by Contributed | Jun 23, 2021 | Technology
This article is contributed. See the original author and article here.
Create Bespoke Chart Designs without Programming, Charticulator requires the use of a mouse or touch screen and is compatible with Microsoft Edge, Google Chrome, and Mozilla Firefox. Free and Open Source from Microsoft Research
Interested in trying Charticulator try it online at Launch Charticulator
Interactive Chart Creation
Charticulator enables you to create bespoke and reusable chart layouts without writing any code.

Infinite Design Possibilities
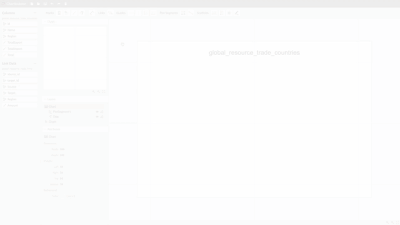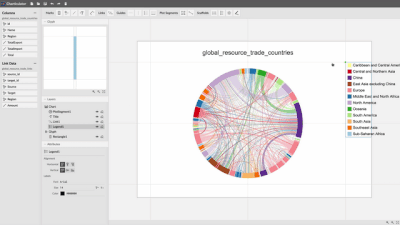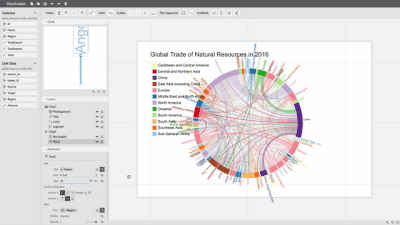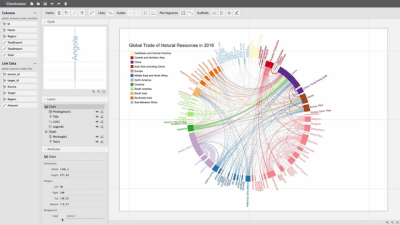
Charticulator enables you to compose a wide range of visual representations.
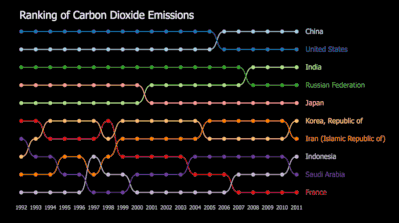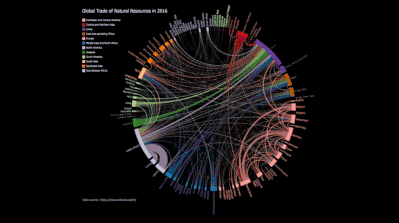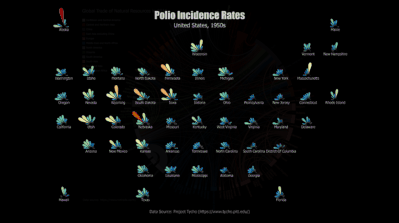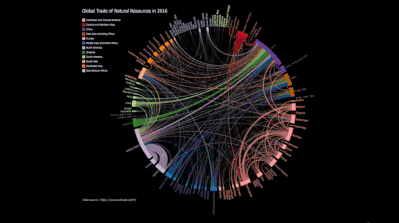
Reusable Chart Designs
Charticulator lets you export chart designs into reusable templates including Microsoft Power BI custom visuals.
What people say about Charticulator
The Charticulator – an amazing way to generate totally new/original/amazing custom visuals for Power BI without writing a single line of code. Fantastic work by the folks at Microsoft Research here.— Amir Netz (Technical Fellow at Microsoft, CTO of Power BI & Intelligence Platform)
See more examples in the Charticulator gallery.
Follow along with these step-by-step video tutorials as you learn how to use Charticulator.
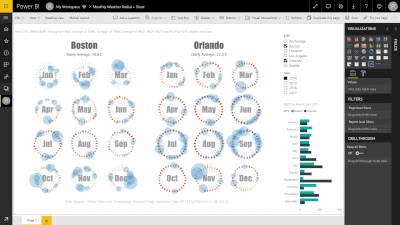
- Radial Bar Chart
- Mobile OS Market Share
- Character Co-occurrence in Les Misearbles
- 200 Samples of Mushrooms
- Boston Weather in a Year
- Fertility Rate v.s. Life Expectancy
- Monthly Weather Radial as a Charticulator Template
- Power BI Custom visual
- Bar Chart with Error Bars
- Daily Weather for Four Cities
- Gender Earnings Disparity
Chart Templates
There are also lots of available chart templates including
by Contributed | Jun 22, 2021 | Technology
This article is contributed. See the original author and article here.
The June 2021 Windows 10 Security update (KB5003637) includes a pre-requisite for the Servicing Stack Update which is included in the May 2021 Windows 10 Security Update (KB5003173). If you use Microsoft Endpoint Configuration Manager with Windows Server Update Services (WSUS) to manage and deploy your monthly cumulative updates, you must install the May 11, 2021 update (KB5003173) before you can install the latest cumulative update.
Because the June 2021 security update supersedes the May 2021 security update, it is possible that the May 2021 security update is no longer deployable in your Configuration Manager environment if you have changed the supersedence rule from the default. This could impact your ability to meet the pre-requisites for the June 2021 security update.
Workarounds
The May 2021 Windows 10 Security Update is not yet expired: To prevent the May 2021 security update from being marked as expired before all your devices are updated, ensure that the supersedence rule’s “Months to wait before a superseded software update is expired” setting is set to the default of 3 months, or to an interval long enough to get the update installed on all required devices.
The May 2021 Windows 10 Security Update has already been expired: If you still need to deploy the May 2021 security update and it has been marked as expired, follow the directions in Supersedence and Expired Software Updates to recover an expired update.
TIP: Use the Software updates deployment re-evaluation behavior upon restart user experience setting. Select this setting to configure software updates deployments to have clients run a software updates compliance scan immediately after a client installs software updates and restarts. This enables the client to check for additional updates that become applicable after the client restarts, then installs them during the same maintenance window. This setting could reduce potential delays between the May 2021 security update install and the June 2021 security update being returned as applicable and installed. By default, software update deployments are reevaluated every 7 days. |
by Contributed | Jun 22, 2021 | Technology
This article is contributed. See the original author and article here.
Typically, a software update that supersedes another software update does one or more of the following actions:
- Enhances, improves, or updates the fix that was provided by one or more previously released updates.
- Improves the efficiency of the superseded update file package, which is installed on clients if the update is approved for installation. For example, the superseded update might contain files that are no longer relevant to the fix or to the operating systems that are supported by the new update. Those files aren’t included in the superseding file package of the update.
- Updates newer versions of a product. In other words, it updates versions that are no longer applicable to older versions or configurations of a product. Updates can also supersede other updates if modifications were made to expand language support. For example, a later revision of a product update for Microsoft 365 Apps might remove the support for an older OS, but it might add additional support for new languages in the initial update release.
Consider the following scenarios in which you might need to deploy a superseded software update:
- A superseding software update supports only newer versions of an OS. Some of your client computers run earlier versions of the OS.
- A superseding software update has more restricted applicability than the software update it supersedes. This behavior would make it inappropriate for some clients.
- If a superseding software update wasn’t approved for deployment in your production environment.
Microsoft Endpoint Configuration Manager current branch provides control for how superseded software updates are handled. Supersedence rules allow you to decide if superseded software updates are immediately expired or expired after a defined period. “Expired” software updates in the context of Configuration Manager are no longer deployable. They can’t be added to new deployments and will also be removed from any existing deployments.
Supersedence rules default to waiting 3 months before superseded updates are expired. It is recommended that you do not assume that superseded updates should be immediately expired in favor of the new, superseding updates. As noted above, there is no guarantee that supersedence is absolute. You should allow enough time to make sure superseded updates are no longer needed by any of your client computers.
Recovering an Expired Update
If you need to deploy a superseded update that has been marked as expired in Configuration Manager, follow the steps below.
- Change the Months to wait before a superseded software update is expired value on the Supersedence Rules tab of the Software Update Point Component properties page, to an interval that is greater than the supersedence age for the update. For example, if the update marked as expired was superseded six months ago, the months to wait interval would need to be greater than six months.
NOTE: If the “Decline expired updates in WSUS according to supersedence rules” option is enabled, the software update(s) may need to be reinstated prior to synchronizing software updates. Also, the interval change is global, meaning any expired update meeting the changed criteria could result in a state change, not just the desired software update(s). |
- Synchronize software updates (scheduled or manual). See Synchronize software updates for more information.
References
Supersedence Rules
Expired Icon
Superseded Icon
by Contributed | Jun 22, 2021 | Technology
This article is contributed. See the original author and article here.
We are currently performing updates to the Hardware Dev Center (HDC). As part of this effort, it is vital that you update/complete your HDC Profile to keep your account active. To keep your HDC account active, you must update/complete your HDC profile by July 2, 2021. Please ensure that the following information is up to date:
- Business name
- Address
- Contact phone
- Email
Even if there are no changes to this information, you must validate the profile settings in HDC to maintain your program access. Remember that HDC access is needed to submit drivers, devices and systems for signing or certification.
To update your HDC Partner Profile:
- Log in to the Microsoft Partner Center Dashboard using the AAD Global Admin account (or account with Global Admin AAD Role assigned).
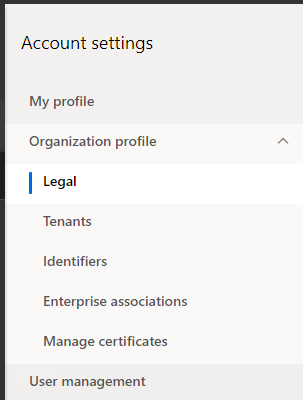
- Click on the “Gear” Icon in the upper right-hand corner of the screen.
- Then click on “Account Settings”.

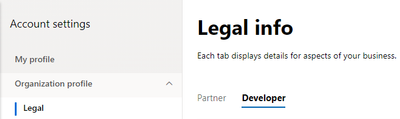
- Click “Organization Profile”, and then click on “Legal”.
- On the “Legal info” page you will see two tabs, Partner and Developer.
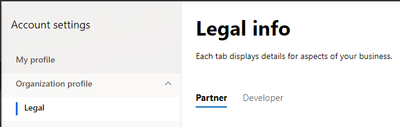
- Click the “Partner” tab and ensure that the information under “Legal business profile” is complete, and correct. If any fields are blank, or any information needs to be updated.
- Under “Contact info”, ensure that all fields are completed with accurate contact information for the person in your organization that is responsible for your Partner Center registration.
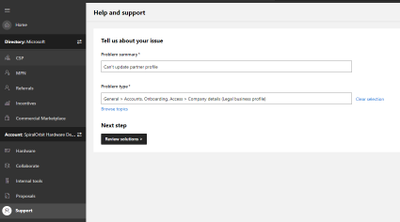
- If you are unable to update your profile information, please open a ticket with Partner Center support.
- Click on the “Support” button. Under “Problem summary” enter “Can’t update partner profile”. Under “Problem type” select “General > Accounts, Onboarding, Access > Company details (legal business profile)”
Thank you for your help in maintaining the Hardware Dev Center! We appreciate your prompt attention to this matter.

by Jenna Restuccia | Jun 22, 2021 | ADA Compliance, American Sign Language
The Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) is a federal law that U.S. Congress enacted and signed into law in July of 1990 and has since expanded. The Act protects individuals with disabilities who work and seek employment within the United States.
The Act’s purpose is to ensure that ALL employees companies are provided with reasonable accommodation to perform their jobs. For instance, companies may require at least one translator (or interpreter) to translate English into Sing Language and vice versa. An interpreter is especially critical in specific fields such as engineering or medicine because of the specialized nature of the information needed. If an employee or client cannot comprehend communications, they will have a hard time understanding crucial information involved in the workplace. These misunderstandings can mean someone’s life in medical settings and someone’s future on legal grounds.
The ADA ensures that individuals with disabilities are given the same opportunity for employment as other individuals. Any individual with a disability who experiences discrimination can use the ADA law for protection in court.
What are some of the steps that a business owner can take to ensure that they comply with the ADA? Business organizations must register with the Department of Labor. Once they become registered, they are required to undergo many tests and monitoring procedures to ensure compliance. Managers and employees should also begin by undergoing cultural competency training and awareness presentations.












Recent Comments