by Contributed | Jan 9, 2022 | Technology
This article is contributed. See the original author and article here.
I want to share with you here in this article an example of SQL Injection, how it can be used to access sensitive data and harm the database, and what are the recommendations and steps that can be done to protect your application or website from being vulnerable to SQL Injection.
I created a simple web site with a few lines of code:
- Added System.Data and System.Data.SqlClient Namespaces.
- Create connection, command and Data Adapter objects to execute an SQL command and fill the data table object.
- The command is a Select command query on one of database tables and the result set is filtered by email address, the value that is entered by the user before hitting search button.
- The result will be shown on a grid view object on the page.
The Web Page code:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Web;
using System.Web.UI;
using System.Web.UI.WebControls;
using System.Data;
using System.Data.SqlClient;
namespace SqlInjection
{
public partial class _Default : Page
{
protected void Page_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
}
protected void BtnSearch_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
string connetionString;
System.Data.SqlClient.SqlConnection cnn;
connetionString = @"Data Source=xxx.database.windows.net;Initial Catalog=xxx;User ID=xxx ;Password=xxx ";
cnn = new SqlConnection(connetionString);
cnn.Open();
SqlCommand command = new SqlCommand("SELECT customerid as ID,Firstname + ' ' + lastname as Name,companyname as Company, emailaddress as Email,phone FROM saleslt.customer WHERE EmailAddress = '" + txtEmail.Text + "'", cnn);
SqlDataAdapter MyDataadapter;
MyDataadapter = new SqlDataAdapter(command);
command.Parameters[0].Value = txtEmail.Text;
command.ExecuteScalar();
DataTable Datatbl;
Datatbl = new DataTable();
MyDataadapter.Fill(Datatbl);
GridView.DataSource = Datatbl;
GridView.DataBind();
cnn.Close();
}
}
}
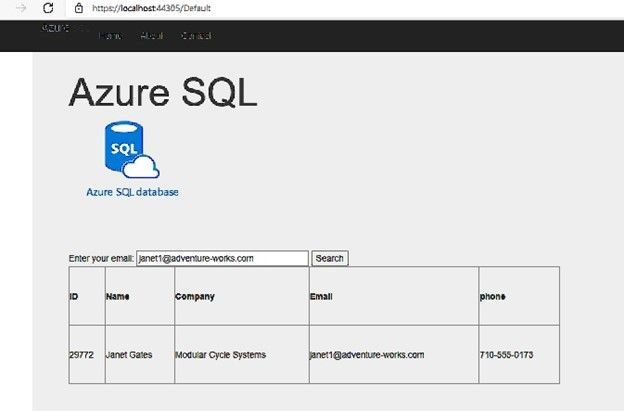
The application is working fine and retrieves data from the database as below screenshot:

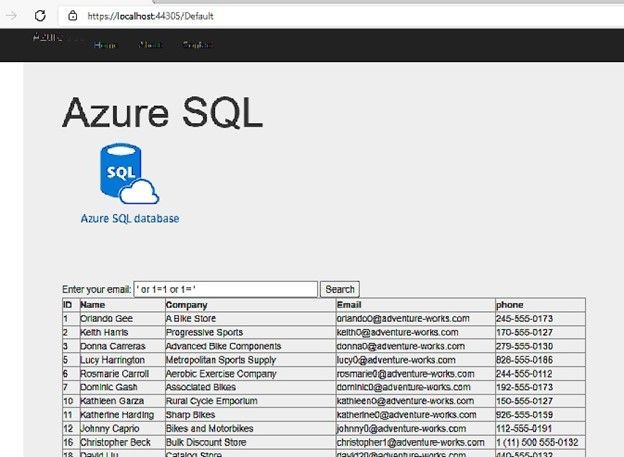
But, if I change the email address value to be ‘ or 1=1 or 1=’ instead of any email address, I will get all the data of the “customers” table, as below screenshot:
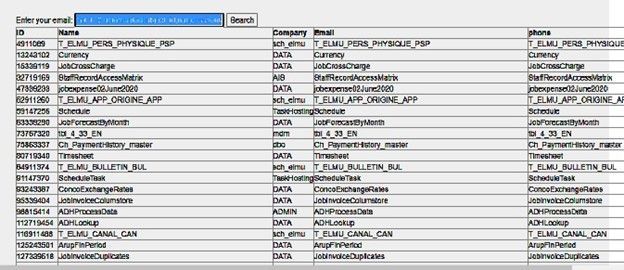
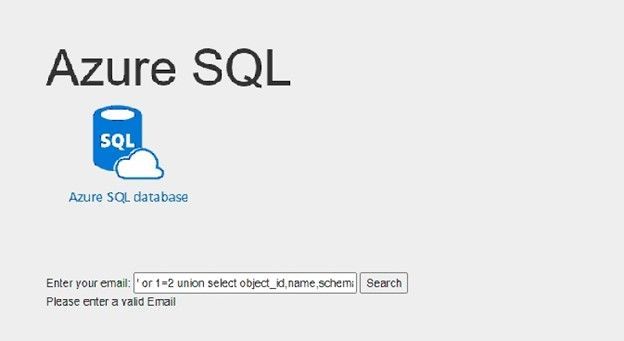
If I try something else, like searching for example: ‘ or 1=2 union select object_id,name,schema_name(schema_id), name , name from sys.tables; select 0 where 1= ‘
Here I did not get the query’s table data, I added union statement to get database tables names using sys.tables system view, and I’ve got the following result:
Now I am able to simply get the list of all database tables and view any table I want, using same SQL injection scenario.
Also, I tried to insert the value : ‘ or 1=2; truncate table dbo.product; select 0 where 1= ‘ ,and I was able to truncate the product table.
The Queries that have been executed on the database are:
(@0 nvarchar(110))SELECT customerid as ID,Firstname + ' ' + lastname as Name,companyname as Company, emailaddress as Email,phone FROM saleslt.customer WHERE EmailAddress = '' or 1=2 union select object_id,name,schema_name(schema_id), name , name from sys.tables; select 0 where 1= ''
(@0 nvarchar(58))SELECT customerid as ID,Firstname + ' ' + lastname as Name,companyname as Company, emailaddress as Email,phone FROM saleslt.customer WHERE EmailAddress = '' or 1=2; truncate table dbo.product; select 0 where 1= ''
How to avoid SQL Injection:
Use Parameters:
I Modified my C# code and added the required parameter to the SQL Command as the following:
protected void BtnSearch_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
string connetionString;
System.Data.SqlClient.SqlConnection cnn;
connetionString = @"Data Source=xxx.database.windows.net;Initial Catalog=xxx;User ID=xxx ;Password=xxxxx ";
cnn = new SqlConnection(connetionString);
cnn.Open();
SqlCommand command = new SqlCommand("SELECT customerid as ID,Firstname + ' ' + lastname as Name,companyname as Company, emailaddress as Email,phone FROM saleslt.customer WHERE EmailAddress = @0", cnn);
command.Parameters.Add(new SqlParameter("0", 1));
SqlDataAdapter MyDataadapter;
MyDataadapter = new SqlDataAdapter(command);
command.Parameters[0].Value = txtEmail.Text;
command.ExecuteScalar();
DataTable Datatbl;
Datatbl = new DataTable();
MyDataadapter.Fill(Datatbl);
GridView.DataSource = Datatbl;
GridView.DataBind();
cnn.Close();
}
Now, if I try the SQL injection it is not working any more, it is giving no result at all:
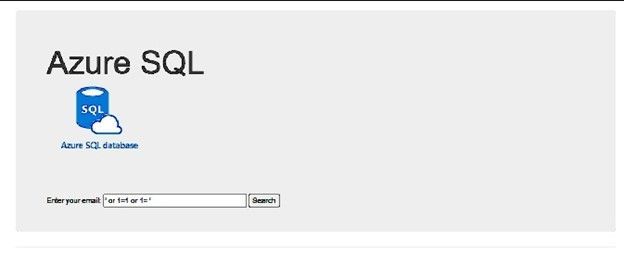
Whatever the value I write on the email text box, the query that is executed on the database is always the following:
(@0 nvarchar(26))SELECT customerid as ID,Firstname + ' ' + lastname as Name,companyname as Company, emailaddress as Email,phone FROM saleslt.customer WHERE EmailAddress = @0
Microsoft Defender:
Microsoft Defender for Cloud – an introduction | Microsoft Docs
Microsoft Defender for Cloud (Azure Security center) can detect such attacks and notify the customer, I received the following email alert:
An application generated a faulty SQL statement on database ‘xxxx’. This may indicate that the application is vulnerable to SQL injection.
|
|
|
Activity details
Severity
|
Medium
|
Subscription ID
|
xxx
|
Subscription name
|
xxx
|
Server
|
xx
|
Database
|
xx
|
IP address
|
81.xx.xx.xx
|
Principal name
|
tr*****
|
Application
|
.Net SqlClient Data Provider
|
Date
|
November 28, 2021 14:50 UTC
|
Threat ID
|
2
|
Potential causes
|
Defect in application code constructing faulty SQL statements; application code doesn’t sanitize user input and may be exploited to inject malicious SQL statements.
|
Investigation steps
|
For details, view the alert in the Azure Security Center.
To investigate further, analyze your audit log.
|
Remediation steps
|
Read more about SQL Injection threats, as well as best practices for writing safe application code. Please refer to Security Reference: SQL Injection.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Give the Application the minimum required permissions:
In the example I shared, the attacker was able to get any data he wants, table names and even was able to truncate or drop tables and more. Maybe it is easier to give permissions as sysadmin or db_owner in one step, but it recommended to give only required permissions (execute permission for example) and only on specific objects required by the application.
Use Application to validate data:
In my web page, the user should use the email address to search for data, it should have an expression special for the email address, and it could not contain spaces and part like 1=1 or .
I added a “Reqular expression Validator” object to the page and linked it to the text box I use for the email address.
Below is the validation expression for the email address:
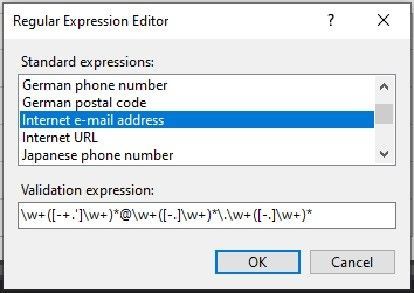
Now I am not able to run the SQL injection again, I get a validation error instead:
by Contributed | Jan 7, 2022 | Technology
This article is contributed. See the original author and article here.
We are thrilled to welcome Barracuda Virtual Reactor® on Azure. With this technology, engineers can simulate fluid, particulate-solid, thermal and chemically reacting behavior in industrial fluid-particle processes while gaining the on-demand and virtually unlimited computing capacity of Azure.
Virtual ReactorTM is the industry-standard tool for many applications in refining, petrochemicals, cement manufacture, power generation and other energy-intensive industries. Today, the same award-winning technology is enabling, and reducing the time to market for, multiple sustainability technologies that are changing our planet for the better. Examples include advanced recycling of plastics, waste-to-energy/fuels/chemicals, renewable fuels, hydrogen production and other decarbonization applications.
Fluid-particle systems in these industries tend to operate 24/7 for years on end, and hence, even small improvements in reliability and performance lead to a tremendous economic impact. Barracuda® reduces the risk of making changes to existing processes by identifying the root cause(s) of underperformance, performing virtual testing of changes and identifying additional optimization opportunities. Similarly, the software empowers those developing new technologies to economically explore a wide range of possibilities during R&D while compressing development, scale-up and commercialization timeframes.
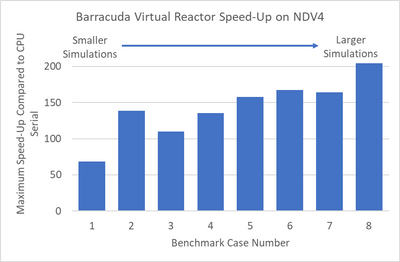
We recently tested Virtual Reactor on Azure’s state-of-the-art NDv4 virtual machines (VMs)to showcase performance scalability across a variety of models. We have highlighted the results of the Virtual Reactor with our ND96asr_v4 VM, and the performance is shown below across 8 different sizes.

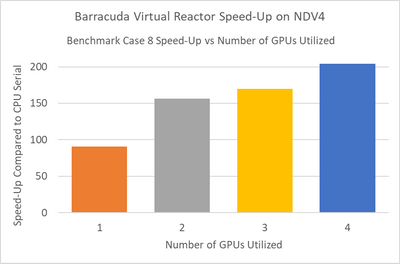
Smaller simulations which in our tests had less than 25 million computational particles, achieved maximum speed-up when running in multi-GPU mode using two NVIDIA A100 Tensor Core GPUs. Larger simulations achieved maximum speed-up when using four GPUs. The speed-up scaling1 from one to four GPUs is shown below for benchmark case 82.
NOTE: Case 8 is a simulation benchmark case containing 55M particles; for additional GPU scaling questions please contact CPFD
The ND A100 v4 series starts with a single virtual machine and eight NVIDIA A100 Tensor Core GPUs. ND A100 v4-based deployments can scale up to thousands of GPUs with 1.6 Tb/s of interconnect bandwidth per VM. Each GPU within the VM is provided with its own dedicated, topology-agnostic NVIDIA Quantum 200Gb/s InfiniBand networking. These connections are automatically configured between VMs occupying the same virtual machine scale set, and support GPUDirect RDMA.
Each GPU features third-generation NVIDIA NVLink connectivity for communication within the VM, and the instance is also backed by 96 physical second-generation AMD Epyc™ CPU cores.
These instances provide excellent performance for many AI, ML and analytics tools that support GPU acceleration ‘out-of-the-box,’ such as TensorFlow, Pytorch, Caffe, RAPIDS and other frameworks. Additionally, the scale-out InfiniBand interconnect is supported by a large set of existing AI and HPC tools built on NVIDIA’s NCCL2 communication libraries for seamless clustering of GPUs.
“Azure’s multi-GPU virtual machines powered by NVIDIA A100 Tensor Core GPUs provide the global Barracuda Virtual Reactor user community with instant access to the latest high performance computing resources without the overhead of purchasing and maintaining on-premise hardware. The observed speed-ups of over 200x, combined with the convenience of the Azure Platform, provide our clients with virtually unlimited, on-demand, compute bandwidth as they tackle some of our planet’s toughest engineering, energy and sustainability challenges.”
Peter Blaser, Vice President of Operations, CPFD Software
“We welcome Barracuda Virtual Reactor to Azure and are excited to showcase this exciting technology to customers in process industries who will benefit immensely from our purpose-built NVIDIA GPU hosts that are designed to deliver superior cost performance for this workload. Azure and CPFD have joined forces to offer customers a compelling range of options to explore Virtual Reactor on Azure and pick the best VM sizing suited to their use case requirements.”
Kurt Niebuhr, Azure Compute HPC | AI Workload Incubation & Ecosystem Team Lead
About CPFD
CPFD Software is advancing multiphase simulation and technology. Our flagship product, Barracuda Virtual Reactor, is a physics-based engineering software package capable of predicting fluid, particulate-solid, thermal and chemically reacting behavior in fluidized bed reactors and other fluid-particle systems reducing the risk associated with design, scale-up, commercialization, and trouble-shooting of industrial processes. The Virtual Reactor technology is accessible through software licensing, consulting, or engineering services.
NOTE:
1For additional GPU scaling questions please contact CPFD
2Case 8 is a simulation benchmark case containing 55M particles
by Contributed | Jan 5, 2022 | Technology
This article is contributed. See the original author and article here.
We are excited to announce the preview release of auto-failover groups for Azure SQL Hyperscale tier. This preview release includes support for forced and planned failover for Azure SQL Hyperscale databases that use active geo-replication and auto-failover groups. Some key benefits of auto-failover groups include:
- Simplified management of a group of geo-replicated databases including ability to failover the entire group of databases.
- Ability for application to maintain the same read/write and read-only endpoints after failover.
- Recovery during loss of an entire region through geo-failover which can be initiated manually or through an automatic failover policy.
- Readable online secondaries that can be used for read-only workloads by connecting with read-only listener endpoints which remain unchanged during geo-failovers.
Hyperscale service tier supports 100 TB of database size, rapid scale (out and up) and nearly instantaneous database backups, removing the limits traditionally seen in cloud databases.
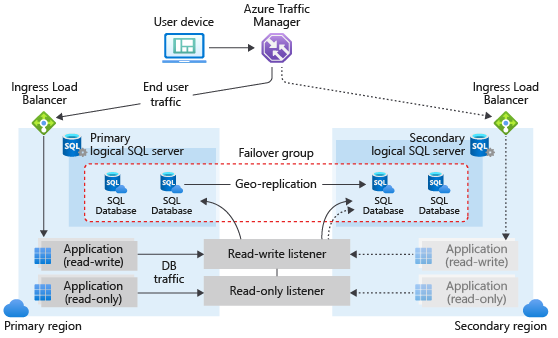
How auto-failover groups work for Hyperscale
Auto-failover groups are created between servers in 2 regions. The groups can include all or some databases in the servers. If a Hyperscale database is selected to be part of the failover group, then this database will failover with the rest of the failover group unit. The following diagram illustrates a typical configuration of a geo-redundant cloud application using multiple databases and auto-failover group.

Available regions
Auto-failover groups for Hyperscale will be supported in all regions where Azure SQL Hyperscale is supported.
Quick start
a. Create an Auto-failover group using Portal.
- Failover groups can be configured at the server level. Select the name of the server under Server name to open the settings for the server.
- Select Failover groups under the Settings pane, and then select Add group to create a new failover group.
- On the Failover Group page, enter or select your desired values for your failover group.
- Add your Hyperscale database to the failover group then select Create.
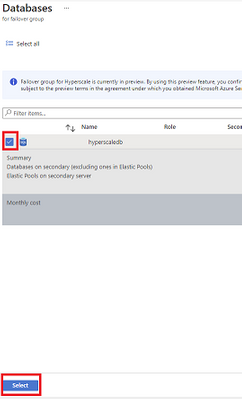
b. Create an Auto-failover group using PowerShell.
c. Create an Auto-failover group using CLI.
d. Create an Auto-failover group using REST API.
Geo-failover examples
Example 1: Planned failover for an auto-failover group
a. Execute a failover of an auto-failover group in Portal.
1. Select your failover group.
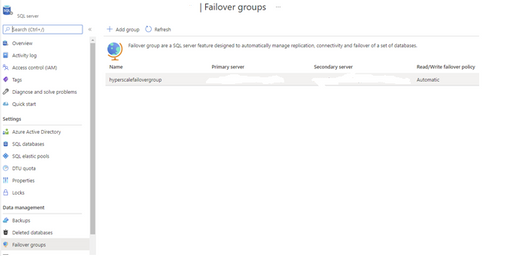
2. Select Failover to initiate failover for your auto-failover group. Once failover is completed you should see that your primary and secondary servers have swapped roles.
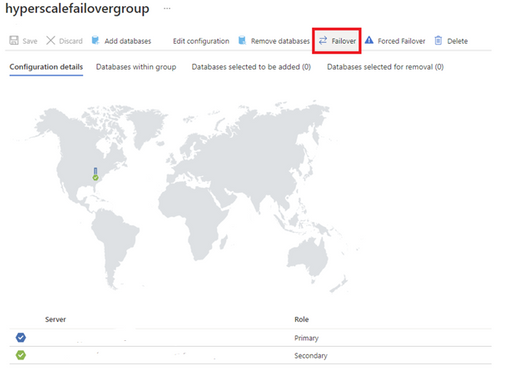
b. Execute a failover of an auto-failover group using Switch-AzSqlDatabaseFailoverGroup in PowerShell.
c. Execute a failover of an auto-failover group using az sql failover-group set-primary in CLI.
d. Execute a failover of an auto-failover group using REST API.
Example 2: Forced failover with active geo-replication
a. Execute a failover using Portal.
1. Select the Replicas tab. In the list of geo replicas click the ellipsis for the secondary you would like to become the new primary. Then select Forced failover.
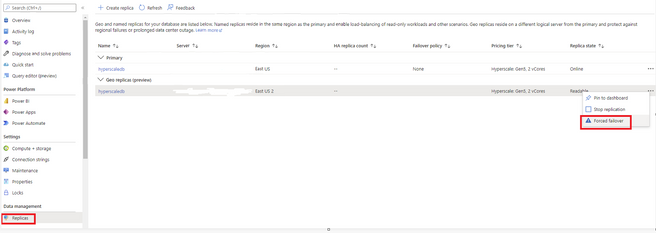
2. You should now see that the primary and secondary have swapped roles.
b. Execute a failover using Set-AzSqlDatabaseSecondary in PowerShell with the -AllowDataLoss parameter specified.
c. Execute a failover using az sql db replica set-primary in CLI with the –allow-data-loss parameter specified.
d. Execute a failover using REST API.
Learn more
https://docs.microsoft.com/azure/azure-sql/database/auto-failover-group-overview
https://aka.ms/activegeoreplication
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/azure-sql/database/service-tier-hyperscale











Recent Comments