI to execute arbitrary commands on the underlying operating system (OS) with root privileges. |
2021-05-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1421
CISCO |
| cisco — hyperflex_hx |
A vulnerability in the web-based management interface of Cisco HyperFlex HX Data Platform could allow an unauthenticated, remote attacker to upload files to an affected device. This vulnerability is due to missing authentication for the upload function. An attacker could exploit this vulnerability by sending a specific HTTP request to an affected device. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to upload files to the affected device with the permissions of the tomcat8 user. |
2021-05-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1499
CISCO |
| cisco — hyperflex_hx |
Multiple vulnerabilities in the web-based management interface of Cisco HyperFlex HX could allow an unauthenticated, remote attacker to perform command injection attacks against an affected device. For more information about these vulnerabilities, see the Details section of this advisory. |
2021-05-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1497
CISCO |
| cisco — hyperflex_hx |
Multiple vulnerabilities in the web-based management interface of Cisco HyperFlex HX could allow an unauthenticated, remote attacker to perform command injection attacks against an affected device. For more information about these vulnerabilities, see the Details section of this advisory. |
2021-05-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1498
CISCO |
| cisco — integrated_management_controller_software |
A vulnerability in the web-based management interface of Cisco Integrated Management Controller (IMC) Software could allow an unauthenticated, remote attacker to redirect a user to a malicious web page. This vulnerability is due to improper input validation of the parameters in an HTTP request. An attacker could exploit this vulnerability by persuading a user to click a crafted link. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to redirect a user to a malicious website. This vulnerability is known as an open redirect attack, which is used in phishing attacks to get users to visit malicious sites without their knowledge. |
2021-05-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1397
CISCO |
| cisco — multiple_routers |
A vulnerability in the internal message processing of Cisco RV340, RV340W, RV345, and RV345P Dual WAN Gigabit VPN Routers could allow an authenticated, local attacker to run arbitrary commands with root privileges on the underlying operating system (OS). This vulnerability exists because an internal messaging service does not properly sanitize input. An attacker could exploit this vulnerability by first authenticating to the device and then sending a crafted request to the internal service. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to run arbitrary commands with root privileges on the underlying OS. To exploit this vulnerability, the attacker must have valid Administrator credentials for the device. |
2021-05-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1520
CISCO |
| cisco — sd-wan_software |
A vulnerability in the CLI of Cisco SD-WAN Software could allow an authenticated, local attacker to inject arbitrary commands to be executed with Administrator privileges on the underlying operating system. This vulnerability is due to insufficient input validation on certain CLI commands. An attacker could exploit this vulnerability by authenticating to the device and submitting crafted input to the CLI. The attacker must be authenticated as a low-privileged user to execute the affected commands. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to execute commands with Administrator privileges. |
2021-05-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1514
CISCO |
| cisco — sd-wan_software |
A vulnerability in the CLI of Cisco SD-WAN Software could allow an authenticated, local attacker to overwrite arbitrary files in the underlying file system of an affected system. This vulnerability is due to insufficient validation of the user-supplied input parameters of a specific CLI command. An attacker could exploit this vulnerability by issuing that command with specific parameters. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to overwrite the content in any arbitrary files that reside on the underlying host file system. |
2021-05-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1512
CISCO |
| cisco — sd-wan_software |
A vulnerability in the vDaemon process of Cisco SD-WAN Software could allow an unauthenticated, remote attacker to cause a device to reload, resulting in a denial of service (DoS) condition. This vulnerability is due to insufficient handling of malformed packets. An attacker could exploit this vulnerability by sending crafted traffic to an affected device. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to cause the device to reload, resulting in a DoS condition. |
2021-05-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1513
CISCO |
| cisco — sd-wan_vedge_software |
Multiple vulnerabilities in Cisco SD-WAN vEdge Software could allow an attacker to execute arbitrary code as the root user or cause a denial of service (DoS) condition on an affected device. For more information about these vulnerabilities, see the Details section of this advisory. |
2021-05-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1509
CISCO |
| cisco — sd-wan_vedge_software |
Multiple vulnerabilities in Cisco SD-WAN vEdge Software could allow an attacker to execute arbitrary code as the root user or cause a denial of service (DoS) condition on an affected device. For more information about these vulnerabilities, see the Details section of this advisory. |
2021-05-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1510
CISCO |
| cisco — sd-wan_vedge_software |
Multiple vulnerabilities in Cisco SD-WAN vEdge Software could allow an attacker to execute arbitrary code as the root user or cause a denial of service (DoS) condition on an affected device. For more information about these vulnerabilities, see the Details section of this advisory. |
2021-05-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1511
CISCO |
| cisco — sd-wan_vmanage_software |
A vulnerability in Cisco SD-WAN vManage Software could allow an unauthenticated, remote attacker to enumerate user accounts. This vulnerability is due to the improper handling of HTTP headers. An attacker could exploit this vulnerability by sending authenticated requests to an affected system. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to compare the HTTP responses that are returned by the affected system to determine which accounts are valid user accounts. |
2021-05-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1486
CISCO |
| cisco — sd-wan_vmanage_software |
A vulnerability in an API of Cisco SD-WAN vManage Software could allow an authenticated, remote attacker to conduct a stored cross-site scripting (XSS) attack against users of the application web-based interface. This vulnerability exists because the API does not properly validate user-supplied input. An attacker could exploit this vulnerability by sending malicious input to the API. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to execute arbitrary script code in the context of the web-based interface or access sensitive, browser-based information. |
2021-05-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1507
CISCO |
| cisco — sd-wan_vmanage_software |
Multiple vulnerabilities in Cisco SD-WAN vManage Software could allow an unauthenticated, remote attacker to execute arbitrary code or gain access to sensitive information, or allow an authenticated, local attacker to gain escalated privileges or gain unauthorized access to the application. For more information about these vulnerabilities, see the Details section of this advisory. |
2021-05-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1275
CISCO |
| cisco — sd-wan_vmanage_software |
Multiple vulnerabilities in Cisco SD-WAN vManage Software could allow an unauthenticated, remote attacker to execute arbitrary code or gain access to sensitive information, or allow an authenticated, local attacker to gain escalated privileges or gain unauthorized access to the application. For more information about these vulnerabilities, see the Details section of this advisory. |
2021-05-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1508
CISCO |
| cisco — sd-wan_vmanage_software |
A vulnerability in Cisco SD-WAN vManage Software could allow an unauthenticated, adjacent attacker to gain access to sensitive information. This vulnerability is due to improper access controls on API endpoints when Cisco SD-WAN vManage Software is running in multi-tenant mode. An attacker with access to a device that is managed in the multi-tenant environment could exploit this vulnerability by sending a request to an affected API endpoint on the vManage system. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to gain access to sensitive information that may include hashed credentials that could be used in future attacks. |
2021-05-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1515
CISCO |
| cisco — sd-wan_vmanage_software |
Multiple vulnerabilities in Cisco SD-WAN vManage Software could allow an unauthenticated, remote attacker to execute arbitrary code or gain access to sensitive information, or allow an authenticated, local attacker to gain escalated privileges or gain unauthorized access to the application. For more information about these vulnerabilities, see the Details section of this advisory. |
2021-05-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1506
CISCO |
| cisco — sd-wan_vmanage_software |
A vulnerability in the cluster management interface of Cisco SD-WAN vManage Software could allow an unauthenticated, remote attacker to view sensitive information on an affected system. To be affected by this vulnerability, the Cisco SD-WAN vManage Software must be in cluster mode. This vulnerability is due to the absence of authentication for sensitive information in the cluster management interface. An attacker could exploit this vulnerability by sending a crafted request to the cluster management interface of an affected system. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to allow the attacker to view sensitive information on the affected system. |
2021-05-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1535
CISCO |
| cisco — sd-wan_vmanage_software |
A vulnerability in the web-based messaging service interface of Cisco SD-WAN vManage Software could allow an unauthenticated, adjacent attacker to bypass authentication and authorization and modify the configuration of an affected system. To exploit this vulnerability, the attacker must be able to access an associated Cisco SD-WAN vEdge device. This vulnerability is due to insufficient authorization checks. An attacker could exploit this vulnerability by sending crafted HTTP requests to the web-based messaging service interface of an affected system. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to gain unauthenticated read and write access to the affected vManage system. With this access, the attacker could access information about the affected vManage system, modify the configuration of the system, or make configuration changes to devices that are managed by the system. |
2021-05-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1284
CISCO |
| cisco — sd-wan_vmanage_software |
Multiple vulnerabilities in Cisco SD-WAN vManage Software could allow an unauthenticated, remote attacker to execute arbitrary code or gain access to sensitive information, or allow an authenticated, local attacker to gain escalated privileges or gain unauthorized access to the application. For more information about these vulnerabilities, see the Details section of this advisory. |
2021-05-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1505
CISCO |
| cisco — sd-wan_vmanage_software |
Multiple vulnerabilities in Cisco SD-WAN vManage Software could allow an unauthenticated, remote attacker to execute arbitrary code or gain access to sensitive information, or allow an authenticated, local attacker to gain escalated privileges or gain unauthorized access to the application. For more information about these vulnerabilities, see the Details section of this advisory. |
2021-05-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1468
CISCO |
| cisco — small_business_series_wireless_access_points |
Multiple vulnerabilities in the web-based management interface of certain Cisco Small Business 100, 300, and 500 Series Wireless Access Points could allow an authenticated, remote attacker to obtain sensitive information from or inject arbitrary commands on an affected device. For more information about these vulnerabilities, see the Details section of this advisory. |
2021-05-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1401
CISCO |
| cisco — small_business_series_wireless_access_points |
Multiple vulnerabilities in the web-based management interface of certain Cisco Small Business 100, 300, and 500 Series Wireless Access Points could allow an authenticated, remote attacker to obtain sensitive information from or inject arbitrary commands on an affected device. For more information about these vulnerabilities, see the Details section of this advisory. |
2021-05-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1400
CISCO |
| cisco — telepresence_collaboration_endpoint_software |
A vulnerability in the video endpoint API (xAPI) of Cisco TelePresence Collaboration Endpoint (CE) Software and Cisco RoomOS Software could allow an authenticated, remote attacker to read arbitrary files from the underlying operating system. This vulnerability is due to insufficient path validation of command arguments. An attacker could exploit this vulnerability by sending a crafted command request to the xAPI. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to read the contents of any file that is located on the device filesystem. |
2021-05-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1532
CISCO |
| cisco — unified_communications_manager |
A vulnerability in the Java Management Extensions (JMX) component of Cisco Unified Communications Manager (Unified CM) and Cisco Unified Communications Manager Session Management Edition (Unified CM SME) could allow an authenticated, remote attacker to cause a denial of service (DoS) condition on an affected system. This vulnerability is due to an unsecured TCP/IP port. An attacker could exploit this vulnerability by accessing the port and restarting the JMX process. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to cause a DoS condition on an affected system. |
2021-05-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1478
CISCO |
| cisco — unified_communications_manager_im |
Multiple vulnerabilities in the web-based management interface of Cisco Unified Communications Manager IM & Presence Service could allow an authenticated, remote attacker to conduct SQL injection attacks on an affected system. These vulnerabilities are due to improper validation of user-submitted parameters. An attacker could exploit these vulnerabilities by authenticating to the application and sending malicious requests to an affected system. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to obtain data or modify data that is stored in the underlying database. |
2021-05-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1365
CISCO |
| cisco — unified_communications_manager_im |
Multiple vulnerabilities in the web-based management interface of Cisco Unified Communications Manager IM & Presence Service could allow an authenticated, remote attacker to conduct SQL injection attacks on an affected system. These vulnerabilities are due to improper validation of user-submitted parameters. An attacker could exploit these vulnerabilities by authenticating to the application and sending malicious requests to an affected system. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to obtain data or modify data that is stored in the underlying database. |
2021-05-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1363
CISCO |
| cisco — video_surveillance_8000_series_ip_cameras |
A vulnerability in the Cisco Discovery Protocol implementation for Cisco Video Surveillance 8000 Series IP Cameras could allow an unauthenticated, adjacent attacker to cause an affected IP camera to reload. This vulnerability is due to missing checks when processing Cisco Discovery Protocol messages. An attacker could exploit this vulnerability by sending a malicious Cisco Discovery Protocol packet to an affected IP camera. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to cause the affected IP camera to reload unexpectedly, resulting in a denial of service (DoS) condition. Note: Cisco Discovery Protocol is a Layer 2 protocol. To exploit this vulnerability, an attacker must be in the same broadcast domain as the affected device (Layer 2 adjacent). |
2021-05-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1521
CISCO |
| cisco — web_security_appliance |
A vulnerability in the web-based management interface of Cisco AsyncOS for Cisco Web Security Appliance (WSA) could allow an unauthenticated, remote attacker to conduct a cross-site scripting (XSS) attack against a user of the interface of an affected device. This vulnerability is due to improper validation of user-supplied input in the web-based management interface. An attacker could exploit this vulnerability by persuading a user to retrieve a crafted file that contains malicious payload and upload it to the affected device. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to execute arbitrary script code in the context of the affected interface or access sensitive, browser-based information. |
2021-05-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1490
CISCO |
| cisco — wide_area_application_services_software |
A vulnerability in Cisco Wide Area Application Services (WAAS) Software could allow an authenticated, local attacker to gain access to sensitive information on an affected device. The vulnerability is due to improper input validation and authorization of specific commands that a user can execute within the CLI. An attacker could exploit this vulnerability by authenticating to an affected device and issuing a specific set of commands. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to read arbitrary files that they originally did not have permissions to access. |
2021-05-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1438
CISCO |
| codesys — automation_server |
The Package Manager of CODESYS Development System 3 before 3.5.17.0 does not check the validity of packages before installation and may be used to install CODESYS packages with malicious content. |
2021-05-04 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-29240
MISC
MISC
MISC |
| codesys — automation_server |
CODESYS Automation Server before 1.16.0 allows cross-site request forgery (CSRF). |
2021-05-03 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-29238
MISC
MISC
MISC |
| codesys — control_runtime |
CODESYS Control Runtime system before 3.5.17.0 has improper input validation. Attackers can send crafted communication packets to change the router’s addressing scheme and may re-route, add, remove or change low level communication packages. |
2021-05-03 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-29242
MISC
MISC
MISC |
| codesys — gateway_3 |
CODESYS Gateway 3 before 3.5.17.0 has a NULL pointer dereference that may result in a denial of service (DoS). |
2021-05-03 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-29241
MISC
MISC
MISC |
| craft — craft |
Craft CMS before 3.6.13 has an XSS vulnerability. |
2021-05-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-32470
MISC
MISC |
| dell — emc_integrated_system |
Dell EMC Integrated System for Microsoft Azure Stack Hub, versions 1906 – 2011, contain an undocumented default iDRAC account. A remote unauthenticated attacker, with the knowledge of the default credentials, could potentially exploit this to log in to the system to gain root privileges. |
2021-05-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-21505
MISC |
| dell — powerscale_onefs |
Dell PowerScale OneFS 8.1.0-9.1.0 contain an improper neutralization of special elements used in an OS command vulnerability. This vulnerability may allow an authenticated user with ISI_PRIV_LOGIN_SSH or ISI_PRIV_LOGIN_CONSOLE privileges to escalate privileges. |
2021-05-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-21527
MISC |
| dell — powerscale_onefs |
Dell EMC PowerScale OneFS 8.1.0-9.1.0 contain an improper neutralization of special elements used in an OS command vulnerability. This vulnerability can allow an authenticated user with ISI_PRIV_LOGIN_SSH or ISI_PRIV_LOGIN_CONSOLE privileges to escalate privileges. |
2021-05-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-21550
MISC |
| django — django |
In Django 2.2 before 2.2.21, 3.1 before 3.1.9, and 3.2 before 3.2.1, MultiPartParser, UploadedFile, and FieldFile allowed directory traversal via uploaded files with suitably crafted file names. |
2021-05-05 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-31542
MISC
MISC
MISC
MISC
MLIST |
| django — django |
In Django 2.2 before 2.2.22, 3.1 before 3.1.10, and 3.2 before 3.2.2 (with Python 3.9.5+), URLValidator does not prohibit newlines and tabs (unless the URLField form field is used). If an application uses values with newlines in an HTTP response, header injection can occur. Django itself is unaffected because HttpResponse prohibits newlines in HTTP headers. |
2021-05-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-32052
MISC
MISC
MISC
MISC |
| drupal — core |
Access bypass vulnerability in Drupal Core allows JSON:API when JSON:API is in read/write mode. Only sites that have the read_only set to FALSE under jsonapi.settings config are vulnerable. This issue affects: Drupal Drupal Core 8.8.x versions prior to 8.8.8; 8.9.x versions prior to 8.9.1; 9.0.x versions prior to 9.0.1. |
2021-05-05 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-13665
CONFIRM |
| drupal — core |
Open Redirect vulnerability in Drupal Core allows a user to be tricked into visiting a specially crafted link which would redirect them to an arbitrary external URL. This issue affects: Drupal Drupal Core 7 version 7.70 and prior versions. |
2021-05-05 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-13662
CONFIRM |
| drupal — core |
Arbitrary PHP code execution vulnerability in Drupal Core under certain circumstances. An attacker could trick an administrator into visiting a malicious site that could result in creating a carefully named directory on the file system. With this directory in place, an attacker could attempt to brute force a remote code execution vulnerability. Windows servers are most likely to be affected. This issue affects: Drupal Drupal Core 8.8.x versions prior to 8.8.8; 8.9.x versions prior to 8.9.1; 9.0.1 versions prior to 9.0.1. |
2021-05-05 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-13664
CONFIRM |
| elasticsearch — elasticsearch |
An SSRF issue in Open Distro for Elasticsearch (ODFE) before 1.13.1.0 allows an existing privileged user to enumerate listening services or interact with configured resources via HTTP requests exceeding the Alerting plugin’s intended scope. |
2021-05-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-31828
CONFIRM
MISC |
| emissary — emissary |
A Cross-site scripting (XSS) vulnerability in the DocumentAction component of U.S. National Security Agency (NSA) Emissary 5.9.0 allows remote attackers to inject arbitrary web script or HTML via the uuid parameter. |
2021-05-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-32092
MISC
MISC |
| emissary — emissary |
U.S. National Security Agency (NSA) Emissary 5.9.0 allows an authenticated user to upload arbitrary files. |
2021-05-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-32094
MISC
MISC |
| emissary — emissary |
The ConsoleAction component of U.S. National Security Agency (NSA) Emissary 5.9.0 allows a CSRF attack that results in injecting arbitrary Ruby code (for an eval call) via the CONSOLE_COMMAND_STRING parameter. |
2021-05-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-32096
MISC
MISC |
emissary — emissary
|
The ConfigFileAction component of U.S. National Security Agency (NSA) Emissary 5.9.0 allows an authenticated user to read arbitrary files via the ConfigName parameter. |
2021-05-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-32093
MISC
MISC |
| emissary — emissary |
U.S. National Security Agency (NSA) Emissary 5.9.0 allows an authenticated user to delete arbitrary files. |
2021-05-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-32095
MISC
MISC |
| emlog — emlog |
emlog v5.3.1 and emlog v6.0.0 have a Remote Code Execution vulnerability due to upload of database backup file in admin/data.php. |
2021-05-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-31737
MISC |
| emote — remote_mouse |
An issue was discovered in Emote Remote Mouse through 4.0.0.0. Attackers can retrieve recently used and running applications, their icons, and their file paths. This information is sent in cleartext and is not protected by any authentication logic. |
2021-05-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-27571
MISC
MISC |
| emote — remote_mouse |
An issue was discovered in Emote Remote Mouse through 4.0.0.0. Remote unauthenticated users can execute arbitrary code via crafted UDP packets with no prior authorization or authentication. |
2021-05-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-27573
MISC
MISC |
| emote — remote_mouse |
An issue was discovered in Emote Remote Mouse through 4.0.0.0. It uses cleartext HTTP to check, and request, updates. Thus, attackers can machine-in-the-middle a victim to download a malicious binary in place of the real update, with no SSL errors or warnings. |
2021-05-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-27574
MISC
MISC |
| emote — remote_mouse |
An issue was discovered in Emote Remote Mouse through 4.0.0.0. Attackers can maximize or minimize the window of a running process by sending the process name in a crafted packet. This information is sent in cleartext and is not protected by any authentication logic. |
2021-05-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-27569
MISC
MISC |
| emote — remote_mouse |
An issue was discovered in Emote Remote Mouse through 3.015. Attackers can close any running process by sending the process name in a specially crafted packet. This information is sent in cleartext and is not protected by any authentication logic. |
2021-05-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-27570
MISC
MISC |
| emote — remote_mouse |
An issue was discovered in Emote Remote Mouse through 4.0.0.0. Authentication Bypass can occur via Packet Replay. Remote unauthenticated users can execute arbitrary code via crafted UDP packets even when passwords are set. |
2021-05-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-27572
MISC
MISC |
| erp_pos — erp_pos |
Special characters of ERP POS news page are not filtered in users’ input, which allow remote authenticated attackers can inject malicious JavaScript and carry out stored XSS (Stored Cross-site scripting) attacks, additionally access and manipulate customer’s information. |
2021-05-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-30171
MISC |
erp_pos — erp_pos
|
Special characters of ERP POS customer profile page are not filtered in users’ input, which allow remote authenticated attackers can inject malicious JavaScript and carry out stored XSS (Stored Cross-site scripting) attacks, additionally access and manipulate customer’s information. |
2021-05-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-30170
MISC |
esri — arcgis_earth
|
A path traversal vulnerability exists in Esri ArcGIS Earth versions 1.11.0 and below which allows arbitrary file creation on an affected system through crafted input. An attacker could exploit this vulnerability to gain arbitrary code execution under security context of the user running ArcGIS Earth by inducing the user to upload a crafted file to an affected system. |
2021-05-05 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-29100
CONFIRM |
esri — arcgis_geoevent_server
|
ArcGIS GeoEvent Server versions 10.8.1 and below has a read-only directory path traversal vulnerability that could allow an unauthenticated, remote attacker to perform directory traversal attacks and read arbitrary files on the system. |
2021-05-05 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-29101
CONFIRM |
eventlet — eventlet
|
Eventlet is a concurrent networking library for Python. A websocket peer may exhaust memory on Eventlet side by sending very large websocket frames. Malicious peer may exhaust memory on Eventlet side by sending highly compressed data frame. A patch in version 0.31.0 restricts websocket frame to reasonable limits. As a workaround, restricting memory usage via OS limits would help against overall machine exhaustion, but there is no workaround to protect Eventlet process. |
2021-05-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-21419
CONFIRM |
ewelink — ewelink
|
Unconstrained Web access to the device’s private encryption key in the QR code pairing mode in the eWeLink mobile application (through 4.9.2 on Android and through 4.9.1 on iOS) allows a physically proximate attacker to eavesdrop on Wi-Fi credentials and other sensitive information by monitoring the Wi-Fi spectrum during a device pairing process. |
2021-05-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-27941
MISC
MISC
MISC |
forkcms — forkcms
|
Cross-site request forgery (CSRF) in Fork-CMS before 5.8.2 allow remote attackers to hijack the authentication of logged administrators. |
2021-05-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-23264
CONFIRM |
forkcms — forkcms
|
Persistent Cross-site scripting vulnerability on Fork CMS version 5.8.2 allows remote attackers to inject arbitrary Javascript code via the “navigation_title” parameter and the “title” parameter in /private/en/pages/add. |
2021-05-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-23263
CONFIRM |
| foxit — reader |
This vulnerability allows remote attackers to execute arbitrary code on affected installations of Foxit Reader 10.1.1.37576. User interaction is required to exploit this vulnerability in that the target must visit a malicious page or open a malicious file. The specific flaw exists within the handling of U3D objects in PDF files. The issue results from the lack of proper validation of user-supplied data, which can result in a write past the end of an allocated data structure. An attacker can leverage this vulnerability to execute code in the context of the current process. Was ZDI-CAN-13239. |
2021-05-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-31442
MISC
MISC |
| foxit — reader |
This vulnerability allows remote attackers to disclose sensitive information on affected installations of Foxit Reader 10.1.1.37576. User interaction is required to exploit this vulnerability in that the target must visit a malicious page or open a malicious file. The specific flaw exists within the handling of U3D objects embedded in PDF files. The issue results from the lack of proper validation of user-supplied data, which can result in a read past the end of an allocated object. An attacker can leverage this in conjunction with other vulnerabilities to execute arbitrary code in the context of the current process. Was ZDI-CAN-13269. |
2021-05-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-31447
MISC
MISC |
| foxit — reader |
This vulnerability allows remote attackers to execute arbitrary code on affected installations of Foxit Reader 10.1.1.37576. User interaction is required to exploit this vulnerability in that the target must visit a malicious page or open a malicious file. The specific flaw exists within the handling of the Decimal element. A crafted leadDigits value in a Decimal element can trigger an overflow of a fixed-length heap-based buffer. An attacker can leverage this vulnerability to execute arbitrary code in the context of the current process. Was ZDI-CAN-13095. |
2021-05-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-31454
MISC
MISC |
| foxit — reader |
This vulnerability allows remote attackers to disclose sensitive information on affected installations of Foxit Reader 10.1.3.37598. User interaction is required to exploit this vulnerability in that the target must visit a malicious page or open a malicious file. The specific flaw exists within the handling of U3D files embedded in PDF documents. The issue results from the lack of proper validation of user-supplied data, which can result in a read past the end of an allocated object. An attacker can leverage this in conjunction with other vulnerabilities to execute arbitrary code in the context of the current process. Was ZDI-CAN-13621. |
2021-05-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-31467
MISC
MISC |
foxit — reader
|
This vulnerability allows remote attackers to execute arbitrary code on affected installations of Foxit Reader 10.1.3.37598. User interaction is required to exploit this vulnerability in that the target must visit a malicious page or open a malicious file. The specific flaw exists within the handling of U3D files embedded in PDF documents. The issue results from the lack of proper validation of user-supplied data, which can result in a read past the end of an allocated data structure. An attacker can leverage this vulnerability to execute code in the context of the current process. Was ZDI-CAN-13620. |
2021-05-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-31468
MISC
MISC |
foxit — reader
|
This vulnerability allows remote attackers to execute arbitrary code on affected installations of Foxit Reader 10.1.3.37598. User interaction is required to exploit this vulnerability in that the target must visit a malicious page or open a malicious file. The specific flaw exists within the handling of U3D objects in PDF files. The issue results from the lack of proper validation of user-supplied data, which can result in a write past the end of an allocated data structure. An attacker can leverage this vulnerability to execute code in the context of the current process. Was ZDI-CAN-13582. |
2021-05-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-31465
MISC
MISC |
foxit — reader
|
This vulnerability allows remote attackers to disclose sensitive information on affected installations of Foxit Reader 10.1.1.37576. User interaction is required to exploit this vulnerability in that the target must visit a malicious page or open a malicious file. The specific flaw exists within the handling of U3D objects embedded in PDF files. The issue results from the lack of proper validation of user-supplied data, which can result in a read past the end of an allocated object. An attacker can leverage this in conjunction with other vulnerabilities to execute arbitrary code in the context of the current process. Was ZDI-CAN-13240. |
2021-05-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-31443
MISC
MISC |
| foxit — reader |
This vulnerability allows remote attackers to disclose sensitive information on affected installations of Foxit Reader 10.1.3.37598. User interaction is required to exploit this vulnerability in that the target must visit a malicious page or open a malicious file. The specific flaw exists within the handling of U3D objects embedded in PDF files. The issue results from the lack of proper validation of user-supplied data, which can result in a read past the end of an allocated object. An attacker can leverage this in conjunction with other vulnerabilities to execute arbitrary code in the context of the current process. Was ZDI-CAN-13574. |
2021-05-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-31464
MISC
MISC |
foxit — reader
|
This vulnerability allows remote attackers to execute arbitrary code on affected installations of Foxit Reader 10.1.1.37576. User interaction is required to exploit this vulnerability in that the target must visit a malicious page or open a malicious file. The specific flaw exists within the handling of XFA forms. The issue results from the lack of validating the existence of an object prior to performing operations on the object. An attacker can leverage this vulnerability to execute code in the context of the current process. Was ZDI-CAN-13084. |
2021-05-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-31450
MISC
MISC |
| foxit — reader |
This vulnerability allows remote attackers to execute arbitrary code on affected installations of Foxit Reader 10.1.1.37576. User interaction is required to exploit this vulnerability in that the target must visit a malicious page or open a malicious file. The specific flaw exists within the handling of XFA Forms. The issue results from the lack of validating the existence of an object prior to performing operations on the object. An attacker can leverage this vulnerability to execute code in the context of the current process. Was ZDI-CAN-13162. |
2021-05-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-31459
MISC
MISC |
foxit — reader
|
This vulnerability allows remote attackers to disclose sensitive information on affected installations of Foxit Reader 10.1.3.37598. User interaction is required to exploit this vulnerability in that the target must visit a malicious page or open a malicious file. The specific flaw exists within the handling of U3D objects embedded in PDF files. The issue results from the lack of proper validation of user-supplied data, which can result in a read past the end of an allocated object. An attacker can leverage this in conjunction with other vulnerabilities to execute arbitrary code in the context of the current process. Was ZDI-CAN-13572. |
2021-05-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-31462
MISC
MISC |
foxit — reader
|
This vulnerability allows remote attackers to execute arbitrary code on affected installations of Foxit Reader 10.1.1.37576. User interaction is required to exploit this vulnerability in that the target must visit a malicious page or open a malicious file. The specific flaw exists within the handling of XFA forms. The issue results from the lack of validating the existence of an object prior to performing operations on the object. An attacker can leverage this vulnerability to execute code in the context of the current process. Was ZDI-CAN-13100. |
2021-05-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-31455
MISC
MISC |
foxit — reader
|
This vulnerability allows remote attackers to disclose sensitive information on affected installations of Foxit Reader 10.1.1.37576. User interaction is required to exploit this vulnerability in that the target must visit a malicious page or open a malicious file. The specific flaw exists within the handling of U3D objects embedded in PDF files. The issue results from the lack of proper validation of user-supplied data, which can result in a read past the end of an allocated object. An attacker can leverage this in conjunction with other vulnerabilities to execute arbitrary code in the context of the current process. Was ZDI-CAN-13241. |
2021-05-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-31444
MISC
MISC |
| foxit — reader |
This vulnerability allows remote attackers to execute arbitrary code on affected installations of Foxit Reader 10.1.1.37576. User interaction is required to exploit this vulnerability in that the target must visit a malicious page or open a malicious file. The specific flaw exists within the handling of U3D objects in PDF files. The issue results from the lack of proper validation of user-supplied data, which can result in a write past the end of an allocated data structure. An attacker can leverage this vulnerability to execute code in the context of the current process. Was ZDI-CAN-13011. |
2021-05-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-31472
MISC
MISC |
| foxit — reader |
This vulnerability allows remote attackers to disclose sensitive information on affected installations of Foxit Reader 10.1.1.37576. User interaction is required to exploit this vulnerability in that the target must visit a malicious page or open a malicious file. The specific flaw exists within the handling of U3D objects embedded in PDF files. The issue results from the lack of proper validation of user-supplied data, which can result in a read past the end of an allocated object. An attacker can leverage this in conjunction with other vulnerabilities to execute arbitrary code in the context of the current process. Was ZDI-CAN-12955. |
2021-05-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-31471
MISC
MISC |
| foxit — reader |
This vulnerability allows remote attackers to execute arbitrary code on affected installations of Foxit Reader 10.1.1.37576. User interaction is required to exploit this vulnerability in that the target must visit a malicious page or open a malicious file. The specific flaw exists within the handling of Annotation objects. The issue results from the lack of validating the existence of an object prior to performing operations on the object. An attacker can leverage this vulnerability to execute code in the context of the current process. Was ZDI-CAN-13102. |
2021-05-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-31456
MISC
MISC |
| foxit — reader |
This vulnerability allows remote attackers to execute arbitrary code on affected installations of Foxit Reader 10.1.1.37576. User interaction is required to exploit this vulnerability in that the target must visit a malicious page or open a malicious file. The specific flaw exists within the handling of Annotation objects. The issue results from the lack of validating the existence of an object prior to performing operations on the object. An attacker can leverage this vulnerability to execute code in the context of the current process. Was ZDI-CAN-13089. |
2021-05-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-31451
MISC
MISC |
foxit — reader
|
This vulnerability allows remote attackers to execute arbitrary code on affected installations of Foxit Reader 10.1.1.37576. User interaction is required to exploit this vulnerability in that the target must visit a malicious page or open a malicious file. The specific flaw exists within the handling of XFA Forms. The issue results from the lack of validating the existence of an object prior to performing operations on the object. An attacker can leverage this vulnerability to execute code in the context of the current process. Was ZDI-CAN-13092. |
2021-05-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-31453
MISC
MISC |
| foxit — reader |
This vulnerability allows remote attackers to execute arbitrary code on affected installations of Foxit Reader 10.1.1.37576. User interaction is required to exploit this vulnerability in that the target must visit a malicious page or open a malicious file. The specific flaw exists within the handling of XFA forms. The issue results from the lack of proper validation of user-supplied data, which can result in a write past the end of an allocated data structure. An attacker can leverage this vulnerability to execute code in the context of the current process. Was ZDI-CAN-13091. |
2021-05-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-31452
MISC
MISC |
foxit — reader
|
This vulnerability allows remote attackers to execute arbitrary code on affected installations of Foxit Reader 10.1.1.37576. User interaction is required to exploit this vulnerability in that the target must visit a malicious page or open a malicious file. The specific flaw exists within the handling of U3D objects embedded in PDF files. The issue results from the lack of validating the existence of an object prior to performing further free operations on the object. An attacker can leverage this vulnerability to execute code in the context of the current process. Was ZDI-CAN-13280. |
2021-05-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-31449
MISC
MISC |
| foxit — reader |
This vulnerability allows remote attackers to disclose sensitive information on affected installations of Foxit Reader 10.1.1.37576. User interaction is required to exploit this vulnerability in that the target must visit a malicious page or open a malicious file. The specific flaw exists within the handling of U3D objects embedded in PDF files. The issue results from the lack of proper validation of user-supplied data, which can result in a read past the end of an allocated object. An attacker can leverage this in conjunction with other vulnerabilities to execute arbitrary code in the context of the current process. Was ZDI-CAN-13273. |
2021-05-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-31448
MISC
MISC |
| foxit — reader |
This vulnerability allows remote attackers to execute arbitrary code on affected installations of Foxit Reader 10.1.1.37576. User interaction is required to exploit this vulnerability in that the target must visit a malicious page or open a malicious file. The specific flaw exists within the handling of Annotation objects. The issue results from the lack of validating the existence of an object prior to performing operations on the object. An attacker can leverage this vulnerability to execute code in the context of the current process. Was ZDI-CAN-13147. |
2021-05-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-31457
MISC
MISC |
| foxit — reader |
This vulnerability allows remote attackers to disclose sensitive information on affected installations of Foxit Reader 10.1.1.37576. User interaction is required to exploit this vulnerability in that the target must visit a malicious page or open a malicious file. The specific flaw exists within the handling of U3D objects embedded in PDF files. The issue results from the lack of proper validation of user-supplied data, which can result in a read past the end of an allocated object. An attacker can leverage this in conjunction with other vulnerabilities to execute arbitrary code in the context of the current process. Was ZDI-CAN-12936. |
2021-05-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-31469
MISC
MISC |
| foxit — reader |
This vulnerability allows remote attackers to execute arbitrary code on affected installations of Foxit Reader 10.1.1.37576. User interaction is required to exploit this vulnerability in that the target must visit a malicious page or open a malicious file. The specific flaw exists within the handling of U3D objects in PDF files. The issue results from the lack of validating the existence of an object prior to performing operations on the object. An attacker can leverage this vulnerability to execute code in the context of the current process. Was ZDI-CAN-12947. |
2021-05-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-31470
MISC
MISC |
foxit — reader
|
This vulnerability allows remote attackers to execute arbitrary code on affected installations of Foxit Reader 10.1.1.37576. User interaction is required to exploit this vulnerability in that the target must visit a malicious page or open a malicious file. The specific flaw exists within the handling of Annotation objects. The issue results from the lack of validating the existence of an object prior to performing operations on the object. An attacker can leverage this vulnerability to execute code in the context of the current process. Was ZDI-CAN-13101. |
2021-05-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-31441
MISC
MISC |
| foxit — reader |
This vulnerability allows remote attackers to execute arbitrary code on affected installations of Foxit Reader 10.1.1.37576. User interaction is required to exploit this vulnerability in that the target must visit a malicious page or open a malicious file. The specific flaw exists within the the handling of app.media objects. The issue results from the lack of proper validation of user-supplied data, which can result in a type confusion condition. An attacker can leverage this vulnerability to execute code in the context of the current process Was ZDI-CAN-13333. |
2021-05-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-31461
MISC
MISC |
| foxit — reader |
This vulnerability allows remote attackers to execute arbitrary code on affected installations of Foxit Reader 10.1.3.37598. User interaction is required to exploit this vulnerability in that the target must visit a malicious page or open a malicious file. The specific flaw exists within the handling of U3D objects in PDF files. The issue results from the lack of proper validation of user-supplied data, which can result in a read past the end of an allocated data structure. An attacker can leverage this vulnerability to execute code in the context of the current process. Was ZDI-CAN-13583. |
2021-05-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-31466
MISC
MISC |
| foxit — reader |
This vulnerability allows remote attackers to disclose sensitive information on affected installations of Foxit Reader 10.1.1.37576. User interaction is required to exploit this vulnerability in that the target must visit a malicious page or open a malicious file. The specific flaw exists within the handling of U3D objects embedded in PDF files. The issue results from the lack of proper validation of user-supplied data, which can result in a read past the end of an allocated object. An attacker can leverage this in conjunction with other vulnerabilities to execute arbitrary code in the context of the current process. Was ZDI-CAN-13245. |
2021-05-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-31446
MISC
MISC |
| foxit — reader |
This vulnerability allows remote attackers to disclose sensitive information on affected installations of Foxit Reader 10.1.1.37576. User interaction is required to exploit this vulnerability in that the target must visit a malicious page or open a malicious file. The specific flaw exists within the handling of U3D objects embedded in PDF files. The issue results from the lack of proper validation of user-supplied data, which can result in a read past the end of an allocated object. An attacker can leverage this in conjunction with other vulnerabilities to execute arbitrary code in the context of the current process. Was ZDI-CAN-13244. |
2021-05-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-31445
MISC
MISC |
| foxit — reader |
This vulnerability allows remote attackers to execute arbitrary code on affected installations of Foxit Reader 10.1.1.37576. User interaction is required to exploit this vulnerability in that the target must visit a malicious page or open a malicious file. The specific flaw exists within the processing of XFA templates. The issue results from the lack of validating the existence of an object prior to performing operations on the object. An attacker can leverage this vulnerability to execute code in the context of the current process. Was ZDI-CAN-13096. |
2021-05-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-31460
MISC
MISC |
| foxit — reader |
This vulnerability allows remote attackers to execute arbitrary code on affected installations of Foxit Reader 10.1.1.37576. User interaction is required to exploit this vulnerability in that the target must visit a malicious page or open a malicious file. The specific flaw exists within the handling of Annotation objects. The issue results from the lack of validating the existence of an object prior to performing operations on the object. An attacker can leverage this vulnerability to execute code in the context of the current process. Was ZDI-CAN-13150. |
2021-05-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-31458
MISC
MISC |
| foxit — reader |
This vulnerability allows remote attackers to disclose sensitive information on affected installations of Foxit Reader 10.1.3.37598. User interaction is required to exploit this vulnerability in that the target must visit a malicious page or open a malicious file. The specific flaw exists within the handling of U3D objects embedded in PDF files. The issue results from the lack of proper validation of user-supplied data, which can result in a read past the end of an allocated object. An attacker can leverage this in conjunction with other vulnerabilities to execute arbitrary code in the context of the current process. Was ZDI-CAN-13573. |
2021-05-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-31463
MISC
MISC |
| git-parse — git-parse |
The “gitDiff” function in Wayfair git-parse <=1.0.4 has a command injection vulnerability. Clients of the git-parse library are unlikely to be aware of this, so they might unwittingly write code that contains a vulnerability. |
2021-05-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-26543
MISC
MISC |
| gitlab — ce/ee |
An issue has been discovered in GitLab CE/EE affecting all versions starting from 13.2. When querying the repository branches through API, GitLab was ignoring a query parameter and returning a considerable amount of results. |
2021-05-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-22210
CONFIRM
MISC |
| gitlab — ce/ee |
An issue has been discovered in GitLab CE/EE affecting all versions starting from 13.7. GitLab Dependency Proxy, under certain circumstances, can impersonate a user resulting in possibly incorrect access handling. |
2021-05-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-22211
MISC
CONFIRM |
| gitlab — ce/ee |
An issue has been discovered in GitLab CE/EE affecting all versions starting from 13.8. GitLab was not properly validating authorisation tokens which resulted in GraphQL mutation being executed. |
2021-05-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-22209
MISC
CONFIRM |
| gitlab — gitlab |
An issue has been discovered in GitLab affecting versions starting with 13.5 up to 13.9.7. Improper permission check could allow the change of timestamp for issue creation or update. |
2021-05-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-22208
MISC
CONFIRM |
| gitlab — gitlab |
An issue has been discovered in GitLab affecting all versions starting from 11.6. Pull mirror credentials are exposed that allows other maintainers to be able to view the credentials in plain-text, |
2021-05-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-22206
MISC
CONFIRM
MISC |
| gnuplot — gnuplot |
The gnuplot package prior to version 0.1.0 for Node.js allows code execution via shell metacharacters in Gnuplot commands. |
2021-05-03 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-29369
MISC
MISC |
| grafana — wise-paas |
The affected product allows attackers to obtain sensitive information from the WISE-PaaS dashboard. The system contains a hard-coded administrator username and password that can be used to query Grafana APIs. Authentication is not required for exploitation on the WISE-PaaS/RMM (versions prior to 9.0.1). |
2021-05-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-27437
MISC |
| hashicorp — hashicorp |
HashiCorp vault-action (aka Vault GitHub Action) before 2.2.0 allows attackers to obtain sensitive information from log files because a multi-line secret was not correctly registered with GitHub Actions for log masking. |
2021-05-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-32074
MISC
MISC
MISC
MISC |
hewlett_packard_enterprise — edgeline_infrastructure_management_software
|
A security vulnerability has been identified in the HPE Edgeline Infrastructure Manager, also known as HPE Edgeline Infrastructure Management Software, prior to version 1.22. The vulnerability could be remotely exploited to bypass remote authentication leading to execution of arbitrary commands, gaining privileged access, causing denial of service, and changing the configuration. HPE has released a software update to resolve the vulnerability in the HPE Edgeline Infrastructure Manager. |
2021-05-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-29203
MISC
MISC |
highcharts — highcharts
|
Highcharts JS is a JavaScript charting library based on SVG. In Highcharts versions 8 and earlier, the chart options structure was not systematically filtered for XSS vectors. The potential impact was that content from untrusted sources could execute code in the end user’s browser. The vulnerability is patched in version 9. As a workaround, implementers who are not able to upgrade may apply DOMPurify recursively to the options structure to filter out malicious markup. |
2021-05-05 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-29489
CONFIRM |
hongdian — h8922_3.0.5_devices
|
Hongdian H8922 3.0.5 devices allow Directory Traversal. The /log_download.cgi log export handler does not validate user input and allows a remote attacker with minimal privileges to download any file from the device by substituting ../ (e.g., ../../etc/passwd) This can be carried out with a web browser by changing the file name accordingly. Upon visiting log_download.cgi?type=../../etc/passwd and logging in, the web server will allow a download of the contents of the /etc/passwd file. |
2021-05-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-28149
MISC
MISC |
| hongdian — h8922_3.0.5_devices |
Hongdian H8922 3.0.5 devices allow the unprivileged guest user to read cli.conf (with the administrator password and other sensitive data) via /backup2.cgi. |
2021-05-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-28150
MISC
MISC |
| hongdian — h8922_3.0.5_devices |
Hongdian H8922 3.0.5 devices allow OS command injection via shell metacharacters into the ip-address (aka Destination) field to the tools.cgi ping command, which is accessible with the username guest and password guest. |
2021-05-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-28151
MISC
MISC |
| hongdian — h8922_3.0.5_devices |
Hongdian H8922 3.0.5 devices have an undocumented feature that allows access to a shell as a superuser. To connect, the telnet service is used on port 5188 with the default credentials of root:superzxmn. |
2021-05-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-28152
MISC
MISC |
| ibm — robotic_process_automation |
IBM Robotic Process Automation with Automation Anywhere 11.0 could allow an attacker on the network to obtain sensitive information or cause a denial of service through username enumeration. IBM X-Force ID: 190992. |
2021-05-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-4901
CONFIRM
XF |
| ibm — tivoli_storage_manager |
** UNSUPPORTED WHEN ASSIGNED ** The ‘id’ parameter of IBM Tivoli Storage Manager Version 5 Release 2 (Command Line Administrative Interface, dsmadmc.exe) is vulnerable to an exploitable stack buffer overflow. Note: the vulnerability can be exploited when it is used in “interactive” mode while, cause of a max number characters limitation, it cannot be exploited in batch or command line usage (e.g. dsmadmc.exe -id=username -password=pwd). NOTE: This vulnerability only affects products that are no longer supported by the maintainer. |
2021-05-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-28198
MISC
MISC |
| impacket — impacket |
Multiple path traversal vulnerabilities exist in smbserver.py in Impacket through 0.9.22. An attacker that connects to a running smbserver instance can list and write to arbitrary files via ../ directory traversal. This could potentially be abused to achieve arbitrary code execution by replacing /etc/shadow or an SSH authorized key. |
2021-05-05 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-31800
MISC
MISC
MISC
MISC
MISC
MISC |
| iwt_ltd — facesentry_access_control_system |
iWT Ltd FaceSentry Access Control System 6.4.8 suffers from an authenticated OS command injection vulnerability using default credentials. This can be exploited to inject and execute arbitrary shell commands as the root user via the ‘strInIP’ POST parameter in pingTest PHP script. |
2021-05-04 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-21999
EXPLOIT-DB
MISC |
| jeecg — jeecg |
Unrestricted File Upload in JEECG v4.0 and earlier allows remote attackers to execute arbitrary code or gain privileges by uploading a crafted file to the component “jeecgFormDemoController.do?commonUpload”. |
2021-05-03 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-23083
MISC |
| jellyfin — jellyfin |
Jellyfin is a free software media system that provides media from a dedicated server to end-user devices via multiple apps. Verions prior to 10.7.3 vulnerable to unauthenticated Server-Side Request Forgery (SSRF) attacks via the imageUrl parameter. This issue potentially exposes both internal and external HTTP servers or other resources available via HTTP `GET` that are visible from the Jellyfin server. The vulnerability is patched in version 10.7.3. As a workaround, disable external access to the API endpoints `/Items/*/RemoteImages/Download`, `/Items/RemoteSearch/Image` and `/Images/Remote` via reverse proxy, or limit to known-friendly IPs. |
2021-05-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-29490
CONFIRM |
| jira — confluence_server |
Affected versions of Team Calendar in Confluence Server before 7.11.0 allow attackers to inject arbitrary HTML or Javascript via a Cross Site Scripting Vulnerability in admin global setting parameters. |
2021-05-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-29444
N/A |
| jira — confluence_server |
Affected versions of Confluence Server before 7.11.0 allow attackers to identify internal hosts and ports via a blind server-side request forgery vulnerability in Team Calendars parameters. |
2021-05-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-29445
N/A |
| kennnyshiwa-cogs — kennnyshiwa-cogs |
Kennnyshiwa-cogs contains cogs for Red Discordbot. An RCE exploit has been found in the Tickets module of kennnyshiwa-cogs. This exploit allows discord users to craft a message that can reveal sensitive and harmful information. Users can upgrade to version 5a84d60018468e5c0346f7ee74b2b4650a6dade7 to receive a patch or, as a workaround, unload tickets to render the exploit unusable. |
2021-05-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-29493
CONFIRM |
| libaom — libaom |
aom_image.c in libaom in AOMedia before 2021-04-07 frees memory that is not located on the heap. |
2021-05-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-30473
MISC
MISC |
| libgetdata — ibgetdata |
A heap memory corruption problem (use after free) can be triggered in libgetdata v0.10.0 when processing maliciously crafted dirfile databases. This degrades the confidentiality, integrity and availability of third-party software that uses libgetdata as a library. This vulnerability may lead to arbitrary code execution or privilege escalation depending on input/skills of attacker. |
2021-05-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-20204
MISC |
| libre — wireless_ls9 |
An issue was discovered on Libre Wireless LS9 LS1.5/p7040 devices. There is Unauthenticated Root ADB Access Over TCP. The LS9 web interface provides functionality to access ADB over TCP. This is not enabled by default, but can be enabled by sending a crafted request to a web management interface endpoint. Requests made to this endpoint do not require authentication. As such, any unauthenticated user who is able to access the web interface will be able to gain root privileges on the LS9 module. |
2021-05-03 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-35757
MISC |
| libre — wireless_ls9 |
An issue was discovered on Libre Wireless LS9 LS1.5/p7040 devices. There is a Authentication Bypass in the Web Interface. This interface does not properly restrict access to internal functionality. Despite presenting a password login page on first access, authentication is not required to access privileged functionality. As such, it’s possible to directly access APIs that should not be exposed to an unauthenticated user. |
2021-05-03 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-35758
MISC |
| libre — wireless_ls9 |
An issue was discovered on Libre Wireless LS9 LS1.5/p7040 devices. There is a luci_service GETPASS Configuration Password Information Leak. The luci_service daemon running on port 7777 does not require authentication to return the device configuration password in cleartext when using the GETPASS command. As such, any unauthenticated person with access to port 7777 on the device will be able to leak the user’s personal device configuration password by issuing the GETPASS command. |
2021-05-03 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-35756
MISC |
| libre — wireless_ls9 |
An issue was discovered on Libre Wireless LS9 LS1.5/p7040 devices. There is a luci_service Read_ NVRAM Direct Access Information Leak. The luci_service deamon running on port 7777 provides a sub-category of commands for which Read_ is prepended. Commands in this category are able to directly read the contents of the device configuration NVRAM. The NVRAM contains sensitive information, such as the Wi-Fi password (in cleartext), as well as connected account tokens for services such as Spotify. |
2021-05-03 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-35755
MISC |
| libreoffice — libreoffice |
In the LibreOffice 7-1 series in versions prior to 7.1.2, and in the 7-0 series in versions prior to 7.0.5, the denylist can be circumvented by manipulating the link so it doesn’t match the denylist but results in ShellExecute attempting to launch an executable type. |
2021-05-03 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-25631
MISC
MISC |
| linux — linux_kernel |
An out-of-bounds (OOB) memory write flaw was found in list_devices in drivers/md/dm-ioctl.c in the Multi-device driver module in the Linux kernel before 5.12. A bound check failure allows an attacker with special user (CAP_SYS_ADMIN) privilege to gain access to out-of-bounds memory leading to a system crash or a leak of internal kernel information. The highest threat from this vulnerability is to system availability. |
2021-05-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-31916
MISC
MISC
MISC |
| linux — linux_kernel |
An out-of-bounds (OOB) memory access flaw was found in x25_bind in net/x25/af_x25.c in the Linux kernel version v5.12-rc5. A bounds check failure allows a local attacker with a user account on the system to gain access to out-of-bounds memory, leading to a system crash or a leak of internal kernel information. The highest threat from this vulnerability is to confidentiality, integrity, as well as system availability. |
2021-05-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-35519
MISC |
| linux — linux_kernel |
A flaw was found in the Linux kernel in versions before 5.12. The value of internal.ndata, in the KVM API, is mapped to an array index, which can be updated by a user process at anytime which could lead to an out-of-bounds write. The highest threat from this vulnerability is to data integrity and system availability. |
2021-05-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-3501
MISC
MISC |
linux — linux_kernel
|
kernel/bpf/verifier.c in the Linux kernel through 5.12.1 performs undesirable speculative loads, leading to disclosure of stack content via side-channel attacks, aka CID-801c6058d14a. The specific concern is not protecting the BPF stack area against speculative loads. Also, the BPF stack can contain uninitialized data that might represent sensitive information previously operated on by the kernel. |
2021-05-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-31829
MISC
MISC |
| livinglogic — livinglogic |
LivingLogic XIST4C before 0.107.8 allows XSS via feedback.htm or feedback.wihtm. |
2021-05-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-26122
MISC
MISC |
| livinglogic — livinglogic |
LivingLogic XIST4C before 0.107.8 allows XSS via login.htm, login.wihtm, or login-form.htm. |
2021-05-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-26123
MISC
MISC |
| mapserver — mapserver |
MapServer before 7.0.8, 7.1.x and 7.2.x before 7.2.3, 7.3.x and 7.4.x before 7.4.5, and 7.5.x and 7.6.x before 7.6.3 does not properly enforce the MS_MAP_NO_PATH and MS_MAP_PATTERN restrictions that are intended to control the locations from which a mapfile may be loaded (with MapServer CGI). |
2021-05-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-32062
MISC
MISC
MISC
MISC |
| mikrotik — routeros |
Mikrotik RouterOs 6.44.6 (long-term tree) suffers from a memory corruption vulnerability in the /nova/bin/traceroute process. An authenticated remote attacker can cause a Denial of Service due via the loop counter variable. |
2021-05-03 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-20218
MISC |
| mikrotik — routeros |
Mikrotik RouterOs before 6.46.5 (stable tree) suffers from a memory corruption vulnerability in the /nova/bin/traceroute process. An authenticated remote attacker can cause a Denial of Service due via the loop counter variable. |
2021-05-03 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-20247
MISC |
| mixme — mixme |
Mixme is a library for recursive merging of Javascript objects. In Node.js mixme v0.5.0, an attacker can add or alter properties of an object via ‘proto’ through the mutate() and merge() functions. The polluted attribute will be directly assigned to every object in the program. This will put the availability of the program at risk causing a potential denial of service (DoS). The problem is corrected starting with version 0.5.1; no workarounds are known to exist. |
2021-05-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-29491
CONFIRM |
| mixme — mixme |
In Node.js mixme, prior to v0.5.1, an attacker can add or alter properties of an object via ‘__proto__’ through the mutate() and merge() functions. The polluted attribute will be directly assigned to every object in the program. This will put the availability of the program at risk causing a potential denial of service (DoS). |
2021-05-03 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-28860
MISC
MISC
MISC
MISC
MISC |
| modsecurity — modsecurity |
ModSecurity 3.x before 3.0.4 mishandles key-value pair parsing, as demonstrated by a “string index out of range” error and worker-process crash for a “Cookie: =abc” header. |
2021-05-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2019-25043
MISC |
| mutt — mutt |
Mutt 1.11.0 through 2.0.x before 2.0.7 (and NeoMutt 2019-10-25 through 2021-05-04) has a $imap_qresync issue in which imap/util.c has an out-of-bounds read in situations where an IMAP sequence set ends with a comma. NOTE: the $imap_qresync setting for QRESYNC is not enabled by default. |
2021-05-05 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-32055
MISC
MISC
MISC |
| nightowl — wdb-2-v2_devices |
An issue exists on NightOwl WDB-20-V2 WDB-20-V2_20190314 devices that allows an unauthenticated user to gain access to snapshots and video streams from the doorbell. The binary app offers a web server on port 80 that allows an unauthenticated user to take a snapshot from the doorbell camera via the /snapshot URI. |
2021-05-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-31793
MISC
MISC |
| nim — nim |
Nim is a statically typed compiled systems programming language. In Nim standard library before 1.4.2, httpClient SSL/TLS certificate verification was disabled by default. Users can upgrade to version 1.4.2 to receive a patch or, as a workaround, set “verifyMode = CVerifyPeer” as documented. |
2021-05-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-29495
CONFIRM |
| nxp — lpc55s6x_microcontrollers |
NXP LPC55S6x microcontrollers (0A and 1B), i.MX RT500 (silicon rev B1 and B2), i.MX RT600 (silicon rev A0, B0), LPC55S6x, LPC55S2x, LPC552x (silicon rev 0A, 1B), and LPC55S1x, LPC551x (silicon rev 0A) include an undocumented ROM patch peripheral that allows unsigned, non-persistent modification of the internal ROM. The peripheral is accessible from any execution mode (secure/privileged, secure/unprivileged, non-secure/privileged, non-secure/unprivileged). The ROM includes a set of APIs intended for use by a secure application to perform flash and in-application programming (IAP) operations. An attacker may use the ROM patch peripheral to modify the implementation of these ROM APIs from a non-secure, unprivileged context. If a non-secure application can also cause the secure application to invoke these ROM APIs, this provides privilege escalation and arbitrary code execution. |
2021-05-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-31532
MISC
MISC |
| october — october |
October is a free, open-source, self-hosted CMS platform based on the Laravel PHP Framework. A bypass of CVE-2020-26231 (fixed in 1.0.470/471 and 1.1.1) was discovered that has the same impact as CVE-2020-26231 & CVE-2020-15247. An authenticated backend user with the `cms.manage_pages`, `cms.manage_layouts`, or `cms.manage_partials` permissions who would **normally** not be permitted to provide PHP code to be executed by the CMS due to `cms.enableSafeMode` being enabled is able to write specific Twig code to escape the Twig sandbox and execute arbitrary PHP. This is not a problem for anyone that trusts their users with those permissions to normally write & manage PHP within the CMS by not having `cms.enableSafeMode` enabled, but would be a problem for anyone relying on `cms.enableSafeMode` to ensure that users with those permissions in production do not have access to write & execute arbitrary PHP. Issue has been patched in Build 472 (v1.0.472) and v1.1.2. As a workaround, apply https://github.com/octobercms/october/commit/f63519ff1e8d375df30deba63156a2fc97aa9ee7 to your installation manually if unable to upgrade to Build 472 or v1.1.2. |
2021-05-03 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-21264
CONFIRM |
| omni-directional — omni-directional |
Local File Inclusion vulnerability of the omni-directional communication system allows remote authenticated attacker inject absolute path into Url parameter and access arbitrary file. |
2021-05-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-30173
MISC |
| online-book-store-project — online-book-store-project |
Incorrect Access Control vulnerability in Online Book Store v1.0 via admin_verify.php, which could let a remote mailicious user bypass authentication and obtain sensitive information. |
2021-05-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-19111
MISC |
| online-book-store-project — online-book-store-project |
Arbitrary File Upload vulnerability in Online Book Store v1.0 in admin_add.php, which may lead to remote code execution. |
2021-05-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-19113
MISC |
| openemr — openemr |
A SQL injection vulnerability exists (with user privileges) in interface/forms/eye_mag/save.php in OpenEMR 5.0.2.1. |
2021-05-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-32104
MISC
MISC
MISC
MISC
MISC |
| openemr — openemr |
A Stored XSS vulnerability in interface/usergroup/usergroup_admin.php in OpenEMR before 5.0.2.1 allows a admin authenticated user to inject arbitrary web script or HTML via the lname parameter. |
2021-05-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-32103
MISC
MISC
MISC
MISC |
| openemr — openemr |
A SQL injection vulnerability exists (with user privileges) in library/custom_template/ajax_code.php in OpenEMR 5.0.2.1. |
2021-05-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-32102
MISC
MISC
MISC
MISC
MISC |
| openemr — openemr |
The Patient Portal of OpenEMR 5.0.2.1 is affected by a incorrect access control system in portal/patient/_machine_config.php. To exploit the vulnerability, an unauthenticated attacker can register an account, bypassing the permission check of this portal’s API. Then, the attacker can then manipulate and read data of every registered patient. |
2021-05-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-32101
MISC
MISC
MISC
MISC |
| openmptcprouter — openmptcprouter |
omr-admin.py in openmptcprouter-vps-admin 0.57.3 and earlier compares the user provided password with the original password in a length dependent manner, which allows remote attackers to guess the password via a timing attack. |
2021-05-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-31245
MISC
MISC
MISC
MISC |
| opnsense — opensense |
An open redirect issue was discovered in OPNsense through 20.1.5. The redirect parameter “url” in login page was not filtered and can redirect user to any website. |
2021-05-03 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-23015
MISC |
| path-parse — path-parse |
All versions of package path-parse are vulnerable to Regular Expression Denial of Service (ReDoS) via splitDeviceRe, splitTailRe, and splitPathRe regular expressions. ReDoS exhibits polynomial worst-case time complexity. |
2021-05-04 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-23343
MISC
MISC
MISC |
| pax_technology — paxstore |
Pax Technology PAXSTORE v7.0.8_20200511171508 and lower is affected by incorrect access control that can lead to remote privilege escalation. PAXSTORE marketplace endpoints allow an authenticated user to read and write data not owned by them, including third-party users, application and payment terminals, where an attacker can impersonate any user which may lead to the unauthorized disclosure, modification, or destruction of information. |
2021-05-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-36126
MISC
MISC
MISC |
| pax_technology — paxstore |
Pax Technology PAXSTORE v7.0.8_20200511171508 and lower is affected by a token spoofing vulnerability. Each payment terminal has a session token (called X-Terminal-Token) to access the marketplace. This allows the store to identify the terminal and make available the applications distributed by its reseller. By intercepting HTTPS traffic from the application store, it is possible to collect the request responsible for assigning the X-Terminal-Token to the terminal, which makes it possible to craft an X-Terminal-Token pretending to be another device. An attacker can use this behavior to authenticate its own payment terminal in the application store through token impersonation. |
2021-05-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-36128
MISC
MISC
MISC |
| pax_technology — paxstore |
Pax Technology PAXSTORE v7.0.8_20200511171508 and lower is affected by XML External Entity (XXE) injection. An authenticated attacker can compromise the private keys of a JWT token and reuse them to manipulate the access tokens to access the platform as any desired user (clients and administrators). |
2021-05-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-36124
MISC
MISC
MISC |
| pax_technology — paxstore |
Pax Technology PAXSTORE v7.0.8_20200511171508 and lower is affected by an information disclosure vulnerability. Through the PUK signature functionality, an administrator will not have access to the current p12 certificate and password. When accessing this functionality, the administrator has the option to replace the current certificate and it is not possible to view the certificate password (p12) already deployed on the platform. The replacement p12 certificate returns to users in base64 with its password, which can be accessed by non-administrator users. |
2021-05-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-36127
MISC
MISC
MISC |
| pax_technology — paxstore |
Pax Technology PAXSTORE v7.0.8_20200511171508 and lower is affected by incorrect access control where password revalidation in sensitive operations can be bypassed remotely by an authenticated attacker through requesting the endpoint directly. |
2021-05-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-36125
MISC
MISC
MISC |
| proofpoint — enterprise_protection |
Proofpoint Enterprise Protection (PPS/PoD) before 8.17.0 contains a vulnerability that could allow an attacker to deliver an email message with a malicious attachment that bypasses scanning and file-blocking rules. The vulnerability exists because messages with certain crafted and malformed multipart structures are not properly handled. |
2021-05-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-14009
MISC
MISC |
| prototype_pollution — prototype_polution |
The package handlebars before 4.7.7 are vulnerable to Prototype Pollution when selecting certain compiling options to compile templates coming from an untrusted source. |
2021-05-04 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-23383
MISC
MISC
MISC
MISC
MISC |
| puppycms — puppycms |
Cross Site Request Forgery (CSRF) vulnerability in puppyCMS v5.1 that can change the admin’s password via /admin/settings.php. |
2021-05-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-18889
MISC |
| puppycms — puppycms |
Rmote Code Execution (RCE) vulnerability in puppyCMS v5.1 due to insecure permissions, which could let a remote malicious user getshell via /admin/functions.php. |
2021-05-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-18890
MISC |
| puppycms — puppycms |
Arbitrary File Deletion vulnerability in puppyCMS v5.1 allows remote malicious attackers to delete the file/folder via /admin/functions.php. |
2021-05-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-18888
MISC |
| python — stdlib_ipaddress |
Improper input validation of octal strings in Python stdlib ipaddress 3.10 and below allows unauthenticated remote attackers to perform indeterminate SSRF, RFI, and LFI attacks on many programs that rely on Python stdlib ipaddress. IP address octects are left stripped instead of evaluated as valid IP addresses. |
2021-05-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-29921
MISC
MISC
MISC
MISC
MISC
MISC
MISC
MISC
MISC |
| qemu — qemu |
A heap buffer overflow was found in the floppy disk emulator of QEMU up to 6.0.0 (including). It could occur in fdctrl_transfer_handler() in hw/block/fdc.c while processing DMA read data transfers from the floppy drive to the guest system. A privileged guest user could use this flaw to crash the QEMU process on the host resulting in DoS scenario, or potential information leakage from the host memory. |
2021-05-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-3507
MISC |
| qualcomm — multiple_snapdragon_products |
Histogram type KPI was teardown with the assumption of the existence of histogram binning info and will lead to null pointer access when histogram binning info is missing due to lack of null check in Snapdragon Auto, Snapdragon Compute, Snapdragon Connectivity, Snapdragon Mobile |
2021-05-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-11273
CONFIRM |
| qualcomm — multiple_snapdragon_products |
Use after free in camera If the threadmanager is being cleaned up while the worker thread is processing objects in Snapdragon Auto, Snapdragon Compute, Snapdragon Connectivity, Snapdragon Consumer IOT, Snapdragon Industrial IOT, Snapdragon Mobile |
2021-05-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-11295
CONFIRM |
| qualcomm — multiple_snapdragon_products |
Out of bound read can happen in Widevine TA while copying data to buffer from user data due to lack of check of buffer length received in Snapdragon Auto, Snapdragon Compute, Snapdragon Connectivity, Snapdragon Consumer IOT, Snapdragon Industrial IOT, Snapdragon IoT, Snapdragon Mobile, Snapdragon Voice & Music, Snapdragon Wearables, Snapdragon Wired Infrastructure and Networking |
2021-05-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-11293
CONFIRM |
| qualcomm — multiple_snapdragon_products |
Buffer over-read while unpacking the RTCP packet we may read extra byte if wrong length is provided in RTCP packets in Snapdragon Auto, Snapdragon Compute, Snapdragon Connectivity, Snapdragon Consumer IOT, Snapdragon Industrial IOT, Snapdragon IoT, Snapdragon Mobile, Snapdragon Voice & Music, Snapdragon Wearables |
2021-05-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-11285
CONFIRM |
| qualcomm — multiple_snapdragon_products |
Memory corruption while processing crafted SDES packets due to improper length check in sdes packets recieved in Snapdragon Auto, Snapdragon Compute, Snapdragon Connectivity, Snapdragon Consumer IOT, Snapdragon Industrial IOT, Snapdragon IoT, Snapdragon Mobile, Snapdragon Voice & Music, Snapdragon Wearables |
2021-05-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-11279
CONFIRM |
| qualcomm — multiple_snapdragon_products |
Locked memory can be unlocked and modified by non secure boot loader through improper system call sequence making the memory region untrusted source of input for secure boot loader in Snapdragon Auto, Snapdragon Compute, Snapdragon Industrial IOT, Snapdragon Mobile, Snapdragon Wired Infrastructure and Networking |
2021-05-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-11284
CONFIRM |
| qualcomm — multiple_snapdragon_products |
Double free in video due to lack of input buffer length check in Snapdragon Auto, Snapdragon Compute, Snapdragon Connectivity, Snapdragon Consumer IOT, Snapdragon Industrial IOT, Snapdragon Mobile, Snapdragon Voice & Music, Snapdragon Wearables |
2021-05-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1910
CONFIRM |
| qualcomm — multiple_snapdragon_products |
Possible use after free due to lack of null check while memory is being freed in FastRPC driver in Snapdragon Auto, Snapdragon Compute, Snapdragon Connectivity, Snapdragon Consumer IOT, Snapdragon Industrial IOT, Snapdragon Mobile, Snapdragon Voice & Music, Snapdragon Wearables, Snapdragon Wired Infrastructure and Networking |
2021-05-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1927
CONFIRM |
| qualcomm — multiple_snapdragon_products |
Out of bound write in logger due to prefix size is not validated while prepended to logging string in Snapdragon Auto, Snapdragon Compute, Snapdragon Connectivity, Snapdragon Consumer IOT, Snapdragon Industrial IOT, Snapdragon Mobile, Snapdragon Wearables |
2021-05-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-11294
CONFIRM |
| qualcomm — multiple_snapdragon_products |
Possible denial of service scenario due to improper handling of group management action frame in Snapdragon Auto, Snapdragon Compute, Snapdragon Connectivity, Snapdragon Consumer Electronics Connectivity, Snapdragon Consumer IOT, Snapdragon Industrial IOT, Snapdragon Mobile, Snapdragon Voice & Music, Snapdragon Wired Infrastructure and Networking |
2021-05-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1925
CONFIRM |
| qualcomm — multiple_snapdragon_products |
Buffer overflow can occur due to improper validation of NDP application information length in Snapdragon Auto, Snapdragon Compute, Snapdragon Connectivity, Snapdragon Consumer Electronics Connectivity, Snapdragon Consumer IOT, Snapdragon Industrial IOT, Snapdragon Mobile, Snapdragon Voice & Music, Snapdragon Wired Infrastructure and Networking |
2021-05-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1915
CONFIRM |
| qualcomm — multiple_snapdragon_products |
Out of bound write can occur in TZ command handler due to lack of validation of command ID in Snapdragon Auto, Snapdragon Compute, Snapdragon Connectivity, Snapdragon Consumer IOT, Snapdragon Industrial IOT, Snapdragon IoT, Snapdragon Mobile, Snapdragon Voice & Music, Snapdragon Wearables, Snapdragon Wired Infrastructure and Networking |
2021-05-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-11289
CONFIRM |
| qualcomm — multiple_snapdragon_products |
Improper handling of address deregistration on failure can lead to new GPU address allocation failure. in Snapdragon Auto, Snapdragon Compute, Snapdragon Connectivity, Snapdragon Consumer IOT, Snapdragon Industrial IOT, Snapdragon Mobile, Snapdragon Voice & Music, Snapdragon Wearables |
2021-05-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1906
CONFIRM |
| qualcomm — multiple_snapdragon_products |
Possible use after free due to improper handling of memory mapping of multiple processes simultaneously. in Snapdragon Auto, Snapdragon Compute, Snapdragon Connectivity, Snapdragon Consumer IOT, Snapdragon Industrial IOT, Snapdragon Mobile, Snapdragon Voice & Music, Snapdragon Wearables |
2021-05-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1905
CONFIRM |
| qualcomm — multiple_snapdragon_products |
A possible use-after-free occurrence in audio driver can happen when pointers are not properly handled in Snapdragon Auto, Snapdragon Compute, Snapdragon Connectivity, Snapdragon Consumer IOT, Snapdragon Industrial IOT, Snapdragon Mobile, Snapdragon Voice & Music, Snapdragon Wearables, Snapdragon Wired Infrastructure and Networking |
2021-05-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1891
CONFIRM |
| qualcomm — multiple_snapdragon_products |
Out of bound write can occur in playready while processing command due to lack of input validation in Snapdragon Auto, Snapdragon Compute, Snapdragon Connectivity, Snapdragon Consumer IOT, Snapdragon Industrial IOT, Snapdragon Mobile, Snapdragon Voice & Music |
2021-05-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-11288
CONFIRM |
| qualcomm — multiple_snapdragon_products |
Denial of service in MODEM due to assert to the invalid configuration in Snapdragon Auto, Snapdragon Compute, Snapdragon Connectivity, Snapdragon Consumer IOT, Snapdragon Industrial IOT, Snapdragon Mobile |
2021-05-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-11274
CONFIRM |
| qualcomm — multiple_snapdragon_products |
Memory corruption during buffer allocation due to dereferencing session ctx pointer without checking if pointer is valid in Snapdragon Auto, Snapdragon Compute, Snapdragon Connectivity, Snapdragon Mobile |
2021-05-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-11254
CONFIRM |
| qualcomm — multiple_snapdragon_products |
Possible integer overflow due to improper length check while flashing an image in Snapdragon Consumer IOT, Snapdragon Industrial IOT, Snapdragon Voice & Music |
2021-05-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1895
CONFIRM |
| qualcomm — snapdragon_auto_and_snapdragon_mobile |
Potential UE reset while decoding a crafted Sib1 or SIB1 that schedules unsupported SIBs and can lead to denial of service in Snapdragon Auto, Snapdragon Mobile |
2021-05-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-11268
CONFIRM |
| qualys — exim |
Exim 4 before 4.94.2 allows Exposure of File Descriptor to Unintended Control Sphere because rda_interpret uses a privileged pipe that lacks a close-on-exec flag. |
2021-05-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-28012
MISC |
| qualys — exim |
Exim 4 before 4.94.2 has Improper Neutralization of Line Delimiters, relevant in non-default configurations that enable Delivery Status Notification (DSN). Certain uses of ORCPT= can place a newline into a spool header file, and indirectly allow unauthenticated remote attackers to execute arbitrary commands as root. |
2021-05-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-28026
MISC |
| qualys — exim |
Exim 4 before 4.94.2 has Improper Initialization that can lead to recursion-based stack consumption or other consequences. This occurs because use of certain getc functions is mishandled when a client uses BDAT instead of DATA. |
2021-05-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-28019
MISC |
| qualys — exim |
Exim 4 before 4.94.2 allows Execution with Unnecessary Privileges. Because Exim operates as root in the spool directory (owned by a non-root user), an attacker can write to a /var/spool/exim4/input spool header file, in which a crafted recipient address can indirectly lead to command execution. |
2021-05-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-28008
MISC |
| qualys — exim |
Exim 4 before 4.94.2 allows Use After Free in smtp_reset in certain situations that may be common for builds with OpenSSL. |
2021-05-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-28018
MISC |
| qualys — exim |
Exim 4 before 4.94.2 allows Execution with Unnecessary Privileges. Because Exim operates as root in the log directory (owned by a non-root user), a symlink or hard link attack allows overwriting critical root-owned files anywhere on the filesystem. |
2021-05-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-28007
MISC |
| qualys — exim |
Exim 4 before 4.94.2 allows Heap-based Buffer Overflow in queue_run via two sender options: -R and -S. This may cause privilege escalation from exim to root. |
2021-05-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-28011
MISC |
| qualys — exim |
Exim 4 before 4.94.2 has Improper Neutralization of Line Delimiters. An authenticated remote SMTP client can insert newline characters into a spool file (which indirectly leads to remote code execution as root) via AUTH= in a MAIL FROM command. |
2021-05-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-28021
MISC |
| qualys — exim |
Exim 4 before 4.94.2 has Execution with Unnecessary Privileges. By leveraging a delete_pid_file race condition, a local user can delete arbitrary files as root. This involves the -oP and -oPX options. |
2021-05-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-27216
MISC |
| qualys — exim |
Exim 4 before 4.94.2 has Improper Restriction of Write Operations within the Bounds of a Memory Buffer. This occurs when processing name=value pairs within MAIL FROM and RCPT TO commands. |
2021-05-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-28022
MISC |
qualys — exim
|
Exim 4 before 4.94.2 allows Buffer Underwrite that may result in unauthenticated remote attackers executing arbitrary commands, because smtp_ungetc was only intended to push back characters, but can actually push back non-character error codes such as EOF. |
2021-05-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-28024
MISC |
| qualys — exim |
Exim 4 before 4.94.2 allows Out-of-bounds Read because pdkim_finish_bodyhash does not validate the relationship between sig->bodyhash.len and b->bh.len; thus, a crafted DKIM-Signature header might lead to a leak of sensitive information from process memory. |
2021-05-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-28025
MISC |
| qualys — exim |
Exim 4 before 4.94.2 allows Integer Overflow to Buffer Overflow because get_stdinput allows unbounded reads that are accompanied by unbounded increases in a certain size variable. NOTE: exploitation may be impractical because of the execution time needed to overflow (multiple days). |
2021-05-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-28009
MISC |
| qualys — exim |
Exim 4 before 4.94.2 allows Out-of-bounds Write because the main function, while setuid root, copies the current working directory pathname into a buffer that is too small (on some common platforms). |
2021-05-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-28010
MISC |
| qualys — exim |
Exim 4 before 4.94.2 allows Heap-based Buffer Overflow because it mishandles “-F ‘.(‘” on the command line, and thus may allow privilege escalation from any user to root. This occurs because of the interpretation of negative sizes in strncpy. |
2021-05-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-28013
MISC |
| qualys — exim |
Exim 4 before 4.94.2 allows Execution with Unnecessary Privileges. The -oP option is available to the exim user, and allows a denial of service because root-owned files can be overwritten. |
2021-05-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-28014
MISC |
| qualys — exim |
Exim 4 before 4.94.2 has Improper Neutralization of Line Delimiters. Local users can alter the behavior of root processes because a recipient address can have a newline character. |
2021-05-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-28015
MISC |
| qualys — exim |
Exim 4 before 4.94.2 allows an off-by-two Out-of-bounds Write because “-F ”” is mishandled by parse_fix_phrase. |
2021-05-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-28016
MISC |
| qualys — exim |
Exim 4 before 4.94.2 allows Integer Overflow to Buffer Overflow in receive_add_recipient via an e-mail message with fifty million recipients. NOTE: remote exploitation may be difficult because of resource consumption. |
2021-05-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-28017
MISC |
| qualys — exim |
Exim 4 before 4.92 allows Integer Overflow to Buffer Overflow, in which an unauthenticated remote attacker can execute arbitrary code by leveraging the mishandling of continuation lines during header-length restriction. |
2021-05-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-28020
MISC |
| qualys — exim |
Exim 4 before 4.94.2 allows Out-of-bounds Read. smtp_setup_msg may disclose sensitive information from process memory to an unauthenticated SMTP client. |
2021-05-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-28023
MISC |
| quan-fang-wei-tong-xun — quan-fang-wei-tong-xun |
Special characters of picture preview page in the Quan-Fang-Wei-Tong-Xun system are not filtered in users’ input, which allow remote authenticated attackers can inject malicious JavaScript and carry out Reflected XSS (Cross-site scripting) attacks, additionally access and manipulate customer’s information. |
2021-05-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-30172
MISC |
| red_hat — red_hat |
A flaw was found in tripleo-ansible version as shipped in Red Hat Openstack 16.1. The Ansible log file is readable to all users during stack update and creation. The highest threat from this vulnerability is to data confidentiality. |
2021-05-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-31918
MISC |
| redis — redis |
Redis is an open source (BSD licensed), in-memory data structure store, used as a database, cache, and message broker. An integer overflow bug in Redis version 6.0 or newer could be exploited using the `STRALGO LCS` command to corrupt the heap and potentially result with remote code execution. The problem is fixed in version 6.2.3 and 6.0.13. An additional workaround to mitigate the problem without patching the redis-server executable is to use ACL configuration to prevent clients from using the `STRALGO LCS` command. |
2021-05-04 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-29477
MISC
CONFIRM |
| redis — redis |
Redis is an open source (BSD licensed), in-memory data structure store, used as a database, cache, and message broker. An integer overflow bug in Redis 6.2 before 6.2.3 could be exploited to corrupt the heap and potentially result with remote code execution. Redis 6.0 and earlier are not directly affected by this issue. The problem is fixed in version 6.2.3. An additional workaround to mitigate the problem without patching the `redis-server` executable is to prevent users from modifying the `set-max-intset-entries` configuration parameter. This can be done using ACL to restrict unprivileged users from using the `CONFIG SET` command. |
2021-05-04 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-29478
CONFIRM
MISC |
| rust — rust |
An issue was discovered in the algorithmica crate through 2021-03-07 for Rust. There is a double free in merge_sort::merge(). |
2021-05-03 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-31996
MISC |
| sabnzbd — sabnzbd |
SABnzbd is an open source binary newsreader. A vulnerability was discovered in SABnzbd that could trick the `filesystem.renamer()` function into writing downloaded files outside the configured Download Folder via malicious PAR2 files. A patch was released as part of SABnzbd 3.2.1RC1. As a workaround, limit downloads to NZBs without PAR2 files, deny write permissions to the SABnzbd process outside areas it must access to perform its job, or update to a fixed version. |
2021-05-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-29488
CONFIRM |
| samba — fedora33 |
A flaw was found in samba. The Samba smbd file server must map Windows group identities (SIDs) into unix group ids (gids). The code that performs this had a flaw that could allow it to read data beyond the end of the array in the case where a negative cache entry had been added to the mapping cache. This could cause the calling code to return those values into the process token that stores the group membership for a user. The highest threat from this vulnerability is to data confidentiality and integrity. |
2021-05-05 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-20254
MISC
MISC
MISC
FEDORA
FEDORA |
| shapeshift — keepkey |
Insufficient length checks in the ShapeShift KeepKey hardware wallet firmware before 7.1.0 allow a stack buffer overflow via crafted messages. The overflow in ethereum_extractThorchainSwapData() in ethereum.c can circumvent stack protections and lead to code execution. The vulnerable interface is reachable remotely over WebUSB. |
2021-05-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-31616
MISC
MISC
MISC
MISC |
| sif — sif |
SIF is an open source implementation of the Singularity Container Image Format. The `siftool new` command and func siftool.New() produce predictable UUID identifiers due to insecure randomness in the version of the `github.com/satori/go.uuid` module used as a dependency. A patch is available in version >= v1.2.3 of the module. Users are encouraged to upgrade. As a workaround, users passing CreateInfo struct should ensure the `ID` field is generated using a version of `github.com/satori/go.uuid` that is not vulnerable to this issue. |
2021-05-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-29499
CONFIRM |
| simplelink — wi-fi |
The affected product is vulnerable to an integer overflow while processing HTTP headers, which may allow an attacker to remotely execute code on the SimpleLink Wi-Fi (MSP432E4 SDK: v4.20.00.12 and prior, CC32XX SDK v4.30.00.06 and prior, CC13X0 SDK versions prior to v4.10.03, CC13X2 and CC26XX SDK versions prior to v4.40.00, CC3200 SDK v1.5.0 and prior, CC3100 SDK v1.3.0 and prior). |
2021-05-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-22679
MISC |
| simplelink — wi-fi |
The affected product is vulnerable to integer overflow while parsing malformed over-the-air firmware update files, which may allow an attacker to remotely execute code on SimpleLink Wi-Fi (MSP432E4 SDK: v4.20.00.12 and prior, CC32XX SDK v4.30.00.06 and prior, CC13X0 SDK versions prior to v4.10.03, CC13X2 and CC26XX SDK versions prior to v4.40.00, CC3200 SDK v1.5.0 and prior, CC3100 SDK v1.3.0 and prior). |
2021-05-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-22675
MISC |
| simplelink — wi-fi |
An integer overflow exists in the APIs of the host MCU while trying to connect to a WIFI network may lead to issues such as a denial-of-service condition or code execution on the SimpleLink Wi-Fi (MSP432E4 SDK: v4.20.00.12 and prior, CC32XX SDK v4.30.00.06 and prior, CC13X0 SDK versions prior to v4.10.03, CC13X2 and CC26XX SDK versions prior to v4.40.00, CC3200 SDK v1.5.0 and prior, CC3100 SDK v1.3.0 and prior). |
2021-05-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-22677
MISC |
| simplelink — wi-fi |
Multiple integer overflow issues exist while processing long domain names, which may allow an attacker to remotely execute code on the SimpleLink Wi-Fi (MSP432E4 SDK: v4.20.00.12 and prior, CC32XX SDK v4.30.00.06 and prior, CC13X0 SDK versions prior to v4.10.03, CC13X2 and CC26XX SDK versions prior to v4.40.00, CC3200 SDK v1.5.0 and prior, CC3100 SDK v1.3.0 and prior). |
2021-05-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-22671
MISC |
| simplelink — wi-fi |
The affected product is vulnerable to stack-based buffer overflow while processing over-the-air firmware updates from the CDN server, which may allow an attacker to remotely execute code on the SimpleLink Wi-Fi (MSP432E4 SDK: v4.20.00.12 and prior, CC32XX SDK v4.30.00.06 and prior, CC13X0 SDK versions prior to v4.10.03, CC13X2 and CC26XX SDK versions prior to v4.40.00, CC3200 SDK v1.5.0 and prior, CC3100 SDK v1.3.0 and prior). |
2021-05-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-22673
MISC |
| solarwinds — serv-u |
An issue was discovered in SolarWinds Serv-U before 15.2.2. Unauthenticated attackers can retrieve cleartext passwords via macro Injection. NOTE: this had a distinct fix relative to CVE-2020-35481. |
2021-05-04 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-3154
MISC |
solarwinds — serv-u
|
SolarWinds Serv-U before 15.2 is affected by Cross Site Scripting (XSS) via the HTTP Host header. |
2021-05-05 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-25179
MISC
MISC
MISC
MISC |
| solarwinds — sery-u |
SolarWinds Serv-U before 15.1.6 Hotfix 3 is affected by Cross Site Scripting (XSS) via a directory name (entered by an admin) containing a JavaScript payload. |
2021-05-05 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-22428
MISC
MISC
MISC
MISC |
| stacklift — localstack |
The dashboard component of StackLift LocalStack 0.12.6 allows attackers to inject arbitrary shell commands via the functionName parameter. |
2021-05-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-32090
MISC
MISC |
| stacklift — localstack |
A Cross-site scripting (XSS) vulnerability exists in StackLift LocalStack 0.12.6. |
2021-05-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-32091
MISC
MISC |
| stormshield — sns |
Stormshield SNS with versions before 3.7.18, 3.11.6 and 4.1.6 has a memory-management defect in the SNMP plugin that can lead to excessive consumption of memory and CPU resources, and possibly a denial of service. |
2021-05-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-28665
MISC
MISC |
| strapi — strapi |
In Strapi through 3.6.0, the admin panel allows the changing of one’s own password without entering the current password. An attacker who gains access to a valid session can use this to take over an account by changing the password. |
2021-05-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-28128
MISC
MISC
MISC |
| suse — linux_enterprise_server |
A Incorrect Default Permissions vulnerability in the packaging of cups of SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 11-SP4-LTSS, SUSE Manager Server 4.0, SUSE OpenStack Cloud Crowbar 9; openSUSE Leap 15.2, Factory allows local attackers with control of the lp users to create files as root with 0644 permissions without the ability to set the content. This issue affects: SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 11-SP4-LTSS cups versions prior to 1.3.9. SUSE Manager Server 4.0 cups versions prior to 2.2.7. SUSE OpenStack Cloud Crowbar 9 cups versions prior to 1.7.5. openSUSE Leap 15.2 cups versions prior to 2.2.7. openSUSE Factory cups version 2.3.3op2-2.1 and prior versions. |
2021-05-05 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-25317
CONFIRM
FEDORA
FEDORA |
| suse — opensuse |
A Incorrect Default Permissions vulnerability in the packaging of virtualbox of openSUSE Factory allows local attackers in the vboxusers groupu to escalate to root. This issue affects: openSUSE Factory virtualbox version 6.1.20-1.1 and prior versions. |
2021-05-05 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-25319
CONFIRM |
| tenda — ac11_devices |
An issue was discovered on Tenda AC11 devices with firmware through 02.03.01.104_CN. A stack buffer overflow vulnerability in /goform/setportList allows attackers to execute arbitrary code on the system via a crafted post request. |
2021-05-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-31758
MISC |
| tenda — ac11_devices |
An issue was discovered on Tenda AC11 devices with firmware through 02.03.01.104_CN. A stack buffer overflow vulnerability in /goform/setVLAN allows attackers to execute arbitrary code on the system via a crafted post request. |
2021-05-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-31757
MISC |
| tenda — ac11_devices |
An issue was discovered on Tenda AC11 devices with firmware through 02.03.01.104_CN. A stack buffer overflow vulnerability in /goform/setmac allows attackers to execute arbitrary code on the system via a crafted post request. |
2021-05-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-31755
MISC |
| tenda — ac11_devices |
An issue was discovered on Tenda AC11 devices with firmware through 02.03.01.104_CN. A stack buffer overflow vulnerability in /gofrom/setwanType allows attackers to execute arbitrary code on the system via a crafted post request. This occurs when input vector controlled by malicious attack get copied to the stack variable. |
2021-05-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-31756
MISC |
| themegrill-demo-importer — themegrill-demo-importer |
themegrill-demo-importer before 1.6.2 does not require authentication for wiping the database, because of a reset_wizard_actions hook. |
2021-05-05 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-36333
MISC
MISC |
| themegrill-demo-importer — themegrill-demo-importer |
themegrill-demo-importer before 1.6.3 allows CSRF, as demonstrated by wiping the database. |
2021-05-05 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-36334
MISC
MISC |
| trend_micro — home_network_security |
Trend Micro Home Network Security 6.5.599 and earlier is vulnerable to a file-parsing vulnerability which could allow an attacker to exploit the vulnerability and cause a denial-of-service to the device. This vulnerability is similar, but not identical to CVE-2021-31518. |
2021-05-05 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-31517
N/A |
| trend_micro — home_network_security |
Trend Micro Home Network Security 6.5.599 and earlier is vulnerable to a file-parsing vulnerability which could allow an attacker to exploit the vulnerability and cause a denial-of-service to the device. This vulnerability is similar, but not identical to CVE-2021-31517. |
2021-05-05 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-31518
N/A |
vaadin — vaadin
|
Insecure temporary directory usage in frontend build functionality of com.vaadin:flow-server versions 2.0.9 through 2.5.2 (Vaadin 14.0.3 through Vaadin 14.5.2), 3.0 prior to 6.0 (Vaadin 15 prior to 19), and 6.0.0 through 6.0.5 (Vaadin 19.0.0 through 19.0.4) allows local users to inject malicious code into frontend resources during application rebuilds. |
2021-05-05 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-31411
CONFIRM
CONFIRM |
| vaadin — vaadin |
Unsafe validation RegEx in EmailValidator component in com.vaadin:vaadin-compatibility-server versions 8.0.0 through 8.12.4 (Vaadin versions 8.0.0 through 8.12.4) allows attackers to cause uncontrolled resource consumption by submitting malicious email addresses. |
2021-05-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-31409
CONFIRM
CONFIRM
CONFIRM |
| veritystream — msow_solutions |
Primary Source Verification in VerityStream MSOW Solutions before 3.1.1 allows an anonymous internet user to discover Social Security Number (SSN) values via a brute-force attack on a (sometimes hidden) search field, because the last four SSN digits are part of the supported combination of search selectors. This discloses doctors’ and nurses’ social security numbers and PII. |
2021-05-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-32077
MISC
MISC |
| vmware — vreaize_business |
VMware vRealize Business for Cloud 7.x prior to 7.6.0 contains a remote code execution vulnerability due to an unauthorised end point. A malicious actor with network access may exploit this issue causing unauthorised remote code execution on vRealize Business for Cloud Virtual Appliance. |
2021-05-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-21984
MISC |
windscribe — windscribe
|
All versions of Windscribe VPN for Mac and Windows <= v2.02.10 contain a local privilege escalation vulnerability in the WindscribeService component. A low privilege user could leverage several openvpn options to execute code as root/SYSTEM. |
2021-05-04 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-27518
MISC
MISC |
| wordpress — wordpress |
The College publisher Import WordPress plugin through 0.1 does not check for the uploaded CSV file to import, allowing high privilege users to upload arbitrary files, such as PHP, leading to RCE. Due to the lack of CSRF check, the issue could also be exploited via a CSRF attack. |
2021-05-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-24254
MISC
CONFIRM |
| wordpress — wordpress |
The “HT Mega – Absolute Addons for Elementor Page Builder” WordPress Plugin before 1.5.7 has several widgets that are vulnerable to stored Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) by lower-privileged users such as contributors, all via a similar method. |
2021-05-05 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-24261
CONFIRM
MISC |
| wordpress — wordpress |
The “Elementor Addon Elements” WordPress Plugin before 1.11.2 has several widgets that are vulnerable to stored Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) by lower-privileged users such as contributors, all via a similar method. |
2021-05-05 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-24259
CONFIRM
MISC |
| wordpress — wordpress |
In the eCommerce module of the NextGEN Gallery Pro WordPress plugin before 3.1.11, there is an action to call get_cart_items via photocrati_ajax , after that the settings[shipping_address][name] is able to inject malicious javascript. |
2021-05-05 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-24293
MISC
CONFIRM |
| wordpress — wordpress |
The “Ultimate Addons for Elementor” WordPress Plugin before 1.30.0 has several widgets that are vulnerable to stored Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) by lower-privileged users such as contributors, all via a similar method. |
2021-05-05 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-24271
CONFIRM
MISC |
| wordpress — wordpress |
The “Rife Elementor Extensions & Templates” WordPress Plugin before 1.1.6 has a widget that is vulnerable to stored Cross-Site Scripting(XSS) by lower-privileged users such as contributors, all via a similar method. |
2021-05-05 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-24265
CONFIRM
MISC |
| wordpress — wordpress |
The “Image Hover Effects – Elementor Addon” WordPress Plugin before 1.3.4 has a widget that is vulnerable to stored Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) by lower-privileged users such as contributors, all via a similar method. |
2021-05-05 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-24264
CONFIRM
MISC |
| wordpress — wordpress |
The “Premium Addons for Elementor” WordPress Plugin before 4.2.8 has several widgets that are vulnerable to stored Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) by lower-privileged users such as contributors, all via a similar method. |
2021-05-05 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-24257
CONFIRM
MISC |
| wordpress — wordpress |
The “Clever Addons for Elementor” WordPress Plugin before 2.1.0 has several widgets that are vulnerable to stored Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) by lower-privileged users such as contributors, all via a similar method. |
2021-05-05 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-24273
MISC
CONFIRM |
| wordpress — wordpress |
The Classyfrieds WordPress plugin through 3.8 does not properly check the uploaded file when an authenticated user adds a listing, only checking the content-type in the request. This allows any authenticated user to upload arbitrary PHP files via the Add Listing feature of the plugin, leading to RCE. |
2021-05-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-24253
CONFIRM
MISC |
| wordpress — wordpress |
The Event Banner WordPress plugin through 1.3 does not verify the uploaded image file, allowing admin accounts to upload arbitrary files, such as .exe, .php, or others executable, leading to RCE. Due to the lack of CSRF check, the issue can also be used via such vector to achieve the same result, or via a LFI as authorisation checks are missing (but would require WP to be loaded) |
2021-05-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-24252
MISC
CONFIRM |
| wordpress — wordpress |
The Business Directory Plugin – Easy Listing Directories for WordPress WordPress plugin before 5.11.1 did not properly check for imported files, forbidding certain extension via a blacklist approach, allowing administrator to import an archive with a .php4 inside for example, leading to RCE |
2021-05-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-24248
CONFIRM |
| wordpress — wordpress |
An AJAX action registered by the WPBakery Page Builder (Visual Composer) Clipboard WordPress plugin before 4.5.8 did not have capability checks, allowing low privilege users, such as subscribers, to update the license options (key, email). |
2021-05-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-24244
CONFIRM
MISC |
| wordpress — wordpress |
The Workscout Core WordPress plugin before 1.3.4, used by the WorkScout Theme did not sanitise the chat messages sent via the workscout_send_message_chat AJAX action, leading to Stored Cross-Site Scripting and Cross-Frame Scripting issues |
2021-05-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-24246
CONFIRM
MISC |
| wordpress — wordpress |
The Essential Addons for Elementor Lite WordPress Plugin before 4.5.4 has two widgets that are vulnerable to stored Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) by lower-privileged users such as contributors, both via a similar method. |
2021-05-05 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-24255
CONFIRM
MISC |
wordpress — wordpress
|
The OpenID Connect Generic Client WordPress plugin 3.8.0 and 3.8.1 did not sanitise the login error when output back in the login form, leading to a reflected Cross-Site Scripting issue. This issue does not require authentication and can be exploited with the default configuration. |
2021-05-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-24214
CONFIRM |
| wordpress — wordpress |
The Contact Form Check Tester WordPress plugin through 1.0.2 settings are visible to all registered users in the dashboard and are lacking any sanitisation. As a result, any registered user, such as subscriber, can leave an XSS payload in the plugin settings, which will be triggered by any user visiting them, and could allow for privilege escalation. The vendor decided to close the plugin. |
2021-05-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-24247
CONFIRM |
| wordpress — wordpress |
An AJAX action registered by the WPBakery Page Builder (Visual Composer) Clipboard WordPress plugin before 4.5.6 did not have capability checks nor sanitization, allowing low privilege users (subscriber+) to call it and set XSS payloads, which will be triggered in all backend pages. |
2021-05-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-24243
CONFIRM
MISC |
| wordpress — wordpress |
The Imagements WordPress plugin through 1.2.5 allows images to be uploaded in comments, however only checks for the Content-Type in the request to forbid dangerous files. This allows unauthenticated attackers to upload arbitrary files by using a valid image Content-Type along with a PHP filename and code, leading to RCE. |
2021-05-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-24236
CONFIRM |
| wordpress — wordpress |
The Business Directory Plugin – Easy Listing Directories for WordPress WordPress plugin before 5.11.2 suffered from a Cross-Site Request Forgery issue, allowing an attacker to make a logged in administrator update arbitrary payment history, such as change their status (from pending to completed to example) |
2021-05-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-24251
CONFIRM |
| wordpress — wordpress |
The Business Directory Plugin – Easy Listing Directories for WordPress WordPress plugin before 5.11 suffered from a Cross-Site Request Forgery issue, allowing an attacker to make a logged in administrator import files. As the plugin also did not validate uploaded files, it could lead to RCE. |
2021-05-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-24179
CONFIRM |
| wordpress — wordpress |
The Business Directory Plugin – Easy Listing Directories for WordPress WordPress plugin before 5.11.1 suffered from Cross-Site Request Forgery issues, allowing an attacker to make a logged in administrator add, edit or delete form fields, which could also lead to Stored Cross-Site Scripting issues. |
2021-05-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-24178
CONFIRM |
| wordpress — wordpress |
The Business Directory Plugin – Easy Listing Directories for WordPress WordPress plugin before 5.11.2 suffered from lack of sanitisation in the label of the Form Fields, leading to Authenticated Stored Cross-Site Scripting issues across various pages of the plugin. |
2021-05-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-24250
CONFIRM |
| wordpress — wordpress |
The Contact Form by Supsystic WordPress plugin before 1.7.15 did not sanitise the tab parameter of its options page before outputting it in an attribute, leading to a reflected Cross-Site Scripting issue |
2021-05-05 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-24276
CONFIRM |
| wordpress — wordpress |
EWWW Image Optimizer before 2.8.5 allows remote command execution because it relies on a protection mechanism involving boolval, which is unavailable before PHP 5.5. |
2021-05-05 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2016-20010
MISC
MISC |
| wordpress — wordpress |
The Business Directory Plugin – Easy Listing Directories for WordPress WordPress plugin before 5.11.2 suffered from a Cross-Site Request Forgery issue, allowing an attacker to make a logged in administrator export files, which could then be downloaded by the attacker to get access to PII, such as email, home addresses etc |
2021-05-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-24249
CONFIRM |
| wordpress — wordpress |
The fitness calculators WordPress plugin before 1.9.6 add calculators for Water intake, BMI calculator, protein Intake, and Body Fat and was lacking CSRF check, allowing attackers to make logged in users perform unwanted actions, such as change the calculator headers. Due to the lack of sanitisation, this could also lead to a Stored Cross-Site Scripting issue |
2021-05-05 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-24272
CONFIRM |
| wordpress — wordpress |
The Stop Spammers WordPress plugin before 2021.9 did not escape user input when blocking requests (such as matching a spam word), outputting it in an attribute after sanitising it to remove HTML tags, which is not sufficient and lead to a reflected Cross-Site Scripting issue. |
2021-05-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-24245
CONFIRM |
| wordpress — wordpress |
The Popup by Supsystic WordPress plugin before 1.10.5 did not sanitise the tab parameter of its options page before outputting it in an attribute, leading to a reflected Cross-Site Scripting issue |
2021-05-05 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-24275
CONFIRM |
| wordpress — wordpress |
The Ultimate Maps by Supsystic WordPress plugin before 1.2.5 did not sanitise the tab parameter of its options page before outputting it in an attribute, leading to a reflected Cross-Site Scripting issue |
2021-05-05 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-24274
CONFIRM |
| wordpress — wordpress |
The “Elementor – Header, Footer & Blocks Template” WordPress Plugin before 1.5.8 has two widgets that are vulnerable to stored Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) by lower-privileged users such as contributors, all via a similar method. |
2021-05-05 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-24256
MISC
CONFIRM |
| wordpress — wordpress |
The “Sina Extension for Elementor” WordPress Plugin before 3.3.12 has several widgets that are vulnerable to stored Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) by lower-privileged users such as contributors, all via a similar method. |
2021-05-05 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-24269
CONFIRM
MISC |
| wordpress — wordpress |
The “All-in-One Addons for Elementor – WidgetKit” WordPress Plugin before 2.3.10 has several widgets that are vulnerable to stored Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) by lower-privileged users such as contributors, all via a similar method. |
2021-05-05 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-24267
CONFIRM
MISC |
| wordpress — wordpress |
The “DeTheme Kit for Elementor” WordPress Plugin before 1.5.5.5 has a widget that is vulnerable to stored Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) by lower-privileged users such as contributors, all via a similar method. |
2021-05-05 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-24270
CONFIRM
MISC |
| wordpress — wordpress |
The “Elementor Addons – PowerPack Addons for Elementor” WordPress Plugin before 2.3.2 for WordPress has several widgets that are vulnerable to stored Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) by lower-privileged users such as contributors, all via a similar method. |
2021-05-05 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-24263
CONFIRM
MISC |
| wordpress — wordpress |
The “WooLentor – WooCommerce Elementor Addons + Builder” WordPress Plugin before 1.8.6 has a widget that is vulnerable to stored Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) by lower-privileged users such as contributors, all via a similar method. |
2021-05-05 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-24262
MISC
CONFIRM |
| wordpress — wordpress |
The “Livemesh Addons for Elementor” WordPress Plugin before 6.8 has several widgets that are vulnerable to stored Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) by lower-privileged users such as contributors, all via a similar method. |
2021-05-05 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-24260
CONFIRM
MISC |
| wordpress — wordpress |
The “The Plus Addons for Elementor Page Builder Lite” WordPress Plugin before 2.0.6 has four widgets that are vulnerable to stored Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) by lower-privileged users such as contributors, all via a similar method. |
2021-05-05 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-24266
CONFIRM
MISC |
| wordpress — wordpress |
The Elements Kit Lite and Elements Kit Pro WordPress Plugins before 2.2.0 have a number of widgets that are vulnerable to stored Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) by lower-privileged users such as contributors, all via a similar method. |
2021-05-05 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-24258
CONFIRM
MISC |

by Contributed | May 10, 2021 | Technology
This article is contributed. See the original author and article here.

Today, May 10, 2021, we launch the second Project 15 from Microsoft video. The next chapter of a story that started with asking the question, “What if?”
I’m religiously anti-spoiler, so I will pause for you to watch the video.
But if you are asking yourself, “the second video?” let’s back up two years, and I will tell you a short history that brings us to today. Spoiler alert, it involves a first video.
 Daisuke Nakahara at the filming of the first Project 15 video – September 2019
Daisuke Nakahara at the filming of the first Project 15 video – September 2019
Part 1: What is Project 15 from Microsoft?
Project 15 started two years ago on a “what if” that Daisuke and I shared. What if we could figure out a way to connect our commercial IoT solutioning world to the scientific developer community? Could we apply our processes to bring our partner solutions to scale in a new realm, rather than reinventing wheels that were stalling projects and/or wasting grant money? If we connected each other’s worlds, we could share knowledge and accelerate desperately needed solutions for our planet.
We asked others to join us on this adventure in learning and growth mindset. As we started our journey, Daisuke and I were unaware of most use cases in conservation, but we were willing to listen and learn to try to find the places we overlap.
Dr. Eric Dinerstein, Director of Biodiversity and Wildlife Solutions Program at RESOLVE was my first mentor. Eric gave me a crash course on anti-poaching in midnight emails while he was filming an episode of Robert Downey Jr.’s YouTube series, The Age of A.I.: Saving the world one algorithm at a time, in The Mara. Eric has an incredibly rich history in conservation. It’s almost beyond words so I will let this picture tell the story. In the photo below, Eric is collaring the first Rhino in 1986. Eric explained to me, “The rhino was sedated by a trained vet and who was an expert on immobilization of wild animals as being the head vet at the Kathmandu Zoo. When we injected the antidote (antagonist) in the rhino’s ear vein, it was on its feet in 30 seconds!” If you look closely, you can see curious elephants in the background.
 Dr. Eric Dinerstein collaring the first Rhino at Kathmandu Zoo – c. 1986
Dr. Eric Dinerstein collaring the first Rhino at Kathmandu Zoo – c. 1986
With Eric’s encouragement, I landed on a promise: that I may not know how to collar a Rhino, but I would gather an army of developers like me who could help him and his friends save the planet. The more I learned, the more I realized that we are out of time for talking about conservation. We all need to get involved in whatever way we can to save endangered animals. Project 15’s name was derived from the statistic that we lose an elephant from the planet every 15 minutes, a fact that Eric taught me.
The first mission of Project 15 was to ring a bell. Not that Daisuke and I had any idea what that meant yet, but we had to try.
 The first Project 15 “napkin drawing” – April 2019
The first Project 15 “napkin drawing” – April 2019
I pitched Lucas Joppa, Chief Environmental Officer at Microsoft by email. He, like Eric, didn’t think it was an outlandish idea either and joined us for our first video.
 Lucas Joppa, Chief Environmental Officer at Microsoft with Sarah on filming day – September 2019
Lucas Joppa, Chief Environmental Officer at Microsoft with Sarah on filming day – September 2019
Eric was the first mentor, and soon, there were many more. We wouldn’t be here today if it weren’t for the space we were given to learn and the grace to be wrong and “try again.”
Part 2: The Phone Rings
The first call.
It took three months before the phone rang. By phone, I mean email. On January 3, 2020, we received an email from Bastiaan den Braber with a company called Zambezi Partners. Bastiaan found the video, our web page, and wrote us. It was a cold pitch from him explaining his business, and I don’t think he thought he would get a direct reply from me.

Zambezi Partners is a start-up focused on conservation with a partner ecosystem. The group wanted to build a platform to grow into a professional services firm that focused on conservation IoT as well as other sustainability use cases.
This was not who we thought would call. We didn’t know there were companies that wanted to focus on building IoT solutions in this area. This was interesting.
The second call.
Call number two came from Sonam Tashi Lama, Program Coordinator of the Red Panda Network. Sonam had been forwarded the Project 15 video and asked if we could help. Did you know that Red Pandas were discovered before Giant Pandas? They aren’t related.

We spent our nights meeting with Sonam, who is located at the base of the Himalayas in Tibet, to create what would be the digital transformation of the Red Panda Network.
The third call was Yoko Watanabe, Global Manager of the GEF Small Grants Programme implemented by the United Nations Development Program.

Yoko heard about Project 15 and asked for me and Daisuke to meet with her team. We knew that our engagement model was working as we were moving right along with our Red Panda Network project and were working with Zambezi Partners on their business model workshop and architectural design session, which is where we create the architecture of solutions on Azure with a partner.
Did I mention we did this on nights and weekends? Which is fine if you have a couple of projects.
The GEF Small Grants Programme has over 3,500 projects currently funded in a range of sustainability areas of focus from conservation of species to urban sustainability. They had 25,000 projects historically.
The goals we established with Yoko and her team were:
- Learn each other’s business language and processes
- Discover the patterns that match commercial solution engagements
- Design the engagement model for scale
Yoko proceeded to identify three projects for us to start with.
Part 3: Getting to Scale, the Project 15 Open Platform is born
So, to level set, by February 2020, Project 15 was just the two of us. A start-up named Zambezi Partners. An NGO saving red pandas. And, the UNDP’s GEF Small Grants Programme with their thousands of projects.
This is a scale problem to solve.
We started with the three projects from Yoko’s team: two in St. Lucia and one in Panama. We realized the developers didn’t need to learn the IoT “plumbing” every time, nor did they want to. Daisuke’s metaphor of not needing to know how to build a piano to write music is spot on.
The next “what if” was to build 80% of the IoT infrastructure that these solutions had in common and put it on GitHub. In building the Project 15 Open Platform, we wanted to spin up a solution that enabled scientific developers to push a button and share it with the open-source community and universities to leverage.
Part 4: Elephants, Graphs, and Platform Zero by Zambezi Partners – oh my
Two years ago, when Project 15 began, I started to apply graph theory to sustainability and conservation.
 The first “napkin drawing” of the Sustainability Graph – September 2019
The first “napkin drawing” of the Sustainability Graph – September 2019
About six months ago, Azure Digital Twins (ADT) became graph-based.
Daisuke updated the Project 15 Open Platform with ADT to give developers a choice to spin up the Azure Digital Twins version. It is a simple flag on the template that launches picking “true” for Azure Digital Twins.
Long story, short, Zambezi Partners took the graph version of the Project 15 Open Platform and commercialized it to make Platform Zero. We had already designed their system with them and one of their device partners. It was based on IoT Hub and other PaaS services in Azure. But when I was talking about my graph theory and then Azure Digital Twins became graph enabled, Bastiaan saw the potential immediately.
 Sustainability Graph : Animal Conservation Sub-Graph v1.0
Sustainability Graph : Animal Conservation Sub-Graph v1.0
A Graph model is a more sophisticated way to model systems in conservation. By putting the devices in this graph there is more awareness around the relationship of devices within an environment and the capabilities to model entities like the animals themselves. Recently I wrote a LinkedIn article that walks through the Sustainability Graph using the sub-graph of animal conservation as I describe here in more detail.
What is so exciting about the approach that Platform Zero is taking by putting conservation up on a graph is that it enables the crossing of the gap between park-side and justice-side systems and is prepared to integrate complex processes: the processes of protecting an animal with connected devices and the processes of detecting animal trafficking.
Part 5: Who is Kate Gilman Williams?
Kate is the founder of Kids Can Save Animals. At the age of nine, she co-authored a book, “Let’s Go on Safari,” to raise awareness and advocate for animals bringing attention to issues like poaching and human wildlife conflict.

Kate became aware of Project 15 from Microsoft and reached out to me on Instagram. She had an idea, and it was a good one. Should you meet her, you will hear the urgency in her voice. She will tell you that we are out of time. She will stress to you that there will be no elephants by the time she is out of college at the rate they are disappearing. She will inspire you to act.
Kate said, “What if I could break the timeline? What if I could build an army of kids that can learn to use tools like the Project 15 Open Platform and fight for the planet?”
 Kate Gilman Williams at the Care For Wild Rhino Sanctuary
Kate Gilman Williams at the Care For Wild Rhino Sanctuary
She made three very important points in her pitch:
1. It will fall on her generation to fix the Earth.
2. “If you wait until I’m older to teach me, there will be nothing left to save.”
3. Given the opportunity, my generation will be part of the solution.
Her pitch was to make a learning club, called Club 15, that she could use as a platform to teach her generation technology through applied use cases in conservation and sustainability. Could I help her architect such a club?
The challenge was, of course, she wanted to create a club that she, herself, needed to join. It’s a Catch 22. So, I designed a game. I would play a kid in the future that had been a member of Club 15 and built a time machine to go back in time to teach her how to build the club so I could exist.
Kate was “in.” To teach her the concepts of IoT and ML, I started with the IoT Learning Path developed by our IoT Developer Advocacy team. Kate ordered a device and started to code. She then added a new element to her club, GitHub. She asked if we could use something like the Animal Detection System lab from Module 3 of the IoT Learning Path designed by Henk Boelman.
After she was up to speed on the concepts of Azure and IoT, we had an Architectural Design Session for what Club 15 would look like.
 Club 15 from Kids Can Save Animals Framework
Club 15 from Kids Can Save Animals Framework
Kate uses 15-minute interviews with experts from three categories of professionals to teach concepts: 1) Scientists double-click on a conservation topic and dig into how technology is used within their specialty; 2) Technologists expand on a tech topic; and 3) Advocates that may be working in other non-scientific fields or non-technical fields discuss finding interesting ways to weave advocacy into their lives and work.
Inspired by the Microsoft focus pillars of sustainability, Kate designed four clubhouses each with a sustainability focus topic: Biodiversity, Water, Waste, and Energy/CO2. The first Club 15 Clubhouse releases today, May 10th, focusing on Biodiversity and Machine Learning with the next one landing in the Fall of 2021 focusing on Water and Sensors.
We worked with Paul DeCarlo and Henk Boelman from our IoT Developer Advocacy group to contribute to Kate’s first lab to teach how to use Custom Vision. As her project grows, other technology partners will follow our example to contribute more learning labs.
Club 15 from Kids Can Save Animals is remarkable in that it is designed to speak to a spectrum of learners: From the tech side, learning the conservation use cases from advocates and scientists; for advocates, learning more about technology concepts and how they are applied to conservation and sustainability. Everyone is welcome.
Joining Kate in her launch of Club 15 are some incredible guests that will share their knowledge.
And the amazing elephants at the Sheldrick Wildlife Trust!
 Kate with the orphans at the Sheldrick Wildlife Trust
Kate with the orphans at the Sheldrick Wildlife Trust
The Butterfly Effect of Innovation
You never know where an idea will come from. You never know where it will take you. Project 15, if you follow it all the way back, starts with my cat Thomas and me rescuing her from a burning building. That moment in time led to Project Edison, which in turn led to Project 15.
Every moment of our lives is created by countless events. Sometimes the conundrum is that some events may be regretful or painful but without them, you wouldn’t be where you are today. The moment we are in with the Earth was created by countless events. It’s dire and I would be remiss to not say that here.
But I’ll tell you a secret I have learned. With all the bad news and the terrible statistics that we can drown in if we aren’t careful, there is a discovery down the path if you choose to follow it. Hope. There is so much hope in this solutioning community. Together, we can fix this place.
There have been many incredible people who have joined us on the Project 15 journey, the ‘Friends of Project 15.’ Daisuke and I are excited to continue with Yoko and her team at GEF Small Grants Programme implemented by the UNDP as we work to unlock scale. Each day we work with our partners to innovate on IoT solutions for sustainability from smart cities to smart manufacturing to smart farms. “Smart” very often now becoming interchangeable with “Sustainable”.
Today, Daisuke and I pass the “what if” baton that was the original spirit of Project 15 to Kate Gilman Williams and Club 15 from Kids Can Save Animals.
What if you could make a club and asked everyone to join? You never know, kid… It just might work.


by Contributed | May 8, 2021 | Technology
This article is contributed. See the original author and article here.
PostgreSQL is an excellent database for a wide range of workloads. Traditionally, the only problem with Postgres is that it is limited to a single machine. If you are using the Azure Database for PostgreSQL managed service, that limitation no longer applies to you because you can use the built-in Hyperscale (Citus) option—to transparently shard and scale out both transactional and analytical workloads. And Hyperscale (Citus) just keeps getting better and better.
The heart of Hyperscale (Citus) is the open source Citus extension which extends Postgres with distributed database superpowers. Every few months we release a new version of Citus. I’m excited to tell you that the latest release, Citus 10, is now available in preview on Hyperscale (Citus) and comes with spectacular new capabilities:
- Columnar storage for Postgres: Compress your PostgreSQL and Hyperscale (Citus) tables to reduce storage cost and speed up your analytical queries!
- Sharding on a single Citus node (Basic Tier): With Basic Tier, you can shard Postgres on a single node, so your application is “scale-out ready”. Also handy for trying out Hyperscale (Citus) at a much lower price point, starting at $0.27 USD/hour.[1]
- Joins and foreign keys between local PostgreSQL tables and Citus tables: Mix and match PostgreSQL and Hyperscale (Citus) tables with foreign keys and joins.
- Function to change the way your tables are distributed: Redistribute your tables in a single step using new alter table functions.
- Much more: Better naming, improved SQL & DDL support, simplified operations.
These new Citus 10 capabilities change what Hyperscale (Citus) can do for you in some fundamental (and useful) ways.
With Citus 10, Hyperscale (Citus) is no longer just about sharding Postgres: you can use the new Citus columnar storage feature to compress large data sets. And Citus is no longer just about multi-node clusters: with Basic Tier in Hyperscale (Citus), you can now shard on a single node to be “scale-out-ready”. Finally, Hyperscale (Citus) is no longer just about transforming Postgres into a distributed database: you can now mix regular (local) Postgres tables and distributed tables in the same Postgres database.
In short, Hyperscale (Citus) in Azure Database for PostgreSQL now empowers you to run Postgres at any scale.
Let’s dive in!
 One of our favourite Postgres memorabilia is the PostgreSQL 9.2 race car poster with the signatures of all the committers from the PGCon auction in 2013. Since Citus 9.2, our open source team has been creating a new racecar image for each new Citus open source release. With Citus 10 giving you columnar, single node (Basic tier), & so much more, the Postgres elephant can now go to any scale!
One of our favourite Postgres memorabilia is the PostgreSQL 9.2 race car poster with the signatures of all the committers from the PGCon auction in 2013. Since Citus 9.2, our open source team has been creating a new racecar image for each new Citus open source release. With Citus 10 giving you columnar, single node (Basic tier), & so much more, the Postgres elephant can now go to any scale!
Columnar storage for PostgreSQL with Hyperscale (Citus)
The data sizes of some new Hyperscale (Citus) customers are truly gigantic, which meant we needed a way to lower storage cost and get more out of the hardware. That is why we implemented columnar storage for Citus. Citus Columnar can give you compression ratios of 3x-10x or more, and even greater I/O reductions. The new Citus columnar feature is available in:
- Citus 10 open source: you can download the latest Citus packages here
- Hyperscale (Citus) in Azure Database for PostgreSQL: at the time of writing, the Citus 10 features are in preview in Hyperscale (Citus). So if you want to try out the new Citus columnar feature, you’ll want to turn the preview features on in the portal when provisioning a new Hyperscale (Citus) server group. Of course, depending on when you read this blog post, these Citus 10 features might already be GA in Hyperscale (Citus).
The best part: you can use columnar in Hyperscale (Citus) with or without the Citus scale-out features! More details about columnar table storage can be found in our Hyperscale (Citus) docs.
Our Citus engineering team has a long history with columnar storage in PostgreSQL, as we originally developed the cstore_fdw extension which offered columnar storage via the foreign data wrapper (fdw) API. PostgreSQL 12 introduced “table access methods”, which allows extensions to define custom storage formats in a much more native way.
Citus makes columnar storage available in PostgreSQL via the table access method APIs, which means that you can now create Citus columnar tables by simply adding USING columnar when creating a table:
CREATE TABLE order_history (…) USING columnar;
If you provision a row-based (“heap”) table that you’d like to later convert to columnar, you can do that too, using the alter_table_set_access_method function:
-- compress a table using columnar storage (indexes are dropped)
SELECT alter_table_set_access_method('orders_2019', 'columnar');
When you use Citus columnar storage, you will typically see a 60-90% reduction in data size. In addition, Citus columnar will only read the columns used in the SQL query. This can give dramatic speed ups for I/O bound queries, and a big reduction in storage cost.
Compared to cstore_fdw, Citus columnar has a better compression ratio thanks to zstd compression. Citus columnar also supports rollback, streaming replication, archival, and pg_upgrade.
There are still a few limitations with Citus columnar to be aware of: Indexes and update/delete are not yet supported, and it is best to avoid single-row inserts, since compression only works well in batches. We plan to address these limitations in future Citus releases, but you can also avoid them using partitioning.
If you partition time series tables by time, you can use row-based storage for recent partitions to enable single-row, update/delete/upsert and indexes—while using columnar storage to archive data that is no longer changing. To make this easy, we also added a function to compress all your old partitions in one go:
-- compress all partitions older than 7 days
CALL alter_old_partitions_set_access_method('order_history', now() – interval '7 days', 'columnar');
This procedure commits after every partition to release locks as quickly as possible. You can use pg_cron to run this new alter function as a nightly compression job.
To learn more, check out Jeff Davis’ blog post: Citus 10 brings columnar compression to Postgres. Jeff also created a video demo, if you’re a more visual person this Citus columnar demo might be a good way to get acquainted.
Starting with Basic Tier in Hyperscale (Citus)—to be “scale-out ready”
We often think of Hyperscale (Citus) as “worry-free Postgres”, because Citus takes away the one concern you may have when choosing Postgres as your database: reaching the limits of a single node. However, when you migrate a complex application from Postgres to Hyperscale (Citus), you may need to make some changes to your application to handle restrictions around unique- and foreign key-constraints and joins, since not every PostgreSQL feature has an efficient distributed implementation.
In Azure, the easiest way to scale your application on Postgres without ever facing the cost of migration (and be truly worry-free) is to use Hyperscale (Citus) from day one, when you first build your application. Applications built on Citus are always 100% compatible with regular PostgreSQL, so there is no risk of lock-in. The only downside of starting on Hyperscale (Citus) so far was the cost and complexity of running a distributed database cluster, but this changes in Citus 10. With Citus 10 and the new Basic tier in Hyperscale (Citus), you can now shard your Postgres tables on a single Citus node to make your database “scale-out-ready”.
To get started with Hyperscale (Citus) on a single node, this post about sharding Postgres with Basic tier is a good place to start. Be sure to enable preview features in the Azure portal when provisioning Azure Database for PostgreSQL—and then select the new “Basic Tier” feature that’s available in preview on Hyperscale (Citus). As of today, you can provision Basic tier for $0.27 USD/hour in US East 1. This means that you can try out Hyperscale (Citus) at a much lower price point: about ~8 hours of kicking the tires and you’ll only pay $2-3 USD.
 Diagram 1: When provisioning the Hyperscale (Citus) deployment option in the Azure portal for Azure Database for PostgreSQL, you’ll now have two choices: Basic Tier and Standard Tier.
Diagram 1: When provisioning the Hyperscale (Citus) deployment option in the Azure portal for Azure Database for PostgreSQL, you’ll now have two choices: Basic Tier and Standard Tier.
Once connected, you can create your first distributed table by running the following commands:
CREATE TABLE data (key text primary key, value jsonb not null);
SELECT create_distributed_table('data', 'key');
The create_distributed_table function will divide the table across 32 (hidden) shards that can be moved to new nodes when a single node is no longer sufficient.
You may experience some overhead from distributed query planning, but you will also see benefits from multi-shard queries being parallelized across cores. You can also make distributed, columnar tables to take advantage of both I/O and storage reduction and parallelism.
The biggest advantage of distributing Postgres tables with Basic tier in Hyperscale (Citus) is that your database will be ready to be scaled out using the Citus shard rebalancer.
Joins & foreign keys between PostgreSQL and Citus tables
With the new Basic Tier feature in Hyperscale (Citus) and the shard rebalancer, you can be ready to scale out by distributing your tables. However, distributing tables does involve certain trade-offs, such as extra network round trips when querying shards on worker nodes, and a few unsupported SQL features.
If you have a very large Postgres table and a data-intensive workload (e.g. the frequently-queried part of the table exceeds memory), then the performance gains from distributing the table over multiple nodes with Hyperscale (Citus) will vastly outweigh any downsides. However, if most of your other Postgres tables are small, then you might end up having to make additional changes without much additional benefit.
A simple solution would be to not distribute the smaller tables at all. In most Hyperscale (Citus) deployments, your application connects to a single coordinator node (which is usually sufficient), and the coordinator is a fully functional PostgreSQL node. That means you could organize your database as follows:
- convert large tables into Citus distributed tables,
- convert smaller tables that frequently JOIN with distributed tables into reference tables,
- convert smaller tables that have foreign keys from distributed tables into reference tables,
- keep all other tables as regular PostgreSQL tables local to the coordinator.
 Diagram 2: Example of a data model where the really large table (clicks) is distributed. Because the Clicks table has a foreign key to Ads, we turn Ads into a reference table. Ads also has foreign keys to other tables, but we can keep those other tables (Campaigns, Publishers, Advertisers) as local tables on the coordinator.
Diagram 2: Example of a data model where the really large table (clicks) is distributed. Because the Clicks table has a foreign key to Ads, we turn Ads into a reference table. Ads also has foreign keys to other tables, but we can keep those other tables (Campaigns, Publishers, Advertisers) as local tables on the coordinator.
That way, you can scale out CPU, memory, and I/O where you need it. And minimize application changes and other trade-offs where you don’t. To make this model work seamlessly, Citus 10 adds support for 2 important features:
- foreign keys between local tables and reference tables
- direct joins between local tables and distributed tables
With these new Citus 10 features in Hyperscale (Citus), you can mix and match PostgreSQL tables and Citus tables to get the best of both worlds without having to separate them in your data model.
Alter all the things!
When you distribute a Postgres table with Hyperscale (Citus), choosing your distribution column is an important step, since the distribution column (sometimes called the sharding key) determines which constraints you can create, how (fast) you can join tables, and more.
Citus 10 adds the alter_distributed_table function so you can change the distribution column, shard count, and co-location of a distributed table. This blog post walks through how when and why to use alter_distributed_table with Hyperscale (Citus).
-- change the distribution column to customer_id
SELECT alter_distributed_table('orders',
distribution_column := 'customer_id');
-- change the shard count to 120
SELECT alter_distributed_table('orders',
shard_count := 120);
-- Co-locate with another table
SELECT alter_distributed_table('orders',
distribution_column := 'product_id',
colocate_with := 'products');
Internally, alter_distributed_table reshuffles the data between the worker nodes, which means it is fast and works well on very large tables. We expect this makes it much easier to experiment with distributing your tables without having to reload your data.
You can also use the alter_distributed_table function in production (it’s fully transactional!), but you do need to (1) make sure that you have enough disk space to store the table several times, and (2) make sure that your application can tolerate blocking all writes to the table for a while.
Many other features in Citus 10—now available in preview in Hyperscale (Citus)
And there’s more!
- DDL support
More DDL commands work seamlessly on distributed Citus tables, including CREATE STATISTICS, ALTER TABLE .. SET LOGGED, and ALTER SCHEMA .. RENAME.
- SQL support
Correlated subqueries can now be used in the SELECT part of the query, as long as the distributed tables are joined by their distribution column.
- New views to see the state of your cluster: citus_tables and citus_shards
citus_tables view shows Citus tables and their distribution column, total size, and access method. The citus_shards view shows the names, locations, and sizes of individual shards.
Two easy ways to start playing with Citus 10
If you are as excited as we are and want to play with these new Citus 10 features, doing so is now easier than ever.
- The Basic Tier in Hyperscale (Citus) makes it very cheap to get started with a managed Citus node in our Azure Database for PostgreSQL managed service. (There’s a Basic tier Quickstart in our Azure docs, too.)
- And you can also run Citus open source on your laptop as a single Docker container! Not only is the single docker run command an easy way to try out Citus—it gives you functional parity between your local dev machine and using Citus in the cloud.
# run PostgreSQL with Citus on port 5500
docker run -d --name citus -p 5500:5432 -e POSTGRES_PASSWORD=mypassword citusdata/citus
# connect
psql -U postgres -d postgres -h localhost -p 5500
You can also check out our lovely new Getting started with Citus page for more resources on how to get started—my teammates have curated some good learning tools there, whether your preferred learning mode is reading, watching, or doing.
More deep-dive blog posts about new Citus 10 capabilities
And since the Citus 10 open source release rolled out, we’ve also published a bunch of deep-dive blog posts (plus a demo!) about the spectacular new capabilities in Citus 10:
Finally, a big thank you to all of you who use Hyperscale (Citus) to scale out Postgres and who have taken the time to give feedback and be part of our journey. If you’ve filed issues on GitHub, submitted PRs, talked to our @citusdata or @AzureDBPostgres team on Twitter, signed up for our monthly Citus technical newsletter, or joined our Citus Public community Q&A… well, thank you. And please, keep the feedback coming. You can always reach our product team via the Ask Azure DB for PostgreSQL email address too.
We can’t wait to see what you do with the new Citus 10 features in Hyperscale (Citus)!
Footnotes
- As of the time of publication, in the East US region on Azure, the cost of a Hyperscale (Citus) Basic tier with 2 vCores, 8 GiB total memory, and 128 GiB of storage on the coordinator node is $0.27/hour or ~$200/month ↩
by Contributed | May 7, 2021 | Technology
This article is contributed. See the original author and article here.
Azure Sentinel Incidents contain detection details which enable security analysts to investigate using a graph view and gain deep insights into related entities. The responsiveness of a security analyst towards the triggered incidents (also known as Mean Time To Acknowledge – MTTA) is crucial as being able to respond to a security incident quickly and efficiently will reduce the incident impact and mitigate the security threats.
The newly introduced Automation Rules allow you to automatically assign incidents to an owner with the built-in action. This is extremely useful when you need to assign specific incidents to a dedicated SME. It will reduce the time of acknowledgement and ensure accountability for each incident.
However, some organizations have a group of analysts working on different shift schedules and required the ability to assign an incident to an analyst automatically based on the working schedule to improve the MTTA.
In this blog, I will discuss how to extend the incident assignment capability in Azure Sentinel by using a Playbook to rotate user assignments based on shift schedules. Plus, I will also discuss how you could manage incident assignments for multiple support groups at the end of the blog.
Considerations and design decisions
Before we dive into the Playbook, let’s discuss some of the important points taken into consideration and the design decisions when implementing this incident assignment Playbook.
- Scheduling tool
- Shifts for Teams is used as the scheduling tool because it is available as part of the Microsoft Teams and it provides the ability to create and manage employee schedules.
- It is easier to automate incident assignment when there is a centralized schedule management tool to keep track of employees’ timesheet or availability.
- Assignment criteria
- The goal is to assign the incidents equally across all analysts. Hence, the analyst with the least number of incidents in current shift will be assigned first.
- We also need to consider the average time a security analyst takes to resolve a security incident (also known as Mean Time To Resolve – MTTR). In this Playbook, I have set a default value of 1 hour as the MTTR (a configurable variable) and I am using it as a condition where a security analyst must have at least 1 hour remaining in the shift to be eligible for incident assignment. For example, if a security analyst is about to go off shift in 30 minutes, the incident won’t be assigned to that analyst as the remaining time is less than the default value of 1 hour.
- Notification
- It is important to notify the assignee when an incident is being assigned.
- In this Playbook, an email will be sent to the assignee and a comment will be added to the incident on the incident assignment.
What is Shifts for Teams?
Shifts is a schedule management application in Microsoft Teams that helps you create, update, and manage schedules for your team. Shifts is enabled by default for all Teams users in your organization. You can add Shifts app to your Teams menu by clicking on the ellipses (…) and select Shifts from the app list.

The first step to get started in Shifts is to populate schedules for your team. You can either create a schedule from scratch (create for yourself or on behalf of your team members) or import an existing one from Excel. In terms of permission, you need to be an Owner of the team to create the schedule. The schedules will not be visible to your team members until you publish it by clicking “Share with team” button.
Here is an example of how a Shifts schedule looks like. If you’re an owner of multiple teams, you can toggle between different Shifts schedules to manage them.
The Logic App
Download link:
Here is the link to the Logic App template.
Prerequisites:
1. User account or Service Principal with Azure Sentinel Responder role
– Create or use an existing user account or Service Principal or Managed Identity with Azure Sentinel Responder role.
– The account will be used in Azure Sentinel connectors (Incident Trigger, Update incident and Add comment to incident) and a HTTP connector.
– This blog will walk you through using System Managed Identity for the above connectors.
2. Setup Shifts schedule
– You must have the Shifts schedule setup in Microsoft Teams.
– The Shifts schedule must be published (Shared with team).
3. User account with Owner role in Microsoft Teams
– Create or use an existing user account with Owner role in a Team.
– The user account will be used in Shifts connector (List all shifts).
4. User account or Service Principal with Log Analytics Reader role
– Create or use an existing user account with Log Analytics Reader role on the Azure Sentinel workspace.
– The user account will be used in Azure Monitor Logs connector (Run query and list results).
5. An O365 account to be used to send email notification.
– The user account will be used in O365 connector (Send an email).
Post Deployment Configuration:
1. Enable Managed Identity and configure role assignment.
a) Once the Playbook is deployed, navigate to the resource blade and click on Identity under Settings.
b) Select On under the System assigned tab. Click Save and select Yes when prompted.
c) Click on Azure role assignments to assign role to the Managed Identity.
d) Click on + Add role assignment.
e) Select Resource group under Scope and select the Subscription and Resource group where the Azure Sentinel Workspace is located.
(Note: it’s the subscription and resource group of the Azure Sentinel workspace, not the Logic App).
f) Select Azure Sentinel Responder under Role and click Save.
2. Configure connections.
a) Edit the Logic App to find the below connectors marked with  .
.
– When Azure Sentinel incident creation rule was triggered.
– List all shifts.
– Run query and list results – Get user with low assignment.
– Update incident.
– Add comment to incident.
– Send an email.
b) We will leverage the Managed Identity we configured in step 1 for the following Azure Sentinel Connectors
(hint: these are the ones with Azure Sentinel logo):
– When Azure Sentinel incident creation rule was triggered.
– Update incident.
– Add comment to incident.
i) On the first connector (trigger), select Add new
ii) Click “Connect with managed Identity”.
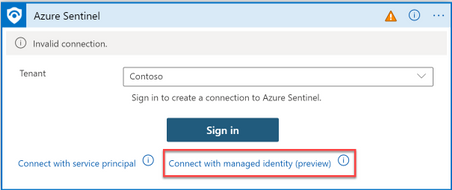
iii) Specify the connection name and click Create.
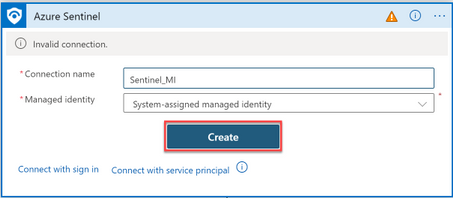
iv) On the remaining Azure Sentinel Connectors, select the connection you created earlier.
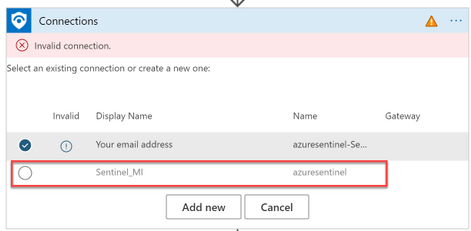
c) Next, fix the below remaining connectors by adding a new connection to each connector and sign in with the accounts described under prerequisites.
– List all shifts.
– Run query and list results – Get user with low assignment.
– Send an email.
3. Select the Shifts schedule
a) On the List all shifts connector, click on the X sign next to Team field for the drop-down list to appear.
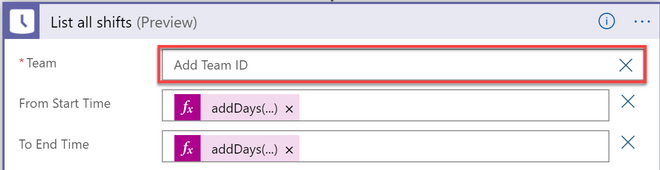
b) Select the Teams channel with your Shifts schedule from the drop-down list.
c) Save the Logic App once you have completed the above steps.
Assign the Playbook to Analytic Rules using Automation Rules
1) Before you begin, ensure you have the following permissions:
– Logic App Contributor on the Playbook.
– Owner permission on the Playbook’s resource group (to grant Azure Sentinel permission to the playbooks’ resource groups).
2) Next, create an Automation Rule to assign the Playbook to your analytic rules with you specified conditions.
3) In the below example, I am creating an Automation Rule to run the incident assignment Playbook for selected Analytic rules and the severity equals to “High” and “Medium”.
4) Uder Actions -> select Run Playbook and choose the Playbook.
Note: If the Playbook appeared as grey-out in the drop-down list, that means Azure Sentinel doesn’t have permission to run this Playbook.
You can grant permission on the spot by selecting the Manage playbook permissions link and grant permission to the playbooks’ resource groups.
5) After that, you will be able to select the Playbook. Click Apply.
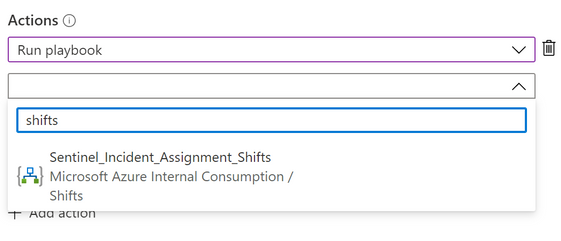
Note: If you received the error message “Caller is missing required Playbook triggering permissions” when saving the Automation Rule, that means you do not have the “Logic App Contributor” permission on the Playbook.
Incident Assignment Logic
1) When an incident is generated, it triggers the Logic app to get a list of analysts who are on-shift at that time (analysts with time-off will be excluded from the incident assignment).
2) Analyst with the least incidents assigned on the current shift will be assigned incident first. When there are multiple analysts with same incident count, the selection be will based on the order of the analyst’s AAD objectId.
3) Analysts must have at least 1 hour left (default value) in their shift to be eligible for assignment.
For example, if the shift of an analyst is ending at 6pm. The analyst will not be assigned between 5pm and 6pm.
You can change the variable value of “ExpectedWorkHoursPerIncident” to 0 if you want the analyst to be assigned during the final shift hour.
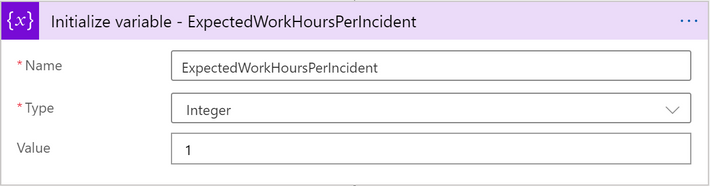
4) Here is a sample assignment flow for your reference:
In this example, the following shift schedules have been configured for 4 analysts.
User Object Id
|
Shift Schedule
|
A1
|
8am to 6pm
|
A2
|
8am to 6pm
|
A3
|
4pm to 2am
|
A4
|
4pm to 2am
|
Here is how the incident assignment would work based on the incident assignment logic:
Incident Creation Time
|
Assign to
|
Total
|
8:00am
|
A1
|
A1=1
A2=0
A3=0
A4=0
|
9:45am
|
A2
|
A1=1
A2=1
A3=0
A4=0
|
2:00pm
|
A1
|
A1=2
A2=1
A3=0
A4=0
|
4:00pm
|
A3
|
A1=2
A2=1
A3=1
A4=0
|
4:10pm
|
A4
|
A1=2
A2=1
A3=1
A4=1
|
5:00pm
|
A3
*A3 is assigned instead of A2 because ExpectedWorkHoursPerIncident is set to 1.
|
A1=2
A2=1
A3=2
A4=1
|
5:50pm
|
A4
*A4 is assigned instead of A2 because ExpectedWorkHoursPerIncident is set to 1.
|
A1=2
A2=1
A3=2
A4=2
|
11:20pm
|
A3
|
A1=2
A2=1
A3=3
A4=2
|
Notification
Email Notification:
- When an incident is assigned, the incident owner will be notified via email.
- The email body has a direct link to the incident page and a banner with color mapped to incident’s severity (High=red, Medium=orange, Low=yellow and Informational=grey).
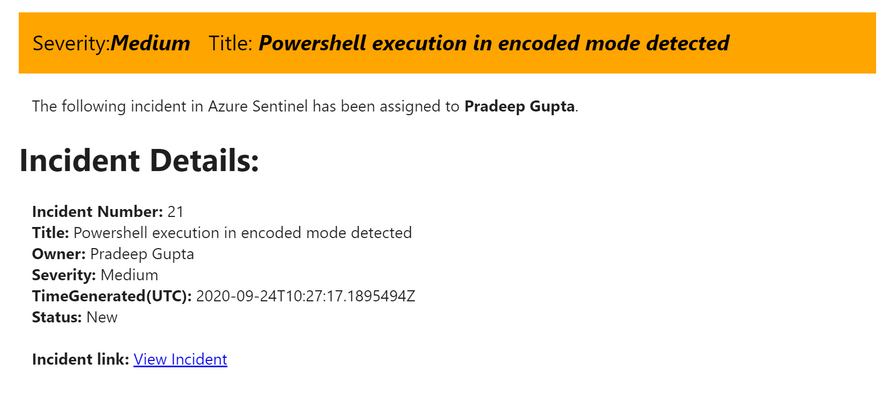
Incident Comment:
- Comment will be added to the incident for the assignment with the name of the Playbook.
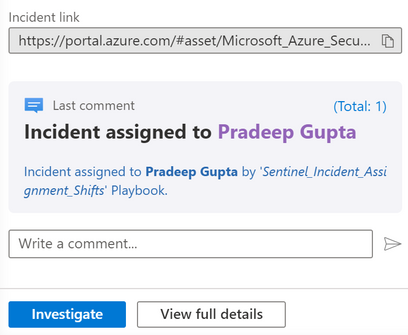
Managing Incident assignment for multiple Support Groups
There are times when you need to assign incidents based on different incident types and support groups. For example, Team A is responsible for Azure AD incidents, Team B is responsible for Office 365 incidents while the rest of the incidents will go to Team C.
This can be achieved by creating Shifts schedule for each support group and deploy a separate Playbook for each group. Then, assign the Logic App to the analytic rules accordingly as illustrated in the diagram below:
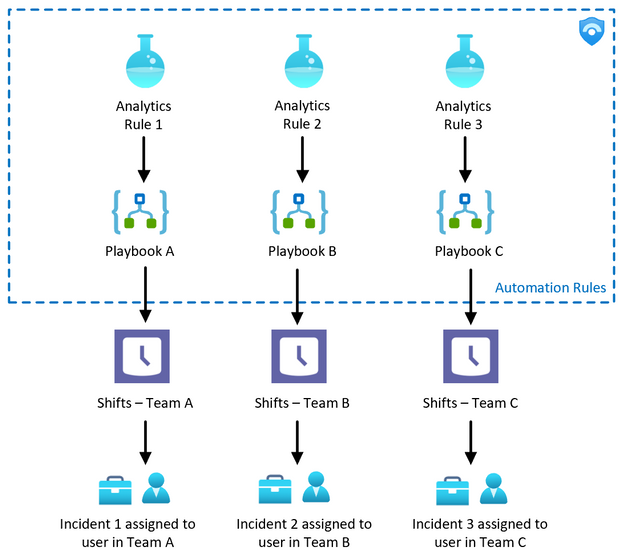
Below are the sample Automation Rules created for multiple Shifts channels (Support Groups).
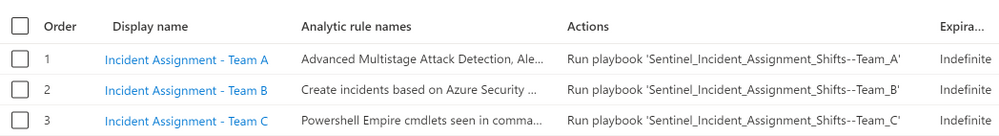
Each Automation Rule is configured for different Team:
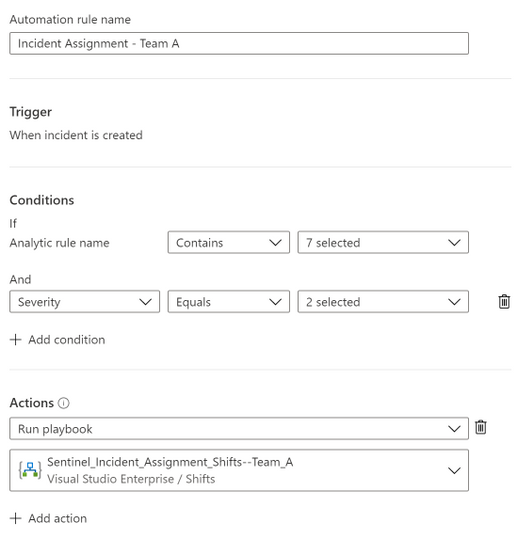
Automation Rule for Team A
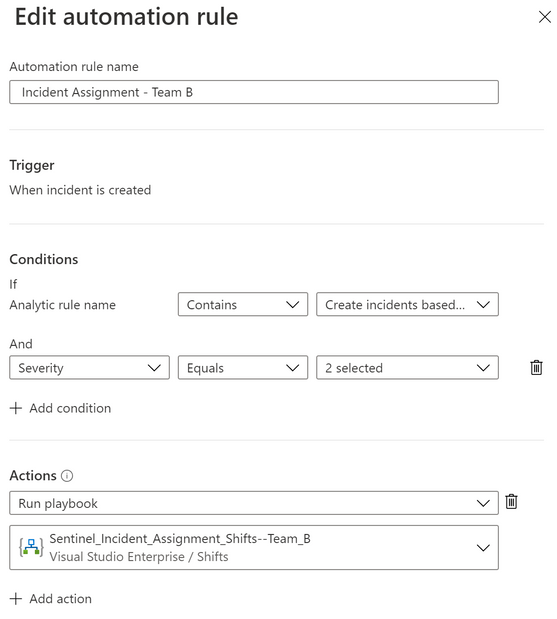
Automation Rule for Team B
Summary
I hope you find this useful. Give it a try and hopefully it would help in reducing the time of acknowledgement (especially for critical incidents) in your environment.
Special thanks to @liortamir , @Yaniv Shasha , @edilahav and @Ofer_Shezaf for the review.

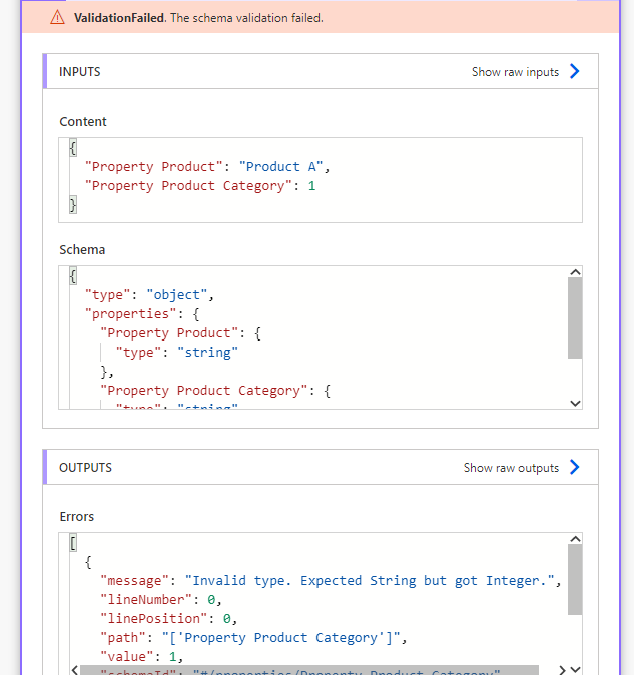

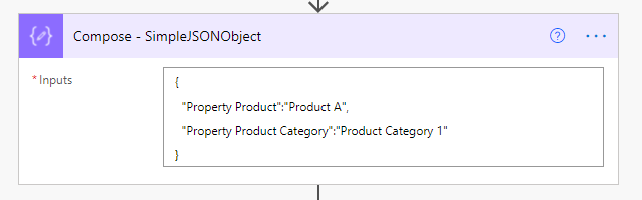
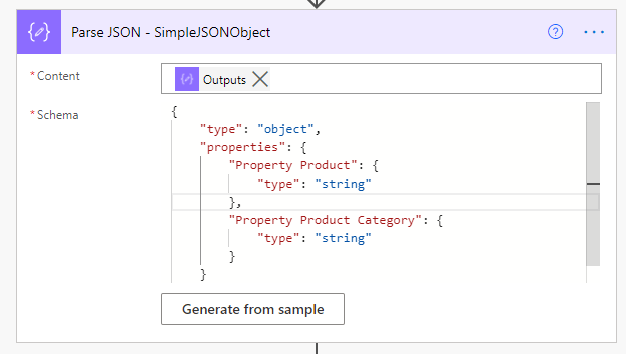
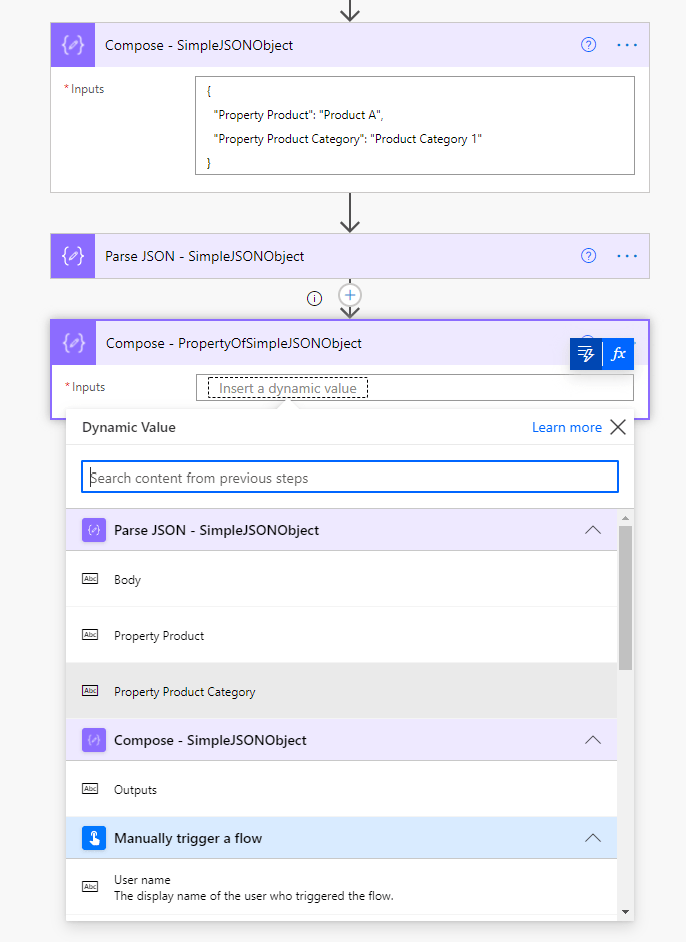










































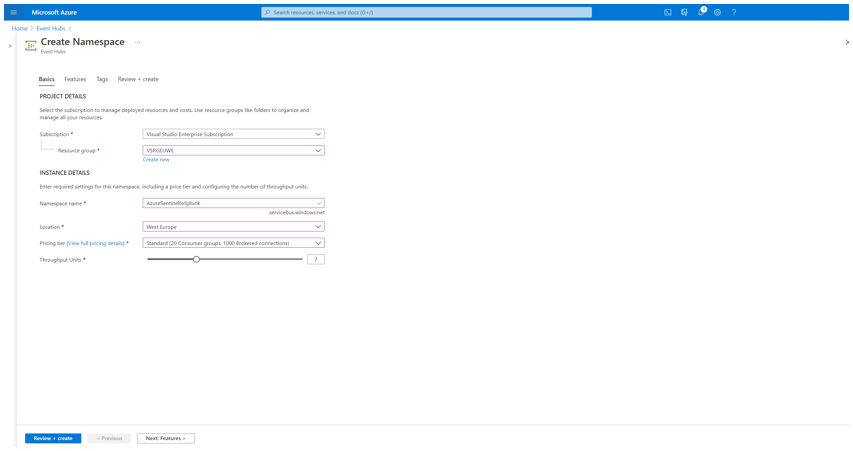
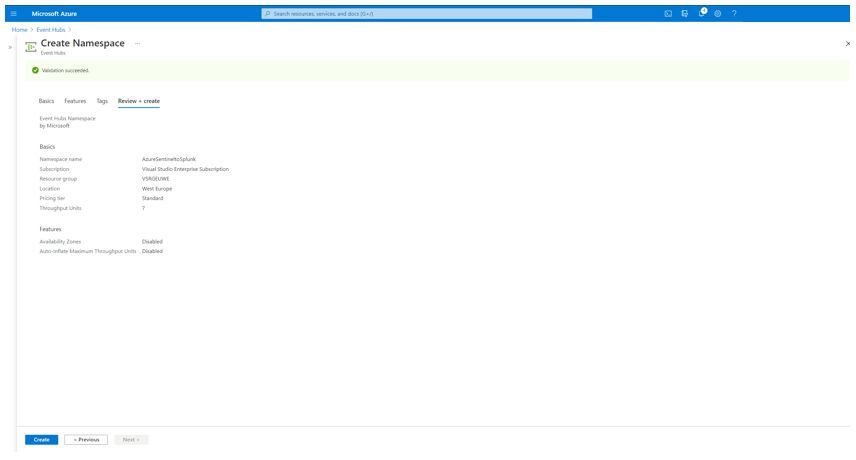
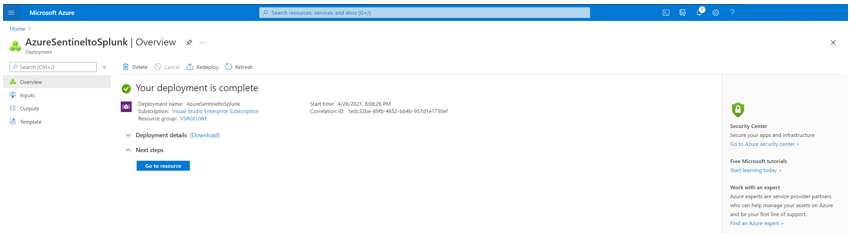


Recent Comments