by Scott Muniz | Apr 12, 2021 | Security, Technology
This article is contributed. See the original author and article here.
admin.php — online_book_store
|
SQL injection in admin.php in Online Book Store 1.0 allows remote attackers to execute arbitrary SQL commands and bypass authentication. |
2021-04-09 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-23763
MISC
MISC |
apple — macos
|
The Proofpoint Insider Threat Management Agents (formerly ObserveIT Agent) for MacOS and Linux perform improper validation of the ITM Server’s certificate, which enables a remote attacker to intercept and alter these communications using a man-in-the-middle attack. All versions before 7.11.1 are affected. Agents for Windows and Cloud are not affected. |
2021-04-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-27899
CONFIRM |
| apple — multiple_products |
A logic issue was addressed with improved restrictions. This issue is fixed in macOS Big Sur 11.2, Security Update 2021-001 Catalina, Security Update 2021-001 Mojave, iOS 14.4 and iPadOS 14.4. A remote attacker may be able to cause arbitrary code execution. Apple is aware of a report that this issue may have been actively exploited.. |
2021-04-02 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1870
FEDORA
FEDORA
MISC
MISC |
apple — multiple_products
|
This issue was addressed with improved iframe sandbox enforcement. This issue is fixed in macOS Big Sur 11.2, Security Update 2021-001 Catalina, Security Update 2021-001 Mojave, watchOS 7.3, tvOS 14.4, iOS 14.4 and iPadOS 14.4. Maliciously crafted web content may violate iframe sandboxing policy. |
2021-04-02 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1801
FEDORA
FEDORA
MISC
MISC
MISC
MISC |
apple — multiple_products
|
A port redirection issue was addressed with additional port validation. This issue is fixed in macOS Big Sur 11.2, Security Update 2021-001 Catalina, Security Update 2021-001 Mojave, tvOS 14.4, watchOS 7.3, iOS 14.4 and iPadOS 14.4, Safari 14.0.3. A malicious website may be able to access restricted ports on arbitrary servers. |
2021-04-02 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1799
FEDORA
FEDORA
MISC
MISC
MISC
MISC
MISC |
aprelium — abyss_web_server
|
An issue was discovered in Aprelium Abyss Web Server X1 2.12.1 and 2.14. A crafted HTTP request can lead to an out-of-bounds read that crashes the application. |
2021-04-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-3328
MISC |
archive — archive
|
Directory traversal vulnerability in Archive collectively operation utility Ver.2.10.1.0 and earlier allows an attacker to create or overwrite files by leading a user to expand a malicious ZIP archives. |
2021-04-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-20692
MISC
MISC |
| asus — bmc_firmware |
The SMTP configuration function in ASUS BMC’s firmware Web management page does not verify the string length entered by users, resulting in a Buffer overflow vulnerability. As obtaining the privileged permission, remote attackers use the leakage to abnormally terminate the Web service. |
2021-04-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-28189
CONFIRM
CONFIRM
CONFIRM |
| asus — bmc_firmware |
The specific function in ASUS BMC’s firmware Web management page (Get Help file function) does not filter the specific parameter. As obtaining the administrator permission, remote attackers can use the means of path traversal to access system files. |
2021-04-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-28207
CONFIRM
CONFIRM
CONFIRM |
| asus — bmc_firmware |
The specific function in ASUS BMC’s firmware Web management page (Generate new SSL certificate) does not verify the string length entered by users, resulting in a Buffer overflow vulnerability. As obtaining the privileged permission, remote attackers use the leakage to abnormally terminate the Web service. |
2021-04-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-28187
CONFIRM
CONFIRM
CONFIRM |
| asus — bmc_firmware |
The specific function in ASUS BMC’s firmware Web management page (ActiveX configuration-1 acquisition) does not verify the string length entered by users, resulting in a Buffer overflow vulnerability. As obtaining the privileged permission, remote attackers use the leakage to abnormally terminate the Web service. |
2021-04-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-28185
CONFIRM
CONFIRM
CONFIRM |
| asus — bmc_firmware |
The specific function in ASUS BMC’s firmware Web management page (Modify user’s information function) does not filter the specific parameter. As obtaining the administrator permission, remote attackers can launch command injection to execute command arbitrary. |
2021-04-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-28204
CONFIRM
CONFIRM
CONFIRM |
| asus — bmc_firmware |
The specific function in ASUS BMC’s firmware Web management page (Web License configuration setting) does not verify the string length entered by users, resulting in a Buffer overflow vulnerability. As obtaining the privileged permission, remote attackers use the leakage to abnormally terminate the Web service. |
2021-04-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-28183
CONFIRM
CONFIRM
CONFIRM |
| asus — bmc_firmware |
The Firmware protocol configuration function in ASUS BMC’s firmware Web management page does not verify the string length entered by users, resulting in a Buffer overflow vulnerability. As obtaining the privileged permission, remote attackers use the leakage to abnormally terminate the Web service. |
2021-04-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-28198
CONFIRM
CONFIRM
CONFIRM |
| asus — bmc_firmware |
The specific function in ASUS BMC’s firmware Web management page (Remote video configuration setting) does not verify the string length entered by users, resulting in a Buffer overflow vulnerability. As obtaining the privileged permission, remote attackers use the leakage to abnormally terminate the Web service. |
2021-04-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-28181
CONFIRM
CONFIRM
CONFIRM |
| asus — bmc_firmware |
The specific function in ASUS BMC’s firmware Web management page (Media support configuration setting) does not verify the string length entered by users, resulting in a Buffer overflow vulnerability. As obtaining the privileged permission, remote attackers use the leakage to abnormally terminate the Web service. |
2021-04-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-28179
CONFIRM
CONFIRM
CONFIRM |
| asus — bmc_firmware |
The UEFI configuration function in ASUS BMC’s firmware Web management page does not verify the string length entered by users, resulting in a Buffer overflow vulnerability. As obtaining the privileged permission, remote attackers use the leakage to abnormally terminate the Web service. |
2021-04-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-28178
CONFIRM
CONFIRM
CONFIRM |
| asus — bmc_firmware |
The LDAP configuration function in ASUS BMC’s firmware Web management page does not verify the string length entered by users, resulting in a Buffer overflow vulnerability. As obtaining the privileged permission, remote attackers use the leakage to abnormally terminate the Web service. |
2021-04-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-28177
CONFIRM
CONFIRM
CONFIRM |
| asus — bmc_firmware |
The specific function in ASUS BMC’s firmware Web management page (Record video file function) does not filter the specific parameter. As obtaining the administrator permission, remote attackers can use the means of path traversal to access system files. |
2021-04-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-28206
CONFIRM
CONFIRM
CONFIRM |
| asus — bmc_firmware |
The CD media configuration function in ASUS BMC’s firmware Web management page does not verify the string length entered by users, resulting in a Buffer overflow vulnerability. As obtaining the privileged permission, remote attackers use the leakage to abnormally terminate the Web service. |
2021-04-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-28200
CONFIRM
CONFIRM
CONFIRM |
asus — bmc_firmware
|
The Service configuration-1 function in ASUS BMC’s firmware Web management page does not verify the string length entered by users, resulting in a Buffer overflow vulnerability. As obtaining the privileged permission, remote attackers use the leakage to abnormally terminate the Web service. |
2021-04-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-28201
CONFIRM
CONFIRM
CONFIRM |
asus — bmc_firmware
|
The specific function in ASUS BMC’s firmware Web management page (Get video file function) does not filter the specific parameter. As obtaining the administrator permission, remote attackers can use the means of path traversal to access system files. |
2021-04-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-28208
CONFIRM
CONFIRM
CONFIRM |
asus — bmc_firmware
|
The specific function in ASUS BMC’s firmware Web management page (Delete video file function) does not filter the specific parameter. As obtaining the administrator permission, remote attackers can use the means of path traversal to access system files. |
2021-04-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-28209
CONFIRM
CONFIRM
CONFIRM |
asus — bmc_firmware
|
The Service configuration-2 function in ASUS BMC’s firmware Web management page does not verify the string length entered by users, resulting in a Buffer overflow vulnerability. As obtaining the privileged permission, remote attackers use the leakage to abnormally terminate the Web service. |
2021-04-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-28202
CONFIRM
CONFIRM
CONFIRM |
asus — bmc_firmware
|
The Web Set Media Image function in ASUS BMC’s firmware Web management page does not filter the specific parameter. As obtaining the administrator permission, remote attackers can launch command injection to execute command arbitrary. |
2021-04-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-28203
CONFIRM
CONFIRM
CONFIRM |
asus — bmc_firmware
|
The specific function in ASUS BMC’s firmware Web management page (Delete SOL video file function) does not filter the specific parameter. As obtaining the administrator permission, remote attackers can use the means of path traversal to access system files. |
2021-04-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-28205
CONFIRM
CONFIRM
CONFIRM |
asus — bmc_firmware
|
The specific function in ASUS BMC’s firmware Web management page (Modify user’s information function) does not verify the string length entered by users, resulting in a Buffer overflow vulnerability. As obtaining the privileged permission, remote attackers use the leakage to abnormally terminate the Web service. |
2021-04-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-28199
CONFIRM
CONFIRM
CONFIRM |
asus — bmc_firmware
|
The Active Directory configuration function in ASUS BMC’s firmware Web management page does not verify the string length entered by users, resulting in a Buffer overflow vulnerability. As obtaining the privileged permission, remote attackers use the leakage to abnormally terminate the Web service. |
2021-04-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-28197
CONFIRM
CONFIRM
CONFIRM |
asus — bmc_firmware
|
The specific function in ASUS BMC’s firmware Web management page (ActiveX configuration-2 acquisition) does not verify the string length entered by users, resulting in a Buffer overflow vulnerability. As obtaining the privileged permission, remote attackers use the leakage to abnormally terminate the Web service. |
2021-04-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-28186
CONFIRM
CONFIRM
CONFIRM |
asus — bmc_firmware
|
The DNS configuration function in ASUS BMC’s firmware Web management page does not verify the string length entered by users, resulting in a Buffer overflow vulnerability. As obtaining the privileged permission, remote attackers use the leakage to abnormally terminate the Web service. |
2021-04-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-28176
CONFIRM
CONFIRM
CONFIRM |
asus — bmc_firmware
|
The Web Service configuration function in ASUS BMC’s firmware Web management page does not verify the string length entered by users, resulting in a Buffer overflow vulnerability. As obtaining the privileged permission, remote attackers use the leakage to abnormally terminate the Web service. |
2021-04-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-28182
CONFIRM
CONFIRM
CONFIRM |
asus — bmc_firmware
|
The Active Directory configuration function in ASUS BMC’s firmware Web management page does not verify the string length entered by users, resulting in a Buffer overflow vulnerability. As obtaining the privileged permission, remote attackers use the leakage to abnormally terminate the Web service. |
2021-04-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-28184
CONFIRM
CONFIRM
CONFIRM |
asus — bmc_firmware
|
The specific function in ASUS BMC’s firmware Web management page (Generate SSL certificate function) does not verify the string length entered by users, resulting in a Buffer overflow vulnerability. As obtaining the privileged permission, remote attackers use the leakage to abnormally terminate the Web service. |
2021-04-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-28196
CONFIRM
CONFIRM
CONFIRM |
asus — bmc_firmware
|
The specific function in ASUS BMC’s firmware Web management page (Modify user’s information function) does not verify the string length entered by users, resulting in a Buffer overflow vulnerability. As obtaining the privileged permission, remote attackers use the leakage to abnormally terminate the Web service. |
2021-04-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-28188
CONFIRM
CONFIRM
CONFIRM |
asus — bmc_firmware
|
The specific function in ASUS BMC’s firmware Web management page (Generate new certificate function) does not verify the string length entered by users, resulting in a Buffer overflow vulnerability. As obtaining the privileged permission, remote attackers use the leakage to abnormally terminate the Web service. |
2021-04-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-28190
CONFIRM
CONFIRM
CONFIRM |
asus — bmc_firmware
|
The Firmware update function in ASUS BMC’s firmware Web management page does not verify the string length entered by users, resulting in a Buffer overflow vulnerability. As obtaining the privileged permission, remote attackers use the leakage to abnormally terminate the Web service. |
2021-04-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-28191
CONFIRM
CONFIRM
CONFIRM |
asus — bmc_firmware
|
The specific function in ASUS BMC’s firmware Web management page (Remote video storage function) does not verify the string length entered by users, resulting in a Buffer overflow vulnerability. As obtaining the privileged permission, remote attackers use the leakage to abnormally terminate the Web service. |
2021-04-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-28192
CONFIRM
CONFIRM
CONFIRM |
asus — bmc_firmware
|
The SMTP configuration function in ASUS BMC’s firmware Web management page does not verify the string length entered by users, resulting in a Buffer overflow vulnerability. As obtaining the privileged permission, remote attackers use the leakage to abnormally terminate the Web service. |
2021-04-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-28193
CONFIRM
CONFIRM
CONFIRM |
asus — bmc_firmware
|
The specific function in ASUS BMC’s firmware Web management page (Remote image configuration setting) does not verify the string length entered by users, resulting in a Buffer overflow vulnerability. As obtaining the privileged permission, remote attackers use the leakage to abnormally terminate the Web service. |
2021-04-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-28194
CONFIRM
CONFIRM
CONFIRM |
asus — bmc_firmware
|
The Radius configuration function in ASUS BMC’s firmware Web management page does not verify the string length entered by users, resulting in a Buffer overflow vulnerability. As obtaining the privileged permission, remote attackers use the leakage to abnormally terminate the Web service. |
2021-04-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-28195
CONFIRM
CONFIRM
CONFIRM |
asus — bmc_firmware
|
The specific function in ASUS BMC’s firmware Web management page (Audit log configuration setting) does not verify the string length entered by users, resulting in a Buffer overflow vulnerability. As obtaining the privileged permission, remote attackers use the leakage to abnormally terminate the Web service. |
2021-04-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-28180
CONFIRM
CONFIRM
CONFIRM |
asus — gputweak_ii
|
AsIO2_64.sys and AsIO2_32.sys in ASUS GPUTweak II before 2.3.0.3 allow low-privileged users to interact directly with physical memory (by calling one of several driver routines that map physical memory into the virtual address space of the calling process) and to interact with MSR registers. This could enable low-privileged users to achieve NT AUTHORITYSYSTEM privileges via a DeviceIoControl. |
2021-04-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-28685
MISC
MISC |
asus — gputweak_ii
|
AsIO2_64.sys and AsIO2_32.sys in ASUS GPUTweak II before 2.3.0.3 allow low-privileged users to trigger a stack-based buffer overflow. This could enable low-privileged users to achieve Denial of Service via a DeviceIoControl. |
2021-04-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-28686
MISC
MISC |
atlassian — jira_server_and_jira_data_center
|
The dashboard gadgets preference resource of the Atlassian gadgets plugin used in Jira Server and Jira Data Center before version 8.13.5, and from version 8.14.0 before version 8.15.1 allows remote anonymous attackers to obtain gadget related settings via a missing permissions check. |
2021-04-09 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-36287
MISC |
bixby — bixby
|
Improper handling of exceptional conditions in Bixby prior to version 3.0.53.02 allows attacker to execute the actions registered by the user. |
2021-04-09 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-25380
CONFIRM
CONFIRM |
cern — indico
|
CERN Indico before 2.3.4 can use an attacker-supplied Host header in a password reset link. |
2021-04-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-30185
MISC
MISC |
cisco — advanced_malware_protection
|
A vulnerability in the dynamic link library (DLL) loading mechanism in Cisco Advanced Malware Protection (AMP) for Endpoints Windows Connector, ClamAV for Windows, and Immunet could allow an authenticated, local attacker to perform a DLL hijacking attack on an affected Windows system. To exploit this vulnerability, the attacker would need valid credentials on the system. The vulnerability is due to insufficient validation of directory search paths at run time. An attacker could exploit this vulnerability by placing a malicious DLL file on an affected system. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to execute arbitrary code with SYSTEM privileges. |
2021-04-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1386
CISCO |
| cisco — clam_antivirus |
A vulnerability in the PDF parsing module in Clam AntiVirus (ClamAV) Software versions 0.103.0 and 0.103.1 could allow an unauthenticated, remote attacker to cause a denial of service condition on an affected device. The vulnerability is due to improper buffer size tracking that may result in a heap buffer over-read. An attacker could exploit this vulnerability by sending a crafted PDF file to an affected device. An exploit could allow the attacker to cause the ClamAV scanning process to crash, resulting in a denial of service condition. |
2021-04-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1405
CISCO |
cisco — clam_antivirus
|
A vulnerability in the Excel XLM macro parsing module in Clam AntiVirus (ClamAV) Software versions 0.103.0 and 0.103.1 could allow an unauthenticated, remote attacker to cause a denial of service condition on an affected device. The vulnerability is due to improper error handling that may result in an infinite loop. An attacker could exploit this vulnerability by sending a crafted Excel file to an affected device. An exploit could allow the attacker to cause the ClamAV scanning process hang, resulting in a denial of service condition. |
2021-04-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1252
CISCO |
cisco — clam_antivirus
|
A vulnerability in the email parsing module in Clam AntiVirus (ClamAV) Software version 0.103.0 and all prior versions could allow an unauthenticated, remote attacker to cause a denial of service condition on an affected device. The vulnerability is due to improper variable initialization that may result in an NULL pointer read. An attacker could exploit this vulnerability by sending a crafted email to an affected device. An exploit could allow the attacker to cause the ClamAV scanning process crash, resulting in a denial of service condition. |
2021-04-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1404
CISCO |
cisco — ios_xr_software
|
A vulnerability in the CLI of Cisco IOS XR Software could allow an authenticated, local attacker to inject arbitrary commands that are executed with root privileges on the underlying Linux operating system (OS) of an affected device. This vulnerability is due to insufficient input validation of commands that are supplied by the user. An attacker could exploit this vulnerability by authenticating to a device and submitting crafted input to an affected command. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to execute commands on the underlying Linux OS with root privileges. |
2021-04-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1485
CISCO |
cisco — multiple_routers
|
Multiple vulnerabilities in the web-based management interface of Cisco RV340, RV340W, RV345, and RV345P Dual WAN Gigabit VPN Routers could allow an authenticated, remote attacker to execute arbitrary code with elevated privileges equivalent to the web service process on an affected device. These vulnerabilities exist because HTTP requests are not properly validated. An attacker could exploit these vulnerabilities by sending a crafted HTTP request to the web-based management interface of an affected device. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to remotely execute arbitrary code on the device. |
2021-04-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1415
CISCO |
cisco — multiple_routers
|
A vulnerability in the web-based management interface of Cisco Small Business RV110W, RV130, RV130W, and RV215W Routers could allow an unauthenticated, remote attacker to execute arbitrary code on an affected device. The vulnerability is due to improper validation of user-supplied input in the web-based management interface. An attacker could exploit this vulnerability by sending crafted HTTP requests to a targeted device. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to execute arbitrary code as the root user on the underlying operating system of the affected device. Cisco has not released software updates that address this vulnerability. |
2021-04-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1459
CISCO |
cisco — multiple_routers
|
Multiple vulnerabilities in the web-based management interface of Cisco RV340, RV340W, RV345, and RV345P Dual WAN Gigabit VPN Routers could allow an authenticated, remote attacker to execute arbitrary code with elevated privileges equivalent to the web service process on an affected device. These vulnerabilities exist because HTTP requests are not properly validated. An attacker could exploit these vulnerabilities by sending a crafted HTTP request to the web-based management interface of an affected device. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to remotely execute arbitrary code on the device. |
2021-04-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1414
CISCO |
cisco — multiple_routers
|
Multiple vulnerabilities in the web-based management interface of Cisco RV340, RV340W, RV345, and RV345P Dual WAN Gigabit VPN Routers could allow an authenticated, remote attacker to execute arbitrary code with elevated privileges equivalent to the web service process on an affected device. These vulnerabilities exist because HTTP requests are not properly validated. An attacker could exploit these vulnerabilities by sending a crafted HTTP request to the web-based management interface of an affected device. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to remotely execute arbitrary code on the device. |
2021-04-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1413
CISCO |
cisco — sd-wan
|
Multiple vulnerabilities in Cisco SD-WAN vManage Software could allow an unauthenticated, remote attacker to execute arbitrary code or allow an authenticated, local attacker to gain escalated privileges on an affected system. For more information about these vulnerabilities, see the Details section of this advisory. |
2021-04-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1137
CISCO |
cisco — sd-wan_vmanage_software
|
Multiple vulnerabilities in Cisco SD-WAN vManage Software could allow an unauthenticated, remote attacker to execute arbitrary code or allow an authenticated, local attacker to gain escalated privileges on an affected system. For more information about these vulnerabilities, see the Details section of this advisory. |
2021-04-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1479
CISCO |
cisco — sd-wan_vmanage_software
|
Multiple vulnerabilities in Cisco SD-WAN vManage Software could allow an unauthenticated, remote attacker to execute arbitrary code or allow an authenticated, local attacker to gain escalated privileges on an affected system. For more information about these vulnerabilities, see the Details section of this advisory. |
2021-04-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1480
CISCO |
| cisco — small_business_rv_series_routers |
Multiple vulnerabilities exist in the Link Layer Discovery Protocol (LLDP) implementation for Cisco Small Business RV Series Routers. An unauthenticated, adjacent attacker could execute arbitrary code or cause an affected router to leak system memory or reload. A memory leak or device reload would cause a denial of service (DoS) condition on an affected device. For more information about these vulnerabilities, see the Details section of this advisory. Note: LLDP is a Layer 2 protocol. To exploit these vulnerabilities, an attacker must be in the same broadcast domain as the affected device (Layer 2 adjacent). |
2021-04-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1308
CISCO |
cisco — small_business_rv_series_routers
|
Multiple vulnerabilities exist in the Link Layer Discovery Protocol (LLDP) implementation for Cisco Small Business RV Series Routers. An unauthenticated, adjacent attacker could execute arbitrary code or cause an affected router to leak system memory or reload. A memory leak or device reload would cause a denial of service (DoS) condition on an affected device. For more information about these vulnerabilities, see the Details section of this advisory. Note: LLDP is a Layer 2 protocol. To exploit these vulnerabilities, an attacker must be in the same broadcast domain as the affected device (Layer 2 adjacent). |
2021-04-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1251
CISCO |
cisco — small_business_rv_series_routers
|
Multiple vulnerabilities exist in the Link Layer Discovery Protocol (LLDP) implementation for Cisco Small Business RV Series Routers. An unauthenticated, adjacent attacker could execute arbitrary code or cause an affected router to leak system memory or reload. A memory leak or device reload would cause a denial of service (DoS) condition on an affected device. For more information about these vulnerabilities, see the Details section of this advisory. Note: LLDP is a Layer 2 protocol. To exploit these vulnerabilities, an attacker must be in the same broadcast domain as the affected device (Layer 2 adjacent). |
2021-04-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1309
CISCO |
cisco — small_business_rv_series_routers
|
Multiple vulnerabilities exist in the web-based management interface of Cisco Small Business RV Series Routers. A remote attacker could execute arbitrary commands or bypass authentication and upload files on an affected device. For more information about these vulnerabilities, see the Details section of this advisory. |
2021-04-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1473
CISCO |
cisco — small_business_rv_series_routers
|
Multiple vulnerabilities exist in the web-based management interface of Cisco Small Business RV Series Routers. A remote attacker could execute arbitrary commands or bypass authentication and upload files on an affected device. For more information about these vulnerabilities, see the Details section of this advisory. |
2021-04-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1472
CISCO |
| cisco — umbrella |
Multiple vulnerabilities in the Admin audit log export feature and Scheduled Reports feature of Cisco Umbrella could allow an authenticated, remote attacker to perform formula and link injection attacks on an affected device. For more information about these vulnerabilities, see the Details section of this advisory. |
2021-04-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1475
CISCO |
cisco — umbrella
|
Multiple vulnerabilities in the Admin audit log export feature and Scheduled Reports feature of Cisco Umbrella could allow an authenticated, remote attacker to perform formula and link injection attacks on an affected device. For more information about these vulnerabilities, see the Details section of this advisory. |
2021-04-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1474
CISCO |
| cisco — unified_communications_manager |
A vulnerability in the Self Care Portal of Cisco Unified Communications Manager (Unified CM) and Cisco Unified Communications Manager Session Management Edition (Unified CM SME) could allow an authenticated, remote attacker to modify data on an affected system without proper authorization. The vulnerability is due to insufficient validation of user-supplied data to the Self Care Portal. An attacker could exploit this vulnerability by sending a crafted HTTP request to an affected system. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to modify information without proper authorization. |
2021-04-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1399
CISCO |
cisco — unified_communications_manager
|
Multiple vulnerabilities in the web-based management interface of Cisco Unified Communications Manager (Unified CM), Cisco Unified Communications Manager IM & Presence Service (Unified CM IM&P), Cisco Unified Communications Manager Session Management Edition (Unified CM SME), and Cisco Unity Connection could allow an unauthenticated, remote attacker to conduct a cross-site scripting (XSS) attack against an interface user. These vulnerabilities exist because the web-based management interface does not properly validate user-supplied input. An attacker could exploit these vulnerabilities by persuading an interface user to click a crafted link. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to execute arbitrary script code in the context of the affected interface or access sensitive browser-based information. |
2021-04-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1380
CISCO |
cisco — unified_communications_manager
|
A vulnerability in the SOAP API endpoint of Cisco Unified Communications Manager, Cisco Unified Communications Manager Session Management Edition, Cisco Unified Communications Manager IM & Presence Service, Cisco Unity Connection, and Cisco Prime License Manager could allow an authenticated, remote attacker to execute arbitrary code on an affected device. This vulnerability is due to improper sanitization of user-supplied input. An attacker could exploit this vulnerability by sending a SOAP API request with crafted parameters to an affected device. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to execute arbitrary code with root privileges on the underlying Linux operating system of the affected device. |
2021-04-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1362
CISCO |
cisco — unified_intelligence_center_software
|
A vulnerability in the web-based management interface of Cisco Unified Intelligence Center Software could allow an unauthenticated, remote attacker to conduct a cross-site scripting (XSS) attack against a user of the interface. This vulnerability exists because the web-based management interface does not properly validate user-supplied input. An attacker could exploit this vulnerability by persuading a user of an affected interface to click a crafted link. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to execute arbitrary script code in the context of the affected interface or access sensitive, browser-based information. |
2021-04-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1463
CISCO |
| cisco — univied_communications_manager |
Multiple vulnerabilities in the web-based management interface of Cisco Unified Communications Manager (Unified CM), Cisco Unified Communications Manager IM & Presence Service (Unified CM IM&P), Cisco Unified Communications Manager Session Management Edition (Unified CM SME), and Cisco Unity Connection could allow an unauthenticated, remote attacker to conduct a cross-site scripting (XSS) attack against an interface user. These vulnerabilities exist because the web-based management interface does not properly validate user-supplied input. An attacker could exploit these vulnerabilities by persuading an interface user to click a crafted link. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to execute arbitrary script code in the context of the affected interface or access sensitive browser-based information. |
2021-04-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1409
CISCO |
cisco — univied_communications_manager
|
Multiple vulnerabilities in the web-based management interface of Cisco Unified Communications Manager (Unified CM), Cisco Unified Communications Manager IM & Presence Service (Unified CM IM&P), Cisco Unified Communications Manager Session Management Edition (Unified CM SME), and Cisco Unity Connection could allow an unauthenticated, remote attacker to conduct a cross-site scripting (XSS) attack against an interface user. These vulnerabilities exist because the web-based management interface does not properly validate user-supplied input. An attacker could exploit these vulnerabilities by persuading an interface user to click a crafted link. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to execute arbitrary script code in the context of the affected interface or access sensitive browser-based information. |
2021-04-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1408
CISCO |
cisco — univied_communications_manager
|
Multiple vulnerabilities in the web-based management interface of Cisco Unified Communications Manager (Unified CM), Cisco Unified Communications Manager IM & Presence Service (Unified CM IM&P), Cisco Unified Communications Manager Session Management Edition (Unified CM SME), and Cisco Unity Connection could allow an unauthenticated, remote attacker to conduct a cross-site scripting (XSS) attack against an interface user. These vulnerabilities exist because the web-based management interface does not properly validate user-supplied input. An attacker could exploit these vulnerabilities by persuading an interface user to click a crafted link. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to execute arbitrary script code in the context of the affected interface or access sensitive browser-based information. |
2021-04-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1407
CISCO |
cisco — univied_communications_manager
|
A vulnerability in Cisco Unified Communications Manager (Unified CM) and Cisco Unified Communications Manager Session Management Edition (Unified CM SME) could allow an authenticated, remote attacker to access sensitive information on an affected device. The vulnerability is due to improper inclusion of sensitive information in downloadable files. An attacker could exploit this vulnerability by authenticating to an affected device and issuing a specific set of commands. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to obtain hashed credentials of system users. To exploit this vulnerability an attacker would need to have valid user credentials with elevated privileges. |
2021-04-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1406
CISCO |
| cisco — webex |
A vulnerability in certain web pages of Cisco Webex Meetings could allow an unauthenticated, remote attacker to modify a web page in the context of a user’s browser. The vulnerability is due to improper checks on parameter values in affected pages. An attacker could exploit this vulnerability by persuading a user to follow a crafted link that is designed to pass HTML code into an affected parameter. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to alter the contents of a web page to redirect the user to potentially malicious websites, or the attacker could use this vulnerability to conduct further client-side attacks. |
2021-04-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1420
CISCO |
cisco — webex
|
A vulnerability in Cisco Webex Meetings for Android could allow an authenticated, remote attacker to modify the avatar of another user. This vulnerability is due to improper authorization checks. An attacker could exploit this vulnerability by sending a crafted request to the Cisco Webex Meetings client of a targeted user of a meeting in which they are both participants. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to modify the avatar of the targeted user. |
2021-04-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1467
CISCO |
citsmart– citsmart
|
CITSmart before 9.1.2.28 mishandles the “filtro de autocomplete.” |
2021-04-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-28142
MISC |
cloud_controller — cloud_controller
|
Cloud Controller API versions prior to 1.106.0 logs service broker credentials if the default value of db logging config field is changed. CAPI database logs service broker password in plain text whenever a job to clean up orphaned items is run by Cloud Controller. |
2021-04-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-22115
MISC |
d-link — dsl-320b-d1_devices
|
** UNSUPPORTED WHEN ASSIGNED ** D-Link DSL-320B-D1 devices through EU_1.25 are prone to multiple Stack-Based Buffer Overflows that allow unauthenticated remote attackers to take over a device via the login.xgi user and pass parameters. NOTE: This vulnerability only affects products that are no longer supported by the maintainer. |
2021-04-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-26709
MISC
FULLDISC
MISC
MISC |
directus — directus
|
Directus 8 before 8.8.2 allows remote authenticated users to execute arbitrary code because file-upload permissions include the ability to upload a .php file to the main upload directory and/or upload a .php file and a .htaccess file to a subdirectory. Exploitation succeeds only for certain installations with the Apache HTTP Server and the local-storage driver (e.g., when the product was obtained from hub.docker.com). |
2021-04-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-29641
MISC
FULLDISC
MISC
MISC
MISC |
discord — recon_server
|
Discord Recon Server is a bot that allows you to do your reconnaissance process from your Discord. Remote code execution in version 0.0.1 would allow remote users to execute commands on the server resulting in serious issues. This flaw is patched in 0.0.2. |
2021-04-09 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-21433
MISC
MISC
CONFIRM |
django — django
|
In Django 2.2 before 2.2.20, 3.0 before 3.0.14, and 3.1 before 3.1.8, MultiPartParser allowed directory traversal via uploaded files with suitably crafted file names. Built-in upload handlers were not affected by this vulnerability. |
2021-04-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-28658
MISC
MISC
MLIST
CONFIRM |
dma — softlab_radius_manager
|
DMA Softlab Radius Manager 4.4.0 allows CSRF with impacts such as adding new manager accounts via admin.php. |
2021-04-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-30147
MISC
MISC
MISC |
dnsmasque — dnsmasque
|
A flaw was found in dnsmasq in versions before 2.85. When configured to use a specific server for a given network interface, dnsmasq uses a fixed port while forwarding queries. An attacker on the network, able to find the outgoing port used by dnsmasq, only needs to guess the random transmission ID to forge a reply and get it accepted by dnsmasq. This flaw makes a DNS Cache Poisoning attack much easier. The highest threat from this vulnerability is to data integrity. |
2021-04-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-3448
MISC |
dolby — audio_x2
|
The Dolby Audio X2 (DAX2) API service before 0.8.8.90 on Windows allows local users to gain privileges. |
2021-04-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-3146
MISC |
| dream_report — r20-1 |
A privilege escalation vulnerability exists in Dream Report 5 R20-2. COM Class Identifiers (CLSID), installed by Dream Report 5 20-2, reference LocalServer32 and InprocServer32 with weak privileges which can lead to privilege escalation when used. An attacker can provide a malicious file to trigger this vulnerability. |
2021-04-09 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-13534
MISC |
dream_report — r20-1
|
A privilege escalation vulnerability exists in Dream Report 5 R20-2. In the default configuration, the Syncfusion Dashboard Service service binary can be replaced by attackers to escalate privileges to NT SYSTEM. An attacker can provide a malicious file to trigger this vulnerability. |
2021-04-09 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-13532
MISC |
dream_report — r20-1
|
A privilege escalation vulnerability exists in Dream Report 5 R20-2. IIn the default configuration, the following registry keys, which reference binaries with weak permissions, can be abused by attackers to effectively ‘backdoor’ the installation files and escalate privileges when a new user logs in and uses the application. |
2021-04-09 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-13533
MISC |
eclipse — mosquitto
|
In Eclipse Mosquitto version 2.0.0 to 2.0.9, if an authenticated client that had connected with MQTT v5 sent a crafted CONNACK message to the broker, a NULL pointer dereference would occur. |
2021-04-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-28166
CONFIRM |
erlang — erlang
|
A local privilege escalation vulnerability was discovered in Erlang/OTP prior to version 23.2.3. By adding files to an existing installation’s directory, a local attacker could hijack accounts of other users running Erlang programs or possibly coerce a service running with “erlsrv.exe” to execute arbitrary code as Local System. This can occur only under specific conditions on Windows with unsafe filesystem permissions. |
2021-04-09 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-29221
MISC
MISC |
| esri — acrgis_online |
A cross-site scripting (XSS) vulnerability in the Document Link of documents in ESRI ArcGIS Online before 10.9 and Enterprise before 10.9 allows remote authenticated users to inject arbitrary JavaScript code via a malicious HTML attribute such as onerror (in the URL field of the Parameters tab). |
2021-04-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-3012
MISC |
exiv2 — exiv2
|
A flaw was found in Exiv2 in versions before and including 0.27.4-RC1. Improper input validation of the rawData.size property in Jp2Image::readMetadata() in jp2image.cpp can lead to a heap-based buffer overflow via a crafted JPG image containing malicious EXIF data. |
2021-04-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-3482
MISC |
ffmpeg — ffmpeg
|
FFmpeg <=4.3 contains a buffer overflow vulnerability in libavcodec through a crafted file that may lead to remote code execution. |
2021-04-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-30123
MISC
MISC
MISC |
forcepoint — web_security_content_gateway
|
Forcepoint Web Security Content Gateway versions prior to 8.5.4 improperly process XML input, leading to information disclosure. |
2021-04-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-6590
CONFIRM |
freebsd — multiple_products
|
In FreeBSD 13.0-STABLE before n245118, 12.2-STABLE before r369552, 11.4-STABLE before r369560, 13.0-RC5 before p1, 12.2-RELEASE before p6, and 11.4-RELEASE before p9, a superuser inside a FreeBSD jail configured with the non-default allow.mount permission could cause a race condition between the lookup of “..” and remounting a filesystem, allowing access to filesystem hierarchy outside of the jail. |
2021-04-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-25584
MISC |
freebsd — multiple_products
|
In FreeBSD 13.0-STABLE before n245050, 12.2-STABLE before r369525, 13.0-RC4 before p0, and 12.2-RELEASE before p6, listening socket accept filters implementing the accf_create callback incorrectly freed a process supplied argument string. Additional operations on the socket can lead to a double free or use after free. |
2021-04-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-29627
MISC |
freebsd — multiple_products
|
In FreeBSD 13.0-STABLE before n245117, 12.2-STABLE before r369551, 11.4-STABLE before r369559, 13.0-RC5 before p1, 12.2-RELEASE before p6, and 11.4-RELEASE before p9, copy-on-write logic failed to invalidate shared memory page mappings between multiple processes allowing an unpriivleged process to maintain a mapping after it is freed, allowing the process to read private data belonging to other processes or the kernel. |
2021-04-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-29626
MISC |
friendica — friendica
|
** DISPUTED ** Module/Settings/UserExport.php in Friendica through 2021.01 allows settings/userexport to be used by anonymous users, as demonstrated by an attempted access to an array offset on a value of type null, and excessive memory consumption. NOTE: the vendor states “the feature still requires a valid authentication cookie even if the route is accessible to non-logged users.” |
2021-04-05 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-30141
MISC
MISC |
gnome — gnome
|
fr-archive-libarchive.c in GNOME file-roller through 3.38.0, as used by GNOME Shell and other software, allows Directory Traversal during extraction because it lacks a check of whether a file’s parent is a symlink in certain complex situations. NOTE: this issue exists because of an incomplete fix for CVE-2020-11736. |
2021-04-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-36314
MISC
MISC |
gnu — chess
|
GNU Chess 6.2.7 allows attackers to execute arbitrary code via crafted PGN (Portable Game Notation) data. This is related to a buffer overflow in the use of a .tmp.epd temporary file in the cmd_pgnload and cmd_pgnreplay functions in frontend/cmd.cc. |
2021-04-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-30184
MISC
MISC |
| google — chrome |
Heap buffer overflow in TabStrip in Google Chrome prior to 89.0.4389.114 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. |
2021-04-09 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-21197
MISC
MISC |
| google — chrome |
Out of bounds read in IPC in Google Chrome prior to 89.0.4389.114 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to potentially perform a sandbox escape via a crafted HTML page. |
2021-04-09 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-21198
MISC
MISC |
| google — chrome |
Heap buffer overflow in TabStrip in Google Chrome on Windows prior to 89.0.4389.114 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. |
2021-04-09 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-21196
MISC
MISC |
google — chrome
|
Use after free in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 89.0.4389.114 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. |
2021-04-09 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-21195
MISC
MISC |
google — chrome
|
Use after free in Aura in Google Chrome on Linux prior to 89.0.4389.114 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. |
2021-04-09 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-21199
MISC
MISC |
google — chrome
|
Use after free in screen sharing in Google Chrome prior to 89.0.4389.114 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. |
2021-04-09 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-21194
MISC
MISC |
grav_admin_plugin — grav_admin_plugin
|
Grav Admin Plugin is an HTML user interface that provides a way to configure Grav and create and modify pages. In versions 1.10.7 and earlier, an unauthenticated user can execute some methods of administrator controller without needing any credentials. Particular method execution will result in arbitrary YAML file creation or content change of existing YAML files on the system. Successfully exploitation of that vulnerability results in configuration changes, such as general site information change, custom scheduler job definition, etc. Due to the nature of the vulnerability, an adversary can change some part of the webpage, or hijack an administrator account, or execute operating system command under the context of the web-server user. This vulnerability is fixed in version 1.10.8. Blocking access to the `/admin` path from untrusted sources can be applied as a workaround. |
2021-04-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-21425
CONFIRM
MISC |
huawei — multiple_products
|
There is a memory leak vulnerability in some Huawei products. An authenticated remote attacker may exploit this vulnerability by sending specific message to the affected product. Due to not release the allocated memory properly, successful exploit may cause some service abnormal. Affected product include some versions of IPS Module, NGFW Module, Secospace USG6300, Secospace USG6500, Secospace USG6600 and USG9500. |
2021-04-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-22312
MISC |
ibm — webspehere_application_server
|
IBM WebSphere Application Server 7.0, 8.0, and 8.5 is vulnerable to server-side request forgery (SSRF). By sending a specially crafted request, a remote authenticated attacker could exploit this vulnerability to obtain sensitive data. IBM X-Force ID: 197502. |
2021-04-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-20480
XF
CONFIRM |
ikuaios — build
|
iKuaiOS 3.4.8 Build 202012291059 has an arbitrary file download vulnerability, which can be exploited by attackers to obtain sensitive information. |
2021-04-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-28075
MISC |
imb — spectrum_scale
|
IBM Spectrum Scale 5.1.0.1 could allow a local attacker to bypass the filesystem audit logging mechanism when file audit logging is enabled. IBM X-Force ID: 199478. |
2021-04-09 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-29671
XF
CONFIRM |
jenkins — multiple_products
|
A cross-site request forgery (CSRF) vulnerability in Jenkins promoted builds Plugin 3.9 and earlier allows attackers to to promote builds. |
2021-04-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-21641
MLIST
CONFIRM |
jenkins — multiple_products
|
Jenkins 2.286 and earlier, LTS 2.277.1 and earlier does not properly check that a newly created view has an allowed name, allowing attackers with View/Create permission to create views with invalid or already-used names. |
2021-04-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-21640
MLIST
CONFIRM |
jenkins — multiple_products
|
Jenkins 2.286 and earlier, LTS 2.277.1 and earlier does not validate the type of object created after loading the data submitted to the `config.xml` REST API endpoint of a node, allowing attackers with Computer/Configure permission to replace a node with one of a different type. |
2021-04-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-21639
MLIST
CONFIRM |
jsrsasign –jsrsasign
|
In the jsrsasign package through 10.1.13 for Node.js, some invalid RSA PKCS#1 v1.5 signatures are mistakenly recognized to be valid. NOTE: there is no known practical attack. |
2021-04-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-30246
MISC
MISC
MISC |
larsens — calender
|
Cross Site Scripting (XSS) vulnerability in the Larsens Calender plugin Version <= 1.2 for WordPress allows remote attackers to execute arbitrary web script via the “titel” column on the “Eintrage hinzufugen” tab. |
2021-04-09 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-23762
MISC
MISC |
learnsite — learnsite
|
Learnsite 1.2.5.0 contains a remote privilege escalation vulnerability in /Manager/index.aspx through the JudgIsAdmin() function. By modifying the initial letter of the key of a user cookie, the key of the administrator cookie can be obtained. |
2021-04-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-27522
MISC |
| lg — mobile_devices |
An issue was discovered on LG mobile devices with Android OS 11 software. Attackers can bypass the lockscreen protection mechanism after an incoming call has been terminated. The LG ID is LVE-SMP-210002 (April 2021). |
2021-04-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-30161
MISC |
lg — mobile_devices
|
An issue was discovered on LG mobile devices with Android OS 4.4 through 11 software. Attackers can leverage ISMS services to bypass access control on specific content providers. The LG ID is LVE-SMP-210003 (April 2021). |
2021-04-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-30162
MISC |
libertro — retroarch
|
The text-to-speech engine in libretro RetroArch for Windows 0.11 passes unsanitized input to PowerShell through platform_win32.c via the accessibility_speak_windows function, which allows attackers who have write access on filesystems that are used by RetroArch to execute code via command injection using specially a crafted file and directory names. |
2021-04-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-28927
MISC
MISC
MISC |
| linux — linux_kernel |
An issue was discovered in the Linux kernel before 5.8.10. virt/kvm/kvm_main.c has a kvm_io_bus_unregister_dev memory leak upon a kmalloc failure, aka CID-f65886606c2d. |
2021-04-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-36312
MISC
MISC |
linux — linux_kernel
|
An issue was discovered in the Linux kernel before 5.8. arch/x86/kvm/svm/svm.c allows a set_memory_region_test infinite loop for certain nested page faults, aka CID-e72436bc3a52. |
2021-04-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-36310
MISC
MISC |
linux — linux_kernel
|
An issue was discovered in the Linux kernel through 5.11.11. synic_get in arch/x86/kvm/hyperv.c has a NULL pointer dereference for certain accesses to the SynIC Hyper-V context, aka CID-919f4ebc5987. |
2021-04-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-30178
MISC |
linux — linux_kernel
|
The fix for XSA-365 includes initialization of pointers such that subsequent cleanup code wouldn’t use uninitialized or stale values. This initialization went too far and may under certain conditions also overwrite pointers which are in need of cleaning up. The lack of cleanup would result in leaking persistent grants. The leak in turn would prevent fully cleaning up after a respective guest has died, leaving around zombie domains. All Linux versions having the fix for XSA-365 applied are vulnerable. XSA-365 was classified to affect versions back to at least 3.11. |
2021-04-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-28688
MISC |
linux — linux_kernel
|
BPF JIT compilers in the Linux kernel through 5.11.12 have incorrect computation of branch displacements, allowing them to execute arbitrary code within the kernel context. This affects arch/x86/net/bpf_jit_comp.c and arch/x86/net/bpf_jit_comp32.c. |
2021-04-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-29154
MISC
MISC |
linux — linux_kernel
|
An issue was discovered in the Linux kernel before 5.9. arch/x86/kvm/svm/sev.c allows attackers to cause a denial of service (soft lockup) by triggering destruction of a large SEV VM (which requires unregistering many encrypted regions), aka CID-7be74942f184. |
2021-04-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-36311
MISC
MISC |
linux — linux_kernel
|
An issue was discovered in the Linux kernel before 5.7. The KVM subsystem allows out-of-range access to memslots after a deletion, aka CID-0774a964ef56. This affects arch/s390/kvm/kvm-s390.c, include/linux/kvm_host.h, and virt/kvm/kvm_main.c. |
2021-04-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-36313
MISC
MISC |
liquidfiles — liquidfiles
|
LiquidFiles 3.4.15 has stored XSS through the “send email” functionality when sending a file via email to an administrator. When a file has no extension and contains malicious HTML / JavaScript content (such as SVG with HTML content), the payload is executed upon a click. This is fixed in 3.5. |
2021-04-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-30140
MISC
MISC
MISC |
litespeed_technologies — openlitespeed_web_server
|
Privilege Escalation in LiteSpeed Technologies OpenLiteSpeed web server version 1.7.8 allows attackers to gain root terminal access and execute commands on the host system. |
2021-04-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-26758
MISC
CONFIRM
EXPLOIT-DB |
magazinerz — magazinerz
|
Cross-site scripting vulnerability in MagazinegerZ v.1.01 allows remote attackers to inject an arbitrary script via unspecified vectors. |
2021-04-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-20684
MISC |
manageengine — servicedesk_plus
|
Insufficient output sanitization in ManageEngine ServiceDesk Plus before version 11200 and ManageEngine AssetExplorer before version 6800 allows a remote, unauthenticated attacker to conduct persistent cross-site scripting (XSS) attacks by uploading a crafted XML asset file. |
2021-04-09 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-20080
MISC |
mark_text — mark_text
|
Mark Text through 0.16.3 allows attackers arbitrary command execution. This could lead to Remote Code Execution (RCE) by opening .md files containing a mutation Cross Site Scripting (XSS) payload. |
2021-04-05 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-29996
MISC |
| mediawiki — mediawiki |
An issue was discovered in MediaWiki before 1.31.13 and 1.32.x through 1.35.x before 1.35.2. When using the MediaWiki API to “protect” a page, a user is currently able to protect to a higher level than they currently have permissions for. |
2021-04-09 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-30152
MISC
DEBIAN |
mediawiki — mediawiki
|
An issue was discovered in MediaWiki before 1.31.12 and 1.32.x through 1.35.x before 1.35.2. Users can bypass intended restrictions on deleting pages in certain “fast double move” situations. MovePage::isValidMoveTarget() uses FOR UPDATE, but it’s only called if Title::getArticleID() returns non-zero with no special flags. Next, MovePage::moveToInternal() will delete the page if getArticleID(READ_LATEST) is non-zero. Therefore, if the page is missing in the replica DB, isValidMove() will return true, and then moveToInternal() will unconditionally delete the page if it can be found in the master. |
2021-04-09 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-30159
MISC
DEBIAN |
mediawiki — mediawiki
|
An issue was discovered in MediaWiki before 1.31.12 and 1.32.x through 1.35.x before 1.35.2. Special:Contributions can leak that a “hidden” user exists. |
2021-04-09 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-30156
MISC |
mediawiki — mediawiki
|
An issue was discovered in MediaWiki before 1.31.12 and 1.32.x through 1.35.x before 1.35.2. ContentModelChange does not check if a user has correct permissions to create and set the content model of a nonexistent page. |
2021-04-09 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-30155
MISC
DEBIAN |
| micro_focus — application_automation_tools_plugin |
Missing Authorization vulnerability in Micro Focus Application Automation Tools Plugin – Jenkins plugin. The vulnerability affects version 6.7 and earlier versions. The vulnerability could allow access without permission checks. |
2021-04-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-22513
MISC |
micro_focus — application_automation_tools_plugin
|
Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF) vulnerability in Micro Focus Application Automation Tools Plugin – Jenkins plugin. The vulnerability affects version 6.7 and earlier versions. The vulnerability could allow form validation without permission checks. |
2021-04-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-22512
MISC |
micro_focus — application_automation_tools_plugin
|
Improper Certificate Validation vulnerability in Micro Focus Application Automation Tools Plugin – Jenkins plugin. The vulnerability affects version 6.7 and earlier versions. The vulnerability could allow unconditionally disabling of SSL/TLS certificates. |
2021-04-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-22511
MISC |
micro_focus — application_automation_tools_plugin
|
Reflected XSS vulnerability in Micro Focus Application Automation Tools Plugin – Jenkins plugin. The vulnerability affects all version 6.7 and earlier versions. |
2021-04-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-22510
MISC |
micro_focus — operations_bridge_manager
|
Authentication bypass vulnerability in Micro Focus Operations Bridge Manager affects versions 2019.05, 2019.11, 2020.05 and 2020.10. The vulnerability could allow remote attackers to bypass user authentication and get unauthorized access. |
2021-04-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-22507
MISC |
mitake — mitake
|
Mitake smart stock selection system contains a broken authentication vulnerability. By manipulating the parameters in the URL, remote attackers can gain the privileged permissions to access transaction record, and fraudulent trading without login. |
2021-04-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-28174
MISC |
mongodb– compass
|
A malicious 3rd party with local access to the Windows machine where MongoDB Compass is installed can execute arbitrary software with the privileges of the user who is running MongoDB Compass. This issue affects: MongoDB Inc. MongoDB Compass 1.x version 1.3.0 on Windows and later versions; 1.x versions prior to 1.25.0 on Windows. |
2021-04-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-20334
MISC |
| mozilla — firefox |
The unity-firefox-extension package could be tricked into dropping a C callback which was still in use, which Firefox would then free, causing Firefox to crash. This could be achieved by adding an action to the launcher and updating it with new callbacks until the libunity-webapps rate limit was hit. Fixed in 3.0.0+14.04.20140416-0ubuntu1.14.04.1 of unity-firefox-extension and in all versions of libunity-webapps by shipping an empty unity-firefox-extension package, thus disabling the extension entirely and invalidating the attack against the libunity-webapps package. |
2021-04-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2013-1055
UBUNTU
UBUNTU |
mozilla — firefox
|
The unity-firefox-extension package could be tricked into destroying the Unity webapps context, causing Firefox to crash. This could be achieved by spinning the event loop inside the webapps initialization callback. Fixed in 3.0.0+14.04.20140416-0ubuntu1.14.04.1 by shipping an empty package, thus disabling the extension entirely. |
2021-04-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2013-1054
UBUNTU
UBUNTU |
| nagios — network_analyzer |
SQL injection vulnerability in Nagios Network Analyzer before 2.4.3 via the o[col] parameter to api/checks/read/. |
2021-04-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-28925
MISC
MISC |
nagios — network_analyzer
|
Self Authenticated XSS in Nagios Network Analyzer before 2.4.2 via the nagiosna/groups/queries page. |
2021-04-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-28924
MISC
MISC |
openresty — openresty
|
ngx_http_lua_module (aka lua-nginx-module) before 0.10.16 in OpenResty allows unsafe characters in an argument when using the API to mutate a URI, or a request or response header. |
2021-04-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-36309
MISC
MISC
MISC |
perl — perl
|
The Net::Netmask module before 2.0000 for Perl does not properly consider extraneous zero characters at the beginning of an IP address string, which (in some situations) allows attackers to bypass access control that is based on IP addresses. |
2021-04-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-29424
MISC
FEDORA
FEDORA
FEDORA
MISC |
php-nuke — php-nuke
|
There is a SQL Injection vulnerability in PHP-Nuke 8.3.3 in the User Registration section, leading to remote code execution. This occurs because the U.S. state is not validated to be two letters, and the OrderBy field is not validated to be one of LASTNAME, CITY, or STATE. |
2021-04-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-30177
MISC |
phpseclib — phpseclib
|
phpseclib before 2.0.31 and 3.x before 3.0.7 mishandles RSA PKCS#1 v1.5 signature verification. |
2021-04-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-30130
MISC
CONFIRM
CONFIRM |
projen — projen
|
`projen` is a project generation tool that synthesizes project configuration files such as `package.json`, `tsconfig.json`, `.gitignore`, GitHub Workflows, `eslint`, `jest`, and more, from a well-typed definition written in JavaScript. Users of projen’s `NodeProject` project type (including any project type derived from it) include a `.github/workflows/rebuild-bot.yml` workflow that may allow any GitHub user to trigger execution of un-trusted code in the context of the “main” repository (as opposed to that of a fork). In some situations, such untrusted code may potentially be able to commit to the “main” repository. The rebuild-bot workflow is triggered by comments including `@projen rebuild` on pull-request to trigger a re-build of the projen project, and updating the pull request with the updated files. This workflow is triggered by an `issue_comment` event, and thus always executes with a `GITHUB_TOKEN` belonging to the repository into which the pull-request is made (this is in contrast with workflows triggered by `pull_request` events, which always execute with a `GITHUB_TOKEN` belonging to the repository from which the pull-request is made). Repositories that do not have branch protection configured on their default branch (typically `main` or `master`) could possibly allow an untrusted user to gain access to secrets configured on the repository (such as NPM tokens, etc). Branch protection prohibits this escalation, as the managed `GITHUB_TOKEN` would not be able to modify the contents of a protected branch and affected workflows must be defined on the default branch. |
2021-04-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-21423
MISC
CONFIRM
MISC |
| proofpoint — insider_threat_management_server |
The Proofpoint Insider Threat Management Server (formerly ObserveIT Server) is vulnerable to XML external entity (XXE) injection in the Web Console. The vulnerability requires admin user privileges and knowledge of the XML file’s encryption key to successfully exploit. All versions before 7.11 are affected. |
2021-04-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-22158
CONFIRM |
proofpoint — insider_threat_management_server
|
The Proofpoint Insider Threat Management Server (formerly ObserveIT Server) is missing an authorization check on several pages in the Web Console. This enables a view-only user to change any configuration setting and delete any registered agents. All versions before 7.11.1 are affected. |
2021-04-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-27900
CONFIRM |
proofpoint — insider_threat_management_server
|
Proofpoint Insider Threat Management Server (formerly ObserveIT Server) before 7.11.1 allows stored XSS. |
2021-04-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-22157
CONFIRM |
| qualcomm — multiple_snapdragon_products |
Memory crash when accessing histogram type KPI input received due to lack of check of histogram definition before accessing it in Snapdragon Auto, Snapdragon Compute, Snapdragon Connectivity, Snapdragon Mobile |
2021-04-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-11237
CONFIRM |
| qualcomm — multiple_snapdragon_products |
Denial of service while processing RTCP packets containing multiple SDES reports due to memory for last SDES packet is freed and rest of the memory is leaked in Snapdragon Auto, Snapdragon Compute, Snapdragon Connectivity, Snapdragon Consumer IOT, Snapdragon Industrial IOT, Snapdragon IoT, Snapdragon Mobile, Snapdragon Wearables |
2021-04-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-11255
CONFIRM |
| qualcomm — multiple_snapdragon_products |
Unintended reads and writes by NS EL2 in access control driver due to lack of check of input validation in Snapdragon Auto, Snapdragon Compute, Snapdragon Connectivity, Snapdragon Consumer IOT, Snapdragon Industrial IOT, Snapdragon Mobile, Snapdragon Wired Infrastructure and Networking |
2021-04-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-11245
CONFIRM |
| qualcomm — multiple_snapdragon_products |
Out of bound memory read while unpacking data due to lack of offset length check in Snapdragon Auto, Snapdragon Compute, Snapdragon Connectivity, Snapdragon Consumer IOT, Snapdragon Industrial IOT, Snapdragon IoT, Snapdragon Mobile, Snapdragon Voice & Music, Snapdragon Wearables |
2021-04-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-11247
CONFIRM |
| qualcomm — multiple_snapdragon_products |
Two threads call one or both functions concurrently leading to corruption of pointers and reference counters which in turn can lead to heap corruption in Snapdragon Compute, Snapdragon Connectivity, Snapdragon Consumer IOT, Snapdragon Industrial IOT, Snapdragon Mobile |
2021-04-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-11231
CONFIRM |
qualcomm — multiple_snapdragon_products
|
Memory corruption due to improper input validation while processing IO control which is nonstandard in Snapdragon Compute, Snapdragon Connectivity, Snapdragon Consumer Electronics Connectivity, Snapdragon Wired Infrastructure and Networking |
2021-04-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1892
CONFIRM |
qualcomm — multiple_snapdragon_products
|
Possible memory corruption in RPM region due to improper XPU configuration in Snapdragon Connectivity, Snapdragon Industrial IOT, Snapdragon Mobile, Snapdragon Wired Infrastructure and Networking |
2021-04-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-11210
CONFIRM |
qualcomm — multiple_snapdragon_products
|
User could gain access to secure memory due to incorrect argument into address range validation api used in SDI to capture requested contents in Snapdragon Industrial IOT, Snapdragon Mobile |
2021-04-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-11242
CONFIRM |
qualcomm — multiple_snapdragon_products
|
RRC sends a connection establishment success to NAS even though connection setup validation returns failure and leads to denial of service in Snapdragon Auto, Snapdragon Compute, Snapdragon Connectivity, Snapdragon Mobile |
2021-04-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-11243
CONFIRM |
qualcomm — multiple_snapdragon_products
|
Memory corruption due to invalid value of total dimension in the non-histogram type KPI could lead to a denial of service in Snapdragon Auto, Snapdragon Compute, Snapdragon Connectivity, Snapdragon Mobile |
2021-04-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-11236
CONFIRM |
qualcomm — multiple_snapdragon_products
|
Trustzone initialization code will disable xPU`s when memory dumps are enabled and lead to information disclosure in Snapdragon Auto, Snapdragon Compute, Snapdragon Connectivity, Snapdragon Consumer IOT, Snapdragon Industrial IOT, Snapdragon Mobile, Snapdragon Voice & Music, Snapdragon Wired Infrastructure and Networking |
2021-04-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-11252
CONFIRM |
qualcomm — multiple_snapdragon_products
|
Out-of-bounds read vulnerability while accessing DTMF payload due to lack of check of buffer length before copying in Snapdragon Auto, Snapdragon Compute, Snapdragon Connectivity, Snapdragon Consumer IOT, Snapdragon Industrial IOT, Snapdragon IoT, Snapdragon Mobile, Snapdragon Voice & Music, Snapdragon Wearables |
2021-04-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-11251
CONFIRM |
qualcomm — multiple_snapdragon_products
|
When sending a socket event message to a user application, invalid information will be passed if socket is freed by other thread resulting in a Use After Free condition in Snapdragon Auto, Snapdragon Compute, Snapdragon Connectivity, Snapdragon Consumer Electronics Connectivity, Snapdragon Consumer IOT, Snapdragon Industrial IOT, Snapdragon Mobile, Snapdragon Voice & Music, Snapdragon Wearables |
2021-04-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-11234
CONFIRM |
qualcomm — multiple_snapdragon_products
|
A double free condition can occur when the device moves to suspend mode during secure playback in Snapdragon Auto, Snapdragon Compute, Snapdragon Connectivity, Snapdragon Consumer IOT, Snapdragon Industrial IOT, Snapdragon Mobile |
2021-04-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-11246
CONFIRM |
qualcomm — multiple_snapdragon_products
|
Out of bound read occurs while processing crafted SDP due to lack of check of null string in Snapdragon Auto, Snapdragon Compute, Snapdragon Connectivity, Snapdragon Consumer Electronics Connectivity, Snapdragon Consumer IOT, Snapdragon Industrial IOT, Snapdragon IoT, Snapdragon Mobile, Snapdragon Voice & Music, Snapdragon Wearables, Snapdragon Wired Infrastructure and Networking |
2021-04-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-11191
CONFIRM |
ranker — ranker
|
Cross-site scripting vulnerability in Click Ranker Ver.3.5 allows remote attackers to inject an arbitrary script via unspecified vectors. |
2021-04-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-20688
MISC |
realtek — rtl8723de_ble_stack
|
An issue was discovered in Realtek rtl8723de BLE Stack <= 4.1 that allows remote attackers to cause a Denial of Service via the interval field to the CONNECT_REQ message. |
2021-04-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-23539
MISC |
red_hat — red-Hat
|
A flaw was found in Red Hat Satellite in tfm-rubygem-foreman_azure_rm in versions before 2.2.0. A credential leak was identified which will expose Azure Resource Manager’s secret key through JSON of the API output. The highest threat from this vulnerability is to data confidentiality and integrity as well as system availability. |
2021-04-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-3413
MISC |
relic — relic
|
In RELIC before 2020-08-01, RSA PKCS#1 v1.5 signature forgery can occur because certain checks of the padding (and of the first two bytes) are inadequate. NOTE: this requires that a low public exponent (such as 3) is being used. The product, by default, does not generate RSA keys with such a low number. |
2021-04-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-36315
MISC
MISC
MISC
MISC |
relic — relic
|
In RELIC before 2021-04-03, there is a buffer overflow in PKCS#1 v1.5 signature verification because garbage bytes can be present. |
2021-04-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-36316
MISC
MISC
MISC
MISC |
| rukovoditel — project_management_app |
An exploitable SQL injection vulnerability exists in “global_lists/choices” page of the Rukovoditel Project Management App 2.7.2. A specially crafted HTTP request can lead to SQL injection. An attacker can make an authenticated HTTP request to trigger this vulnerability, this can be done either with administrator credentials or through cross-site request forgery. |
2021-04-09 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-13592
MISC |
rukovoditel — project_management_app
|
An exploitable SQL injection vulnerability exists in the “forms_fields_rules/rules” page of the Rukovoditel Project Management App 2.7.2. A specially crafted HTTP request can lead to SQL injection. An attacker can make an authenticated HTTP request to trigger this vulnerability, this can be done either with administrator credentials or through cross-site request forgery. |
2021-04-09 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-13587
MISC |
rukovoditel — project_management_app
|
An exploitable SQL injection vulnerability exists in the “access_rules/rules_form” page of the Rukovoditel Project Management App 2.7.2. A specially crafted HTTP request can lead to SQL injection. An attacker can make an authenticated HTTP request to trigger this vulnerability, this can be done either with administrator credentials or through cross-site request forgery. |
2021-04-09 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-13591
MISC |
rust — id-map
|
An issue was discovered in the id-map crate through 2021-02-26 for Rust. A double free can occur in remove_set upon a panic in a Drop impl. |
2021-04-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-30457
MISC |
rust — id-map
|
An issue was discovered in the id-map crate through 2021-02-26 for Rust. A double free can occur in get_or_insert upon a panic of a user-provided f function. |
2021-04-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-30456
MISC |
rust — id-map
|
An issue was discovered in the id-map crate through 2021-02-26 for Rust. A double free can occur in IdMap::clone_from upon a .clone panic. |
2021-04-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-30455
MISC |
rust — outer_cgi
|
An issue was discovered in the outer_cgi crate before 0.2.1 for Rust. A user-provided Read instance receives an uninitialized memory buffer from KeyValueReader. |
2021-04-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-30454
MISC |
| samsung — mobile |
An improper permission management in CertInstaller prior to SMR APR-2021 Release 1 allows untrusted applications to delete certain local files. |
2021-04-09 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-25362
CONFIRM
CONFIRM |
| samsung — mobile |
An improper access control in ActivityManagerService prior to SMR APR-2021 Release 1 allows untrusted applications to access running processesdelete some local files. |
2021-04-09 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-25363
CONFIRM
CONFIRM |
| samsung — mobile |
Using predictable index for attachments in Samsung Email prior to version 6.1.41.0 allows remote attackers to get attachments of another emails when users open the malicious attachment. |
2021-04-09 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-25375
CONFIRM
CONFIRM |
| samsung — mobile |
An improper authorization vulnerability in Samsung Members “samsungrewards” scheme for deeplink in versions 2.4.83.9 in Android O(8.1) and below, and 3.9.00.9 in Android P(9.0) and above allows remote attackers to access a user data related with Samsung Account. |
2021-04-09 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-25374
CONFIRM
CONFIRM |
| samsung — mobile |
Intent redirection vulnerability in Gallery prior to version 5.4.16.1 allows attacker to execute privileged action. |
2021-04-09 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-25379
CONFIRM
CONFIRM |
| samsung — mobile |
An improper access control vulnerability in stickerCenter prior to SMR APR-2021 Release 1 allows local attackers to read or write arbitrary files of system process via untrusted applications. |
2021-04-09 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-25361
CONFIRM
CONFIRM |
| samsung — mobile |
A pendingIntent hijacking vulnerability in Create Movie prior to SMR APR-2021 Release 1 in Android O(8.x) and P(9.0), 3.4.81.1 in Android Q(10,0), and 3.6.80.7 in Android R(11.0) allows unprivileged applications to access contact information. |
2021-04-09 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-25357
CONFIRM
CONFIRM |
| samsung — mobile |
An improper caller check vulnerability in Managed Provisioning prior to SMR APR-2021 Release 1 allows unprivileged application to install arbitrary application, grant device admin permission and then delete several installed application. |
2021-04-09 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-25356
CONFIRM
CONFIRM |
samsung — mobile
|
An improper synchronization logic in Samsung Email prior to version 6.1.41.0 can leak messages in certain mailbox in plain text when STARTTLS negotiation is failed. |
2021-04-09 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-25376
CONFIRM
CONFIRM |
samsung — mobile
|
Using unsafe PendingIntent in Customization Service prior to version 2.2.02.1 in Android O(8.x), 2.4.03.0 in Android P(9.0), 2.7.02.1 in Android Q(10.0) and 2.9.01.1 in Android R(11.0) allows local attackers to perform unauthorized action without permission via hijacking the PendingIntent. |
2021-04-09 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-25373
CONFIRM
CONFIRM |
samsung — mobile
|
Intent redirection in Samsung Experience Service versions 10.8.0.4 in Android P(9.0) below, and 12.2.0.5 in Android Q(10.0) above allows attacker to execute privileged action. |
2021-04-09 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-25377
CONFIRM
CONFIRM |
samsung — mobile
|
Improper access control of certain port in SmartThings prior to version 1.7.63.6 allows remote temporary denial of service. |
2021-04-09 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-25378
CONFIRM
CONFIRM |
samsung — mobile
|
A pendingIntent hijacking vulnerability in Secure Folder prior to SMR APR-2021 Release 1 allows unprivileged applications to access contact information. |
2021-04-09 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-25364
CONFIRM
CONFIRM |
samsung — mobile
|
An improper exception control in softsimd prior to SMR APR-2021 Release 1 allows unprivileged applications to access the API in softsimd. |
2021-04-09 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-25365
CONFIRM
CONFIRM |
samsung — mobile
|
Using unsafe PendingIntent in Samsung Account in versions 10.8.0.4 in Android P(9.0) and below, and 12.1.1.3 in Android Q(10.0) and above allows local attackers to perform unauthorized action without permission via hijacking the PendingIntent. |
2021-04-09 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-25381
CONFIRM
CONFIRM |
samsung — mobile
|
An improper input validation vulnerability in libswmfextractor library prior to SMR APR-2021 Release 1 allows attackers to execute arbitrary code on mediaextractor process. |
2021-04-09 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-25360
CONFIRM
CONFIRM |
samsung — mobile
|
An improper SELinux policy prior to SMR APR-2021 Release 1 allows local attackers to access AP information without proper permissions via untrusted applications. |
2021-04-09 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-25359
CONFIRM
CONFIRM |
samsung — mobile
|
A vulnerability that stores IMSI values in an improper path prior to SMR APR-2021 Release 1 allows local attackers to access IMSI values without any permission via untrusted applications. |
2021-04-09 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-25358
CONFIRM
CONFIRM |
seafile — seafile
|
Seafile 7.0.5 (2019) allows Persistent XSS via the “share of library functionality.” |
2021-04-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-30146
MISC |
serentiyos — serenityos
|
SerenityOS 2021-03-27 contains a buffer overflow vulnerability in the EndOfCentralDirectory::read() function. |
2021-04-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-30045
MISC
MISC
MISC |
skyworth_digital_technology — rn510
|
Skyworth Digital Technology RN510 V.3.1.0.4 is affected by an incorrect access control vulnerability in/cgi-bin/test_version.asp. If Wi-Fi is connected but an unauthenticated user visits a URL, the SSID password and web UI password may be disclosed. |
2021-04-09 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-25326
MISC |
skyworth_digital_technology — rn510
|
Skyworth Digital Technology RN510 V.3.1.0.4 RN510 V.3.1.0.4 contains a buffer overflow vulnerability in /cgi-bin/app-staticIP.asp. An authenticated attacker can send a specially crafted request to endpoint which can lead to a denial of service (DoS) or possible code execution on the device. |
2021-04-09 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-25328
MISC |
skyworth_digital_technology — rn510
|
Skyworth Digital Technology RN510 V.3.1.0.4 contains a cross-site request forgery (CSRF) vulnerability in /cgi-bin/net-routeadd.asp and /cgi-bin/sec-urlfilter.asp. Missing CSRF protection in devices can lead to XSRF, as the above pages are vulnerable to cross-site scripting (XSS). |
2021-04-09 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-25327
MISC |
sonicwall — email_security
|
A vulnerability in the SonicWall Email Security version 10.0.9.x allows an attacker to create an administrative account by sending a crafted HTTP request to the remote host. |
2021-04-09 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-20021
CONFIRM |
sonicwall — email_security
|
SonicWall Email Security version 10.0.9.x contains a vulnerability that allows a post-authenticated attacker to upload an arbitrary file to the remote host. |
2021-04-09 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-20022
CONFIRM |
sonicwall — gms
|
A command execution vulnerability in SonicWall GMS 9.3 allows a remote unauthenticated attacker to locally escalate privilege to root. |
2021-04-10 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-20020
CONFIRM |
sopel-channelmgnt — sopel-channelmgnt
|
sopel-channelmgnt is a channelmgnt plugin for sopel. In versions prior to 2.0.1, on some IRC servers, restrictions around the removal of the bot using the kick/kickban command could be bypassed when kicking multiple users at once. We also believe it may have been possible to remove users from other channels but due to the wonder that is IRC and following RfCs, We have no POC for that. Freenode is not affected. This is fixed in version 2.0.1. As a workaround, do not use this plugin on networks where TARGMAX > 1. |
2021-04-09 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-21431
MISC
CONFIRM
MISC |
squirro — insights_engine
|
The Squirro Insights Engine was affected by a Reflected Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) vulnerability affecting versions 2.0.0 up to and including 3.2.4. An attacker can use the vulnerability to inject malicious JavaScript code into the application, which will execute within the browser of any user who views the relevant application content. The attacker-supplied code can perform a wide variety of actions, such as stealing victims’ session tokens or login credentials, performing arbitrary actions on their behalf, and logging their keystrokes. |
2021-04-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-27945
CONFIRM |
subrion — cms_version
|
Cross Site Scripting (XSS) vulnerability in subrion CMS Version <= 4.2.1 allows remote attackers to execute arbitrary web script via the “payment gateway” column on transactions tab. |
2021-04-09 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-23761
MISC
MISC |
syncthing — syncthing
|
Syncthing is a continuous file synchronization program. In Syncthing before version 1.15.0, the relay server `strelaysrv` can be caused to crash and exit by sending a relay message with a negative length field. Similarly, Syncthing itself can crash for the same reason if given a malformed message from a malicious relay server when attempting to join the relay. Relay joins are essentially random (from a subset of low latency relays) and Syncthing will by default restart when crashing, at which point it’s likely to pick another non-malicious relay. This flaw is fixed in version 1.15.0. |
2021-04-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-21404
MISC
MISC
CONFIRM
MISC |
teradici — pcoip_connection_manager_and_security_gateway
|
Sensitive smart card data is logged in default INFO logs by Teradici’s PCoIP Connection Manager and Security Gateway prior to version 21.01.3. |
2021-04-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-25692
MISC |
timelybills — timelybills
|
Cleartext Storage in a File or on Disk in TimelyBills <= 1.7.0 for iOS and versions <= 1.21.115 for Android allows attacker who can locally read user’s files obtain JWT tokens for user’s account due to insufficient cache clearing mechanisms. A threat actor can obtain sensitive user data by decoding the tokens as JWT is signed and encoded, not encrypted. |
2021-04-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-26833
MISC |
umoci — umoci
|
Open Container Initiative umoci before 0.4.7 allows attackers to overwrite arbitrary host paths via a crafted image that causes symlink traversal when “umoci unpack” or “umoci raw unpack” is used. |
2021-04-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-29136
MISC
CONFIRM
CONFIRM |
unibox — u-50_and_enterprise_series
|
Unibox SMB 2.4 and UniBox Enterprise Series 2.4 and UniBox Campus Series 2.4 contain a cross-site request forgery (CSRF) vulnerability in /tools/network-trace, /list_users, /list_byod?usertype=raduser, /dhcp_leases, /go?rid=202 in which a specially crafted HTTP request may reconfigure the device. |
2021-04-09 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-21884
MISC
MISC
MISC |
unibox — u-50_and_enterprise_series
|
Unibox U-50 2.4 and UniBox Enterprise Series 2.4 and UniBox Campus Series 2.4 contain a OS command injection vulnerability in /tools/ping, which can leads to complete device takeover. |
2021-04-09 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-21883
MISC
MISC
MISC |
valve_stream — valve_stream
|
Valve Steam through 2021-04-10, when a Source engine game is installed, allows remote authenticated users to execute arbitrary code because of a buffer overflow that occurs for a Steam invite after one click. |
2021-04-10 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-30481
MISC
MISC
MISC
MISC |
vela — vela
|
Vela is a Pipeline Automation (CI/CD) framework built on Linux container technology written in Golang. An authentication mechanism added in version 0.7.0 enables some malicious user to obtain secrets utilizing the injected credentials within the `~/.netrc` file. Refer to the referenced GitHub Security Advisory for complete details. This is fixed in version 0.7.5. |
2021-04-09 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-21432
MISC
MISC
MISC
CONFIRM
MISC |
vestacp — vestacp
|
VestaCP through 0.9.8-24 allows attackers to gain privileges by creating symlinks to files for which they lack permissions. After reading the RKEY value from user.conf under the /usr/local/vesta/data/users/admin directory, the admin password can be changed via a /reset/?action=confirm&user=admin&code= URI. This occurs because chmod is used unsafely. |
2021-04-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-30463
MISC |
vestacp — vestacp
|
VestaCP through 0.9.8-24 allows the admin user to escalate privileges to root because the Sudo configuration does not require a password to run /usr/local/vesta/bin scripts. |
2021-04-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-30462
MISC |
vigra — computer_vision_library
|
VIGRA Computer Vision Library Version-1-11-1 contains a segmentation fault vulnerability in the impex.hxx read_image_band() function, in which a crafted file can cause a denial of service. |
2021-04-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-30046
MISC |
| wcms — wcms |
Cross Site Scripting (XSS) vulnerability in wcms 0.3.2 allows remote attackers to inject arbitrary web script and HTML via the pagename parameter to wex/html.php. |
2021-04-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-24138
MISC |
| wcms — wcms |
Server-side request forgery in Wcms 0.3.2 lets an attacker send crafted requests from the back-end server of a vulnerable web application via the path parameter to wex/cssjs.php. It can help identify open ports, local network hosts and execute command on local services. |
2021-04-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-24139
MISC |
| wcms — wcms |
Directory traversal vulnerability in Wcms 0.3.2 allows an attacker to read arbitrary files on the server that is running an application via the path parameter to wex/cssjs.php. |
2021-04-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-24137
MISC |
wcms — wcms
|
Directory traversal in Wcms 0.3.2 allows an attacker to read arbitrary files on the server that is running an application via the pagename parameter to wex/html.php. |
2021-04-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-24136
MISC |
wcms — wcms
|
Server-side request forgery in Wcms 0.3.2 let an attacker send crafted requests from the back-end server of a vulnerable web application via the pagename parameter to wex/html.php. It can help identify open ports, local network hosts and execute command on local services. |
2021-04-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-24140
MISC |
wcms — wcms
|
A Reflected Cross Site Scripting (XSS) Vulnerability was discovered in Wcms 0.3.2, which allows remote attackers to inject arbitrary web script and HTML via the type parameter to wex/cssjs.php. |
2021-04-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-24135
MISC |
| web-school_erp — web_school_erp |
A blind XSS vulnerability exists in Web-School ERP V 5.0 via (Add Events) in event name and description fields. An attacker can inject a JavaScript code that will be stored in the page. If any visitor sees the event, then the payload will be executed and sends the victim’s information to the attacker website. |
2021-04-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-30113
MISC
MISC
MISC |
web-school_erp — web_school_erp
|
Web-School ERP V 5.0 contains a cross-site request forgery (CSRF) vulnerability that allows a remote attacker to create a student_leave_application request through module/core/studentleaveapplication/create. The application fails to validate the CSRF token for a POST request using Guardian privilege. |
2021-04-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-30112
MISC
MISC
MISC |
web-school_erp — web_school_erp
|
A stored XSS vulnerability exists in Web-School ERP V 5.0 via (Add Events) in the event name and description fields. An attack can inject a JavaScript code that will be stored in the page. If any visitor sees the events, then the payload will be executed. |
2021-04-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-30111
MISC
MISC
MISC |
web-school_erp — web_school_erp
|
Web-School ERP V 5.0 contains a cross-site request forgery (CSRF) vulnerability that allows a remote attacker to create a voucher payment request through module/accounting/voucher/create. The application fails to validate the CSRF token for a POST request using admin privilege. |
2021-04-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-30114
MISC
MISC
MISC |
whatsapp — whatsapp
|
A cache configuration issue prior to WhatsApp for Android v2.21.4.18 and WhatsApp Business for Android v2.21.4.18 may have allowed a third party with access to the device’s external storage to read cached TLS material. |
2021-04-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-24027
CONFIRM |
whatsapp — whatsapp
|
A missing bounds check within the audio decoding pipeline for WhatsApp calls in WhatsApp for Android prior to v2.21.3, WhatsApp Business for Android prior to v2.21.3, WhatsApp for iOS prior to v2.21.32, and WhatsApp Business for iOS prior to v2.21.32 could have allowed an out-of-bounds write. |
2021-04-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-24026
CONFIRM |
wikimedia — parsoid
|
An issue was discovered in Wikimedia Parsoid before 0.11.1 and 0.12.x before 0.12.2. An attacker can send crafted wikitext that Utils/WTUtils.php will transform by using a <meta> tag, bypassing sanitization steps, and potentially allowing for XSS. |
2021-04-09 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-30458
MISC
MISC |
| wordpress — wordpress |
The editor of the WP Page Builder WordPress plugin before 1.2.4 allows lower-privileged users to insert unfiltered HTML, including JavaScript, into pages via the “Raw HTML” widget and the “Custom HTML” widgets (though the custom HTML widget requires sending a crafted request – it appears that this widget uses some form of client side validation but not server side validation), all of which are added via the “page_builder_data” parameter when performing the “wppb_page_save” AJAX action. It is also possible to insert malicious JavaScript via the “wppb_page_css” parameter (this can be done by closing out the style tag and opening a script tag) when performing the “wppb_page_save” AJAX action. |
2021-04-05 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-24208
CONFIRM
MISC |
| wordpress — wordpress |
By default, the WP Page Builder WordPress plugin before 1.2.4 allows subscriber-level users to edit and make changes to any and all posts pages – user roles must be specifically blocked from editing posts and pages. |
2021-04-05 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-24207
CONFIRM
MISC |
| wordpress — wordpress |
The WordPress Related Posts plugin through 3.6.4 contains an authenticated (admin+) stored XSS vulnerability in the title field on the settings page. By exploiting that an attacker will be able to execute JavaScript code in the user’s browser. |
2021-04-05 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-24211
CONFIRM |
| wordpress — wordpress |
The WooCommerce Help Scout WordPress plugin before 2.9.1 (https://woocommerce.com/products/woocommerce-help-scout/) allows unauthenticated users to upload any files to the site which by default will end up in wp-content/uploads/hstmp. |
2021-04-05 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-24212
MISC
CONFIRM |
| wordpress — wordpress |
The Theme Editor WordPress plugin before 2.6 did not validate the GET file parameter before passing it to the download_file() function, allowing administrators to download arbitrary files on the web server, such as /etc/passwd |
2021-04-05 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-24154
CONFIRM |
wordpress — wordpress
|
There is an open redirect in the PhastPress WordPress plugin before 1.111 that allows an attacker to malform a request to a page with the plugin and then redirect the victim to a malicious page. There is also a support comment from another user one year ago (https://wordpress.org/support/topic/phast-php-used-for-remote-fetch/) that says that the php involved in the request only go to whitelisted pages but it’s possible to redirect the victim to any domain. |
2021-04-05 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-24210
MISC
CONFIRM |
wordpress — wordpress
|
The WooCommerce Upload Files WordPress plugin before 59.4 ran a single sanitization pass to remove blocked extensions such as .php. It was possible to bypass this and upload a file with a PHP extension by embedding a “blocked” extension within another “blocked” extension in the “wcuf_file_name” parameter. It was also possible to perform a double extension attack and upload files to a different location via path traversal using the “wcuf_current_upload_session_id” parameter. |
2021-04-05 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-24171
CONFIRM
MISC |
wordpress — wordpress
|
Due to the lack of sanitization and lack of nonce protection on the custom CSS feature, an attacker could craft a request to inject malicious JavaScript on a site using the Contact Form 7 Style WordPress plugin through 3.1.9. If an attacker successfully tricked a site’s administrator into clicking a link or attachment, then the request could be sent and the CSS settings would be successfully updated to include malicious JavaScript. |
2021-04-05 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-24159
CONFIRM
MISC |
wordpress — wordpress
|
The WP Super Cache WordPress plugin before 1.7.2 was affected by an authenticated (admin+) RCE in the settings page due to input validation failure and weak $cache_path check in the WP Super Cache Settings -> Cache Location option. Direct access to the wp-cache-config.php file is not prohibited, so this vulnerability can be exploited for a web shell injection. |
2021-04-05 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-24209
MISC
MISC
CONFIRM |
wordpress — wordpress
|
The WordPress Backup and Migrate Plugin – Backup Guard WordPress plugin before 1.6.0 did not ensure that the imported files are of the SGBP format and extension, allowing high privilege users (admin+) to upload arbitrary files, including PHP ones, leading to RCE. |
2021-04-05 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-24155
CONFIRM |
wordpress — wordpress
|
The LikeBtn WordPress Like Button Rating ♥ LikeBtn WordPress plugin before 2.6.32 was vulnerable to Unauthenticated Full-Read Server-Side Request Forgery (SSRF). |
2021-04-05 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-24150
CONFIRM |
xiaomi — ax1800_routers
|
On Xiaomi router AX1800 rom version < 1.0.336 and RM1800 root version < 1.0.26, the encryption scheme for a user’s backup files uses hard-coded keys, which can expose sensitive information such as a user’s password. |
2021-04-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-14099
MISC |
xiaomi — ax3600_routers
|
A RACE CONDITION on XQBACKUP causes a decompression path error on Xiaomi router AX3600 with ROM version =1.0.50. |
2021-04-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-14104
MISC |
xiaomi — mobile_phones
|
The application in the mobile phone can unauthorized access to the list of running processes in the mobile phone, Xiaomi Mobile Phone MIUI < 2021.01.26. |
2021-04-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-14106
MISC |
xiaomi — mobile_phones
|
The application in the mobile phone can read the SNO information of the device, Xiaomi 10 MIUI < 2020.01.15. |
2021-04-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-14103
MISC |
zoom — zoom
|
Zoom Chat through 2021-04-09 on Windows and macOS allows certain remote authenticated attackers to execute arbitrary code without user interaction. An attacker must be within the same organization, or an external party who has been accepted as a contact. NOTE: this is specific to the Zoom Chat software, which is different from the chat feature of the Zoom Meetings and Zoom Video Webinars software. |
2021-04-09 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-30480
MISC
MISC
MISC
MISC
MISC
MISC |
| zte — zxa10_c300m |
A ZTE product has a configuration error vulnerability. Because a certain port is open by default, an attacker can consume system processing resources by flushing a large number of packets to the port, and successfully exploiting this vulnerability could reduce system processing capabilities. This affects: ZXA10 C300M all versions up to V4.3P8. |
2021-04-09 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-21728
MISC |
zzcms — zzcms
|
zzcms 201910 contains an access control vulnerability through escalation of privileges in /user/adv.php, which allows an attacker to modify data for further attacks such as CSRF. |
2021-04-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-23426
MISC |
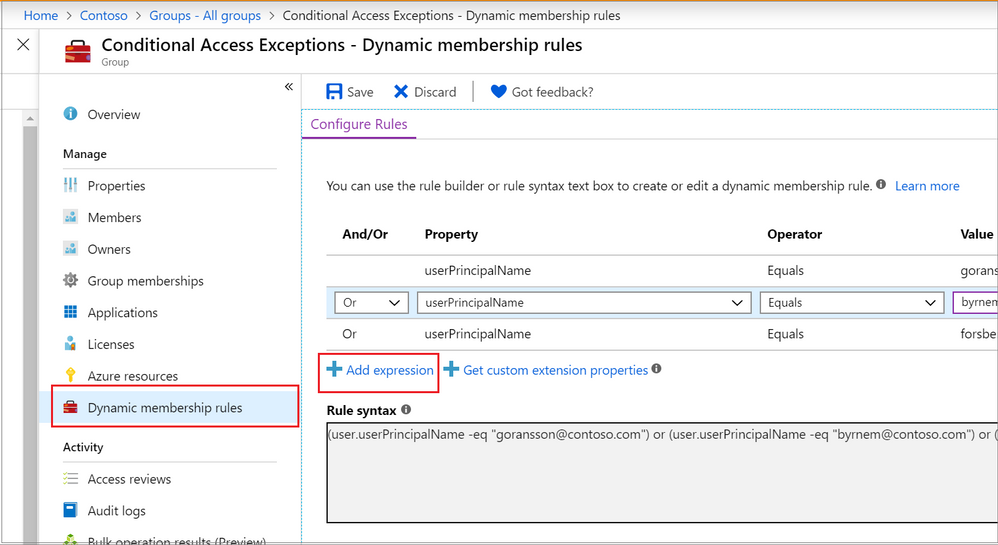
by Contributed | Apr 12, 2021 | Technology
This article is contributed. See the original author and article here.
When I first started in IT, my large organization had an entirely separate “Data Security” team who were responsible for user management – adds/moves/deletes and password resets. They were a small but busy team, handling both calls from users via the helpdesk and requests generated by HR. Apart from using some Active Directory automation scripting with VBScript instead of the GUI, each request was handled individually.
Fast forward to 2021 and as well as replacing those scripts with PowerShell, we can use dynamic groups to maintain the group members based on the attributes of those members.
Why would you use Dynamic Groups?
Using a query-based membership, when you update the attributes of a user or device they will be added to or removed from the dynamic groups that are now relevant to them, without you having to do any other steps. You might have a dynamic group for people who have the same department name or location specified in their user account. You can combine more than one attribute so, for example, the group members have to both be in the Finance department and be located in Brisbane, Australia. You can even create a “direct reports” dynamic group for people who report to the same manager.
Devices can also be group members but you can’t mix both users and devices in the same group. You could create dynamic groups of devices with the same operating system version, Intune device property label or enrolment profile name, for example.
For a full list of supported attribute queries and syntax, visit Dynamic membership rules for groups in Azure Active Directory.
Licensing
Dynamic membership is supported in security groups and Microsoft 365 groups. It requires an Azure AD P1 license for each unique user who is a member of one of or more dynamic groups. This is an overall count though – the P1 license doesn’t have to be assigned to the people you want to be included in dynamic groups, but the total member count of people in dynamic groups must match or be exceeded by the total number of P1 licenses owned by your organization. Some Microsoft 365 license plans include this Azure AD premium functionality – E3, E5, MF1 and MF3. No licenses are required for devices that are members of dynamic groups.
Dynamic Groups in Azure Active Directory
The Azure portal provides a graphical-based rule builder for dynamic membership, which supports adding up to five expressions, and the ability to enter your query string directly into the text editor. You also need to use the text editor for the “direct reports” scenario I mentioned above, setting operator precedence, and for writing more complex rules.
 Adding a dynamic membership rule to a group in the Azure Portal
Adding a dynamic membership rule to a group in the Azure Portal
Operator precedence is where we want a part of the query to be evaluated before another part. For example, we can use parenthesis to build a list of matching department names (finance or HR) and add that to the Brisbane location:
user.city -eq "Brisbane"-and (user.department -eq "Finance" -or user.department -eq "HR")
To build more complex queries, you can use the following operators:
-eq -ne -startsWith -notStartsWith -contains -notContains -match –notMatch -in -notIn
-not
-and
-or
-any -all
Example: Direct Reports
This rule maintains members who have their Manager property set to the same Manager ID. The Manager ID is the unique object identifier found in the manager’s profile. It does not support subgroups and can’t be combined with any other membership rules.
Direct Reports for "{objectID_of_manager}" for example Direct Reports for "62e19b97-8b3d-4d4a-a106-4ce66896a863"
Example: On-premises domain membership
If you’re synchronizing identities from Active Directory to Azure Active Directory, you can build dynamic groups based on which Active Directory Domain the user belongs to. This is based on the user’s Security Identifier (SID). You can use PowerShell to query the users with a domain filter to get the start of the SID that you need:
Get-ADUser -Filter * -SearchBase "dc=domain,dc=local" | select Name,SID
Then use the rule syntax that queries Azure AD for the user.onPremisesSecurityIdentifier attribute:
(user.onPremisesSecurityIdentifier -startsWith "S-1-5-21-12345678-1234567891-123456789")
Verifying members of your dynamic group
When an identity attribute of a user or a device changes, Azure AD evaluates all dynamic membership rules that exist in that directory, triggering any relevant membership additions or removals. You can also see the list of current group members via the Azure portal, or use the following PowerShell command for a simple list:
(Get-AzADGroup -DisplayName "<DisplayNameofGroup>" | Get-AzADGroupMember).DisplayName
Note: This requires the Azure Active Directory PowerShell module that you can download here.
In preview, is the ability to validate your rules against up to 20 users or devices. The Validate Rules tab will run your query against your selected target users or devices and confirm if they would meet the requirements to be a group member or not. For more information, visit Validate a dynamic group membership rule (preview) in Azure Active Directory.
Microsoft 365 groups and Microsoft Teams dynamic membership
Microsoft 365 groups (as a group type) provision access across a selection of Microsoft 365 services for a group of people who will be working together. They are designed to prove quick and easy access, removing the administration overhead of an IT Pro needing to set permission on several different Microsoft 365 services, including Teams, a SharePoint Online site, a Planner Plan, a Power BI workspace and a shared mailbox. This group type also supports dynamic membership, created via the Azure Portal the same as you would an Azure AD security group.
By using this group type and dynamic membership, you can add and remove members to a Microsoft Team automatically, without the team owner needing to do any administration tasks.
To achieve this, you can either:
Create your Microsoft 365 group in Azure Active Directory, adding your dynamic membership rule.
Then either create a new team from this group (after giving Azure AD time to update).
Or apply dynamic membership to an existing team by changing its group membership from static to dynamic.
For more details, visit Overview of dynamic membership for Teams.
What about dynamic distribution groups?
Yes, Exchange Online supports dynamic membership for email distribution groups! Unlike security groups, the group membership is calculated each time a message is sent to the group. To set up and manage dynamic distribution groups, you need to use the Exchange Admin Center or Exchange Online PowerShell.
This example creates a dynamic group of Full Time Employees by querying a custom attribute:
New-DynamicDistributionGroup -Name "Full Time Employees" -RecipientFilter "(RecipientTypeDetails -eq 'UserMailbox') -and (CustomAttribute10 -eq 'FullTimeEmployee')"
For details, visit Manage dynamic distribution groups.
You also need to use Exchange Online PowerShell to query the list of group members at this point in time, as they can’t be viewed in the Exchange Admin Center or the Azure Portal:
$FTE = Get-DynamicDistributionGroup "Full Time Employees"
Get-Recipient -ResultSize Unlimited -RecipientPreviewFilter $FTE.RecipientFilter -OrganizationalUnit $FTE.RecipientContainer | Format-Table Name,Primary*
Check out View members of a dynamic distribution group for more details.
Conclusion
Dynamic group membership is a powerful feature, but like any technology capability it requires planning and alignment with your organization’s needs and its business processes. What scenarios do you have where dynamic groups would be useful? Need help writing more complex queries? Let us know in the comments!
by Contributed | Apr 11, 2021 | Technology
This article is contributed. See the original author and article here.
Suppose you are a community leader or an instructor who will run a hands-on lab session for Power Platform. You got content for it. Now it’s time for setting up the lab environment. There are roughly three approaches for the preparation.
- Ask the participants to bring their existing Power Platform environment,
- Ask the participants to set up their environment by themselves, or
- The session leader is preparing the environment for the participants to use.
Each effort has its pros and cons like:
- The first approach would be the easiest and the most convenient for the instructor because it’s based on the assumption that everyone is ready for the exercise. However, you never know if every participant has the same configurations as you expect. It really depends on their organisation’s policy. After all, you, as the session leader, will probably suffer from a lot of unexpected circumstances.
- The second one can be convenient for you as the session leader. It might be as tricky as the first approach. Delegating the environment set-up efforts to the participants may make you free, but at the same time, you should provide an instructional document very thoroughly and carefully. Even if you do so, it entirely depends on the participants’ capability. After all, you should start the lab session by confirming the environment set-up anyway.
- The last option goes to you as the session leader. You prepare everything for the participants. They just come, sit and practice. If you do this set-up by hand, it would be awful. You will not want to do that.
Therefore, as a hands-on lab session leader, I’m going to discuss how to automate all the provisioning process and minimise human intervention by running one PowerShell script.
The PowerShell script used in this post is downloadable from this GitHub repository.
One-Liner Script
Let’s say you use the following information for the admin account.
- Tenant Name:
powerplatformhandsonlab
- Tenant URL:
powerplatformhandsonlab.onmicrosoft.com
- Admin E-mail:
admin@powerplatformhandsonlab.onmicrosoft.com
- Admin Password:
Pa$$W0rd!@#$
With this information, how can you set up the lab environment in just one go? Here’s the entire script and you just run the command below.
./Set-Environment.ps1 `
-AdminUsername “admin” `
-AdminPassword “Pa`$`$W0rd!@#`$” `
-TenantName “powerplatformhandsonlab”
Wait, what? What’s going on? Here’s the magic. Let’s find them together.
Create Microsoft 365 Tenant
The first step to do as the session leader is to create a Microsoft 365 tenant. Microsoft 365 offers a free trial for 30 days. It includes 25 seats, including the admin account, which is suitable for the lab. Click this link, http://aka.ms/Office365E5Trial, and create the Microsoft 365 E5 plan’s trial tenant.
After filling out the form below, you get the trial tenant!
As you’ve got a new tenant, let’s configure the lab environment in PowerShell. Please note that you HAVE TO use the PowerShell console with the admin privilege.
Provisioning Order
There is no particular order for the environment provisioning. However, I would recommend following this order because there’s incompatibility found between PowerShell modules especially between Power Apps and AzureAD:
- Activate Microsoft Dataverse for Power Platform Default Environment
- Add User Accounts
- Assign Microsoft 365 Roles to Accounts
- Assign Microsoft 365 Licenses to Accounts
- Assign Azure Roles to Accounts
If you do the Microsoft Dataverse initialisation later than Azure AD, you will get an error. I’ll discuss it later how to avoid it.
NOTE: To use any of the PowerShell module mentioned in this post, you need PowerShell v5.1 running on Windows. PowerShell Core (v6 and later) doesn’t support this scenario. For more details about this, refer to this page, Connect to Microsoft 365 with PowerShell.
Install AzureAD Module
You can add a new user account to a Microsoft 365 tenant through the AzureAD module. As of this writing, the latest version of the module is 2.0.2.130. Use the Install-Module cmdlet to install the module. If you append these two parameters, -Force -AllowClobber (line #3), it always installs the newest version regardless it’s already installed or not.
Install-Module -Name AzureAD `
-Scope AllUsers -Repository PSGallery `
-Force -AllowClobber
Log-in to AzureAD as Admin
After installing the module, log into the Azure AD as the tenant admin. For automation, you should stay within the console. Therefore, the following command is more efficient for sign-in.
$tenantName = “powerplatformhandsonlab”
$adminUpn = “admin@$tenantName.onmicrosoft.com”
$adminPW = ConvertTo-SecureString “Pa`$`$W0rd!@#`$” -AsPlainText -Force
$adminCredential = New-Object `
-TypeName System.Management.Automation.PSCredential `
-ArgumentList ($adminUpn, $adminPW)
$connected = Connect-AzureAD -Credential $adminCredential
Add User Accounts
It’s time to add user accounts. As the trial tenant includes 25 licenses, you can add up to 24 accounts. For more details to add a new user account, refer to this document, Create Microsoft 365 User Accounts with PowerShell. But you just run the following commands. Here are some assumptions:
- Each user has the same password of
UserPa$$W0rd!@#$ for convenience, and it’s not allowed change (line #2-4).
- Each user has the same location where the tenant resides. For now, it’s
KR (line #6).
- You need to create up to 24 accounts, so
ForEach-Object is the go (line #9).
- All user accounts created are added to the
$users array object (line #18).
$userPWProfile = New-Object -TypeName Microsoft.Open.AzureAD.Model.PasswordProfile
$userPWProfile.Password = “UserPa`$`$W0rd!@#`$”
$userPWProfile.EnforceChangePasswordPolicy = $false
$userPWProfile.ForceChangePasswordNextLogin = $false
$usageLocation = “KR”
$users = @()
(1..24) | ForEach-Object {
$user = New-AzureADUser `
-DisplayName $(“PPUser” + $_.ToString(“00”)) -GivenName $(“User” + $_.ToString(“00”)) -SurName “PP” `
-UserPrincipalName $(“ppuser” + $_.ToString(“00”) + “@$tenantName.onmicrosoft.com”) `
-UsageLocation $usageLocation `
-MailNickName $(“ppuser” + $_.ToString(“00”)) `
-PasswordProfile $userPWProfile `
-AccountEnabled $true
$users += $user
}
Assign Microsoft 365 Roles to User Accounts
The user accounts need to have appropriate Microsoft 365 roles. As it’s the hands-on lab configuration, you can assign the Power Platform admin role to each user account. For more details of the Microsoft roles assignment, refer to this Assign Admin Roles to Microsoft 365 User Accounts with PowerShell page. Run the following command to activate the Power Platform admin role.
$roleName=”Power Platform Administrator”
$role = Get-AzureADDirectoryRole | Where-Object { $_.DisplayName -eq $roleName }
if ($role -eq $null) {
$roleTemplate = Get-AzureADDirectoryRoleTemplate | Where-Object { $_.DisplayName -eq $roleName }
$enabled = Enable-AzureADDirectoryRole -RoleTemplateId $roleTemplate.ObjectId
$role = Get-AzureADDirectoryRole | Where-Object { $_.DisplayName -eq $roleName }
}
The admin role has now been stored in the $role object. Now, iterate the $users array to assign the role.
$users | ForEach-Object {
$assigned = Add-AzureADDirectoryRoleMember `
-ObjectId $role.ObjectId `
-RefObjectId $_.ObjectId
}
Assign License to User Accounts
To use Power Platform within the tenant, each user MUST have a license for it. You can assign the license through the PowerShell command. For more details, visit this Assign Microsoft 365 licenses to user accounts with PowerShell page.
First of all, let’s find out the licenses. As soon as you create the trial tenant, there SHOULD be only one license, whose name is ENTERPRISEPREMIUM.
Get-AzureADSubscribedSku
Then, run the following command to assign the license to all users by iterating the $users array.
$sku = Get-AzureADSubscribedSku
$license = New-Object -TypeName Microsoft.Open.AzureAD.Model.AssignedLicense
$license.SkuId = $sku.SkuId
$licensesToAssign = New-Object -TypeName Microsoft.Open.AzureAD.Model.AssignedLicenses
$licensesToAssign.AddLicenses = $license
$users | ForEach-Object {
$assigned = Set-AzureADUserLicense -ObjectId $_.ObjectId -AssignedLicenses $licensesToAssign
}
So far, you’ve completed automating processes to create a trial tenant, create user accounts, and assign roles and licenses.
Activate Microsoft Dataverse for Power Platform Default Environment
Power Platform internally uses Microsoft Dataverse as its database. Microsoft Dataverse is fundamentally essential for other Microsoft 365 services to use. You can also initialise it through PowerShell commands. For more details, visit the Power Apps Cmdlets for Administrators page.
First, you need to install both PowerShell modules, Microsoft.PowerApps.Administration.PowerShell and Microsoft.PowerApps.PowerShell. Like the previous installation process, use the -Force -AllowClobber option to install the modules or reinstall both if they already exist (line #3, 7).
Install-Module -Name Microsoft.PowerApps.Administration.PowerShell `
-Scope AllUsers -Repository PSGallery `
-Force -AllowClobber
Install-Module -Name Microsoft.PowerApps.PowerShell `
-Scope AllUsers -Repository PSGallery `
-Force -AllowClobber
Log into the Power Apps admin environment, using $adminUpn and $adminPW values.
$connected = Add-PowerAppsAccount -Username $adminUpn -Password $adminPW
NOTE: You might not be able to log into the Power Apps admin environment with the following error.
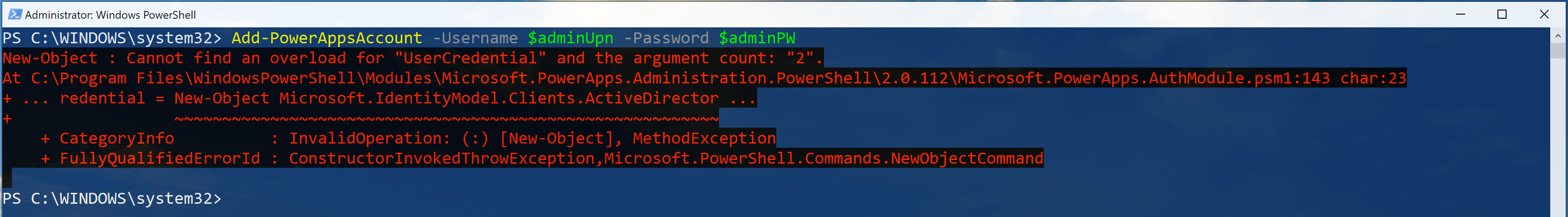
It’s because the internal log-in process for both Microsoft 365 tenant and Power Apps environment are different from each other. If it happens to you, don’t panic. Just open a new PowerShell console with an admin privilege and attempt to log in.
Here are some assumptions for the Microsoft Dataverse initialisation:
- Initialise Microsoft Dataverse on the default environment (line #1),
- Follow the currency settings of the default environment (line #5), and
- Follow the language settings of the default environment (line #10).
$paenv = Get-AdminPowerAppEnvironment -Default
if ($paenv.CommonDataServiceDatabaseProvisioningState -ne “Succeeded”) {
$currency = Get-AdminPowerAppCdsDatabaseCurrencies `
-LocationName $paenv.Location | Where-Object {
$_.IsTenantDefaultCurrency -eq $true
}
$language = Get-AdminPowerAppCdsDatabaseLanguages `
-LocationName $paenv.Location | Where-Object {
$_.IsTenantDefaultLanguage -eq $true
}
$activated = New-AdminPowerAppCdsDatabase `
-EnvironmentName $paenv.EnvironmentName `
-CurrencyName $currency.CurrencyName `
-LanguageName $language.LanguageName
}
Assign Azure Subscription
Building custom connectors is inevitable while using Power Platform. In this case, you might need to handle resources on Azure, which requires an Azure subscription. If you create the trial tenant for Microsoft 365, you can also activate the trial Azure subscription. As it requires credit card verification, it MUST be done within Azure Portal. If you log into Azure Portal with your admin account, you can see the following screen.
Click the Start button to sign-up for the trial subscription.
Once completing the trial subscription, log in to Azure using the PowerShell command below. The $adminCredential object is the same one used for Azure AD log-in.
$connected = Connect-AzAccount -Credential $adminCredential
NOTE: You SHOULD install the Az module beforehand.
Install-Module -Name Az -Scope AllUsers -Repository PSGallery -Force -AllowClobber
Only a limited number of resources are available in the trial subscription. For custom connectors, mainly Azure Logic Apps, Asture Storage Account, Azure Virtual Network, Azure API Management and Azure Cosmos DB are supposed to use. Therefore, to use those resources, run the following command to register those resource providers.
$namespaces = @(
“Microsoft.Logic”,
“Microsoft.Storage”,
“Microsoft.Network”,
“Microsoft.ApiManagement”,
“Microsoft.DocumentDB”
)
$namespaces | ForEach-Object {
$provider = Get-AzResourceProvider `
-ProviderNamespace $_ | Where-Object { $_.RegistrationState -eq “Registered” }
if (($provider -eq $null) -or ($provider.Count -eq 0)) {
$registered = Register-AzResourceProvider -ProviderNamespace $_
}
}
Then, assign the subscription to each user account. For Azure Roles, visit this Assign Azure Roles Using Azure PowerShell page for more details.
NOTE: Instead of scoping the entire subscription to each user account, it’s better to create a resource group for each user, scope to the resource group and assign it to each account. For the resource group, you need a location. In this example, koreacentral is used.
$role = Get-AzRoleDefinition | Where-Object { $_.Name -eq “Contributor” }
$location = “koreacentral”
$users | ForEach-Object {
$rg = Get-AzResourceGroup | Where-Object {
$_.ResourceGroupName -eq $(“rg-” + $_.MailNickName)
}
if ($rg -eq $null) {
$rg = New-AzResourceGroup `
-Name $(“rg-” + $_.MailNickName) `
-Location $location
}
$assigned = New-AzRoleAssignment `
-ObjectId $_.ObjectId `
-RoleDefinitionId $role.Id `
-Scope $rg.ResourceId
}
All users are now able to access to Azure resources for the exercise.
So far, we’ve walked through how to automatically provision a Power Platform environment for hands-on labs, using PowerShell. Now, if you are going to run a hands-on lab session and need a new environment, simply run the code above. Then, it’s all good to go!
This article was originally published on Dev Kimchi.

 Of Microsoft Dynamics 365 Remote Assist report Be sure to also check out the following customer evidence stories to discover how your organization can similarly leverage Dynamics 365 Remote Assist for accelerated deployment, thorough inspections, and efficient break/fix resolution. Ecolab Watch the video with Ecolab’s David Goforth, Vice President Sales North America, and Rick Stokes, Area Technical Support Manager, as they speak with Rodney Clark, Vice President IoT and Mixed Reality Sales at Microsoft, about how Ecolab Food and Beverage is transforming business processes to better serve customers and employees in the face of emerging challenges. Musashi Musashi Seimitsu Industry is an automotive parts manufacturer with production and sales facilities in 14 countries and 35 hubs worldwide. The global brand slogan, Power to Value, has represented its innovative manufacturing style since 1938. This can-do spirit has protected corporate infrastructure amidst COVID-19. By merging the real and digital worlds with Dynamics 365 Remote Assist on HoloLens 2, the company launched a new production line in Mexico without a single engineer leaving Japan. Musashi Seimitsu is embracing the post COVID-19 new normal with its swift digital transformation. Saint-Gobain Saint-Gobain is a global leader in the manufacture of sustainable, high-performance building materials. The craftsmanship and innovation underlying the company’s technologically advanced products, particularly its specialized glass offerings, hinge on stellar production machine maintenance and in-depth training. Since the Saint-Gobain process experts who provide that deep expertise can’t be everywhere at once, the company turned to Dynamics 365 Remote Assist to deliver remote expert assistance in real-time. Now, maintenance and training are faster, more impactful, and with dramatically less travel required, helping Saint-Gobain be aligned with their sustainability goals. Dynamics 365 Remote Assist resources Learn more about Dynamics 365 Remote Assist. Register to attend upcoming Dynamics 365 Remote Assist Microsoft Reactor sessions. Complete the Dynamics 365 Remote Assist Learning Path. Read Dynamics 365 Remote Assist customer stories. See how mixed reality solutions on HoloLens 2 can help your business be more productive. Find information on Microsoft Dynamics 365 partners for manufacturing. Listen to the Dynamics 365 Connected and Ready podcast episode on mixed reality, “Ford goes from vehicles to ventilators, with Dr. Graham Hoare OBE.” Sources: The Total Economic Impact
Of Microsoft Dynamics 365 Remote Assist report Be sure to also check out the following customer evidence stories to discover how your organization can similarly leverage Dynamics 365 Remote Assist for accelerated deployment, thorough inspections, and efficient break/fix resolution. Ecolab Watch the video with Ecolab’s David Goforth, Vice President Sales North America, and Rick Stokes, Area Technical Support Manager, as they speak with Rodney Clark, Vice President IoT and Mixed Reality Sales at Microsoft, about how Ecolab Food and Beverage is transforming business processes to better serve customers and employees in the face of emerging challenges. Musashi Musashi Seimitsu Industry is an automotive parts manufacturer with production and sales facilities in 14 countries and 35 hubs worldwide. The global brand slogan, Power to Value, has represented its innovative manufacturing style since 1938. This can-do spirit has protected corporate infrastructure amidst COVID-19. By merging the real and digital worlds with Dynamics 365 Remote Assist on HoloLens 2, the company launched a new production line in Mexico without a single engineer leaving Japan. Musashi Seimitsu is embracing the post COVID-19 new normal with its swift digital transformation. Saint-Gobain Saint-Gobain is a global leader in the manufacture of sustainable, high-performance building materials. The craftsmanship and innovation underlying the company’s technologically advanced products, particularly its specialized glass offerings, hinge on stellar production machine maintenance and in-depth training. Since the Saint-Gobain process experts who provide that deep expertise can’t be everywhere at once, the company turned to Dynamics 365 Remote Assist to deliver remote expert assistance in real-time. Now, maintenance and training are faster, more impactful, and with dramatically less travel required, helping Saint-Gobain be aligned with their sustainability goals. Dynamics 365 Remote Assist resources Learn more about Dynamics 365 Remote Assist. Register to attend upcoming Dynamics 365 Remote Assist Microsoft Reactor sessions. Complete the Dynamics 365 Remote Assist Learning Path. Read Dynamics 365 Remote Assist customer stories. See how mixed reality solutions on HoloLens 2 can help your business be more productive. Find information on Microsoft Dynamics 365 partners for manufacturing. Listen to the Dynamics 365 Connected and Ready podcast episode on mixed reality, “Ford goes from vehicles to ventilators, with Dr. Graham Hoare OBE.” Sources: The Total Economic Impact Of Microsoft Dynamics 365 Remote Assist, a commissioned study conducted by Forrester Consulting on behalf of Microsoft, June 2020
Of Microsoft Dynamics 365 Remote Assist, a commissioned study conducted by Forrester Consulting on behalf of Microsoft, June 2020

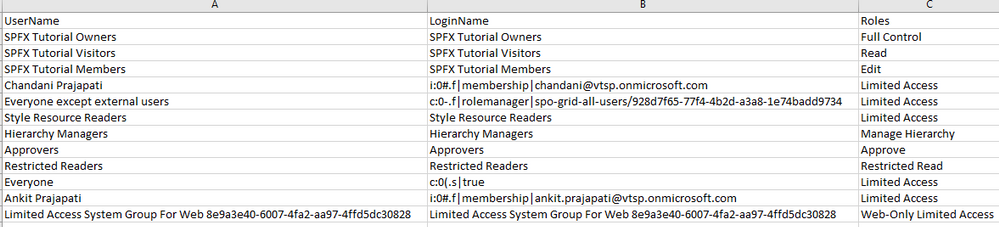







Recent Comments