Today we are excited to announce the new guided tour for Microsoft Dynamics 365 Intelligent Order Management. We are also taking this opportunity to talk about businesses’ need for order management solutions to move beyond the limitations of traditional enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems and keep pace with the fast-changing landscape of e-commerce.
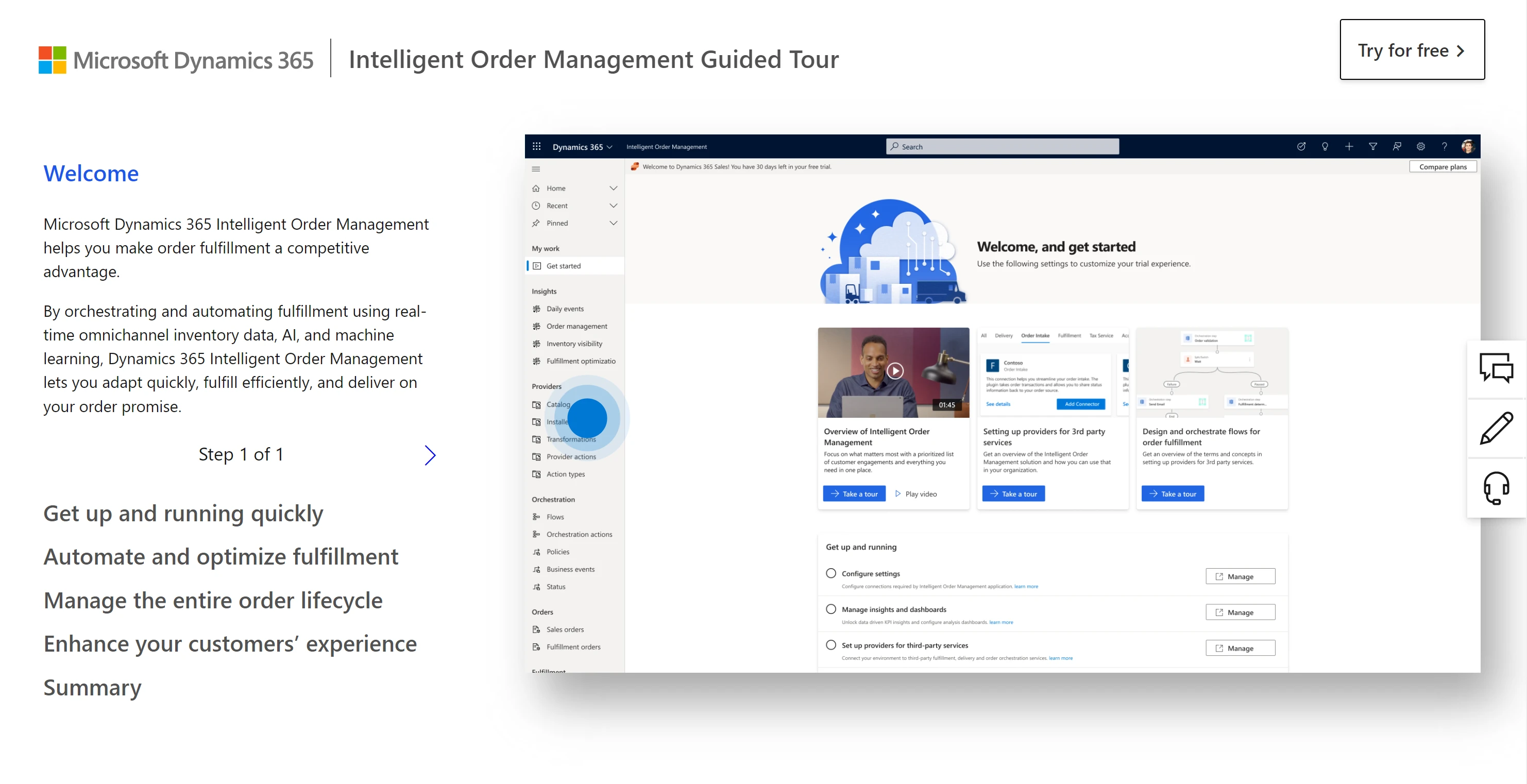
View of one of the steps of Dynamics 365 Intelligent Order Management guided tour.
Moving beyond traditional ERP
An excellent customer experience is a requirement for organizational success in today’s modern business environment. This is particularly true for retailers, distributors, and manufacturers that are embracing direct-to-consumer business models. When it comes to selling, manufacturing, or distributing physical goods, a critical component of providing an excellent customer experience is ensuring that customer orders are shipped On Time and In Full (OTIF), every time.
And more and more companies are realizing that traditional ERP systems lack the adaptability, agility, and resiliency necessary to keep pace with the ever-evolving demands and growing complexity of modern digital commerce. To meet these challenges, forward-thinking organizations have found that order management solutions provide them the required capability to accept orders from anywhere and fulfill them everywhere in a cost-efficient manner. To this end, let’s look at two ways that Dynamics 365 Intelligent Order Management allows businesses to move beyond the limitations of traditional ERP systems.
Faster delivery
The accelerated shift to buying online that accompanied the global pandemic came alongside the trend of consumers demanding shorter delivery times. The result is that for companies interested in selling direct-to-consumer, delivering within two daysif not soonerbecame table stakes. It makes sense then that when McKinsey & Company surveyed apparel, hard goods, and specialty retailers in 2021, they found that the overwhelming majority75 percenthad active plans to build out fulfillment networks that offer two-day or faster delivery times by 2022.1
And this is just one area where traditional ERP systems face challenges and where organizations need advanced solutions to move beyond their limitations. For example, consider that modern digital commerce companies frequently need to add new partners and apps for e-commerce, customer relationship management (CRM), shipping, billing, tax calculations, etc. To be effective this requires an easy-to-deploy solution that integrates with internal and external ecosystems without the need for costly and time-consuming rip and replace processes. Enter Dynamics 365 Intelligent Order Management, a modern, and open platform that allows organizations to overcome supply chain constraints and disruptions, and capitalize seasonal peak volumes.
Composable approach
Gartner predicts that by 2023, organizations that have adopted a composable approach will outpace the competition by 80 percent in the speed of new feature implementation.2 A primary reason for adopting a composable approach is because it provides greater agility and resiliency. Traditional ERP falls short on delivering this agility and resiliency because of their lack of real-time inventory visibility into siloed data. Plus, traditional ERPs don’t have the ability to easily support customized rules for the latest fulfillment methods such as Buy-online, Pickup in-store (BOPIS), and AI and machine learning capabilities.
Dynamics 365 Intelligent Order Management seamlessly works with existing ERPs and supply chain solutions to enhance end-to-end visibility. It enables customers to create an execution-based control tower, suited to companies that must delight customers with accurate, timely fulfillment of frequent orders, perhaps using third-party logistics (3PL) providers.
It uses rules based-fulfillment orchestration and AI-based anomaly detection models to proactively identify and address fulfillment constraints and improve delivery times while reducing costs. This helps accelerate decision-making to mitigate the impact of disruptions. As massive amounts of data are generated across the order management processes, technologies such as AI and machine learning are increasingly necessary because businesses must be able to deliver actionable insights at scale.
Dynamics 365 Intelligent Order Management enables organizations to extend and operate in complex environments, where there are many internal and external supply chain partners. Moreover, it is designed to easily configure order orchestration flows through low-code or no-code interfaces and quickly scale by adding new partners’ connectors to the best-of-breed solutions for e-commerce, shipping, tax calculation, and more.
At this point, it makes sense to conclude that order management systems need to be open and flexible solutions, capable of handling and integrating with multiple order sources and order orchestration applications. In this way, Dynamics 365 Intelligent Order Management is far more flexible than traditional ERPs. It can be used as a started point to build a control tower with this desirable composable approach, as it integrates with existing ERPs, making them much faster and cheaper to customize and support.
In summary, this composable approach is what makes it possible for organizations to connect their existing supply chain systems, enhance these systems with an order management solution, and to integrate all business platforms with new e-commerce, payments, shipping, taxes, and other partners. This is accomplished by using prebuilt connectors to manage the entire order life cycle more efficiently and to provide more organizational agility and resiliency in the process.
Learn more about how to create agile and digital supply chains in this webinar.
What’s next?
We have reviewed some of the areas where Dynamics 365 Intelligent Order Management allows businesses to move beyond the limitations of traditional ERP systems. We invite you to experience a free trial of Dynamics 365 Intelligent Order Management or visit our new guided tour to learn more.
1-McKinsey & Company, Retail’s need for speed: Unlocking value in omnichannel delivery, September 2021.
2-Gartner, Composable Commerce Must Be Adopted for the Future of Applications, June 2020. GARTNER is a registered trademark and service mark of Gartner Inc., in the U.S. and internationally, and is used herein with permission. All rights reserved.
The post Dynamics 365 Intelligent Order Management launches new guided tour appeared first on Microsoft Dynamics 365 Blog.
Brought to you by Dr. Ware, Microsoft Office 365 Silver Partner, Charleston SC.







Recent Comments