
by Contributed | Nov 29, 2021 | Technology
This article is contributed. See the original author and article here.
Building fast, fluid Microsoft 365 web applications is one of our core focus areas on the SharePoint engineering team. Over the course of this year, we’ve double-downed on performance – making our web apps load faster, delivering up to a 57% improvement in page interactivity, along with the ability to work with data offline. We’re pleased to announce we’ve reached general availability for Microsoft Lists customers. The focus of this article is to share how it all works and how we went about designing and developing it.
 We’re pleased to announce that we’ve reached general availability for Microsoft Lists: Fast and offline.
We’re pleased to announce that we’ve reached general availability for Microsoft Lists: Fast and offline.
And we didn’t stop there. Our ambition is to deliver experiences that are consistently fast for every user on all kinds of networks and devices – even when there is no connection to the Internet. To help us accomplish this, we looked beyond the fundamentals to unlock new levels of web performance and enable new ways for our customers to experience Microsoft 365 web applications. We do this by blending Progressive Web Apps (PWAs) and expanding Project Nucleus.
 The combination of Progressive Web Apps (PWAs) and the expansion of Project Nucleus enables faster Web applications – even when offline.
The combination of Progressive Web Apps (PWAs) and the expansion of Project Nucleus enables faster Web applications – even when offline.
Transforming Microsoft 365 apps into PWAs
As part of our ongoing effort to improve performance and design new experiences, we began transforming our web applications into Progressive Web Apps (PWAs) starting with Microsoft Lists and OneDrive.
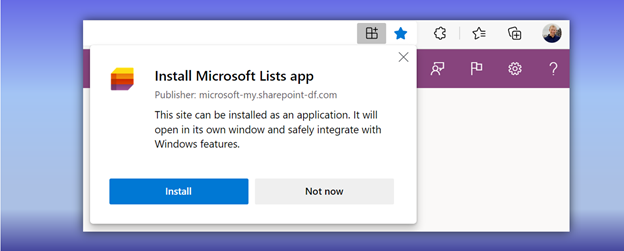 Install Microsoft Lists as a Progressive Web Apps (PWA) from your browser.
Install Microsoft Lists as a Progressive Web Apps (PWA) from your browser.
PWAs allow us to provide access to open web technologies for cross-platform interoperability. And in turn, you get an app-like experience customized for your devices. They are websites progressively enhanced to function like installed apps. PWAs allow us to combine the best of the web and native apps, like websites with app features: The ability to load offline, run within the local operating system, support push notifications and periodic background updates, access hardware features, and more.
When installed, PWAs are just like other apps on Windows. They can be added to the Start Menu, pinned to the Taskbar, work with files, run on user login, and more.
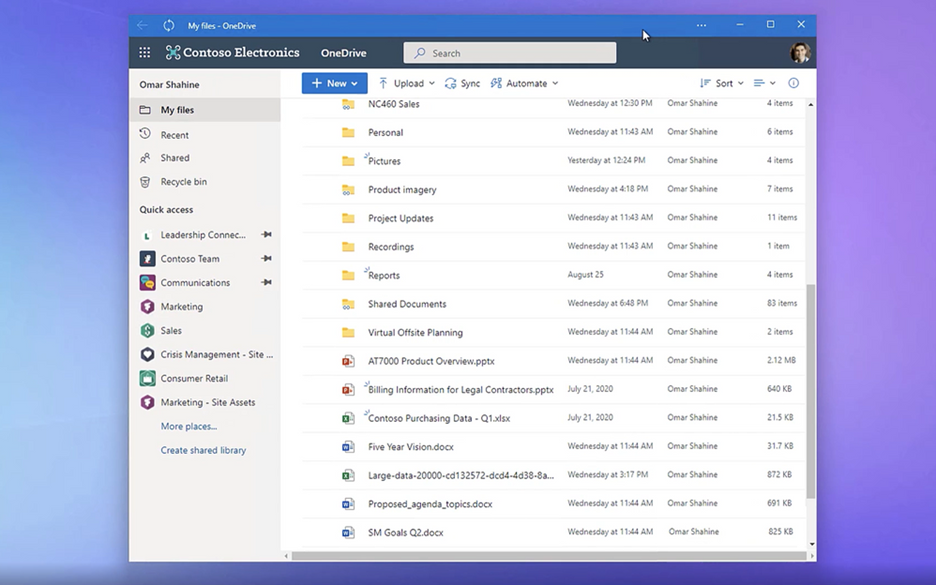 OneDrive as a PWA running on the Windows desktop.
OneDrive as a PWA running on the Windows desktop.
To build web experiences that load and function offline – including support for editing – we had to look beyond PWAs. Enter Project Nucleus.
It all started as ‘Project Nucleus’
Project Nucleus was the codename behind our initiative of building a new client-side component to supercharge existing web apps, like Microsoft Lists, by providing a consistently fast and smooth experience on all kinds of devices and networks – again, even working when offline.
By leveraging local storage for fast data retrieval, it also enables our customers to seamlessly work with large and complex datasets made available through our web apps, like Lists with hundreds or thousands of rows. Operations on web app data, like sort and filter, are blazing fast because they occur on the local device. All offline changes synchronize back to the cloud once reconnected to the Internet.
Behind Project Nucleus is Microsoft.SharePoint.exe, a new component delivered alongside OneDrive sync – leveraging the existing OneDrive install and update mechanism. Once installed, it links with the web app by making a smart cache of web app data on the local device. It then acts as a local web server by pulling and pushing data to and from that local cache, instead of the web app always retrieving it from the cloud. This enables offline editing; changes to content occur within the local cache first and then get pushed to the cloud once connection is restored. The result helps save on network bandwidth and eliminate bottlenecks, too.
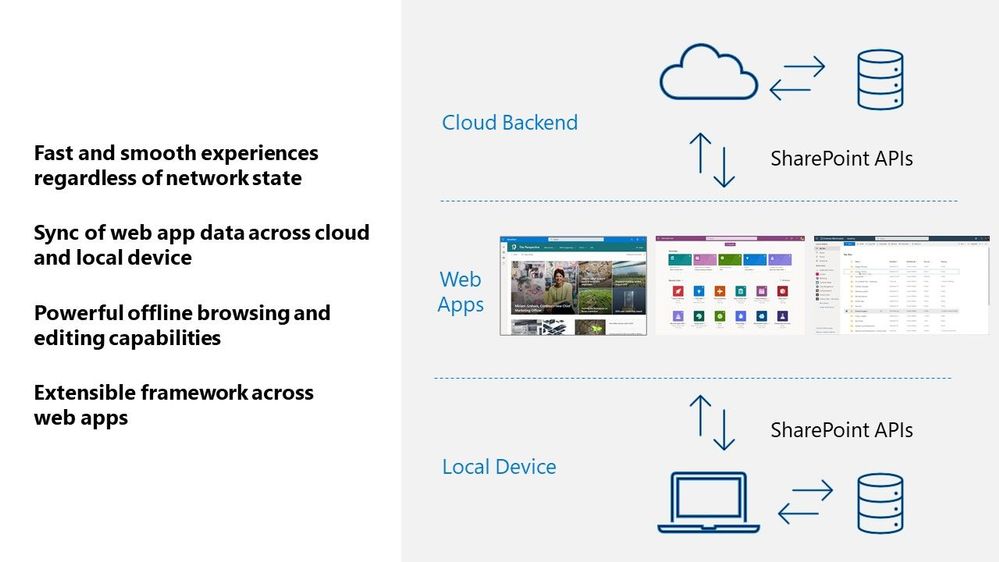 A visual diagram showing how web apps interact across your local Windows device and cloud services in Microsoft 365.
A visual diagram showing how web apps interact across your local Windows device and cloud services in Microsoft 365.
Microsoft Lists is our first web application that leverages these new capabilities. First, it means you can load the Lists app to view and edit list data whether your online or offline. Second, loading and interacting with lists gets supercharged in all modalities. Finally, views inside synced lists never get throttled – regardless of the number of items in the view or whether those columns are indexed.
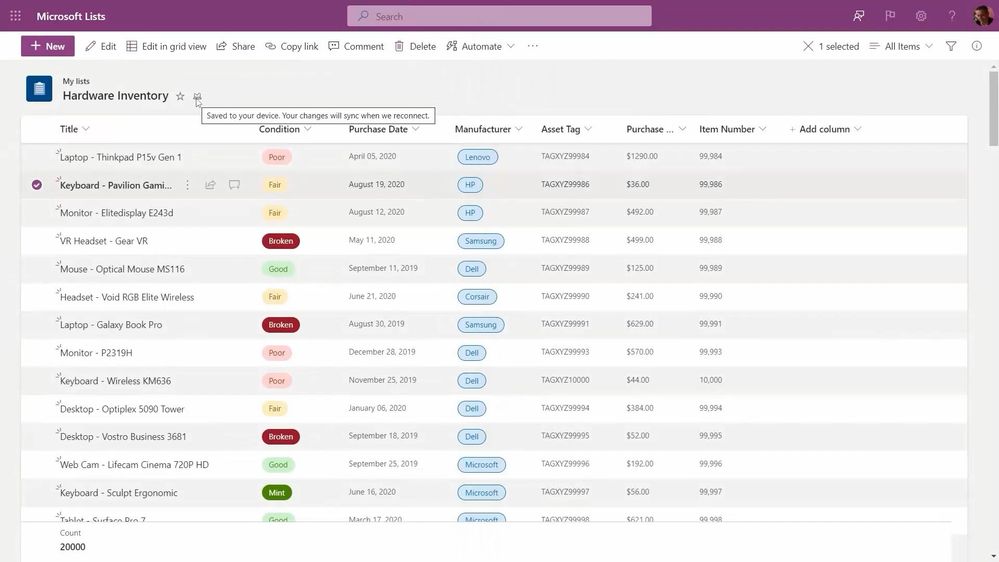 New Lists indicators show when your items are being save to your device (offline; as shown above), when the list is synchronizing, and when all is up to date (synced).
New Lists indicators show when your items are being save to your device (offline; as shown above), when the list is synchronizing, and when all is up to date (synced).
Moving forward…
In short, your lists are always on, lightning fast, and less impacted by service-imposed limitations. This is where we start, and we plan to bring these benefits to other web apps over time. Stay tuned – online or offline – for future updates in this space.
Learn more about Progressive Web Apps, including ‘how to’ information for end users. Review all Microsoft Lists new from Microsoft Ignite – including the general availability announcement for Microsoft Lists: Fast and offline [Roadmap ID: 68809]. We have a new end-user ‘how to’ edit lists offline. And admins can review policies to control Lists sync settings.
Take a peek at the technology in action from the related Microsoft Ignite session, “What’s new with Microsoft Lists” (published on November 2nd, 2021 – jump to 13:30 to see the “Fast and offline access to list data” segment):
Thanks for your time to learn more, Andrey Esipov – Principal program manager, Microsoft
by Scott Muniz | Nov 29, 2021 | Security, Technology
This article is contributed. See the original author and article here.
| xen — xen |
guests may exceed their designated memory limit When a guest is permitted to have close to 16TiB of memory, it may be able to issue hypercalls to increase its memory allocation beyond the administrator established limit. This is a result of a calculation done with 32-bit precision, which may overflow. It would then only be the overflowed (and hence small) number which gets compared against the established upper bound. |
2021-11-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-28706
MISC |
afreecatv — afreecatv
|
The vulnerability function is enabled when the streamer service related to the AfreecaTV communicated through web socket using 21201 port. A stack-based buffer overflow leading to remote code execution was discovered in strcpy() operate by “FanTicket” field. It is because of stored data without validation of length. |
2021-11-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-7881
MISC |
| aim — aim |
Aim is an open-source, self-hosted machine learning experiment tracking tool. Versions of Aim prior to 3.1.0 are vulnerable to a path traversal attack. By manipulating variables that reference files with “dot-dot-slash (../)� sequences and its variations or by using absolute file paths, it may be possible to access arbitrary files and directories stored on file system including application source code or configuration and critical system files. The vulnerability issue is resolved in Aim v3.1.0. |
2021-11-23 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-43775
MISC
CONFIRM
MISC
MISC
MISC |
| alfasado_inc — powercms |
PowerCMS XMLRPC API of PowerCMS 5.19 and earlier, PowerCMS 4.49 and earlier, PowerCMS 3.295 and earlier, and PowerCMS 2 Series (End-of-Life, EOL) allows a remote attacker to execute an arbitrary OS command via unspecified vectors. |
2021-11-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-20850
MISC
MISC |
| amazon_web_service — iot_devices |
Connections initialized by the AWS IoT Device SDK v2 for Java (versions prior to 1.4.2), Python (versions prior to 1.6.1), C++ (versions prior to 1.12.7) and Node.js (versions prior to 1.5.3) did not verify server certificate hostname during TLS handshake when overriding Certificate Authorities (CA) in their trust stores on MacOS. This issue has been addressed in aws-c-io submodule versions 0.10.5 onward. This issue affects: Amazon Web Services AWS IoT Device SDK v2 for Java versions prior to 1.4.2 on macOS. Amazon Web Services AWS IoT Device SDK v2 for Python versions prior to 1.6.1 on macOS. Amazon Web Services AWS IoT Device SDK v2 for C++ versions prior to 1.12.7 on macOS. Amazon Web Services AWS IoT Device SDK v2 for Node.js versions prior to 1.5.3 on macOS. Amazon Web Services AWS-C-IO 0.10.4 on macOS. |
2021-11-23 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-40829
MISC
MISC
MISC
MISC
MISC |
| amazon_web_service — iot_devices |
The AWS IoT Device SDK v2 for Java, Python, C++ and Node.js appends a user supplied Certificate Authority (CA) to the root CAs instead of overriding it on Unix systems. TLS handshakes will thus succeed if the peer can be verified either from the user-supplied CA or the system’s default trust-store. Attackers with access to a host’s trust stores or are able to compromise a certificate authority already in the host’s trust store (note: the attacker must also be able to spoof DNS in this case) may be able to use this issue to bypass CA pinning. An attacker could then spoof the MQTT broker, and either drop traffic and/or respond with the attacker’s data, but they would not be able to forward this data on to the MQTT broker because the attacker would still need the user’s private keys to authenticate against the MQTT broker. The ‘aws_tls_ctx_options_override_default_trust_store_*’ function within the aws-c-io submodule has been updated to override the default trust store. This corrects this issue. This issue affects: Amazon Web Services AWS IoT Device SDK v2 for Java versions prior to 1.5.0 on Linux/Unix. Amazon Web Services AWS IoT Device SDK v2 for Python versions prior to 1.6.1 on Linux/Unix. Amazon Web Services AWS IoT Device SDK v2 for C++ versions prior to 1.12.7 on Linux/Unix. Amazon Web Services AWS IoT Device SDK v2 for Node.js versions prior to 1.5.3 on Linux/Unix. Amazon Web Services AWS-C-IO 0.10.4 on Linux/Unix. |
2021-11-23 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-40830
MISC
MISC
MISC
MISC
MISC |
| amazon_web_service — iot_devices |
The AWS IoT Device SDK v2 for Java, Python, C++ and Node.js appends a user supplied Certificate Authority (CA) to the root CAs instead of overriding it on macOS systems. Additionally, SNI validation is also not enabled when the CA has been “overridden”. TLS handshakes will thus succeed if the peer can be verified either from the user-supplied CA or the system’s default trust-store. Attackers with access to a host’s trust stores or are able to compromise a certificate authority already in the host’s trust store (note: the attacker must also be able to spoof DNS in this case) may be able to use this issue to bypass CA pinning. An attacker could then spoof the MQTT broker, and either drop traffic and/or respond with the attacker’s data, but they would not be able to forward this data on to the MQTT broker because the attacker would still need the user’s private keys to authenticate against the MQTT broker. The ‘aws_tls_ctx_options_override_default_trust_store_*’ function within the aws-c-io submodule has been updated to address this behavior. This issue affects: Amazon Web Services AWS IoT Device SDK v2 for Java versions prior to 1.5.0 on macOS. Amazon Web Services AWS IoT Device SDK v2 for Python versions prior to 1.7.0 on macOS. Amazon Web Services AWS IoT Device SDK v2 for C++ versions prior to 1.14.0 on macOS. Amazon Web Services AWS IoT Device SDK v2 for Node.js versions prior to 1.6.0 on macOS. Amazon Web Services AWS-C-IO 0.10.7 on macOS. |
2021-11-23 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-40831
MISC
MISC
MISC
MISC
MISC |
amazon_web_service — iot_devices
|
Connections initialized by the AWS IoT Device SDK v2 for Java (versions prior to 1.3.3), Python (versions prior to 1.5.18), C++ (versions prior to 1.12.7) and Node.js (versions prior to 1.5.1) did not verify server certificate hostname during TLS handshake when overriding Certificate Authorities (CA) in their trust stores on Windows. This issue has been addressed in aws-c-io submodule versions 0.9.13 onward. This issue affects: Amazon Web Services AWS IoT Device SDK v2 for Java versions prior to 1.3.3 on Microsoft Windows. Amazon Web Services AWS IoT Device SDK v2 for Python versions prior to 1.5.18 on Microsoft Windows. Amazon Web Services AWS IoT Device SDK v2 for C++ versions prior to 1.12.7 on Microsoft Windows. Amazon Web Services AWS IoT Device SDK v2 for Node.js versions prior to 1.5.3 on Microsoft Windows. |
2021-11-23 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-40828
MISC
MISC
MISC
MISC
MISC |
apache — jspwiki
|
Remote attackers may delete arbitrary files in a system hosting a JSPWiki instance, versions up to 2.11.0.M8, by using a carefuly crafted http request on logout, given that those files are reachable to the user running the JSPWiki instance. Apache JSPWiki users should upgrade to 2.11.0 or later. |
2021-11-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-44140
MISC
MISC |
apache — jspwiki
|
A carefully crafted plugin link invocation could trigger an XSS vulnerability on Apache JSPWiki, related to the Denounce plugin, which could allow the attacker to execute javascript in the victim’s browser and get some sensitive information about the victim. Apache JSPWiki users should upgrade to 2.11.0 or later. |
2021-11-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-40369
MISC
MISC |
backstage — backstage
|
Backstage is an open platform for building developer portals. In affected versions the auth-backend plugin allows a malicious actor to trick another user into visiting a vulnerable URL that executes an XSS attack. This attack can potentially allow the attacker to exfiltrate access tokens or other secrets from the user’s browser. The default CSP does prevent this attack, but it is expected that some deployments have these policies disabled due to incompatibilities. This is vulnerability is patched in version `0.4.9` of `@backstage/plugin-auth-backend`. |
2021-11-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-43776
CONFIRM
MISC |
barcode — barcode
|
Barcode is a GLPI plugin for printing barcodes and QR codes. GLPI instances version 2.x prior to version 2.6.1 with the barcode plugin installed are vulnerable to a path traversal vulnerability. This issue was patched in version 2.6.1. As a workaround, delete the `front/send.php` file. |
2021-11-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-43778
CONFIRM
MISC
MISC
MISC |
| basercms — basercms |
BaserCMS is an open source content management system with a focus on Japanese language support. In affected versions users with upload privilege may upload crafted zip files capable of path traversal on the host operating system. This is a vulnerability that needs to be addressed when the management system is used by an unspecified number of users. If you are eligible, please update to the new version as soon as possible. |
2021-11-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-41279
CONFIRM
MISC |
basercms — basercms
|
There is a Potential Zip Slip Vulnerability and OS Command Injection Vulnerability on the management system of baserCMS. Users with permissions to upload files may upload crafted zip files which may execute arbitrary commands on the host operating system. This is a vulnerability that needs to be addressed when the management system is used by an unspecified number of users. If you are eligible, please update to the new version as soon as possible. |
2021-11-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-41243
CONFIRM
MISC |
bitdefender — endpoint_security_tools
|
A Server-Side Request Forgery (SSRF) vulnerability in the EPPUpdateService component of Bitdefender Endpoint Security Tools allows an attacker to proxy requests to the relay server. This issue affects: Bitdefender Endpoint Security Tools versions prior to 6.6.27.390; versions prior to 7.1.2.33. Bitdefender GravityZone 6.24.1-1. |
2021-11-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-3552
MISC |
bitdefender — endpoint_security_tools
|
Improper Access Control vulnerability in the patchesUpdate API as implemented in Bitdefender Endpoint Security Tools for Linux as a relay role allows an attacker to manipulate the remote address used for pulling patches. This issue affects: Bitdefender Endpoint Security Tools for Linux versions prior to 6.6.27.390; versions prior to 7.1.2.33. Bitdefender Unified Endpoint versions prior to 6.2.21.160. Bitdefender GravityZone versions prior to 6.24.1-1. |
2021-11-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-3554
MISC |
bitdefender — endpoint_security_tools
|
A Server-Side Request Forgery (SSRF) vulnerability in the EPPUpdateService of Bitdefender Endpoint Security Tools allows an attacker to use the Endpoint Protection relay as a proxy for any remote host. This issue affects: Bitdefender Endpoint Security Tools versions prior to 6.6.27.390; versions prior to 7.1.2.33. Bitdefender Unified Endpoint for Linux versions prior to 6.2.21.160. Bitdefender GravityZone versions prior to 6.24.1-1. |
2021-11-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-3553
MISC |
d-link — dwr-932c
|
Missing Authentication for Critical Function vulnerability in debug_post_set.cgi of D-Link DWR-932C E1 firmware allows an unauthenticated attacker to execute administrative actions. |
2021-11-23 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-42783
MISC |
d-link — dwr-932c
|
OS Command Injection vulnerability in debug_fcgi of D-Link DWR-932C E1 firmware allows a remote attacker to perform command injection via a crafted HTTP request. |
2021-11-23 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-42784
MISC |
dell — idrac
|
Dell iDRAC 9 prior to version 4.40.40.00 and iDRAC 8 prior to version 2.80.80.80 contain a Stack Buffer Overflow in Racadm. An authenticated remote attacker may potentially exploit this vulnerability to control process execution and gain access to the underlying operating system. |
2021-11-23 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-36301
CONFIRM |
django — django-wiki
|
In Django-wiki, versions 0.0.20 to 0.7.8 are vulnerable to Stored Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) in Notifications Section. An attacker who has access to edit pages can inject JavaScript payload in the title field. When a victim gets a notification regarding the changes made in the application, the payload in the notification panel renders and loads external JavaScript. |
2021-11-23 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-25986
CONFIRM
MISC |
f-secure — f-secure
|
A vulnerability affecting F-Secure antivirus engine was discovered whereby unpacking UPX file can lead to denial-of-service. The vulnerability can be exploited remotely by an attacker. A successful attack will result in denial-of-service of the antivirus engine. |
2021-11-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-40833
MISC
MISC |
gin-vue-admin — gin-vue-admin
|
Gin-Vue-Admin before 2.4.6 mishandles a SQL database. |
2021-11-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-44219
MISC
MISC |
hejhome — gwk-ic052
|
HejHome GKW-IC052 IP Camera contained a hard-coded credentials vulnerability. This issue allows remote attackers to operate the IP Camera.(reboot, factory reset, snapshot etc..) |
2021-11-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-26611
MISC |
hitachi — multiple_devices
|
Improper Input Validation vulnerability in the APDU parser in the Bidirectional Communication Interface (BCI) IEC 60870-5-104 function of Hitachi Energy RTU500 series allows an attacker to cause the receiving RTU500 CMU of which the BCI is enabled to reboot when receiving a specially crafted message. By default, BCI IEC 60870-5-104 function is disabled (not configured). This issue affects: Hitachi Energy RTU500 series CMU Firmware version 12.0.* (all versions); CMU Firmware version 12.2.* (all versions); CMU Firmware version 12.4.* (all versions). |
2021-11-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-35533
CONFIRM |
huawei — multiple_products
|
There is a weak secure algorithm vulnerability in Huawei products. A weak secure algorithm is used in a module. Attackers can exploit this vulnerability by capturing and analyzing the messages between devices to obtain information. This can lead to information leak.Affected product versions include: IPS Module V500R005C00SPC100, V500R005C00SPC200; NGFW Module V500R005C00SPC100, V500R005C00SPC200; Secospace USG6300 V500R001C30SPC200, V500R001C30SPC600, V500R001C60SPC500, V500R005C00SPC100, V500R005C00SPC200; Secospace USG6500 V500R001C30SPC200, V500R001C30SPC600, V500R001C60SPC500, V500R005C00SPC100, V500R005C00SPC200; Secospace USG6600 V500R001C30SPC200, V500R001C30SPC600, V500R001C60SPC500, V500R005C00SPC100, V500R005C00SPC200; USG9500 V500R001C30SPC200, V500R001C30SPC600, V500R001C60SPC500, V500R005C00SPC100, V500R005C00SPC200. |
2021-11-23 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-22356
MISC |
| huawei — smartphones |
There is an Improper permission vulnerability in Huawei Smartphone.Successful exploitation of this vulnerability may affect service availability. |
2021-11-23 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-37030
MISC |
| huawei — smartphones |
There is an Identity verification vulnerability in Huawei Smartphone.Successful exploitation of this vulnerability may affect service availability. |
2021-11-23 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-37029
MISC |
| huawei — smartphones |
There is a Improper Input Validation vulnerability in Huawei Smartphone.Successful exploitation of this vulnerability will cause kernel crash. |
2021-11-23 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-37026
MISC |
| huawei — smartphones |
There is a Improper Input Validation vulnerability in Huawei Smartphone.Successful exploitation of this vulnerability will cause kernel crash. |
2021-11-23 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-37025
MISC |
| huawei — smartphones |
There is a Improper Input Validation vulnerability in Huawei Smartphone.Successful exploitation of this vulnerability will cause kernel crash. |
2021-11-23 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-37024
MISC |
| huawei — smartphones |
There is a Data Processing Errors vulnerability in Huawei Smartphone.Successful exploitation of this vulnerability will cause kernel crash. |
2021-11-23 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-37018
MISC |
| huawei — smartphones |
There is a Improper Input Validation vulnerability in Huawei Smartphone.Successful exploitation of this vulnerability will cause the availability of users is affected. |
2021-11-23 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-37013
MISC |
| huawei — smartphones |
There is a Out-of-bounds Read vulnerability in Huawei Smartphone.Successful exploitation of this vulnerability will cause kernel crash. |
2021-11-23 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-37007
MISC |
| huawei — smartphones |
There is a Remote DoS vulnerability in Huawei Smartphone.Successful exploitation of this vulnerability will cause the app to exit unexpectedly. |
2021-11-23 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-37031
MISC |
| huawei — smartphones |
There is a Bypass vulnerability in Huawei Smartphone.Successful exploitation of this vulnerability may cause Digital Balance to fail to work. |
2021-11-23 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-37032
MISC |
| huawei — smartphones |
The affected controllers do not properly sanitize the input containing code syntax. As a result, an attacker could craft code to alter the intended controller flow of the software. |
2021-11-22 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-38448
CONFIRM |
| huawei — smartphones |
There is an Injection attack vulnerability in Huawei Smartphone.Successful exploitation of this vulnerability may affect service availability. |
2021-11-23 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-37033
MISC |
| huawei — smartphones |
There is a Improper Input Validation vulnerability in Huawei Smartphone.Successful exploitation of this vulnerability will cause kernel crash. |
2021-11-23 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-37017
MISC |
huawei — smartphones
|
There is a Remote DoS vulnerability in Huawei Smartphone.Successful exploitation of this vulnerability will cause the app to exit unexpectedly. |
2021-11-23 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-37035
MISC |
huawei — smartphones
|
There is a Data Processing Errors vulnerability in Huawei Smartphone.Successful exploitation of this vulnerability will cause kernel crash. |
2021-11-23 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-37012
MISC |
huawei — smartphones
|
There is a Improper Input Validation vulnerability in Huawei Smartphone.Successful exploitation of this vulnerability will cause kernel crash. |
2021-11-23 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-37019
MISC |
huawei — smartphones
|
There is a Improper Input Validation vulnerability in Huawei Smartphone.Successful exploitation of this vulnerability will cause kernel crash. |
2021-11-23 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-37003
MISC |
huawei — smartphones
|
There is a Out-of-bounds Read vulnerability in Huawei Smartphone.Successful exploitation of this vulnerability will cause Information Disclosure or Denial of Service. |
2021-11-23 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-37016
MISC |
huawei — smartphones
|
There is a Out-of-bounds Read vulnerability in Huawei Smartphone.Successful exploitation of this vulnerability will cause kernel crash. |
2021-11-23 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-37015
MISC |
huawei — smartphones
|
There is an Unstandardized field names in Huawei Smartphone.Successful exploitation of this vulnerability may affect service confidentiality. |
2021-11-23 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-37034
MISC |
huawei — smartphones
|
There is a Exposure of Sensitive Information to an Unauthorized Actor vulnerability in Huawei Smartphone.Successful exploitation of this vulnerability will cause the confidentiality of users is affected. |
2021-11-23 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-37010
MISC |
huawei — smartphones
|
There is a Improper Access Control vulnerability in Huawei Smartphone.Successful exploitation of this vulnerability will cause media files which can be reads and writes in non-distributed directories on any device on the network.. |
2021-11-23 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-37023
MISC |
huawei — smartphones
|
There is a Configuration vulnerability in Huawei Smartphone.Successful exploitation of this vulnerability will cause the confidentiality of users is affected. |
2021-11-23 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-37009
MISC |
huawei — smartphones
|
There is a Improper Input Validation vulnerability in Huawei Smartphone.Successful exploitation of this vulnerability will cause kernel crash. |
2021-11-23 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-37008
MISC |
huawei — smartphones
|
There is a Improper Preservation of Permissions vulnerability in Huawei Smartphone.Successful exploitation of this vulnerability will cause the confidentiality of users is affected. |
2021-11-23 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-37006
MISC |
huawei — smartphones
|
There is a Improper Input Validation vulnerability in Huawei Smartphone.Successful exploitation of this vulnerability will cause kernel crash. |
2021-11-23 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-37005
MISC |
huawei — smartphones
|
There is a Improper Input Validation vulnerability in Huawei Smartphone.Successful exploitation of this vulnerability will cause kernel crash. |
2021-11-23 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-37004
MISC |
huawei — smartphones
|
There is a Heap-based Buffer Overflow vulnerability in Huawei Smartphone.Successful exploitation of this vulnerability will cause root permission which can be escalated. |
2021-11-23 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-37022
MISC |
ibm — sterling_connect
|
IBM Sterling Connect:Direct Web Services 1.0 and 6.0 uses an inadequate account lockout setting that could allow a remote attacker to brute force account credentials. IBM X-Force ID: 209507. |
2021-11-23 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-38890
CONFIRM
XF |
ibm — sterling_connect
|
IBM Sterling Connect:Direct Web Services 1.0 and 6.0 uses weaker than expected cryptographic algorithms that could allow an attacker to decrypt highly sensitive information. IBM X-Force ID: 209508. |
2021-11-23 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-38891
CONFIRM
XF |
janus-gateway — janus-gateway
|
janus-gateway is vulnerable to Improper Neutralization of Input During Web Page Generation (‘Cross-site Scripting’) |
2021-11-27 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-4020
CONFIRM
MISC |
joeattardi — emoji-button
|
@joeattardi/emoji-button is a Vanilla JavaScript emoji picker component. In affected versions there are two vectors for XSS attacks: a URL for a custom emoji, and an i18n string. In both of these cases, a value can be crafted such that it can insert a `script` tag into the page and execute malicious code. |
2021-11-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-43785
CONFIRM
MISC
MISC |
kaspersky — password_manager
|
A component in Kaspersky Password Manager could allow an attacker to elevate a process Integrity level from Medium to High. |
2021-11-23 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-35052
MISC |
keepalived — keepalived
|
In Keepalived through 2.2.4, the D-Bus policy does not sufficiently restrict the message destination, allowing any user to inspect and manipulate any property. This leads to access-control bypass in some situations in which an unrelated D-Bus system service has a settable (writable) property |
2021-11-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-44225
MISC
MISC |
mcafee — policy_auditor
|
A Reflected Cross-Site Scripting vulnerability in McAfee Policy Auditor prior to 6.5.2 allows a remote unauthenticated attacker to inject arbitrary web script or HTML via the profileNodeID request parameters. The malicious script is reflected unmodified into the Policy Auditor web-based interface which could lead to the extraction of end user session token or login credentials. These may be used to access additional security-critical applications or conduct arbitrary cross-domain requests. |
2021-11-23 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-31851
CONFIRM |
mcafee — policy_auditor
|
A Reflected Cross-Site Scripting vulnerability in McAfee Policy Auditor prior to 6.5.2 allows a remote unauthenticated attacker to inject arbitrary web script or HTML via the UID request parameter. The malicious script is reflected unmodified into the Policy Auditor web-based interface which could lead to the extract of end user session token or login credentials. These may be used to access additional security-critical applications or conduct arbitrary cross-domain requests. |
2021-11-23 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-31852
CONFIRM |
microsoft — azure
|
Azure Active Directory Information Disclosure Vulnerability |
2021-11-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-42306
N/A |
microsoft — edge
|
Microsoft Edge (Chromium-based) Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
2021-11-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-43221
N/A |
microsoft — edge
|
Microsoft Edge (Chromium-based) Spoofing Vulnerability |
2021-11-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-42308
N/A |
microsoft — edge
|
Microsoft Edge for iOS Spoofing Vulnerability |
2021-11-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-43220
N/A |
microsoft — windows
|
Windows 10 Update Assistant Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability This CVE ID is unique from CVE-2021-42297. |
2021-11-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-43211
N/A |
microsoft — windows
|
Windows 10 Update Assistant Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability This CVE ID is unique from CVE-2021-43211. |
2021-11-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-42297
N/A
MISC |
mitsubishi_electric — mercari_app
|
Improper authorization in handler for custom URL scheme vulnerability in Android App ‘Mercari (Merpay) – Marketplace and Mobile Payments App’ (Japan version) versions prior to 4.49.1 allows a remote attacker to lead a user to access an arbitrary website and the website launches an arbitrary Activity of the app via the vulnerable App, which may result in Mercari account’s access token being obtained. |
2021-11-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-20835
MISC |
mitsubishi_electric — multiple_got2000_series
|
Improper input validation vulnerability in GOT2000 series GT27 model all versions, GOT2000 series GT25 model all versions, GOT2000 series GT23 model all versions, GOT2000 series GT21 model all versions, GOT SIMPLE series GS21 model all versions, and GT SoftGOT2000 all versions allows an remote unauthenticated attacker to write a value that exceeds the configured input range limit by sending a malicious packet to rewrite the device value. As a result, the system operation may be affected, such as malfunction. |
2021-11-23 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-20601
MISC
MISC
MISC |
| mongodb — mongodb |
An authorized user may trigger an invariant which may result in denial of service or server exit if a relevant aggregation request is sent to a shard. Usually, the requests are sent via mongos and special privileges are required in order to know the address of the shards and to log in to the shards of an auth enabled environment. |
2021-11-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-32037
MISC |
octopus — tentacle
|
When Octopus Tentacle is installed on a Linux operating system, the systemd service file permissions are misconfigured. This could lead to a local unprivileged user modifying the contents of the systemd service file to gain privileged access. |
2021-11-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-31822
MISC |
qnap — viostor
|
A command injection vulnerability has been reported to affect QNAP device, VioStor. If exploited, this vulnerability allows remote attackers to run arbitrary commands. We have already fixed this vulnerability in the following versions of QVR: QVR FW 5.1.6 build 20211109 and later |
2021-11-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-38685
CONFIRM |
qnap — viostor
|
An improper authentication vulnerability has been reported to affect QNAP device, VioStor. If exploited, this vulnerability allows attackers to compromise the security of the system. We have already fixed this vulnerability in the following versions of QVR: QVR FW 5.1.6 build 20211109 and later |
2021-11-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-38686
CONFIRM |
redash — redash
|
Redash is a package for data visualization and sharing. If an admin sets up Redash versions 10.0.0 and prior without explicitly specifying the `REDASH_COOKIE_SECRET` or `REDASH_SECRET_KEY` environment variables, a default value is used for both that is the same across all installations. In such cases, the instance is vulnerable to attackers being able to forge sessions using the known default value. This issue only affects installations where the `REDASH_COOKIE_SECRET or REDASH_SECRET_KEY` environment variables have not been explicitly set. This issue does not affect users of the official Redash cloud images, Redash’s Digital Ocean marketplace droplets, or the scripts in the `getredash/setup` repository. These instances automatically generate unique secret keys during installation. One can verify whether one’s instance is affected by checking the value of the `REDASH_COOKIE_SECRET` environment variable. If it is `c292a0a3aa32397cdb050e233733900f`, should follow the steps to secure the instance, outlined in the GitHub Security Advisory. |
2021-11-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-41192
CONFIRM
MISC |
redash — redash
|
Redash is a package for data visualization and sharing. In Redash version 10.0 and prior, the implementation of Google Login (via OAuth) incorrectly uses the `state` parameter to pass the next URL to redirect the user to after login. The `state` parameter should be used for a Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF) token, not a static and easily predicted value. This vulnerability does not affect users who do not use Google Login for their instance of Redash. A patch in the `master` and `release/10.x.x` branches addresses this by replacing `Flask-Oauthlib` with `Authlib` which automatically provides and validates a CSRF token for the state variable. The new implementation stores the next URL on the user session object. As a workaround, one may disable Google Login to mitigate the vulnerability. |
2021-11-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-43777
CONFIRM
MISC |
redash — redash
|
Redash is a package for data visualization and sharing. In versions 10.0 and priorm the implementation of URL-loading data sources like JSON, CSV, or Excel is vulnerable to advanced methods of Server Side Request Forgery (SSRF). These vulnerabilities are only exploitable on installations where a URL-loading data source is enabled. As of time of publication, the `master` and `release/10.x.x` branches address this by applying the Advocate library for making http requests instead of the requests library directly. Users should upgrade to version 10.0.1 to receive this patch. There are a few workarounds for mitigating the vulnerability without upgrading. One can disable the vulnerable data sources entirely, by adding the following env variable to one’s configuration, making them unavailable inside the webapp. One can switch any data source of certain types (viewable in the GitHub Security Advisory) to be `View Only` for all groups on the Settings > Groups > Data Sources screen. For users unable to update an admin may modify Redash’s configuration through environment variables to mitigate this issue. Depending on the version of Redash, an admin may also need to run a CLI command to re-encrypt some fields in the database. The `master` and `release/10.x.x` branches as of time of publication have removed the default value for `REDASH_COOKIE_SECRET`. All future releases will also require this to be set explicitly. For existing installations, one will need to ensure that explicit values are set for the `REDASH_COOKIE_SECRET` and `REDASH_SECRET_KEY `variables. |
2021-11-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-43780
CONFIRM
MISC |
sophos — hitmanpro_alert
|
A local administrator could prevent the HMPA service from starting despite tamper protection using an unquoted service path vulnerability in the HMPA component of Sophos Intercept X Advanced and Sophos Intercept X Advanced for Server before version 2.0.23, as well as Sophos Exploit Prevention before version 3.8.3. |
2021-11-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-25269
CONFIRM |
sophos — sophos
|
An authenticated user could potentially execute code via an SQLi vulnerability in the user portal of SG UTM before version 9.708 MR8. |
2021-11-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-36807
CONFIRM |
symfony — symfony
|
Symfony/SecurityBundle is the security system for Symfony, a PHP framework for web and console applications and a set of reusable PHP components. Since the rework of the Remember me cookie in version 5.3.0, the cookie is not invalidated when the user changes their password. Attackers can therefore maintain their access to the account even if the password is changed as long as they have had the chance to login once and get a valid remember me cookie. Starting with version 5.3.12, Symfony makes the password part of the signature by default. In that way, when the password changes, then the cookie is not valid anymore. |
2021-11-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-41268
CONFIRM
MISC
MISC
MISC |
symfony — symfony
|
Symfony/Http-Kernel is the HTTP kernel component for Symfony, a PHP framework for web and console applications and a set of reusable PHP components. Headers that are not part of the “trusted_headers” allowed list are ignored and protect users from “Cache poisoning” attacks. In Symfony 5.2, maintainers added support for the `X-Forwarded-Prefix` headers, but this header was accessible in SubRequest, even if it was not part of the “trusted_headers” allowed list. An attacker could leverage this opportunity to forge requests containing a `X-Forwarded-Prefix` header, leading to a web cache poisoning issue. Versions 5.3.12 and later have a patch to ensure that the `X-Forwarded-Prefix` header is not forwarded to subrequests when it is not trusted. |
2021-11-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-41267
CONFIRM
MISC
MISC
MISC |
symfony — symfony
|
Symfony/Serializer handles serializing and deserializing data structures for Symfony, a PHP framework for web and console applications and a set of reusable PHP components. Symfony versions 4.1.0 before 4.4.35 and versions 5.0.0 before 5.3.12 are vulnerable to CSV injection, also known as formula injection. In Symfony 4.1, maintainers added the opt-in `csv_escape_formulas` option in the `CsvEncoder`, to prefix all cells starting with `=`, `+`, `-` or `@` with a tab `t`. Since then, OWASP added 2 chars in that list: Tab (0x09) and Carriage return (0x0D). This makes the previous prefix char (Tab `t`) part of the vulnerable characters, and OWASP suggests using the single quote `’` for prefixing the value. Starting with versions 4.4.34 and 5.3.12, Symfony now follows the OWASP recommendations and uses the single quote `’` to prefix formulas and add the prefix to cells starting by `t`, `r` as well as `=`, `+`, `-` and `@`. |
2021-11-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-41270
MISC
CONFIRM
MISC
MISC |
synapse — synapse
|
Synapse is a package for Matrix homeservers written in Python 3/Twisted. Prior to version 1.47.1, Synapse instances with the media repository enabled can be tricked into downloading a file from a remote server into an arbitrary directory. No authentication is required for the affected endpoint. The last 2 directories and file name of the path are chosen randomly by Synapse and cannot be controlled by an attacker, which limits the impact. Homeservers with the media repository disabled are unaffected. Homeservers with a federation whitelist are also unaffected, since Synapse will check the remote hostname, including the trailing `../`s, against the whitelist. Server administrators should upgrade to 1.47.1 or later. Server administrators using a reverse proxy could, at the expense of losing media functionality, may block the certain endpoints as a workaround. Alternatively, non-containerized deployments can be adapted to use the hardened systemd config. |
2021-11-23 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-41281
MISC
CONFIRM
MISC |
| synk — synk |
This affects all versions of package docker-cli-js. If the command parameter of the Docker.command method can at least be partially controlled by a user, they will be in a position to execute any arbitrary OS commands on the host system. |
2021-11-22 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-23732
CONFIRM |
synk — synk
|
This affects all versions of package html-to-csv. When there is a formula embedded in a HTML page, it gets accepted without any validation and the same would be pushed while converting it into a CSV file. Through this a malicious actor can embed or generate a malicious link or execute commands via CSV files. |
2021-11-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-23654
CONFIRM
CONFIRM |
tightvnc — viewer
|
Buffer Overflow vulnerability in tvnviewer.exe of TightVNC Viewer allows a remote attacker to execute arbitrary instructions via a crafted FramebufferUpdate packet from a VNC server. |
2021-11-23 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-42785
MISC |
ubuntu — ark_library
|
ARK library allows attackers to execute remote code via the parameter(path value) of Ark_NormalizeAndDupPAthNameW function because of an integer overflow. |
2021-11-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-26615
MISC |
unifi — protect
|
A Cross-Origin Resource Sharing (CORS) vulnerability found in UniFi Protect application Version 1.19.2 and earlier allows a malicious actor who has convinced a privileged user to access a URL with malicious code to take over said user’s account.This vulnerability is fixed in UniFi Protect application Version 1.20.0 and later. |
2021-11-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-22957
MISC |
vmware — vsphere_web_client
|
The vSphere Web Client (FLEX/Flash) contains an unauthorized arbitrary file read vulnerability. A malicious actor with network access to port 443 on vCenter Server may exploit this issue to gain access to sensitive information. |
2021-11-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-21980
MISC |
vmware — vsphere_web_client
|
The vSphere Web Client (FLEX/Flash) contains an SSRF (Server Side Request Forgery) vulnerability in the vSAN Web Client (vSAN UI) plug-in. A malicious actor with network access to port 443 on vCenter Server may exploit this issue by accessing a URL request outside of vCenter Server or accessing an internal service. |
2021-11-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-22049
MISC |
| wordpress — wordpress |
The ImageBoss WordPress plugin before 3.0.6 does not sanitise and escape its Source Name setting, which could allow high privilege users to perform Cross-Site Scripting attacks |
2021-11-23 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-24888
MISC |
wordpress — wordpress
|
WordPress before 5.8 lacks support for the Update URI plugin header. This makes it easier for remote attackers to execute arbitrary code via a supply-chain attack against WordPress installations that use any plugin for which the slug satisfies the naming constraints of the WordPress.org Plugin Directory but is not yet present in that directory. |
2021-11-25 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-44223
MISC
MISC |
wordpress — wordpress
|
The Elementor Website Builder WordPress plugin before 3.1.4 does not sanitise or escape user input appended to the DOM via a malicious hash, resulting in a DOM Cross-Site Scripting issue |
2021-11-23 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-24891
MISC
MISC |
wordpress — wordpress
|
Insecure Direct Object Reference in edit function of Advanced Forms (Free & Pro) before 1.6.9 allows authenticated remote attacker to change arbitrary user’s email address and request for reset password, which could lead to take over of WordPress’s administrator account. To exploit this vulnerability, an attacker must register to obtain a valid WordPress’s user and use such user to authenticate with WordPress in order to exploit the vulnerable edit function. |
2021-11-23 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-24892
MISC
MISC |
wordpress — wordpress
|
The Reviews Plus WordPress plugin before 1.2.14 does not validate the submitted rating, allowing submission of long integer, causing a Denial of Service in the review section when an authenticated user submit such rating and the reviews are set to be displayed on the post/page |
2021-11-23 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-24894
CONFIRM
MISC |
| xen — xen |
issues with partially successful P2M updates on x86 T[his CNA information record relates to multiple CVEs; the text explains which aspects/vulnerabilities correspond to which CVE.] x86 HVM and PVH guests may be started in populate-on-demand (PoD) mode, to provide a way for them to later easily have more memory assigned. Guests are permitted to control certain P2M aspects of individual pages via hypercalls. These hypercalls may act on ranges of pages specified via page orders (resulting in a power-of-2 number of pages). In some cases the hypervisor carries out the requests by splitting them into smaller chunks. Error handling in certain PoD cases has been insufficient in that in particular partial success of some operations was not properly accounted for. There are two code paths affected – page removal (CVE-2021-28705) and insertion of new pages (CVE-2021-28709). (We provide one patch which combines the fix to both issues.) |
2021-11-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-28705
MISC |
xen — xen
|
PoD operations on misaligned GFNs T[his CNA information record relates to multiple CVEs; the text explains which aspects/vulnerabilities correspond to which CVE.] x86 HVM and PVH guests may be started in populate-on-demand (PoD) mode, to provide a way for them to later easily have more memory assigned. Guests are permitted to control certain P2M aspects of individual pages via hypercalls. These hypercalls may act on ranges of pages specified via page orders (resulting in a power-of-2 number of pages). The implementation of some of these hypercalls for PoD does not enforce the base page frame number to be suitably aligned for the specified order, yet some code involved in PoD handling actually makes such an assumption. These operations are XENMEM_decrease_reservation (CVE-2021-28704) and XENMEM_populate_physmap (CVE-2021-28707), the latter usable only by domains controlling the guest, i.e. a de-privileged qemu or a stub domain. (Patch 1, combining the fix to both these two issues.) In addition handling of XENMEM_decrease_reservation can also trigger a host crash when the specified page order is neither 4k nor 2M nor 1G (CVE-2021-28708, patch 2). |
2021-11-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-28704
MISC |
xen — xen
|
PoD operations on misaligned GFNs T[his CNA information record relates to multiple CVEs; the text explains which aspects/vulnerabilities correspond to which CVE.] x86 HVM and PVH guests may be started in populate-on-demand (PoD) mode, to provide a way for them to later easily have more memory assigned. Guests are permitted to control certain P2M aspects of individual pages via hypercalls. These hypercalls may act on ranges of pages specified via page orders (resulting in a power-of-2 number of pages). The implementation of some of these hypercalls for PoD does not enforce the base page frame number to be suitably aligned for the specified order, yet some code involved in PoD handling actually makes such an assumption. These operations are XENMEM_decrease_reservation (CVE-2021-28704) and XENMEM_populate_physmap (CVE-2021-28707), the latter usable only by domains controlling the guest, i.e. a de-privileged qemu or a stub domain. (Patch 1, combining the fix to both these two issues.) In addition handling of XENMEM_decrease_reservation can also trigger a host crash when the specified page order is neither 4k nor 2M nor 1G (CVE-2021-28708, patch 2). |
2021-11-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-28707
MISC |
xen — xen
|
PoD operations on misaligned GFNs T[his CNA information record relates to multiple CVEs; the text explains which aspects/vulnerabilities correspond to which CVE.] x86 HVM and PVH guests may be started in populate-on-demand (PoD) mode, to provide a way for them to later easily have more memory assigned. Guests are permitted to control certain P2M aspects of individual pages via hypercalls. These hypercalls may act on ranges of pages specified via page orders (resulting in a power-of-2 number of pages). The implementation of some of these hypercalls for PoD does not enforce the base page frame number to be suitably aligned for the specified order, yet some code involved in PoD handling actually makes such an assumption. These operations are XENMEM_decrease_reservation (CVE-2021-28704) and XENMEM_populate_physmap (CVE-2021-28707), the latter usable only by domains controlling the guest, i.e. a de-privileged qemu or a stub domain. (Patch 1, combining the fix to both these two issues.) In addition handling of XENMEM_decrease_reservation can also trigger a host crash when the specified page order is neither 4k nor 2M nor 1G (CVE-2021-28708, patch 2). |
2021-11-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-28708
MISC |
xen — xen
|
issues with partially successful P2M updates on x86 T[his CNA information record relates to multiple CVEs; the text explains which aspects/vulnerabilities correspond to which CVE.] x86 HVM and PVH guests may be started in populate-on-demand (PoD) mode, to provide a way for them to later easily have more memory assigned. Guests are permitted to control certain P2M aspects of individual pages via hypercalls. These hypercalls may act on ranges of pages specified via page orders (resulting in a power-of-2 number of pages). In some cases the hypervisor carries out the requests by splitting them into smaller chunks. Error handling in certain PoD cases has been insufficient in that in particular partial success of some operations was not properly accounted for. There are two code paths affected – page removal (CVE-2021-28705) and insertion of new pages (CVE-2021-28709). (We provide one patch which combines the fix to both issues.) |
2021-11-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-28709
MISC |
yamaha — multiple_routers
|
Improper neutralization of HTTP request headers for scripting syntax vulnerability in the Web GUI of RTX830 Rev.15.02.17 and earlier, NVR510 Rev.15.01.18 and earlier, NVR700W Rev.15.00.19 and earlier, and RTX1210 Rev.14.01.38 and earlier allows a remote authenticated attacker to obtain sensitive information via a specially crafted web page. |
2021-11-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-20844
MISC
MISC
MISC
MISC |
yamaha — multiple_routers
|
Cross-site script inclusion vulnerability in the Web GUI of RTX830 Rev.15.02.17 and earlier, NVR510 Rev.15.01.18 and earlier, NVR700W Rev.15.00.19 and earlier, and RTX1210 Rev.14.01.38 and earlier allows a remote authenticated attacker to alter the settings of the product via a specially crafted web page. |
2021-11-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-20843
MISC
MISC
MISC
MISC |
zoom — client_for_meetings
|
A buffer overflow vulnerability was discovered in Zoom Client for Meetings (for Android, iOS, Linux, macOS, and Windows) before version 5.8.4, Zoom Client for Meetings for Blackberry (for Android and iOS) before version 5.8.1, Zoom Client for Meetings for intune (for Android and iOS) before version 5.8.4, Zoom Client for Meetings for Chrome OS before version 5.0.1, Zoom Rooms for Conference Room (for Android, AndroidBali, macOS, and Windows) before version 5.8.3, Controllers for Zoom Rooms (for Android, iOS, and Windows) before version 5.8.3, Zoom VDI before version 5.8.4, Zoom Meeting SDK for Android before version 5.7.6.1922, Zoom Meeting SDK for iOS before version 5.7.6.1082, Zoom Meeting SDK for macOS before version 5.7.6.1340, Zoom Meeting SDK for Windows before version 5.7.6.1081, Zoom Video SDK (for Android, iOS, macOS, and Windows) before version 1.1.2, Zoom On-Premise Meeting Connector Controller before version 4.8.12.20211115, Zoom On-Premise Meeting Connector MMR before version 4.8.12.20211115, Zoom On-Premise Recording Connector before version 5.1.0.65.20211116, Zoom On-Premise Virtual Room Connector before version 4.4.7266.20211117, Zoom On-Premise Virtual Room Connector Load Balancer before version 2.5.5692.20211117, Zoom Hybrid Zproxy before version 1.0.1058.20211116, and Zoom Hybrid MMR before version 4.6.20211116.131_x86-64. This can potentially allow a malicious actor to crash the service or application, or leverage this vulnerability to execute arbitrary code. |
2021-11-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-34423
MISC |
zoom — client_for_meetings
|
A vulnerability was discovered in the Zoom Client for Meetings (for Android, iOS, Linux, macOS, and Windows) before version 5.8.4, Zoom Client for Meetings for Blackberry (for Android and iOS) before version 5.8.1, Zoom Client for Meetings for intune (for Android and iOS) before version 5.8.4, Zoom Client for Meetings for Chrome OS before version 5.0.1, Zoom Rooms for Conference Room (for Android, AndroidBali, macOS, and Windows) before version 5.8.3, Controllers for Zoom Rooms (for Android, iOS, and Windows) before version 5.8.3, Zoom VDI before version 5.8.4, Zoom Meeting SDK for Android before version 5.7.6.1922, Zoom Meeting SDK for iOS before version 5.7.6.1082, Zoom Meeting SDK for macOS before version 5.7.6.1340, Zoom Meeting SDK for Windows before version 5.7.6.1081, Zoom Video SDK (for Android, iOS, macOS, and Windows) before version 1.1.2, Zoom on-premise Meeting Connector before version 4.8.12.20211115, Zoom on-premise Meeting Connector MMR before version 4.8.12.20211115, Zoom on-premise Recording Connector before version 5.1.0.65.20211116, Zoom on-premise Virtual Room Connector before version 4.4.7266.20211117, Zoom on-premise Virtual Room Connector Load Balancer before version 2.5.5692.20211117, Zoom Hybrid Zproxy before version 1.0.1058.20211116, and Zoom Hybrid MMR before version 4.6.20211116.131_x86-64 which potentially allowed for the exposure of the state of process memory. This issue could be used to potentially gain insight into arbitrary areas of the product’s memory. |
2021-11-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-34424
MISC |
zyxel — multiple_firmware
|
A vulnerability in specific versions of Zyxel NBG6818, NBG7815, WSQ20, WSQ50, WSQ60, and WSR30 firmware with pre-configured password management could allow an attacker to obtain root access of the device, if the local attacker dismantles the device and uses a USB-to-UART cable to connect the device, or if the remote assistance feature had been enabled by an authenticated user. |
2021-11-23 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-35033
CONFIRM |
by Contributed | Nov 27, 2021 | Technology
This article is contributed. See the original author and article here.
Before implementing data extraction from SAP systems please always verify your licensing agreement. |
Welcome to the third episode of this mini blog series, where I show you how to deal with OData extraction from the SAP system using Synapse Pipelines. In the first episode, we’ve built a simple pipeline that extracts data from a selected OData service and saves it to the data lake. Then, a week later, we enhanced the design to support parameters, which eliminated some of the hardcoded values. It allows us to change the OData service we want to use without modifying the pipeline or resources.
It was a great improvement, but the process still has two main disadvantages. The extraction job can only extract a single OData service at a time, and we still have to provide parameter values manually. If we want to extract data from many services, we have to start the pipeline multiple times, each time providing the OData service name, entity and host. Not the most effective approach.
But what if we could provide all OData services upfront in an external datastore? That’s the plan for today. Let’s further enhance our pipeline and make it even more agile!
THE METADATA STORE
To store information about OData services, we need a service, that is easy to provision and maintain. We could use a SQL database, which meets many of our goals, but it is quite a heavy service. Instead, use Azure Table Storage which seems to offer exactly the functionality we need. It can be part of the same storage account that we use for data lake, it’s simple to deploy, and it doesn’t require any maintenance. And, as we store small amounts of data, the cost will be minimal.
To create a Table in Azure Storage, open the Storage Account blade in Azure Portal and choose Tables from the menu. Click the plus button, provide the table name and click OK to confirm. That couldn’t be more straightforward.

You can use Storage Explorer to add entries to the table. Select the table that you’ve just created and click the plus button to add an entry. By default, each Azure Table has two properties: PartitionKey and RowID, that together form the primary key. You can add more properties if needed. In the PartitionKey I store the OData service name and the RowID keeps the Entity name. In the pipeline, we’ve defined three parameters so we have to create an additional property for the Host information.
I add two previously used OData services to the table.
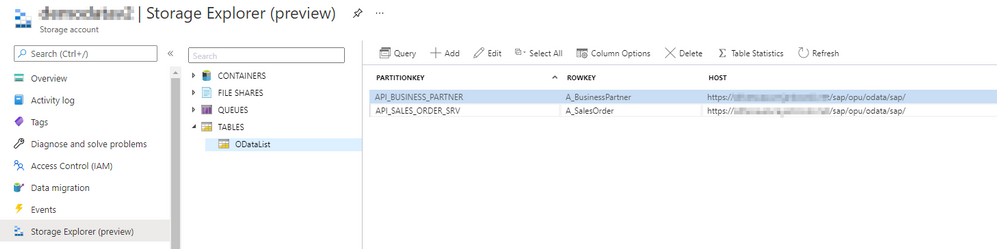
The metadata table is now ready!
READING METADATA FROM THE PIPELINE
To access the metadata table from the pipeline we have to create resources in Synapse Studio. There is a dedicated connector that allows us to consume data from Azure Table. Create the Linked Service and a dataset as we did in previously in this series.
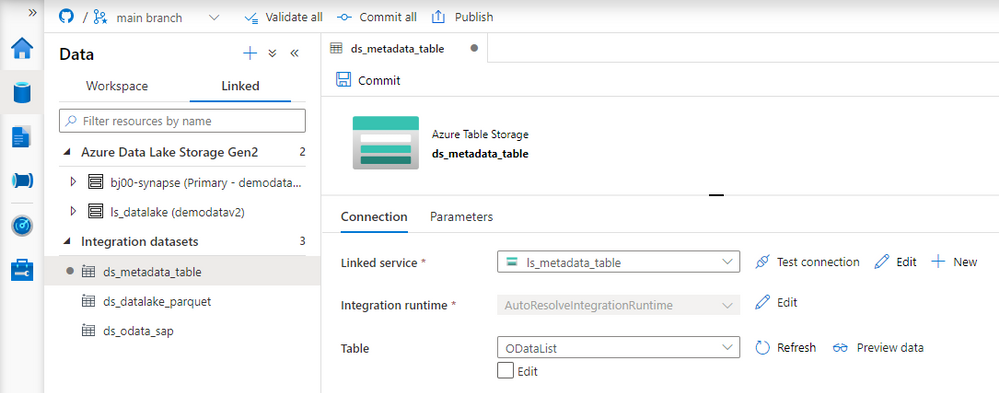
To read the metadata table, we will create another pipeline that will fetch information about OData services to process and then, one by one, it will trigger the child pipeline responsible for the extraction. The child pipeline is the one that we’ve been working on during previous episodes.
Create a new pipeline and add the Lookup activity. On the Settings tab, choose the dataset associated with the Azure Table. Uncheck the option First Row only as we want to read all data from the table.
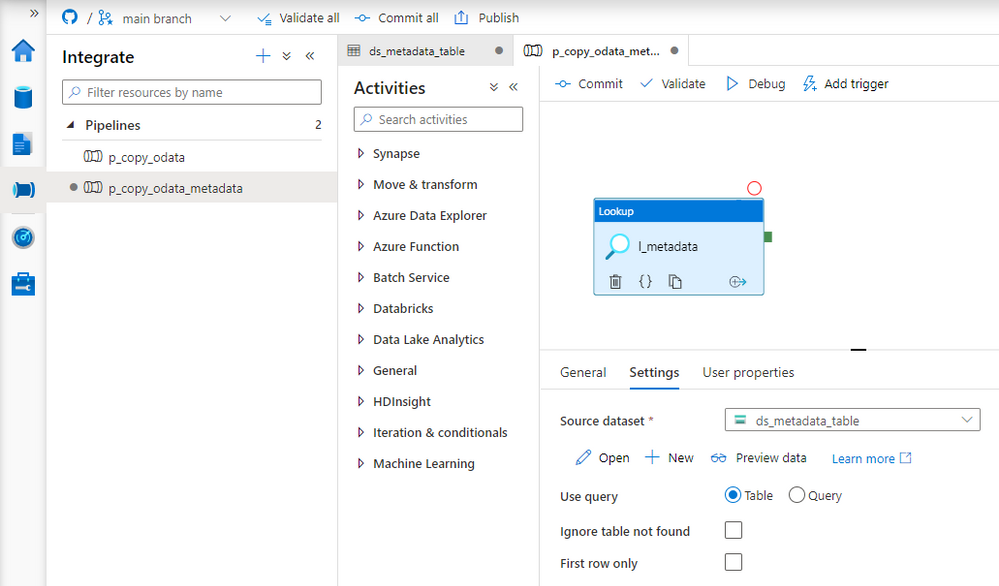
The Lookup activity reads all records from the table and exposes them as an array in the pipeline, which we can pass to subsequent activities. Each OData defined in the table should trigger the child pipeline. To achieve that, we will use the ForEach loop that goes through the array, and each record starts the pipeline that we’ve created in previous episodes.
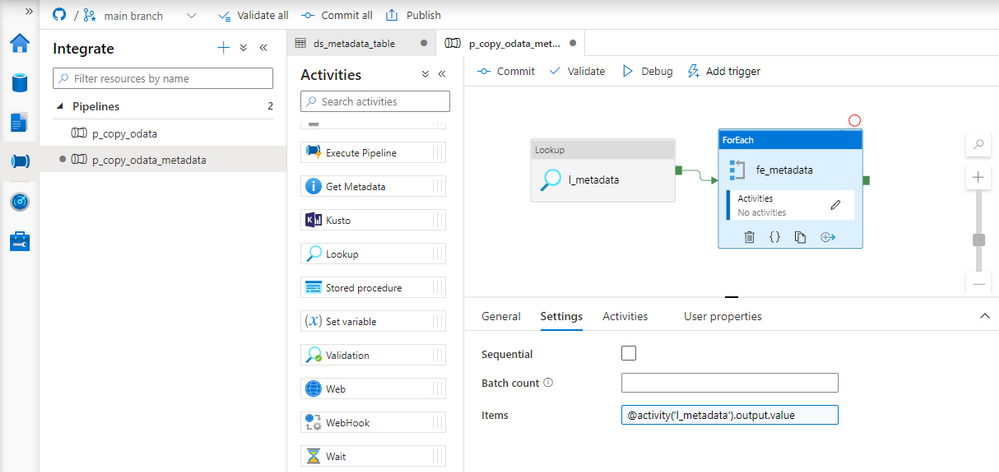
Add ForEach loop to the pipeline. Connect the Lookup activity with the loop. Open the Settings tab and provide the following expression in the Items field to pass the array to the ForEach loop.
@activity('l_metadata').output.value
Great! The ForEach loop iterates through all elements of the array. Click on the small pencil button to define actions contained in the loop. On the new screen, add the Execute Pipeline activity and select the pipeline with the Copy Data process that we’ve created in previous episodes. You’ll notice three input boxes that correspond to the pipeline parameters. We will use them to pass information from the metadata table about the current OData service to process. Referencing items from the loop is quite simple:
URL: @item().Host
ODataService: @item().PartitionKey
Entity: @item().RowKey
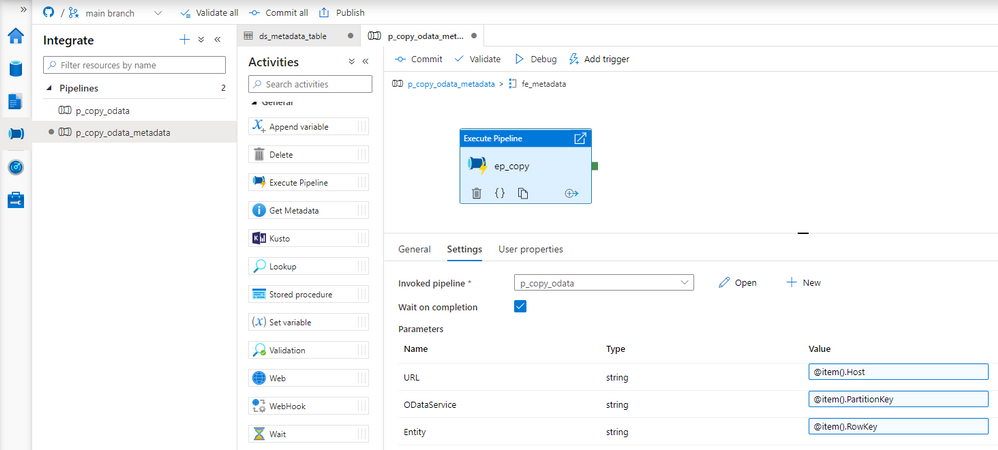
Each record stored in the metadata table will trigger the pipeline with Copy Data activity. Values stored in the table are passed to the child pipeline as parameters. Using the external metadata store allows maintaining the list of OData services independently of the pipeline. To add a new record, we don’t have to launch Synapse Studio. It’s enough to add an entry to the table.
EXECUTION AND MONITORING
There is one important setting in the ForEach loop, that I haven’t mentioned earlier. You can decide to run the loop sequentially, or in parallel, which is the default behavior. This setting has a significant influence on job performance. Triggering multiple parallel extraction processes can decrease the overall time required to extract data, but at the same time, it increases the load on the application server. As long as we’re working with one or two OData services it should not cause any troubles. But if you plan to run the extraction on a larger scale, I’d recommend defining the maximum number of concurrent jobs in the Batch Count field.
We’ve created two entries in the metadata table – one for the sales order and one for the business partner.
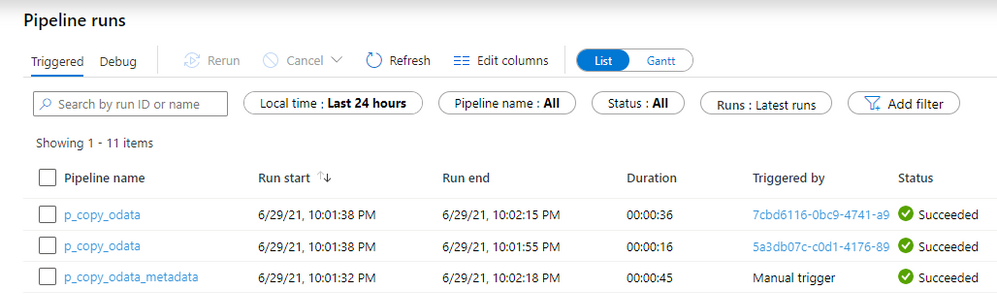
You can immediately spot the difference. This time we can see three pipelines executed instead of one! One for the parent pipeline that read values from the Azure Table, and then triggered two child pipelines that run the extraction. The number of child pipelines is directly related to the number of OData services defined in the metadata table.
Adding a new OData service doesn’t require any changes in the Synapse Studio. Instead, you can define it directly in the Azure Table Storage. Whenever you run the extraction, the job automatically picks up all entries and process them in parallel.
So far, I haven’t explained how to deal with large data volumes. My test system contains only a couple hundred sales orders. In real life, you probably have to deal with millions of records, which can cause serious troubles. In the next episode, I’ll focus on extracting a large amount of data – it’s easier than you think!

by Contributed | Nov 26, 2021 | Technology
This article is contributed. See the original author and article here.

Microsoft 365 Patterns and Practices (PnP) Community November 2021 update is out with a summary of the latest guidance, samples, and solutions from Microsoft or from the community for the community. This article is a summary of all the different areas and topics around the community work we do around Microsoft 365 ecosystem during the past month. Thank you for being part of this success.
Sharing is caring! ?
What is Microsoft 365 Community (PnP)
Microsoft 365 PnP is a nick-name for Microsoft 365 platform community activities coordinated by numerous teams inside of the Microsoft 365 engineering organizations. PnP is a community-driven open source initiative where Microsoft and external community members are sharing their learning’s around implementation practices for Microsoft 365.
Topics vary from Microsoft Viva, Microsoft Graph, Microsoft Teams, Power Platform, OneDrive and SharePoint. Active development and contributions happen in GitHub by providing contributions to the samples, reusable components, and documentation for different areas. PnP is owned and coordinated by Microsoft engineering, but this is work done by the community for the community.
The initiative is facilitated by Microsoft, but we have multiple community members as part of the PnP team (see team details in end of the article) and we are always looking to extend the PnP team with more community members. Notice that since this is open source community initiative, so there’s no SLAs for the support for the samples provided through GitHub. Obviously, all officially released components and libraries are under official support from Microsoft.
Main resources around Microsoft 365 Community:
✍ Latest Dev Blog posts
Here are the latest blog posts and announcements around Microsoft 365 development topics from https://developer.microsoft.com/en-us/microsoft-365/blogs.
Latest community posts at https://aka.ms/m365pnp/community/blog
Community call recording blog posts:
- 18th of November – Viva Connections & SharePoint Framework Community Call – 18th of November, 2021
- 16th of November – Microsoft 365 Platform Call – 16th of November, 2021
- 11th of November – Microsoft 365 Developer Community Call recording – 11th of November, 2021
- 10th of November – Adaptive Cards community call – October 2021
- 10th of November – Microsoft 365 Platform Call – 9th of November, 2021
- 5th of November – Microsoft 365 Platform Call – 2nd of November, 2021 – Microsoft Ignite 2021 watch party
- 4th of November – SharePoint Framework Community Call – 4th of November, 2021 – Microsoft Tech Community
- 28th of October – Microsoft 365 Developer Community Call recording – 28th of October, 2021
- 26th of October – Microsoft 365 Platform Call – 26th of October, 2021
- 25th of October – Power Apps Community Call – October 2021
- 22nd of October – Office Add-ins community call – October 13, 2021
- 21st of October – SharePoint Framework Community Call – 21st of October, 2021
Microsoft 365 Developer Podcasts
Microsoft 365 PnP Weekly Podcasts and vlogs
Community Calls
There are numerous different community calls on different areas. All calls are being recorded and published either from Microsoft 365 Developer or Microsoft 365 Community (PnP) YouTube channels. Recordings are typically released within the following 24 hours after the call. You can find a detailed agenda and links to specific covered topics on blog post articles at the Microsoft 365 developer blog when the videos are published.
- Microsoft 365 Platform Call – https://aka.ms/m365-dev-call – Updates and demos from Microsoft as weekly call on Tuesdays – topics vary from Microsoft Teams, Microsoft Graph, Power Platform, SharePoint, OneDrive and more
- Adaptive Cards https://aka.ms/adaptivecardscommunitycall – Updates and news around Adaptive Cards with live demos
- Microsoft identity platform https://aka.ms/IDDevCommunityCalendar – Latest on the identity side
- Office Add-ins https://aka.ms/officeaddinscommunitycall – News and community work around Office add-ins with live demos
- PowerApps https://aka.ms/PowerAppsMonthlyCall – Monthly summary on PowerApps community with live demos
- M365 Community Call https://aka.ms/spdev-sig-call – Bi-weekly – General topics on Microsoft 365 Dev from various aspects – Microsoft Teams, Microsoft Graph Toolkit, Provisioning, Automation, Scripting, Power Automate, Solution design
- SharePoint Framework Community call https://aka.ms/spdev-spfx-call – Bi-weekly – Consists of topics around SharePoint Framework and JavaScript-based development in the Microsoft Teams and in SharePoint platform.
If you are interested in doing a live demo of your solution or sample in these calls, please do reach out to the PnP Team members (contacts later in this post) and they are able to help with the right setup. These are great opportunities to gain visibility for example for existing MVPs, for community members who would like to be MVPs in the future or any community member who’d like to share some of their learnings.
Microsoft 365 Community (PnP) Ecosystem in GitHub
Most of the community driven repositories are in the PnP GitHub organization as samples are not product specifics as they can contain numerous different solutions or the solution works in multiple different applications.
- Microsoft Graph Toolkit – Repository and project on Microsoft Graph Toolkit controls – welcomes community contributors
- PnPjs – PnPjs Framework repository
- CLI Microsoft 365 – Cross-OS command line interface to manage Office 365 tenant settings
- generator-spfx – Open-source Yeoman generator which extends the out-of-the-box Yeoman generator for SharePoint with additional capabilities
- generator-teams – Open-source Microsoft Teams Yeoman generator – Bots, Messaging Extensions, Tabs, Connectors, Outgoing Web hooks and more
- teams-dev-samples – Microsoft Teams targeted samples from community and Microsoft engineering
- script-samples – Scripting samples for automating operations in Microsoft 365 with PowerShell modules or CLIs
- Sharing is Caring – Getting started on learning how to contribute and be active on the community from GitHub perspective.
- pnpcore – The PnP Core SDK is an SDK designed to work against Microsoft 365 with Microsoft Graph API first approach
- powershell – PnP PowerShell module which is PowerShell Core module targeted for Microsoft 365
- pnpframework – PnP Framework is a .Net Standard 2.0 library targeting Microsoft 365 containing the PnP Provisioning engine and a ton of other useful extensions
- spfx-reference-scenarios – Samples for the Microsoft Teams and Viva Connections, implemented using SharePoint Framework
- sp-dev-fx-aces – Samples on the Adaptive Card Extensions for Microsoft Viva
- sp-dev-fx-webparts – Client-side web part samples from community and Microsoft engineering
- sp-dev-fx-extensions – Samples and tutorial code around SharePoint Framework Extensions
- sp-dev-fx-library-components – Samples and tutorial code around the SharePoint Framework library components
- sp-starter-kit – Starter kit solution for SharePoint modern experiences
- sp-dev-build-extensions – Different build extensions like gulp tasks and gulp plugins from the community and engineering around SharePoint development
- sp-dev-solutions – Repository for more polished and fine-tuned reusable solutions build with SharePoint Framework
- sp-dev-samples – Repository for other samples related on the SharePoint development topics – WebHooks etc.
- sp-dev-fx-controls-react – Reusable content controls for SharePoint Framework solutions build with React
- sp-dev-fx-property-controls – Reusable property pane controls to be used in web parts
- list-formatting – Open-source community-driven repository for the column and view formatting JSON definitions
- sp-dev-site-scripts – Open-source community-driven repository for community Site Designs and Site Scripts
- sp-dev-modernization – Tooling and guidance around modernizing SharePoint from classic to modern
- sp-power-platform-solutions – Solution and sample code for SharePoint Power Platform solutions
- powerfx-samples – Samples that demonstrate different usage patterns for the Power Fx low-code programming language
- powerapps-samples – Samples that demonstrate different usage patterns for Power Apps
- powerautomate-samples – Samples that demonstrate different usage patterns for Power Automate
- powerva-samples – Samples that demonstrate different usage patterns for Power Virtual Agents
All SharePoint specific repositories or services supported directly by Microsoft are located in the SharePoint GitHub organization
Classic PnP named repositories – older tooling
- PnP-Tools – Tools and scripts targeted more for IT Pro’s and for on-premises for SP2013 and SP2016
- PnP-Provisioning-Schema – PnP Provisioning engine schema repository
Repositories in the GitHub Microsoft Search organization controlled by the PnP initiative
Other related resources from GitHub
What’s supportability story around the community tooling and assets?
Following statements apply across all of the community lead and contributed samples and solutions, including samples, core component(s) and solutions, like SharePoint Starter Kit, yo teams or PnP PowerShell. All Microsoft released SDKs and tools are supported based on the specific tool policies.
- PnP guidance and samples are created by Microsoft & by the Community
- PnP guidance and samples are maintained by Microsoft & community
- PnP uses supported and recommended techniques
- PnP is an open-source initiative by the community – people who work on the initiative for the benefit of others, have their normal day job as well
- PnP is NOT a product and therefore it’s not supported by Premier Support or other official support channels
- PnP is supported in similar ways as other open source projects done by Microsoft with support from the community by the community
- There are numerous partners that utilize PnP within their solutions for customers. Support for this is provided by the Partner. When PnP material is used in deployments, we recommend being clear with your customer/deployment owner on the support model
Please see the specifics on the supportability on the tool, SDK or component repository or download page.
Microsoft 365 PnP team model

In April 2020 we announced our new Microsoft 365 PnP team model and grew the MVP team quite significantly. PnP model exists for having more efficient engagement between Microsoft engineering and community members. Let’s build things together. Your contributions and feedback is always welcome! During August, we also crew the team with 5 new members. PnP Team coordinates and leads the different open-source and community efforts we execute in the Microsoft 365 platform.
We welcome all community members to get involved on the community and open-source efforts. Your input do matter!
- New Microsoft 365 Patterns and Practices (PnP) team members – November 2021 – Geetha Sivasailam (Artis Consulting) | @GSiVed, Natalie Pienkowska (Microsoft) | @NataliePienkow1, Derek Cash-Peterson (Sympraxis Consulting) | @spdcp, João J. Mendes (Valo) | @joaojmendes, Joel Rodrigues (Storm Technology) | @JoelFMRodrigues, Rick Van Rousselt (Advantive) | @RickVanRousselt, Stephan Bisser (Solvion) | @stephanbisser, Tetsuya Kawahara | @techan_k, and Thomas Gölles (Solvion) | @thomyg
- New Microsoft 365 Patterns and Practices (PnP) team members – May 2021 – Gautam Sheth (Valo) and Patrick Lamber (Experts Inside AG)
- New Microsoft 365 Patterns and Practices (PnP) team members – February 2021 – April Dunnam (Microsoft), Emily Mancini (Sympraxis Consulting) and Veronique Lengelle (CPS)
- New Microsoft 365 Patterns and Practices (PnP) team members – December 2020 – Luise Freese and Sébastien Levert
- New Microsoft 365 Patterns and Practices (PnP) team members – August 2020 – Albert-Jan Schot (BLIS Digital), Koen Zomers (Microsoft), Paul Bullock (CaPa Creative), Rabia Williams (Microsoft) and Yannick Plenevaux (PVX Solutions)
Got feedback, suggestions or ideas? – Please let us know. Everything we do in this program is for your benefit. Feedback and ideas are more than welcome so that we can adjust the process for benefitting you even more.
Microsoft 365 PnP Recognition Program

We are excited to announce new community contributor program for all the active community members. Through this program you can get officially acknowledged with the a Credly badge around your work on our open-source and community channels. See more from
https://aka.ms/m365pnp-recognition. Thank you for being part of this journey with us.
⚙ Area-specific updates
These are different areas which are closely involved on the community work across the PnP initiative. Some are lead and coordinated by engineering organizations, some are coordinated by the community and MVPs.
Microsoft Graph Toolkit

Microsoft Graph Toolkit is engineering lead initiative, which works closely with the community on the open-source areas. The Microsoft Graph Toolkit is a collection of reusable, framework-agnostic web components and helpers for accessing and working with Microsoft Graph. The components are fully functional right of out of the box, with built in providers that authenticate with and fetch data from Microsoft Graph.
All the latest updates on the Microsoft Graph Toolkit is being presented in our bi-weekly Microsoft 365 Generic Dev community call, including the latest community contributors.
Microsoft 365 Community docs
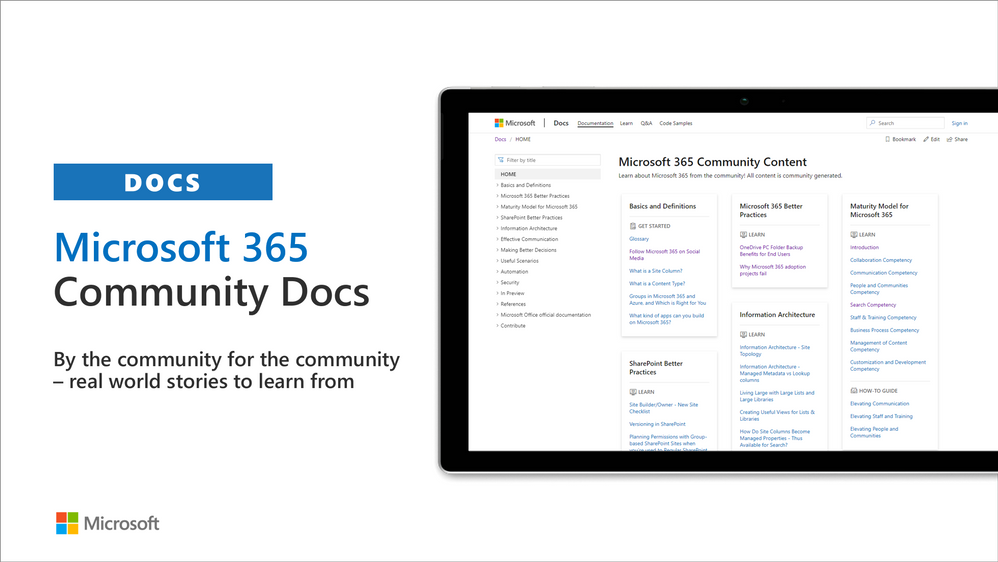
Community docs model was announced in the April 2020 and it’s great to see the interest for community to help each other by providing new guidance on the non-dev areas. See more on the announcement from the SharePoint blog – Announcing the Microsoft 365 Community Docs. We do welcome contributions from the community – our objective is to build a valuable location for articles from Microsoft and community together.
Have ideas for articles or want to contribute yourself? – Get involved! Here are also some additional resources explaining the model more detailed.
SharePoint Framework development samples
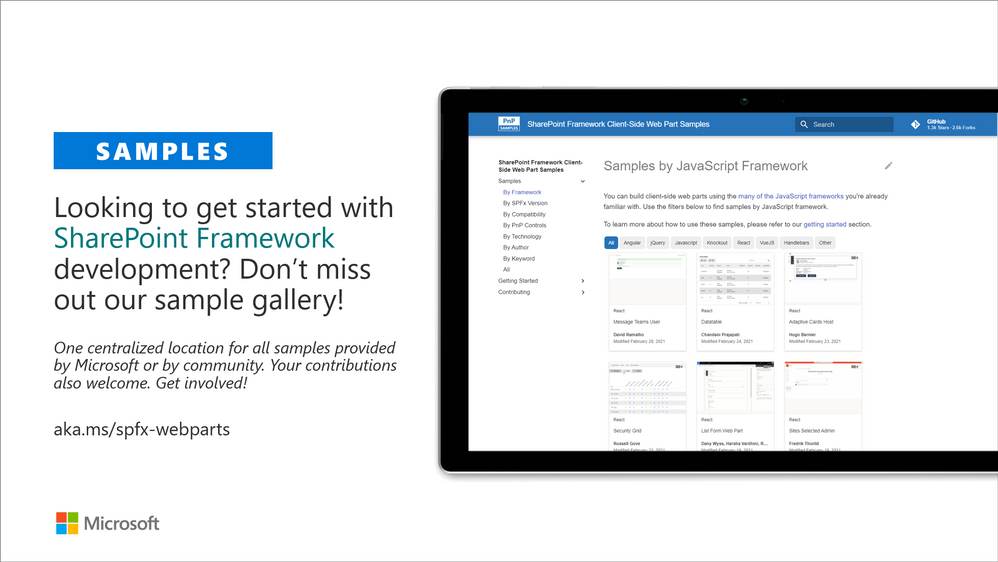
These are the updated SharePoint Framework samples which are available from the the different repositories.
How to find what’s relevant for you? Take advantage of our SharePoint Framework web part and extension sample galleries – includes also solutions which work in Microsoft Teams
Microsoft Teams community samples
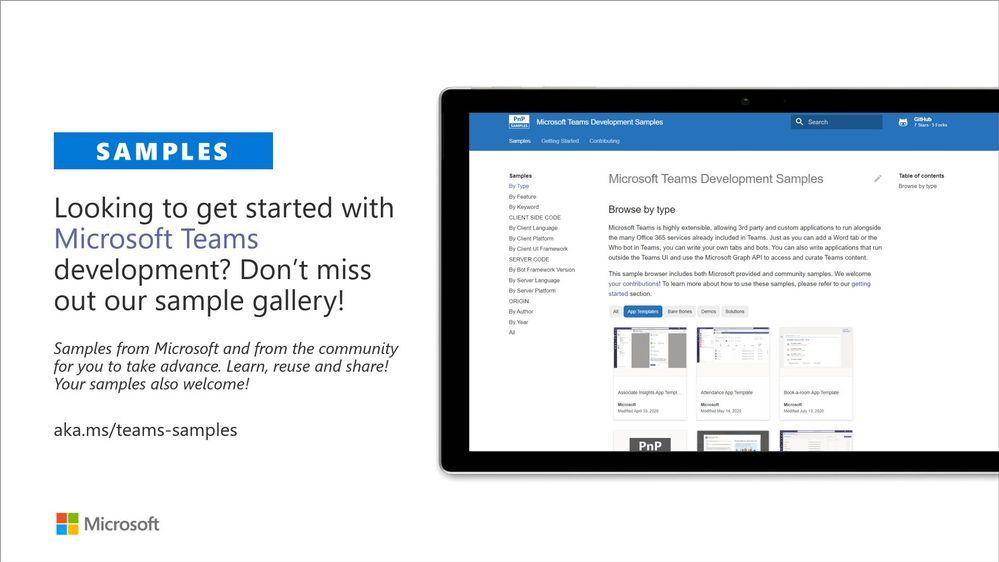
These are samples which have been contributed on the community samples since last summary. We do welcome all Microsoft Teams samples to this gallery. They can be implemented using in any technology.
- New sample tab-sso-graph-upload-as-pdf by Markus Möller (Avanade) | @Moeller2_0 to enable users to upload files via drag n drop and convert the file to a PDF using the current channel as a folder name
If you are interested on Microsoft Teams samples, we have just released also new Microsoft Teams sample gallery. Contributions to Microsoft Teams samples is also more than welcome. This gallery already surfaces all Microsoft samples, Microsoft Teams app templates and community samples.
Power Platform samples
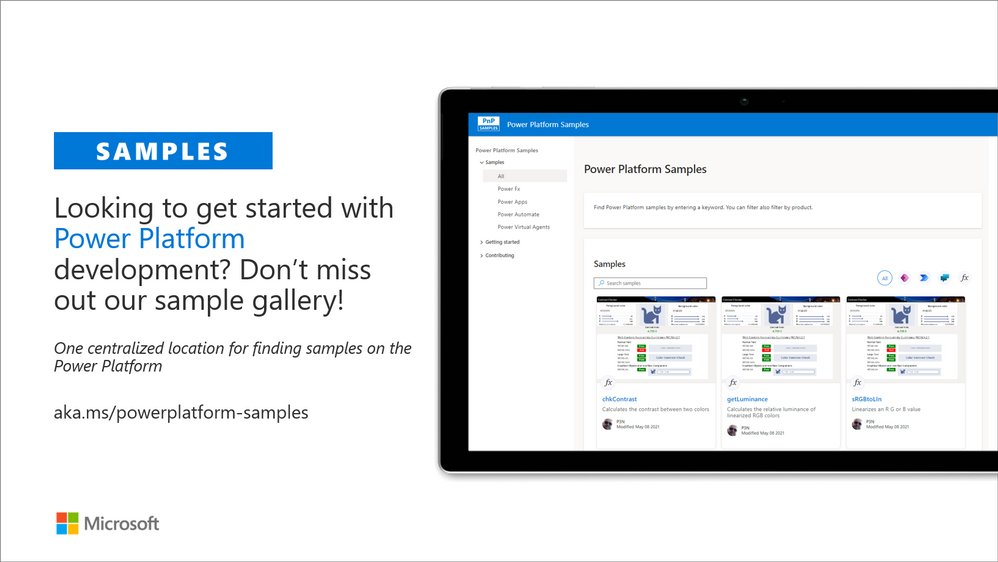
There was numerous smaller updates on the different Power Platforms samples. See more details on available samples from following location:
If you have any existing samples which you’d be willing to share with others – please submit a pull request or contact the PnP team members to get started on getting more closely involved on this initiative. Here to help.
Microsoft 365 Script Samples
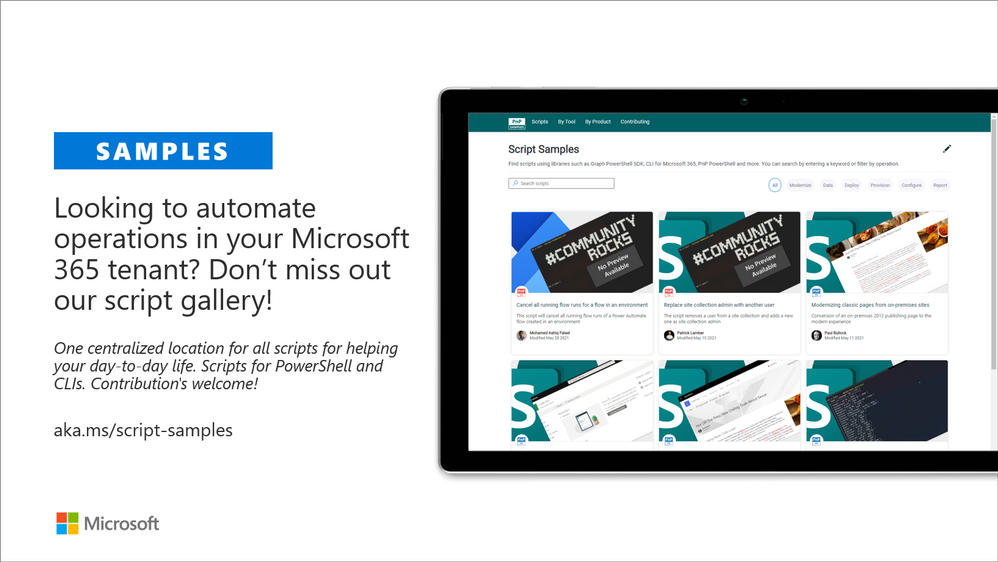
We have released new Microsoft 365 Script Sample gallery within past month. We welcome all scripts on Microsoft 365 automation to this centralized repository, targeted to help to manage and automate day-to-day operations.
Here are the latest updates on the Script Samples
If you have any existing scripts which you’d be willing to share with others – please submit a pull request or contact the PnP team members to get started on getting more closely involved on this initiative.
Independent Connectors Program
Microsoft Power Platform comes with a huge variety of already built-in connectors and also provides you with the ability of creating your own custom connectors. As of July 2021, anyone can submit the connectors they built to Microsoft Power Platform so that they can be used by others as well. Previously, only API owners could publish their connectors. The Independent Publisher Connector Program’s mission is to bring the best together: the best people, connecting great ideas to data, apps, and flows. We want to make it easier for connector developers to collaborate on connectors.
For more information, you can watch this video on Publish a connector to the Publish a connector to the Power Platform with Independent Publisher Connector Program gram and check out Microsoft Power Platform Connectors on GitHub
These are the latest connectors:
Sharing is Caring initiative
The “Sharing Is Caring” imitative is targeted for learning the basics around making changes in Microsoft Docs, in GitHub, submitting pull requests to the PnP repositories and in GitHub in general. Take advantage of this instructor lead training for learning how to contribute to docs or to open-source solutions. Everyone is welcome to learn how to get started on contributing to open-source docs or code!
- See more from the guidance documentation – including all upcoming instructor lead sessions which you can participate!
✍ Different Microsoft 365 related open-source initiatives build together with the community
See exact details on the latest updates from the specific open-source project release notes. You can also follow up on the project updates from our community calls. There are numerous active projects which are releasing new versions with the community even on weekly basis. Get involved!
- Microsoft Look Book – Discover the modern experiences you can build with SharePoint in Microsoft 365. Look book provides design examples for SharePoint Online which can be automatically provisioned to any tenant in the world. See more from https://lookbook.microsoft.com. This service is also provided as open-source solution sample from GitHub.
- yo teams – Open-source Yeoman generator for Microsoft Teams extensibility. Supports creation of bots, messaging extensions, tabs (with SSO), connectors and outgoing Webhooks. See more from https://aka.ms/yoteams.
- PnP Framework – .NET Standard 2.0 SDK containing the classic PnP Sites Core features for SharePoint Online. More around this package from GitHub.
- PnP Core SDK – The PnP Core SDK is an SDK designed to work for Microsoft 365 with Graph API first approach. It provides a unified object model for working with SharePoint Online and Teams which is agnostic to the underlying API’s being called. See more around the SDK from documentation.
- PnP PowerShell – PnP PowerShell is a .NET Core 3.1 / .NET Framework 4.6.1 based PowerShell Module providing over 400 cmdlets that work with Microsoft 365 environments and more specifically SharePoint Online and Microsoft Teams. See more details from documentation.
- Reusable SharePoint Framework controls – Reusable controls for SharePoint Framework web part and extension development. Separate projects for React content controls and Property Pane controls for web parts. These controls are using Office UI Fabric React controls under the covers and they are SharePoint aware to increase the productivity of developers.
- Office 365 CLI – Using the Office 365 CLI, you can manage your Microsoft Office 365 tenant and SharePoint Framework projects on any platform. See release notes for the latest updates.
- PnPJs – PnPJs encapsulates SharePoint REST APIs and provides a fluent and easily usable interface for querying data from SharePoint sites. It’s a replacement of already deprecated pnp-js-core library. See changelog for the latest updates.
- PnP Provisioning Engine and PnP CSOM Core – PnP provisioning engine is part of the PnP CSOM extension. They encapsulate complex business driven operations behind easily usable API surface, which extends out-of-the-box CSOM NuGet packages. See changelog for the latest updates.
- PnP PowerShell – PnP PowerShell cmdlets are open-source complement for the SharePoint Online cmdlets. There are more than 300 different cmdlets to use and you can use them to manage tenant settings or to manipulate actual SharePoint sites. They See changelog for the latest updates.
- PnP Modern Search solution – The PnP ‘Modern Search’ solution is a set of SharePoint Online modern Web Parts allowing SharePoint super users, webmasters and developers to create highly flexible and personalized search based experiences in minutes. See more details on the different supported capabilities from https://aka.ms/pnp-search.
- Modernization tooling – All tools and guidance on helping you to transform you SharePoint to modern experiences from http://aka.ms/sppnp-modernize.
- SharePoint Starter Kit v2 – Building modern experiences with Microsoft Teams flavors for SharePoint Online and SharePoint 2019 – reference solution in GitHub.
- List formatting definitions – Community contributed samples around the column and view formatting in GitHub.
- Site Designs and Site Scripts – Community contributed samples around SharePoint Site Designs and Site Scripts in GitHub.
- DevOps tooling and scripts – Community contributed scripts and tooling automation around DevOps topics (CI/CD) in GitHub.
- Teams provisioning solution – Set of open-source Azure Functions for Microsoft Teams provisioning. See more details from GitHub.
✍ Documentation updates
Please see all the Microsoft 365 development documentation updates from the related documentation sets and repositories as listed below:
? Microsoft 365 Developer and Microsoft 365 Community YouTube video channels
You can find all Microsoft 365 related videos on our YouTube Channel at http://aka.ms/m365pnp/videos or at Microsoft 365 Dev. These channels contains already a significant amount of detailed training material, demo videos, and community call recordings.
Here are the new Microsoft demo or guidance videos released since the last monthly summary:
Community demos as following:
Key contributors to the November2021 update
Here’s the list of active contributors (in alphabetical order) since last release details in GitHub repositories or community channels. PnP is really about building tooling and knowledge together with the community for the community, so your contributions are highly valued across the Microsoft 365 customers, partners and obviously also at Microsoft.
Thank you for your assistance and contributions on behalf of the community. You are truly making a difference! If we missed someone, please let us know.
Companies: Here’s the companies, which provided support the community initiative for this month by allowing their employees working for the benefit of others in the community. There were also people who contributed from other companies during last month, but we did not get their logos and approval to show them in time for these communications. If you still want your logo for this month’s release, please let us know and share the logo with us. Thx.

Microsoft people: Here’s the list of Microsoft people who have been closely involved with the PnP work during last month.
MVP Community team
MVP Community team (PnP Team) manages the PnP community work in the GitHub and also coordinates different open-source projects around Microsoft 365 topics. PnP Team members have a significant impact on driving adoption of Microsoft 365 topics. They have shown their commitment to the open-source and community-driven work by constantly contributing to the benefit of the others in the community.
Thank you for all that you do!
Here are the Microsoft Internal PnP Core team members:
Next steps
See all of the available community calls, tools, components and other assets from https://aka.ms/m365pnp. Get involved!
Got ideas or feedback on the topics to cover, additional partnerships, product feature capabilities? – let us know. Your input is important for us, so that we can support your journey in Microsoft 365.
“Sharing is caring” ?
Microsoft 365 Community (PnP) – November 26th 2021

 We’re pleased to announce that we’ve reached general availability for Microsoft Lists: Fast and offline.
We’re pleased to announce that we’ve reached general availability for Microsoft Lists: Fast and offline. The combination of Progressive Web Apps (PWAs) and the expansion of Project Nucleus enables faster Web applications – even when offline.
The combination of Progressive Web Apps (PWAs) and the expansion of Project Nucleus enables faster Web applications – even when offline. Install Microsoft Lists as a Progressive Web Apps (PWA) from your browser.
Install Microsoft Lists as a Progressive Web Apps (PWA) from your browser. OneDrive as a PWA running on the Windows desktop.
OneDrive as a PWA running on the Windows desktop. A visual diagram showing how web apps interact across your local Windows device and cloud services in Microsoft 365.
A visual diagram showing how web apps interact across your local Windows device and cloud services in Microsoft 365. New Lists indicators show when your items are being save to your device (offline; as shown above), when the list is synchronizing, and when all is up to date (synced).
New Lists indicators show when your items are being save to your device (offline; as shown above), when the list is synchronizing, and when all is up to date (synced).
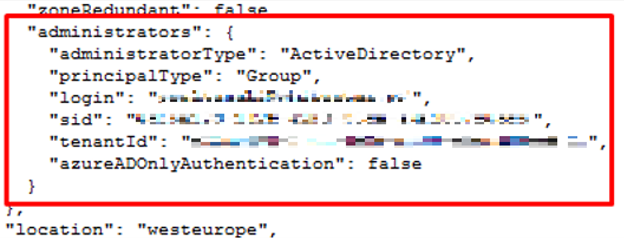
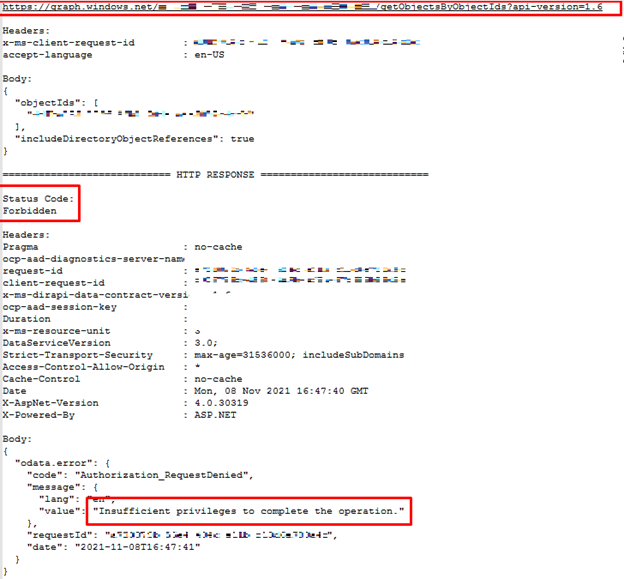




















Recent Comments