by Scott Muniz | Nov 22, 2021 | Security, Technology
This article is contributed. See the original author and article here.
| adobe — after_effects |
Adobe After Effects version 18.4.1 (and earlier) is affected by a Null pointer dereference vulnerability when parsing a specially crafted file. An unauthenticated attacker could leverage this vulnerability to achieve an application denial-of-service in the context of the current user. Exploitation of this issue requires user interaction in that a victim must open a malicious file. |
2021-11-18 |
4.3 |
CVE-2021-40761
MISC |
| adobe — after_effects |
Adobe After Effects version 18.4.1 (and earlier) is affected by a Null pointer dereference vulnerability when parsing a specially crafted file. An unauthenticated attacker could leverage this vulnerability to achieve an application denial-of-service in the context of the current user. Exploitation of this issue requires user interaction in that a victim must open a malicious file. |
2021-11-18 |
4.3 |
CVE-2021-40756
MISC |
| adobe — animate |
Acrobat Animate versions 21.0.9 (and earlier)is affected by an out-of-bounds read vulnerability that could lead to disclosure of sensitive memory. An attacker could leverage this vulnerability to bypass mitigations such as ASLR. Exploitation of this issue requires user interaction in that a victim must open a malicious file. |
2021-11-18 |
4.3 |
CVE-2021-42525
MISC |
| adobe — animate |
Adobe Animate version 21.0.9 (and earlier) is affected by a Null pointer dereference vulnerability when parsing a specially crafted FLA file. An unauthenticated attacker could leverage this vulnerability to achieve an application denial-of-service in the context of the current user. Exploitation of this issue requires user interaction in that a victim must open a malicious file. |
2021-11-18 |
4.3 |
CVE-2021-42268
MISC |
| adobe — campaign |
Adobe Campaign version 21.2.1 (and earlier) is affected by a Path Traversal vulnerability that could lead to reading arbitrary server files. By leveraging an exposed XML file, an unauthenticated attacker can enumerate other files on the server. |
2021-11-17 |
5 |
CVE-2021-40745
MISC |
| adobe — experience_manager |
Adobe Experience Manager version 6.5.9.0 (and earlier) are affected by an improper access control vulnerability that leads to a security feature bypass. By manipulating referer headers, an unauthenticated attacker could gain access to arbitrary pages that they are not authorized to access. |
2021-11-16 |
5 |
CVE-2021-42725
MISC |
| advantech — webaccess_hmi_designer |
This vulnerability could allow an attacker to disclose information and execute arbitrary code on affected installations of WebAccess/MHI Designer |
2021-11-15 |
4.6 |
CVE-2021-42706
MISC |
| advantech — webaccess_hmi_designer |
This vulnerability could allow an attacker to send malicious Javascript code resulting in hijacking of the user’s cookie/session tokens, redirecting the user to a malicious webpage, and performing unintended browser action. |
2021-11-15 |
4.3 |
CVE-2021-42703
MISC |
| aifu — cashier_accounting_management_system |
The permission control of AIFU cashier management salary query function can be bypassed, thus after obtaining general user’s permission, the remote attacker can access account information except passwords by crafting URL parameters. |
2021-11-16 |
4 |
CVE-2021-42337
MISC |
| alquistai — alquist |
AlquistManager branch as of commit 280d99f43b11378212652e75f6f3159cde9c1d36 is affected by a directory traversal vulnerability in alquist/IO/input.py. This attack can cause the disclosure of critical secrets stored anywhere on the system and can significantly aid in getting remote code access. |
2021-11-15 |
5 |
CVE-2021-43495
MISC |
| alquistai — alquist |
AlquistManager branch as of commit 280d99f43b11378212652e75f6f3159cde9c1d36 is affected by a directory traversal vulnerability. This attack can cause the disclosure of critical secrets stored anywhere on the system andcan significantly aid in getting remote code access. |
2021-11-12 |
5 |
CVE-2021-43492
MISC |
| amd — epyc_7003_firmware |
When the AMD Platform Security Processor (PSP) boot rom loads, authenticates, and subsequently decrypts an encrypted FW, due to insufficient verification of the integrity of decrypted image, arbitrary code may be executed in the PSP when encrypted firmware images are used. |
2021-11-16 |
4.6 |
CVE-2021-26315
MISC |
| amd — epyc_7003_firmware |
Race condition in PSP FW could allow less privileged x86 code to perform PSP SMM operations. |
2021-11-16 |
4.4 |
CVE-2020-12951
MISC |
| amd — epyc_7003_firmware |
Insufficient bounds checking in System Management Unit (SMU) may cause invalid memory accesses/updates that could result in SMU hang and subsequent failure to service any further requests from other components. |
2021-11-16 |
4.9 |
CVE-2021-26336
MISC |
| amd — epyc_7003_firmware |
A potential vulnerability exists in AMD Platform Security Processor (PSP) that may allow an attacker to zero any privileged register on the System Management Network which may lead to bypassing SPI ROM protections. |
2021-11-16 |
4.6 |
CVE-2020-12961
MISC |
| amd — epyc_7232p_firmware |
Failure to validate SEV Commands while SNP is active may result in a potential impact to memory integrity. |
2021-11-16 |
4.6 |
CVE-2021-26323
MISC |
| amd — epyc_7601_firmware |
Insufficient validation of BIOS image length by PSP Firmware could lead to arbitrary code execution. |
2021-11-16 |
4.6 |
CVE-2020-12944
MISC |
| amd — epyc_7601_firmware |
Insufficient ID command validation in the SEV Firmware may allow a local authenticated attacker to perform a denial of service of the PSP. |
2021-11-16 |
4.9 |
CVE-2021-26321
MISC |
| amd — epyc_7601_firmware |
Persistent platform private key may not be protected with a random IV leading to a potential “two time pad attack”. |
2021-11-16 |
5 |
CVE-2021-26322
MISC |
| amd — epyc_7f72_firmware |
Insufficient input validation in PSP firmware for discrete TPM commands could allow a potential loss of integrity and denial of service. |
2021-11-16 |
6.6 |
CVE-2020-12946
MISC |
| amd — radeon_software |
Improper parameters validation in some trusted applications of the PSP contained in the AMD Graphics Driver may allow a local attacker to bypass security restrictions and achieve arbitrary code execution . |
2021-11-15 |
4.6 |
CVE-2020-12929
MISC |
| amd — radeon_software |
Out of Bounds Write and Read in AMD Graphics Driver for Windows 10 in Escape 0x6002d03 may lead to escalation of privilege or denial of service. |
2021-11-15 |
4.6 |
CVE-2020-12903
MISC |
| amd — radeon_software |
A potential privilege escalation/denial of service issue exists in the AMD Radeon Kernel Mode driver Escape 0x2000c00 Call handler. An attacker with low privilege could potentially induce a Windows BugCheck or write to leak information. |
2021-11-15 |
4.6 |
CVE-2020-12964
MISC |
| amd — radeon_software |
Escape call interface in the AMD Graphics Driver for Windows may cause privilege escalation. |
2021-11-15 |
4.6 |
CVE-2020-12962
MISC |
| amd — radeon_software |
An arbitrary write vulnerability in the AMD Radeon Graphics Driver for Windows 10 potentially allows unprivileged users to gain Escalation of Privileges and cause Denial of Service. |
2021-11-15 |
4.6 |
CVE-2020-12900
MISC |
| amd — radeon_software |
Stack Buffer Overflow in AMD Graphics Driver for Windows 10 may lead to escalation of privilege or denial of service. |
2021-11-15 |
4.6 |
CVE-2020-12898
MISC |
| amd — radeon_software |
Arbitrary Decrement Privilege Escalation in AMD Graphics Driver for Windows 10 may lead to escalation of privilege or denial of service. |
2021-11-15 |
4.6 |
CVE-2020-12902
MISC |
| amd — radeon_software |
Pool/Heap Overflow in AMD Graphics Driver for Windows 10 in Escape 0x110037 may lead to escalation of privilege, information disclosure or denial of service. |
2021-11-15 |
4.6 |
CVE-2020-12895
MISC |
| amd — radeon_software |
An untrusted search path in AMD Radeon settings Installer may lead to a privilege escalation or unauthorized code execution. |
2021-11-15 |
4.4 |
CVE-2020-12892
MISC |
| amd — radeon_software |
Stack Buffer Overflow in AMD Graphics Driver for Windows 10 in Escape 0x15002a may lead to escalation of privilege or denial of service. |
2021-11-15 |
4.6 |
CVE-2020-12893
MISC |
| apache — ozone |
In Apache Ozone before 1.2.0, Authenticated users with valid Ozone S3 credentials can create specific OM requests, impersonating any other user. |
2021-11-19 |
6.5 |
CVE-2021-39236
MISC
MLIST |
| apache — ozone |
In Apache Ozone before 1.2.0, Ozone Datanode doesn’t check the access mode parameter of the block token. Authenticated users with valid READ block token can do any write operation on the same block. |
2021-11-19 |
4 |
CVE-2021-39235
MISC
MLIST |
| apache — ozone |
In Apache Ozone versions prior to 1.2.0, Authenticated users knowing the ID of an existing block can craft specific request allowing access those blocks, bypassing other security checks like ACL. |
2021-11-19 |
4.9 |
CVE-2021-39234
MISC
MLIST |
| apache — ozone |
In Apache Ozone versions prior to 1.2.0, Container related Datanode requests of Ozone Datanode were not properly authorized and can be called by any client. |
2021-11-19 |
6.4 |
CVE-2021-39233
MISC
MLIST |
| apache — ozone |
In Apache Ozone versions prior to 1.2.0, certain admin related SCM commands can be executed by any authenticated users, not just by admins. |
2021-11-19 |
6.5 |
CVE-2021-39232
MISC
MLIST |
| apache — ozone |
In Apache Ozone before 1.2.0, Recon HTTP endpoints provide access to OM, SCM and Datanode metadata. Due to a bug, any unauthenticated user can access the data from these endpoints. |
2021-11-19 |
5 |
CVE-2021-41532
MISC
MLIST |
| apache — ozone |
In Apache Ozone versions prior to 1.2.0, Various internal server-to-server RPC endpoints are available for connections, making it possible for an attacker to download raw data from Datanode and Ozone manager and modify Ratis replication configuration. |
2021-11-19 |
6.4 |
CVE-2021-39231
MISC
MLIST |
| apache — superset |
Apache Superset up to and including 1.3.1 allowed for database connections password leak for authenticated users. This information could be accessed in a non-trivial way. |
2021-11-12 |
4 |
CVE-2021-41972
CONFIRM
CONFIRM |
| apache — superset |
Improper output neutralization for Logs. A specific Apache Superset HTTP endpoint allowed for an authenticated user to forge log entries or inject malicious content into logs. |
2021-11-17 |
4 |
CVE-2021-42250
CONFIRM
MLIST |
| arangodb — arangodb |
In ArangoDB, versions v3.7.6 through v3.8.3 are vulnerable to Insufficient Session Expiration. When a user’s password is changed by the administrator, the session isn’t invalidated, allowing a malicious user to still be logged in and perform arbitrary actions within the system. |
2021-11-16 |
6 |
CVE-2021-25940
MISC
MISC |
| area17 — twill |
twill is vulnerable to Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF) |
2021-11-13 |
4.3 |
CVE-2021-3932
CONFIRM
MISC |
| asus — gt-axe11000_firmware |
ASUS routers Wi-Fi protected access protocol (WPA2 and WPA3-SAE) has improper control of Interaction frequency vulnerability, an unauthenticated attacker can remotely disconnect other users’ connections by sending specially crafted SAE authentication frames. |
2021-11-12 |
5 |
CVE-2021-37910
MISC |
| atmail — atmail |
** UNSUPPORTED WHEN ASSIGNED ** WebAdmin Control Panel in Atmail 6.5.0 (a version released in 2012) allows XSS via the format parameter to the default URI. NOTE: This vulnerability only affects products that are no longer supported by the maintainer. |
2021-11-15 |
4.3 |
CVE-2021-43574
MISC
MISC |
| binatoneglobal — halo+_camera_firmware |
Some device communications in some Motorola-branded Binatone Hubble Cameras with backend Hubble services are not encrypted which could lead to the communication channel being accessible by an attacker. |
2021-11-12 |
5 |
CVE-2021-3792
CONFIRM |
| binatoneglobal — halo+_camera_firmware |
An unauthenticated remote code execution vulnerability was reported in some Motorola-branded Binatone Hubble Cameras that could allow an attacker on the same network unauthorized access to the device. |
2021-11-12 |
5.8 |
CVE-2021-3577
CONFIRM |
| binatoneglobal — halo+_camera_firmware |
An improper access control vulnerability was reported in some Motorola-branded Binatone Hubble Cameras which could allow an unauthenticated attacker on the same network as the device to access administrative pages that could result in information disclosure or device firmware update with verified firmware. |
2021-11-12 |
5 |
CVE-2021-3793
CONFIRM |
| binatoneglobal — halo+_camera_firmware |
A vulnerability was reported in some Motorola-branded Binatone Hubble Cameras that could allow an attacker with local access to obtain the MQTT credentials that could result in unauthorized access to backend Hubble services. |
2021-11-12 |
4.6 |
CVE-2021-3787
CONFIRM |
| binatoneglobal — halo+_camera_firmware |
An exposed debug interface was reported in some Motorola-branded Binatone Hubble Cameras that could allow an attacker with physical access unauthorized access to the device. |
2021-11-12 |
4.6 |
CVE-2021-3788
CONFIRM |
| broadcom — emulex_hba_manager |
Broadcom Emulex HBA Manager/One Command Manager versions before 11.4.425.0 and 12.8.542.31, if not installed in Strictly Local Management mode, have a vulnerability in the remote firmware download feature that could allow a user to place or replace an arbitrary file on the remote host. In non-secure mode, the user is unauthenticated. |
2021-11-12 |
6.4 |
CVE-2021-42775
MISC
CONFIRM |
| broadcom — emulex_hba_manager |
Broadcom Emulex HBA Manager/One Command Manager versions before 11.4.425.0 and 12.8.542.31, if not installed in Strictly Local Management mode, could allow a user to retrieve an arbitrary file from a remote host with the GetDumpFile command. In non-secure mode, the user is unauthenticated. |
2021-11-12 |
5 |
CVE-2021-42773
MISC
CONFIRM |
| busybox — busybox |
An attacker-controlled pointer free in Busybox’s hush applet leads to denial of service and possible code execution when processing a crafted shell command, due to the shell mishandling the &&& string. This may be used for remote code execution under rare conditions of filtered command input. |
2021-11-15 |
6.8 |
CVE-2021-42377
N/A |
| busybox — busybox |
A use-after-free in Busybox’s awk applet leads to denial of service and possibly code execution when processing a crafted awk pattern in the getvar_i function |
2021-11-15 |
6.5 |
CVE-2021-42378
N/A |
| busybox — busybox |
A use-after-free in Busybox’s awk applet leads to denial of service and possibly code execution when processing a crafted awk pattern in the next_input_file function |
2021-11-15 |
6.5 |
CVE-2021-42379
N/A |
| busybox — busybox |
A use-after-free in Busybox’s awk applet leads to denial of service and possibly code execution when processing a crafted awk pattern in the clrvar function |
2021-11-15 |
6.5 |
CVE-2021-42380
N/A |
| busybox — busybox |
A use-after-free in Busybox’s awk applet leads to denial of service and possibly code execution when processing a crafted awk pattern in the hash_init function |
2021-11-15 |
6.5 |
CVE-2021-42381
N/A |
| busybox — busybox |
A use-after-free in Busybox’s awk applet leads to denial of service and possibly code execution when processing a crafted awk pattern in the getvar_s function |
2021-11-15 |
6.5 |
CVE-2021-42382
N/A |
| busybox — busybox |
A use-after-free in Busybox’s awk applet leads to denial of service and possibly code execution when processing a crafted awk pattern in the handle_special function |
2021-11-15 |
6.5 |
CVE-2021-42384
N/A |
| busybox — busybox |
A use-after-free in Busybox’s awk applet leads to denial of service and possibly code execution when processing a crafted awk pattern in the evaluate function |
2021-11-15 |
6.5 |
CVE-2021-42383
N/A |
| busybox — busybox |
A use-after-free in Busybox’s awk applet leads to denial of service and possibly code execution when processing a crafted awk pattern in the evaluate function |
2021-11-15 |
6.5 |
CVE-2021-42385
N/A |
| busybox — busybox |
A use-after-free in Busybox’s awk applet leads to denial of service and possibly code execution when processing a crafted awk pattern in the nvalloc function |
2021-11-15 |
6.5 |
CVE-2021-42386
N/A |
| cacti — cacti |
Cacti before 1.2.18 allows remote attackers to trigger XSS via template import for the midwinter theme. |
2021-11-14 |
4.3 |
CVE-2020-14424
CONFIRM
CONFIRM |
| calibre-web_project — calibre-web |
In Calibre-web, versions 0.6.0 to 0.6.13 are vulnerable to Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF). By luring an authenticated user to click on a link, an attacker can create a new user role with admin privileges and attacker-controlled credentials, allowing them to take over the application. |
2021-11-16 |
6.8 |
CVE-2021-25965
MISC
MISC |
| clustering_project — clustering |
Clustering master branch as of commit 53e663e259bcfc8cdecb56c0bb255bd70bfcaa70 is affected by a directory traversal vulnerability. This attack can cause the disclosure of critical secrets stored anywhere on the system and can significantly aid in getting remote code access. |
2021-11-12 |
5 |
CVE-2021-43496
MISC |
| codingforentrepreneurs — opencv_rest_api |
OpenCV-REST-API master branch as of commit 69be158c05d4dd5a4aff38fdc680a162dd6b9e49 is affected by a directory traversal vulnerability. This attack can cause the disclosure of critical secrets stored anywhere on the system and can significantly aid in getting remote code access. |
2021-11-12 |
5 |
CVE-2021-43494
MISC |
| cron-utils_project — cron-utils |
cron-utils is a Java library to define, parse, validate, migrate crons as well as get human readable descriptions for them. In affected versions A template Injection was identified in cron-utils enabling attackers to inject arbitrary Java EL expressions, leading to unauthenticated Remote Code Execution (RCE) vulnerability. Versions up to 9.1.2 are susceptible to this vulnerability. Please note, that only projects using the @Cron annotation to validate untrusted Cron expressions are affected. The issue was patched and a new version was released. Please upgrade to version 9.1.6. There are no known workarounds known. |
2021-11-15 |
6.8 |
CVE-2021-41269
MISC
MISC
CONFIRM
MISC |
| darwin — factor |
In Factor (App Framework & Headless CMS) forum plugin, versions 1.3.5 to 1.8.30, are vulnerable to reflected Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) at the “search” parameter in the URL. An unauthenticated attacker can execute malicious JavaScript code and steal the session cookies. |
2021-11-16 |
4.3 |
CVE-2021-25982
MISC
MISC |
| darwin — factor |
In Factor (App Framework & Headless CMS) forum plugin, versions v1.3.8 to v1.8.30, are vulnerable to reflected Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) at the “tags” and “category” parameters in the URL. An unauthenticated attacker can execute malicious JavaScript code and steal the session cookies. |
2021-11-16 |
4.3 |
CVE-2021-25983
MISC
MISC |
| darwin — factor |
In Factor (App Framework & Headless CMS) forum plugin, versions v1.3.3 to v1.8.30, are vulnerable to stored Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) at the “post reply” section. An unauthenticated attacker can execute malicious JavaScript code and steal the session cookies. |
2021-11-16 |
4.3 |
CVE-2021-25984
MISC
MISC |
| dell — emc_powerscale_onefs |
Dell EMC PowerScale OneFS versions 9.1.0, 9.2.0.x, 9.2.1.x contain an Exposure of Information through Directory Listing vulnerability. This vulnerability is triggered when upgrading from a previous versions. |
2021-11-12 |
5 |
CVE-2021-21528
MISC |
| dell — emc_powerscale_onefs |
Dell PowerScale OneFS contains an Unsynchronized Access to Shared Data in a Multithreaded Context in SMB CA handling. An authenticated user of SMB on a cluster with CA could potentially exploit this vulnerability, leading to a denial of service over SMB. |
2021-11-12 |
4 |
CVE-2021-36305
MISC |
| discourse — discourse |
Discourse is a platform for community discussion. In affected versions a maliciously crafted request could cause an error response to be cached by intermediate proxies. This could cause a loss of confidentiality for some content. This issue is patched in the latest stable, beta and tests-passed versions of Discourse. |
2021-11-15 |
5 |
CVE-2021-41271
CONFIRM
MISC |
| discourse — rails_multisite |
rails_multisite provides multi-db support for Rails applications. In affected versions this vulnerability impacts any Rails applications using `rails_multisite` alongside Rails’ signed/encrypted cookies. Depending on how the application makes use of these cookies, it may be possible for an attacker to re-use cookies on different ‘sites’ within a multi-site Rails application. The issue has been patched in v4 of the `rails_multisite` gem. Note that this upgrade will invalidate all previous signed/encrypted cookies. The impact of this invalidation will vary based on the application architecture. |
2021-11-15 |
6 |
CVE-2021-41263
MISC
CONFIRM |
| django-helpdesk_project — django-helpdesk |
django-helpdesk is vulnerable to Improper Neutralization of Input During Web Page Generation (‘Cross-site Scripting’) |
2021-11-13 |
4.3 |
CVE-2021-3945
MISC
CONFIRM |
| dotnetfoundation — piranha_cms |
In PiranhaCMS, versions 4.0.0-alpha1 to 9.2.0 are vulnerable to cross-site request forgery (CSRF) when performing various actions supported by the management system, such as deleting a user, deleting a role, editing a post, deleting a media folder etc., when an ID is known. |
2021-11-16 |
4 |
CVE-2021-25976
CONFIRM
MISC |
| email_log_project — email_log |
The Email Log WordPress plugin before 2.4.7 does not properly validate, sanitise and escape the “orderby” and “order” GET parameters before using them in SQL statement in the admin dashboard, leading to SQL injections |
2021-11-17 |
6.5 |
CVE-2021-24758
MISC |
| firefly-iii — firefly_iii |
firefly-iii is vulnerable to Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF) |
2021-11-13 |
4.3 |
CVE-2021-3921
CONFIRM
MISC |
| fruity_project — fruity |
An issue was discovered in the fruity crate through 0.2.0 for Rust. Security-relevant validation of filename extensions is plausibly affected. Methods of NSString for conversion to a string may return a partial result. Because they call CStr::from_ptr on a pointer to the string buffer, the string is terminated at the first ” byte, which might not be the end of the string. |
2021-11-15 |
5 |
CVE-2021-43620
MISC
MISC
MISC |
| gesundheit-bewegt — colorful_categories |
The Colorful Categories WordPress plugin before 2.0.15 does not enforce nonce checks which could allow attackers to make a logged in admin or editor change taxonomy colors via a CSRF attack |
2021-11-17 |
4.3 |
CVE-2021-24802
MISC |
| gmplib — gmp |
GNU Multiple Precision Arithmetic Library (GMP) through 6.2.1 has an mpz/inp_raw.c integer overflow and resultant buffer overflow via crafted input, leading to a segmentation fault on 32-bit platforms. |
2021-11-15 |
5 |
CVE-2021-43618
MISC
MISC
MISC |
| gnu — mailman |
In GNU Mailman before 2.1.36, a crafted URL to the Cgi/options.py user options page can execute arbitrary JavaScript for XSS. |
2021-11-12 |
4.3 |
CVE-2021-43331
MISC
CONFIRM |
| gnu — mailman |
In GNU Mailman before 2.1.36, the CSRF token for the Cgi/admindb.py admindb page contains an encrypted version of the list admin password. This could potentially be cracked by a moderator via an offline brute-force attack. |
2021-11-12 |
4 |
CVE-2021-43332
MISC
CONFIRM |
| google — android |
In mdlactl driver, there is a possible memory corruption due to an incorrect bounds check. This could lead to local escalation of privilege with System execution privileges needed. User interaction is not needed for exploitation. Patch ID: ALPS05673424; Issue ID: ALPS05673424. |
2021-11-18 |
4.6 |
CVE-2021-0655
MISC |
| google — android |
In edma driver, there is a possible memory corruption due to a use after free. This could lead to local escalation of privilege with System execution privileges needed. User interaction is not needed for exploitation. Patch ID: ALPS05709376; Issue ID: ALPS05709376. |
2021-11-18 |
4.6 |
CVE-2021-0656
MISC |
| google — android |
In apusys, there is a possible out of bounds write due to a stack-based buffer overflow. This could lead to local escalation of privilege with System execution privileges needed. User interaction is not needed for exploitation. Patch ID: ALPS05672103; Issue ID: ALPS05672103. |
2021-11-18 |
4.6 |
CVE-2021-0657
MISC |
| google — android |
In apusys, there is a possible out of bounds write due to a missing bounds check. This could lead to local escalation of privilege with System execution privileges needed. User interaction is not needed for exploitation. Patch ID: ALPS05672107; Issue ID: ALPS05672107. |
2021-11-18 |
4.6 |
CVE-2021-0658
MISC |
| google — android |
In ccu, there is a possible memory corruption due to a use after free. This could lead to local escalation of privilege with System execution privileges needed. User interaction is not needed for exploitation. Patch ID: ALPS05827158; Issue ID: ALPS05827158. |
2021-11-18 |
4.6 |
CVE-2021-0664
MISC |
| google — android |
In apusys, there is a possible memory corruption due to a use after free. This could lead to local escalation of privilege with System execution privileges needed. User interaction is not needed for exploitation. Patch ID: ALPS05670581; Issue ID: ALPS05670581. |
2021-11-18 |
4.6 |
CVE-2021-0667
MISC |
| grafana — grafana |
Grafana is an open-source platform for monitoring and observability. In affected versions when the fine-grained access control beta feature is enabled and there is more than one organization in the Grafana instance admins are able to access users from other organizations. Grafana 8.0 introduced a mechanism which allowed users with the Organization Admin role to list, add, remove, and update users’ roles in other organizations in which they are not an admin. With fine-grained access control enabled, organization admins can list, add, remove and update users’ roles in another organization, where they do not have organization admin role. All installations between v8.0 and v8.2.3 that have fine-grained access control beta enabled and more than one organization should be upgraded as soon as possible. If you cannot upgrade, you should turn off the fine-grained access control using a feature flag. |
2021-11-15 |
6.5 |
CVE-2021-41244
MISC
CONFIRM
MLIST |
| ibm — iris_xe_max_dedicated_graphics |
Improper access control in the installer for some Intel(R) Iris(R) Xe MAX Dedicated Graphics Drivers for Windows 10 before version 27.20.100.9466 may allow authenticated user to potentially enable escalation of privilege via local access. |
2021-11-17 |
4.6 |
CVE-2021-0121
MISC |
| ibm — security_guardium_key_lifecycle_manager |
IBM Tivoli Key Lifecycle Manager 3.0, 3.0.1, 4.0, and 4.1 does not set the secure attribute on authorization tokens or session cookies. Attackers may be able to get the cookie values by sending a http:// link to a user or by planting this link in a site the user goes to. The cookie will be sent to the insecure link and the attacker can then obtain the cookie value by snooping the traffic. IBM X-Force ID: 212782. |
2021-11-15 |
4.3 |
CVE-2021-38977
CONFIRM
XF |
| ibm — security_guardium_key_lifecycle_manager |
IBM Tivoli Key Lifecycle Manager 3.0, 3.0.1, 4.0, and 4.1 uses weaker than expected cryptographic algorithms that could allow an attacker to decrypt highly sensitive information. IBM X-Force ID: 212792. |
2021-11-15 |
5 |
CVE-2021-38983
XF
CONFIRM |
| ibm — security_guardium_key_lifecycle_manager |
IBM Tivoli Key Lifecycle Manager 3.0, 3.0.1, 4.0, and 4.1 could allow a remote attacker to obtain sensitive information, caused by the failure to properly enable HTTP Strict Transport Security. An attacker could exploit this vulnerability to obtain sensitive information using man in the middle techniques. IBM X-Force ID: 212783. |
2021-11-15 |
4.3 |
CVE-2021-38978
CONFIRM
XF |
| ibm — security_guardium_key_lifecycle_manager |
IBM Tivoli Key Lifecycle Manager 3.0, 3.0.1, 4.0, and 4.1 uses a one-way cryptographic hash against an input that should not be reversible, such as a password, but the software does not also use a salt as part of the input. IBM X-Force ID: 212785. |
2021-11-15 |
5 |
CVE-2021-38979
XF
CONFIRM |
| ibm — security_guardium_key_lifecycle_manager |
IBM Tivoli Key Lifecycle Manager 3.0, 3.0.1, 4.0, and 4.1 receives input or data, but it does not validate or incorrectly validates that the input has the properties that are required to process the data safely and correctly. |
2021-11-12 |
4 |
CVE-2021-38985
XF
CONFIRM |
| ibm — security_guardium_key_lifecycle_manager |
IBM Tivoli Key Lifecycle Manager 3.0, 3.0.1, 4.0, and 4.1 receives input or data, but it does not validate or incorrectly validates that the input has the properties that are required to process the data safely and correctly. |
2021-11-12 |
4 |
CVE-2021-38973
CONFIRM
XF |
| ibm — security_guardium_key_lifecycle_manager |
IBM Tivoli Key Lifecycle Manager 3.0, 3.0.1, 4.0, and 4.1 could allow an authenticated user to cause a denial of service using specially crafted HTTP requests. IBM X-Force ID: 212779. |
2021-11-15 |
4 |
CVE-2021-38974
CONFIRM
XF |
| ibm — security_guardium_key_lifecycle_manager |
IBM Tivoli Key Lifecycle Manager 3.0, 3.0.1, 4.0, and 4.1 receives input or data, but it does not validate or incorrectly validates that the input has the properties that are required to process the data safely and correctly. |
2021-11-12 |
4 |
CVE-2021-38972
XF
CONFIRM |
| ibm — security_guardium_key_lifecycle_manager |
IBM Tivoli Key Lifecycle Manager 3.0, 3.0.1, 4.0, and 4.1 could allow a remote attacker to obtain sensitive information when a detailed technical error message is returned in the browser. This information could be used in further attacks against the system. IBM X-Force ID: 212788. |
2021-11-15 |
5 |
CVE-2021-38981
XF
CONFIRM |
| ibm — security_guardium_key_lifecycle_manager |
IBM Tivoli Key Lifecycle Manager 3.0, 3.0.1, 4.0, and 4.1 uses weaker than expected cryptographic algorithms that could allow an attacker to decrypt highly sensitive information. IBM X-Force ID: 212793. |
2021-11-15 |
5 |
CVE-2021-38984
XF
CONFIRM |
| ibm — security_guardium_key_lifecycle_manager |
IBM Tivoli Key Lifecycle Manager 3.0, 3.0.1, 4.0, and 4.1 could allow an authenticated user to to obtain sensitive information from a specially crafted HTTP request. IBM X-Force ID: 212780. |
2021-11-15 |
4 |
CVE-2021-38975
XF
CONFIRM |
| ibm — security_siteprotector_system |
IBM Security SiteProtector System 3.1.1 could allow a remote attacker to obtain sensitive information, caused by missing ‘HttpOnly’ flag. A remote attacker could exploit this vulnerability to obtain sensitive information. IBM X-Force ID: 174129. |
2021-11-12 |
5 |
CVE-2020-4146
CONFIRM
XF |
| idreamsoft — icms |
iCMS v7.0.15 was discovered to contain a Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF) via /admincp.php?app=members&do=add. |
2021-11-12 |
6.8 |
CVE-2020-21141
MISC |
| insert_pages_project — insert_pages |
The Insert Pages WordPress plugin before 3.7.0 allows users with a role as low as Contributor to access content and metadata from arbitrary posts/pages regardless of their author and status (ie private), using a shortcode. Password protected posts/pages are not affected by such issue. |
2021-11-17 |
4 |
CVE-2021-24851
CONFIRM
MISC |
| intel — ax210_firmware |
Improper input validation in software for some Intel(R) PROSet/Wireless WiFi and Killer(TM) WiFi in Windows 10 may allow an unauthenticated user to potentially enable denial of service or information disclosure via adjacent access. |
2021-11-17 |
6.8 |
CVE-2021-0078
MISC |
| intel — ax210_firmware |
Improper input validation in firmware for some Intel(R) PROSet/Wireless WiFi in UEFI may allow an unauthenticated user to potentially enable escalation of privilege via adjacent access. |
2021-11-17 |
5.8 |
CVE-2021-0071
MISC |
| intel — ax210_firmware |
Improper input validation in firmware for some Intel(R) PROSet/Wireless WiFi and Killer(TM) WiFi in Windows 10 may allow an unauthenticated user to potentially enable denial of service via adjacent access. |
2021-11-17 |
6.1 |
CVE-2021-0063
MISC |
| intel — ax210_firmware |
Insecure inherited permissions in the Intel(R) PROSet/Wireless WiFi software installer for Windows 10 before version 22.40 may allow an authenticated user to potentially enable escalation of privilege via local access. |
2021-11-17 |
4.6 |
CVE-2021-0064
MISC |
| intel — ax210_firmware |
Incorrect default permissions in the Intel(R) PROSet/Wireless WiFi software installer for Windows 10 before version 22.40 may allow an authenticated user to potentially enable escalation of privilege via local access. |
2021-11-17 |
4.6 |
CVE-2021-0065
MISC |
| intel — ax210_firmware |
Improper input validation in software for some Intel(R) PROSet/Wireless WiFi and Killer(TM) WiFi in Windows 10 may allow an unauthenticated user to potentially enable denial of service via adjacent access. |
2021-11-17 |
6.1 |
CVE-2021-0079
MISC |
| intel — endpoint_management_assistant |
Improper input validation for Intel(R) EMA before version 1.5.0 may allow an unauthenticated user to potentially enable denial of service via network access. |
2021-11-17 |
5 |
CVE-2021-0013
MISC |
| intel — nuc7i3dn_firmware |
Improper authentication in the software installer for the Intel(R) NUC HDMI Firmware Update Tool for NUC7i3DN, NUC7i5DN, NUC7i7DN before version 1.78.1.1 may allow an authenticated user to potentially enable escalation of privilege via local access. |
2021-11-17 |
4.6 |
CVE-2021-0096
MISC |
| intel — nuc_hdmi_firmware_update_tool |
Improper access control in the software installer for the Intel(R) NUC HDMI Firmware Update Tool for NUC8i3BE, NUC8i5BE, NUC8i7BE before version 1.78.4.0.4 may allow an authenticated user to potentially enable escalation of privilege via local access. |
2021-11-17 |
4.6 |
CVE-2021-33089
MISC |
| intel — nuc_m15_laptop_kit_lapbc510_firmware |
Out-of-bounds write in firmware for some Intel(R) NUCs may allow an authenticated user to potentially enable denial of service via local access. |
2021-11-17 |
4.9 |
CVE-2021-33086
MISC |
| intel — nuc_m15_laptop_kit_management_engine_driver_pack |
Improper authentication in the installer for the Intel(R) NUC M15 Laptop Kit Management Engine driver pack before version 15.0.10.1508 may allow an authenticated user to potentially enable denial of service via local access. |
2021-11-17 |
4.9 |
CVE-2021-33087
MISC |
| intel — safestring_library |
Integer overflow in the Safestring library maintained by Intel(R) may allow an authenticated user to potentially enable escalation of privilege via local access. |
2021-11-17 |
4.6 |
CVE-2021-33106
MISC |
| intel — thunderbolt_non-dch_driver |
Improper permissions in the installer for the Intel(R) Thunderbolt(TM) non-DCH driver, all versions, for Windows may allow an authenticated user to potentially enable escalation of privilege via local access. |
2021-11-17 |
4.6 |
CVE-2020-8741
MISC |
| jenkins — owasp_dependency-check |
Jenkins OWASP Dependency-Check Plugin 5.1.1 and earlier does not configure its XML parser to prevent XML external entity (XXE) attacks. |
2021-11-12 |
5.5 |
CVE-2021-43577
CONFIRM
MLIST |
| jenkins — performance |
Jenkins Performance Plugin 3.20 and earlier does not configure its XML parser to prevent XML external entity (XXE) attacks. |
2021-11-12 |
4 |
CVE-2021-21701
CONFIRM
MLIST
MISC |
| jenkins — pom2config |
Jenkins pom2config Plugin 1.2 and earlier does not configure its XML parser to prevent XML external entity (XXE) attacks, allowing attackers with Overall/Read and Item/Read permissions to have Jenkins parse a crafted XML file that uses external entities for extraction of secrets from the Jenkins controller or server-side request forgery. |
2021-11-12 |
4.3 |
CVE-2021-43576
CONFIRM
MLIST
MISC |
| jenkins — squash_tm_publisher |
Jenkins Squash TM Publisher (Squash4Jenkins) Plugin 1.0.0 and earlier implements an agent-to-controller message that does not implement any validation of its input, allowing attackers able to control agent processes to replace arbitrary files on the Jenkins controller file system with an attacker-controlled JSON string. |
2021-11-12 |
5.5 |
CVE-2021-43578
CONFIRM
MLIST |
| lenovo — antilles |
A dependency confusion vulnerability was reported in the Antilles open-source software prior to version 1.0.1 that could allow for remote code execution during installation due to a package listed in requirements.txt not existing in the public package index (PyPi). MITRE classifies this weakness as an Uncontrolled Search Path Element (CWE-427) in which a private package dependency may be replaced by an unauthorized package of the same name published to a well-known public repository such as PyPi. The configuration has been updated to only install components built by Antilles, removing all other public package indexes. Additionally, the antilles-tools dependency has been published to PyPi. |
2021-11-12 |
6.8 |
CVE-2021-3840
CONFIRM |
| lenovo — ideacentre_c5-14mb05_firmware |
A vulnerability was reported in some Lenovo Desktop models that could allow unauthorized access to the boot menu, when the “BIOS Password At Boot Device List” BIOS setting is Yes. |
2021-11-12 |
6.9 |
CVE-2021-3519
CONFIRM |
| linphone — belle-sip |
Belledonne Belle-sip before 5.0.20 can crash applications such as Linphone via ” ” in the display name of a From header. |
2021-11-12 |
5 |
CVE-2021-43611
MISC
MISC |
| linphone — belle-sip |
Belledonne Belle-sip before 5.0.20 can crash applications such as Linphone via an invalid From header (request URI without a parameter) in an unauthenticated SIP message, a different issue than CVE-2021-33056. |
2021-11-12 |
5 |
CVE-2021-43610
MISC
MISC |
| linux — linux_kernel |
In the Linux kernel through 5.15.2, hw_atl_utils_fw_rpc_wait in drivers/net/ethernet/aquantia/atlantic/hw_atl/hw_atl_utils.c allows an attacker (who can introduce a crafted device) to trigger an out-of-bounds write via a crafted length value. |
2021-11-17 |
4.6 |
CVE-2021-43975
MISC
MISC |
| llhttp — llhttp |
The parser in accepts requests with a space (SP) right after the header name before the colon. This can lead to HTTP Request Smuggling (HRS) in llhttp < v2.1.4 and < v6.0.6. |
2021-11-15 |
6.4 |
CVE-2021-22959
MISC |
| min — minio_console |
Minio console is a graphical user interface for the for MinIO operator. Minio itself is a multi-cloud object storage project. Affected versions are subject to an authentication bypass issue in the Operator Console when an external IDP is enabled. All users on release v0.12.2 and before are affected and are advised to update to 0.12.3 or newer. Users unable to upgrade should add automountServiceAccountToken: false to the operator-console deployment in Kubernetes so no service account token will get mounted inside the pod, then disable the external identity provider authentication by unset the CONSOLE_IDP_URL, CONSOLE_IDP_CLIENT_ID, CONSOLE_IDP_SECRET and CONSOLE_IDP_CALLBACK environment variable and instead use the Kubernetes service account token. |
2021-11-15 |
6.8 |
CVE-2021-41266
MISC
CONFIRM |
| montala — resourcespace |
ResourceSpace before 9.6 rev 18290 is affected by a reflected Cross-Site Scripting vulnerability in plugins/wordpress_sso/pages/index.php via the wordpress_user parameter. If an attacker is able to persuade a victim to visit a crafted URL, malicious JavaScript content may be executed within the context of the victim’s browser. |
2021-11-15 |
4.3 |
CVE-2021-41951
MISC |
| montala — resourcespace |
A directory traversal issue in ResourceSpace 9.6 before 9.6 rev 18277 allows remote unauthenticated attackers to delete arbitrary files on the ResourceSpace server via the provider and variant parameters in pages/ajax/tiles.php. Attackers can delete configuration or source code files, causing the application to become unavailable to all users. |
2021-11-15 |
6.4 |
CVE-2021-41950
MISC
MISC |
| mousewheel_smooth_scroll_project — mousewheel_smooth_scroll |
The MouseWheel Smooth Scroll WordPress plugin before 5.7 does not have CSRF check in place on its settings page, which could allow attackers to make a logged in admin change them via a CSRF attack |
2021-11-17 |
4.3 |
CVE-2021-24852
MISC |
| my_tickets_project — my_tickets |
The My Tickets WordPress plugin before 1.8.31 does not properly sanitise and escape the Email field of booked tickets before outputting it in the Payment admin dashboard, which could allow unauthenticated users to perform Cross-Site Scripting attacks against admins |
2021-11-17 |
4.3 |
CVE-2021-24796
MISC |
| nextcloud — talk |
Nextcloud is an open-source, self-hosted productivity platform. The Nextcloud Talk application was vulnerable to a stored Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) vulnerability. For exploitation, a user would need to right-click on a malicious file and open the file in a new tab. Due the strict Content-Security-Policy shipped with Nextcloud, this issue is not exploitable on modern browsers supporting Content-Security-Policy. It is recommended that the Nextcloud Talk application is upgraded to patched versions 10.0.7, 10.1.4, 11.1.2, 11.2.0 or 12.0.0. As a workaround, use a browser that has support for Content-Security-Policy. |
2021-11-15 |
4.3 |
CVE-2021-39222
CONFIRM
MISC
MISC |
| ni — ni_service_locator |
There is an Unquoted Service Path in NI Service Locator (nisvcloc.exe) in versions prior to 18.0 on Windows. This may allow an authorized local user to insert arbitrary code into the unquoted service path and escalate privileges. |
2021-11-12 |
4.6 |
CVE-2021-42563
MISC |
| ohmyz — ohmyzsh |
ohmyzsh is vulnerable to Improper Neutralization of Special Elements used in an OS Command |
2021-11-12 |
5.1 |
CVE-2021-3934
CONFIRM
MISC |
| opendesign — drawings_sdk |
An Out-of-bounds Read vulnerability exists in the DGN file reading procedure in Open Design Alliance Drawings SDK before 2022.11. Crafted data in a DGN file and lack of verification of input data can trigger a read past the end of an allocated buffer. An attacker can leverage this vulnerability to execute code in the context of the current process. |
2021-11-14 |
4.3 |
CVE-2021-43273
MISC
MISC
MISC |
| opendesign — drawings_software_developemnt_kit |
An Out-of-bounds Read vulnerability exists in the OBJ file reading procedure in Open Design Alliance Drawings SDK before 2022.11. The lack of validating the input length can trigger a read past the end of an allocated buffer. An attacker can leverage this vulnerability to execute code in the context of the current process. |
2021-11-14 |
6.8 |
CVE-2021-43278
MISC |
| opendesign — drawings_software_development_kit |
A Use After Free vulnerability exists in the DGN file reading procedure in Open Design Alliance Drawings SDK before 2022.8. The issue results from the lack of validating the existence of an object prior to performing operations on the object. An attacker can leverage this vulnerability to execute code in the context of the current process. |
2021-11-14 |
6.8 |
CVE-2021-43275
MISC |
| opendesign — drawings_software_development_kit |
A Use After Free Vulnerability exists in the Open Design Alliance Drawings SDK before 2022.11. The specific flaw exists within the parsing of DWF files. The issue results from the lack of validating the existence of an object prior to performing operations on the object. An attacker can leverage this in conjunction with other vulnerabilities to execute arbitrary code in the context of the current process. |
2021-11-14 |
6.8 |
CVE-2021-43274
MISC |
| opendesign — drawings_software_development_kit |
A stack-based buffer overflow vulnerability exists in the DWF file reading procedure in Open Design Alliance Drawings SDK before 2022.8. The issue results from the lack of proper validation of the length of user-supplied data before copying it to a stack-based buffer. An attacker can leverage this vulnerability to execute code in the context of the current process. |
2021-11-14 |
6.8 |
CVE-2021-43280
MISC |
| opendesign — drawings_software_development_kit |
An Out-of-Bounds Write vulnerability exists when reading a DXF file using Open Design Alliance Drawings SDK before 2022.11. The specific issue exists within the parsing of DXF files. Crafted data in a DXF file (an invalid number of properties) can trigger a write operation past the end of an allocated buffer. An attacker can leverage this vulnerability to execute code in the context of the current process. |
2021-11-14 |
6.8 |
CVE-2021-43336
MISC |
| opendesign — drawings_software_development_kit |
An Out-of-Bounds Write vulnerability exists when reading a DGN file using Open Design Alliance Drawings SDK before 2022.11. The specific issue exists within the parsing of DGN files. Crafted data in a DGN file and lack of proper validation of input data can trigger a write operation past the end of an allocated buffer. An attacker can leverage this vulnerability to execute code in the context of the current process. |
2021-11-14 |
6.8 |
CVE-2021-43390
MISC |
| opendesign — drawings_software_development_kit |
An Out-of-Bounds Read vulnerability exists when reading a DXF file using Open Design Alliance Drawings SDK before 2022.11. The specific issue exists within the parsing of DXF files. Crafted data in a DXF file (an invalid dash counter in line types) can trigger a read past the end of an allocated buffer. An attacker can leverage this vulnerability to execute code in the context of the current process. |
2021-11-14 |
6.8 |
CVE-2021-43391
MISC |
| opendesign — oda_prc_software_development_kit |
An out-of-bounds read vulnerability exists in the U3D file reading procedure in Open Design Alliance PRC SDK before 2022.10. Crafted data in a U3D file can trigger a read past the end of an allocated buffer. An attacker can leverage this in conjunction with other vulnerabilities to execute arbitrary code in the context of the current process. |
2021-11-14 |
6.8 |
CVE-2021-43277
MISC |
| opendesign — oda_prc_software_development_kit |
An out-of-bounds write vulnerability exists in the U3D file reading procedure in Open Design Alliance PRC SDK before 2022.10. Crafted data in a U3D file can trigger a write past the end of an allocated buffer. An attacker can leverage this in conjunction with other vulnerabilities to execute arbitrary code in the context of the current process. |
2021-11-14 |
6.8 |
CVE-2021-43279
MISC |
| opendesign — oda_viewer |
An Out-of-bounds Read vulnerability exists in Open Design Alliance ODA Viewer before 2022.8. Crafted data in a DWF file can trigger a read past the end of an allocated buffer. An attacker can leverage this in conjunction with other vulnerabilities to execute arbitrary code in the context of the current process |
2021-11-14 |
6.8 |
CVE-2021-43276
MISC |
| optical_character_recognition_project — optical_character_recognition |
A stack-based buffer overflow vulnerability was discovered in gocr through 0.53-20200802 in try_to_divide_boxes() in pgm2asc.c. |
2021-11-17 |
6.8 |
CVE-2021-33481
MISC
MISC |
| optical_character_recognition_project — optical_character_recognition |
A stack-based buffer overflow vulnerability was discovered in gocr through 0.53-20200802 in measure_pitch() in pgm2asc.c. |
2021-11-17 |
6.8 |
CVE-2021-33479
MISC
MISC |
| optical_character_recognition_project — optical_character_recognition |
An use-after-free vulnerability was discovered in gocr through 0.53-20200802 in context_correction() in pgm2asc.c. |
2021-11-17 |
4.3 |
CVE-2021-33480
MISC
MISC
MISC |
| orckestra — c1_cms |
This vulnerability allows remote attackers to execute arbitrary code on affected installations of Orckestra C1 CMS 6.10. Authentication is required to exploit this vulnerability. The specific flaw exists within Composite.dll. The issue results from the lack of proper validation of user-supplied data, which can result in deserialization of untrusted data. An attacker can leverage this vulnerability to execute code in the context of the service account. Was ZDI-CAN-14740. |
2021-11-15 |
6.5 |
CVE-2021-34992
MISC
MISC |
| osisoft — pi_vision |
PI Vision could disclose information to a user with insufficient privileges for an AF attribute that is the child of another attribute and is configured as a Limits property. |
2021-11-17 |
4 |
CVE-2021-43553
MISC |
| preview_e-mails_for_woocommerce_project — preview_e-mails_for_woocommerce |
The Preview E-Mails for WooCommerce WordPress plugin is vulnerable to Reflected Cross-Site Scripting via the search_order parameter found in the ~/views/form.php file which allows attackers to inject arbitrary web scripts, in versions up to and including 1.6.8. |
2021-11-19 |
4.3 |
CVE-2021-42363
MISC
MISC
MISC |
| qnap — qmailagent |
A cross-site scripting (XSS) vulnerability has been reported to affect QNAP device running QmailAgent. If exploited, this vulnerability allows remote attackers to inject malicious code. We have already fixed this vulnerability in the following versions of QmailAgent: QmailAgent 3.0.2 ( 2021/08/25 ) and later |
2021-11-13 |
4.3 |
CVE-2021-34357
MISC |
| qr_redirector_project — qr_redirector |
The QR Redirector WordPress plugin before 1.6 does not have capability and CSRF checks when saving bulk QR Redirector settings via the qr_save_bulk AJAX action, which could allow any authenticated user, such as subscriber to change the redirect response status code of arbitrary QR Redirects |
2021-11-17 |
4.3 |
CVE-2021-24853
MISC |
| qualcomm — apq8009_firmware |
Possible information exposure and denial of service due to NAS not dropping messages when integrity check fails in Snapdragon Auto, Snapdragon Compute, Snapdragon Connectivity, Snapdragon Consumer IOT, Snapdragon Industrial IOT, Snapdragon IoT, Snapdragon Mobile, Snapdragon Voice & Music, Snapdragon Wearables |
2021-11-12 |
6.4 |
CVE-2021-30284
CONFIRM |
| qualcomm — apq8009_firmware |
Possible use after free due improper validation of reference from call back to internal store table in Snapdragon Auto, Snapdragon Connectivity, Snapdragon Consumer IOT, Snapdragon Industrial IOT, Snapdragon Mobile, Snapdragon Voice & Music, Snapdragon Wearables, Snapdragon Wired Infrastructure and Networking |
2021-11-12 |
4.6 |
CVE-2021-30264
CONFIRM |
| qualcomm — apq8009_firmware |
Possible use after free due to improper memory validation when initializing new interface via Interface add command in Snapdragon Auto, Snapdragon Compute, Snapdragon Connectivity, Snapdragon Consumer IOT, Snapdragon Industrial IOT, Snapdragon Mobile, Snapdragon Voice & Music, Snapdragon Wired Infrastructure and Networking |
2021-11-12 |
4.6 |
CVE-2021-30266
CONFIRM |
| qualcomm — apq8017_firmware |
Possible buffer over read due to improper IE size check of Bearer capability IE in MT setup request from network in Snapdragon Auto, Snapdragon Compute, Snapdragon Connectivity, Snapdragon Consumer IOT, Snapdragon Industrial IOT, Snapdragon Mobile |
2021-11-12 |
6.4 |
CVE-2021-1981
CONFIRM |
| qualcomm — apq8053_firmware |
Possible memory corruption due to improper validation of memory address while processing user-space IOCTL for clearing Filter and Route statistics in Snapdragon Auto, Snapdragon Compute, Snapdragon Connectivity, Snapdragon Consumer IOT, Snapdragon Industrial IOT, Snapdragon Mobile, Snapdragon Voice & Music, Snapdragon Wearables |
2021-11-12 |
4.6 |
CVE-2021-30265
CONFIRM |
| qualcomm — aqt1000_firmware |
Possible memory corruption due to Improper handling of hypervisor unmap operations for concurrent memory operations in Snapdragon Auto, Snapdragon Compute, Snapdragon Connectivity, Snapdragon Consumer IOT, Snapdragon Industrial IOT, Snapdragon Mobile |
2021-11-12 |
6.9 |
CVE-2021-1921
CONFIRM |
| qualcomm — aqt1000_firmware |
Possible denial of service scenario can occur due to lack of length check on Channel Switch Announcement IE in beacon or probe response frame in Snapdragon Auto, Snapdragon Compute, Snapdragon Connectivity, Snapdragon Consumer Electronics Connectivity, Snapdragon Consumer IOT, Snapdragon Industrial IOT, Snapdragon Mobile, Snapdragon Voice & Music, Snapdragon Wired Infrastructure and Networking |
2021-11-12 |
5 |
CVE-2021-1903
CONFIRM |
| qualcomm — aqt1000_firmware |
Possible race condition can occur due to lack of synchronization mechanism when On-Device Logging node open twice concurrently in Snapdragon Compute, Snapdragon Industrial IOT, Snapdragon Mobile, Snapdragon Voice & Music |
2021-11-12 |
4.4 |
CVE-2021-30263
CONFIRM |
| qualcomm — ar8035_firmware |
Possible denial of service scenario due to improper input validation of received NAS OTA message in Snapdragon Auto, Snapdragon Compute, Snapdragon Connectivity, Snapdragon Consumer IOT, Snapdragon Industrial IOT, Snapdragon Mobile |
2021-11-12 |
5 |
CVE-2021-1982
CONFIRM |
| ruijie — rg-uac_6000-e50_firmware |
Ruijie RG-UAC 6000-E50 commit 9071227 was discovered to contain a cross-site scripting (XSS) vulnerability via the rule_name parameter. This vulnerability allows attackers to execute arbitrary web scripts or HTML via a crafted payload. |
2021-11-16 |
4.3 |
CVE-2020-21639
MISC |
| ruijie — rg-uac_firmware |
Ruijie RG-UAC commit 9071227 was discovered to contain a vulnerability in the component /current_action.php?action=reboot, which allows attackers to cause a denial of service (DoS) via unspecified vectors. |
2021-11-16 |
5 |
CVE-2020-21627
MISC |
| schedmd — slurm |
SchedMD Slurm 21.08.* before 21.08.4 has Incorrect Access Control. On sites using the new AccountingStoreFlags=job_script and/or job_env options, the access control rules in SlurmDBD may permit users to request job scripts and environment files to which they should not have access. |
2021-11-17 |
4 |
CVE-2021-43337
MISC
MISC
CONFIRM
CONFIRM |
| servermanagement_project — servermanagement |
ServerManagement master branch as of commit 49491cc6f94980e6be7791d17be947c27071eb56 is affected by a directory traversal vulnerability. This vulnerability can be used to extract credentials which can in turn be used to execute code. |
2021-11-12 |
5 |
CVE-2021-43493
MISC |
| showdoc — showdoc |
showdoc is vulnerable to Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF) |
2021-11-13 |
5.8 |
CVE-2021-3775
MISC
CONFIRM |
| showdoc — showdoc |
showdoc is vulnerable to Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF) |
2021-11-13 |
5.8 |
CVE-2021-3776
MISC
CONFIRM |
| showdoc — showdoc |
showdoc is vulnerable to Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF) |
2021-11-13 |
4.3 |
CVE-2021-3683
CONFIRM
MISC |
| simple_jwt_login_project — simple_jwt_login |
The Simple JWT Login WordPress plugin before 3.2.1 does not have nonce checks when saving its settings, allowing attackers to make a logged in admin changed them. Settings such as HMAC verification secret, account registering and default user roles can be updated, which could result in site takeover. |
2021-11-17 |
6.8 |
CVE-2021-24804
MISC |
| smartertools — smartermail |
SmarterTools SmarterMail 16.x through 100.x before 100.0.7803 allows XSS. |
2021-11-17 |
4.3 |
CVE-2021-43977
MISC
MISC |
| snipeitapp — snipe-it |
snipe-it is vulnerable to Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF) |
2021-11-13 |
4.3 |
CVE-2021-3931
CONFIRM
MISC |
| talariax — sendquick_alert_plus_server_admin |
A SQL Injection vulnerability in /appliance/shiftmgn.php in TalariaX sendQuick Alert Plus Server Admin 4.3 before 8HF11 allows attackers to obtain sensitive information via a Roster Time to Roster Management. |
2021-11-14 |
6.5 |
CVE-2021-26795
MISC
MISC |
| vice — webopac |
Grand Vice info Co. webopac7 book search field parameter does not properly restrict the input of special characters, thus unauthenticated attackers can inject JavaScript syntax remotely, and further perform reflective XSS attacks. |
2021-11-15 |
4.3 |
CVE-2021-42838
MISC |
| webfactoryltd — wp_reset_pro |
Authenticated Database Reset vulnerability in WordPress WP Reset PRO Premium plugin (versions <= 5.98) allows any authenticated user to wipe the entire database regardless of their authorization. It leads to a complete website reset and takeover. |
2021-11-18 |
5.5 |
CVE-2021-36909
MISC
CONFIRM
MISC |
| webfactoryltd — wp_reset_pro |
Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF) vulnerability leading to Database Reset in WordPress WP Reset PRO Premium plugin (versions <= 5.98) allows attackers to trick authenticated into making unintentional database reset. |
2021-11-18 |
6.8 |
CVE-2021-36908
CONFIRM
CONFIRM
CONFIRM |
| wordpress_popular_posts_project — wordpress_popular_posts |
The WordPress Popular Posts WordPress plugin is vulnerable to arbitrary file uploads due to insufficient input file type validation found in the ~/src/Image.php file which makes it possible for attackers with contributor level access and above to upload malicious files that can be used to obtain remote code execution, in versions up to and including 5.3.2. |
2021-11-17 |
6.5 |
CVE-2021-42362
MISC
MISC
MISC
MISC |
| wp-buy — seo_redirection-301_redirect_manager |
The importFromRedirection AJAX action of the SEO Redirection Plugin – 301 Redirect Manager WordPress plugin before 8.2, available to any authenticated user, does not properly sanitise the offset parameter before using it in a SQL statement, leading an SQL injection when the redirection plugin is also installed |
2021-11-17 |
6.5 |
CVE-2021-24847
MISC |
| wp_performance_score_booster_project — wp_performance_score_booster |
The WP Performance Score Booster WordPress plugin before 2.1 does not have CSRF check when saving its settings, which could allow attackers to make a logged in admin change them via a CSRF attack. |
2021-11-17 |
4.3 |
CVE-2021-24776
MISC |
| xwp — stream |
The Stream WordPress plugin before 3.8.2 does not sanitise and validate the order GET parameter from the Stream Records admin dashboard before using it in a SQL statement, leading to an SQL injection issue. |
2021-11-17 |
6.5 |
CVE-2021-24772
MISC
CONFIRM |
| yop-poll — yop_poll |
The YOP Poll WordPress plugin before 6.3.1 is affected by a stored Cross-Site Scripting vulnerability which exists in the Create Poll – Options module where a user with a role as low as author is allowed to execute arbitrary script code within the context of the application. This vulnerability is due to insufficient validation of custom label parameters – vote button label , results link label and back to vote caption label. |
2021-11-17 |
4.3 |
CVE-2021-24834
MISC
CONFIRM
MISC |
| zoho — manageengine_remote_access_plus_server |
Zoho Remote Access Plus Server Windows Desktop Binary fixed in 10.1.2132.6 is affected by a sensitive information disclosure vulnerability. Due to improper privilege management, the process launches as the logged in user, so memory dump can be done by non-admin also. Remotely, an attacker can dump all sensitive information including DB Connection string, entire IT infrastructure details, commands executed by IT admin including credentials, secrets, private keys and more. |
2021-11-17 |
6.5 |
CVE-2021-42956
MISC |
| zohocorp — manageengine_remote_access_plus |
Zoho Remote Access Plus Server Windows Desktop Binary fixed from 10.1.2121.1 is affected by incorrect access control. The installation directory is vulnerable to weak file permissions by allowing full control for Windows Everyone user group (non-admin or any guest users), thereby allowing privilege escalation, unauthorized password reset, stealing of sensitive data, access to credentials in plaintext, access to registry values, tampering with configuration files, etc. |
2021-11-17 |
4.6 |
CVE-2021-42954
MISC |
by Contributed | Nov 21, 2021 | Technology
This article is contributed. See the original author and article here.
APIs are everywhere and there are many ways to host them in Azure! Let us see what are the different possibilities with the pros & cons of each. I am not going to discuss the bits and bytes about each possibility. The purpose of this post is to give you a rough idea of what is possible for a simple scenario (single region, high-availability and disaster recovery are out of scope). I will provide small diagrams for more advanced scenarios.
1) Function App – Consumption tier
Function Apps ship with HTTP-triggered functions. These can be suitable to expose tiny APIs.
Pros: Cost-friendly (economies of scale), Easy to deploy, Fully elastic with built-in auto-scaling from 0 to n instances.
Cons: Limited security controls. Network ACLs are the only way to limit public exposure. Data accessed by such functions must be public from a connectivity perspective. Cold start due to serverless tier. Limited execution time as well as per-execution resource consumption. No WAF (Web Application Firewall) features.
Use cases: Lab, PoC, Prototyping, Limited budgets, Basic API needs (ie: no catalog, no versioning, etc.), asynchronous APIs, Synchronous APIs that can live with the cold start, No strong compliance requirements.
2) Multi-Tenant App Service – Standard tier
Like functions, Web Apps are pretty neat and easy to get started with. Microsoft is managing everything for you under the hoods.
Pros: Cost-friendly (economies of scale) but fixed cost incurred (unlike functions on consumption tier), Easy to deploy, Auto-scaling plans. Resource is limited to the capacity you are willing to pay. No cold start!
Cons: Limited security controls. Network ACLs are the only way to limit public exposure. Data accessed by such apps must be public from a network perspective. No WAF.
Use cases: Lab, PoC, Prototyping, Limited budgets, Basic API needs (ie: no catalog, no versioning, etc.), No strong compliance requirements.
3) Azure Container Instances (ACI)
While Azure Container Instances can be used to host long-running services, I would advise against this idea and keep the ACIs for asynchronous job operations, short-lived executions and as the serverless (virtual kubelets) part of Azure Kubernetes Service.
Pros: Cost-friendly (pay per second of execution), providing the API is not constantly up and running.
Cons: Limited security controls with Windows Containers, better with Linux as Linux-based ACIs can integrate with virtual networks.
Use cases: Lab, PoC, Prototyping, Limited budgets, Basic API needs (ie: no catalog, no versioning, etc.), No strong compliance requirements. Lift & shift of plain old legacy Windows-based backend services.
4) Functions Apps Consumption tier or App Service standard+ Azure API Management (APIM) Consumption tier
In this setup, you intend to publish APIs through Azure API Management. The pros & cons of the underlying hosting option (app service or function apps) remain as explained earlier and are not repeated below.
Pros: Cost-friendly because the serverless flavor of APIM has no fixed cost. It will auto-scale with the actual demand. You can add features to your APIs such as enforcing policies (JWT validation, headers checks etc.) as well as version them.
Cons: More security controls but there is still a few major caveats: network ACLs remain the only way to limit public exposure of the backend and traffic cannot be forced through APIM because the consumption tier has no static IP so this can’t be used as a network ACL on the backend side. Data accessed by such apps must still be public from a network perspective. Still no WAF because APIM is a a PEP (Policy Enforcement Point) but not a WAF.
Use cases: Lab, PoC, Prototyping, Limited budgets, More advanced API needs (catalog, versioning, consistent way of exposing APIs etc.), No strong compliance requirements.
5) Functions Apps Consumption tier or App Service standard+ Azure API Management (APIM) Basic or Standard tier
In this setup, you intend to publish APIs (and enforce routing) through Azure API Management.
Pros: You benefit from APIM capabilities AND you can restrict traffic to the backend to your APIM instance because as of the basic tier, APIM comes with a static IP.
Cons: A bit more expensive (fixed cost for APIM). Manual scaling for the Basic tier (plans possible as of Standard). Data stores accessed by the backends must still be public from a network perspective. Still no WAF because APIM is a a PEP (Policy Enforcement Point) but not a WAF.
Use cases: Limited budgets, More advanced API needs (catalog, versioning, consistent way of exposing APIs etc.), No strong compliance requirements.
6) App Service (or Functions) on Premium tier+Private Endpoint+VNET Integration+WAF
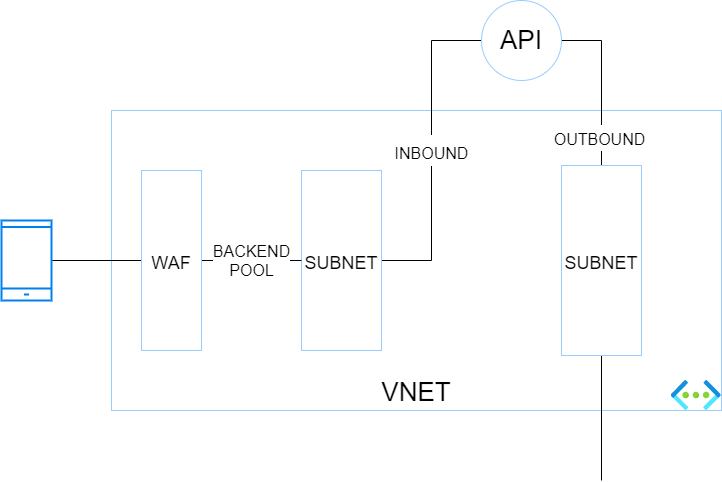
In this setup, you want isolate your backend services totally from internet and make them only accessible through a web application firewall (WAF). Because it is a little more complex, here is a small diagram showing the different blocs and their interactions.

The traffic flies from a caller (here a mobile device) to a WAF which has a public IP. The WAF has a backend pool targeting the endpoints defined in the corresponding private endpoint subnet. The app service is integrated with Azure Private Link (and private DNS zone) for the INBOUND traffic. VNET integration for the App Service (or function app) is enabled to handle the OUTBOUND traffic through another VNET’s subnet.
Pros: This hosting option is more secure than the preceding ones because the data stores can be firewalled thanks to the control over the outbound traffic of the API. The backend services are isolated from internet and proxied by a WAF.
Cons: This architecture is a bit convoluted and is not the best one to run at scale.
Use cases: Stronger focus on security. Basic API needs (no more APIM in the picture).
7) App Service (or Functions) on Premium tier+Private Endpoint+VNET Integration+WAF+APIM Premium
The purpose of this setup is the same as the previous one but you want to combine both WAF & APIM (how it should be) before hitting backend services.
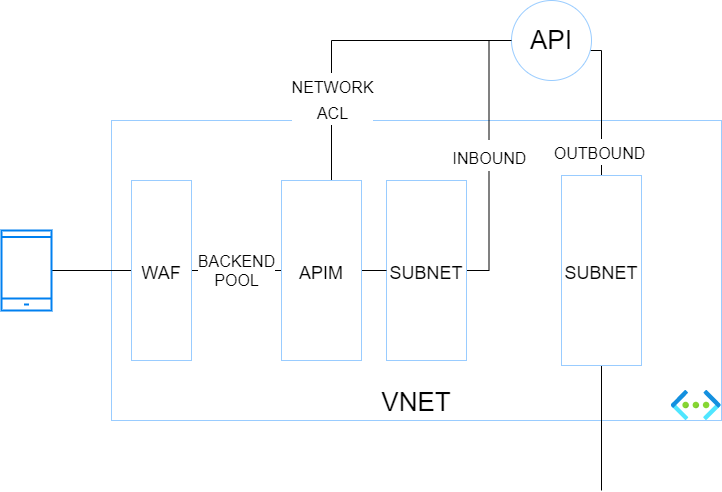
Pros: Inbound traffic is more secure because it traverses a WAF and a PEP. Network ACLs can be set at backend level to only let the API gateway (which has a static IP) call the backend. Outbound traffic of the API gateway can be controlled by a NVA or Azure Firewall.
Cons: This architecture is a bit convoluted and is not the best one to run at scale. APIM premium is expensive but is required because at the time of writing (11/2021), only the Premium tier integrates with Virtual Networks.
Use cases: Stronger focus on security, advanced API needs and possible geo-distributed APIs setup.
WAF+APIM Premium+App Service Environment (ASE)
Before ASE v3, ILB ASEs had a rather bad reputation because of their cost (flat fees), and their complexity. It was indeed quite easy to break them with improperly configured firewall rules. ASE v3 are a breeze to setup and are less expensive (no more flat fee). Therefore ILB ASE comes back as a very interesting option because it offers the best-in-class security at an affordable price, at least from a backend hosting perspective.
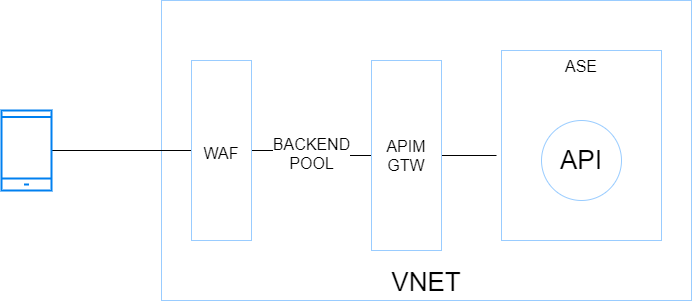
Pros: Inbound and outbound traffic can be fully controlled by an NVA or Azure Firewall. Intra VNET traffic can be controlled with Network Security Groups. Backends are totally isolated from internet. This setup is scalable because the ASE can most tons of backends and functions. The underlying compute is based on a single-tenant architecture (Isolated tier).
Cons: Costs (incurred by the isolated tiers and APIM premium) and complexity. Although ASE v3 is a breeze compared to its predecessors, this setup is often part of a larger Hub & Spoke architecture, which involves a lot of networking and firewalling work. You do not get started with it over night!
Use cases: Stronger compliance requirements, advanced API needs and possible geo-distributed APIs setup. This setup is perfectly suitable as a Web Landing Zone that hosts tons of web apps and APIs.
WAF+APIM Premium+AKS
Kubernetes has become a first-class citizen everywhere and AKS is the Microsoft-managed K8s offering on Azure (By the way, Azure Arc also has a ton of handy features to manage K8s clusters at scale wherever they are hosted). So, with this in mind, I could not skip it. Here is a very simplified diagram showing the different building blocks:
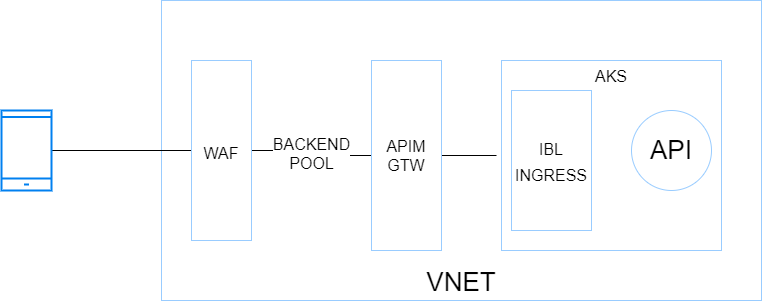
Pros: Very similar to the previous architecture with regards to inbound and outbound, Hub & Spoke integration, etc.. although AKS adds a serious bits of extra complexity network-wise. AKS allows you to host nearly anything and has a very rich ecosystem. When I think AKS, I think all the benefits of VMs with all the benefits of cloud native architectures (Infrastructure as Code, increased resilience, zero downtime, releases during business hours, polyglot apps, etc.).
Cons: Costs incurred by APIM premium and the AKS node pools, which should involve at least 3 nodes but ideally 5 for a minimal production-grade setup. Another potential deal-breaker for some organizations is the complexity of K8s (AKS). App Services and Function Apps are way easier to work with and it is a Kubernetes lover who tells you this!
Use cases: Stronger compliance requirements, advanced API needs and possible geo-distributed APIs setup. This setup is perfectly suitable as a Web Landing Zone that hosts tons of web apps and APIs. Microservices architectures (K8s and its ecosystem, including service meshes, are very supportive of microservices architectures).
10) Container Apps
This new service (public preview in 11/2021) is very promising because it comes with some of the AKS promises without the complexity because Microsoft manages nearly everything for you. Container apps remind me to some extend Service Fabric Mesh, let’s hope they have a better future. However, at the time of writing, it is no way in line with typical enterprise needs (Hub & Spoke) but Microsoft is working on a BYO VNET feature. It is still a little early to come with pros & cons but here are a few of them.
Pros: Cost friendly since it scales from 0 to n, like Azure Functions. Easy to deploy and manage.
Cons: N/A (too early)
Use cases: right now, PoCs and protoyping only. In the future, microservices architectures, which is why this service has been built from the ground up.
by Contributed | Nov 20, 2021 | Technology
This article is contributed. See the original author and article here.
Before implementing data extraction from SAP systems please always verify your licensing agreement. |
OData services have become one the most powerful interfaces in SAP systems. In the last episode, we’ve built a simple pipeline that extracts business information from an OData service to a data lake and makes them available for further processing and analytics. We’ve created all required resources, including linked services and datasets, and we’ve used them to define the Copy Data activity. The extraction process run without any issues, and we were able to display data from the lake.
But imagine you’d like to change the data source. Instead of Sales Orders, you’d like to get information about Business Partners. To make such a change, you’d have to go through all resources and modify them. You’d have to alter the URL of the OData service, target location and entity. Quite a few changes! Alternatively, you could create a new set of objects, including the Copy Data activity. Both solutions are not ideal. As your project grows, maintaining a large set of resources can become a tremendous job. Not to mention the likelihood of making a mistake!
Fortunately, there is a solution! The Synapse Pipelines are highly customizable, and we can use dynamic parameters. Instead of hardcoding the URL of the OData service, we can use a parameter and provide the value before the pipeline starts. You can use the same approach also to customize the target directory or entity name. Pretty much everything can be parametrized, and it’s only up to you how flexible the pipeline will be.
Today I’ll show you how to use parameters to customize some of the resources. It is the first step towards making the pipeline metadata-driven. In the next episode, we’ll expand the solution even further and describe how to read parameters from an external service. This way you’ll be able to add or modify the OData service without making any changes to the pipeline.
DEFINING PARAMETERS
Parameters are external values that you use to replace hardcoded text. You can define them for every resource – a pipeline, a dataset or a linked service – they all accept external values. To assign parameters at the runtime, you can use expressions that I find very similar to Excel formulas. We will use this feature quite often in this blog series.
Let’s start by defining the initial set of parameters at the pipeline level. We will use them to set the URL, name and entity of the OData service. Open the pipeline we’ve built last time. At the bottom of the screen, you’ll notice four tabs. Click on the one named Parameters.

When you click the Parameters tab, the window enlarges, revealing the “New” button to define parameters. Add three entries:
Name |
Type |
URL |
String |
ODataService |
String |
Entity |
String |
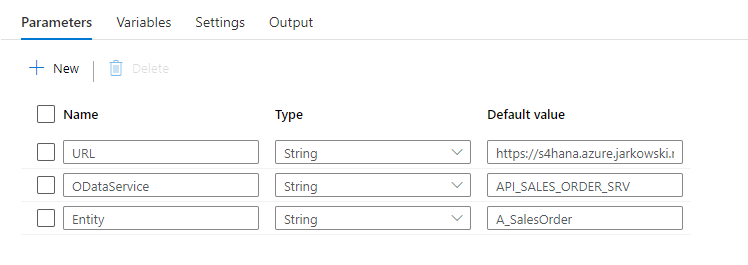
You can use values that are passed to the pipeline as parameters in datasets and linked services. I want all files with extracted data to be saved in the directory named after the OData service. The directory structure should look as follows:
/odata/<OData_Service>/<Entity>
For example:
/data/API_SALES_ORDER_SRV/A_SalesOrder
That’s quite easy. You define the target file location in the data lake dataset – therefore the first step is to modify it to accept external parameters. Open the resource definition and go to the Parameters tab. Create a new entry:
Now we need to define the target location using the parameter. Open the Connection tab. Replace the current value in the directory field with the following expression to reference the Path parameter. The value that we pass to this parameter will be used as the directory name.
@dataset().Path
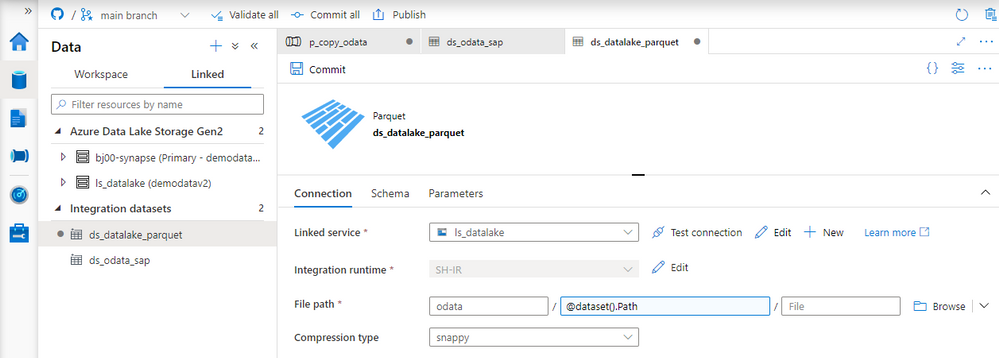
Dataset knows what to do with the value passed to the Path parameter. Now we have to maintain it. Open the Copy Data activity and go to the Sink tab. You’ll notice an additional field under Dataset properties that wasn’t there before. The parameter defined at the dataset level is now waiting for a value.
As my directory hierarchy should be <ODataService>/<Entity> I use the Concat expression to combine parameters defined at the pipeline level:
@concat(pipeline().parameters.ODataService, '/', pipeline().parameters.Entity)
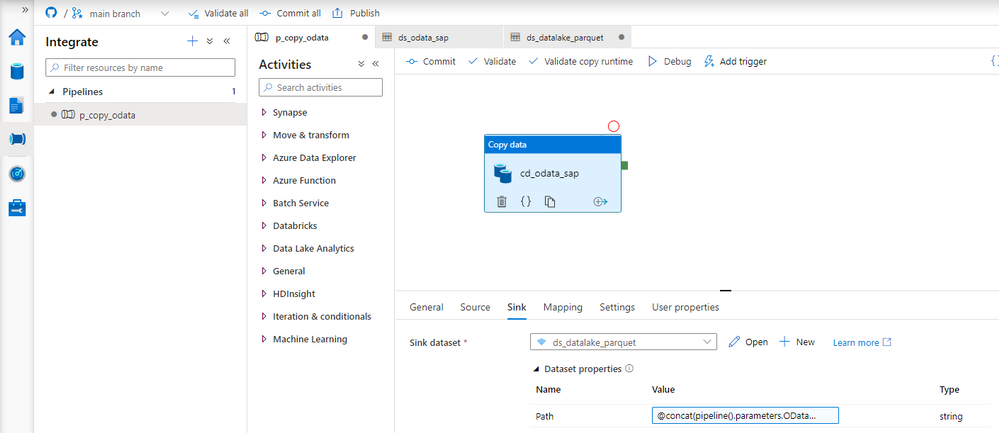
The target dataset now accepts values passed from the pipeline. We can switch to the source dataset that points to the SAP system. Similarly as before, open the OData dataset and define two parameters. They will tell which OData service and Entity should be extracted.
Name |
Type |
ODataURL |
String |
Entity |
String |
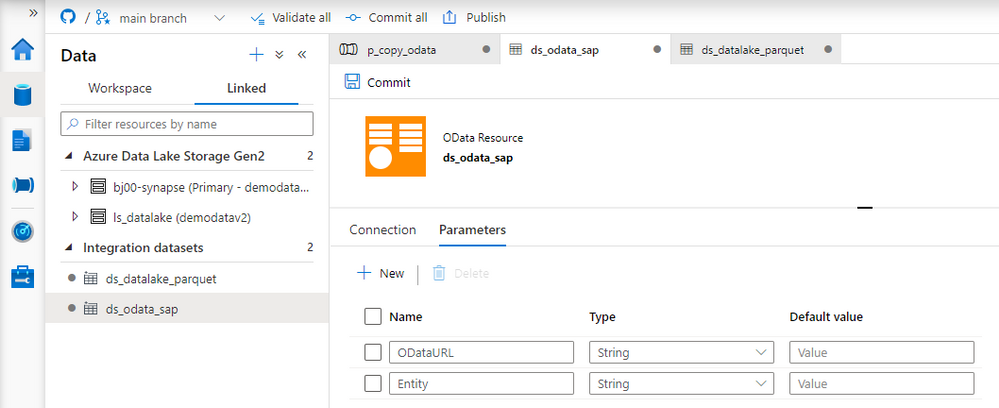
The dataset can use the Entity parameter, which can replace the value in the Path field. But the OData URL parameter has to be passed to the underlying Linked Service. Provide the following expression to the Path field on the Connection tab:
@dataset().Entity
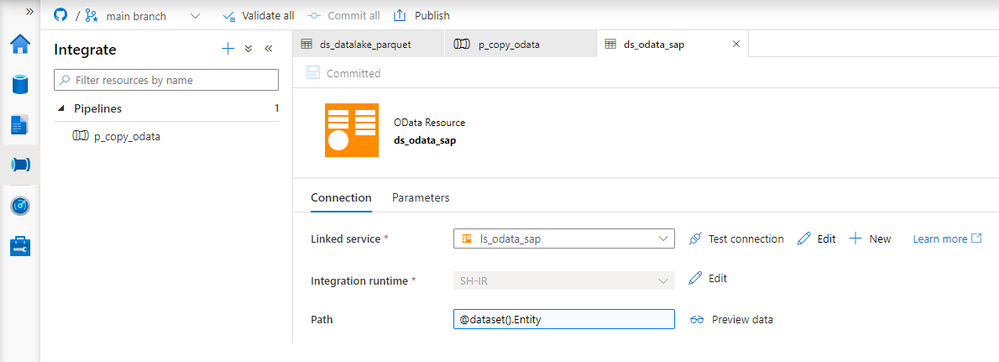
Adding parameters to the Linked Service is slightly more difficult, and it requires modifying the JSON definition of the resource. So far, we’ve only used the user interface. Choose Manage from the left menu and choose Linked Services. To edit the source code of the Linked Service, click the {} icon next to its name:
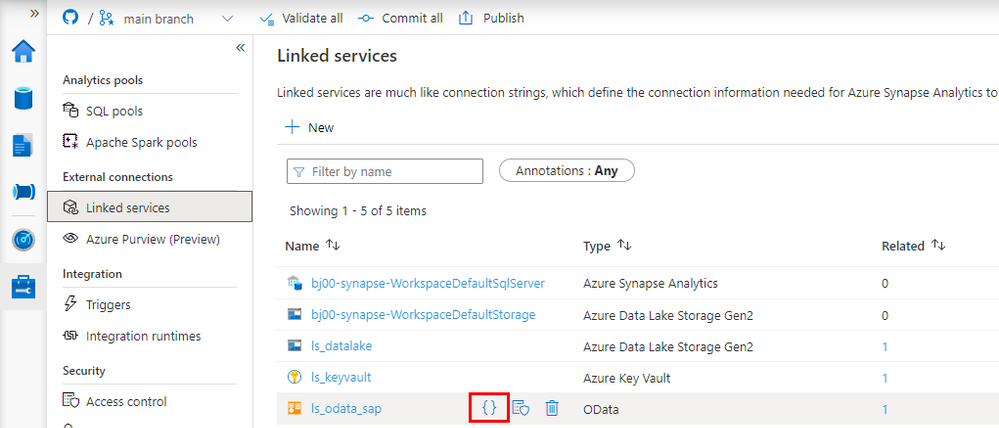
There are two changes to make. The first one is to define the parameter. Enter the following piece of code just under “annotations”:
"parameters": {
"ODataURL": {
"type": "String"
}
},
The second change tells the Linked Service to substitute the URL of the OData service with the value of the ODataURL parameter. Change the value of “url” property with the following expression:
"@{linkedService().ODataURL}"
For reference here is the full definition of the Linked Service:
{
"name": "ls_odata_sap",
"type": "Microsoft.Synapse/workspaces/linkedservices",
"properties": {
"annotations": [],
"parameters": {
"ODataURL": {
"type": "String"
}
},
"type": "OData",
"typeProperties": {
"url": "@{linkedService().ODataURL}",
"authenticationType": "Basic",
"userName": "bjarkowski",
"password": {
"type": "AzureKeyVaultSecret",
"store": {
"referenceName": "ls_keyvault",
"type": "LinkedServiceReference"
},
"secretName": "s4hana"
}
},
"connectVia": {
"referenceName": "SH-IR",
"type": "IntegrationRuntimeReference"
}
}
}
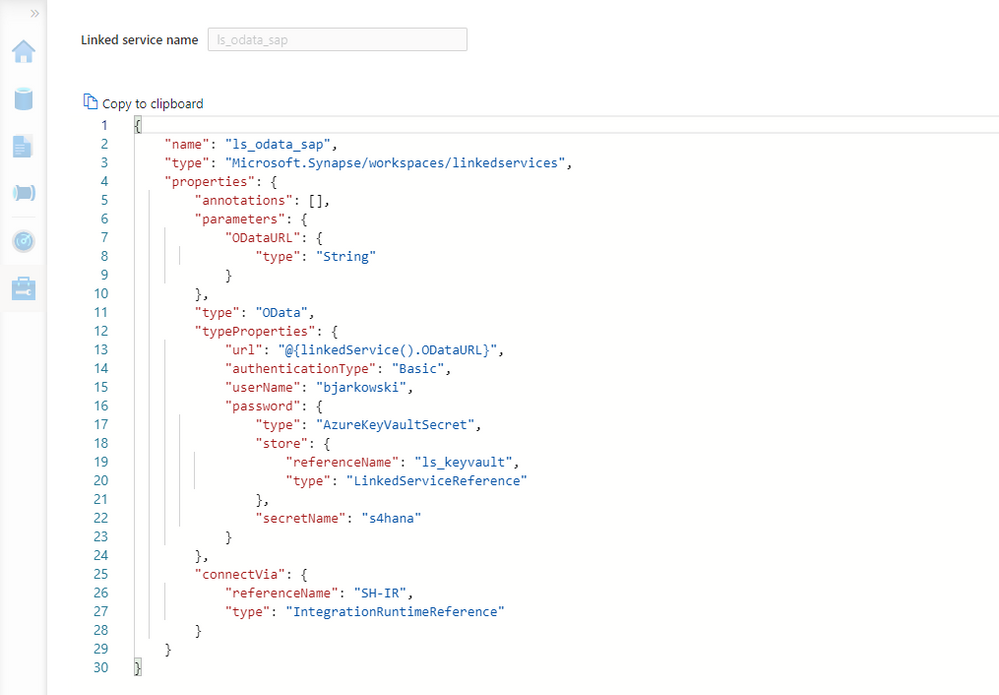
Click Apply to save the settings. When you open the OData dataset you’ll notice the ODataURL parameter waiting for a value. Reference the dataset parameter of the same name:
@dataset().ODataURL
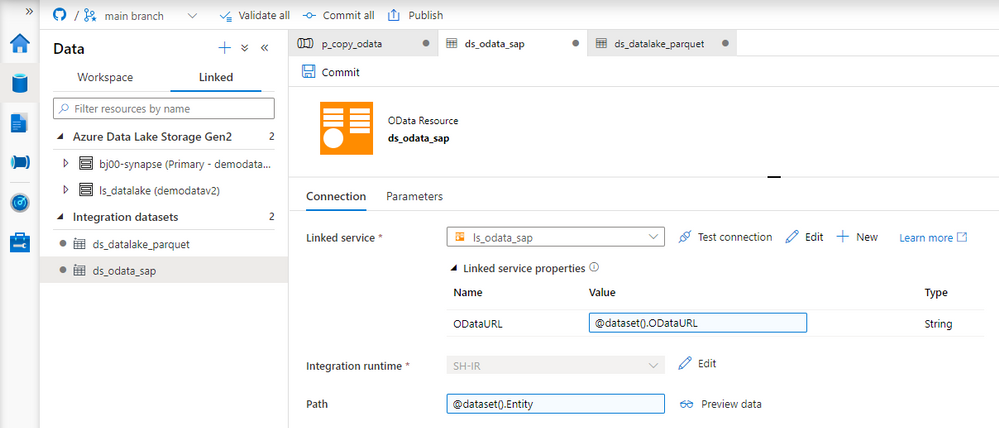
The only thing left to do is to pass a value to both of the dataset parameters. Open the Copy Data activity and go to the Source tab. There are two new fields that we use to pass a value to a dataset. To pass the address of the OData service I concatenate URL and ODataService parameters defined at the pipeline level. The Entity doesn’t require any transformation.
ODataURL: @concat(pipeline().parameters.URL, pipeline().parameters.ODataService)
Entity: @pipeline().parameters.Entity
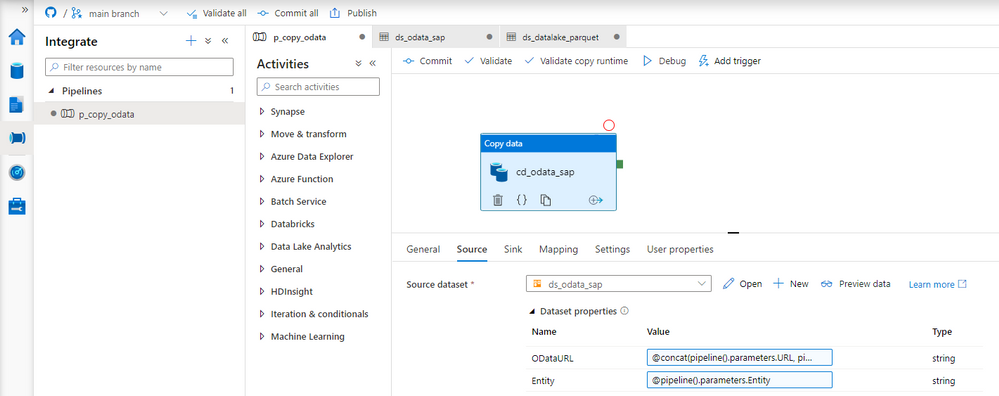
Publish your changes. We’re ready for the test run! We’ve replaced three hardcoded values, and now we don’t have to modify the pipeline, or any of the resources, whenever we want to extract data from another OData service. It is a great improvement as it makes the process more generic and easy to scale.
EXECUTION AND MONITORING
To verify changes, run the pipeline twice, extracting data from two OData services. Previously, it would require us to make changes inside the pipeline. Now, whenever we start the extraction process, Synapse Studio asks us to provide the URL, OData service name and Entity. We’re not making any changes for the first run, and as before, we extract sales orders. For the second execution, use the API_BUSINESS_PARTNER OData service to get the full list of my customers.
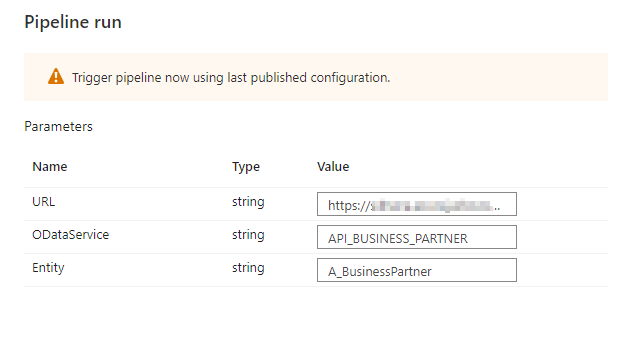
A moment of uncertainty. Have we made all the required changes?
No surprise this time, everything works as expected. We were able to extract data from both OData services. The target directory structure looks correct, and as planned, it consists of the OData and Entity name.
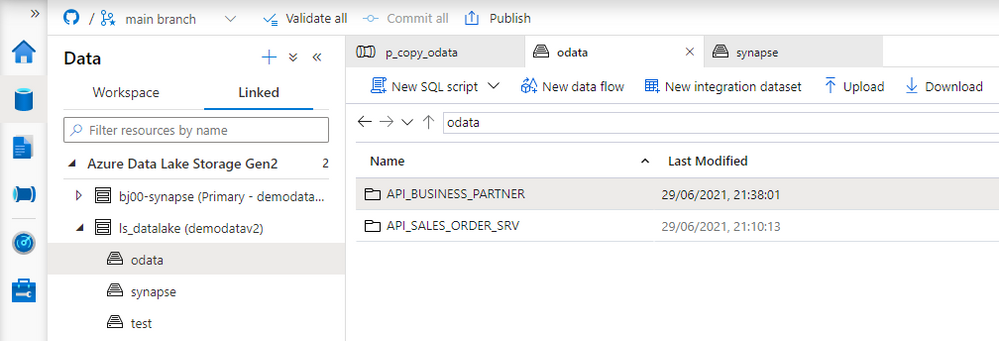
The final test is to display extracted data.
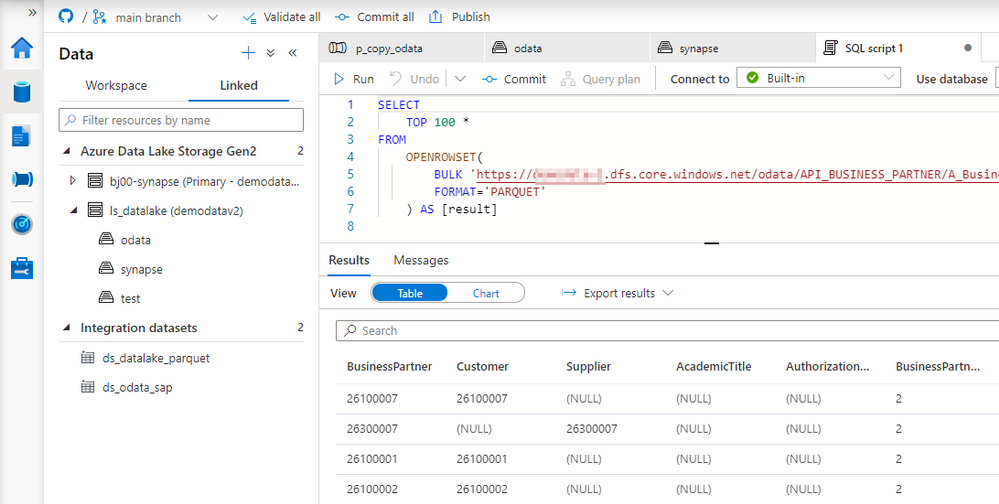
Today you’ve learnt how to use parameters to avoid hardcoding values in the pipeline. We’ve used three parameters that allow us to customize the URL, OData name and the Entity. We will build on top of this next week to make the pipeline even more agile by creating a metadata database that stores all information about OData services to fetch.




















Recent Comments