by Contributed | May 24, 2021 | Technology
This article is contributed. See the original author and article here.
When you see your cloud-based application architecture, no matter it is microservices architecture or not, many systems are inter-connected and send/receive messages in real-time, near real-time or asynchronously. You all know, in this environment, at some stage, some messages are often failed to deliver to their respective destinations or halted while processing them.
In the cloud environment, components in a system run with their rhythm. Therefore, you should assume that a particular component gets hiccup at any point in time and design the architecture based on this assumption. Therefore, to minimise message loss, you should be able to trace them from one end to the other end. We use the term “Observability” and “Traceability” for it.
In my previous post, a citizen dev in a fusion team uses an Azure Functions app that enables the OpenAPI capability, and build a Power Apps app. This time, I’m going to add a capability that traces the workout data from the Power Apps app to Azure Cosmos DB through Azure Monitor and Application Insights. I will also discuss how this ability is related to the concepts from Open Telemetry.
You can find the sample code used in this post at this GitHub repository.
Scenario
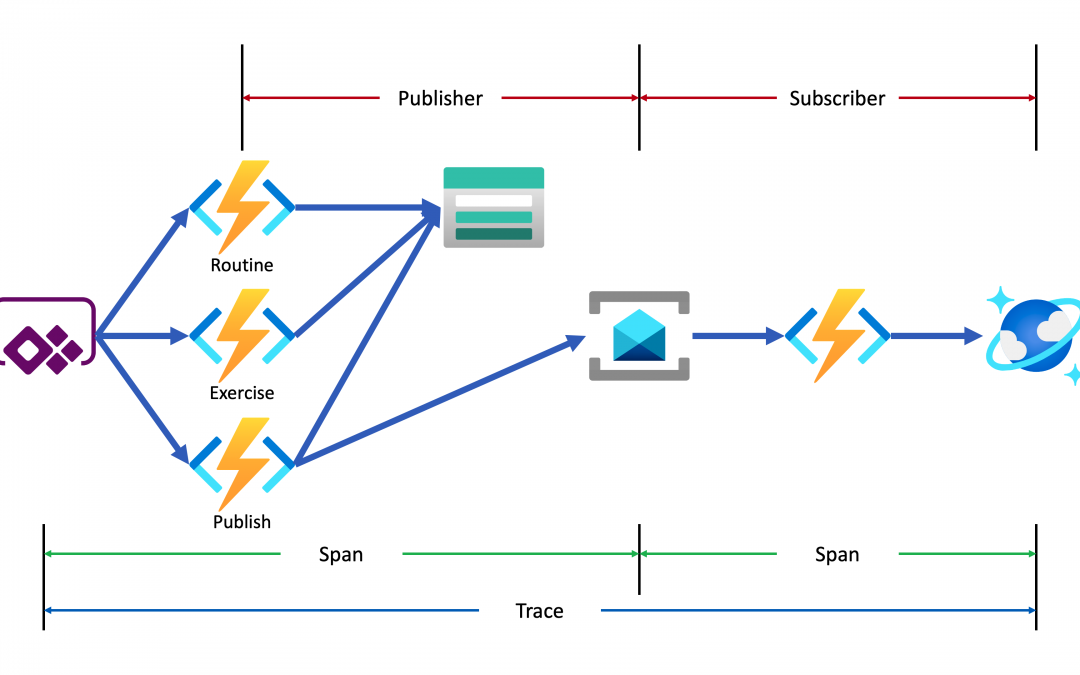
Lamna Healthcare Company runs a fitness centre in Korea for their members. The centre provides their members with a Power Apps app to record their workout details. Ji Min, the trainer team lead, recently got some feedback from her members that the app gets crashed while putting their workout logs. As she represents the trainers in the fusion team, she started discussing this issue with Su Bin, the pro dev in the team. As a result, Su Bin decided to add a tracing logic into the Function app. Here’s the high-level diagram that describes the data processing flow.
Let’s analyse the diagram based on the Open Telemetry spec.
- The entire data flow from Power Apps to Cosmos DB is called “Trace“.
- The whole flow is divided into two distinctive parts by Azure Service Bus because both sides are totally different and independent applications (Publisher and Subscriber). So, these two individual parts are called “Span“. In other words, the Span is a unit of work that handles messages.
In the picture above, the Publisher consists of three actions, routine, exercise and publish. Although you can split it into three sub Spans, let’s use one Span for now.
- The Subscriber receives the message from Azure Service Bus, transforms the message and stores it to Cosmos DB.
- When a message traverses over spans, you need a carrier for metadata so that you can trace the message within the whole Trace. The metadata is called “Span Context“.
Power Apps Update
As mentioned earlier, trace starts from the Power Apps app. Therefore, the app needs an update for the tracing capability. Generate both correlationId and spanId when tapping the Start button and send both to API through the routine action.
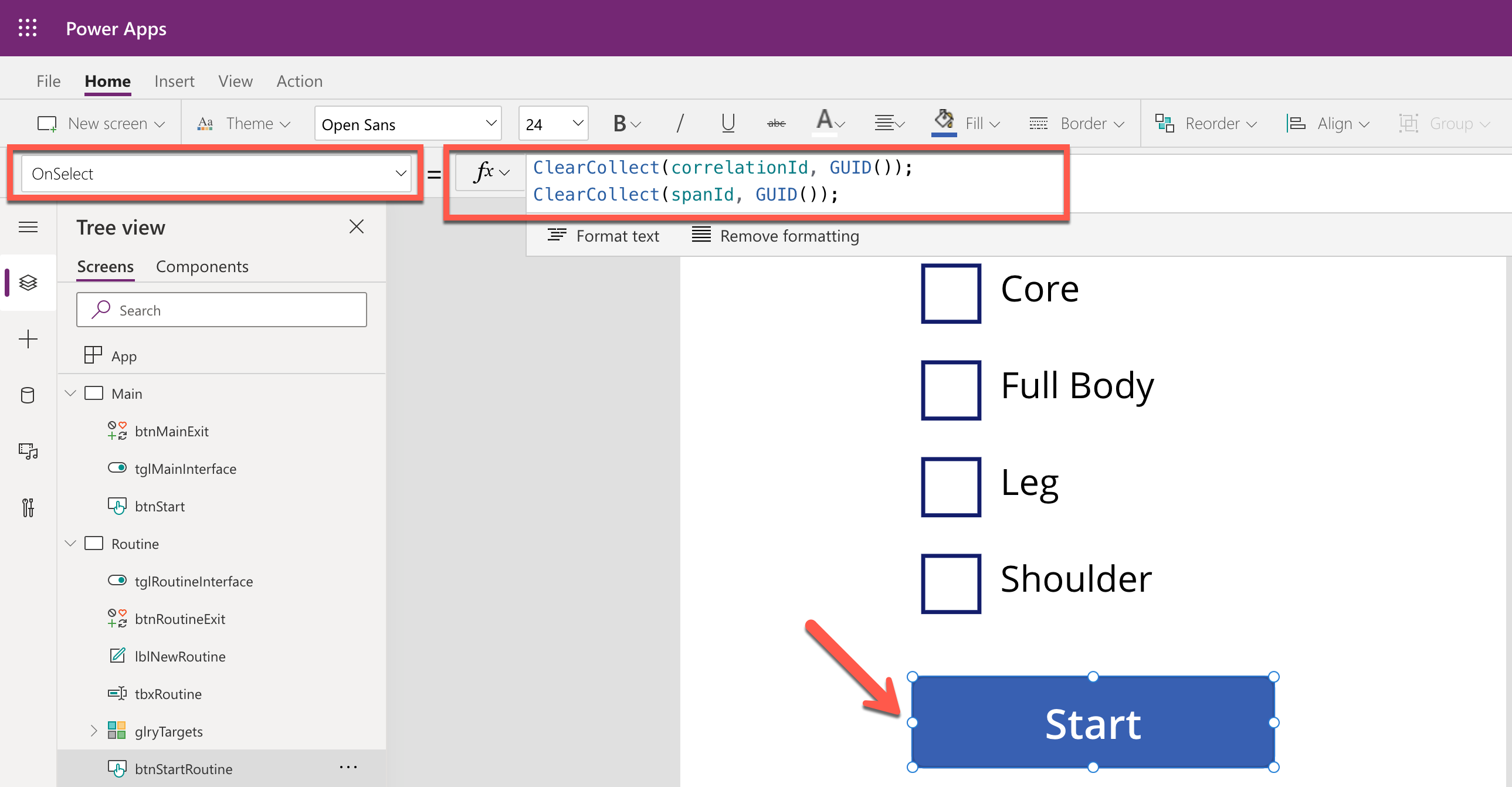
By doing so, you know the tracing starts from the Power Apps app side while monitoring, and the first Span starts from it as well. Both correlationId and spanId travels until the publish action is completed. Moreover, the correlationId is transferred to the other Span through the Span Context.
Backend Update
As long as the Azure Functions app knows the instrumentation key from an Application Insights instance, it traces almost everything. OpenTelemetry.NET is one of the Open Telemetry implementations, which has recently released v1.0 for tracing. Both metrics and logging are close to GA. However, it doesn’t work well with Azure Functions. Therefore, in this post, let’s manually implement the tracing at the log level, which is sent to Application Insights.
Publisher – HTTP Trigger
When do we take the log?
In this example, the backend APIs consist of routine, exercise and publish actions. Each action stores data to Azure Table Storage, by following the event sourcing approach. So, it’s good to take logs around the data handling as checkpoints. In addition to that, while invoking the publish action, it aggregates the data stored from the previous actions and sends the one to Azure Service Bus, which is another good point that takes the log as a checkpoint.
All the logging features used in Azure Functions implement the ILogger interface. Through this interface, you can store custom telemetry values to Application Insights. Then, what could be the values for the custom telemetry?
- Event Type: Action and its invocation result –
RoutineReceived, ExerciseCreated or MessageNotPublished
- Event Status: Success or failure of the event –
Succeeded or Failed
- Event ID: Azure Functions invocation ID – whenever a new request comes in a new GUID is assigned.
- Span Type: Type of Span –
Publisher or Subscriber
- Span Status: Current Span status –
PublisherInitiated, SubscriberInProgress or PublisherCompleted
- Span ID: GUID assigned to Span each time it is invoked
- Interface Type: Type of user interface –
Test Harness or Power Apps App
- Correlation ID: Unique ID for the whole Trace
It could be the bare minimum stored to Application Insights. Once you capture them, you will be able to monitor in which trace (correlation ID) the data flow through which user interface (interface type), span (span type), and event (event type) successfully or not (event status).
Here’s the extension method for the ILogger interface. Let’s have a look at the sample code below that checks in the request data from Power Apps is successfully captured on the routine action. Both correlationId and spanId are sent from Power Apps (line #9-10). The invocationId fro the Azure Functions context has become the eventId (line #12). Finally, event type, event status, span type, span status, interface type and correlation ID are logged (line #14-17).
public async Task<IActionResult> CreateRoutineAsync(
[HttpTrigger(AuthorizationLevel.Function, HttpVerbs.Post, Route = “routines”)] HttpRequest req,
ExecutionContext context,
ILogger log)
{
var request = await req.ToRequestMessageAsync<RoutineRequestMessage>().ConfigureAwait(false);
var @interface = request.Interface;
var correlationId = request.CorrelationId;
var spanId = request.SpanId;
var eventId = context.InvocationId;
log.LogData(LogLevel.Information, request,
EventType.RoutineReceived, EventStatusType.Succeeded, eventId,
SpanType.Publisher, SpanStatusType.PublisherInitiated, spanId,
@interface, correlationId);
…
}
The code below shows another checkpoint. Store the request data to Azure Table Storage (line #14). If it’s successful, log it (line #18-23). If not, throw an exception, handle it and log the exception details (line #29-34).
public async Task<IActionResult> CreateRoutineAsync(
[HttpTrigger(AuthorizationLevel.Function, HttpVerbs.Post, Route = “routines”)] HttpRequest req,
ExecutionContext context,
ILogger log)
{
…
try
{
…
await this._client.CreateTableIfNotExistsAsync(this._settings.GymLog.StorageAccount.Table.TableName).ConfigureAwait(false);
var table = this._client.GetTableClient(this._settings.GymLog.StorageAccount.Table.TableName);
var response = await table.UpsertEntityAsync(entity).ConfigureAwait(false);
…
log.LogData(response.Status.ToLogLevel(), res.Value,
EventType.RoutineCreated, EventStatusType.Succeeded, eventId,
SpanType.Publisher, SpanStatusType.PublisherInProgress, spanId,
@interface, correlationId,
clientRequestId: response.ClientRequestId,
message: response.Status.ToResponseMessage(res));
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
…
log.LogData(LogLevel.Error, res.Value,
EventType.RoutineNotCreated, EventStatusType.Failed, eventId,
SpanType.Publisher, SpanStatusType.PublisherInProgress, spanId,
@interface, correlationId,
ex: ex,
message: ex.Message);
}
…
}
In similar ways, the other exercise and publish actions capture the checkpoint logs.
Publisher – Span Context
The publish action in the Publisher Span doesn’t only capture the checkpoint log, but it should also implement Span Context. Span Context contains metadata for tracing, like correlation ID. Depending on the message transfer method, use either the HTTP request header or message envelope. As this system uses Azure Service Bus, use the ApplicationProperties dictionary in its message envelope.
Let’s have a look at the code for the publish action. This part describes that the message body is about the workout details (line #23-24). Other data is stored to CorrelationId and MessageId properties of the message object (line #26-27) and the ApplicationProperties dictionary so that the subscriber application makes use of them (line #30-33). Finally, after sending the message to Azure Service Bus, capture another checkpoint that message has been successfully sent (line #37-42).
public async Task<IActionResult> PublishRoutineAsync(
[HttpTrigger(AuthorizationLevel.Function, HttpVerbs.Post, Route = “routines/{routineId}/publish”)] HttpRequest req,
Guid routineId,
ExecutionContext context,
[ServiceBus(GymLogTopicKey)] IAsyncCollector<ServiceBusMessage> collector,
ILogger log)
{
var request = await req.ToRequestMessageAsync<PublishRequestMessage>().ConfigureAwait(false);
var @interface = request.Interface;
var correlationId = request.CorrelationId;
var spanId = request.SpanId;
var eventId = context.InvocationId;
try
{
…
var messageId = Guid.NewGuid();
var subSpanId = Guid.NewGuid();
var timestamp = DateTimeOffset.UtcNow;
var message = (RoutineQueueMessage)(PublishResponseMessage)res.Value;
var msg = new ServiceBusMessage(message.ToJson())
{
CorrelationId = correlationId.ToString(),
MessageId = messageId.ToString(),
ContentType = ContentTypes.ApplicationJson,
};
msg.ApplicationProperties.Add(“pubSpanId”, spanId);
msg.ApplicationProperties.Add(“subSpanId”, subSpanId);
msg.ApplicationProperties.Add(“interface”, @interface.ToString());
msg.ApplicationProperties.Add(“timestamp”, timestamp.ToString(CultureInfo.InvariantCulture));
await collector.AddAsync(msg).ConfigureAwait(false);
log.LogData(LogLevel.Information, msg,
EventType.MessagePublished, EventStatusType.Succeeded, eventId,
SpanType.Publisher, SpanStatusType.PublisherInProgress, spanId,
@interface, correlationId,
messageId: messageId.ToString(),
message: EventType.MessagePublished.ToDisplayName());
…
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
…
}
…
}
Subscriber – Service Bus Trigger
As the tracing metadata is transferred from Publisher via Span Context, Subscriber simply uses it. The following code describes how to interpret the message envelop. Restore the correlation ID (line #10) and Message ID (line #13). And capture another checkpoint whether the message restore is successful or not (line #16-19).
public async Task IngestAsync(
[ServiceBusTrigger(GymLogTopicKey, GymLogSubscriptionKey)] ServiceBusReceivedMessage msg,
ExecutionContext context,
ILogger log)
{
…
var @interface = Enum.Parse<InterfaceType>(msg.ApplicationProperties[“interface”] as string, ignoreCase: true);
var correlationId = Guid.Parse(msg.CorrelationId);
var spanId = (Guid)msg.ApplicationProperties[“subSpanId”];
var messageId = Guid.Parse(msg.MessageId);
var eventId = context.InvocationId;
log.LogData(LogLevel.Information, message,
EventType.MessageReceived, EventStatusType.Succeeded, eventId,
SpanType.Subscriber, SpanStatusType.SubscriberInitiated, spanId,
@interface, correlationId);
…
}
Then, store the message to Azure Cosmos DB (line #12), log another checkpoint (line #16-21). If there’s an error while processing the message, handle the exception and capture the checkpoint as well (line #25-30).
public async Task IngestAsync(
[ServiceBusTrigger(GymLogTopicKey, GymLogSubscriptionKey)] ServiceBusReceivedMessage msg,
ExecutionContext context,
ILogger log)
{
…
try
{
…
var response = await container.UpsertItemAsync<RoutineRecordItem>(record, new PartitionKey(record.ItemType.ToString())).ConfigureAwait(false);
…
log.LogData(LogLevel.Information, message,
EventType.MessageProcessed, EventStatusType.Succeeded, eventId,
SpanType.Subscriber, SpanStatusType.SubscriberCompleted, spanId,
@interface, correlationId,
recordId: record.EntityId.ToString(),
message: response.StatusCode.ToMessageEventType().ToDisplayName());
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
log.LogData(LogLevel.Error, message,
EventType.MessageNotProcessed, EventStatusType.Failed, eventId,
SpanType.Subscriber, SpanStatusType.SubscriberCompleted, spanId,
@interface, correlationId,
ex: ex,
message: ex.Message);
…
}
}
So far, all paths the data sways have been marked as checkpoints and store the check-in log to Application Insights. Now, how can we check all the traces on Azure Monitor?
KUSTO Query on Azure Monitor
This time, Ji Min received another feedback that a new error has occurred while storing the workout details with screenshots.
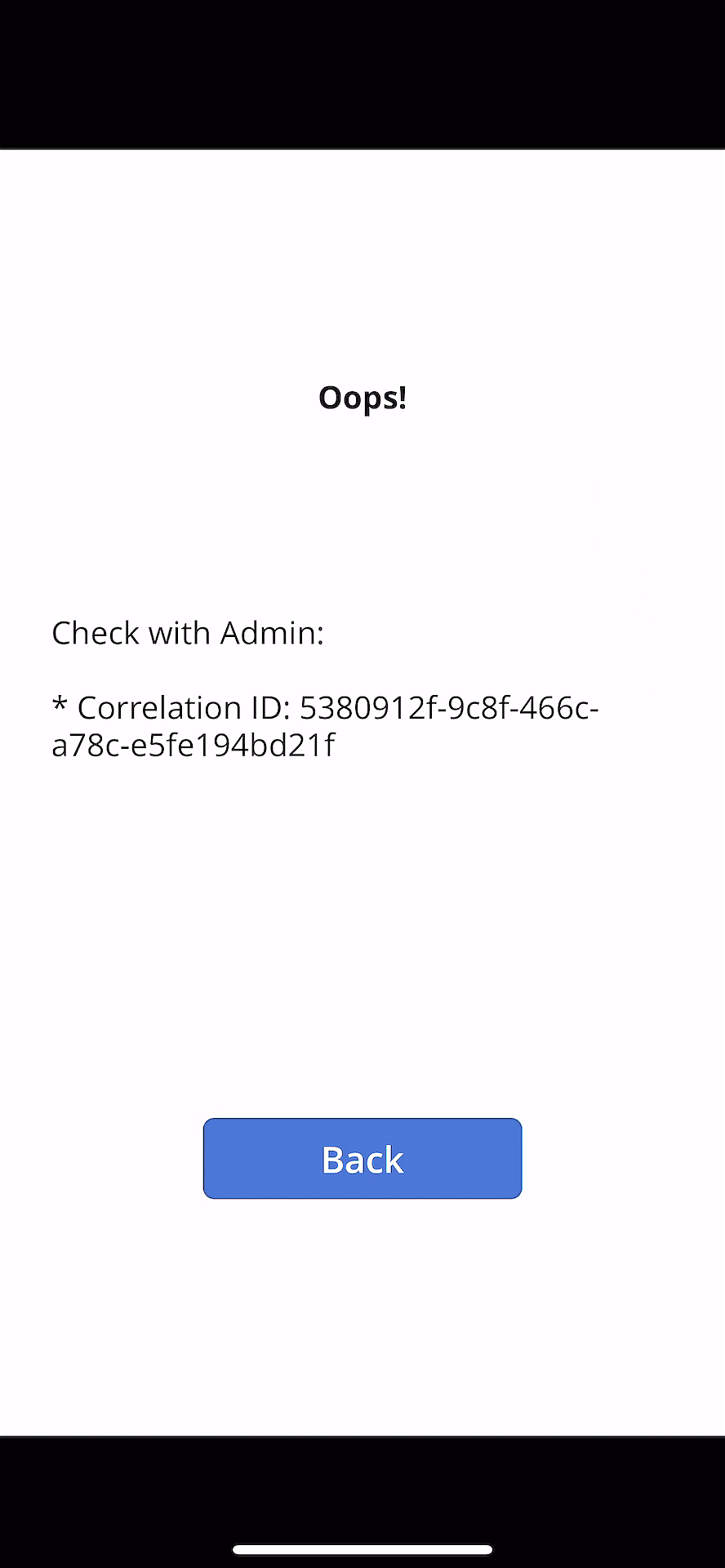
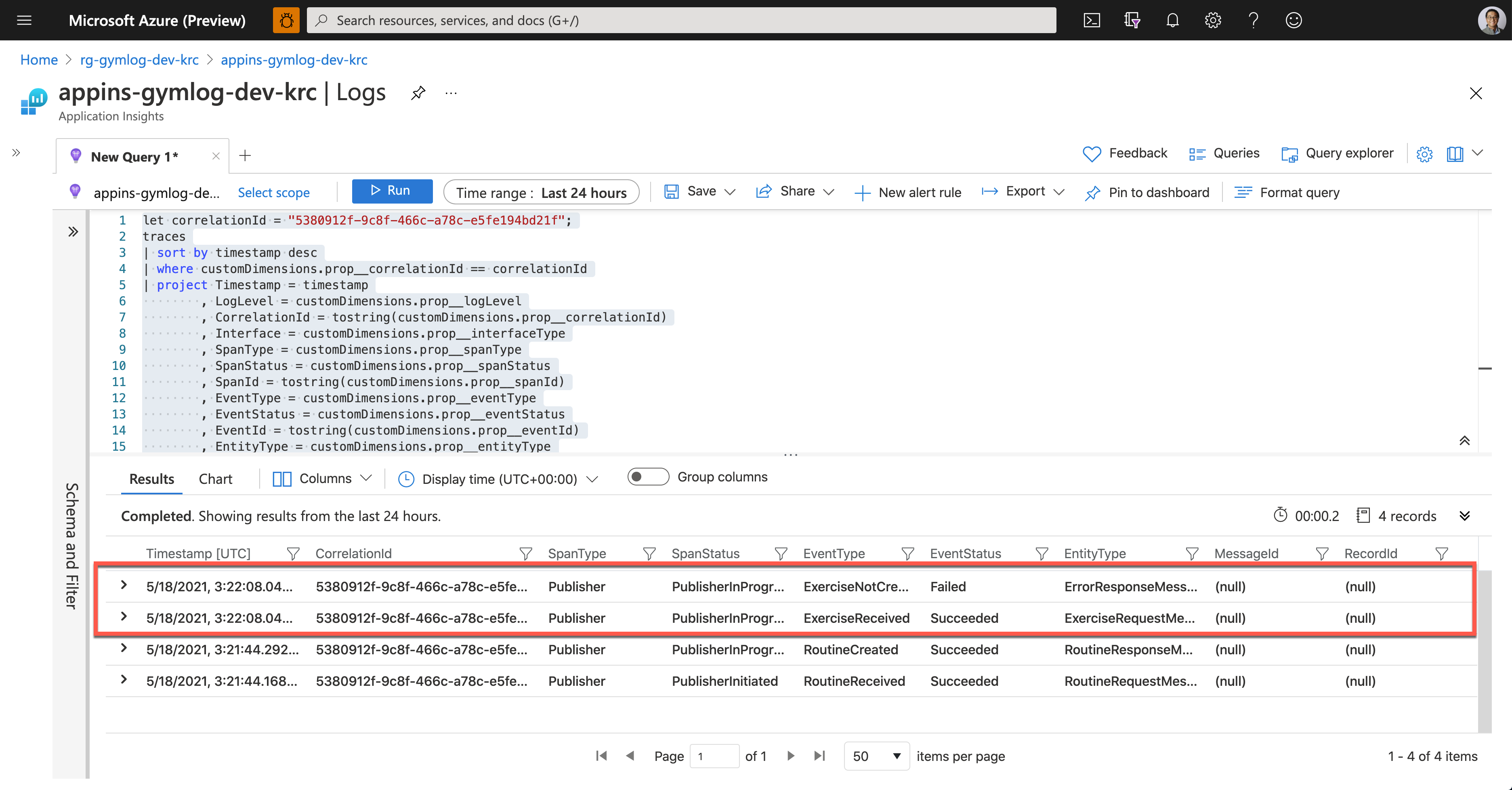
As soon as Ji Min shared the pictures with Su Bin, Su Bin wrote a Kusto query and ran it on Application Insights. Assign the correlationId value for tracing (line #1). Then use the custom telemetry values for the query. As all the custom properties start with customDimensions.prop__, include them in the where clause with the correlation ID for filtering (line #4), and in the project clause to select fields that I want to see (line #5-18).
let correlationId = “5380912f-9c8f-466c-a78c-e5fe194bd21f”;
traces
| sort by timestamp desc
| where customDimensions.prop__correlationId == correlationId
| project Timestamp = timestamp
, LogLevel = customDimensions.prop__logLevel
, CorrelationId = tostring(customDimensions.prop__correlationId)
, Interface = customDimensions.prop__interfaceType
, SpanType = customDimensions.prop__spanType
, SpanStatus = customDimensions.prop__spanStatus
, SpanId = tostring(customDimensions.prop__spanId)
, EventType = customDimensions.prop__eventType
, EventStatus = customDimensions.prop__eventStatus
, EventId = tostring(customDimensions.prop__eventId)
, EntityType = customDimensions.prop__entityType
, ClientRequestId = customDimensions.prop__clientRequestId
, MessageId = customDimensions.prop__messageId
, RecordId = customDimensions.prop__recordId
| project Timestamp
, CorrelationId
, SpanType
, SpanStatus
, EventType
, EventStatus
, EntityType
, MessageId
, RecordId
And here’s the query result. It says it was OK to receive the exercise data, but it failed to store it to Azure Table Storage.
Now, Su Bin found out where the error has occurred. She fixed the code and deployed the API again, and all is good! The following screenshot shows one of the successful end-to-end tracking logs. A Message sent from Publisher has processed well on the Subscriber side, and the message has become a record based on the logic implemented on the Subscriber side.
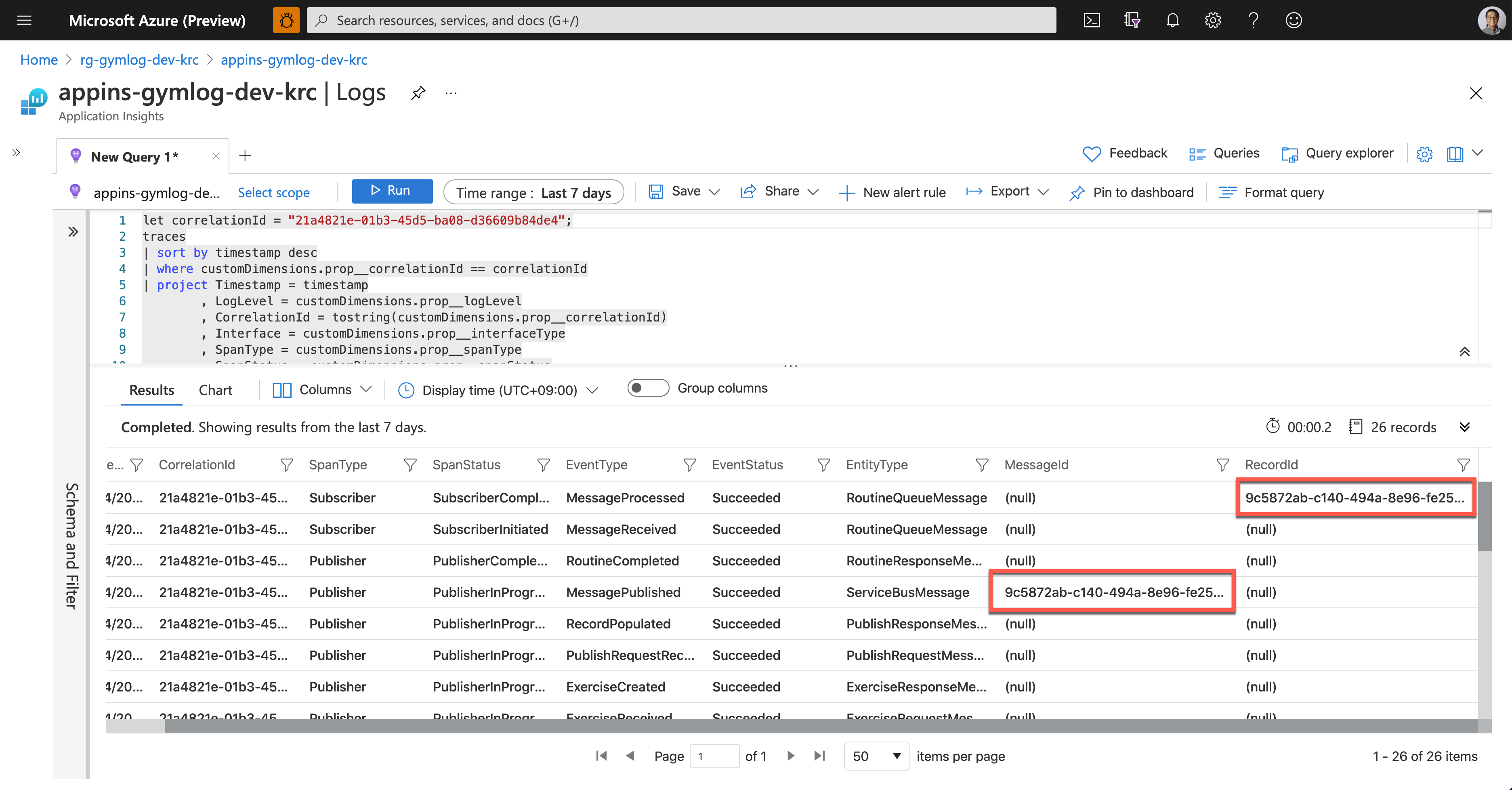
So, we confirm that the data tracing logic has been implemented by following the Open Telemetry concepts through Application Insights. Ji Min and her trainer crews, and all the members in the gym are now able to know the reference ID for tracing.
So far, we’ve walked through the implementation of data tracing logic with the concept of Open Telemetry, from Power Apps to Cosmos DB through Application Insights.
Unfortunately, the OpenTelemetry.NET doesn’t work in Azure Functions as expected for now. But we can still implement the concept through Application Insights for the time being. In the next post, let’s try the DevOps journey with Power Apps.
This article was originally published on Dev Kimchi.
by Scott Muniz | May 24, 2021 | Security, Technology
This article is contributed. See the original author and article here.
acymailing — acymailing
|
When subscribing using AcyMailing, the ‘redirect’ parameter isn’t properly sanitized. Turning the request from POST to GET, an attacker can craft a link containing a potentially malicious landing page and send it to the victim. |
2021-05-17 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-24288
CONFIRM |
admidio — admidio
|
Admidio is a free, open source user management system for websites of organizations and groups. In Admidio before version 4.0.4, there is an authenticated RCE via .phar file upload. A php web shell can be uploaded via the Documents & Files upload feature. Someone with upload permissions could rename the php shell with a .phar extension, visit the file, triggering the payload for a reverse/bind shell. This can be mitigated by excluding a .phar file extension to be uploaded (like you did with .php .phtml .php5 etc). The vulnerability is patched in version 4.0.4. |
2021-05-20 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-32630
MISC
CONFIRM
MISC |
adminer — adminer
|
Adminer is open-source database management software. A cross-site scripting vulnerability in Adminer versions 4.6.1 to 4.8.0 affects users of MySQL, MariaDB, PgSQL and SQLite. XSS is in most cases prevented by strict CSP in all modern browsers. The only exception is when Adminer is using a `pdo_` extension to communicate with the database (it is used if the native extensions are not enabled). In browsers without CSP, Adminer versions 4.6.1 to 4.8.0 are affected. The vulnerability is patched in version 4.8.1. As workarounds, one can use a browser supporting strict CSP or enable the native PHP extensions (e.g. `mysqli`) or disable displaying PHP errors (`display_errors`). |
2021-05-19 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-29625
MISC
MISC
CONFIRM |
arm — trustzone_cryptocell
|
The elliptic curve cryptography (ECC) hardware accelerator, part of the ARM® TrustZone® CryptoCell 310, contained in the NordicSemiconductor nRF52840 through 2021-03-29 has a non-constant time ECDSA implemenation. This allows an adversary to recover the private ECC key used during an ECDSA operation. |
2021-05-21 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-29415
MISC
MISC |
bitdefender — endpoint_security_tools
|
An Improper Access Control vulnerability in the logging component of Bitdefender Endpoint Security Tools for Windows versions prior to 6.6.23.320 allows a regular user to learn the scanning exclusion paths. This issue was discovered during external security research. |
2021-05-18 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-15279
CONFIRM |
bitdefender — gravityzone_business_security
|
Uncontrolled Search Path Element vulnerability in the openssl component as used in Bitdefender GravityZone Business Security allows an attacker to load a third party DLL to elevate privileges. This issue affects Bitdefender GravityZone Business Security versions prior to 6.6.23.329. |
2021-05-18 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-3423
CONFIRM |
bludit — bludit
|
A file upload vulnerability was discovered in the file path /bl-plugins/backup/plugin.php on Bludit version 3.12.0. If an attacker is able to gain Administrator rights they will be able to use unsafe plugins to upload a backup file and control the server. |
2021-05-21 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-23765
MISC |
bmc — remedy_mid_tier_9.1sp3
|
BMC Remedy 9.1SP3 is affected by authenticated code execution. Authenticated users that have the right to create reports can use BIRT templates to run code. |
2021-05-19 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2017-17677
MISC
MISC
MISC
MISC |
bmc — remedy_mid_tier_9.1sp3
|
BMC Remedy Mid Tier 9.1SP3 is affected by cross-site scripting (XSS). A DOM-based cross-site scripting vulnerability was discovered in a legacy utility. |
2021-05-19 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2017-17678
MISC
MISC
MISC
MISC |
bmc — remedy_mid_tier_9.1sp3
|
BMC Remedy Mid Tier 9.1SP3 is affected by remote and local file inclusion. Due to the lack of restrictions on what can be targeted, the system can be vulnerable to attacks such as system fingerprinting, internal port scanning, Server Side Request Forgery (SSRF), or remote code execution (RCE). |
2021-05-19 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2017-17674
MISC
MISC
MISC
MISC |
bmc — remedy_mid_tier_9.1sp3
|
BMC Remedy Mid Tier 9.1SP3 is affected by log hijacking. Remote logging can be accessed by unauthenticated users, allowing for an attacker to hijack the system logs. This data can include user names and HTTP data. |
2021-05-19 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2017-17675
MISC
MISC
MISC
MISC |
boostnote — boostnote
|
In Boostnote 0.12.1, exporting to PDF contains opportunities for XSS attacks. |
2021-05-18 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-19924
MISC |
bounty_castle — bounty_castle
|
Bouncy Castle BC Java before 1.66, BC C# .NET before 1.8.7, BC-FJA before 1.0.1.2, 1.0.2.1, and BC-FNA before 1.0.1.1 have a timing issue within the EC math library that can expose information about the private key when an attacker is able to observe timing information for the generation of multiple deterministic ECDSA signatures. |
2021-05-20 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-15522
MISC
MISC
MISC |
| centos — web+panel |
The unprivileged user portal part of CentOS Web Panel is affected by a SQL Injection via the ‘idsession’ HTTP POST parameter. |
2021-05-18 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-31316
MISC |
centos — web_panel
|
The unprivileged user portal part of CentOS Web Panel is affected by a Command Injection vulnerability leading to root Remote Code Execution. |
2021-05-18 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-31324
MISC |
cflow — cflow
|
Use-after-Free vulnerability in cflow 1.6 in the void call(char *name, int line) function at src/parser.c, which could cause a denial of service via the pointer variable caller->callee. |
2021-05-18 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-23856
MISC
MISC |
| cisco — dna_spaces_connector |
Multiple vulnerabilities in Cisco DNA Spaces Connector could allow an authenticated, remote attacker to perform a command injection attack on an affected device. These vulnerabilities are due to insufficient input sanitization when executing affected commands. A high-privileged attacker could exploit these vulnerabilities on a Cisco DNA Spaces Connector by injecting crafted input during command execution. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to execute arbitrary commands as root within the Connector docker container. |
2021-05-22 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1559
CISCO |
| cisco — dna_spaces_connector |
Multiple vulnerabilities in Cisco DNA Spaces Connector could allow an authenticated, remote attacker to perform a command injection attack on an affected device. These vulnerabilities are due to insufficient input sanitization when executing affected commands. A high-privileged attacker could exploit these vulnerabilities on a Cisco DNA Spaces Connector by injecting crafted input during command execution. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to execute arbitrary commands as root within the Connector docker container. |
2021-05-22 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1560
CISCO |
| cisco — dna_spaces_connector |
Multiple vulnerabilities in Cisco DNA Spaces Connector could allow an authenticated, local attacker to elevate privileges and execute arbitrary commands on the underlying operating system as root. These vulnerabilities are due to insufficient restrictions during the execution of affected CLI commands. An attacker could exploit these vulnerabilities by leveraging the insufficient restrictions during execution of these commands. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to elevate privileges from dnasadmin and execute arbitrary commands on the underlying operating system as root. |
2021-05-22 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1557
CISCO |
cisco — dna_spaces_connector
|
Multiple vulnerabilities in Cisco DNA Spaces Connector could allow an authenticated, local attacker to elevate privileges and execute arbitrary commands on the underlying operating system as root. These vulnerabilities are due to insufficient restrictions during the execution of affected CLI commands. An attacker could exploit these vulnerabilities by leveraging the insufficient restrictions during execution of these commands. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to elevate privileges from dnasadmin and execute arbitrary commands on the underlying operating system as root. |
2021-05-22 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1558
CISCO |
cisco — finesse
|
A vulnerability in the web-based management interface of Cisco Finesse could allow an unauthenticated, remote attacker to redirect a user to an undesired web page. This vulnerability is due to improper input validation of the URL parameters in an HTTP request that is sent to an affected system. An attacker could exploit this vulnerability by persuading a user of the interface to click a crafted link. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to cause the interface to redirect the user to a specific, malicious URL. This type of vulnerability is known as an open redirect and is used in phishing attacks that get users to unknowingly visit malicious sites. |
2021-05-22 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1358
CISCO |
cisco — finesse
|
Multiple vulnerabilities in the web-based management interface of Cisco Finesse could allow an authenticated, remote attacker to conduct a cross-site scripting (XSS) attack against a user of the interface. These vulnerabilities are due to insufficient validation of user-supplied input by the web-based management interface of the affected software. An attacker could exploit these vulnerabilities by injecting malicious code into the web-based management interface and persuading a user to click a malicious link. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to execute arbitrary script code in the context of the affected interface or access sensitive, browser-based information. An attacker needs valid administrator credentials to inject the malicious script code. |
2021-05-22 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1254
CISCO |
cisco — modeling_labs
|
A vulnerability in the web UI of Cisco Modeling Labs could allow an authenticated, remote attacker to execute arbitrary commands with the privileges of the web application on the underlying operating system of an affected Cisco Modeling Labs server. This vulnerability is due to insufficient validation of user-supplied input to the web UI. An attacker could exploit this vulnerability by sending a crafted HTTP request to an affected server. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to execute arbitrary commands with the privileges of the web application, virl2, on the underlying operating system of the affected server. To exploit this vulnerability, the attacker must have valid user credentials on the web UI. |
2021-05-22 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1531
CISCO |
cisco — multiple_products
|
A vulnerability in the restricted shell of Cisco Evolved Programmable Network (EPN) Manager, Cisco Identity Services Engine (ISE), and Cisco Prime Infrastructure could allow an authenticated, local attacker to identify directories and write arbitrary files to the file system. This vulnerability is due to improper validation of parameters that are sent to a CLI command within the restricted shell. An attacker could exploit this vulnerability by logging in to the device and issuing certain CLI commands. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to identify file directories on the affected device and write arbitrary files to the file system on the affected device. To exploit this vulnerability, the attacker must be an authenticated shell user. |
2021-05-22 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1306
CISCO |
cisco — prime_infrastructure_and_evolved_programmable_network_manager
|
A vulnerability in the web-based management interface of Cisco Prime Infrastructure and Evolved Programmable Network (EPN) Manager could allow an authenticated, remote attacker to execute arbitrary commands on an affected system. The vulnerability is due to insufficient validation of user-supplied input to the web-based management interface. An attacker could exploit this vulnerability by sending crafted HTTP requests to the interface. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to execute arbitrary commands on the underlying operating system (OS) with the permissions of a special non-root user. In this way, an attacker could take control of the affected system, which would allow them to obtain and alter sensitive data. The attacker could also affect the devices that are managed by the affected system by pushing arbitrary configuration files, retrieving device credentials and confidential information, and ultimately undermining the stability of the devices, causing a denial of service (DoS) condition. |
2021-05-22 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1487
CISCO |
| cisco — small_business |
Multiple vulnerabilities in the web-based management interface of certain Cisco Small Business 100, 300, and 500 Series Wireless Access Points could allow an authenticated, remote attacker to perform command injection attacks against an affected device. These vulnerabilities are due to improper validation of user-supplied input. An attacker could exploit these vulnerabilities by sending crafted HTTP requests to the web-based management interface of an affected system. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to execute arbitrary commands with root privileges on the device. To exploit these vulnerabilities, the attacker must have valid administrative credentials for the device. |
2021-05-22 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1549
CISCO |
| cisco — small_business |
Multiple vulnerabilities in the web-based management interface of certain Cisco Small Business 100, 300, and 500 Series Wireless Access Points could allow an authenticated, remote attacker to perform command injection attacks against an affected device. These vulnerabilities are due to improper validation of user-supplied input. An attacker could exploit these vulnerabilities by sending crafted HTTP requests to the web-based management interface of an affected system. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to execute arbitrary commands with root privileges on the device. To exploit these vulnerabilities, the attacker must have valid administrative credentials for the device. |
2021-05-22 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1555
CISCO |
| cisco — small_business |
Multiple vulnerabilities in the web-based management interface of certain Cisco Small Business 100, 300, and 500 Series Wireless Access Points could allow an authenticated, remote attacker to perform command injection attacks against an affected device. These vulnerabilities are due to improper validation of user-supplied input. An attacker could exploit these vulnerabilities by sending crafted HTTP requests to the web-based management interface of an affected system. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to execute arbitrary commands with root privileges on the device. To exploit these vulnerabilities, the attacker must have valid administrative credentials for the device. |
2021-05-22 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1551
CISCO |
| cisco — small_business |
Multiple vulnerabilities in the web-based management interface of certain Cisco Small Business 100, 300, and 500 Series Wireless Access Points could allow an authenticated, remote attacker to perform command injection attacks against an affected device. These vulnerabilities are due to improper validation of user-supplied input. An attacker could exploit these vulnerabilities by sending crafted HTTP requests to the web-based management interface of an affected system. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to execute arbitrary commands with root privileges on the device. To exploit these vulnerabilities, the attacker must have valid administrative credentials for the device. |
2021-05-22 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1552
CISCO |
cisco — small_business
|
Multiple vulnerabilities in the web-based management interface of certain Cisco Small Business 100, 300, and 500 Series Wireless Access Points could allow an authenticated, remote attacker to perform command injection attacks against an affected device. These vulnerabilities are due to improper validation of user-supplied input. An attacker could exploit these vulnerabilities by sending crafted HTTP requests to the web-based management interface of an affected system. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to execute arbitrary commands with root privileges on the device. To exploit these vulnerabilities, the attacker must have valid administrative credentials for the device. |
2021-05-22 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1548
CISCO |
cisco — small_business
|
Multiple vulnerabilities in the web-based management interface of certain Cisco Small Business 100, 300, and 500 Series Wireless Access Points could allow an authenticated, remote attacker to perform command injection attacks against an affected device. These vulnerabilities are due to improper validation of user-supplied input. An attacker could exploit these vulnerabilities by sending crafted HTTP requests to the web-based management interface of an affected system. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to execute arbitrary commands with root privileges on the device. To exploit these vulnerabilities, the attacker must have valid administrative credentials for the device. |
2021-05-22 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1553
CISCO |
cisco — small_business
|
Multiple vulnerabilities in the web-based management interface of certain Cisco Small Business 100, 300, and 500 Series Wireless Access Points could allow an authenticated, remote attacker to perform command injection attacks against an affected device. These vulnerabilities are due to improper validation of user-supplied input. An attacker could exploit these vulnerabilities by sending crafted HTTP requests to the web-based management interface of an affected system. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to execute arbitrary commands with root privileges on the device. To exploit these vulnerabilities, the attacker must have valid administrative credentials for the device. |
2021-05-22 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1554
CISCO |
cisco — small_business
|
Multiple vulnerabilities in the web-based management interface of certain Cisco Small Business 100, 300, and 500 Series Wireless Access Points could allow an authenticated, remote attacker to perform command injection attacks against an affected device. These vulnerabilities are due to improper validation of user-supplied input. An attacker could exploit these vulnerabilities by sending crafted HTTP requests to the web-based management interface of an affected system. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to execute arbitrary commands with root privileges on the device. To exploit these vulnerabilities, the attacker must have valid administrative credentials for the device. |
2021-05-22 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1550
CISCO |
cisco — small_business
|
Multiple vulnerabilities in the web-based management interface of certain Cisco Small Business 100, 300, and 500 Series Wireless Access Points could allow an authenticated, remote attacker to perform command injection attacks against an affected device. These vulnerabilities are due to improper validation of user-supplied input. An attacker could exploit these vulnerabilities by sending crafted HTTP requests to the web-based management interface of an affected system. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to execute arbitrary commands with root privileges on the device. To exploit these vulnerabilities, the attacker must have valid administrative credentials for the device. |
2021-05-22 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1547
CISCO |
cmswing — cmswing
|
There is a cross site scripting vulnerability on CmsWing 1.3.7. This vulnerability (stored XSS) is triggered when visitors access the article module. |
2021-05-17 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-24993
MISC |
cmswing — cmswing
|
There is a cross site scripting vulnerability on CmsWing 1.3.7. This vulnerability (stored XSS) is triggered when an administrator accesses the content management module. |
2021-05-17 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-24992
MISC |
concerto — concerto
|
Persistent cross-site scripting (XSS) in the web interface of Concerto through 2.3.6 allows an unauthenticated remote attacker to introduce arbitrary JavaScript by injecting an XSS payload into the First Name or Last Name parameter upon registration. When a privileged user attempts to delete the account, the XSS payload will be executed. |
2021-05-19 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-31930
MISC
MISC |
couchbase_server — couchbase_server
|
An issue was discovered in Couchbase Server 6.x through 6.6.1. The Couchbase Server UI is insecurely logging session cookies in the logs. This allows for the impersonation of a user if the log files are obtained by an attacker before a session cookie expires. |
2021-05-19 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-27924
MISC
MISC |
couchbase_server — couchbase_server
|
In the Query Engine in Couchbase Server 6.5.x and 6.6.x through 6.6.1, Common Table Expression queries were not correctly checking the user’s permissions, allowing read-access to resources beyond what those users were explicitly allowed to access. |
2021-05-19 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-31158
MISC
MISC |
couchbase_server — couchbase_server
|
An issue was discovered in Couchbase Server 6.5.x and 6.6.x through 6.6.1. When using the View Engine and Auditing is enabled, a crash condition can (depending on a race condition) cause an internal user with administrator privileges, @ns_server, to have its credentials leaked in cleartext in the ns_server.info.log file. |
2021-05-19 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-27925
MISC
MISC |
couchbase_server — couchbase_server
|
An issue was discovered in Couchbase Server 5.x and 6.x through 6.6.1 and 7.0.0 Beta. Incorrect commands to the REST API can result in leaked authentication information being stored in cleartext in the debug.log and info.log files, and is also shown in the UI visible to administrators. |
2021-05-19 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-25644
MISC
MISC |
d-link — dir-842_routers
|
An authentication brute-force protection mechanism bypass in telnetd in D-Link Router model DIR-842 firmware version 3.0.2 allows a remote attacker to circumvent the anti-brute-force cool-down delay period via a timing-based side-channel attack |
2021-05-17 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-27342
MISC
MISC
CONFIRM |
dell — emc_xtremio
|
Dell EMC XtremIO Versions prior to 6.3.3-8, contain a Cross-Site Request Forgery Vulnerability in XMS. A non-privileged attacker could potentially exploit this vulnerability, leading to a privileged victim application user being tricked into sending state-changing requests to the vulnerable application, causing unintended server operations. |
2021-05-21 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-21549
CONFIRM |
dell — wyse_windows_embedded_system
|
Dell Wyse Windows Embedded System versions WIE10 LTSC 2019 and earlier contain an improper authorization vulnerability. A local authenticated malicious user with low privileges may potentially exploit this vulnerability to bypass the restricted environment and perform unauthorized actions on the affected system. |
2021-05-21 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-21552
CONFIRM |
delta_industrial_automation — cncsoft_screeneditor
|
Delta Industrial Automation CNCSoft ScreenEditor Versions 1.01.28 (with ScreenEditor Version 1.01.2) and prior are vulnerable to an out-of-bounds read while processing project files, which may allow an attacker to execute arbitrary code. |
2021-05-16 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-22668
MISC |
dns-package — dns-package
|
This affects the package dns-packet before 5.2.2. It creates buffers with allocUnsafe and does not always fill them before forming network packets. This can expose internal application memory over unencrypted network when querying crafted invalid domain names. |
2021-05-20 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-23386
MISC
MISC
MISC
MISC |
doracms — doracms
|
Weak Encoding for Password in DoraCMS v2.1.1 and earlier allows attackers to obtain sensitive information as it does not use a random salt or IV for its AES-CBC encryption, causes password encrypted for users to be susceptible to dictionary attacks. |
2021-05-20 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-18220
MISC |
draeger — x-dock_firmware
|
Draeger X-Dock Firmware before 03.00.13 has Hard-Coded Credentials, leading to remote code execution by an authenticated attacker. |
2021-05-20 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-28111
MISC
CONFIRM
MISC |
draeger — x-dock_firmware
|
Draeger X-Dock Firmware before 03.00.13 has Active Debug Code on a debug port, leading to remote code execution by an authenticated attacker. |
2021-05-20 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-28112
MISC
CONFIRM |
drupal — core_workspaces
|
Access bypass vulnerability in of Drupal Core Workspaces allows an attacker to access data without correct permissions. The Workspaces module doesn’t sufficiently check access permissions when switching workspaces, leading to an access bypass vulnerability. An attacker might be able to see content before the site owner intends people to see the content. This vulnerability is mitigated by the fact that sites are only vulnerable if they have installed the experimental Workspaces module. This issue affects Drupal Core8.8.X versions prior to 8.8.10; 8.9.X versions prior to 8.9.6; 9.0.X versions prior to 9.0.6. |
2021-05-17 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-13667
CONFIRM |
| emerson — rosemont_x-stream_gas_analyzer |
A vulnerability has been found in multiple revisions of Emerson Rosemount X-STREAM Gas Analyzer. The affected applications do not validate webpage input, which could allow an attacker to inject arbitrary HTML code into a webpage. This would allow an attacker to modify the page and display incorrect or undesirable data. |
2021-05-20 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-27465
MISC |
emerson — rosemont_x-stream_gas_analyzer
|
A vulnerability has been found in multiple revisions of Emerson Rosemount X-STREAM Gas Analyzer. The affected applications utilize persistent cookies where the session cookie attribute is not properly invalidated, allowing an attacker to intercept the cookies and gain access to sensitive information. |
2021-05-20 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-27463
MISC |
emerson — rosemont_x-stream_gas_analyzer
|
A vulnerability has been found in multiple revisions of Emerson Rosemount X-STREAM Gas Analyzer. The affected products utilize a weak encryption algorithm for storage of sensitive data, which may allow an attacker to more easily obtain credentials used for access. |
2021-05-20 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-27457
MISC |
emerson — rosemont_x-stream_gas_analyzer
|
A vulnerability has been found in multiple revisions of Emerson Rosemount X-STREAM Gas Analyzer. The affected webserver applications allow access to stored data that can be obtained by using specially crafted URLs. |
2021-05-20 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-27461
MISC |
emerson — rosemont_x-stream_gas_analyzer
|
A vulnerability has been found in multiple revisions of Emerson Rosemount X-STREAM Gas Analyzer. The affected product’s web interface allows an attacker to route click or keystroke to another page provided by the attacker to gain unauthorized access to sensitive information. |
2021-05-20 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-27467
MISC |
emerson — rosemont_x-stream_gas_analyzer
|
A vulnerability has been found in multiple revisions of Emerson Rosemount X-STREAM Gas Analyzer. The webserver of the affected products allows unvalidated files to be uploaded, which an attacker could utilize to execute arbitrary code. |
2021-05-20 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-27459
MISC |
emissary — emissary
|
Emissary is a distributed, peer-to-peer, data-driven workflow framework. Emissary 6.4.0 is vulnerable to Unsafe Deserialization of post-authenticated requests to the [`WorkSpaceClientEnqueue.action`](https://github.com/NationalSecurityAgency/emissary/blob/30c54ef16c6eb6ed09604a929939fb9f66868382/src/main/java/emissary/server/mvc/internal/WorkSpaceClientEnqueueAction.java) REST endpoint. This issue may lead to post-auth Remote Code Execution. This issue has been patched in version 6.5.0. As a workaround, one can disable network access to Emissary from untrusted sources. |
2021-05-21 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-32634
CONFIRM
MISC |
emlog — emlog
|
Cross Site Scripting (XSS) in emlog v6.0.0 allows remote attackers to execute arbitrary code by adding a crafted script as a link to a new blog post. |
2021-05-17 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-18194
MISC |
envoy — envoy
|
An issue was discovered in Envoy 1.14.0. There is a remotely exploitable crash for HTTP2 Metadata, because an empty METADATA map triggers a Reachable Assertion. |
2021-05-20 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-29258
MISC
MISC
MISC
MISC |
envoy — envoy
|
An issue was discovered in Envoy through 1.71.1. There is a remotely exploitable NULL pointer dereference and crash in TLS when an unknown TLS alert code is received. |
2021-05-20 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-28683
MISC
MISC
MISC |
envoy — envoy
|
An issue was discovered in Envoy through 1.71.1. There is a remotely exploitable integer overflow in which a very large grpc-timeout value leads to unexpected timeout calculations. |
2021-05-20 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-28682
MISC
MISC
MISC |
epic_games — psyonix_rocket_league
|
Epic Games / Psyonix Rocket League <=1.95 is affected by Buffer Overflow. Stack-based buffer overflow occurs when Rocket League handles UPK object files that can result in code execution and denial of service scenario. |
2021-05-18 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-32238
MISC
MISC
MISC |
exiv2 — exiv2
|
Exiv2 is a command-line utility and C++ library for reading, writing, deleting, and modifying the metadata of image files. An inefficient algorithm (quadratic complexity) was found in Exiv2 versions v0.27.3 and earlier. The inefficient algorithm is triggered when Exiv2 is used to write metadata into a crafted image file. An attacker could potentially exploit the vulnerability to cause a denial of service, if they can trick the victim into running Exiv2 on a crafted image file. The bug is fixed in version v0.27.4. Note that this bug is only triggered when _writing_ the metadata, which is a less frequently used Exiv2 operation than _reading_ the metadata. For example, to trigger the bug in the Exiv2 command-line application, you need to add an extra command-line argument such as `rm`. |
2021-05-17 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-32617
MISC
CONFIRM |
fastify-csrf — fastify-csrf
|
fastify-csrf is an open-source plugin helps developers protect their Fastify server against CSRF attacks. Versions of fastify-csrf prior to 3.1.0 have a “double submit” mechanism using cookies with an application deployed across multiple subdomains, e.g. “heroku”-style platform as a service. Version 3.1.0 of the fastify-csrf fixes it. the vulnerability. The user of the module would need to supply a `userInfo` when generating the CSRF token to fully implement the protection on their end. This is needed only for applications hosted on different subdomains. |
2021-05-19 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-29624
MISC
MISC
MISC
CONFIRM
MISC
MISC |
fedroa_project — fedora_project
|
A flaw was found in the RPM package in the read functionality. This flaw allows an attacker who can convince a victim to install a seemingly verifiable package or compromise an RPM repository, to cause RPM database corruption. The highest threat from this vulnerability is to data integrity. This flaw affects RPM versions before 4.17.0-alpha. |
2021-05-19 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-3421
MISC
FEDORA
FEDORA
FEDORA |
ffjpeg — ffjpeg
|
A heap based buffer overflow vulnerability exists in ffjpeg through 2020-07-02 in the jfif_decode(void *ctxt, BMP *pb) function at ffjpeg/src/jfif.c (line 544 & line 545), which could cause a denial of service by submitting a malicious jpeg image. |
2021-05-18 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-23852
MISC |
ffjpeg — ffjpeg
|
A stack-based buffer overflow vulnerability exists in ffjpeg through 2020-07-02 in the jfif_decode(void *ctxt, BMP *pb) function at ffjpeg/src/jfif.c:513:28, which could cause a denial of service by submitting a malicious jpeg image. |
2021-05-18 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-23851
MISC |
firely — spark
|
Firely/Incendi Spark before 1.5.5-r4 lacks Content-Disposition headers in certain situations, which may cause crafted files to be delivered to clients such that they are rendered directly in a victim’s web browser. |
2021-05-14 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-32054
CONFIRM
CONFIRM
CONFIRM |
| flask — flask |
The Python “Flask-Security-Too” package is used for adding security features to your Flask application. It is an is an independently maintained version of Flask-Security based on the 3.0.0 version of Flask-Security. All versions of Flask-Security-Too allow redirects after many successful views (e.g. /login) by honoring the ?next query param. There is code in FS to validate that the url specified in the next parameter is either relative OR has the same netloc (network location) as the requesting URL. This check utilizes Pythons urlsplit library. However many browsers are very lenient on the kind of URL they accept and ‘fill in the blanks’ when presented with a possibly incomplete URL. As a concrete example – setting http://login?next=github.com will pass FS’s relative URL check however many browsers will gladly convert this to http://github.com. Thus an attacker could send such a link to an unwitting user, using a legitimate site and have it redirect to whatever site they want. This is considered a low severity due to the fact that if Werkzeug is used (which is very common with Flask applications) as the WSGI layer, it by default ALWAYS ensures that the Location header is absolute – thus making this attack vector mute. It is possible for application writers to modify this default behavior by setting the ‘autocorrect_location_header=False`. |
2021-05-17 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-32618
MISC
CONFIRM |
foxit — reader
|
This vulnerability allows remote attackers to execute arbitrary code on affected installations of Foxit Reader 10.1.3.37598. User interaction is required to exploit this vulnerability in that the target must visit a malicious page or open a malicious file. The specific flaw exists within the browseForDoc function. The issue results from the lack of proper validation of user-supplied data, which can result in a write past the end of an allocated data structure. An attacker can leverage this vulnerability to execute code in the context of the current process. Was ZDI-CAN-13523. |
2021-05-21 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-31473
MISC
MISC |
| fusionpbx — fusionpbx |
Directory Traversal vulnerability in FusionPBX 4.5.7, which allows a remote malicious user to delete folders on the system via the folder variable to app/edit/folderdelete.php. |
2021-05-20 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-21057
MISC
MISC |
fusionpbx — fusionpbx
|
Directory Traversal vulnerability exists in FusionPBX 4.5.7, which allows a remote malicious user to create folders via the folder variale to appeditfoldernew.php. |
2021-05-20 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-21056
MISC
MISC |
fusionpbx — fusionpbx
|
Cross Site Scripting (XSS) vulnerability in FusionPBX 4.5.7 allows remote malicious users to inject arbitrary web script or HTML via an unsanitized “f” variable in appvarsvars_textarea.php. |
2021-05-20 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-21054
MISC
MISC |
fusionpbx — fusionpbx
|
A Directory Traversal vulnerability exists in FusionPBX 4.5.7 allows malicoius users to rename any file of the system.via the (1) folder, (2) filename, and (3) newfilename variables in appeditfilerename.php. |
2021-05-20 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-21055
MISC
MISC |
fusionpbx — fusionpbx
|
Cross Site Scriptiong (XSS) vulnerability exists in FusionPBX 4.5.7 allows remote malicious users to inject arbitrary web script or HTML via an unsanitized “query_string” variable in appdevicesdevice_imports.php. |
2021-05-20 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-21053
MISC
MISC |
github — enterprise_server
|
A UI misrepresentation vulnerability was identified in GitHub Enterprise Server that allowed more permissions to be granted during a GitHub App’s user-authorization web flow than was displayed to the user during approval. To exploit this vulnerability, an attacker would need to create a GitHub App on the instance and have a user authorize the application through the web authentication flow. All permissions being granted would properly be shown during the first authorization, but in certain circumstances, if the user revisits the authorization flow after the GitHub App has configured additional user-level permissions, those additional permissions may not be shown, leading to more permissions being granted than the user potentially intended. This vulnerability affected GitHub Enterprise Server 3.0.x prior to 3.0.7 and 2.22.x prior to 2.22.13. It was fixed in versions 3.0.7 and 2.22.13. This vulnerability was reported via the GitHub Bug Bounty program. |
2021-05-14 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-22866
CONFIRM
CONFIRM |
gnu_libredwg — gnu_libredwg
|
A heap based buffer overflow vulnerability exists in GNU LibreDWG 0.10 via read_2004_section_handles ../../src/decode.c:2637. |
2021-05-17 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-21831
MISC
MISC |
gnu_libredwg — gnu_libredwg
|
A heap based buffer overflow issue exists in GNU LibreDWG 0.10.2641 via output_TEXT ../../programs/dwg2SVG.c:114. |
2021-05-17 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-21813
MISC
MISC
MISC |
gnu_libredwg — gnu_libredwg
|
GNU LibreDWG 0.10 is affected by: memcpy-param-overlap. The impact is: execute arbitrary code (remote). The component is: read_2004_section_header ../../src/decode.c:2580. |
2021-05-17 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-21844
MISC
MISC |
gnu_libredwg — gnu_libredwg
|
A heap based buffer overflow vulnerability exists in GNU LibreDWG 0.10 via read_2004_compressed_section ../../src/decode.c:2379. |
2021-05-17 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-21827
MISC
MISC |
halo — halo
|
Cross Site Scripting (XSS) vulnerability in Halo 1.1.3 via post publish components in the manage panel, which lets a remote malicious user execute arbitrary code. |
2021-05-20 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-21345
MISC |
hedgedoc — hedgedoc
|
HedgeDoc is a platform to write and share markdown. HedgeDoc before version 1.8.2 is vulnerable to a cross-site scripting attack using the YAML-metadata of a note. An attacker with write access to a note can embed HTML tags in the Open Graph metadata section of the note, resulting in the frontend rendering the script tag as part of the `<head>` section. Unless your instance prevents guests from editing notes, this vulnerability allows unauthenticated attackers to inject JavaScript into notes that allow guest edits. If your instance prevents guests from editing notes, this vulnerability allows authenticated attackers to inject JavaScript into any note pages they have write-access to. This vulnerability is patched in version 1.8.2. As a workaround, one can disable guest edits until the next update. |
2021-05-19 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-29503
MISC
CONFIRM
MISC |
hewlett_packard_enterprises — laser_jet_products
|
A potential buffer overflow in the software drivers for certain HP LaserJet products and Samsung product printers could lead to an escalation of privilege. |
2021-05-20 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-3438
MISC |
hirschmann — hios
|
Hirschmann HiOS 07.1.01, 07.1.02, and 08.1.00 through 08.5.xx and HiSecOS 03.3.00 through 03.5.01 allow remote attackers to change the credentials of existing users. |
2021-05-17 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-27734
MISC |
homee — brain_cube
|
The USB firmware update script of homee Brain Cube v2 (2.28.2 and 2.28.4) devices allows an attacker with physical access to install compromised firmware. This occurs because of insufficient validation of the firmware image file and can lead to code execution on the device. |
2021-05-20 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-24395
MISC
MISC |
homee — brain_cube
|
homee Brain Cube v2 (2.28.2 and 2.28.4) devices have sensitive SSH keys within downloadable and unencrypted firmware images. This allows remote attackers to use the support server as a SOCKS proxy. |
2021-05-20 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-24396
MISC
MISC |
hongcms — hongcms
|
Path Traversal in HongCMS v4.0.0 allows remote attackers to view, edit, and delete arbitrary files via a crafted POST request to the component “/hcms/admin/index.php/language/ajax.” |
2021-05-18 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-18178
MISC |
htmly — htmly
|
An arbitrary file deletion vulnerability was discovered on htmly v2.7.5 which allows remote attackers to use any absolute path to delete any file in the server should they gain Administrator privileges. |
2021-05-21 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-23766
MISC |
ibm — cloud_pak
|
IBM Cloud Pak for Multicloud Management prior to 2.3 allows web pages to be stored locally which can be read by another user on the system. IBM X-Force ID: 188902. |
2021-05-19 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-4765
CONFIRM
XF |
| ibm — control_center |
IBM Control Center 6.2.0.0 is vulnerable to cross-site scripting. This vulnerability allows users to embed arbitrary JavaScript code in the Web UI thus altering the intended functionality potentially leading to credentials disclosure within a trusted session. IBM X-Force ID: 198761. |
2021-05-19 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-20528
XF
CONFIRM |
ibm — control_center
|
IBM Control Center 6.2.0.0 could allow a user to obtain sensitive version information that could be used in further attacks against the system. IBM X-Force ID: 198763. |
2021-05-19 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-20529
XF
CONFIRM |
| ibm — infosphere_information_server |
IBM InfoSphere Information Server 11.7 could allow a remote attacker to obtain highly sensitive information due to a vulnerability in the authentication mechanism. IBM X-Force ID: 201775. |
2021-05-17 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-29747
CONFIRM
XF |
ibm — infosphere_information_server
|
IBM InfoSphere Information Server 11.7 could allow an attacker to obtain sensitive information by injecting parameters into an HTML query. This information could be used in further attacks against the system. IBM X-Force ID: 199918. |
2021-05-21 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-29681
XF
CONFIRM |
ibm — maximo_asset_manager
|
IBM Maximo Asset Management 7.6.0 and 7.6.1 is vulnerable to stored cross-site scripting. This vulnerability allows users to embed arbitrary JavaScript code in the Web UI thus altering the intended functionality potentially leading to credentials disclosure within a trusted session. IBM X-Force ID: 195522. |
2021-05-19 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-20374
CONFIRM
XF |
ibm — planning_analytics_local
|
IBM Planning Analytics Local 2.0 connects to a MongoDB server. MongoDB, a document-oriented database system, is listening on the remote port, and it is configured to allow connections without password authentication. A remote attacker can gain unauthorized access to the database. IBM X-Force ID: 184600. |
2021-05-17 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-4669
CONFIRM
XF |
ibm — planning_analytics_local
|
IBM Planning Analytics Local 2.0 connects to a Redis server. The Redis server, an in-memory data structure store, running on the remote host is not protected by password authentication. A remote attacker can exploit this to gain unauthorized access to the server. IBM X-Force ID: 186401. |
2021-05-17 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-4670
CONFIRM
XF |
| ibm — security_identity_manager |
IBM Security Identity Manager 7.0.2 could allow a remote attacker to obtain sensitive information when a detailed technical error message is returned in the browser. This information could be used in further attacks against the system. IBM X-Force ID: 200102. |
2021-05-20 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-29688
XF
CONFIRM
CONFIRM |
| ibm — security_identity_manager |
IBM Security Identity Manager 7.0.2 could allow a remote attacker to obtain sensitive information, caused by the failure to properly enable HTTP Strict Transport Security. An attacker could exploit this vulnerability to obtain sensitive information using man in the middle techniques. IBM X-Force ID: 200253. |
2021-05-20 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-29692
XF
CONFIRM |
ibm — security_identity_manager
|
IBM Security Identity Manager 7.0.2 could allow an authenticated user to bypass security and perform actions that they should not have access to. IBM X-Force ID: 200015 |
2021-05-20 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-29686
XF
CONFIRM |
ibm — security_identity_manager
|
IBM Security Identity Manager 7.0.2 contains hard-coded credentials, such as a password or cryptographic key, which it uses for its own inbound authentication, outbound communication to external components, or encryption of internal data. IBM X-Force ID: 200252. |
2021-05-20 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-29691
XF
CONFIRM |
ibm — security_identity_manager
|
IBM Security Identity Manager 7.0.2 could allow a remote user to enumerate usernames due to a difference of responses from valid and invalid login attempts. IBM X-Force ID: 200018 |
2021-05-20 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-29687
CONFIRM
XF |
ibm — security_identity_manager
|
IBM Security Identity Manager 7.0.2 could allow a remote attacker to obtain sensitive information when a detailed technical error message is returned in the browser. This information could be used in further attacks against the system. IBM X-Force ID: 199997 |
2021-05-20 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-29682
CONFIRM
XF |
ibm — security_identity_manager
|
IBM Security Identity Manager 7.0.2 stores user credentials in plain clear text which can be read by an authenticated user. IBM X-Force ID: 199998. |
2021-05-20 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-29683
CONFIRM
XF |
ibm — spetrum_scale
|
IBM Spectrum Scale 1.1.1.0 through 1.1.8.4 Transparent Cloud Tiering could allow a remote attacker to obtain sensitive information, caused by the leftover files after configuration. IBM X-Force ID: 190298. |
2021-05-20 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-4850
XF
CONFIRM |
ibm — sterling_b2b_integrator_standard+edition
|
IBM Sterling B2B Integrator Standard Edition 5.2.0.0 through 5.2.6.5, 6.0.0.0 through 6.0.3.3, and 6.1.0.0 through 6.1.0.2 could allow an authenticated user to view pages they shoiuld not have access to due to improper authorization control. |
2021-05-19 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-4646
XF
CONFIRM |
| intelbras — router_rf_301k_firmware |
Intelbras Router RF 301K Firmware 1.1.2 is vulnerable to Cross Site Request Forgery (CSRF) due to lack of security mechanisms for token protection and unsafe inputs and modules. |
2021-05-17 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-32403
MISC |
intelbras — router_rf_301k_firmware
|
Intelbras Router RF 301K Firmware 1.1.2 is vulnerable to Cross Site Request Forgery (CSRF) due to lack of validation and insecure configurations in inputs and modules. |
2021-05-17 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-32402
MISC |
invoiceplane — invoiceplane
|
InvoicePlane 1.5.11 doesn’t have any rate-limiting for password reset and the reset token is generated using a weak mechanism that is predictable. |
2021-05-17 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-29023
MISC |
invoiceplane — invoiceplane
|
In InvoicePlane 1.5.11 a misconfigured web server allows unauthenticated directory listing and file download. Allowing an attacker to directory traversal and download files suppose to be private without authentication. |
2021-05-17 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-29024
MISC |
koa-remove-trailing-slashes — koa-remove-trailing-slashes
|
The package koa-remove-trailing-slashes before 2.0.2 are vulnerable to Open Redirect via the use of trailing double slashes in the URL when accessing the vulnerable endpoint (such as https://example.com//attacker.example/). The vulnerable code is in index.js::removeTrailingSlashes(), as the web server uses relative URLs instead of absolute URLs. |
2021-05-17 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-23384
MISC
MISC |
konawiki2 — konawiki2
|
SQL injection vulnerability in the KonaWiki2 versions prior to 2.2.4 allows remote attackers to execute arbitrary SQL commands and to obtain/alter the information stored in the database via unspecified vectors. |
2021-05-20 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-20720
MISC
MISC |
konawiki2 — konawiki2
|
KonaWiki2 versions prior to 2.2.4 allows a remote attacker to upload arbitrary files via unspecified vectors. If the file contains PHP scripts, arbitrary code may be executed. |
2021-05-20 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-20721
MISC
MISC |
libdnf — libdnf
|
A flaw was found in libdnf’s signature verification functionality in versions before 0.60.1. This flaw allows an attacker to achieve code execution if they can alter the header information of an RPM package and then trick a user or system into installing it. The highest risk of this vulnerability is to confidentiality, integrity, as well as system availability. |
2021-05-19 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-3445
FEDORA
MISC
FEDORA |
libredwg — libredwg
|
A heap-based buffer overflow vulnerability exists in LibreDWG 0.10.1 via the read_system_page function at libredwg-0.10.1/src/decode_r2007.c:666:5, which causes a denial of service by submitting a dwg file. |
2021-05-18 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-23861
MISC |
libsolv — libsolv
|
Buffer overflow vulnerability in libsolv 2020-12-13 via the Solver * testcase_read(Pool *pool, FILE *fp, const char *testcase, Queue *job, char **resultp, int *resultflagsp function at src/testcase.c: line 2334, which could cause a denial of service |
2021-05-18 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-3200
MISC
MISC |
libwebp — applyfilter
|
A flaw was found in libwebp in versions before 1.0.1. An out-of-bounds read was found in function ApplyFilter. The highest threat from this vulnerability is to data confidentiality and to the service availability. |
2021-05-21 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2018-25010
MISC |
| libwebp — libwebp |
A flaw was found in libwebp in versions before 1.0.1. A use-after-free was found due to a thread being killed too early. The highest threat from this vulnerability is to data confidentiality and integrity as well as system availability. |
2021-05-21 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-36329
MISC |
libwebp — libwebp
|
A flaw was found in libwebp in versions before 1.0.1. A heap-based buffer overflow in function WebPDecodeRGBInto is possible due to an invalid check for buffer size. The highest threat from this vulnerability is to data confidentiality and integrity as well as system availability. |
2021-05-21 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-36328
MISC |
libwebp — libwebp
|
A flaw was found in libwebp in versions before 1.0.1. An out-of-bounds read was found in function ChunkAssignData. The highest threat from this vulnerability is to data confidentiality and to the service availability. |
2021-05-21 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-36331
MISC |
libwebp — libwebp
|
A flaw was found in libwebp in versions before 1.0.1. An out-of-bounds read was found in function ChunkVerifyAndAssign. The highest threat from this vulnerability is to data confidentiality and to the service availability. |
2021-05-21 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-36330
MISC |
libwebp — libwebp
|
A flaw was found in libwebp in versions before 1.0.1. When reading a file libwebp allocates an excessive amount of memory. The highest threat from this vulnerability is to the service availability. |
2021-05-21 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-36332
MISC |
libwebp — putle16
|
A flaw was found in libwebp in versions before 1.0.1. A heap-based buffer overflow was found in PutLE16(). The highest threat from this vulnerability is to data confidentiality and integrity as well as system availability. |
2021-05-21 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2018-25011
MISC |
libwebp — webpmuxcreateinternal
|
A flaw was found in libwebp in versions before 1.0.1. An out-of-bounds read was found in function WebPMuxCreateInternal. The highest threat from this vulnerability is to data confidentiality and to the service availability. |
2021-05-21 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2018-25009
MISC |
libwebp — webpmuxcreateinternal
|
A flaw was found in libwebp in versions before 1.0.1. An out-of-bounds read was found in function WebPMuxCreateInternal. The highest threat from this vulnerability is to data confidentiality and to the service availability. |
2021-05-21 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2018-25012
MISC |
libwebp — readsymbol
|
A flaw was found in libwebp in versions before 1.0.1. An unitialized variable is used in function ReadSymbol. The highest threat from this vulnerability is to data confidentiality and integrity as well as system availability. |
2021-05-21 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2018-25014
MISC |
libwebp — shiftbytes
|
A flaw was found in libwebp in versions before 1.0.1. An out-of-bounds read was found in function ShiftBytes. The highest threat from this vulnerability is to data confidentiality and to the service availability. |
2021-05-21 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2018-25013
MISC |
| libxml2 — libxml2 |
There’s a flaw in libxml2 in versions before 2.9.11. An attacker who is able to submit a crafted file to be processed by an application linked with libxml2 could trigger a use-after-free. The greatest impact from this flaw is to confidentiality, integrity, and availability. |
2021-05-18 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-3518
FEDORA
MLIST
MISC |
libxml2 — libxml2
|
There is a flaw in the xml entity encoding functionality of libxml2 in versions before 2.9.11. An attacker who is able to supply a crafted file to be processed by an application linked with the affected functionality of libxml2 could trigger an out-of-bounds read. The most likely impact of this flaw is to application availability, with some potential impact to confidentiality and integrity if an attacker is able to use memory information to further exploit the application. |
2021-05-19 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-3517
MISC
FEDORA
MLIST |
libyang — libyang
|
In function read_yin_leaf() in libyang <= v1.0.225, it doesn’t check whether the value of retval->ext[r] is NULL. In some cases, it can be NULL, which leads to the operation of retval->ext[r]->flags that results in a crash. |
2021-05-20 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-28906
CONFIRM |
libyang — libyang
|
In function read_yin_container() in libyang <= v1.0.225, it doesn’t check whether the value of retval->ext[r] is NULL. In some cases, it can be NULL, which leads to the operation of retval->ext[r]->flags that results in a crash. |
2021-05-20 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-28902
CONFIRM |
libyang — libyang
|
A stack overflow in libyang <= v1.0.225 can cause a denial of service through function lyxml_parse_mem(). lyxml_parse_elem() function will be called recursively, which will consume stack space and lead to crash. |
2021-05-20 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-28903
CONFIRM |
libyang — libyang
|
In function ext_get_plugin() in libyang <= v1.0.225, it doesn’t check whether the value of revision is NULL. If revision is NULL, the operation of strcmp(revision, ext_plugins[u].revision) will lead to a crash. |
2021-05-20 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-28904
CONFIRM |
libyang — libyang
|
In function lys_node_free() in libyang <= v1.0.225, it asserts that the value of node->module can’t be NULL. But in some cases, node->module can be null, which triggers a reachable assertion (CWE-617). |
2021-05-20 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-28905
CONFIRM |
| liferay — portal |
Cross-site scripting (XSS) vulnerability in the Redirect module’s redirection administration page in Liferay Portal 7.3.2 through 7.3.5, and Liferay DXP 7.3 before fix pack 1 allows remote attackers to inject arbitrary web script or HTML via the _com_liferay_redirect_web_internal_portlet_RedirectPortlet_destinationURL parameter. |
2021-05-17 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-29045
MISC
MISC |
| liferay — portal |
The JSON web services in Liferay Portal 7.3.4 and earlier, and Liferay DXP 7.0 before fix pack 97, 7.1 before fix pack 20 and 7.2 before fix pack 10 may provide overly verbose error messages, which allows remote attackers to use the contents of error messages to help launch another, more focused attacks via crafted inputs. |
2021-05-16 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-29040
MISC
MISC |
| liferay — portal |
The SimpleCaptcha implementation in Liferay Portal 7.3.4, 7.3.5 and Liferay DXP 7.3 before fix pack 1 does not invalidate CAPTCHA answers after it is used, which allows remote attackers to repeatedly perform actions protected by a CAPTCHA challenge by reusing the same CAPTCHA answer. |
2021-05-16 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-29047
MISC
MISC |
| liferay — portal |
Cross-site scripting (XSS) vulnerability in the Site module’s membership request administration pages in Liferay Portal 7.0.0 through 7.3.5, and Liferay DXP 7.0 before fix pack 97, 7.1 before fix pack 21, 7.2 before fix pack 10 and 7.3 before fix pack 1 allows remote attackers to inject arbitrary web script or HTML via the _com_liferay_site_my_sites_web_portlet_MySitesPortlet_comments parameter. |
2021-05-17 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-29044
MISC
MISC |
liferay — portal
|
Denial-of-service (DoS) vulnerability in the Multi-Factor Authentication module in Liferay DXP 7.3 before fix pack 1 allows remote authenticated attackers to prevent any user from authenticating by (1) enabling Time-based One-time password (TOTP) on behalf of the other user or (2) modifying the other user’s TOTP shared secret. |
2021-05-16 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-29041
MISC
MISC |
liferay — portal
|
Cross-site scripting (XSS) vulnerability in the Layout module’s page administration page in Liferay Portal 7.3.4, 7.3.5 and Liferay DXP 7.2 before fix pack 11 and 7.3 before fix pack 1 allows remote attackers to inject arbitrary web script or HTML via the _com_liferay_layout_admin_web_portlet_GroupPagesPortlet_name parameter. |
2021-05-17 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-29048
MISC
MISC |
liferay — portal
|
The Portal Store module in Liferay Portal 7.0.0 through 7.3.5, and Liferay DXP 7.0 before fix pack 97, 7.1 before fix pack 21, 7.2 before fix pack 10 and 7.3 before fix pack 1 does not obfuscate the S3 store’s proxy password, which allows attackers to steal the proxy password via man-in-the-middle attacks or shoulder surfing. |
2021-05-17 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-29043
MISC
MISC |
liferay — portal
|
Multiple SQL injection vulnerabilities in Liferay Portal 7.3.5 and Liferay DXP 7.3 before fix pack 1 allow remote authenticated users to execute arbitrary SQL commands via the classPKField parameter to (1) CommerceChannelRelFinder.countByC_C, or (2) CommerceChannelRelFinder.findByC_C. |
2021-05-17 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-29053
MISC
MISC |
liferay — portal
|
Cross-site scripting (XSS) vulnerability in the Asset module’s categories administration page in Liferay Portal 7.3.4 allows remote attackers to inject arbitrary web script or HTML via the site name. |
2021-05-16 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-29039
MISC
MISC |
liferay — portal
|
Cross-site scripting (XSS) vulnerability in the Asset module’s Asset Publisher app in Liferay Portal 7.2.1 through 7.3.5, and Liferay DXP 7.1 before fix pack 21, 7.2 before fix pack 10 and 7.3 before fix pack 1 allows remote attackers to inject arbitrary web script or HTML via the _com_liferay_asset_publisher_web_portlet_AssetPublisherPortlet_INSTANCE_XXXXXXXXXXXX_assetEntryId parameter. |
2021-05-17 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-29051
MISC
MISC |
liferay — portal
|
The Data Engine module in Liferay Portal 7.3.0 through 7.3.5, and Liferay DXP 7.3 before fix pack 1 does not check permissions in DataDefinitionResourceImpl.getSiteDataDefinitionByContentTypeByDataDefinitionKey, which allows remote authenticated users to view DDMStructures via GET API calls. |
2021-05-17 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-29052
MISC
MISC |
liferay — portal
|
Cross-site scripting (XSS) vulnerability in the Asset module’s category selector input field in Liferay Portal 7.3.5 and Liferay DXP 7.3 before fix pack 1, allows remote attackers to inject arbitrary web script or HTML via the _com_liferay_asset_categories_admin_web_portlet_AssetCategoriesAdminPortlet_title parameter. |
2021-05-17 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-29046
MISC
MISC |
linux — linux_kernel
|
This vulnerability allows local attackers to escalate privileges on affected installations of Linux Kernel 5.11.15. An attacker must first obtain the ability to execute low-privileged code on the target system in order to exploit this vulnerability. The specific flaw exists within the handling of eBPF programs. The issue results from the lack of proper validation of user-supplied eBPF programs prior to executing them. An attacker can leverage this vulnerability to escalate privileges and execute arbitrary code in the context of the kernel. Was ZDI-CAN-13661. |
2021-05-21 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-31440
MISC
MISC |
linux — linux_kernel
|
TCP firewalls could be circumvented by sending a SYN Packets with other flags (like e.g. RST flag) set, which was not correctly discarded by the Linux TCP stack after firewalling. |
2021-05-18 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2002-2438
MLIST
CERT-VN
MLIST
MISC
MLIST
MLIST
MLIST
MISC
MLIST
MLIST
MLIST
MISC
MLIST
MLIST
MLIST |
linux — linux_kernel
|
A flaw was found in the Nosy driver in the Linux kernel. This issue allows a device to be inserted twice into a doubly-linked list, leading to a use-after-free when one of these devices is removed. The highest threat from this vulnerability is to confidentiality, integrity, as well as system availability. Versions before kernel 5.12-rc6 are affected |
2021-05-17 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-3483
MLIST
MISC |
linux_kernel — linux_kernel
|
The Linux kernel before 5.11.14 has a use-after-free in cipso_v4_genopt in net/ipv4/cipso_ipv4.c because the CIPSO and CALIPSO refcounting for the DOI definitions is mishandled, aka CID-ad5d07f4a9cd. This leads to writing an arbitrary value. |
2021-05-14 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-33033
MISC
MISC
MISC
MISC
MISC
MISC |
linux_kernel — linux_kernel
|
In the Linux kernel before 5.12.4, net/bluetooth/hci_event.c has a use-after-free when destroying an hci_chan, aka CID-5c4c8c954409. This leads to writing an arbitrary value. |
2021-05-14 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-33034
MISC
MISC
MISC
MISC
FEDORA |
| manageone — manageone |
There is a denial of service vulnerability in some versions of ManageOne. There is a logic error in the implementation of a function of a module. When the service pressure is heavy, there is a low probability that an exception may occur. Successful exploit may cause some services abnormal. |
2021-05-20 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-22409
MISC |
manageone — manageone
|
There is a denial of service vulnerability in some versions of ManageOne. In specific scenarios, due to the insufficient verification of the parameter, an attacker may craft some specific parameter. Successful exploit may cause some services abnormal. |
2021-05-20 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-22339
MISC |
matrix-react-sdk — matrix-react-sdk
|
Matrix-React-SDK is a react-based SDK for inserting a Matrix chat/voip client into a web page. Before version 3.21.0, when uploading a file, the local file preview can lead to execution of scripts embedded in the uploaded file. This can only occur after several user interactions to open the preview in a separate tab. This only impacts the local user while in the process of uploading. It cannot be exploited remotely or by other users. This vulnerability is patched in version 3.21.0. |
2021-05-17 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-32622
MISC
CONFIRM |
micro-ecc — library
|
The ECDSA operation of the micro-ecc library 1.0 is vulnerable to simple power analysis attacks which allows an adversary to extract the private ECC key. |
2021-05-20 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-27209
MISC
MISC
MISC
MISC |
mikrotik — routeros
|
Mikrotik RouterOs before 6.47 (stable tree) in the /ram/pckg/advanced-tools/nova/bin/netwatch process. An authenticated remote attacker can cause a Denial of Service due to a divide by zero error. |
2021-05-19 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-20264
MISC
MISC |
mikrotik — routeros
|
Mikrotik RouterOs before 6.47 (stable tree) suffers from a memory corruption vulnerability in the /nova/bin/lcdstat process. An authenticated remote attacker can cause a Denial of Service (NULL pointer dereference). |
2021-05-18 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-20254
MISC
FULLDISC |
mikrotik — routeros
|
Mikrotik RouterOs before 6.47 (stable tree) suffers from a memory corruption vulnerability in the /nova/bin/dot1x process. An authenticated remote attacker can cause a Denial of Service (NULL pointer dereference). |
2021-05-19 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-20266
MISC
MISC |
mikrotik — routeros
|
Mikrotik RouterOs before 6.47 (stable tree) suffers from a divison by zero vulnerability in the /nova/bin/lcdstat process. An authenticated remote attacker can cause a Denial of Service due to a divide by zero error. |
2021-05-18 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-20253
MISC
FULLDISC |
mitsubishielectric — multiple_products
|
Buffer access with incorrect length value vulnerability in GOT2000 series GT27 model communication driver versions 01.19.000 through 01.38.000, GT25 model communication driver versions 01.19.000 through 01.38.000, GT23 model communication driver versions 01.19.000 through 01.38.000 and GT21 model communication driver versions 01.21.000 through 01.39.000, GOT SIMPLE series GS21 model communication driver versions 01.21.000 through 01.39.000, GT SoftGOT2000 versions 1.170C through 1.250L and Tension Controller LE7-40GU-L Screen package data for MODBUS/TCP V1.00 allows a remote unauthenticated attacker to stop the communication function of the products via specially crafted packets. |
2021-05-19 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-20589
MISC
MISC |
moodle — mushtache
|
A vulnerability was found in Moodle where javaScript injection was possible in some Mustache templates via recursive rendering from contexts. Mustache helper tags that were included in template contexts were not being escaped before that context was injected into another Mustache helper, which could result in script injection in some templates. This affects versions 3.7 to 3.7.1, 3.6 to 3.6.5, 3.5 to 3.5.7 and earlier unsupported versions. |
2021-05-17 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2019-14827
MISC
MISC |
mozilla — firefox
|
A flaw in Mozilla’s embedded certificate code might allow web sites to install root certificates on devices without user approval. |
2021-05-17 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2007-5967
MISC |
mpv — mpv
|
A format string vulnerability in mpv through 0.33.0 allows user-assisted remote attackers to achieve code execution via a crafted m3u playlist file. |
2021-05-18 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-30145
MISC
MISC
MISC
MISC |
netgear — multiple_devices
|
Certain NETGEAR devices are affected by command injection by an unauthenticated attacker via the vulnerable /sqfs/lib/libsal.so.0.0 library used by a CGI application, as demonstrated by setup.cgi?token=’;$HTTP_USER_AGENT;’ with an OS command in the User-Agent field. This affects GC108P before 1.0.7.3, GC108PP before 1.0.7.3, GS108Tv3 before 7.0.6.3, GS110TPPv1 before 7.0.6.3, GS110TPv3 before 7.0.6.3, GS110TUPv1 before 1.0.4.3, GS710TUPv1 before 1.0.4.3, GS716TP before 1.0.2.3, GS716TPP before 1.0.2.3, GS724TPPv1 before 2.0.4.3, GS724TPv2 before 2.0.4.3, GS728TPPv2 before 6.0.6.3, GS728TPv2 before 6.0.6.3, GS752TPPv1 before 6.0.6.3, GS752TPv2 before 6.0.6.3, MS510TXM before 1.0.2.3, and MS510TXUP before 1.0.2.3. |
2021-05-21 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-33514
MISC
MISC |
nitrokey — fido2
|
The flash read-out protection (RDP) level is not enforced during the device initialization phase of the SoloKeys Solo 4.0.0 & Somu and the Nitrokey FIDO2 token. This allows an adversary to downgrade the RDP level and access secrets such as private ECC keys from SRAM via the debug interface. |
2021-05-21 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-27208
MISC
MISC
MISC
MISC
MISC |
nitrokey — fido_u2f
|
An issue was discovered in Nitrokey FIDO U2F firmware through 1.1. Communication between the microcontroller and the secure element transmits credentials in plain. This allows an adversary to eavesdrop the communication and derive the secrets stored in the microcontroller. As a result, the attacker is able to arbitrarily manipulate the firmware of the microcontroller. |
2021-05-21 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-12061
MISC
MISC
MISC |
nordic — semiconductor_nrf52840_devices
|
Nordic Semiconductor nRF52840 devices through 2020-10-19 have improper protection against physical side channels. The flash read-out protection (APPROTECT) can be bypassed by injecting a fault during the boot phase. |
2021-05-21 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-27211
MISC
MISC
MISC
MISC |
opc_foundation — opc_foundation
|
Products with Unified Automation .NET based OPC UA Client/Server SDK Bundle: Versions V3.0.7 and prior (.NET 4.5, 4.0, and 3.5 Framework versions only) are vulnerable to an uncontrolled recursion, which may allow an attacker to trigger a stack overflow. |
2021-05-20 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-27434
MISC |
opc_foundation — opc_foundation
|
OPC Foundation UA .NET Standard versions prior to 1.4.365.48 and OPC UA .NET Legacy are vulnerable to an uncontrolled recursion, which may allow an attacker to trigger a stack overflow. |
2021-05-20 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-27432
MISC |
openid — providers
|
It was found that various OpenID Providers (OPs) had TLS Server Certificates that used weak keys, as a result of the Debian Predictable Random Number Generator (CVE-2008-0166). In combination with the DNS Cache Poisoning issue (CVE-2008-1447) and the fact that almost all SSL/TLS implementations do not consult CRLs (currently an untracked issue), this means that it is impossible to rely on these OPs. |
2021-05-21 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2008-3280
MISC
MISC |
openldap — openldap
|
A flaw was found in OpenLDAP. This flaw allows an attacker who can send a malicious packet to be processed by OpenLDAP’s slapd server, to trigger an assertion failure. The highest threat from this vulnerability is to system availability. |
2021-05-18 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-25709
MLIST
DEBIAN
MISC
FULLDISC
CONFIRM |
| opennms — horizon |
In OpenNMS Horizon, versions opennms-1-0-stable through opennms-27.1.0-1; OpenNMS Meridian, versions meridian-foundation-2015.1.0-1 through meridian-foundation-2019.1.18-1; meridian-foundation-2020.1.0-1 through meridian-foundation-2020.1.6-1 are vulnerable to Stored Cross-Site Scripting, since the function `validateFormInput()` performs improper validation checks on the input sent to the `groupName` and `groupComment` parameters. Due to this flaw, an authenticated attacker could inject arbitrary script and trick other admin users into downloading malicious files which can cause severe damage to the organization using opennms. |
2021-05-20 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-25933
MISC
MISC
MISC
MISC |
opennms — horizon
|
In OpenNMS Horizon, versions opennms-1-0-stable through opennms-27.1.0-1; OpenNMS Meridian, versions meridian-foundation-2015.1.0-1 through meridian-foundation-2019.1.18-1; meridian-foundation-2020.1.0-1 through meridian-foundation-2020.1.6-1 are vulnerable to CSRF, due to no CSRF protection, and since there is no validation of an existing user name while renaming a user. As a result, privileges of the renamed user are being overwritten by the old user and the old user is being deleted from the user list. |
2021-05-20 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-25930
MISC
MISC
MISC |
opennms — horizon
|
In OpenNMS Horizon, versions opennms-1-0-stable through opennms-27.1.0-1; OpenNMS Meridian, versions meridian-foundation-2015.1.0-1 through meridian-foundation-2019.1.18-1; meridian-foundation-2020.1.0-1 through meridian-foundation-2020.1.6-1 are vulnerable to CSRF, due to no CSRF protection at `/opennms/admin/userGroupView/users/updateUser`. This flaw allows assigning `ROLE_ADMIN` security role to a normal user. Using this flaw, an attacker can trick the admin user to assign administrator privileges to a normal user by enticing him to click upon an attacker-controlled website. |
2021-05-20 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-25931
MISC
MISC
MISC |
opennms — horizon
|
In OpenNMS Horizon, versions opennms-1-0-stable through opennms-27.1.0-1; OpenNMS Meridian, versions meridian-foundation-2015.1.0-1 through meridian-foundation-2019.1.18-1; meridian-foundation-2020.1.0-1 through meridian-foundation-2020.1.6-1 are vulnerable to Stored Cross-Site Scripting since there is no validation on the input being sent to the `name` parameter in `noticeWizard` endpoint. Due to this flaw an authenticated attacker could inject arbitrary script and trick other admin users into downloading malicious files. |
2021-05-20 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-25929
MISC
MISC
MISC |
owncloud — owncloud
|
ownCloud 10.7 has an incorrect access control vulnerability, leading to remote information disclosure. Due to a bug in the related API endpoint, the attacker can enumerate all users in a single request by entering three whitespaces. Secondary, the retrieval of all users on a large instance could cause higher than average load on the instance. |
2021-05-20 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-29659
MISC
MISC |
pajbot — pajbot
|
Pajbot is a Twitch chat bot. Pajbot versions prior to 1.52 are vulnerable to cross-site request forgery (CSRF). Hosters of the bot should upgrade to `v1.52` or `stable` to install the patch or, as a workaround, can add one modern dependency. |
2021-05-20 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-32632
MISC
MISC
CONFIRM |
phppyun– phppyun
|
An information disclosure vulnerability was discovered in alipay_function.php in the log file of Alibaba payment interface on PHPPYUN prior to version 5.0.1. If exploited, this vulnerability will allow attackers to obtain users’ personally identifiable information including e-mail address and telephone numbers. |
2021-05-21 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-23768
MISC |
plone — plone
|
Plone through 5.2.4 allows XSS via a full name that is mishandled during rendering of the ownership tab of a content item. |
2021-05-21 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-33508
MISC
MLIST |
plone — plone
|
Plone through 5.2.4 allows stored XSS attacks (by a Contributor) by uploading an SVG or HTML document. |
2021-05-21 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-33512
MISC
MLIST |
plone — plone
|
Plone though 5.2.4 allows SSRF via the lxml parser. This affects Diazo themes, Dexterity TTW schemas, and modeleditors in plone.app.theming, plone.app.dexterity, and plone.supermodel. |
2021-05-21 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-33511
MISC
MLIST |
plone — plone
|
Plone through 5.2.4 allows remote authenticated managers to conduct SSRF attacks via an event ical URL, to read one line of a file. |
2021-05-21 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-33510
MISC
MLIST |
plone — plone
|
Plone through 5.2.4 allows remote authenticated managers to perform disk I/O via crafted keyword arguments to the ReStructuredText transform in a Python script. |
2021-05-21 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-33509
MISC
MLIST |
plone — plone
|
Plone through 5.2.4 allows XSS via the inline_diff methods in Products.CMFDiffTool. |
2021-05-21 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-33513
MISC
MLIST |
plone_cms — plone_cms
|
Plone CMS until version 5.2.4 has a stored Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) vulnerability in the user fullname property and the file upload functionality. The user’s input data is not properly encoded when being echoed back to the user. This data can be interpreted as executable code by the browser and allows an attacker to execute JavaScript in the context of the victim’s browser if the victim opens a vulnerable page containing an XSS payload. |
2021-05-20 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-3313
MISC
MISC
MISC
MLIST |
| pluck — pluck |
In Pluck-4.7.10-dev2 admin background, a remote command execution vulnerability exists when uploading files. |
2021-05-18 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-20951
MISC |
| pluck — pluck |
Cross Site Request Forgery (CSRF) in Pluck CMS v4.7.9 allows remote attackers to execute arbitrary code and delete specific images via the component ” /admin.php?action=images.” |
2021-05-17 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-18198
MISC |
pluck — pluck
|
An issue was discovered in Pluck 4.7.10-dev2. There is a CSRF vulnerability that can editpage via a /admin.php?action=editpage |
2021-05-18 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-24740
MISC |
pluck — pluck
|
Cross Site Request Forgery (CSRF) in Pluck CMS v4.7.9 allows remote attackers to execute arbitrary code and delete a specific article via the component ” /admin.php?action=page.” |
2021-05-17 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-18195
MISC |
postgresql — postgresql
|
In the pg_partman (aka PG Partition Manager) extension before 4.5.1 for PostgreSQL, arbitrary code execution can be achieved via SECURITY DEFINER functions because an explicit search_path is not set. |
2021-05-19 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-33204
MISC
MISC |
progress — moveit_transfer
|
In Progress MOVEit Transfer before 2021.0 (13.0), a SQL injection vulnerability has been found in the MOVEit Transfer web app that could allow an authenticated attacker to gain unauthorized access to MOVEit Transfer’s database. Depending on the database engine being used (MySQL, Microsoft SQL Server, or Azure SQL), an attacker may be able to infer information about the structure and contents of the database in addition to executing SQL statements that alter or destroy database elements. This is in MOVEit.DMZ.WebApp in SILHuman.vb. |
2021-05-18 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-31827
MISC
MISC
MISC |
project_worlds — online_examination_system
|
XSS in signup form in Project Worlds Online Examination System 1.0 allows remote attacker to inject arbitrary code via the name field |
2021-05-17 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-29205
MISC
MISC |
prometheus — prometheus
|
Prometheus is an open-source monitoring system and time series database. In 2.23.0, Prometheus changed its default UI to the New ui. To ensure a seamless transition, the URL’s prefixed by /new redirect to /. Due to a bug in the code, it is possible for an attacker to craft an URL that can redirect to any other URL, in the /new endpoint. If a user visits a prometheus server with a specially crafted address, they can be redirected to an arbitrary URL. The issue was patched in the 2.26.1 and 2.27.1 releases. In 2.28.0, the /new endpoint will be removed completely. The workaround is to disable access to /new via a reverse proxy in front of Prometheus. |
2021-05-19 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-29622
CONFIRM
MISC
MISC |
putty — putty
|
PuTTY before 0.75 on Windows allows remote servers to cause a denial of service (Windows GUI hang) by telling the PuTTY window to change its title repeatedly at high speed, which results in many SetWindowTextA or SetWindowTextW calls. NOTE: the same attack methodology may affect some OS-level GUIs on Linux or other platforms for similar reasons. |
2021-05-21 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-33500
MISC
MISC
MISC |
python — python
|
There’s a flaw in Python 3’s pydoc. A local or adjacent attacker who discovers or is able to convince another local or adjacent user to start a pydoc server could access the server and use it to disclose sensitive information belonging to the other user that they would not normally be able to access. The highest risk of this flaw is to data confidentiality. This flaw affects Python versions before 3.8.9, Python versions before 3.9.3 and Python versions before 3.10.0a7. |
2021-05-20 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-3426
FEDORA
FEDORA
FEDORA
MLIST
FEDORA
FEDORA
MISC
FEDORA
GENTOO
FEDORA |
qibosoftx1 — qibosoftx1
|
A code injection vulnerability has been discovered in the Upgrade function of QibosoftX1 v1.0. An attacker is able execute arbitrary PHP code via exploitation of client_upgrade_edition.php and Upgrade.php. |
2021-05-21 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-27811
MISC
MISC |
qnap — nas
|
A relative path traversal vulnerability has been reported to affect QNAP NAS running QTS and QuTS hero. If exploited, this vulnerability allows attackers to modify files that impact system integrity. QNAP have already fixed this vulnerability in the following versions: QTS 4.5.2.1630 Build 20210406 and later QTS 4.3.6.1663 Build 20210504 and later QTS 4.3.3.1624 Build 20210416 and later QuTS hero h4.5.2.1638 Build 20210414 and later QNAP NAS running QTS 4.5.3 are not affected. |
2021-05-21 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-28798
CONFIRM |
rabbitmq — rabbitmq
|
RabbitMQ installers on Windows prior to version 3.8.16 do not harden plugin directory permissions, potentially allowing attackers with sufficient local filesystem permissions to add arbitrary plugins. |
2021-05-18 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-22117
MISC |
rageframe2 — rageframe2
|
TinyShop, a free and open source mall based on RageFrame2, has a stored XSS vulnerability that affects version 1.2.0. TinyShop allows XSS via the explain_first and again_explain parameters of the /evaluate/index.php page. The vulnerability may be exploited remotely, resulting in cross-site scripting (XSS) or information disclosure. |
2021-05-18 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-24026
MISC
MISC
MISC |
red_hat — red_hat
|
A flaw was found in the Red Hat Ceph Storage RadosGW (Ceph Object Gateway) in versions before 14.2.21. The vulnerability is related to the injection of HTTP headers via a CORS ExposeHeader tag. The newline character in the ExposeHeader tag in the CORS configuration file generates a header injection in the response when the CORS request is made. In addition, the prior bug fix for CVE-2020-10753 did not account for the use of r as a header separator, thus a new flaw has been created. |
2021-05-17 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-3524
MISC
FEDORA
FEDORA
FEDORA |
red_hat — red_hat
|
A flaw was found in the Red Hat Ceph Storage RGW in versions before 14.2.21. When processing a GET Request for a swift URL that ends with two slashes it can cause the rgw to crash, resulting in a denial of service. The greatest threat to the system is of availability. |
2021-05-18 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-3531
MISC
MLIST
MLIST
FEDORA
FEDORA
FEDORA |
red_hat — red_hat
|
A Zip Slip vulnerability was found in the oc binary in openshift-clients where an arbitrary file write is achieved by using a specially crafted raw container image (.tar file) which contains symbolic links. The vulnerability is limited to the command `oc image extract`. If a symbolic link is first created pointing within the tarball, this allows further symbolic links to bypass the existing path check. This flaw allows the tarball to create links outside the tarball’s parent directory, allowing for executables or configuration files to be overwritten, resulting in arbitrary code execution. The highest threat from this vulnerability is to confidentiality, integrity, as well as system availability. Versions up to and including openshift-clients-4.7.0-202104250659.p0.git.95881af are affected. |
2021-05-14 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-27833
MISC
CONFIRM |
rfntps — firmware
|
RFNTPS firmware versions System_01000004 and earlier, and Web_01000004 and earlier allow an attacker on the same network segment to execute arbitrary OS commands with a root privilege via unspecified vectors. |
2021-05-20 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-20719
MISC
MISC |
rxvt-unicode — rxvt-unicode
|
rxvt-unicode 9.22, rxvt 2.7.10, mrxvt 0.5.4, and Eterm 0.9.7 allow (potentially remote) code execution because of improper handling of certain escape sequences (ESC G Q). A response is terminated by a newline. |
2021-05-20 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-33477
MISC
MISC
MISC
MISC
MISC
MISC
MISC
MISC |
searchblox — searchblox
|
A local file inclusion vulnerability in the FileServlet in all SearchBlox before 9.2.2 allows remote, unauthenticated users to read arbitrary files from the operating system via a /searchblox/servlet/FileServlet?col=url= request. Additionally, this may be used to read the contents of the SearchBlox configuration file (e.g., searchblox/WEB-INF/config.xml), which contains both the Super Admin’s API key and the base64 encoded SHA1 password hashes of other SearchBlox users. |
2021-05-20 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-35580
MISC
MISC |
| sitel — cap/prx_firmware |
SITEL CAP/PRX firmware version 5.2.01, allows an attacker with access to the device´s network to cause a denial of service condition on the device. An attacker could exploit this vulnerability by sending HTTP requests massively. |
2021-05-17 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-32455
CONFIRM |
| sitel — cap/prx_firmware |
SITEL CAP/PRX firmware version 5.2.01 allows an attacker with access to the local network of the device to obtain the authentication passwords by analysing the network traffic. |
2021-05-17 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-32456
CONFIRM |
sitel — cap/prx_firmware
|
SITEL CAP/PRX firmware version 5.2.01 allows an attacker with access to the local network, to access via HTTP to the internal configuration database of the device without any authentication. An attacker could exploit this vulnerability in order to obtain information about the device´s configuration. |
2021-05-17 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-32453
CONFIRM |
sitel — cap/prx_firmware
|
SITEL CAP/PRX firmware version 5.2.01 makes use of a hardcoded password. An attacker with access to the device could modify these credentials, leaving the administrators of the device without access. |
2021-05-17 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-32454
CONFIRM |
slapi-nis — slapi-nis
|
A flaw was found in slapi-nis in versions before 0.56.7. A NULL pointer dereference during the parsing of the Binding DN could allow an unauthenticated attacker to crash the 389-ds-base directory server. The highest threat from this vulnerability is to system availability. |
2021-05-20 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-3480
MISC |
smartstore — smartstore
|
An issue was discovered in Smartstore (aka SmartStoreNET) before 4.1.0. Administration/Controllers/ImportController.cs allows path traversal (for copy and delete actions) in the ImportController.Create method via a TempFileName field. |
2021-05-19 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-36364
MISC
MISC |
smartstore — smartstore
|
Smartstore (aka SmartStoreNET) before 4.1.0 allows CommonController.ClearCache, ClearDatabaseCache, RestartApplication, and ScheduleTaskController.Edit open redirect. |
2021-05-19 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-36365
MISC |
solarwinds — network_performance_monitor
|
This vulnerability allows remote attackers to execute arbitrary code on affected installations of SolarWinds Network Performance Monitor 2020.2.1. Authentication is not required to exploit this vulnerability. The specific flaw exists within the SolarWinds.Serialization library. The issue results from the lack of proper validation of user-supplied data, which can result in deserialization of untrusted data. An attacker can leverage this vulnerability to execute code in the context of SYSTEM. Was ZDI-CAN-12213. |
2021-05-21 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-31474
MISC
MISC |
| solarwinds — orion_job_scheduler |
This vulnerability allows remote attackers to execute arbitrary code on affected installations of SolarWinds Orion Job Scheduler 2020.2.1 HF 2. Authentication is required to exploit this vulnerability. The specific flaw exists within the JobRouterService WCF service. The issue is due to the WCF service configuration, which allows a critical resource to be accessed by unprivileged users. An attacker can leverage this vulnerability to execute code in the context of an administrator. Was ZDI-CAN-12007. |
2021-05-21 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-31475
MISC
MISC |
sophos — endpoint_products
|
In multiple versions of Sophos Endpoint products for MacOS, a local attacker could execute arbitrary code with administrator privileges. |
2021-05-17 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-25264
CONFIRM
MISC |
stmicroelectronics — stm32l4_devices
|
STMicroelectronics STM32L4 devices through 2020-10-19 have incorrect access control. The flash read-out protection (RDP) can be degraded from RDP level 2 (no access via debug interface) to level 1 (limited access via debug interface) by injecting a fault during the boot phase. |
2021-05-21 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-27212
MISC
MISC |
stmmicroelectronics — stm32l4_devices
|
STMicroelectronics STM32L4 devices through 2021-03-29 have incorrect physical access control. |
2021-05-21 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-29414
MISC |
synology — diskstation_manager
|
This vulnerability allows network-adjacent attackers to execute arbitrary code on affected installations of Synology DiskStation Manager. Authentication is not required to exploit this vulnerablity. The specific flaw exists within the processing of DSI structures in Netatalk. The issue results from the lack of proper validation of the length of user-supplied data prior to copying it to a heap-based buffer. An attacker can leverage this vulnerability to execute code in the context of the current process. Was ZDI-CAN-12326. |
2021-05-21 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-31439
MISC
MISC |
| telegram — multiple_products |
Telegram Android <7.1.0 (2090), Telegram iOS <7.1, and Telegram macOS <7.1 are affected by a Stack Based Overflow in the gray_split_cubic function of their custom fork of the rlottie library. A remote attacker might be able to overwrite Telegram’s stack memory out-of-bounds on a victim device via a malicious animated sticker. |
2021-05-18 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-31321
MISC
MISC |
| telegram — multiple_products |
Telegram Android <7.1.0 (2090), Telegram iOS <7.1, and Telegram macOS <7.1 are affected by a Heap Buffer Overflow in the LottieParserImpl::parseDashProperty function of their custom fork of the rlottie library. A remote attacker might be able to access heap memory out-of-bounds on a victim device via a malicious animated sticker. |
2021-05-18 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-31323
MISC
MISC |
| telegram — multiple_products |
Telegram Android <7.1.0 (2090), Telegram iOS <7.1, and Telegram macOS <7.1 are affected by a Type Confusion in the LOTCompLayerItem::LOTCompLayerItem function of their custom fork of the rlottie library. A remote attacker might be able to access heap memory out-of-bounds on a victim device via a malicious animated sticker. |
2021-05-18 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-31318
MISC
MISC |
telegram — multiple_products
|
Telegram Android <7.1.0 (2090), Telegram iOS <7.1, and Telegram macOS <7.1 are affected by a Heap Buffer Overflow in the VGradientCache::generateGradientColorTable function of their custom fork of the rlottie library. A remote attacker might be able to overwrite heap memory out-of-bounds on a victim device via a malicious animated sticker. |
2021-05-18 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-31320
MISC
MISC |
telegram — multiple_products
|
Telegram Android <7.1.0 (2090), Telegram iOS <7.1, and Telegram macOS <7.1 are affected by a Heap Buffer Overflow in the LOTGradient::populate function of their custom fork of the rlottie library. A remote attacker might be able to access heap memory out-of-bounds on a victim device via a malicious animated sticker. |
2021-05-18 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-31322
MISC
MISC |
telegram — multiple_products
|
Telegram Android <7.1.0 (2090), Telegram iOS <7.1, and Telegram macOS <7.1 are affected by an Integer Overflow in the LOTGradient::populate function of their custom fork of the rlottie library. A remote attacker might be able to access heap memory out-of-bounds on a victim device via a malicious animated sticker. |
2021-05-18 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-31319
MISC
MISC |
telegram — multiple_products
|
Telegram Android <7.1.0 (2090), Telegram iOS <7.1, and Telegram macOS <7.1 are affected by a Type Confusion in the VDasher constructor of their custom fork of the rlottie library. A remote attacker might be able to access Telegram’s heap memory out-of-bounds on a victim device via a malicious animated sticker. |
2021-05-18 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-31317
MISC
MISC |
telegram — multiple_products
|
Telegram Android <7.1.0 (2090), Telegram iOS <7.1, and Telegram macOS <7.1 are affected by a Stack Based Overflow in the blit function of their custom fork of the rlottie library. A remote attacker might be able to access Telegram’s stack memory out-of-bounds on a victim device via a malicious animated sticker. |
2021-05-18 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-31315
MISC
MISC |
trusted_firmware-m — trusted_firmware-m
|
In Trusted Firmware-M through 1.3.0, cleaning up the memory allocated for a multi-part cryptographic operation (in the event of a failure) can prevent the abort() operation in the associated cryptographic library from freeing internal resources, causing a memory leak. |
2021-05-21 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-32032
CONFIRM
MISC
MISC |
ubiquiti — unifi_video
|
In Ubiquiti UniFi Video v3.10.13, when the executable starts, its first library validation is in the current directory. This allows the impersonation and modification of the library to execute code on the system. This was tested in (Windows 7 x64/Windows 10 x64). |
2021-05-17 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-24755
MISC |
| vmd — vmd |
vmd through 1.34.0 allows ‘div class=”markdown-body”‘ XSS, as demonstrated by Electron remote code execution via require(‘child_process’).execSync(‘calc.exe’) on Windows and a similar attack on macOS. |
2021-05-17 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-33041
MISC |
websvn — websvn
|
WebSVN before 2.6.1 allows remote attackers to execute arbitrary commands via shell metacharacters in the search parameter. |
2021-05-18 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-32305
MISC |
wildfly — wildflt
|
A flaw was found in Wildfly in versions before 23.0.2.Final while creating a new role in domain mode via the admin console, it is possible to add a payload in the name field, leading to XSS. This affects Confidentiality and Integrity. |
2021-05-20 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-3536
MISC |
| wordpress — wordpress |
The tab parameter of the settings page of the 404 SEO Redirection WordPress plugin through 1.3 is vulnerable to a reflected Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) issue as user input is not properly sanitised or escaped before being output in an attribute. |
2021-05-17 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-24325
CONFIRM |
| wordpress — wordpress |
When taxes are enabled, the “Additional tax classes” field was not properly sanitised or escaped before being output back in the admin dashboard, allowing high privilege users such as admin to use XSS payloads even when the unfiltered_html is disabled |
2021-05-17 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-24323
CONFIRM |
| wordpress — wordpress |
The Happy Addons for Elementor WordPress plugin before 2.24.0, Happy Addons Pro for Elementor WordPress plugin before 1.17.0 have a number of widgets that are vulnerable to stored Cross-Site Scripting(XSS) by lower-privileged users such as contributors, all via a similar method: The “Card” widget accepts a “title_tag” parameter. Although the element control lists a fixed set of possible html tags, it is possible to send a ‘save_builder’ request with the “heading_tag” set to “script”, and the actual “title” parameter set to JavaScript to be executed within the script tags added by the “heading_tag” parameter. |
2021-05-17 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-24292
MISC
CONFIRM |
| wordpress — wordpress |
The SEO Redirection Plugin – 301 Redirect Manager WordPress plugin before 6.4 did not sanitise the Redirect From and Redirect To fields when creating a new redirect in the dashboard, allowing high privilege users (even with the unfiltered_html disabled) to set XSS payloads |
2021-05-17 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-24327
CONFIRM |
wordpress — wordpress
|
It was possible to exploit an Unauthenticated Time-Based Blind SQL Injection vulnerability in the Spam protection, AntiSpam, FireWall by CleanTalk WordPress Plugin before 5.153.4. The update_log function in lib/Cleantalk/ApbctWP/Firewall/SFW.php included a vulnerable query that could be injected via the User-Agent Header by manipulating the cookies set by the Spam protection, AntiSpam, FireWall by CleanTalk WordPress plugin before 5.153.4, sending an initial request to obtain a ct_sfw_pass_key cookie and then manually setting a separate ct_sfw_passed cookie and disallowing it from being reset. |
2021-05-17 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-24295
MISC
CONFIRM |
wordpress — wordpress
|
There is functionality in the Store Locator Plus for WordPress plugin through 5.5.14 that made it possible for authenticated users to update their user meta data to become an administrator on any site using the plugin. |
2021-05-17 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-24289
MISC
CONFIRM |
wordpress — wordpress
|
The tab parameter of the settings page of the All 404 Redirect to Homepage WordPress plugin before 1.21 was vulnerable to an authenticated reflected Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) issue as user input was not properly sanitised before being output in an attribute. |
2021-05-17 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-24326
CONFIRM |
wordpress — wordpress
|
There are several endpoints in the Store Locator Plus for WordPress plugin through 5.5.15 that could allow unauthenticated attackers the ability to inject malicious JavaScript into pages. |
2021-05-17 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-24290
CONFIRM
MISC |
wordpress — wordpress
|
The ReDi Restaurant Reservation WordPress plugin before 21.0426 provides the functionality to let users make restaurant reservations. These reservations are stored and can be listed on an ‘Upcoming’ page provided by the plugin. An unauthenticated user can fill in the form to make a restaurant reservation. The form to make a restaurant reservation field called ‘Comment’ does not use proper input validation and can be used to store XSS payloads. The XSS payloads will be executed when the plugin user goes to the ‘Upcoming’ page, which is an external website https://upcoming.reservationdiary.eu/ loaded in an iframe, and the stored reservation with XSS payload is loaded. |
2021-05-17 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-24299
CONFIRM |
wordpress — wordpress
|
The Goto WordPress theme before 2.1 did not sanitise, validate of escape the keywords GET parameter from its listing page before using it in a SQL statement, leading to an Unauthenticated SQL injection issue |
2021-05-17 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-24314
CONFIRM
MISC |
wordpress — wordpress
|
The GiveWP – Donation Plugin and Fundraising Platform WordPress plugin before 2.10.4 did not sanitise or escape the Background Image field of its Stripe Checkout Setting and Logo field in its Email settings, leading to authenticated (admin+) Stored XSS issues. |
2021-05-17 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-24315
MISC
CONFIRM |
wordpress — wordpress
|
The 404 SEO Redirection WordPress plugin through 1.3 is lacking CSRF checks in all its settings, allowing attackers to make a logged in user change the plugin’s settings. Due to the lack of sanitisation and escaping in some fields, it could also lead to Stored Cross-Site Scripting issues |
2021-05-17 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-24324
CONFIRM |
yara — yara
|
An integer overflow and several buffer overflow reads in libyara/modules/macho/macho.c in YARA v4.0.3 and earlier could allow an attacker to either cause denial of service or information disclosure via a malicious Mach-O file. Affects all versions before libyara 4.0.4 |
2021-05-14 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-3402
MISC
FEDORA
FEDORA
MISC
MISC |
zam64 — zam64
|
Incorrect access control in zam64.sys, zam32.sys in MalwareFox AntiMalware 2.74.0.150 where IOCTL’s 0x80002014, 0x80002018 expose unrestricted disk read/write capabilities respectively. A non-privileged process can open a handle to .ZemanaAntiMalware, register with the driver using IOCTL 0x80002010 and send these IOCTL’s to escalate privileges by overwriting the boot sector or overwriting critical code in the pagefile. |
2021-05-17 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-31727
MISC |
zam64 — zam64
|
Incorrect access control in zam64.sys, zam32.sys in MalwareFox AntiMalware 2.74.0.150 allows a non-privileged process to open a handle to .ZemanaAntiMalware, register itself with the driver by sending IOCTL 0x80002010, allocate executable memory using a flaw in IOCTL 0x80002040, install a hook with IOCTL 0x80002044 and execute the executable memory using this hook with IOCTL 0x80002014 or 0x80002018, this exposes ring 0 code execution in the context of the driver allowing the non-privileged process to elevate privileges. |
2021-05-17 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-31728
MISC |
zmartzone — mod_auth_openidc
|
mod_auth_openidc 2.4.0 to 2.4.7 allows a remote attacker to cause a denial-of-service (DoS) condition via unspecified vectors. |
2021-05-20 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-20718
MISC
MISC
MISC |
zoho — manageengine_adselfservice_plus
|
Zoho ManageEngine ADSelfService Plus before 6104 allows stored XSS on the /webclient/index.html#/directory-search user search page via the e-mail address field. |
2021-05-20 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-27956
CONFIRM
MISC
MISC |
zope — zope
|
Zope Products.CMFCore before 2.5.1 and Products.PluggableAuthService before 2.6.2, as used in Plone through 5.2.4 and other products, allow Reflected XSS. |
2021-05-21 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-33507
MISC
MLIST |
zope — zope
|
Zope is an open-source web application server. In Zope versions prior to 4.6 and 5.2, users can access untrusted modules indirectly through Python modules that are available for direct use. By default, only users with the Manager role can add or edit Zope Page Templates through the web, but sites that allow untrusted users to add/edit Zope Page Templates through the web are at risk from this vulnerability. The problem has been fixed in Zope 5.2 and 4.6. As a workaround, a site administrator can restrict adding/editing Zope Page Templates through the web using the standard Zope user/role permission mechanisms. Untrusted users should not be assigned the Zope Manager role and adding/editing Zope Page Templates through the web should be restricted to trusted users only. |
2021-05-21 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-32633
MISC
CONFIRM
MLIST
MLIST |
| zte — axon_11_mobile_devices |
A mobile phone of ZTE is impacted by improper access control vulnerability. Due to improper permission settings, third-party applications can read some files in the proc file system without authorization. Attackers could exploit this vulnerability to obtain sensitive information. This affects Axon 11 5G ZTE/CN_P725A12/P725A12:10/QKQ1.200816.002/20201116.175317:user/release-keys. |
2021-05-19 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-21732
MISC |
zxcdn — zxcdn
|
The management system of ZXCDN is impacted by the information leak vulnerability. Attackers can make further analysis according to the information returned by the program, and then obtain some sensitive information. This affects ZXCDN V7.01 all versions up to IAMV7.01.01.02. |
2021-05-19 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-21733
MISC |


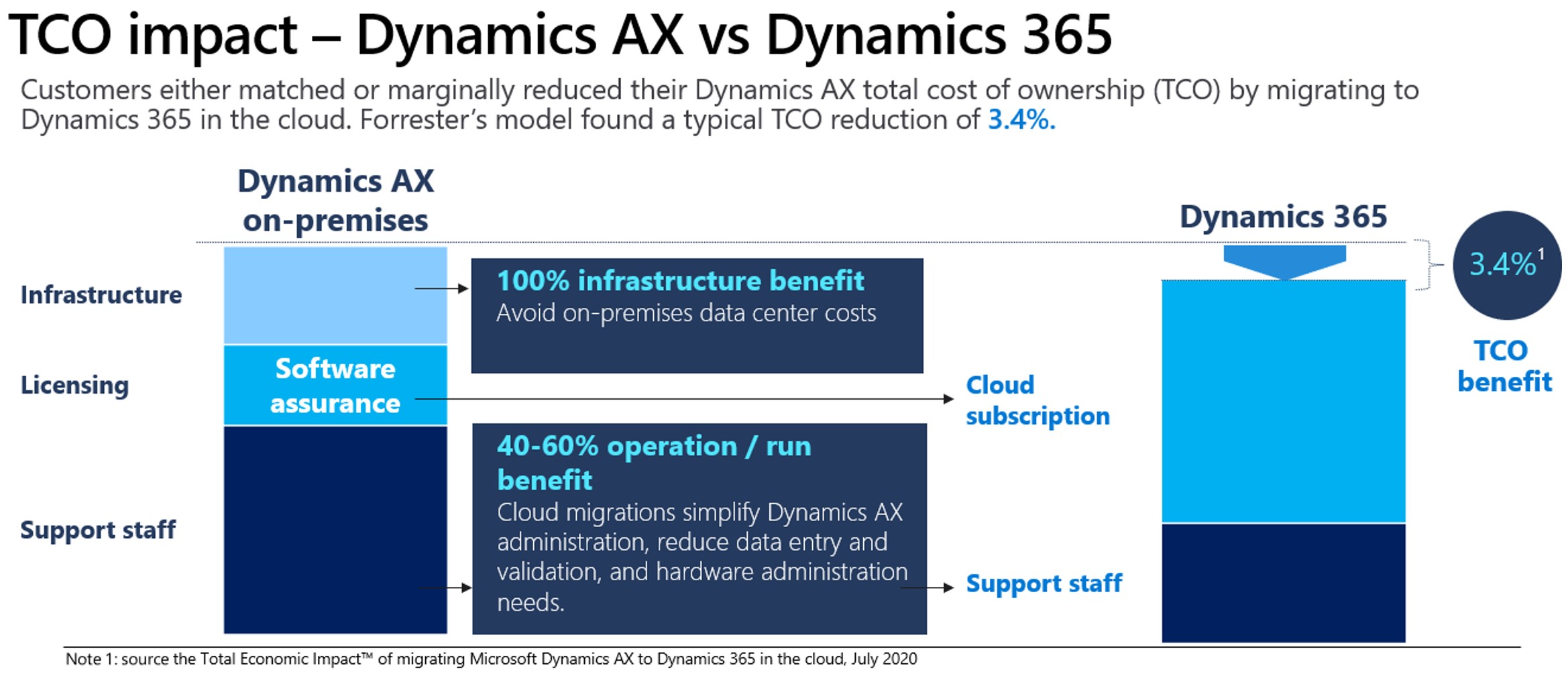
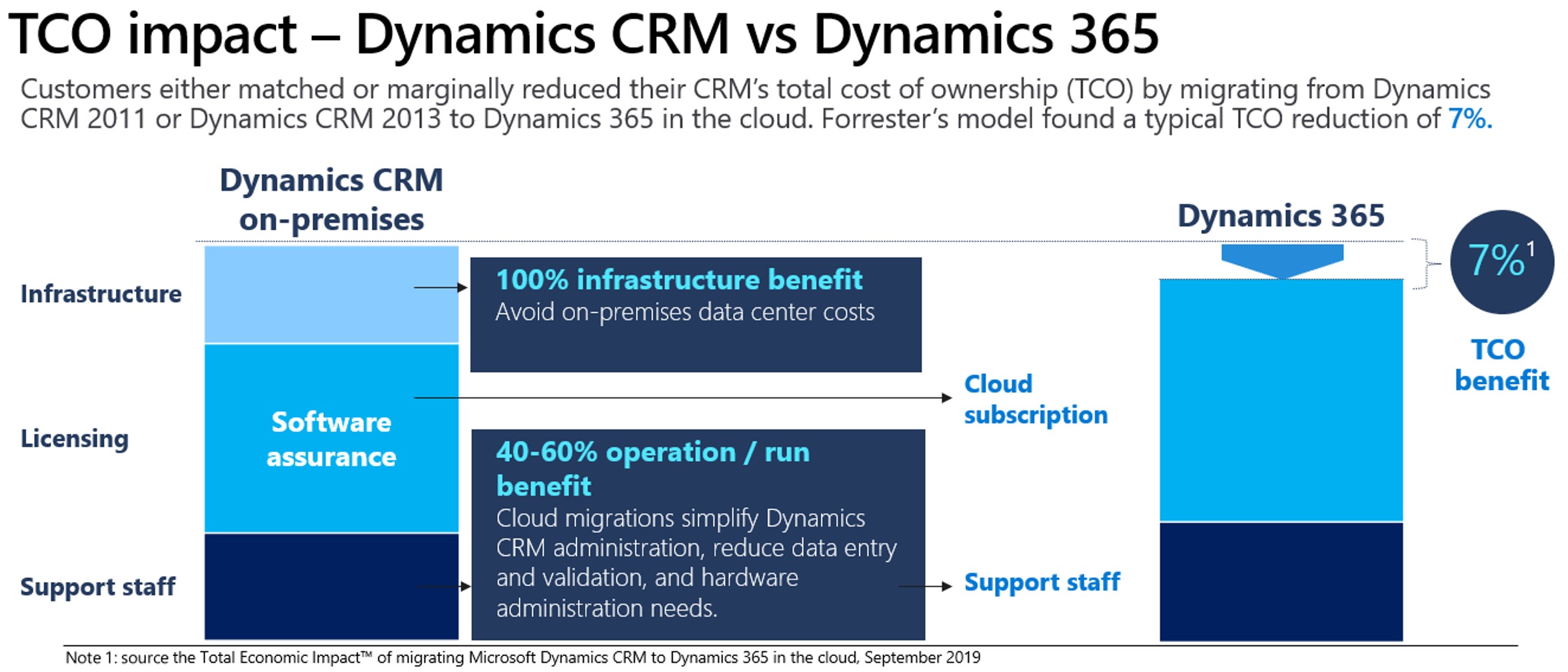
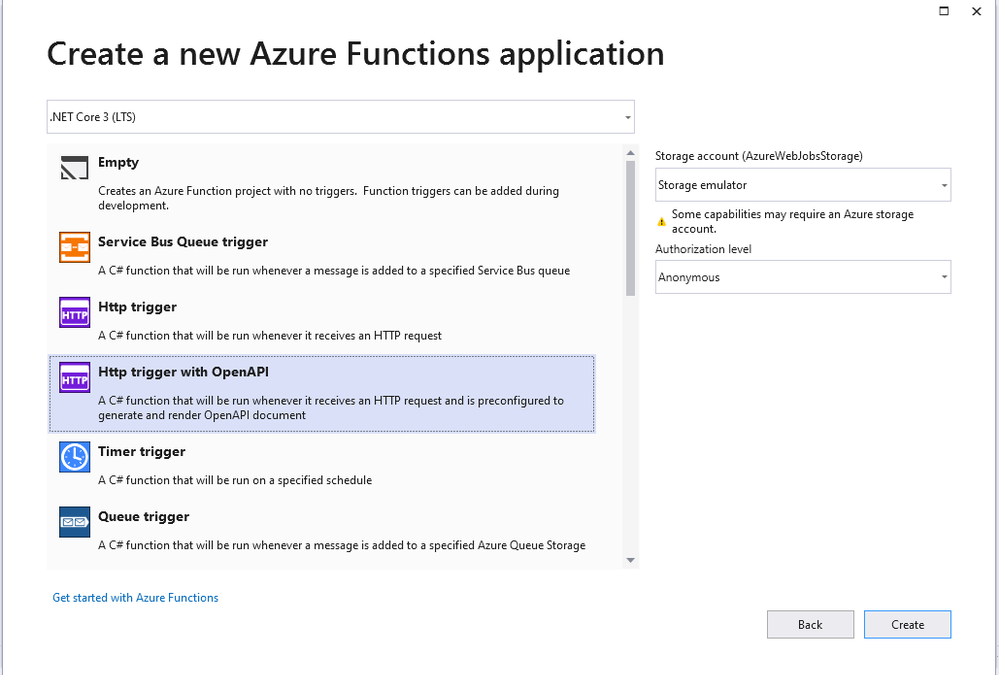
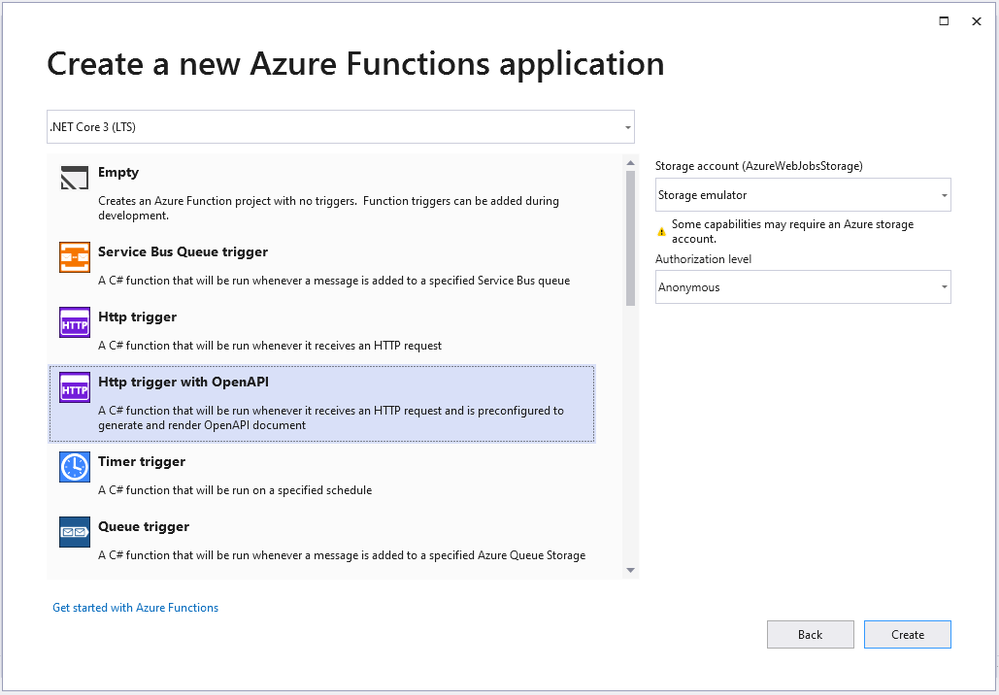

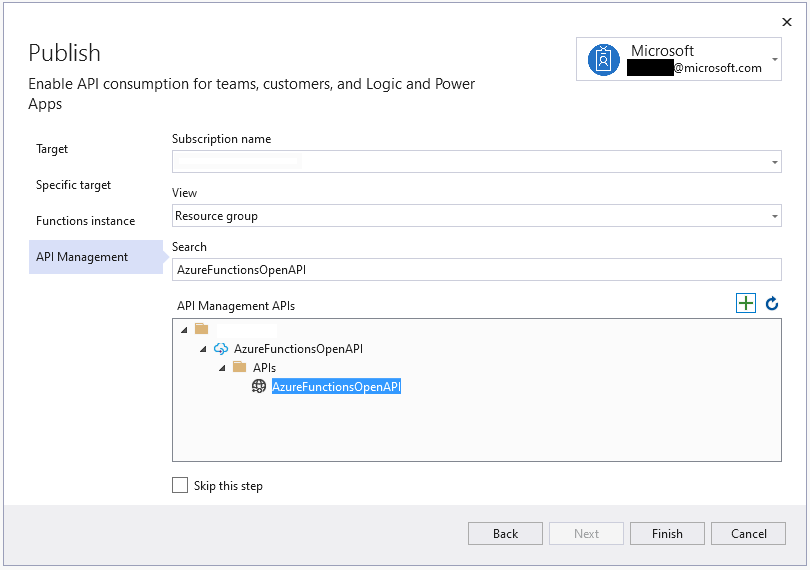
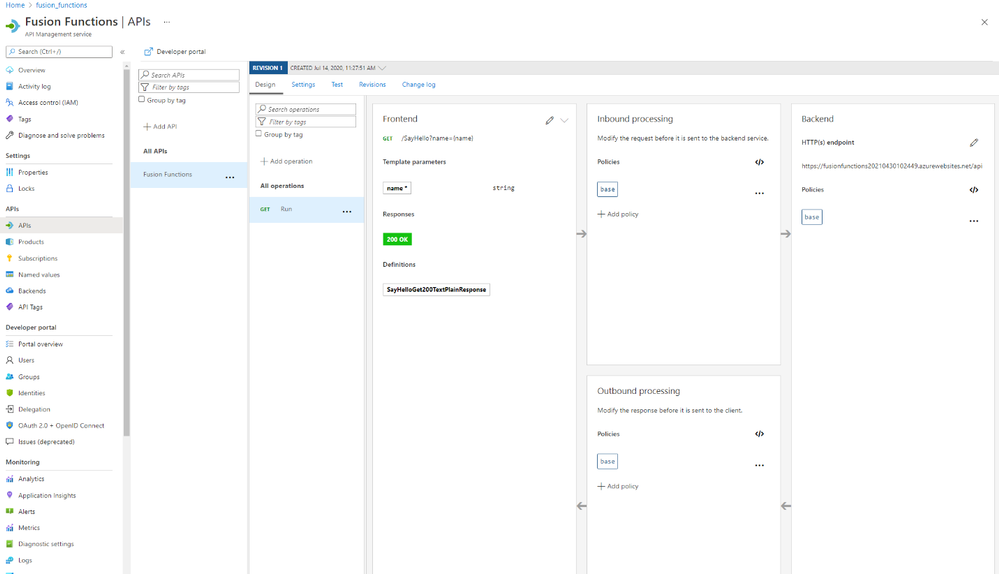
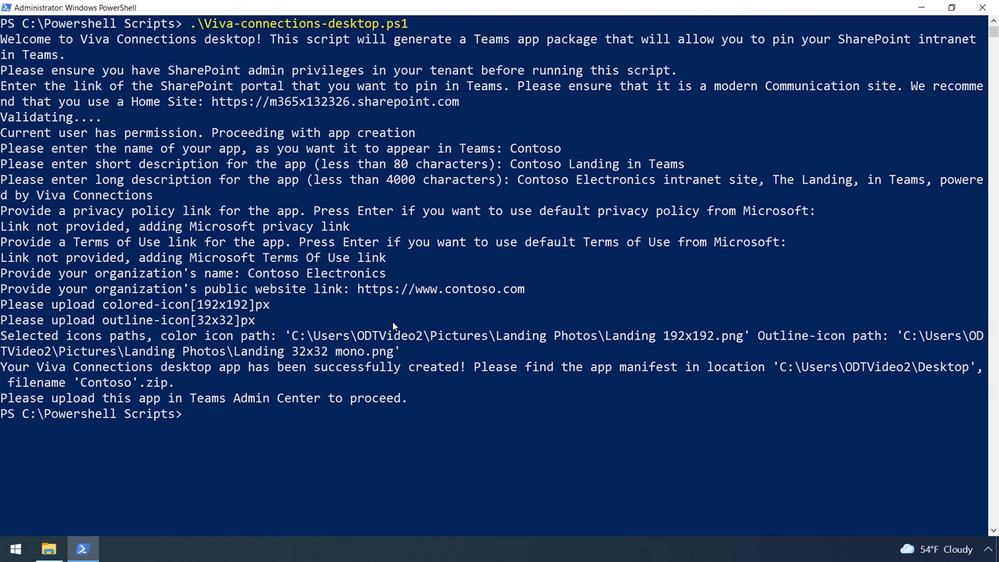












Recent Comments