by Contributed | Feb 6, 2023 | Technology
This article is contributed. See the original author and article here.
No último trimestre realizei algumas análises de performance em Web API’S desenvolvidas utilizando o ASP.NET Core, e a maioria estava com o mesmo problema: O uso incorreto dos objetos de tipo HttpClient. Percebi então que havia um padrão problemático na sua utilização.
Portanto resolvi escrever este artigo, com o intuito de ajudar os desenvolvedores a utilizarem corretamente esse tipo de objeto.
O problema
Realizar chamadas HTTP é uma tarefa simples, você só precisa criar instanciar de um objeto do tipo HttpClient, configurar algumas propriedades e pronto, você está apto a realizar sua chamada HTTP. A classe HttpClient implementa a interface IDisposable, o que significa que se você é um desenvolvedor atento, invocará o método Dispose, para que o GC possa liberar os recursos nativos apropriadamente quando essa instância for descartada.
A implementação mais comum segue um padrão parecido com:
using HttpClient client = new HttpClient();
client.BaseAddress = new Uri(“https://google.com”);
var response = await client.GetAsync(“”);
A palavra reservada using garante que o método Dispose da instância denominada client, será invocada no final do escopo do seu contexto execução. Essa sintaxe do using é relativamente nova, você pode se deparar com o seu uso da seguinte forma: using(HttpClient client = new HttpClient()){}.
O código acima deve funcionar em alguns cenários, porém, em um momento de alto volume de requisições, sua aplicação pode apresentar um aumento no tempo de resposta, chegando até a ficar indisponível, e você pode começar a observar exceções do tipo System.Net.Sockets.SocketException sendo lançadas com a mensagem: Only one usage of each socket address (protocol/network address/port) is normally permitted.
Reprodução do problema
Para que você possa entender melhor esse comportamento, uma boa estratégia é reproduzi-lo em um ambiente controlado. Para esse exemplo, você precisará do .NET Core 6.0.
Projeto
Em uma pasta de sua preferência crie um projeto utilizando o template de Console do .NET CLI, através do comando dotnet new console.
No arquivo Program.cs copie o código abaixo:
while(true)
{
using (var client = new HttpClient())
{
var result = await client.GetAsync(“http://techcommunity.microsoft.com/t5/desenvolvedores-br/bg-p/DesenvolvedoresBR”);
Console.WriteLine(result.StatusCode);
}
}
O código acima implementa um laço infinito, onde cada iteração instancia um novo HttpClient e realiza uma requisição ao endereço [http://techcommunity.microsoft.com/t5/desenvolvedores-br/bg-p/DesenvolvedoresBR].
Execute o programa de teste com o comando: dotnet run.
Netstat
Primeiro precisamos descobrir o endereço IP do nome techcommunity.microsoft.com. Para tal, abra um prompt de comando, e rode o comando nslookup techcommunity.microsoft.com. Você verá um resultado parecido com:
Server: UnKnown
Address: 192.168.86.1
Non-authoritative answer:
Name: e8318.dsca.akamaiedge.net
Addresses: 2600:1419:4e00:286::207e
2600:1419:4e00:28c::207e
96.6.215.78
Aliases: techcommunity.microsoft.com
gxcuf89792.lithium.com
techcommunity.microsoft.com.edgekey.net
Os endereços IPs que precisamos estão no campo Addresses (2600:1419:4e00:286::207e, 2600:1419:4e00:28c::207e e 96.6.215.78), guarde-os para usarmos na análise.
Deixe a aplicação rodando por alguns minutos, e termine o processo em seguida.
Utilizaremos a ferramenta netstat para visualizarmos as conexões TCP, em seguida realizaremos um filtro utilizando os endereços de IP que capturamos anteriormente. Para isso rode o comando:
netstat -an | findstr /c:”2600:1419:4e00:286::207e” /c:”2600:1419:4e00:28c::207e” /c:”96.6.215.78″
No meu caso, o resultado foi:
TCP [2804:431:d728:afa7:61bf:a077:45be:68b3]:65293 [2600:1419:1e00:58b::207e]:80 TIME_WAIT
TCP [2804:431:d728:afa7:61bf:a077:45be:68b3]:65295 [2600:1419:1e00:58b::207e]:80 TIME_WAIT
TCP [2804:431:d728:afa7:61bf:a077:45be:68b3]:65297 [2600:1419:1e00:582::207e]:80 TIME_WAIT
TCP [2804:431:d728:afa7:61bf:a077:45be:68b3]:65301 [2600:1419:1e00:582::207e]:80 TIME_WAIT
TCP [2804:431:d728:afa7:61bf:a077:45be:68b3]:65303 [2600:1419:1e00:582::207e]:80 TIME_WAIT
TCP [2804:431:d728:afa7:61bf:a077:45be:68b3]:65305 [2600:1419:1e00:582::207e]:80 TIME_WAIT
TCP [2804:431:d728:afa7:61bf:a077:45be:68b3]:65307 [2600:1419:1e00:582::207e]:80 TIME_WAIT
TCP [2804:431:d728:afa7:61bf:a077:45be:68b3]:65309 [2600:1419:1e00:582::207e]:80 TIME_WAIT
TCP [2804:431:d728:afa7:61bf:a077:45be:68b3]:65311 [2600:1419:1e00:582::207e]:80 TIME_WAIT
TCP [2804:431:d728:afa7:61bf:a077:45be:68b3]:65313 [2600:1419:1e00:58b::207e]:80 TIME_WAIT
TCP [2804:431:d728:afa7:61bf:a077:45be:68b3]:65315 [2600:1419:1e00:58b::207e]:80 TIME_WAIT
TCP [2804:431:d728:afa7:61bf:a077:45be:68b3]:65318 [2600:1419:1e00:58b::207e]:80 TIME_WAIT
TCP [2804:431:d728:afa7:61bf:a077:45be:68b3]:65320 [2600:1419:1e00:58b::207e]:80 TIME_WAIT
TCP [2804:431:d728:afa7:61bf:a077:45be:68b3]:65322 [2600:1419:1e00:58b::207e]:80 TIME_WAIT
TCP [2804:431:d728:afa7:61bf:a077:45be:68b3]:65324 [2600:1419:1e00:58b::207e]:80 TIME_WAIT
TCP [2804:431:d728:afa7:61bf:a077:45be:68b3]:65326 [2600:1419:1e00:58b::207e]:80 TIME_WAIT
TCP [2804:431:d728:afa7:61bf:a077:45be:68b3]:65328 [2600:1419:1e00:58b::207e]:80 TIME_WAIT
TCP [2804:431:d728:afa7:61bf:a077:45be:68b3]:65330 [2600:1419:1e00:58b::207e]:80 TIME_WAIT
TCP [2804:431:d728:afa7:61bf:a077:45be:68b3]:65332 [2600:1419:1e00:58b::207e]:80 TIME_WAIT
TCP [2804:431:d728:afa7:61bf:a077:45be:68b3]:65336 [2600:1419:1e00:58b::207e]:80 TIME_WAIT
TCP [2804:431:d728:afa7:61bf:a077:45be:68b3]:65338 [2600:1419:1e00:58b::207e]:80 TIME_WAIT
TCP [2804:431:d728:afa7:61bf:a077:45be:68b3]:65371 [2600:1419:1e00:58b::207e]:80 TIME_WAIT
TCP [2804:431:d728:afa7:61bf:a077:45be:68b3]:65373 [2600:1419:1e00:58b::207e]:80 TIME_WAIT
TCP [2804:431:d728:afa7:61bf:a077:45be:68b3]:65375 [2600:1419:1e00:58b::207e]:80 TIME_WAIT
TCP [2804:431:d728:afa7:61bf:a077:45be:68b3]:65377 [2600:1419:1e00:58b::207e]:80 TIME_WAIT
TCP [2804:431:d728:afa7:61bf:a077:45be:68b3]:65380 [2600:1419:1e00:58b::207e]:80 TIME_WAIT
TCP [2804:431:d728:afa7:61bf:a077:45be:68b3]:65382 [2600:1419:1e00:58b::207e]:80 TIME_WAIT
TCP [2804:431:d728:afa7:61bf:a077:45be:68b3]:65384 [2600:1419:1e00:58b::207e]:80 TIME_WAIT
Repare que mesmo após parar o processo ainda existem 27 conexões no estado de: TIME_WAIT.
Este problema é conhecido como: exaustão de portas TCP ou TCP port exhaustion em inglês. Significa que todas as portas elegíveis à estabelecer a conexão TCP, estão em uso.
Time Wait
Vamos revisar o código da aplicação, para entender melhor o seu comportamento:
while(true)
{
using (var client = new HttpClient())
{
var result = await client.GetAsync(“http://techcommunity.microsoft.com/t5/desenvolvedores-br/bg-p/DesenvolvedoresBR”);
Console.WriteLine(result.StatusCode);
}
}
Quando a instrução new HttpClient() é executada, uma nova conexão TCP é criada, porém quando o método Dispose é executado no final do bloco using, a porta TCP usada pela aplicação não é liberada instantaneamente, ao invés disso, ela entra em um estado de: TIME_WAIT.
O SO mantém essas conexões por um tempo pré-definido. Por padrão, o estado de TIME_WAIT é mantido por 240 segundos, sendo configurável através da chave de registro: HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESYSTEMCurrentControlSetServicesTcpipParametersTcpTimedWaitDelay]. Mas não é uma boa ideia modificar essa chave, a não ser que você saiba muito bem o que está fazendo.
Conclusão
Para evitar o problema de exaustão de sockets, devemos criar uma conexão, e reutilizá-la o máximo de vezes possível. Uma saída é criar os objetos HttpClient como singleton ou estáticos.
No nosso exemplo o código ficaria assim:
var client = new HttpClient();
while(true)
{
var result = await client.GetAsync(“http://techcommunity.microsoft.com/t5/desenvolvedores-br/bg-p/DesenvolvedoresBR”);
Console.WriteLine(result.StatusCode);
}
Essa segunda abordagem, evitaria o problema, porém, no contexto de uma aplicação Web, ela pode trazer alguns problemas, se acontecer alguma mudança em relação a resolução de DNS, o código acima não será resiliente a ponto de resolvê-la novamente.
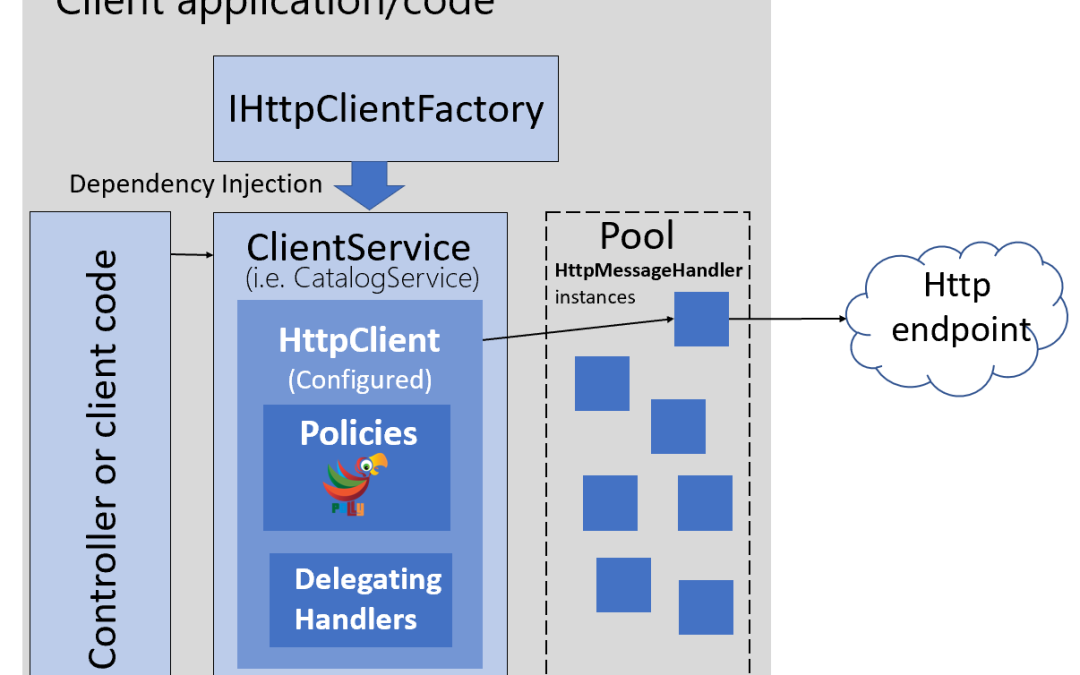
Para endereçar esse e outros problemas, o time do ASP.NET Core implementou a interface IHttpClientFactory.
Basicamente essa interface funciona como uma fábrica de HttpClient, ela será responsável por implementar um pool de objetos do tipo HttpMessageHandler’s, e os reutilizará.
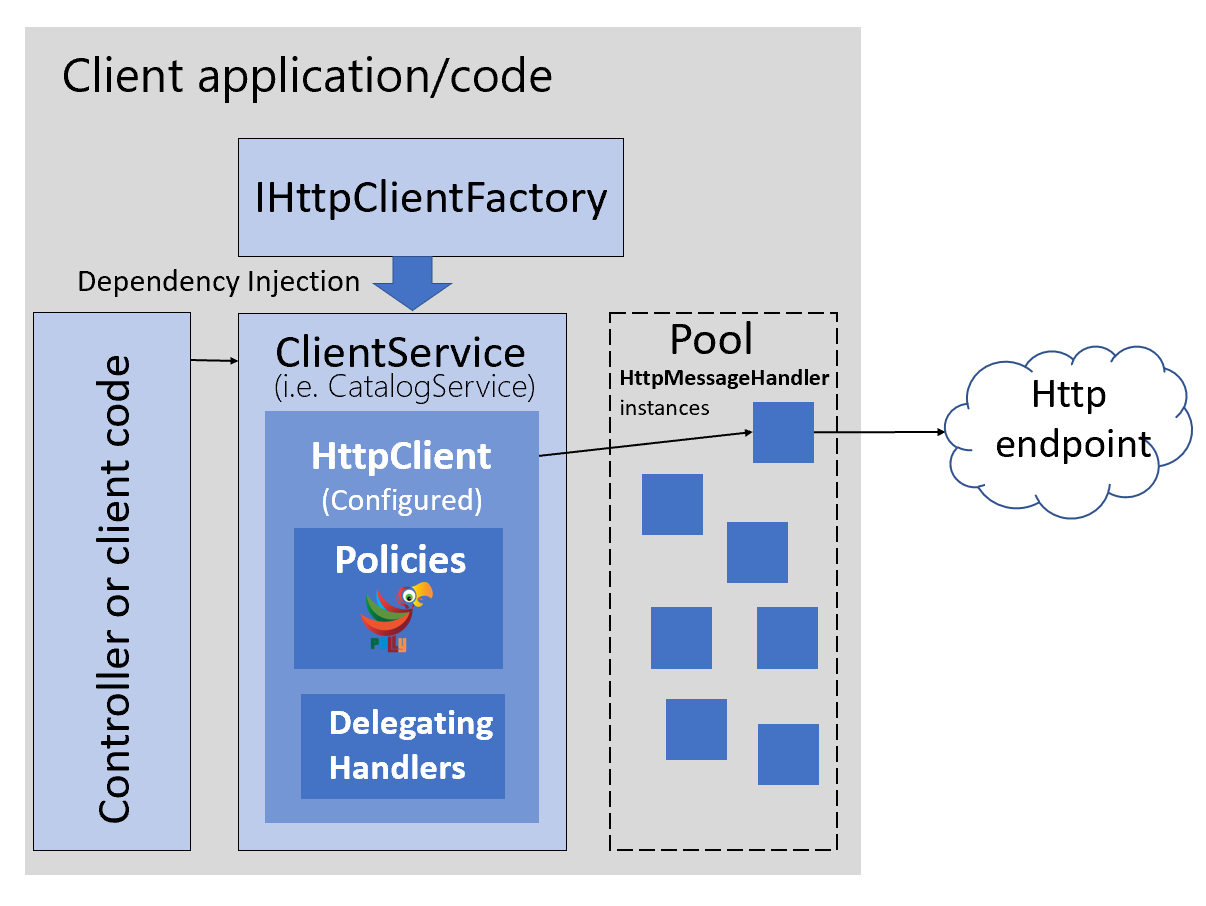
Você pode usar essa fábrica com diferentes estratégias, a minha preferida é a nomeada de: Typed Clients ou Cliente tipado em português.
Com essa estratégia podemos criar classes de serviços específicos, e injetar um HttpClient no seu construtor através do container de injeção de dependências, por exemplo:
public class CatalogService : ICatalogService
{
private readonly HttpClient _httpClient;
private readonly string _remoteServiceBaseUrl;
public CatalogService(HttpClient httpClient)
{
_httpClient = httpClient;
}
public async Task GetCatalogItems(int page, int take,
int? brand, int? type)
{
var uri = API.Catalog.GetAllCatalogItems(_remoteServiceBaseUrl,
page, take, brand, type);
var responseString = await _httpClient.GetStringAsync(uri);
var catalog = JsonConvert.DeserializeObject(responseString);
return catalog;
}
}
Agora bastaria configurar o nosso container de injeção, na classe Program.cs, ou na classe Startup.cs em versões anteriores ao .NET 6, da seguinte forma:
services.AddHttpClient<ICatalogService, CatalogService>()
Se você tem dúvidas de como funciona a injeção de dependência no ASP.NET core, sugiro a breve leitura do artigo de um dos meus mestres aqui na Microsoft: Entendendo Injeção de Dependência com .NET.
Particularmente acho essa última abordagem muito elegante, pois, podemos isolar os pontos de integração com outros serviços, de forma desacoplada do resto do projeto. Recomendo fortemente a ler sobre as outras estratégias de criação de objetos HttpClient, viabilizadas pela IHttpClientFactory: Use o IHttpClientFactory para implementar solicitações HTTP resilientes.
by Contributed | Feb 4, 2023 | Technology
This article is contributed. See the original author and article here.
SAP ASE 16.0 on Azure NetApp Files for SAP Workloads on SLES15
Introduction
This document will show how you can install SAP NetWeaver 7.5 based on ASE 16.0 and SLES15 SP2 in Azure using Azure NetApp Files (ANF) as storage platform for data and log areas.
SAP Installation Documentation:
Installation Guide for Linux (sap.com)
SAP ASE Home – SAP ASE – Community Wiki
1554717 – SYB: Planning information for SAP on ASE – SAP ONE Support Launchpad
1928533 – SAP Applications on Microsoft Azure: Supported Products and Azure VM types
2015553 – SAP on Microsoft Azure: Support prerequisites
1492000 – General Support Statement for Virtual Environments – SAP ONE Support Launchpad
Note: Screenshots, input into dialogs, or operating system commands are based on the most recent versions of SWPM, SAP ASE 16.0, and SLES 15 SP2 as of January 2023. All these dialogs and/or commands can change with successor versions.
Download the ASE Software from the SAP Service marketplace

Download the Patch SP04 (or newer) from the SAP Service Marketplace
Download the DB Client
Download the NetWeaver 7.5 Stack – Export

The Kernel

And as last the SWPM

The IGS
The IGS Helper
And last but not least …the SAP Host Agent
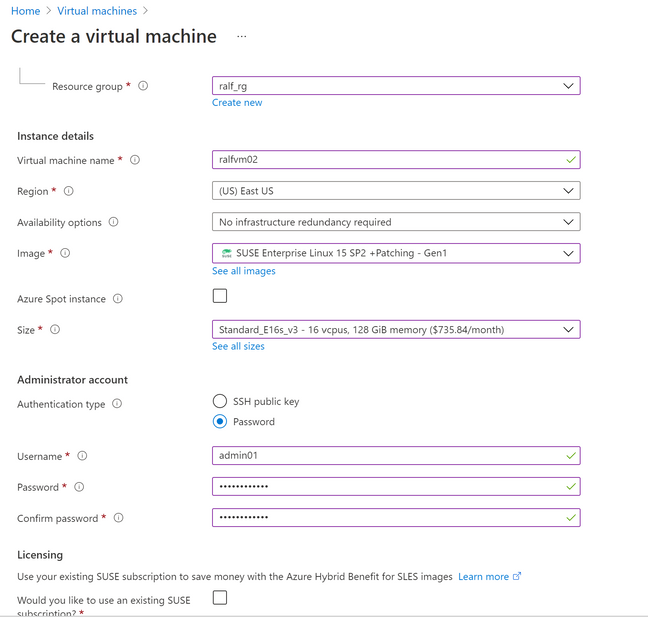
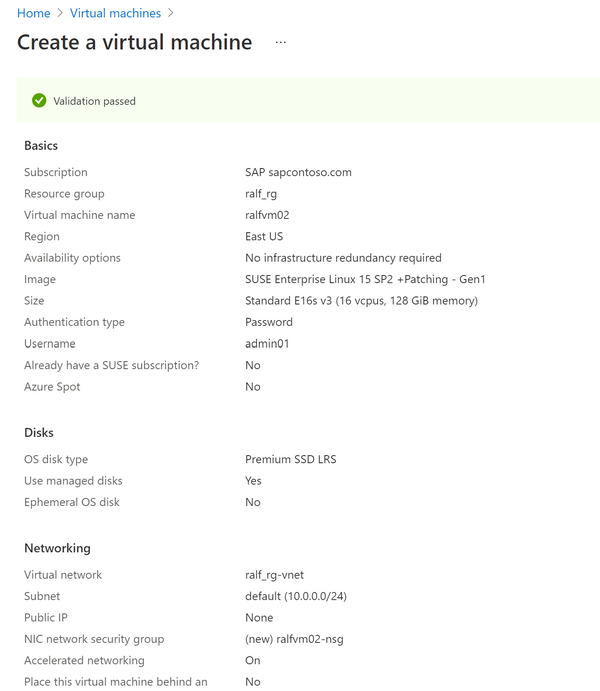
Create an Azure VM in your Azure Subscription
In this case we created an E16-8ds_v4 with 128GB of RAM and deployed SLES12SP5 on it.
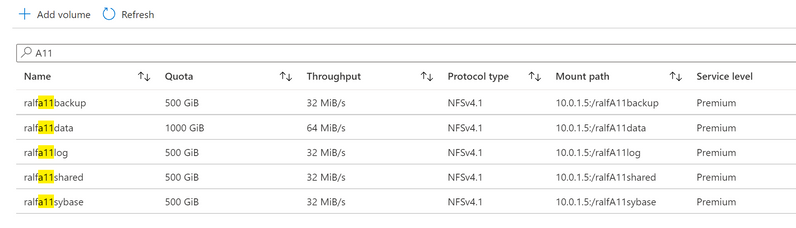
Volume design on ANF
Create the volume structure on ANF. The size of each volume is depending on a proper capacity and performance sizing-
Mount the volumes and create the directories.
vi /etc/idmapd.conf
# Example
[General]
Domain = defaultv4iddomain.com
[Mapping]
Nobody-User = nobody
Nobody-Group = nobody
update the system
zypper up
Install the RPM’s regarding the installation manual
zypper in motif libXtst-devel libXp-devel libX11-devel libSM-devel libICE-devel
zypper in glibc-32bit
zypper in sapconf
check that sapconf is running and that it is enabled.
systemctl status sapconf
sapconf.service – sapconf Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/sapconf.service; enabled; vendor preset: enable> Active: active (exited) since Fri 12:54:21 UTC; 5min ago
create the group ID for your SAP systems (should be the same for all SAP systems)
groupadd sapsys -g 79
ASE Volume design for non XXL installations
As usual create one shared volume for the Application Server part , a Sybase volume for the database specific directories, data and log volume and the backup volume ideally on a different storage endpoint.
This diagram virtualizes the volume structure for ASE
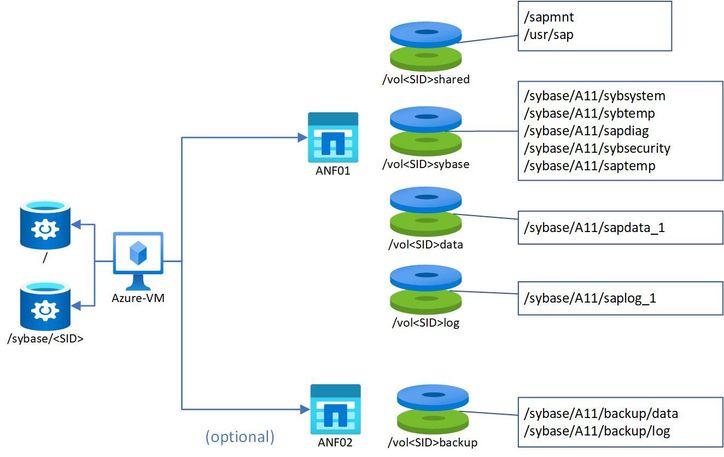
Create the directory structure on the OS and on the NetApp volumes.
Create the SAP App server structure
mount -o rsize=262144,wsize=262144,sec=sys,vers=4.1 anf02:/ralfA11shared /mnt
mkdir -p /mnt/sapmnt /mnt/usr_sap
mkdir -p /usr/sap/A11 /sapmnt
umount /mnt
Create the Sybase “shared” structure
mount -t nfs -o rw,hard,sync,rsize=262144,wsize=262144,sec=sys,vers=4.1,tcp 10.0.1.5:/ralfA11sybase /mnt
mkdir -p /sybase/A11 /sybase/A11/sybsystem /sybase/A11/sybtemp /sybase/A11/sapdiag /sybase/A11/sybsecurity /sybase/A11/saptemp
mkdir -p /mnt/sybsystem /mnt/sybtemp /mnt/sapdiag /mnt/sybsecurity /mnt/saptemp
umount /mnt
Create the data structure
mount -t nfs -o rw,hard,sync,rsize=262144,wsize=262144,sec=sys,vers=4.1,tcp 10.0.1.5:/ralfA11data /mnt
mkdir -p /sybase/A11/sapdata_1
mkdir -p /mnt/sapdata_1
umount /mnt
Create the log structure
mount -t nfs -o rw,hard,sync,rsize=262144,wsize=262144,sec=sys,vers=4.1,tcp 10.0.1.5:/ralfA11log /mnt
mkdir /sybase/A11/saplog_1
mkdir /mnt/saplog_1
umount /mnt
Create the backup structure
mount -t nfs -o rw,hard,sync,rsize=262144,wsize=262144,sec=sys,vers=4.1,tcp 10.0.1.5:/ralfA11backup /mnt
mkdir -p /sybase/A11/backup/data /sybase/A11/backup/log
mkdir -p /mnt/data /mnt/log
umount /mnt
Create the fstab
vi /etc/fstab
…
..
anf02:/ralfASEsoftware /Software nfs rw,hard,timeo=600,vers=4.1,nconnect=8,rsize=262144,wsize=262144,noatime,lock 0 0
#
anf02:/ralfA11shared/sapmnt /sapmnt nfs rw,hard,timeo=600,vers=4.1,nconnect=8,rsize=262144,wsize=262144,noatime,lock 0 0
anf02:/ralfA11shared/usr_sap /usr/sap/A11 nfs rw,hard,timeo=600,vers=4.1,nconnect=8,rsize=262144,wsize=262144,noatime,lock 0 0
#
anf02:/ralfA11sybase/sybsystem /sybase/A11/sybsystem nfs rw,hard,timeo=600,vers=4.1,nconnect=8,rsize=262144,wsize=262144,noatime,lock 0 0
anf02:/ralfA11sybase/sybtemp /sybase/A11/sybtemp nfs rw,hard,timeo=600,vers=4.1,nconnect=8,rsize=262144,wsize=262144,noatime,lock 0 0
anf02:/ralfA11sybase/sapdiag /sybase/A11/sapdiag nfs rw,hard,timeo=600,vers=4.1,nconnect=8,rsize=262144,wsize=262144,noatime,lock 0 0
anf02:/ralfA11sybase/sybsecurity /sybase/A11/sybsecurity nfs rw,hard,timeo=600,vers=4.1,nconnect=8,rsize=262144,wsize=262144,noatime,lock 0 0
anf02:/ralfA11sybase/saptemp /sybase/A11/saptemp nfs rw,hard,timeo=600,vers=4.1,nconnect=8,rsize=262144,wsize=262144,noatime,lock 0 0
anf02:/ralfA11data/sapdata_1 /sybase/A11/sapdata_1 nfs rw,hard,timeo=600,vers=4.1,nconnect=8,rsize=262144,wsize=262144,noatime,lock 0 0
anf02:/ralfA11log/saplog_1 /sybase/A11/saplog_1 nfs rw,hard,timeo=600,vers=4.1,nconnect=8,rsize=262144,wsize=262144,noatime,lock 0 0
Prepare the SAP installation
Download the required packages from the SAP Software Download Center. Store the files in /Software
/Software # ll
-rw-r–r– 1 root root 3692226709 Sep 21 11:03 51050829_3.ZIP
-rw-r–r– 1 root root 2373751114 Sep 21 11:00 51055060_1.ZIP
-rw-r–r– 1 root root 11462898 Sep 21 11:07 ASEBC16004P_1-20012478.SAR
-rw-r–r– 1 root root 2825640866 Sep 21 11:01 ASEBS16004P_1-10013281.SAR
-rw-r–r– 1 root root 4483040 Aug 25 09:21 SAPCAR.EXE
-rw-r–r– 1 root root 4742096 Sep 15 12:58 SAPCAR_win.EXE
-rw-r–r– 1 root root 25524734 Sep 21 11:12 SAPEXEDB_801-80002684.SAR
-rw-r–r– 1 root root 370681480 Sep 21 11:14 SAPEXE_801-80002674.SAR
-rw-r–r– 1 root root 79045422 Sep 21 13:13 SAPHOSTAGENT53_53-80004822.SAR
-rw-r–r– 1 root root 550097396 Sep 21 11:16 SWPM10SP32_6-20009701.SAR
-rw-r–r– 1 root root 104064440 Sep 21 11:57 igsexe_13-80003187.sar
-rw-r–r– 1 root root 62964377 Sep 21 11:57 igshelper_17-10010245.sar
/Software # mkdir Kernel_753
/Software # mv SAPEXE_801-80002674.SAR SAPEXEDB_801-80002684.SAR SAPHOSTAGENT53_53-80004822.SAR igsexe_13-80003187.sar igshelper_17-10010245.sar Kernel_753
Maintain the hosts file
vi /etc/hosts
127.0.0.1 localhost
10.0.0.10 ralfvm02.local ralfvm02
10.0.1.4 anf01
10.0.1.5 anf02
Extend the hostname
vi /etc/hostname
ralfvm02.local
Copy the SAPCAR to /usr/bin which allows you an easier usage.
cp SAPCAR.EXE /usr/bin/SAPCAR
chmod 775 /usr/bin/SAPCAR
set the root password on the VM (required for the SAP installation)
sudo su –
passwd
Changing password for user root.
New password: *********
Retype new password: *******
passwd: all authentication tokens updated successfully.
df -h
df -h
Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on
/dev/sda4 29G 2.9G 26G 10% /
/dev/sda3 1014M 108M 907M 11% /boot
/dev/sda2 512M 3.1M 509M 1% /boot/efi
10.0.1.5:/ralfASEsoftware 500G 17G 484G 4% /mnt
anf02:/ralfASEsoftware 500G 17G 484G 4% /Software
anf02:/ralfA11shared/sapmnt 500G 0 500G 0% /sapmnt
anf02:/ralfA11shared/usr_sap 500G 0 500G 0% /usr/sap/A11
anf02:/ralfA11sybase/sybsystem 500G 0 500G 0% /sybase/A11/sybsystem
anf02:/ralfA11sybase/sybtemp 500G 0 500G 0% /sybase/A11/sybtemp
anf02:/ralfA11sybase/sapdiag 500G 0 500G 0% /sybase/A11/sapdiag
anf02:/ralfA11sybase/sybsecurity 500G 0 500G 0% /sybase/A11/sybsecurity
anf02:/ralfA11sybase/saptemp 500G 0 500G 0% /sybase/A11/saptemp
anf02:/ralfA11data/sapdata_1 1000G 0 1000G 0% /sybase/A11/sapdata_1
anf02:/ralfA11log/saplog_1 500G 0 500G 0% /sybase/A11/saplog_1
extract the DB files
/Software # mkdir -p ASE/patch ASE/DB
/Software # mv ASEBS16004P_1-10013281.SAR ASE/patch
/Software # mv 51055060_1.ZIP ASE/DB
extract the SWPM
/Software # mkdir SWPM
/Software # mv SWPM10SP32_6-20009701.SAR SWPM
/Software # cd SWPM
/Software/SWPM # SAPCAR -xf SWPM10SP32_6-20009701.SAR
check that sapconf is running
systemctl status sapconf
sapconf.service – sapconf
Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/sapconf.service; enabled; vendor preset: enabled)
Active: active (exited) since Fri 2021-05-14 11:37 UTC; 3min 1s ago
Process: 3827 ExecStart=/usr/sbin/sapconf start (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)
Main PID: 3827 (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)
Tasks: 0 (limit: 512)
CPU: 0
CGroup: /system.slice/sapconf.service
Disable the Firewall
systemctl stop firewalld
systemctl disable firewalld
Set the installation directory rights to 777 to prevent access issues from the installer
/ # chmod -R 777 /Software
Start the SAP Installation
Start the SWPM
ralfvm02:/Software/SWPM # ./sapinst
start your Browser and select the mentioned URL from the sapinst
https://10.0.0.10:4237/sapinst/docs/index.html
Select Advanced
Sign in to the service as root
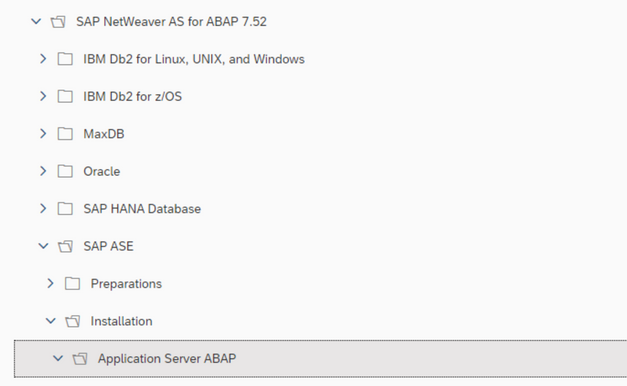
Select NetWeaver 7.52 and ASE
Next
We select a standard system
Next
Select custom Installation
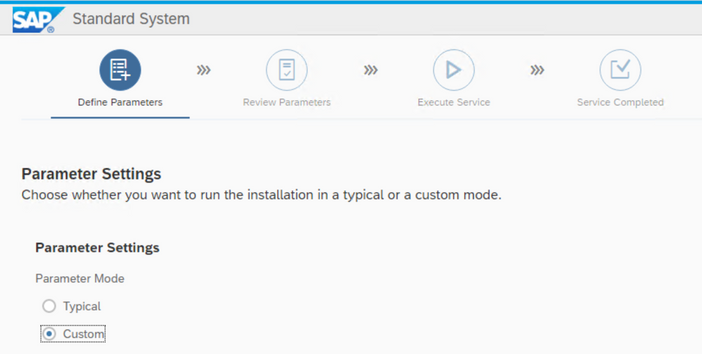
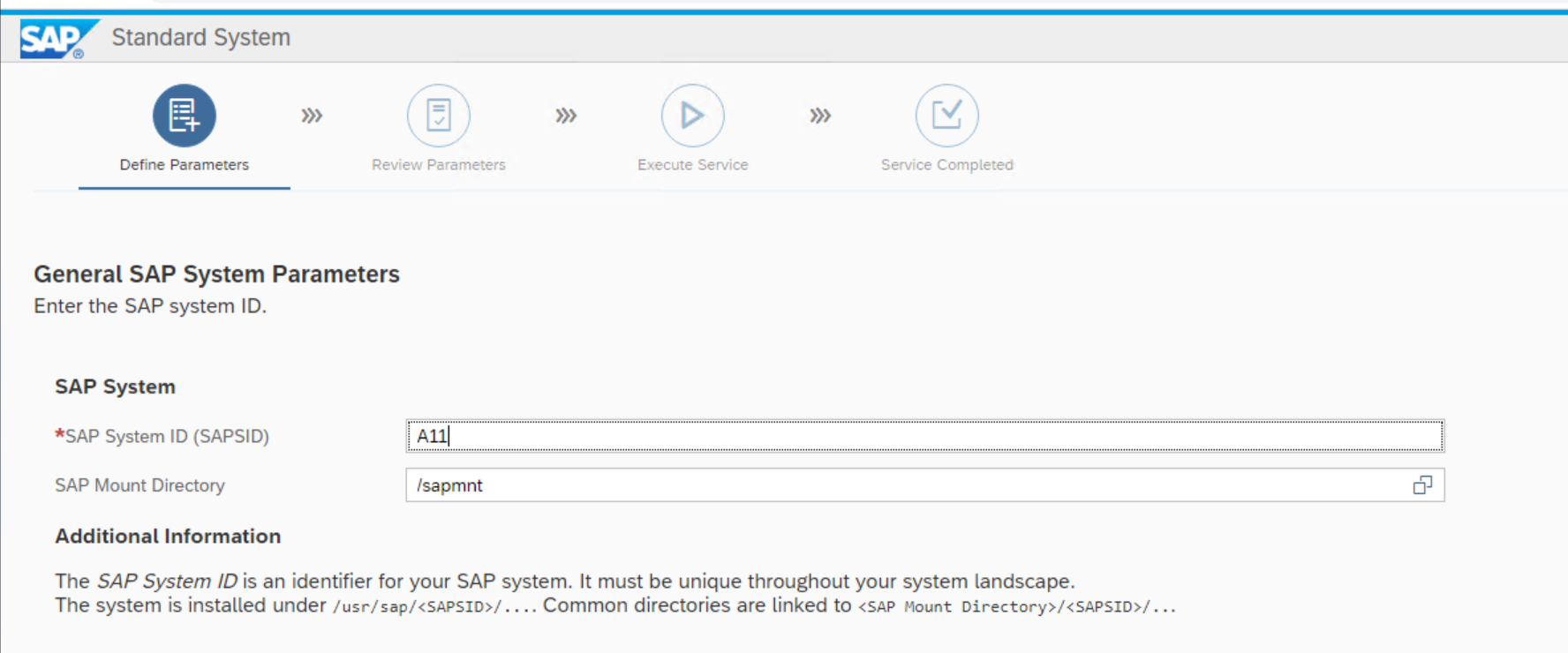
Specify the SID
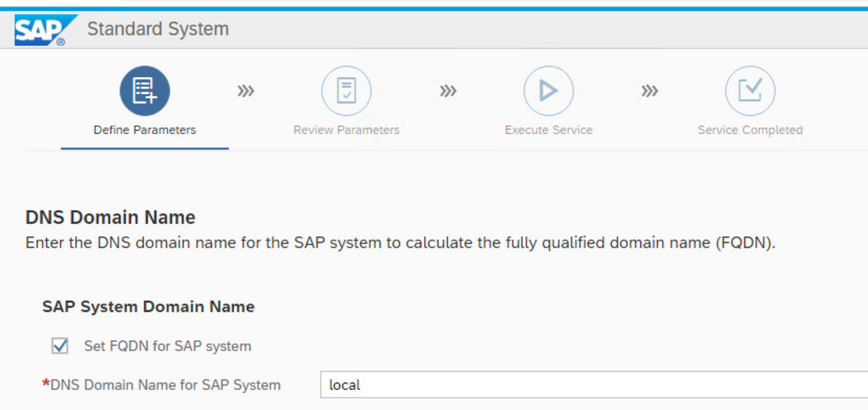
Set the domain
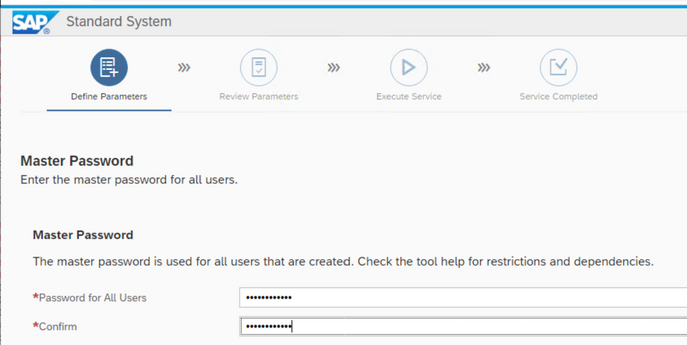
Set the default password
Specify the (sapsys) group
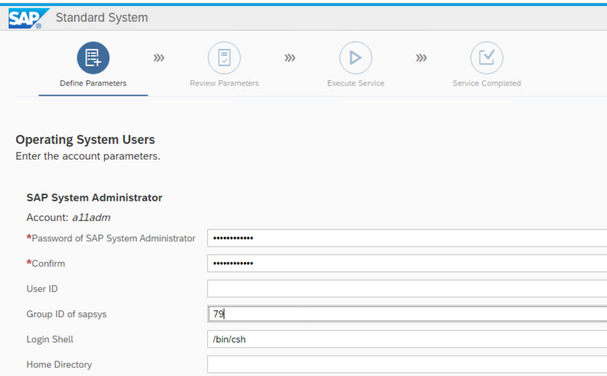
specify the ASE account
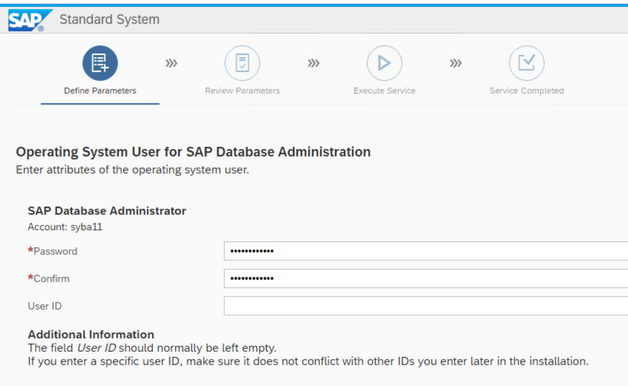
specify the kernel components directory
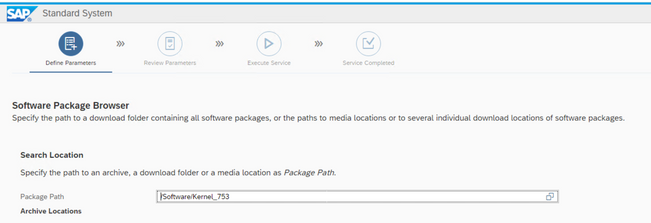
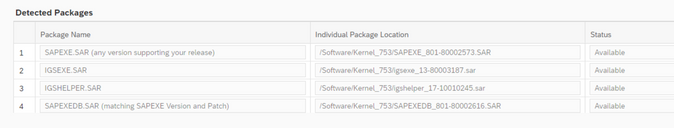
All packages must have been identified
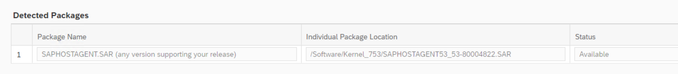
Specify the sapadm user details
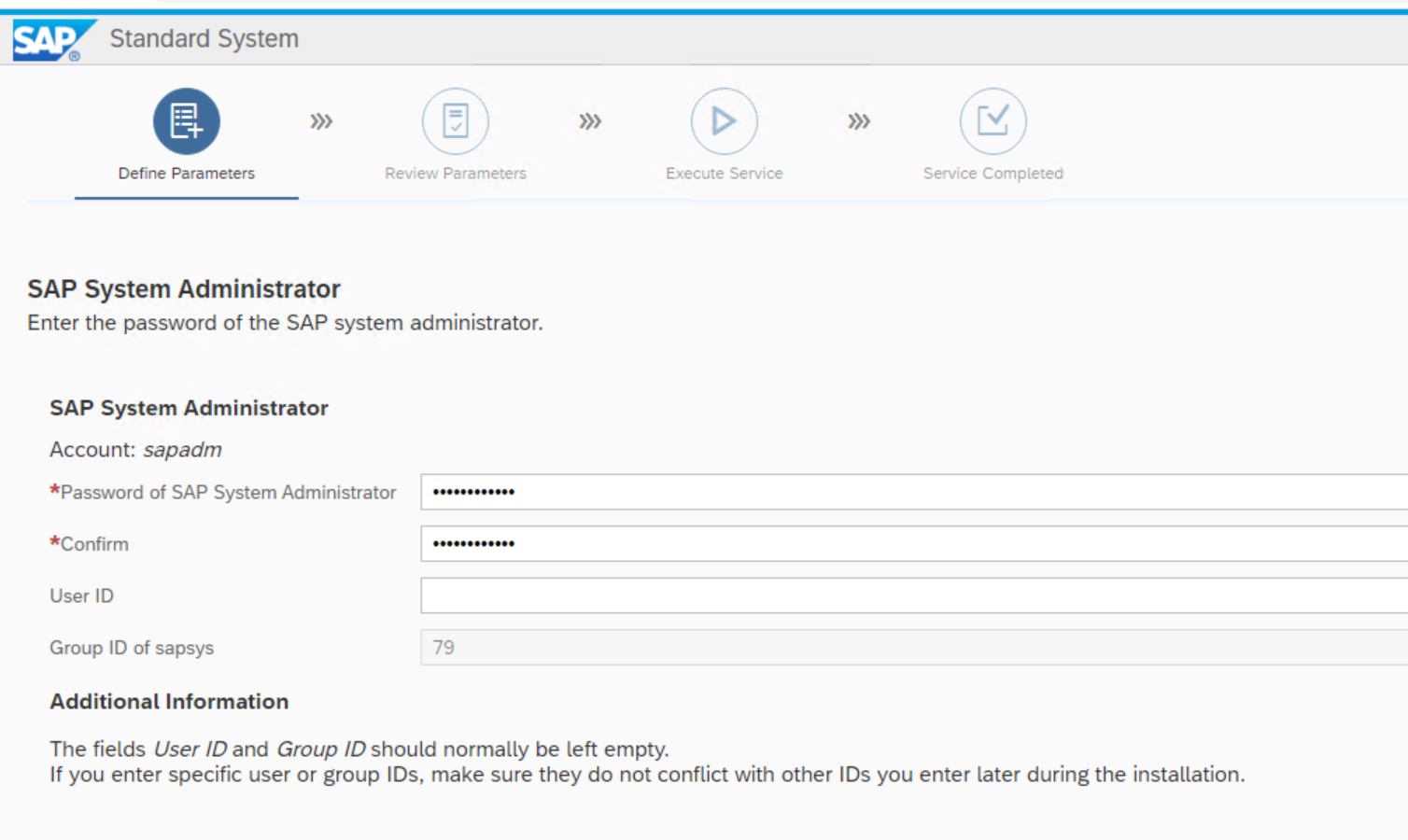
Specify the ASE source package …
51055060_1.ZIP
Then the Export location
The right location is not easy to find….
In SAP Software Downloads, navigate to Installation & Upgrade > By Category > SAP Netweaver and Complementary Products > NW AS ABAP INNOVATION PACKAGE > NW AS ABAP 7.52 > Installation > 51051806_1 and 51051806_2
zypper in unrar
ls -l
-rw-r–r– 1 root root 4000000000 Sep 28 12:59 51051806_part1.exe
-rw-r–r– 1 root root 1064422459 Sep 28 12:56 51051806_part2.rar
/Software/exp # unrar x 51051806_part1.exe
51051806_part1.exe: Embedded RAR
51051806/DATA_UNITS/EXP1/DATA/REPOSRC-1.001 (454063104 B)…
Specify the path of the directory 51051806 in the menu
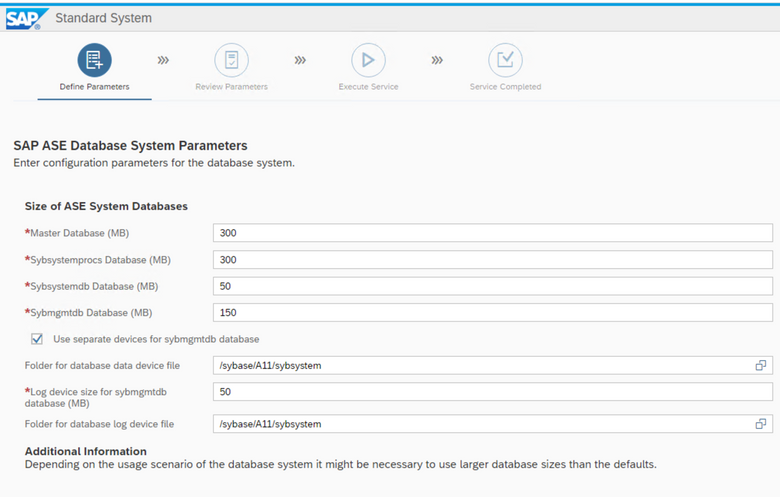
Specify the DB sizes in the next screen.
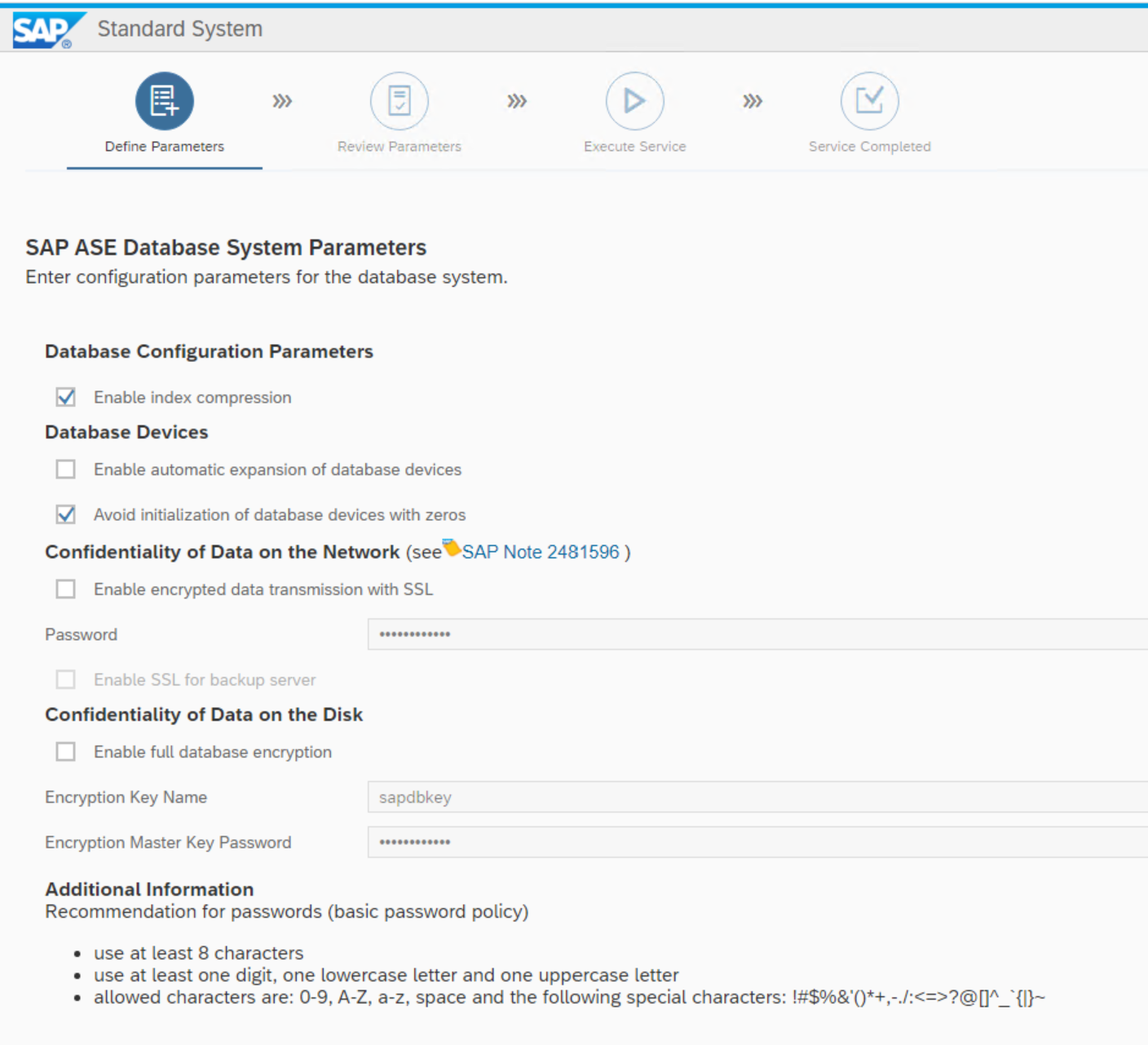
Here you e.g. can enable encryption.
Disklayout
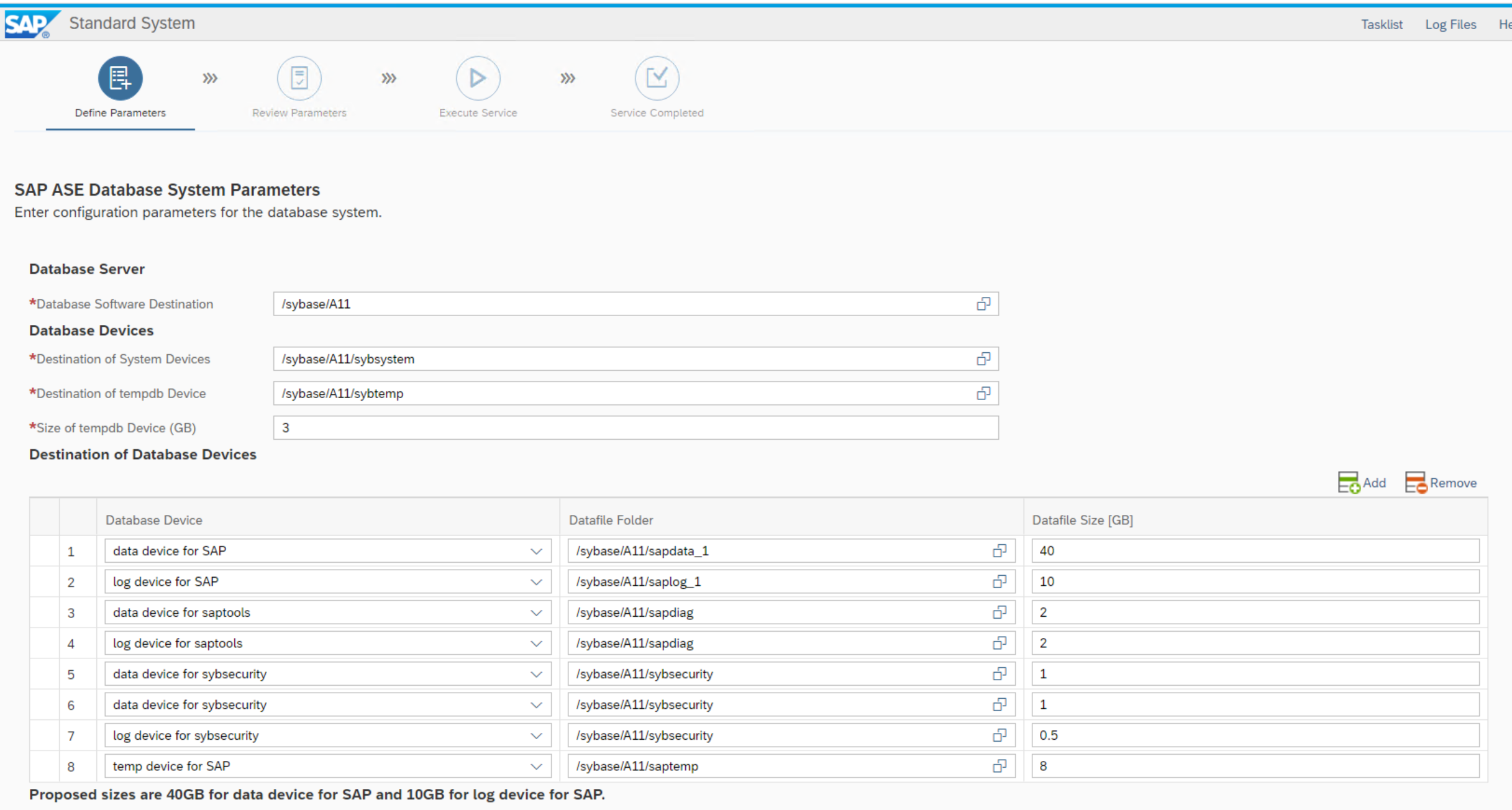
ASE System parameter
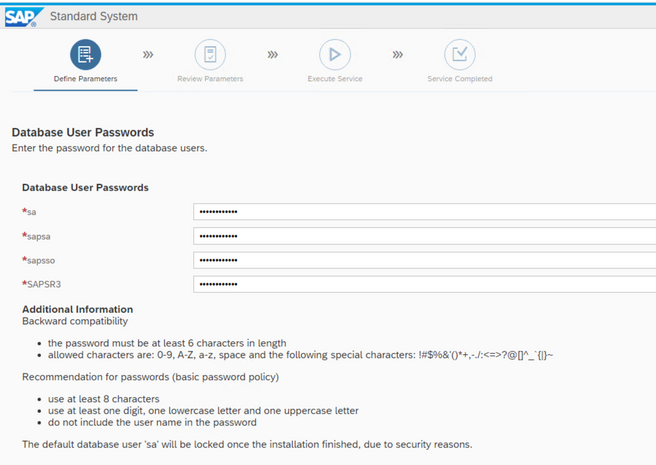
Here the option to change the database passwords
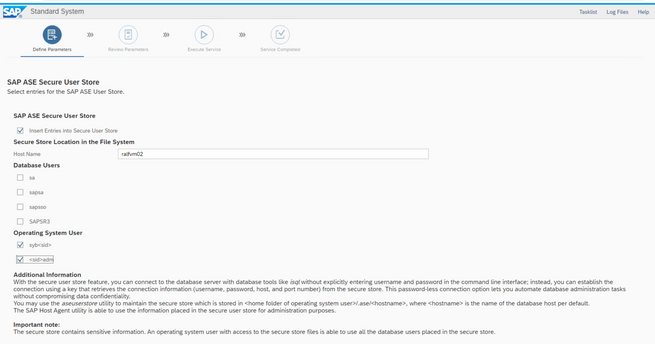
I selected the two OS user for backup purposes in the user store.
System memory
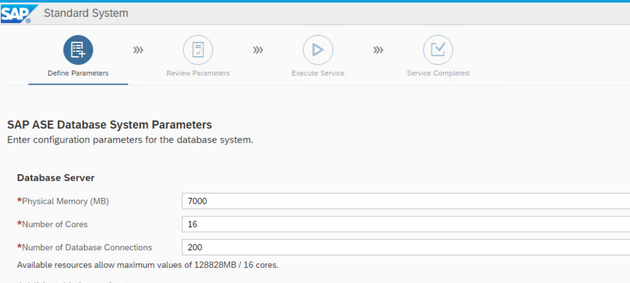
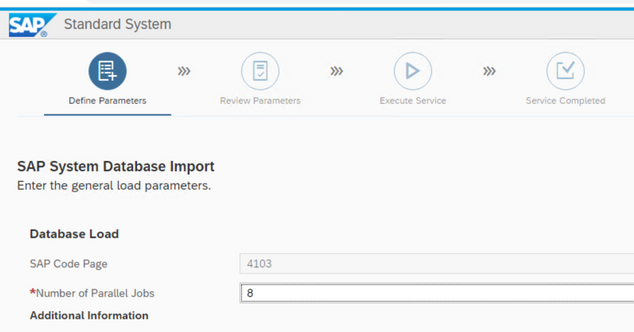
With 8 import jobs I do not overload the system….
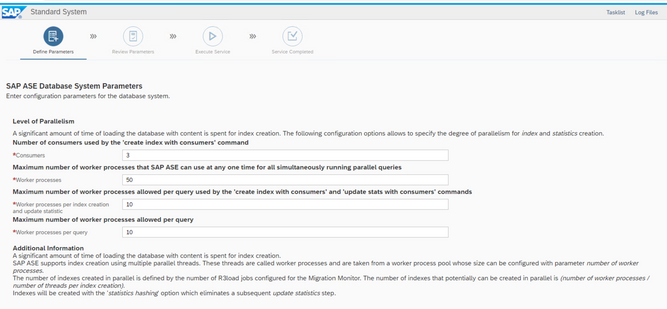
I keep the default here
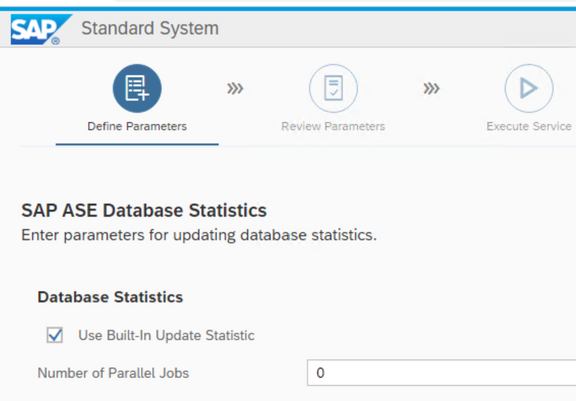
I keep the default here
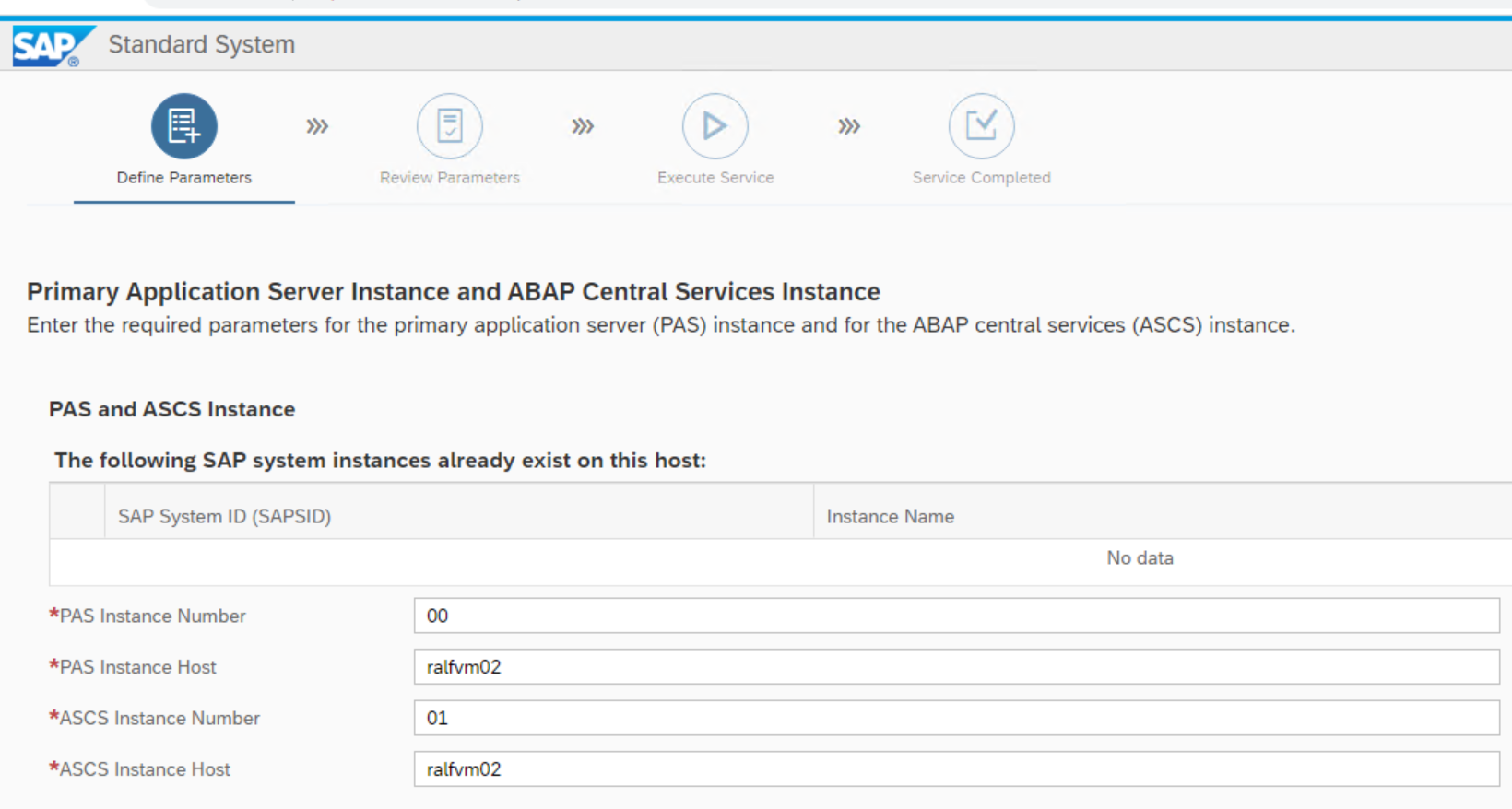
The PAS parameter
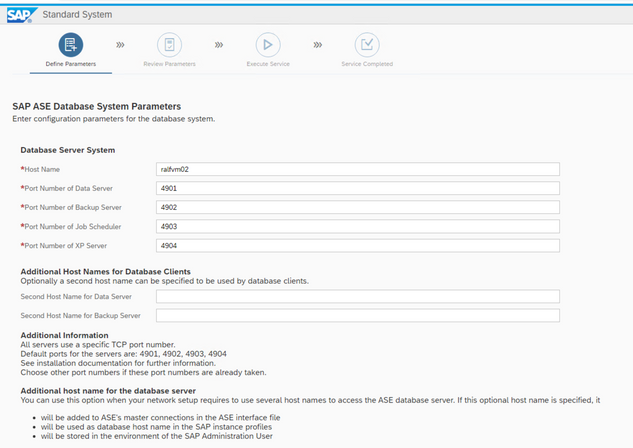
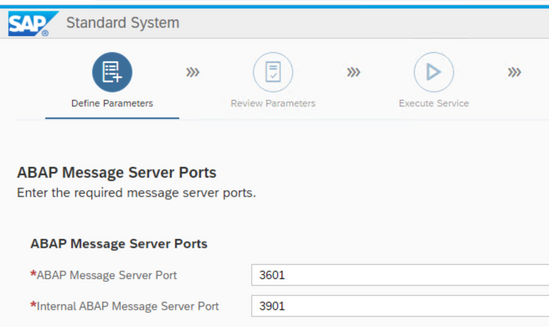
The default ports
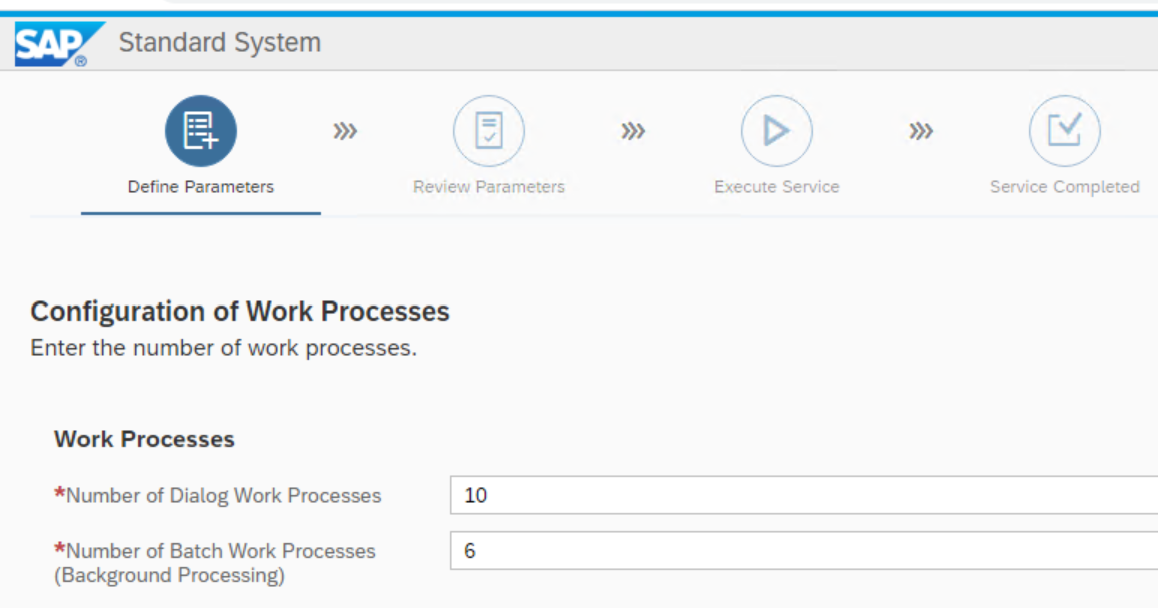
For this PoC the default work process count is good enough
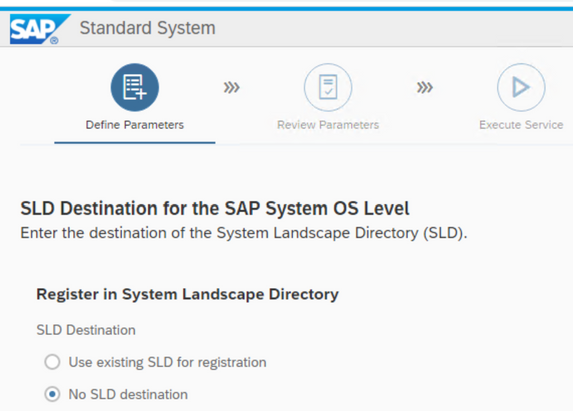
No SLD integration for me here…
The default secure store key is good enough for me
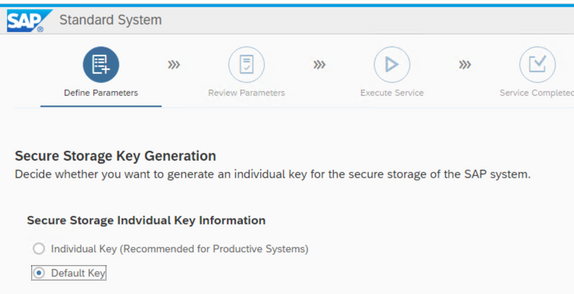
Start the installation after checking the parameter again.
Finished
Verify the DB access
Try to connect to the DB as syb
su – syba11
/sybase/A11% isql -Usapsa -SA11 -X
Password:
1>
2> select @@version
3> go
—————————————————————————
Adaptive Server Enterprise/16.0 SP04 PL01/EBF 29704 SMP/P/x86_64/SLES
12.4/ase160sp04pl01x/3473/64-bit/FBO/Tue Jul 20 07:58:11 2021
(1 row affected)
Backup
There is some very good documentation available
How to get backup of Sybase ASE 16.0 | SAP Community
DATABASE BACKUP IN SYBASE | SAP Community
Backup strategy for Sybase ASE | SAP Community
Guided steps to Setup Disaster Recovery (DR) Site for SAP ASE (Sybase) Database running with SAP Business Suite Applications | SAP Blogs
2570084 – How to start Backup Server manually – SAP ASE – SAP ONE Support Launchpad
2307016 – How to manually configure and start ASE Cockpit for an existing ASE server – SAP ASE – SAP ONE Support Launchpad
2199714 – Error 4208 DUMP Transaction to a dump device is not allowed while the trunc log on chkpt option is enabled – SAP ASE – SAP ONE Support Launchpad
2199714 – Error 4208 DUMP Transaction to a dump device is not allowed while the trunc log on chkpt option is enabled – SAP ASE – SAP ONE Support Launchpad
1887068 – SYB: Using external backup and restore with SAP ASE – SAP ONE Support Launchpad
1585981 SYB: Ensuring Recoverability for Sybase ASE
1588316 SYB: Configure automatic database and log backups
1611715 SYB: How to restore a Sybase ASE database server (Windows)
1618817 SYB: How to restore a Sybase ASE database server (UNIX)
1887068 SYB: Using external backup and restore with SAP Sybase ASE
Define the backup location for data and log:
Change the access rights to the backup directory
chown -R syba11:sapsys /sybase/A11/backup
First need to login with ”sybsid”
su – syba11
isql -Usapsa -SA11 -X
Password: *******
use master
go ( SID Transaction Log Database Backup configuration )
sp_config_dump @config_name=’A11LOG’,
@stripe_dir = ‘/sybase/A11/backup/log’ ,
@compression = ‘101’ ,
@verify = ‘header’
go
The change is completed. The option is dynamic and ASE need not be rebooted for
the change to take effect.
(return status = 0)
1>
Wait for the restart until the data-path is configured
( SID Database Backup configuration )
sp_config_dump @config_name=’A11DB’,
@stripe_dir = ‘/sybase/A11/backup/data’,
@compression = ‘101’ ,
@verify = ‘header’
go
The change is completed. The option is dynamic and ASE need not be rebooted for
the change to take effect.
(return status = 0)
Now restart the DB
su – a11adm
a11adm 13> stopsap db
a11adm 14> startsap db
verify that the DB is running (as syba11)
showserver
F S UID PID PPID C PRI NI ADDR SZ WCHAN STIME TTY TIME CMD
0 S syba11 83111 83109 0 80 0 – 7873 x64_sy 13:47 ? 00:00:00 /sybase/A11/ASE-16_0/bin/backupserver -e/sybase/A11/ASE-16_0/install/A11_BS.log -N25 -C20 -I/sybase/A11/interfaces -M/sybase/A11/ASE-16_0/bin/sybmultbuf -SA11_BS -f/sybase/A11/ASE-16_0/A11_BS.cfg
0 S syba11 83018 83016 39 80 0 – 2395958 – 13:47 ? 00:00:36 /sybase/A11/ASE-16_0/bin/dataserver -d/sybase/A11/sybsystem/master.dat -e/sybase/A11/ASE-16_0/install/A11.log -c/sybase/A11/ASE-16_0/A11.cfg -M/sybase/A11/ASE-16_0 -N/sybase/A11/ASE-16_0/sysam/A11.properties -i/sybase/A11 -sA11
Try to create a DB backup :
dump database master using config = A11DB
go
dump database model using config = A11DB
go
dump database saptempdb using config = A11DB
go
dump database saptools using config = A11DB
go
dump database A11 using config = A11DB
go
Trans log backup :
dump transaction A11 using config = A11LOG
go
Creating DB SnapShots
ASE Snapshot Backup Before taking a storage Snapshot copy, the database is put into a consistent state by quiescing the user database and master database. The following steps show how to perform database backup by using a storage Snapshot copy.
Using the aseuserstore Utility With Other SAP ASE Utilities – SAP Help Portal
quiesce database – SAP Help Portal
Install the Azure CLI on Linux | Microsoft Docs (SLES)
Download the azacsnap tool
https://aka.ms/azacsnapinstaller
Get started with Azure Application Consistent Snapshot tool for Azure NetApp Files | Microsoft Learn
Prepare the SIDadm user to be able to use isql
cd
pwd
/home/a11adm
vi .sapenv_ralfvm02.csh
setenv LC_ALL en_US.UTF-8 #(at the end of the file)
# end SAP R/3 Environment
exit
su – a11adm
env |grep UTF
LANG=C.UTF-8
LC_ALL=en_US.UTF-8
Configure the ASE User Secure Store for SIDadm
We create a user store key with the name SNAP…
aseuserstore set SNAP ralfvm02:4901@A11 sapsa
Check the DB connect with this key
isql -k SNAP -X
select @@version
go
—————————————————————————
Adaptive Server Enterprise/16.0 SP04 PL01/EBF 29704 SMP/P/x86_64/SLES 12.4/ase160sp04pl01x/3473/64-bit/FBO/Tue Jul 20 07:58:11 2021
(1 row affected)
The manual quiesce process:
quiesce database A11_for_SNAP hold A11, sybmgmtdb, saptools, master, sybsecurity for external dump
go
select is_quiesced(4)
go
———–
1
(1 row affected)
You should create SnapShots for the data AND Sybase volume!!!
In the “data” volume is “only” the A11 database, the “sybase” volume is the location of the master- and the security database. Both are important for the recovery.
Now create the snapshot in the portal, azacsnap or Azure CLI
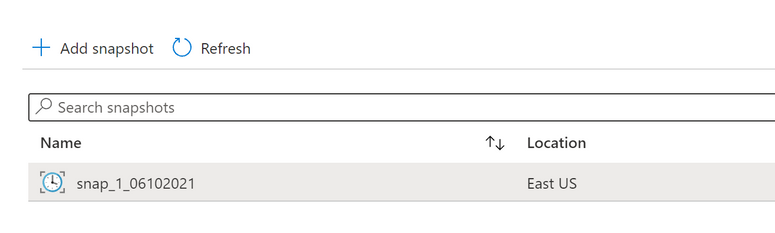
Un-quiesce the DB
quiesce database A11_for_SNAP release
go
select is_quiesced(4)
go
———–
0
(1 row affected)
Device Overview
1> sp_helpdevice
2> go
device_name physical_name description status cntrltype vdevno vpn_low vpn_high
————— —— ——— —— ——- ——–
A11_data_001 /sybase/A11/sapdata_1/A11_data_001.dat file system device, special, dsync off, directio on, physical disk, 40960.00 MB, Free: 0.00 MB 2 0 6 0 20971519
A11_log_001 /sybase/A11/saplog_1/A11_log_001.dat file system device, special, dsync off, directio on, physical disk, 10240.00 MB, Free: 0.00 MB 2 0 7 0 5242879
master /sybase/A11/sybsystem/master.dat file system device, special, dsync on, directio off, physical disk, 450.00 MB, Free: 78.00 MB 2 0 0 0 230399
saptempdb_data_001 /sybase/A11/saptemp/saptempdb_data_001.dat file system device, special, dsync off, directio on, physical disk, 8192.00 MB, Free: 0.00 MB 2 0 13 0 4194303
saptools_data_001 /sybase/A11/sapdiag/saptools_data_001.dat file system device, special, dsync off, directio on, physical disk, 2048.00 MB, Free: 0.00 MB 2 0 8 0 1048575
saptools_log_001 /sybase/A11/sapdiag/saptools_log_001.dat file system device, special, dsync off, directio on, physical disk, 2048.00 MB, Free: 0.00 MB 2 0 9 0 1048575
sybmgmtdev /sybase/A11/sybsystem/sybmgmtdb_data_001.dat file system device, special, dsync off, directio on, physical disk, 150.00 MB, Free: 2.00 MB 2 0 4 0 76799
sybmgmtlogdev /sybase/A11/sybsystem/sybmgmtdb_log_001.dat file system device, special, dsync off, directio on, physical disk, 50.00 MB, Free: 2.00 MB 2 0 5 0 25599
sybsecurity_data_001 /sybase/A11/sybsecurity/sybsecurity_data_001.dat file system device, special, dsync off, directio on, physical disk, 1024.00 MB, Free: 0.00 MB 2 0 10 0 524287
sybsecurity_data_002 /sybase/A11/sybsecurity/sybsecurity_data_002.dat file system device, special, dsync off, directio on, physical disk, 1024.00 MB, Free: 0.00 MB 2 0 11 0 524287
sybsecurity_log_001 /sybase/A11/sybsecurity/sybsecurity_log_001.dat file system device, special, dsync off, directio on, physical disk, 512.00 MB, Free: 0.00 MB 2 0 12 0 262143
sysprocsdev /sybase/A11/sybsystem/sysprocs.dat file system device, special, dsync off, directio on, physical disk, 300.00 MB, Free: 0.00 MB 2 0 1 0 153599
systemdbdev /sybase/A11/sybsystem/sybsysdb.dat file system device, special, dsync off, directio on, physical disk, 50.00 MB, Free: 2.00 MB 2 0 2 0 25599
tempdbdev /sybase/A11/sybtemp/tempdbdev.dat file system device, special, dsync off, directio off, physical disk, 3072.00 MB, Free: 0.00 MB 2 0 3 0 1572863
(return status = 0)
Configure azacsnap
Install the Azure Application Consistent Snapshot tool for Azure NetApp Files | Microsoft Learn
Azacsnap is supporting only HANA, DB2 and Oracle at the moment. It is, however, possible to take a snapshot from the data volume and use the new feature in the version 7 with pre and post automation.
Create the service principal for your subscription and install azacsnap – in the Azure Portal
Store the output in a file I used /tmp/auth.json
az ad sp create-for-rbac –name “AzAcSnap” –role Contributor –scopes /subscriptions/{subscription-id} –sdk-auth
You will get an output which looks similar to this:
{
“clientId”: “0815**4711-4**-a91f-d937*********1”,
“clientSecret”: “d~_8Q~****Zk*****Y_********”,
“subscriptionId”: “47110815-***-****-***-**********”,
“tenantId”: “K47110815-****-4ecc-bda0-**********”,
“activeDirectoryEndpointUrl”: “https://login.microsoftonline.com”,
“resourceManagerEndpointUrl”: “https://management.azure.com/”,
“activeDirectoryGraphResourceId”: “https://graph.windows.net/”,
“sqlManagementEndpointUrl”: “https://management.core.windows.net:8443/”,
“galleryEndpointUrl”: “https://gallery.azure.com/”,
“managementEndpointUrl”: “https://management.core.windows.net/”
}
Create an auth.conf file and copy the content into this file
vi /tmp/auth.json
ls -la /tmp
-rw-r–r– 1 root root 25148727 Aug 2 11:02 azacsnap_6_installer.run
-rw-r–r– 1 root root 629 Nov 7 14:32 auth.json
Install azacsnap
./azacsnap_7_installer.run -I
Configure azacsnap
azacsnap -c configure –configuration=new
Building new config file
Add comment to config file (blank entry to exit adding comments): ASE Test
Add comment to config file (blank entry to exit adding comments):
Enter the database type to add, ‘hana’, ‘oracle’, or ‘exit’ (for no database): oracle
=== Add Oracle Database details ===
Oracle Database SID (e.g. CDB1): A11
Database Server’s Address (hostname or IP address): 10.0.0.10
Oracle connect string (e.g. /@AZACSNAP):
=== Azure NetApp Files Storage details ===
Are you using Azure NetApp Files for the database? (y/n) [n]: y
— DATA Volumes have the Application put into a consistent state before they are snapshot —
Add Azure NetApp Files resource to DATA Volume section of Database configuration? (y/n) [n]: n
— OTHER Volumes are snapshot immediately without preparing any application for snapshot —
Add Azure NetApp Files resource to OTHER Volume section of Database configuration? (y/n) [n]: y
Full Azure NetApp Files Storage Volume Resource ID (e.g. /subscriptions/…/resourceGroups/…/providers/Microsoft.NetApp/netAppAccounts/…/capacityPools/Premium/volumes/…): /subscriptions/08154711-4***-**********/resourceGroups/*****/providers/Microsoft.NetApp/netAppAccounts/********/capacityPools/anfpool/volumes/A11data
Service Principal Authentication filename or Azure Key Vault Resource ID (e.g. auth-file.json or https://…): auth.json
Add Azure NetApp Files resource to OTHER Volume section of Database configuration? (y/n) [n]: y
Full Azure NetApp Files Storage Volume Resource ID (e.g. /subscriptions/…/resourceGroups/…/providers/Microsoft.NetApp/netAppAccounts/…/capacityPools/Premium/volumes/…): /subscriptions/08154711-4***-**********/resourceGroups/*****/providers/Microsoft.NetApp/netAppAccounts/********/capacityPools/anfpool/volumes/A11sybase
Service Principal Authentication filename or Azure Key Vault Resource ID (e.g. auth-file.json or https://…): auth.json
Add Azure NetApp Files resource to OTHER Volume section of Database configuration? (y/n) [n]: n
=== Azure Managed Disk details ===
Are you using Azure Managed Disks for the database? (y/n) [n]: n
=== Azure Large Instance (Bare Metal) Storage details ===
Are you using Azure Large Instance (Bare Metal) for the database? (y/n) [n]: n
Enter the database type to add, ‘hana’, ‘oracle’, or ‘exit’ (for no database): exit
Editing configuration complete, writing output to ‘azacsnap.json’.
Test the storage connection, at this point we “only” can test the storage connection. The ASE backup-mode will be scheduled as “runbefore” and “runafter”.
azacsnap -c test –test=storage
BEGIN : Test process started for ‘storage’
BEGIN : Storage test snapshots on ‘data’ volumes
BEGIN : Test Snapshots for Storage Volume Type ‘data’
PASSED: Storage test completed successfully for all ‘data’ Volumes
END : Storage tests complete
END : Test process complete for ‘storage’
Create the .bashrc for the azacsnap user (compare the environment from the SIDadm user)
vi .bashrc
…
export LANG=C.UTF-8
export LC_ALL=en_US.UTF-8
export PATH=$PATH:/sybase/A11/OCS-16_0/bin:/usr/sap/A11/SYS/exe/uc/linuxx86_64:/usr/sap/A11/SYS/exe/run:/home/a11adm:/sybase/A11/ASE-16_0/jobscheduler/bin:/sybase/A11/ASE-16_0/bin:/sybase/A11/ASE-16_0/install:/sybase/A11/WLA/bin::/sybase/A11/OCS-16_0/bin:
export RSEC_SSFS_DATAPATH=/usr/sap/A11/SYS/global/security/rsecssfs/data
export RSEC_SSFS_KEYPATH=/usr/sap/A11/SYS/global/security/rsecssfs/key
export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=/usr/sap/A11/SYS/exe/run:/usr/sap/A11/SYS/exe/uc/linuxx86_64:/usr/sap/A11/SYS/global/syb/linuxx86_64/sybodbc:/sybase/A11/ASE-16_0/lib:/sybase/A11/OCS-16_0/lib:/sybase/A11/OCS-16_0/lib3p64:/sybase/A11/OCS-16_0/lib3p:
export SYBASE_OCS=OCS-16_0
export SYBASE=/sybase/A11
export SYBASE_ASE=ASE-16_0
export SYBASE_JRE_RTDS=/sybase/A11/shared/SAPJRE-8_1_075_64BIT
export SYBASE_WS=WS-16_0
We create a user store key with the name SNAP…
aseuserstore set SNAP ralfvm02:4901@A11 sapsa
Create the two Quice and Unquice scripts. (no Microsoft support) this is only an example.
vi aseQuiesce.sh
#!/bin/bash
SID=”$1″
KEY=”$2″
SAVEPOINT=”SNAPSHOT_BACKUP”
if [[ “$SID” == “” || “$KEY” == “” ]]; then
echo “Usage: `basename $0` ” exit 1
fi
sqlFile=$(mktemp)
cat > $sqlFile << EOF
quiesce database $SAVEPOINT hold $SID, sybmgmtdb, saptools, master, sybsecurity for external dump
go
select is_quiesced(4)
go
EOF
rc=`isql -k $KEY -X -i $sqlFile -b | head -1 | tr -d “[:blank:]”`
rm $sqlFile
if [ $rc = 1 ]; then
echo “Database $SID succesfully quiesced.” exit 0
else
echo “Error quiescing database $SID.” exit 1
fi
vi aseUnquiesce.sh
#!/bin/bash
SID=”$1″
KEY=”$2″
SAVEPOINT=”SNAPSHOT_BACKUP”
if [[ “$SID” == “” || “$KEY” == “” ]]; then
echo “Usage: `basename $0` ” exit 1
fi
sqlFile=$(mktemp)
cat > $sqlFile << EOF
quiesce database $SAVEPOINT release
go
select is_quiesced(4)
go
EOF
rc=`isql -k $KEY -X -i $sqlFile -b | head -1 | tr -d “[:blank:]”`
rm $sqlFile
if [ $rc = 0 ]; then
echo “Database $SID successfully unquiesced.” exit 0
else
echo “Error unquiescing database $SID.” exit 1
fi
Test the scripts and the logon with user azacsnap
Logon via isql
su – azacsnap
cd bin
isql -k SNAP -X
1> exit
Test the Quice and Unquics script
su – azacsnap
cd bin
aseQuiece.sh A11 SNAP
Database A11 succesfully quiesced. exit 0
aseUnquiesce.sh A11 SNAP
Database A11 successfully unquiesced. exit 0
Now create an application consistent snapshot using azacsnap
su – azacsnap
cd bin
aseQuiece.sh A11 SNAP
Database A11 succesfully quiesced. exit 0
azacsnap -c backup –volume other –prefix ASE_hourly –retention 3
aseUnquiesce.sh A11 SNAP
Database A11 successfully unquiesced. exit 0
Check the portal is the snapshot exists
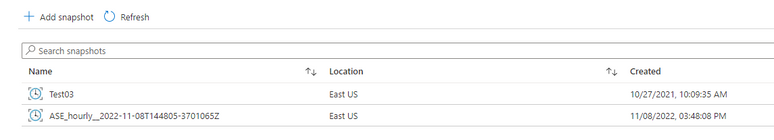
List the taken SnapShots
azacsnap -c details
List snapshot details called with snapshotFilter ”
#, Volume, SnapshotName
#1, ralfA11data, ASE_hourly__2022-11-08T144805-3701065Z
#2, ralfA11data, Test03
#1, ralfA11sybase, ASE_hourly__2022-11-08T144805-3701065Z
Fully automat the snapshot creation
azacsnap -c backup –volume other –prefix ASE_hourly –runbefore ‘/home/azacsnap/bin/aseQuiece.sh’ –runafter ‘/home/azacsnap/bin/aseUnquiesce.sh’ –retention 3
azacsnap -c details
List snapshot details called with snapshotFilter ”
#, Volume, SnapshotName
#1, ralfA11data, ASE_hourly__2022-11-12T070552-5533842Z
#2, ralfA11data, ASE_hourly__2022-11-08T144805-3701065Z
#3, ralfA11data, Test03
#1, ralfA11sybase, ASE_hourly__2022-11-12T070552-5533842Z
#2, ralfA11sybase, ASE_hourly__2022-11-08T144805-3701065Z
Restore using azacsnap
Shutdown SAP and ASE (if possible – if not simply “kill” the DB. We are restoring anyway.
stopsap all
kill all Sybase processes
killall -u syba11
Umount the data directory (we keep the Sybase exe volume) we assume only the data volume must be restored)
umount /sybase/A11/sapdata_1
At the moment azacsnap does not support “Revert Volume” for ANF. If you would like to keep the volume names you have the option to “revert a volume using the Azure Portal.
See:
su – azacsnap
cd bin
azacsnap -c restore –dbsid A11 –restore revertvolume –configfile azacsnap.json –snapshotfilter ASE_hourly__2022-11-08T144805-3701065Z
…
Azure NetApp Files volumes not supported for revertvolume, will not revert volume.
With ANF you do have the option to clone a volume. This is probably the better option anyway. How to clone a volume for a recovery is demonstrated here:
AzAcSnap is designed to restore a collection of dataVolumes and otherVolumes. AzAcSnap makes sure all the dataVolumes share the same snapshot to be restored and the otherVolumes the latest snapshot to be restored. In a deployment with multiple data volumes (e.g., SAP HANA Scale-Out) this can save a lot of time trying to ensure all the snapshots match in the Azure Portal before cloning or reverting the volumes. This means when using a setup with custom scripts to quiesce/unquiesce the database it’s necessary to create a copy of the backup configfile and change “otherVolume” to “dataVolume” and change “dataVolume” to “otherVolume” effectively switching them.
cp azacsnap.json azacsnap_snaptovol.json
vi azacsnap_snaptovol.json
“anfStorage”: [
{
“otherVolume”: [],
“dataVolume”: [
Down here are the specifications of your ANF volumes à keep unchanged change only dataVolume to otherVolume and otherVolume to dataVolume.
list the available SnapShots
azacsnap -c details
List snapshot details called with snapshotFilter ”
#, Volume, SnapshotName
#1, ralfA11data, ASE_hourly__2022-11-08T144805-3701065Z
#1, ralfA11sybase, ASE_hourly__2022-11-08T144805-3701065Z
azacsnap -c restore –dbsid A11 –restore revertvolume –configfile azacsnap_snaptovol.json –snapshotfilter ASE_hourly__2022-11-08T144805-3701065Z
create the new /etc/fstab
pwd
/home/azacsnap/bin
grep rwclone ./logs/*.log
… Creating new volume ‘ralfa11data-rwclone-20221111-0732’
… Volume ‘ralfa11data-rwclone-20221111-0732’ successfully created from snapshot.
…
… Creating new volume ‘ralfa11sybase-rwclone-20221111-0732’
… Volume ‘ralfa11sybase-rwclone-20221111-0732’ successfully created from snapshot.
Since I only recover the data volume I only change the data volume location must be done as root.
exit
vi /etc/fstab
anf02:/ralfASEsoftware /Software nfs rw,hard,timeo=600,vers=4.1,nconnect=8,rsize=262144,wsize=262144,noatime,lock 0 0
#
anf02:/ralfA11shared/sapmnt /sapmnt nfs rw,hard,timeo=600,vers=4.1,nconnect=8,rsize=262144,wsize=262144,noatime,lock 0 0
anf02:/ralfA11shared/usr_sap /usr/sap/A11 nfs rw,hard,timeo=600,vers=4.1,nconnect=8,rsize=262144,wsize=262144,noatime,lock 0 0
#
anf02:/ralfA11sybase/sybsystem /sybase/A11/sybsystem nfs rw,hard,timeo=600,vers=4.1,nconnect=8,rsize=262144,wsize=262144,noatime,lock 0 0
anf02:/ralfA11sybase/sybtemp /sybase/A11/sybtemp nfs rw,hard,timeo=600,vers=4.1,nconnect=8,rsize=262144,wsize=262144,noatime,lock 0 0
anf02:/ralfA11sybase/sapdiag /sybase/A11/sapdiag nfs rw,hard,timeo=600,vers=4.1,nconnect=8,rsize=262144,wsize=262144,noatime,lock 0 0
anf02:/ralfA11sybase/sybsecurity /sybase/A11/sybsecurity nfs rw,hard,timeo=600,vers=4.1,nconnect=8,rsize=262144,wsize=262144,noatime,lock 0 0
anf02:/ralfA11sybase/saptemp /sybase/A11/saptemp nfs rw,hard,timeo=600,vers=4.1,nconnect=8,rsize=262144,wsize=262144,noatime,lock 0 0
#
anf02:/ralfa11data-rwclone-20221111-0732/sapdata_1 /sybase/A11/sapdata_1 nfs rw,hard,timeo=600,vers=4.1,nconnect=8,rsize=262144,wsize=262144,noatime,lock 0 0anf02:/ralfA11log/saplog_1 /sybase/A11/saplog_1 nfs rw,hard,timeo=600,vers=4.1,nconnect=8,rsize=262144,wsize=262144,noatime,lock 0 0
the clone of the “ralfA11sybase” volume should (must) be deleted manually. It is not required for a “normal” database recovery. We require only the data-volume.
mount the clone volumes
mount -a
anf02:/ralfA11shared/usr_sap 100G 3.6G 97G 4% /usr/sap/A11
anf02:/ralfA11log/saplog_1 100G 11G 90G 11% /sybase/A11/saplog_1
anf02:/ralfASEsoftware 100G 17G 84G 17% /Software
anf02:/ralfA11shared/sapmnt 100G 3.6G 97G 4% /sapmnt
anf02:/ralfA11sybase/sybsystem 100G 9.3G 91G 10% /sybase/A11/sybsystem
anf02:/ralfA11sybase/sybtemp 100G 9.3G 91G 10% /sybase/A11/sybtemp
anf02:/ralfA11sybase/sapdiag 100G 9.3G 91G 10% /sybase/A11/sapdiag
anf02:/ralfA11sybase/sybsecurity 100G 9.3G 91G 10% /sybase/A11/sybsecurity
anf02:/ralfA11sybase/saptemp 100G 9.3G 91G 10% /sybase/A11/saptemp
anf02:/ralfa11data-rwclone-20221111-0732/sapdata_1 100G 41G 60G 41% /sybase/A11/sapdata_1
su – a11adm
startdb
starting database A11 …
Log file: /sybase/A11/startdb.log
parse level 0: identified message ‘Database ‘master’ is now online.’
parse level 1: identified message ‘Database ‘tempdb’ is now online.’
parse level 2: identified message ‘Database ‘sybsystemprocs’ is now online.’
parse level 3: identified message ‘Recovery complete.’
Recovery Complete
startdb completed successfully
grep identified /sybase/A11/startdb.log
parse level 0: identified message ‘Database ‘master’ is now online.’
parse level 1: identified message ‘Database ‘tempdb’ is now online.’
parse level 2: identified message ‘Database ‘sybsystemprocs’ is now online.’
parse level 3: identified message ‘Recovery complete.’
Recovery Complete
Restore – manual
The restore process is easy.
After you discover an issue and you need to restore the ASE DB you stop the DB (if possible).
Make sure you have all logfile backups available in its original location
stopdb
stopping database A11 …
stop database completed successfully
kill all Sybase processes
killall -u syba11
Unmount the volume and revert it
umount /sybase/A11/sapdata_1
Revert the volume
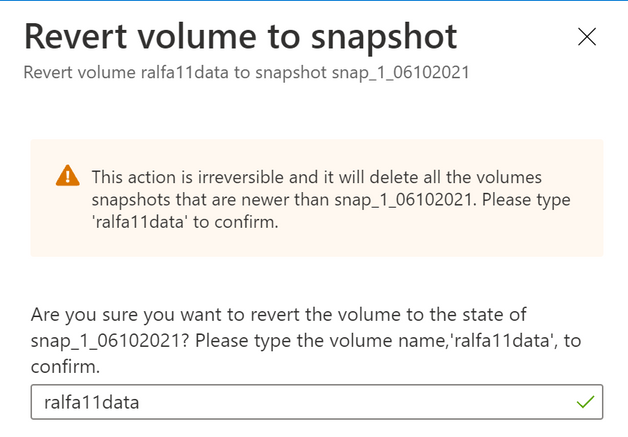
Mount the data volume
mount -a
Start the DB and check the logfile
su – a11adm
startdb
starting database A11 …
Log file: /sybase/A11/startdb.log
parse level 0: identified message ‘Database ‘master’ is now online.’
parse level 1: identified message ‘Database ‘tempdb’ is now online.’
parse level 2: identified message ‘Database ‘sybsystemprocs’ is now online.’
parse level 3: identified message ‘Recovery complete.’
Recovery Complete
startdb completed successfully
grep identified /sybase/A11/startdb.log
parse level 0: identified message ‘Database ‘master’ is now online.’
parse level 1: identified message ‘Database ‘tempdb’ is now online.’
parse level 2: identified message ‘Database ‘sybsystemprocs’ is now online.’
parse level 3: identified message ‘Recovery complete.’
Recovery Complete
Now the media recovery is complete. Start SAP
su – a11adm
startsap all
Done…
have fun..





Recent Comments