by Scott Muniz | May 31, 2021 | Security, Technology
This article is contributed. See the original author and article here.
101eip — 101eip
|
Add event in calendar function in the 101EIP system does not filter special characters in specific fields, which allows remote authenticated users to inject JavaScript and perform a stored XSS attack. |
2021-05-28 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-32539
CONFIRM |
101eip — 101eip
|
Add announcement function in the 101EIP system does not filter special characters, which allows authenticated users to inject JavaScript and perform a stored XSS attack. |
2021-05-28 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-32540
CONFIRM |
1cdn — 1cdn
|
1CDN is open-source file sharing software. In 1CDN before commit f88a2730fa50fc2c2aeab09011f6f142fd90ec25, there is a basic cross-site scripting vulnerability that allows an attacker to inject /<script>//code</script> and execute JavaScript code on the client side. |
2021-05-28 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-32616
CONFIRM
MISC |
3scale — dev_portal
|
3scale dev portal login form does not verify CSRF token, and so does not protect against login CSRF. |
2021-05-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2019-14836
MISC
MISC |
ab_initio — ab_initio
|
Local File Inclusion vulnerability in Ab Initio Control>Center before 4.0.2.6 allows remote attackers to retrieve arbitrary files. Fixed in v4.0.2.6 and v4.0.3.1. |
2021-05-27 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-33408
CONFIRM |
| acronis — true_image |
An issue was discovered in Acronis True Image 2020 24.5.22510. anti_ransomware_service.exe includes functionality to quarantine files by copying a suspected ransomware file from one directory to another using SYSTEM privileges. Because unprivileged users have write permissions in the quarantine folder, it is possible to control this privileged write with a hardlink. This means that an unprivileged user can write/overwrite arbitrary files in arbitrary folders. Escalating privileges to SYSTEM is trivial with arbitrary writes. While the quarantine feature is not enabled by default, it can be forced to copy the file to the quarantine by communicating with anti_ransomware_service.exe through its REST API. |
2021-05-25 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-9452
MISC
MISC
MISC |
acronis — true_image
|
An issue was discovered in Acronis True Image 2020 24.5.22510. anti_ransomware_service.exe keeps a log in a folder where unprivileged users have write permissions. The logs are generated in a predictable pattern, allowing an unprivileged user to create a hardlink from a (not yet created) log file to anti_ransomware_service.exe. On reboot, this forces the anti_ransomware_service to try to write its log into its own process, crashing in a SHARING VIOLATION. This crash occurs on every reboot. |
2021-05-25 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-9451
MISC
MISC
MISC |
adobe — coldfusion
|
The Adobe ColdFusion installer fails to set a secure access-control list (ACL) on the default installation directory, such as C:ColdFusion2021. By default, unprivileged users can create files in this directory structure, which creates a privilege-escalation vulnerability. |
2021-05-27 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-10145
MISC |
| ansible — ansible |
A flaw was found in ansible module where credentials are disclosed in the console log by default and not protected by the security feature when using the bitbucket_pipeline_variable module. This flaw allows an attacker to steal bitbucket_pipeline credentials. The highest threat from this vulnerability is to confidentiality. |
2021-05-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-20178
MISC
FEDORA
FEDORA
MISC
MISC |
ansible — ansible
|
A flaw was found in ansible. Credentials, such as secrets, are being disclosed in console log by default and not protected by no_log feature when using those modules. An attacker can take advantage of this information to steal those credentials. The highest threat from this vulnerability is to data confidentiality. Versions before ansible 2.9.18 are affected. |
2021-05-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-20191
MISC |
| ansible — tower |
A flaw was found in Ansible Tower when running jobs. This flaw allows an attacker to access the stdout of the executed jobs which are run from other organizations. Some sensible data can be disclosed. However, critical data should not be disclosed, as it should be protected by the no_log flag when debugging is enabled. This flaw affects Ansible Tower versions before 3.6.4, Ansible Tower versions before 3.5.6 and Ansible Tower versions before 3.4.6. |
2021-05-27 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-10698
MISC |
ansible — tower
|
A security flaw was found in Ansible Tower when requesting an OAuth2 token with an OAuth2 application. Ansible Tower uses the token to provide authentication. This flaw allows an attacker to obtain a refresh token that does not expire. The original token granted to the user still has access to Ansible Tower, which allows any user that can gain access to the token to be fully authenticated to Ansible Tower. This flaw affects Ansible Tower versions before 3.6.4 and Ansible Tower versions before 3.5.6. |
2021-05-27 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-10709
MISC |
ansible — tower
|
A flaw was found in the use of insufficiently random values in Ansible. Two random password lookups of the same length generate the equal value as the template caching action for the same file since no re-evaluation happens. The highest threat from this vulnerability would be that all passwords are exposed at once for the file. This flaw affects Ansible Engine versions before 2.9.6. |
2021-05-27 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-10729
MISC
MISC |
ansible — tower
|
A flaw was found in Ansible Tower when running Openshift. Tower runs a memcached, which is accessed via TCP. An attacker can take advantage of writing a playbook polluting this cache, causing a denial of service attack. This attack would not completely stop the service, but in the worst-case scenario, it can reduce the Tower performance, for which memcached is designed. Theoretically, more sophisticated attacks can be performed by manipulating and crafting the cache, as Tower relies on memcached as a place to pull out setting values. Confidential and sensitive data stored in memcached should not be pulled, as this information is encrypted. This flaw affects Ansible Tower versions before 3.6.4, Ansible Tower versions before 3.5.6 and Ansible Tower versions before 3.4.6. |
2021-05-27 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-10697
MISC |
ansible — tower
|
A Server-side request forgery (SSRF) flaw was found in Ansible Tower in versions before 3.6.5 and before 3.7.2. Functionality on the Tower server is abused by supplying a URL that could lead to the server processing it. This flaw leads to the connection to internal services or the exposure of additional internal services by abusing the test feature of lookup credentials to forge HTTP/HTTPS requests from the server and retrieving the results of the response. |
2021-05-27 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-14327
MISC |
ansible — tower
|
A flaw was found in Ansible Tower in versions before 3.7.2. A Server Side Request Forgery flaw can be abused by supplying a URL which could lead to the server processing it connecting to internal services or exposing additional internal services and more particularly retrieving full details in case of error. The highest threat from this vulnerability is to data confidentiality. |
2021-05-27 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-14328
MISC |
ansible — tower
|
A data exposure flaw was found in Ansible Tower in versions before 3.7.2, where sensitive data can be exposed from the /api/v2/labels/ endpoint. This flaw allows users from other organizations in the system to retrieve any label from the organization and also disclose organization names. The highest threat from this vulnerability is to confidentiality. |
2021-05-27 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-14329
MISC |
apache — fineract
|
Apache Fineract prior to 1.5.0 disables HTTPS hostname verification in ProcessorHelper in the configureClient method. Under typical deployments, a man in the middle attack could be successful. |
2021-05-27 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-17514
CONFIRM
MLIST
MLIST |
apache — pulsar
|
If Apache Pulsar is configured to authenticate clients using tokens based on JSON Web Tokens (JWT), the signature of the token is not validated if the algorithm of the presented token is set to “none”. This allows an attacker to connect to Pulsar instances as any user (incl. admins). |
2021-05-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-22160
MISC
MLIST
MLIST
MLIST
MLIST
MLIST
MLIST
MLIST |
apache — wicket
|
A DNS proxy and possible amplification attack vulnerability in WebClientInfo of Apache Wicket allows an attacker to trigger arbitrary DNS lookups from the server when the X-Forwarded-For header is not properly sanitized. This DNS lookup can be engineered to overload an internal DNS server or to slow down request processing of the Apache Wicket application causing a possible denial of service on either the internal infrastructure or the web application itself. This issue affects Apache Wicket Apache Wicket 9.x version 9.2.0 and prior versions; Apache Wicket 8.x version 8.11.0 and prior versions; Apache Wicket 7.x version 7.17.0 and prior versions and Apache Wicket 6.x version 6.2.0 and later versions. |
2021-05-25 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-23937
MISC
MLIST
MLIST
MLIST |
apple — macos
|
Private Tunnel installer for macOS version 3.0.1 and older versions may corrupt system critical files it should not have access via symlinks in /tmp. |
2021-05-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-15076
MISC |
arm — trusted_firmware
|
In Arm Trusted Firmware M through 1.2, the NS world may trigger a system halt, an overwrite of secure data, or the printing out of secure data when calling secure functions under the NSPE handler mode. |
2021-05-25 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-27562
MISC
CONFIRM |
arm — trustzone_cryptocell
|
The elliptic curve cryptography (ECC) hardware accelerator, part of the ARM® TrustZone® CryptoCell 310, contained in the NordicSemiconductor nRF52840 through 2021-03-29 has a non-constant time ECDSA implemenation. This allows an adversary to recover the private ECC key used during an ECDSA operation. |
2021-05-21 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-29415
MISC
MISC
MISC |
authelia — authelia
|
Authelia is a a single sign-on multi-factor portal for web apps. This affects uses who are using nginx ngx_http_auth_request_module with Authelia, it allows a malicious individual who crafts a malformed HTTP request to bypass the authentication mechanism. It additionally could theoretically affect other proxy servers, but all of the ones we officially support except nginx do not allow malformed URI paths. The problem is rectified entirely in v4.29.3. As this patch is relatively straightforward we can back port this to any version upon request. Alternatively we are supplying a git patch to 4.25.1 which should be relatively straightforward to apply to any version, the git patches for specific versions can be found in the references. The most relevant workaround is upgrading. You can also add a block which fails requests that contains a malformed URI in the internal location block. |
2021-05-28 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-32637
CONFIRM
MISC |
| autodesk_licensing_services — autodesk_licensing_services |
Autodesk Licensing Services was found to be vulnerable to privilege escalation issues. A limited privileges malicious user could run any number of tools on a system to identify services which are configured with weak permissions and are running under elevated privileges. These weak permissions could allow all users on the operating system to modify the service configuration, and take ownership of the service. This issue was found by an external security researcher. |
2021-05-28 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-27032
MISC
MISC |
binutils — obdump
|
An out of bounds flaw was found in GNU binutils objdump utility version 2.36. An attacker could use this flaw and pass a large section to avr_elf32_load_records_from_section() probably resulting in a crash or in some cases memory corruption. The highest threat from this vulnerability is to integrity as well as system availability. |
2021-05-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-3549
MISC |
bitfrost — multiple_products
|
. The Arm Mali GPU kernel driver allows an unprivileged user to achieve access to freed memory, leading to information disclosure or root privilege escalation. This affects Bifrost r16p0 through r29p0 before r30p0, Valhall r19p0 through r29p0 before r30p0, and Midgard r28p0 through r30p0. |
2021-05-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-29256
CONFIRM |
bluetooth_sig — bluetooth_core_specification
|
Bluetooth legacy BR/EDR PIN code pairing in Bluetooth Core Specification 1.0B through 5.2 may permit an unauthenticated nearby device to spoof the BD_ADDR of the peer device to complete pairing without knowledge of the PIN. |
2021-05-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-26555
MISC
MISC
FEDORA |
| bluetooth_sig — bluetooth_le_and_br/edr |
Bluetooth LE and BR/EDR secure pairing in Bluetooth Core Specification 2.1 through 5.2 may permit a nearby man-in-the-middle attacker to identify the Passkey used during pairing (in the Passkey authentication procedure) by reflection of the public key and the authentication evidence of the initiating device, potentially permitting this attacker to complete authenticated pairing with the responding device using the correct Passkey for the pairing session. The attack methodology determines the Passkey value one bit at a time. |
2021-05-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-26558
MISC
MISC
FEDORA |
bluetooth_sig — bluetooth_mesh
|
Mesh Provisioning in the Bluetooth Mesh profile 1.0 and 1.0.1 may permit a nearby device, able to conduct a successful brute-force attack on an insufficiently random AuthValue before the provisioning procedure times out, to complete authentication by leveraging Malleable Commitment. |
2021-05-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-26556
MISC
MISC |
bluetooth_sig — bluetooth_mesh
|
Mesh Provisioning in the Bluetooth Mesh profile 1.0 and 1.0.1 may permit a nearby device (without possession of the AuthValue used in the provisioning protocol) to determine the AuthValue via a brute-force attack (unless the AuthValue is sufficiently random and changed each time). |
2021-05-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-26557
MISC
MISC |
bluetooth_sig — bluetooth_mesh
|
Bluetooth Mesh Provisioning in the Bluetooth Mesh profile 1.0 and 1.0.1 may permit a nearby device (participating in the provisioning protocol) to identify the AuthValue used given the Provisioner’s public key, and the confirmation number and nonce provided by the provisioning device. This could permit a device without the AuthValue to complete provisioning without brute-forcing the AuthValue. |
2021-05-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-26559
MISC
MISC |
bluetooth_sig — bluetooth_mesh
|
Bluetooth Mesh Provisioning in the Bluetooth Mesh profile 1.0 and 1.0.1 may permit a nearby device, reflecting the authentication evidence from a Provisioner, to complete authentication without possessing the AuthValue, and potentially acquire a NetKey and AppKey. |
2021-05-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-26560
MISC
MISC |
boa — boa
|
Boa 0.94.13 allows remote attackers to obtain sensitive information via a misconfiguration involving backup.html, preview.html, js/log.js, log.html, email.html, online-users.html, and config.js. |
2021-05-27 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-33558
MISC
MISC |
bytecode_alliance — cranelift
|
Cranelift is an open-source code generator maintained by Bytecode Alliance. It translates a target-independent intermediate representation into executable machine code. There is a bug in 0.73 of the Cranelift x64 backend that can create a scenario that could result in a potential sandbox escape in a Wasm program. This bug was introduced in the new backend on 2020-09-08 and first included in a release on 2020-09-30, but the new backend was not the default prior to 0.73. The recently-released version 0.73 with default settings, and prior versions with an explicit build flag to select the new backend, are vulnerable. The bug in question performs a sign-extend instead of a zero-extend on a value loaded from the stack, under a specific set of circumstances. If those circumstances occur, the bug could allow access to memory addresses upto 2GiB before the start of the Wasm program heap. If the heap bound is larger than 2GiB, then it would be possible to read memory from a computable range dependent on the size of the heaps bound. The impact of this bug is highly dependent on heap implementation, specifically: * if the heap has bounds checks, and * does not rely exclusively on guard pages, and * the heap bound is 2GiB or smaller * then this bug cannot be used to reach memory from another Wasm program heap. The impact of the vulnerability is mitigated if there is no memory mapped in the range accessible using this bug, for example, if there is a 2 GiB guard region before the Wasm program heap. The bug in question performs a sign-extend instead of a zero-extend on a value loaded from the stack, when the register allocator reloads a spilled integer value narrower than 64 bits. This interacts poorly with another optimization: the instruction selector elides a 32-to-64-bit zero-extend operator when we know that an instruction producing a 32-bit value actually zeros the upper 32 bits of its destination register. Hence, we rely on these zeroed bits, but the type of the value is still i32, and the spill/reload reconstitutes those bits as the sign extension of the i32’s MSB. The issue would thus occur when: * An i32 value in a Wasm program is greater than or equal to 0x8000_0000; * The value is spilled and reloaded by the register allocator due to high register pressure in the program between the value’s definition and its use; * The value is produced by an instruction that we know to be “special” in that it zeroes the upper 32 bits of its destination: add, sub, mul, and, or; * The value is then zero-extended to 64 bits in the Wasm program; * The resulting 64-bit value is used. Under these circumstances there is a potential sandbox escape when the i32 value is a pointer. The usual code emitted for heap accesses zero-extends the Wasm heap address, adds it to a 64-bit heap base, and accesses the resulting address. If the zero-extend becomes a sign-extend, the program could reach backward and access memory up to 2GiB before the start of its heap. In addition to assessing the nature of the code generation bug in Cranelift, we have also determined that under specific circumstances, both Lucet and Wasmtime using this version of Cranelift may be exploitable. See referenced GitHub Advisory for more details. |
2021-05-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-32629
MISC
CONFIRM
MISC
MISC |
ceph-ansible — playbook
|
A flaw was found in the ceph-ansible playbook where it contained hardcoded passwords that were being used as default passwords while deploying Ceph services. Any authenticated attacker can abuse this flaw to brute-force Ceph deployments, and gain administrator access to Ceph clusters via the Ceph dashboard to initiate read, write, and delete Ceph clusters and also modify Ceph cluster configurations. Versions before ceph-ansible 6.0.0alpha1 are affected. |
2021-05-28 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-1716
MISC |
| cesanta — mjs |
Stack overflow vulnerability in parse_equality Cesanta MJS 1.20.1, allows remote attackers to cause a Denial of Service (DoS) via a crafted file. |
2021-05-28 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-36375
MISC |
| cesanta — mjs |
Stack overflow vulnerability in parse_comparison Cesanta MJS 1.20.1, allows remote attackers to cause a Denial of Service (DoS) via a crafted file. |
2021-05-28 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-36374
MISC |
cesanta — mjs
|
Stack overflow vulnerability in parse_plus_minus Cesanta MJS 1.20.1, allows remote attackers to cause a Denial of Service (DoS) via a crafted file. |
2021-05-28 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-36372
MISC |
cesanta — mjs
|
Stack overflow vulnerability in parse_mul_div_rem Cesanta MJS 1.20.1, allows remote attackers to cause a Denial of Service (DoS) via a crafted file. |
2021-05-28 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-36371
MISC |
cesanta — mjs
|
Stack overflow vulnerability in parse_unary Cesanta MJS 1.20.1, allows remote attackers to cause a Denial of Service (DoS) via a crafted file. |
2021-05-28 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-36370
MISC |
cesanta — mjs
|
Stack overflow vulnerability in parse_statement_list Cesanta MJS 1.20.1, allows remote attackers to cause a Denial of Service (DoS) via a crafted file. |
2021-05-28 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-36369
MISC |
cesanta — mjs
|
Stack overflow vulnerability in parse_statement Cesanta MJS 1.20.1, allows remote attackers to cause a Denial of Service (DoS) via a crafted file. |
2021-05-28 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-36368
MISC |
cesanta — mjs
|
Stack overflow vulnerability in parse_array Cesanta MJS 1.20.1, allows remote attackers to cause a Denial of Service (DoS) via a crafted file. |
2021-05-28 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-18392
MISC |
cesanta — mjs
|
Stack overflow vulnerability in parse_shifts Cesanta MJS 1.20.1, allows remote attackers to cause a Denial of Service (DoS) via a crafted file. |
2021-05-28 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-36373
MISC |
cesanta — mjs
|
Stack overflow vulnerability in parse_block Cesanta MJS 1.20.1, allows remote attackers to cause a Denial of Service (DoS) via a crafted file. |
2021-05-28 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-36367
MISC |
cesanta — mjs
|
Stack overflow vulnerability in parse_value Cesanta MJS 1.20.1, allows remote attackers to cause a Denial of Service (DoS) via a crafted file. |
2021-05-28 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-36366
MISC |
chach20-poly1305 — chacha20-poly1305
|
A flaw was found in the way CHACHA20-POLY1305 was implemented in NSS in versions before 3.55. When using multi-part Chacha20, it could cause out-of-bounds reads. This issue was fixed by explicitly disabling multi-part ChaCha20 (which was not functioning correctly) and strictly enforcing tag length. The highest threat from this vulnerability is to confidentiality and system availability. |
2021-05-27 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-12403
MISC
MISC |
checkbox — survey
|
Deserialization of Untrusted Data vulnerability in CheckboxWeb.dll of Checkbox Survey allows an unauthenticated remote attacker to execute arbitrary code. This issue affects: Checkbox Survey versions prior to 7. |
2021-05-27 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-27852
MISC |
citrix — sharefile_storage_zones_controller
|
A missing authorization vulnerability exists in Citrix ShareFile Storage Zones Controller before 5.7.3, 5.8.3, 5.9.3, 5.10.1 and 5.11.18 may allow unauthenticated remote compromise of the Storage Zones Controller. |
2021-05-27 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-22891
MISC |
citrix — workspace_app
|
An improper access control vulnerability exists in Citrix Workspace App for Windows potentially allows privilege escalation in CR versions prior to 2105 and 1912 LTSR prior to CU4. |
2021-05-27 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-22907
MISC |
couchebase — server
|
An issue was discovered in Couchbase Server 5.x and 6.x before 6.5.2 and 6.6.x before 6.6.2. Internal users with administrator privileges, @cbq-engine-cbauth and @index-cbauth, leak credentials in cleartext in the indexer.log file when they make a /listCreateTokens, /listRebalanceTokens, or /listMetadataTokens call. |
2021-05-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-25643
MISC |
covid19_testing_management_system — covid19_testing_management_system
|
COVID19 Testing Management System 1.0 is vulnerable to SQL Injection via the admin panel. |
2021-05-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-33470
MISC
MISC |
covid19_testing_management_system — covid19_testing_management_system
|
COVID19 Testing Management System 1.0 is vulnerable to Cross Site Scripting (XSS) via the “Admin name” parameter. |
2021-05-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-33469
MISC
MISC |
css-what — css-what
|
The css-what package before 5.0.1 for Node.js does not ensure that attribute parsing has Linear Time Complexity relative to the size of the input. |
2021-05-28 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-33587
MISC |
cts — web_trading_system
|
The parameters of the specific functions in the CTS Web trading system do not filter special characters, which allows unauthenticated attackers can remotely perform reflected XSS and obtain the users’ connection token that triggered the attack. |
2021-05-28 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-32542
CONFIRM |
cts — web_transaction_system
|
The CTS Web transaction system related to authentication management is implemented incorrectly. After login, remote attackers can manipulate cookies to access other accounts and trade in the stock market with spoofed identity. |
2021-05-28 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-32543
CONFIRM |
cts — web_transaction_system
|
The CTS Web transaction system related to authentication and session management is implemented incorrectly, which allows remote unauthenticated attackers can send a large number of valid usernames, and force those logged-in account to log out, causing the user to be unable to access the services |
2021-05-28 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-32541
CONFIRM |
| cubecart — cubecart |
Cubecart 6.4.2 allows Session Fixation. The application does not generate a new session cookie after the user is logged in. A malicious user is able to create a new session cookie value and inject it to a victim. After the victim logs in, the injected cookie becomes valid, giving the attacker access to the user’s account through the active session. |
2021-05-27 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-33394
CONFIRM
MISC |
| datakit_software — multiple_products |
Datakit Software libraries CatiaV5_3dRead, CatiaV6_3dRead, Step3dRead, Ug3dReadPsr, Jt3dReadPsr modules in KeyShot Versions v10.1 and prior lack proper validation of user-supplied data when parsing PRT files. This could lead to pointer dereferences of a value obtained from an untrusted source. An attacker could leverage this vulnerability to execute code in the context of the current process. |
2021-05-27 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-27496
CONFIRM
MISC
MISC |
| datakit_software — multiple_products |
Datakit Software libraries CatiaV5_3dRead, CatiaV6_3dRead, Step3dRead, Ug3dReadPsr, Jt3dReadPsr modules in KeyShot Versions v10.1 and prior lack proper validation of user-supplied data when parsing STP files. This could result in a stack-based buffer overflow. An attacker could leverage this vulnerability to execute code in the context of the current process. |
2021-05-27 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-27494
CONFIRM
MISC
MISC |
datakit_software — multiple_products
|
Datakit Software libraries CatiaV5_3dRead, CatiaV6_3dRead, Step3dRead, Ug3dReadPsr, Jt3dReadPsr modules in KeyShot Versions v10.1 and prior lack proper validation of user-supplied data when parsing CATPart files. This could result in an out-of-bounds write past the end of an allocated structure. An attacker could leverage this vulnerability to execute code in the context of the current process. |
2021-05-27 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-27488
CONFIRM
MISC
MISC |
datakit_software — multiple_products
|
Datakit Software libraries CatiaV5_3dRead, CatiaV6_3dRead, Step3dRead, Ug3dReadPsr, Jt3dReadPsr modules in KeyShot Versions v10.1 and prior are vulnerable to an out-of-bounds read, which may allow an attacker to execute arbitrary code. |
2021-05-27 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-27490
CONFIRM
MISC
MISC |
datakit_software — multiple_products
|
When opening a specially crafted 3DXML file, the application containing Datakit Software libraries CatiaV5_3dRead, CatiaV6_3dRead, Step3dRead, Ug3dReadPsr, Jt3dReadPsr modules in KeyShot Versions v10.1 and prior could disclose arbitrary files to remote attackers. This is because of the passing of specially crafted content to the underlying XML parser without taking proper restrictions such as prohibiting an external DTD. |
2021-05-27 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-27492
CONFIRM
MISC
MISC |
dmg2img — dmg2img
|
A flaw was found in dmg2img through 20170502. fill_mishblk() does not check the length of the read buffer, and copy 0xCC bytes from it. The length of the buffer is controlled by an attacker. By providing a length smaller than 0xCC, memcpy reaches out of the malloc’ed bound. This possibly leads to memory layout information leaking in the data. This might be used in a chain of vulnerability in order to reach code execution. |
2021-05-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-32614
MISC |
dmg2img — dmg2img
|
A flaw was found in dmg2img through 20170502. dmg2img did not validate the size of the read buffer during memcpy() inside the main() function. This possibly leads to memory layout information leaking in the data. This might be used in a chain of vulnerability in order to reach code execution. |
2021-05-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-3548
MISC |
dragonfly — dragonfly
|
An argument injection vulnerability in the Dragonfly gem before 1.4.0 for Ruby allows remote attackers to read and write to arbitrary files via a crafted URL when the verify_url option is disabled. This may lead to code execution. The problem occurs because the generate and process features mishandle use of the ImageMagick convert utility. |
2021-05-29 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-33564
MISC
MISC
MISC
MISC
MISC
MISC |
edgemax — edgerouter
|
A vulnerability found in EdgeMAX EdgeRouter V2.0.9 and earlier could allow a malicious actor to execute a man-in-the-middle (MitM) attack during a firmware update. This vulnerability is fixed in EdgeMAX EdgeRouter V2.0.9-hotfix.1 and later. |
2021-05-27 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-22909
MISC |
| envoy — envoy |
### Impact _What kind of vulnerability is it? Who is impacted?_ The vulnerable component could be crashed when the configuration file is intentionally/ unintentionally containing the special characters. All the applications which are using could fail to generate their dlt logs in system. ### Patches _Has the problem been patched? What versions should users upgrade to?_ There is solution for the problem but the patch is not integrated yet. ### Workarounds _Is there a way for users to fix or remediate the vulnerability without upgrading?_ Check the integrity of information in configuration file manually. ### References _Are there any links users can visit to find out more?_ N/A ### For more information If you have any questions or comments about this advisory: * Open an issue in [ GENIVI/dlt-daemon ](https://github.com/GENIVI/dlt-daemon/issues) * Email us at [Mailinglist](mailto:https://lists.genivi.org/mailman/listinfo/genivi-diagnostic-log-and-trace_lists.genivi.org) |
2021-05-28 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-29507
CONFIRM |
envoy — envoy
|
### Impact The vulnerability may allow a remote attacker has sufficient rights to execute commands of the host only by manipulating the processed input stream. No user is affected, who followed the recommendation to setup XStream’s security framework with a whitelist limited to the minimal required types. ### Patches If you rely on XStream’s default blacklist of the Security Framework, you will have to use at least version 1.4.17. ### Workarounds See [workarounds](https://x-stream.github.io/security.html#workaround) for the different versions covering all CVEs. ### References See full information about the nature of the vulnerability and the steps to reproduce it in XStream’s documentation for [CVE-2021-xxxxx](https://x-stream.github.io/CVE-2021-xxxxx.html). ### Credits V3geB1rd, white hat hacker from Tencent Security Response Center found and reported the issue to XStream and provided the required information to reproduce it. ### For more information If you have any questions or comments about this advisory: * Open an issue in [XStream](https://github.com/x-stream/xstream/issues) * Email us at [XStream Google Group](https://groups.google.com/group/xstream-user) |
2021-05-28 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-29505
CONFIRM |
envoy — envoy
|
### Description Envoy does not decode escaped slash sequences `%2F` and `%5C` in HTTP URL paths in versions 1.18.2 and before. A remote attacker may craft a path with escaped slashes, e.g. `/something%2F..%2Fadmin`, to bypass access control, e.g. a block on `/admin`. A backend server could then decode slash sequences and normalize path and provide an attacker access beyond the scope provided for by the access control policy. ### Impact Escalation of Privileges when using RBAC or JWT filters with enforcement based on URL path. Users with back end servers that interpret `%2F` and `/` and `%5C` and “ interchangeably are impacted. ### Attack Vector URL paths containing escaped slash characters delivered by untrusted client. ### Patches Envoy versions 1.18.3, 1.17.3, 1.16.4, 1.15.5 contain new path normalization option to decode escaped slash characters. ### Workarounds If back end servers treat `%2F` and `/` and `%5C` and “ interchangeably and a URL path based access control is configured, we recommend reconfiguring back end server to not treat `%2F` and `/` and `%5C` and “ interchangeably if feasible. ### Credit Ruilin Yang (ruilin.yrl@gmail.com) ### References https://blog.envoyproxy.io https://github.com/envoyproxy/envoy/releases ### For more information If you have any questions or comments about this advisory: * Open an issue in [Envoy repo](https://github.com/envoyproxy/envoy/issues) * Email us at [envoy-security](mailto:envoy-security@googlegroups.com) |
2021-05-28 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-29492
CONFIRM |
ettercap — ettercap
|
The gtkui_conf_read function in src/interfaces/gtk/ec_gtk_conf.c in Ettercap 0.7.3, when the GTK interface is used, does not ensure that the contents of the .ettercap_gtk file are controlled by the root user, which allows local users to conduct stack-based buffer overflow attacks and possibly execute arbitrary code, cause a denial of service (memory consumption), or possibly have unspecified other impact via crafted lines in this file. |
2021-05-28 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2010-3843
MISC
MISC
MISC
MISC
MISC
MISC
MISC |
fc5 — fc5
|
Mounting /proc filesystem via chroot command silently mounts it in read-write mode. The user could bypass the chroot environment and gain write access to files, he would never have otherwise. |
2021-05-27 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2008-2544
MISC |
| ffmpeg — ffmpeg |
A heap-based Buffer Overflow vulnerability exists FFmpeg 4.2 at libavfilter/vf_edgedetect.c in gaussian_blur, which might lead to memory corruption and other potential consequences. |
2021-05-27 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-22032
MISC |
| ffmpeg — ffmpeg |
Buffer Overflow vulnerability in FFmpeg 4.2 at convolution_y_10bit in libavfilter/vf_vmafmotion.c, which could let a remote malicious user cause a Denial of Service. |
2021-05-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-22019
MISC |
| ffmpeg — ffmpeg |
A heap-based Buffer Overflow vulnerability exits in FFmpeg 4.2 in deflate16 at libavfilter/vf_neighbor.c, which might lead to memory corruption and other potential consequences. |
2021-05-27 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-22027
MISC
MISC |
| ffmpeg — ffmpeg |
A heap-based Buffer Overflow vulnerabililty exists in FFmpeg 4.2 in filter_frame at libavfilter/vf_bitplanenoise.c, which might lead to memory corruption and other potential consequences. |
2021-05-27 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-22023
MISC |
ffmpeg — ffmpeg
|
A heap-based Buffer Overflow vulnerability exists in FFmpeg 4.2 at ff_fill_rectangle in libavfilter/drawutils.c, which might lead to memory corruption and other potential consequences. |
2021-05-27 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-22017
MISC |
ffmpeg — ffmpeg
|
Buffer Overflow vulnerability in FFmpeg 4.2 at the lagfun_frame16 function in libavfilter/vf_lagfun.c, which could let a remote malicious user cause Denial of Service. |
2021-05-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-22024
MISC |
ffmpeg — ffmpeg
|
Buffer Overflow vulnerability in FFmpeg 4.2 in the build_diff_map function in libavfilter/vf_fieldmatch.c, which could let a remote malicious user cause a Denial of Service. |
2021-05-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-22020
MISC
MISC |
ffmpeg — ffmpeg
|
Buffer Overflow vulnerability in FFmpeg 4.2 at filter_edges function in libavfilter/vf_yadif.c, which could let a remote malicious user cause a Denial of Service. |
2021-05-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-22021
MISC |
ffmpeg — ffmpeg
|
A heap-based Buffer Overflow vulnerability exists in FFmpeg 4.2 in filter_frame at libavfilter/vf_fieldorder.c, which might lead to memory corruption and other potential consequences. |
2021-05-27 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-22022
MISC |
ffmpeg — ffmpeg
|
Buffer Overflow vulnerability exists in FFmpeg 4.2 in the config_input function at libavfilter/af_tremolo.c, which could let a remote malicious user cause a Denial of Service. |
2021-05-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-22026
MISC |
ffmpeg — ffmpeg
|
A heap-based Buffer Overflow vulnerability exists in gaussian_blur at libavfilter/vf_edgedetect.c, which might lead to memory corruption and other potential consequences. |
2021-05-27 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-22025
MISC |
ffmpeg — ffmpeg
|
Buffer Overflow vulnerability in FFmpeg 4.2 in mov_write_video_tag due to the out of bounds in libavformat/movenc.c, which could let a remote malicious user obtain sensitive information, cause a Denial of Service, or execute arbitrary code. |
2021-05-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-22015
MISC |
ffmpeg — ffmpeg
|
Buffer Overflow vulnerability exists in FFmpeg 4.2 in filter_vertically_8 at libavfilter/vf_avgblur.c, which could cause a remote Denial of Service. |
2021-05-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-22028
MISC |
ffmpeg — ffmpeg
|
A heap-based Buffer Overflow vulnerability exists in FFmpeg 4.2 at libavfilter/vf_colorconstancy.c: in slice_get_derivative, which crossfade_samples_fltp, which might lead to memory corruption and other potential consequences. |
2021-05-27 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-22029
MISC
MISC |
ffmpeg — ffmpeg
|
A heap-based Buffer Overflow vulnerability exists in FFmpeg 4.2 at libavfilter/af_afade.c in crossfade_samples_fltp, which might lead to memory corruption and other potential consequences. |
2021-05-27 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-22030
MISC |
ffmpeg — ffmpeg
|
A Heap-based Buffer Overflow vulnerability exists in FFmpeg 4.2 at libavfilter/vf_w3fdif.c in filter16_complex_low, which might lead to memory corruption and other potential consequences. |
2021-05-27 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-22031
MISC
MISC |
ffmpeg — ffmpeg
|
A heap-based Buffer Overflow vulnerability in FFmpeg 4.2 at libavcodec/get_bits.h when writing .mov files, which might lead to memory corruption and other potential consequences. |
2021-05-27 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-22016
MISC |
figdev — figdev
|
An Out of Bounds flaw was found fig2dev version 3.2.8a. A flawed bounds check in read_objects() could allow an attacker to provide a crafted malicious input causing the application to either crash or in some cases cause memory corruption. The highest threat from this vulnerability is to integrity as well as system availability. |
2021-05-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-3561
MISC
MISC
MISC |
freebsd — multiple_products
|
In FreeBSD 13.0-STABLE before n245764-876ffe28796c, 12.2-STABLE before r369857, 13.0-RELEASE before p1, and 12.2-RELEASE before p7, a system call triggering a fault could cause SMAP protections to be disabled for the duration of the system call. This weakness could be combined with other kernel bugs to craft an exploit. |
2021-05-28 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-29628
MISC |
freebsd — multiple_products
|
In FreeBSD 13.0-STABLE before n245765-bec0d2c9c841, 12.2-STABLE before r369859, 11.4-STABLE before r369866, 13.0-RELEASE before p1, 12.2-RELEASE before p7, and 11.4-RELEASE before p10, missing message validation in libradius(3) could allow malicious clients or servers to trigger denial of service in vulnerable servers or clients respectively. |
2021-05-28 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-29629
MISC |
frontier — ichris
|
Frontier ichris through 5.18 mishandles making a DNS request for the hostname in the HTTP Host header, as demonstrated by submitting 127.0.0.1 multiple times for DoS. |
2021-05-29 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-31702
MISC |
frontier — ichris
|
Frontier ichris through 5.18 allows users to upload malicious executable files that might later be downloaded and run by any client user. |
2021-05-29 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-31703
MISC |
fusioncompute — fusioncompute
|
There is an insufficient input validation vulnerability in FusionCompute 8.0.0. Due to the input validation is insufficient, an attacker can exploit this vulnerability to upload any files to the device. Successful exploit may cause the service abnormal. |
2021-05-27 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-22358
MISC |
gama — gama
|
A NULL-pointer deference issue was discovered in GNU_gama::set() in ellipsoid.h in Gama 2.04 which can lead to a denial of service (DOS) via segment faults caused by crafted inputs. |
2021-05-28 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-18395
MISC |
gattlib — gattlib
|
GattLib 0.3-rc1 has a stack-based buffer over-read in get_device_path_from_mac in dbus/gattlib.c. |
2021-05-27 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-33590
MISC |
gdk-pixbuf — gdk-pixbuf
|
A flaw was found in gdk-pixbuf in versions before 2.42.0. An integer wraparound leading to an out of bounds write can occur when a crafted GIF image is loaded. An attacker may cause applications to crash or could potentially execute code on the victim system. The highest threat from this vulnerability is to data confidentiality and integrity as well as system availability. |
2021-05-28 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-20240
MISC
FEDORA
FEDORA
FEDORA |
github — codeql
|
Github’s CodeQL action is provided to run CodeQL-based code scanning on non-GitHub CI/CD systems and requires a GitHub access token to connect to a GitHub repository. The runner and its documentation previously suggested passing the GitHub token as a command-line parameter to the process instead of reading it from a file, standard input, or an environment variable. This approach made the token visible to other processes on the same machine, for example in the output of the `ps` command. If the CI system publicly exposes the output of `ps`, for example by logging the output, then the GitHub access token can be exposed beyond the scope intended. Users of the CodeQL runner on 3rd-party systems, who are passing a GitHub token via the `–github-auth` flag, are affected. This applies to both GitHub.com and GitHub Enterprise users. Users of the CodeQL Action on GitHub Actions are not affected. The `–github-auth` flag is now considered insecure and deprecated. The undocumented `–external-repository-token` flag has been removed. To securely provide a GitHub access token to the CodeQL runner, users should **do one of the following instead**: Use the `–github-auth-stdin` flag and pass the token on the command line via standard input OR set the `GITHUB_TOKEN` environment variable to contain the token, then call the command without passing in the token. The old flag remains present for backwards compatibility with existing workflows. If the user tries to specify an access token using the `–github-auth` flag, there is a deprecation warning printed to the terminal that directs the user to one of the above options. All CodeQL runner releases codeql-bundle-20210304 onwards contain the patches. We recommend updating to a recent version of the CodeQL runner, storing a token in your CI system’s secret storage mechanism, and passing the token to the CodeQL runner using `–github-auth-stdin` or the `GITHUB_TOKEN` environment variable. If still using the old flag, ensure that process output, such as from `ps`, is not persisted in CI logs. |
2021-05-25 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-32638
CONFIRM
MISC
MISC
MISC
MISC |
github — dexidp_dex_library
|
A vulnerability exists in the SAML connector of the github.com/dexidp/dex library used to process SAML Signature Validation. This flaw allows an attacker to bypass SAML authentication. The highest threat from this vulnerability is to confidentiality, integrity, as well as system availability. This flaw affects dex versions before 2.27.0. |
2021-05-28 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-27847
MISC
MISC
MISC |
glpi — glpi
|
GLPi 9.5.4 does not sanitize the metadata. This way its possible to insert XSS into plugins to execute JavaScript code. |
2021-05-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-3486
MISC
MISC
MISC |
gnu_c_library — gnu_c_library
|
The mq_notify function in the GNU C Library (aka glibc) through 2.33 has a use-after-free. It may use the notification thread attributes object (passed through its struct sigevent parameter) after it has been freed by the caller, leading to a denial of service (application crash) or possibly unspecified other impact. |
2021-05-25 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-33574
MISC |
| go — go |
Go through 1.15.12 and 1.16.x through 1.16.4 has a golang.org/x/net/html infinite loop via crafted ParseFragment input. |
2021-05-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-33194
CONFIRM |
go — go
|
net/http in Go before 1.15.12 and 1.16.x before 1.16.4 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (panic) via a large header to ReadRequest or ReadResponse. Server, Transport, and Client can each be affected in some configurations. |
2021-05-27 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-31525
MISC
MISC |
| hewlett_packard_enterprises — multiple_products |
A remote xss vulnerability was discovered in HPE Integrated Lights-Out 4 (iLO 4); HPE SimpliVity 380 Gen9; HPE Integrated Lights-Out 5 (iLO 5) for HPE Gen10 Servers; HPE SimpliVity 380 Gen10; HPE SimpliVity 2600; HPE SimpliVity 380 Gen10 G; HPE SimpliVity 325; HPE SimpliVity 380 Gen10 H version(s): Prior to version 2.78. |
2021-05-25 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-29211
MISC |
| hewlett_packard_enterprises — multiple_products |
A remote dom xss, crlf injection vulnerability was discovered in HPE Integrated Lights-Out 4 (iLO 4); HPE SimpliVity 380 Gen9; HPE Integrated Lights-Out 5 (iLO 5) for HPE Gen10 Servers; HPE SimpliVity 380 Gen10; HPE SimpliVity 2600; HPE SimpliVity 380 Gen10 G; HPE SimpliVity 325; HPE SimpliVity 380 Gen10 H version(s): Prior to version 2.78. |
2021-05-25 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-29208
MISC |
| hewlett_packard_enterprises — multiple_products |
A remote xss vulnerability was discovered in HPE Integrated Lights-Out 4 (iLO 4); HPE SimpliVity 380 Gen9; HPE Integrated Lights-Out 5 (iLO 5) for HPE Gen10 Servers; HPE SimpliVity 380 Gen10; HPE SimpliVity 2600; HPE SimpliVity 380 Gen10 G; HPE SimpliVity 325; HPE SimpliVity 380 Gen10 H version(s): Prior to version 2.78. |
2021-05-25 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-29205
MISC |
hewlett_packard_enterprises — multiple_products
|
A remote dom xss, crlf injection vulnerability was discovered in HPE Integrated Lights-Out 4 (iLO 4); HPE SimpliVity 380 Gen9; HPE Integrated Lights-Out 5 (iLO 5) for HPE Gen10 Servers; HPE SimpliVity 380 Gen10; HPE SimpliVity 2600; HPE SimpliVity 380 Gen10 G; HPE SimpliVity 325; HPE SimpliVity 380 Gen10 H version(s): Prior to version 2.78. |
2021-05-25 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-29210
MISC |
hewlett_packard_enterprises — multiple_products
|
A remote dom xss, crlf injection vulnerability was discovered in HPE Integrated Lights-Out 4 (iLO 4); HPE SimpliVity 380 Gen9; HPE Integrated Lights-Out 5 (iLO 5) for HPE Gen10 Servers; HPE SimpliVity 380 Gen10; HPE SimpliVity 2600; HPE SimpliVity 380 Gen10 G; HPE SimpliVity 325; HPE SimpliVity 380 Gen10 H version(s): Prior to version 2.78. |
2021-05-25 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-29209
MISC |
hewlett_packard_enterprises — multiple_products
|
A remote xss vulnerability was discovered in HPE Integrated Lights-Out 4 (iLO 4); HPE SimpliVity 380 Gen9; HPE Integrated Lights-Out 5 (iLO 5) for HPE Gen10 Servers; HPE SimpliVity 380 Gen10; HPE SimpliVity 2600; HPE SimpliVity 380 Gen10 G; HPE SimpliVity 325; HPE SimpliVity 380 Gen10 H version(s): Prior to version 2.78. |
2021-05-25 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-29206
MISC |
hewlett_packard_enterprises — multiple_products
|
A remote xss vulnerability was discovered in HPE Integrated Lights-Out 4 (iLO 4); HPE SimpliVity 380 Gen9; HPE Integrated Lights-Out 5 (iLO 5) for HPE Gen10 Servers; HPE SimpliVity 380 Gen10; HPE SimpliVity 2600; HPE SimpliVity 380 Gen10 G; HPE SimpliVity 325; HPE SimpliVity 380 Gen10 H version(s): Prior to version 2.78. |
2021-05-25 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-29207
MISC |
hewlett_packard_enterprises — multiple_products
|
A local buffer overflow vulnerability was discovered in HPE Integrated Lights-Out 4 (iLO 4); HPE SimpliVity 380 Gen9; HPE Integrated Lights-Out 5 (iLO 5) for HPE Gen10 Servers; HPE SimpliVity 380 Gen10; HPE SimpliVity 2600; HPE SimpliVity 380 Gen10 G; HPE SimpliVity 325; HPE SimpliVity 380 Gen10 H version(s): Prior to version 2.78. |
2021-05-25 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-29202
MISC |
hewlett_packard_enterprises — multiple_products
|
A remote xss vulnerability was discovered in HPE Integrated Lights-Out 4 (iLO 4); HPE SimpliVity 380 Gen9; HPE Integrated Lights-Out 5 (iLO 5) for HPE Gen10 Servers; HPE SimpliVity 380 Gen10; HPE SimpliVity 2600; HPE SimpliVity 380 Gen10 G; HPE SimpliVity 325; HPE SimpliVity 380 Gen10 H version(s): Prior to version 2.78. |
2021-05-25 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-29201
MISC |
hewlett_packard_enterprises — multiple_products
|
A remote xss vulnerability was discovered in HPE Integrated Lights-Out 4 (iLO 4); HPE SimpliVity 380 Gen9; HPE Integrated Lights-Out 5 (iLO 5) for HPE Gen10 Servers; HPE SimpliVity 380 Gen10; HPE SimpliVity 2600; HPE SimpliVity 380 Gen10 G; HPE SimpliVity 325; HPE SimpliVity 380 Gen10 H version(s): Prior to version 2.78. |
2021-05-25 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-29204
MISC |
http4s — http4s
|
Http4s is a Scala interface for HTTP services. `StaticFile.fromUrl` can leak the presence of a directory on a server when the `URL` scheme is not `file://`, and the URL points to a fetchable resource under its scheme and authority. The function returns `F[None]`, indicating no resource, if `url.getFile` is a directory, without first checking the scheme or authority of the URL. If a URL connection to the scheme and URL would return a stream, and the path in the URL exists as a directory on the server, the presence of the directory on the server could be inferred from the 404 response. The contents and other metadata about the directory are not exposed. This affects http4s versions: 0.21.7 through 0.21.23, 0.22.0-M1 through 0.22.0-M8, 0.23.0-M1, and 1.0.0-M1 through 1.0.0-M22. The [patch](https://github.com/http4s/http4s/commit/52e1890665410b4385e37b96bc49c5e3c708e4e9) is available in the following versions: v0.21.24, v0.22.0-M9, v0.23.0-M2, v1.0.0-M23. As a workaround users can avoid calling `StaticFile.fromUrl` with non-file URLs. |
2021-05-27 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-32643
CONFIRM
MISC
MISC |
huawei — mate_30
|
There is a denial of service vulnerability in the versions 10.1.0.126(C00E125R5P3) of HUAWEI Mate 30 and 10.1.0.152(C00E136R7P2) of HUAWEI Mate 30 (5G) . A module does not verify certain parameters sufficiently and it leads to some exceptions. Successful exploit could cause a denial of service condition. |
2021-05-27 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-22364
MISC |
huawei — multiple_products
|
There is an out-of-bounds write vulnerability in some Huawei products. The code of a module have a bad judgment logic. Attackers can exploit this vulnerability by performing multiple abnormal activities to trigger the bad logic and cause out-of-bounds write. This may compromise the normal service of the module.Affected product versions include: NGFW Module versions V500R005C00SPC100,V500R005C00SPC200;Secospace USG6300 versions V500R001C30SPC200,V500R001C30SPC600,V500R001C60SPC500,V500R005C00SPC100,V500R005C00SPC200;Secospace USG6500 versions V500R001C30SPC200,V500R001C30SPC600,V500R001C60SPC500,V500R005C00SPC100,V500R005C00SPC200;Secospace USG6600 versions V500R001C30SPC200,V500R001C30SPC600,V500R001C60SPC500,V500R005C00SPC100,V500R005C00SPC200;USG9500 versions V500R001C60SPC500,V500R005C00SPC100,V500R005C00SPC200. |
2021-05-27 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-22411
MISC |
huawei — multiple_products
|
There is a resource management error vulnerability in the verisions V500R001C60SPC500, V500R005C00SPC100, V500R005C00SPC200 of USG9500. An authentication attacker needs to perform specific operations to exploit the vulnerability on the affected device. Due to improper resource management of the function, the vulnerability can be exploited to cause service abnormal on affected devices. |
2021-05-27 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-22360
MISC |
huawei — multiple_products
|
There is an out of bounds write vulnerability in some Huawei products. An attacker can exploit this vulnerability by sending crafted data in the packet to the target device. Due to insufficient validation of message, successful exploit can cause certain service abnormal.Affected product versions include:CloudEngine 12800 versions V200R002C50SPC800,V200R003C00SPC810,V200R005C00SPC800,V200R005C10SPC800,V200R019C00SPC800,V200R019C10SPC800;CloudEngine 5800 versions V200R002C50SPC800,V200R003C00SPC810,V200R005C00SPC800,V200R005C10SPC800,V200R019C00SPC800,V200R019C10SPC800@;CloudEngine 6800 versions V200R002C50SPC800,V200R003C00SPC810,V200R005C00SPC800,V200R005C10SPC800,V200R005C20SPC800,V200R019C00SPC800,V200R019C10SPC800;CloudEngine 7800 versions V200R002C50SPC800,V200R003C00SPC810,V200R005C00SPC800,V200R005C10SPC800,V200R019C00SPC800,V200R019C10SPC800. |
2021-05-27 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-22362
MISC |
huawei — s5700_and_s6700_devices
|
There is a denial of service vulnerability in the verisions V200R005C00SPC500 of S5700 and V200R005C00SPC500 of S6700. An attacker could exploit this vulnerability by sending specific message to a targeted device. Due to insufficient input validation, successful exploit can cause the service abnormal. |
2021-05-27 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-22359
MISC |
hyerkitty — hyperkitty
|
An issue was discovered in management/commands/hyperkitty_import.py in HyperKitty through 1.3.4. When importing a private mailing list’s archives, these archives are publicly visible for the duration of the import. For example, sensitive information might be available on the web for an hour during a large migration from Mailman 2 to Mailman 3. |
2021-05-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-33038
CONFIRM
CONFIRM
DEBIAN |
ibm — cloud_pak
|
IBM Cloud Pak for Data 3.0 could allow an authenticated user to obtain sensitive information when installed with additional plugins. IBM X-Force ID: 197668. |
2021-05-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-20486
CONFIRM
XF |
ibm — dd2
|
IBM Db2 for Linux, UNIX and Windows (includes Db2 Connect Server) 9.7, 10.1, 10.5, 11.1, and 11.5 could allow a local user to execute arbitrary code and conduct DLL hijacking attacks. |
2021-05-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2019-4588
XF
CONFIRM |
ibm — host_firmware
|
IBM Host firmware for LC-class Systems could allow a remote attacker to traverse directories on the system. An attacker could send a specially-crafted URL request that would allow them to delete arbitrary files on the system. IBM X-Force ID: 200558. |
2021-05-25 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-29695
CONFIRM
XF |
ibm — power9_self_boot_engine
|
IBM Power9 Self Boot Engine(SBE) could allow a privileged user to inject malicious code and compromise the integrity of the host firmware bypassing the host firmware signature verification process. |
2021-05-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-20487
CONFIRM
XF |
ibm — spectrum_scale
|
IBM Spectrum Scale 5.1.0.1 could allow a local with access to the GUI pod container to obtain sensitive cryptographic keys that could allow them to elevate their privileges. IBM X-Force ID: 200883. |
2021-05-25 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-29708
XF
CONFIRM |
ibm — websphere_applcation_server
|
IBM WebSphere Application Server 8.0, 8.5, 9.0, and Liberty Java Batch is vulnerable to an XML External Entity Injection (XXE) attack when processing XML data. A remote attacker could exploit this vulnerability to expose sensitive information or consume memory resources. IBM X-Force ID: 197793. |
2021-05-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-20492
XF
CONFIRM |
icms — icms
|
A Cross Site Request Forgery (CSRF) vulnerability was discovered in iCMS 7.0.16 which can allow an attacker to execute arbitrary web scripts. |
2021-05-28 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-26641
MISC |
inspircd — inspircd
|
InspIRCd 3.8.0 through 3.9.x before 3.10.0 allows any user (able to connect to the server) to access recently deallocated memory, aka the “malformed PONG” issue. |
2021-05-27 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-33586
MISC
MISC |
isc — dhcp
|
In ISC DHCP 4.1-ESV-R1 -> 4.1-ESV-R16, ISC DHCP 4.4.0 -> 4.4.2 (Other branches of ISC DHCP (i.e., releases in the 4.0.x series or lower and releases in the 4.3.x series) are beyond their End-of-Life (EOL) and no longer supported by ISC. From inspection it is clear that the defect is also present in releases from those series, but they have not been officially tested for the vulnerability), The outcome of encountering the defect while reading a lease that will trigger it varies, according to: the component being affected (i.e., dhclient or dhcpd) whether the package was built as a 32-bit or 64-bit binary whether the compiler flag -fstack-protection-strong was used when compiling In dhclient, ISC has not successfully reproduced the error on a 64-bit system. However, on a 32-bit system it is possible to cause dhclient to crash when reading an improper lease, which could cause network connectivity problems for an affected system due to the absence of a running DHCP client process. In dhcpd, when run in DHCPv4 or DHCPv6 mode: if the dhcpd server binary was built for a 32-bit architecture AND the -fstack-protection-strong flag was specified to the compiler, dhcpd may exit while parsing a lease file containing an objectionable lease, resulting in lack of service to clients. Additionally, the offending lease and the lease immediately following it in the lease database may be improperly deleted. if the dhcpd server binary was built for a 64-bit architecture OR if the -fstack-protection-strong compiler flag was NOT specified, the crash will not occur, but it is possible for the offending lease and the lease which immediately followed it to be improperly deleted. |
2021-05-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-25217
CONFIRM |
istio — istio
|
Istio before 1.8.6 and 1.9.x before 1.9.5 has a remotely exploitable vulnerability where an HTTP request path with multiple slashes or escaped slash characters (%2F or %5C) could potentially bypass an Istio authorization policy when path based authorization rules are used. |
2021-05-27 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-31920
CONFIRM |
jakarta — expression_language
|
In the Jakarta Expression Language implementation 3.0.3 and earlier, a bug in the ELParserTokenManager enables invalid EL expressions to be evaluated as if they were valid. |
2021-05-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-28170
CONFIRM
CONFIRM |
jenkins — filesystem_trigger_plugin
|
Jenkins Filesystem Trigger Plugin 0.40 and earlier does not configure its XML parser to prevent XML external entity (XXE) attacks. |
2021-05-25 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-21657
CONFIRM
MLIST |
jenkins — markdown_formatter_plugin
|
Jenkins Markdown Formatter Plugin 0.1.0 and earlier does not sanitize crafted link target URLs, resulting in a stored cross-site scripting (XSS) vulnerability exploitable by attackers with the ability to edit any description rendered using the configured markup formatter. |
2021-05-25 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-21660
CONFIRM
MISC
MLIST |
jenkins — nuget_plugin
|
Jenkins Nuget Plugin 1.0 and earlier does not configure its XML parser to prevent XML external entity (XXE) attacks. |
2021-05-25 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-21658
CONFIRM
MLIST |
jitsi — meet
|
jitsi-meet-prosody in Jitsi Meet before 5026 does not ensure that restrict_room_creation is set by default. |
2021-05-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-33506
CONFIRM
MISC |
js-extend — js-extend
|
Prototype pollution vulnerability in ‘js-extend’ versions 0.0.1 through 1.0.1 allows attacker to cause a denial of service and may lead to remote code execution. |
2021-05-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-25945
MISC |
json — web_token
|
A flaw was found in ceph-dashboard. The JSON Web Token (JWT) used for user authentication is stored by the frontend application in the browser’s localStorage which is potentially vulnerable to attackers via XSS attacks. The highest threat from this vulnerability is to data confidentiality and integrity. |
2021-05-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-27839
MISC |
keycloak — keycloak
|
A flaw was found in keycloak in versions before 13.0.0. A Self Stored XSS attack vector escalating to a complete account takeover is possible due to user-supplied data fields not being properly encoded and Javascript code being used to process the data. The highest threat from this vulnerability is to data confidentiality and integrity as well as system availability. |
2021-05-28 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-20195
MISC |
keycloak — keycloak
|
A flaw was found in Keycloak before version 12.0.0 where it is possible to update the user’s metadata attributes using Account REST API. This flaw allows an attacker to change its own NameID attribute to impersonate the admin user for any particular application. |
2021-05-28 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-27826
MISC |
kiali — kiali
|
An authentication bypass vulnerability was found in Kiali in versions before 1.31.0 when the authentication strategy `OpenID` is used. When RBAC is enabled, Kiali assumes that some of the token validation is handled by the underlying cluster. When OpenID `implicit flow` is used with RBAC turned off, this token validation doesn’t occur, and this allows a malicious user to bypass the authentication. |
2021-05-28 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-20278
MISC
MISC |
koel — koel
|
Koel before 5.1.4 lacks login throttling, lacks a password strength policy, and shows whether a failed login attempt had a valid username. This might make brute-force attacks easier. |
2021-05-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-33563
MISC
MISC |
kubevirt — kubevirt
|
A flaw was found in the KubeVirt main virt-handler versions before 0.26.0 regarding the access permissions of virt-handler. An attacker with access to create VMs could attach any secret within their namespace, allowing them to read the contents of that secret. |
2021-05-27 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-1701
MISC |
| libcaca — libcaca |
A flaw was found in libcaca. A buffer overflow of export.c in function export_troff might lead to memory corruption and other potential consequences. |
2021-05-27 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-30499
MISC
MISC |
libcaca — libcaca
|
A flaw was found in libcaca. A heap buffer overflow in export.c in function export_tga might lead to memory corruption and other potential consequences. |
2021-05-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-30498
MISC
MISC |
libgrss — libgrss
|
libgrss through 0.7.0 fails to perform TLS certificate verification when downloading feeds, allowing remote attackers to manipulate the contents of feeds without detection. This occurs because of the default behavior of SoupSessionSync. |
2021-05-25 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2016-20011
MISC
MISC |
libvirt — libvirt
|
An information disclosure vulnerability was found in libvirt in versions before 6.3.0. HTTP cookies used to access network-based disks were saved in the XML dump of the guest domain. This flaw allows an attacker to access potentially sensitive information in the domain configuration via the `dumpxml` command. |
2021-05-27 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-14301
MISC |
libvirt — virconnectlistallnodedevices
|
A flaw was found in libvirt in the virConnectListAllNodeDevices API in versions before 7.0.0. It only affects hosts with a PCI device and driver that supports mediated devices (e.g., GRID driver). This flaw could be used by an unprivileged client with a read-only connection to crash the libvirt daemon by executing the ‘nodedev-list’ virsh command. The highest threat from this vulnerability is to system availability. |
2021-05-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-3559
MISC |
| linux — linux_kernel |
A vulnerability was found in Linux kernel where non-blocking socket in llcp_sock_connect() leads to leak and eventually hanging-up the system. |
2021-05-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-25673
FEDORA
MLIST
FEDORA
MISC
FEDORA |
| linux — linux_kernel |
A vulnerability was found in Linux Kernel where refcount leak in llcp_sock_bind() causing use-after-free which might lead to privilege escalations. |
2021-05-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-25670
FEDORA
MLIST
FEDORA
MLIST
MISC
FEDORA |
linux — linux_kernel
|
A memory disclosure flaw was found in the Linux kernel’s versions before 4.18.0-193.el8 in the sysctl subsystem when reading the /proc/sys/kernel/rh_features file. This flaw allows a local user to read uninitialized values from the kernel memory. The highest threat from this vulnerability is to confidentiality. |
2021-05-27 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-10774
MISC |
linux — linux_kernel
|
A vulnerability was found in the Linux Kernel where the function sunkbd_reinit having been scheduled by sunkbd_interrupt before sunkbd being freed. Though the dangling pointer is set to NULL in sunkbd_disconnect, there is still an alias in sunkbd_reinit causing Use After Free. |
2021-05-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-25669
MISC
MLIST
MLIST
MLIST
MLIST
MISC
MISC |
linux — linux_kernel
|
kernel/bpf/verifier.c in the Linux kernel through 5.12.7 enforces incorrect limits for pointer arithmetic operations, aka CID-bb01a1bba579. This can be abused to perform out-of-bounds reads and writes in kernel memory, leading to local privilege escalation to root. In particular, there is a corner case where the off reg causes a masking direction change, which then results in an incorrect final aux->alu_limit. |
2021-05-27 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-33200
MISC |
linux — linux_kernel
|
A flaw was found in Linux Kernel because access to the global variable fg_console is not properly synchronized leading to a use after free in con_font_op. |
2021-05-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-25668
MLIST
MLIST
MISC
MISC
MLIST
MISC
MLIST
MISC |
linux — linux_kernel
|
A flaw was found in the JFS filesystem code in the Linux Kernel which allows a local attacker with the ability to set extended attributes to panic the system, causing memory corruption or escalating privileges. The highest threat from this vulnerability is to confidentiality, integrity, as well as system availability. |
2021-05-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-27815
MISC
MISC
MLIST
MISC
DEBIAN
MISC
MLIST
MLIST
MLIST |
linux — linux_kernel
|
A flaw was found in the Linux kernel’s implementation of string matching within a packet. A privileged user (with root or CAP_NET_ADMIN) when inserting iptables rules could insert a rule which can panic the system. Kernel before kernel 5.5-rc1 is affected. |
2021-05-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-20177
MISC |
linux — linux_kernel
|
An issue was discovered in the Linux: KVM through Improper handling of VM_IO|VM_PFNMAP vmas in KVM can bypass RO checks and can lead to pages being freed while still accessible by the VMM and guest. This allows users with the ability to start and control a VM to read/write random pages of memory and can result in local privilege escalation. |
2021-05-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-22543
MISC
MLIST
MLIST
MLIST |
linux — linux_kernel
|
There is a flaw reported in the Linux kernel in versions before 5.9 in drivers/gpu/drm/nouveau/nouveau_sgdma.c in nouveau_sgdma_create_ttm in Nouveau DRM subsystem. The issue results from the lack of validating the existence of an object prior to performing operations on the object. An attacker with a local account with a root privilege, can leverage this vulnerability to escalate privileges and execute code in the context of the kernel. |
2021-05-28 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-20292
MISC |
linux — linux_kernel
|
A flaw was found in the Linux kernel in versions before 5.4.92 in the BPF protocol. This flaw allows an attacker with a local account to leak information about kernel internal addresses. The highest threat from this vulnerability is to confidentiality. |
2021-05-28 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-20239
MISC |
linux — linux_kernel
|
A vulnerability was found in Linux Kernel, where a refcount leak in llcp_sock_connect() causing use-after-free which might lead to privilege escalations. |
2021-05-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-25671
FEDORA
MLIST
FEDORA
MISC
FEDORA |
mariadb — mariadb
|
A flaw was found in the mysql-wsrep component of mariadb. Lack of input sanitization in `wsrep_sst_method` allows for command injection that can be exploited by a remote attacker to execute arbitrary commands on galera cluster nodes. This threatens the system’s confidentiality, integrity, and availability. This flaw affects mariadb versions before 10.1.47, before 10.2.34, before 10.3.25, before 10.4.15 and before 10.5.6. |
2021-05-27 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-15180
MISC
MLIST
GENTOO
CONFIRM
DEBIAN |
micro_focus — sitescope
|
Execute arbitrary code vulnerability in Micro Focus SiteScope product, affecting versions 11.40,11.41 , 2018.05(11.50), 2018.08(11.51), 2018.11(11.60), 2019.02(11.70), 2019.05(11.80), 2019.08(11.90), 2019.11(11.91), 2020.05(11.92), 2020.10(11.93). The vulnerability could allow remote attackers to execute arbitrary code on affected installations of SiteScope. |
2021-05-28 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-22519
MISC |
microsoft — windows
|
A buffer overflow vulnerability exists in Windows File Resource Profiles in 9.X allows a remote authenticated user with privileges to browse SMB shares to execute arbitrary code as the root user. As of version 9.1R3, this permission is not enabled by default. |
2021-05-27 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-22908
MISC |
modicon — m241/m251_controllers
|
Improper Input Validation vulnerability exists in Modicon M241/M251 logic controllers firmware prior to V5.1.9.1 that could cause denial of service when specific crafted requests are sent to the controller over HTTP. |
2021-05-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-22699
MISC |
modicon — managed_switch
|
Weak Password Recovery Mechanism for Forgotten Password vulnerability exists on Modicon Managed Switch MCSESM* and MCSESP* V8.21 and prior which could cause an unauthorized password change through HTTP / HTTPS when basic user information is known by a remote attacker. |
2021-05-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-22731
MISC |
modicon — modicon
|
Improper Restriction of Operations within the Bounds of a Memory Buffer vulnerability exists that could cause denial of service or unauthorized access to system information when interacting directly with a driver installed by Vijeo Designer or EcoStruxure Machine Expert |
2021-05-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-22705
MISC |
mongodb — rocket_chat
|
An information disclosure vulnerability exists in the Rocket.Chat server fixed v3.13, v3.12.2 & v3.11.3 that allowed email addresses to be disclosed by enumeration and validation checks. |
2021-05-27 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-22892
MISC |
mongodb — rocket_chat
|
A improper input sanitization vulnerability exists in Rocket.Chat server 3.11, 3.12 & 3.13 that could lead to unauthenticated NoSQL injection, resulting potentially in RCE. |
2021-05-27 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-22911
MISC |
naver — comic_viewer
|
An exposed remote debugging port in Naver Comic Viewer prior to 1.0.15.0 allowed a remote attacker to execute arbitrary code via a crafted HTML page. |
2021-05-28 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-33591
CONFIRM |
networkmanager — networkmanager
|
A flaw was found in NetworkManager in versions before 1.30.0. Setting match.path and activating a profile crashes NetworkManager. The highest threat from this vulnerability is to system availability. |
2021-05-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-20297
MISC |
nordic — semiconductor_nrf52840_devices
|
Nordic Semiconductor nRF52840 devices through 2020-10-19 have improper protection against physical side channels. The flash read-out protection (APPROTECT) can be bypassed by injecting a fault during the boot phase. |
2021-05-21 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-27211
MISC
MISC
MISC
MISC
MISC |
open — vswitch
|
A flaw was found in openstack-neutron’s default Open vSwitch firewall rules. By sending carefully crafted packets, anyone in control of a server instance connected to the virtual switch can impersonate the IPv6 addresses of other systems on the network, resulting in denial of service or in some cases possibly interception of traffic intended for other destinations. Only deployments using the Open vSwitch driver are affected. Source: OpenStack project. Versions before openstack-neutron 15.3.3, openstack-neutron 16.3.1 and openstack-neutron 17.1.1 are affected. |
2021-05-28 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-20267
MISC |
openldap — openldap
|
A flaw was found in OpenLDAP in versions before 2.4.56. This flaw allows an attacker who sends a malicious packet processed by OpenLDAP to force a failed assertion in csnNormalize23(). The highest threat from this vulnerability is to system availability. |
2021-05-28 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-25710
MLIST
MISC
DEBIAN
MISC |
| opennms — horizon |
In OpenNMS Horizon, versions opennms-17.0.0-1 through opennms-27.1.0-1; OpenNMS Meridian, versions meridian-foundation-2015.1.0-1 through meridian-foundation-2019.1.18-1; meridian-foundation-2020.1.0-1 through meridian-foundation-2020.1.7-1 are vulnerable to Stored Cross-Site Scripting, since the function `add()` performs improper validation checks on the input sent to the `foreign-source` parameter. Due to this flaw an attacker could bypass the existing regex validation and inject an arbitrary script which will be stored in the database. |
2021-05-25 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-25935
MISC
MISC
MISC |
opennms — horizon
|
In OpenNMS Horizon, versions opennms-18.0.0-1 through opennms-27.1.0-1; OpenNMS Meridian, versions meridian-foundation-2015.1.0-1 through meridian-foundation-2019.1.18-1; meridian-foundation-2020.1.0-1 through meridian-foundation-2020.1.7-1 are vulnerable to Stored Cross-Site Scripting, since the function `createRequisitionedNode()` does not perform any validation checks on the input sent to the `node-label` parameter. Due to this flaw an attacker could inject an arbitrary script which will be stored in the database. |
2021-05-25 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-25934
MISC
MISC
MISC |
openshift — openshift
|
A flaw was found in the OpenShift web console, where the access token is stored in the browser’s local storage. An attacker can use this flaw to get the access token via physical access, or an XSS attack on the victim’s browser. This flaw affects openshift/console versions before openshift/console-4. |
2021-05-27 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-1761
MISC |
openwrt — luci
|
A stored cross-site scripting (XSS) vulnerability was discovered in the Web Interface for OpenWRT LuCI version 19.07 which allows attackers to inject arbitrary Javascript in the OpenWRT Hostname via the Hostname Change operation. |
2021-05-25 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-33425
MISC |
openwrt — luci
|
The Web Interface for OpenWRT LuCI version 19.07 and lower has been discovered to have a cross-site scripting vulnerability which can lead to attackers carrying out arbitrary code execution. |
2021-05-25 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-27821
MISC
MISC |
pixar — ruby_jss_gem
|
The Pixar ruby-jss gem before 1.6.0 allows remote attackers to execute arbitrary code because of the Plist gem’s documented behavior of using Marshal.load during XML document processing. |
2021-05-25 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-33575
MISC
MISC |
pki-core — pki-core
|
A flaw was found in pki-core 10.9.0. A specially crafted POST request can be used to reflect a DOM-based cross-site scripting (XSS) attack to inject code into the search query form which can get automatically executed. The highest threat from this vulnerability is to data integrity. |
2021-05-28 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-25715
MISC |
| podofo — podofo |
A flaw was found in PoDoFo 0.9.7. A stack-based buffer overflow in PdfEncryptMD5Base::ComputeOwnerKey function in PdfEncrypt.cpp is possible because of a improper check of the keyLength value. |
2021-05-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-30472
MISC |
podofo — podofo
|
A flaw was found in PoDoFo 0.9.7. An uncontrolled recursive call among PdfTokenizer::ReadArray(), PdfTokenizer::GetNextVariant() and PdfTokenizer::ReadDataType() functions can lead to a stack overflow. |
2021-05-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-30470
MISC |
podofo — podofo
|
A flaw was found in PoDoFo 0.9.7. An uncontrolled recursive call in PdfNamesTree::AddToDictionary function in src/podofo/doc/PdfNamesTree.cpp can lead to a stack overflow. |
2021-05-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-30471
MISC |
podofo — podofo
|
A flaw was found in PoDoFo 0.9.7. An use-after-free in PoDoFo::PdfVecObjects::Clear() function can cause a denial of service via a crafted PDF file. |
2021-05-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-30469
MISC |
pon — mdu_devices
|
Some PON MDU devices of ZTE stored sensitive information in plaintext, and users with login authority can obtain it by inputing command. This affects: ZTE PON MDU device ZXA10 F821 V1.7.0P3T22, ZXA10 F822 V1.4.3T6, ZXA10 F819 V1.2.1T5, ZXA10 F832 V1.1.1T7, ZXA10 F839 V1.1.0T8, ZXA10 F809 V3.2.1T1, ZXA10 F822P V1.1.1T7, ZXA10 F832 V2.00.00.01 |
2021-05-28 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-21734
MISC |
pulse_connect_secure — pulse_connect_secure
|
A vulnerability allowed multiple unrestricted uploads in Pulse Connect Secure before 9.1R11.4 that could lead to an authenticated administrator to perform a file write via a maliciously crafted archive upload in the administrator web interface. |
2021-05-27 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-22900
MISC |
pulse_connect_secure — pulse_connect_secure
|
A command injection vulnerability exists in Pulse Connect Secure before 9.1R11.4 allows a remote authenticated attacker to perform remote code execution via Windows Resource Profiles Feature |
2021-05-27 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-22899
MISC |
pulse_connect_secure — pulse_connect_secure
|
A buffer overflow vulnerability exists in Pulse Connect Secure before 9.1R11.4 allows a remote authenticated attacker to execute arbitrary code as the root user via maliciously crafted meeting room. |
2021-05-27 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-22894
MISC |
qemu — qemu
|
A use-after-free vulnerability was found in the am53c974 SCSI host bus adapter emulation of QEMU in versions before 6.0.0 during the handling of the ‘Information Transfer’ command (CMD_TI). This flaw allows a privileged guest user to crash the QEMU process on the host, resulting in a denial of service or potential code execution with the privileges of the QEMU process. |
2021-05-28 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-35506
MLIST
MISC
MISC |
qemu — qemu
|
A NULL pointer dereference flaw was found in the SCSI emulation support of QEMU in versions before 6.0.0. This flaw allows a privileged guest user to crash the QEMU process on the host, resulting in a denial of service. The highest threat from this vulnerability is to system availability. |
2021-05-28 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-35504
MLIST
MISC
MISC |
qemu — qemu
|
A missing authorization flaw was found in the libvirt API responsible for changing the QEMU agent response timeout. This flaw allows read-only connections to adjust the time that libvirt waits for the QEMU guest agent to respond to agent commands. Depending on the timeout value that is set, this flaw can make guest agent commands fail because the agent cannot respond in time. Unprivileged users with a read-only connection could abuse this flaw to set the response timeout for all guest agent messages to zero, potentially leading to a denial of service. This flaw affects libvirt versions before 6.2.0. |
2021-05-27 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-10701
MISC |
qemu — qemu
|
A flaw was found in the USB redirector device (usb-redir) of QEMU. Small USB packets are combined into a single, large transfer request, to reduce the overhead and improve performance. The combined size of the bulk transfer is used to dynamically allocate a variable length array (VLA) on the stack without proper validation. Since the total size is not bounded, a malicious guest could use this flaw to influence the array length and cause the QEMU process to perform an excessive allocation on the stack, resulting in a denial of service. |
2021-05-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-3527
MISC
MISC
MISC
MISC |
qemu — qemu
|
A NULL pointer dereference flaw was found in the floppy disk emulator of QEMU. This issue occurs while processing read/write ioport commands if the selected floppy drive is not initialized with a block device. This flaw allows a privileged guest user to crash the QEMU process on the host, resulting in a denial of service. The highest threat from this vulnerability is to system availability. |
2021-05-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-20196
MISC
MISC |
qemu — qemu
|
An user able to alter the savevm data (either on the disk or over the wire during migration) could use this flaw to to corrupt QEMU process memory on the (destination) host, which could potentially result in arbitrary code execution on the host with the privileges of the QEMU process. |
2021-05-28 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2013-4536
MISC |
qemu — qemu
|
A NULL pointer dereference flaw was found in the am53c974 SCSI host bus adapter emulation of QEMU in versions before 6.0.0. This issue occurs while handling the ‘Information Transfer’ command. This flaw allows a privileged guest user to crash the QEMU process on the host, resulting in a denial of service. The highest threat from this vulnerability is to system availability. |
2021-05-28 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-35505
MLIST
MISC
MISC |
qnd — advance/premium/standard
|
Privilege escalation vulnerability in QND Advance/Premium/Standard Ver.11.0.4i and earlier allows an attacker who can log in to the PC where the product’s Windows client is installed to gain administrative privileges via unspecified vectors. As a result, sensitive information may be altered/obtained or unintended operations may be performed. |
2021-05-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-20713
MISC
MISC |
radsecproxy — radsecproxy
|
radsecproxy is a generic RADIUS proxy that supports both UDP and TLS (RadSec) RADIUS transports. Missing input validation in radsecproxy’s `naptr-eduroam.sh` and `radsec-dynsrv.sh` scripts can lead to configuration injection via crafted radsec peer discovery DNS records. Users are subject to Information disclosure, Denial of Service, Redirection of Radius connection to a non-authenticated server leading to non-authenticated network access. Updated example scripts are available in the master branch and 1.9 release. Note that the scripts are not part of the installation package and are not updated automatically. If you are using the examples, you have to update them manually. The dyndisc scripts work independently of the radsecproxy code. The updated scripts can be used with any version of radsecproxy. |
2021-05-28 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-32642
MISC
CONFIRM |
| red_hat — red_hat |
It has been discovered that redhat-certification does not properly limit the number of recursive definitions of entities in XML documents while parsing the status of a host. A remote attacker could use this vulnerability to consume all the memory of the server and cause a Denial of Service. This flaw affects redhat-certification version 7. |
2021-05-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2018-10868
MISC |
| red_hat — red_hat |
A flaw was found in Red Hat Quay, where it has a persistent Cross-site Scripting (XSS) vulnerability when displaying a repository’s notification. This flaw allows an attacker to trick a user into performing a malicious action to impersonate the target user. The highest threat from this vulnerability is to confidentiality, integrity, as well as system availability. |
2021-05-27 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-27832
MISC |
red_hat — red_hat
|
It has been discovered that redhat-certification does not perform an authorization check and it allows an unauthenticated user to remove a “system” file, that is an xml file with host related information, not belonging to him. This flaw affects redhat-certification version 7. |
2021-05-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2018-10866
MISC |
red_hat — red_hat
|
It has been discovered that redhat-certification does not perform an authorization check and allows an unauthenticated user to call a “restart” RPC method on any host accessible by the system. An attacker could use this flaw to send requests to port 8009 of any host or to keep restarting the RHCertD daemon on a host of another customer. This flaw affects redhat-certification version 7. |
2021-05-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2018-10865
MISC |
red_hat — red_hat
|
A flaw was found in Red Hat Ceph Storage 4, in the Dashboard component. In response to CVE-2020-27839, the JWT token was moved from localStorage to an httpOnly cookie. However, token cookies are used in the body of the HTTP response for the documentation, which again makes it available to XSS.The greatest threat to the system is for confidentiality, integrity, and availability. |
2021-05-27 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-3509
MISC
MISC
MISC
MISC
MISC |
red_hat — red_hat
|
It has been discovered that redhat-certification does not restrict file access in the /update/results page. A remote attacker could use this vulnerability to remove any file accessible by the user which is running httpd. This flaw affects redhat-certification version 7. |
2021-05-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2018-10867
MISC |
red_hat — red_hat
|
A malicious container image can consume an unbounded amount of memory when being pulled to a container runtime host, such as Red Hat Enterprise Linux using podman, or OpenShift Container Platform. An attacker can use this flaw to trick a user, with privileges to pull container images, into crashing the process responsible for pulling the image. This flaw affects containers-image versions before 5.2.0. |
2021-05-27 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-1702
MISC |
red_hat — red_hat
|
A flaw was found in Red Hat Satellite’s Job Invocation, where the “User Input” entry was not properly restricted to the view. This flaw allows a malicious Satellite user to scan through the Job Invocation, with the ability to search for passwords and other sensitive data. This flaw affects tfm-rubygem-foreman_ansible versions before 4.0.3.4. |
2021-05-27 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-10716
MISC
MISC |
red_hat — red_hat
|
A flaw was found in Red Hat Quay, where it does not properly protect the authorization token when authorizing email addresses for repository email notifications. This flaw allows an attacker to add email addresses they do not own to repository notifications. |
2021-05-27 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-27831
MISC |
red_hat — red_hat
|
A flaw was found in Red Hat 3scale’s API docs URL, where it is accessible without credentials. This flaw allows an attacker to view sensitive information or modify service APIs. Versions before 3scale-2.10.0-ER1 are affected. |
2021-05-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-25634
MISC |
red_hat — red_hat
|
An insecure modification flaw in the /etc/passwd file was found in the redhat-sso-7 container. An attacker with access to the container can use this flaw to modify the /etc/passwd and escalate their privileges. |
2021-05-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-10695
MISC |
red_hat — red_hat
|
It has been discovered that redhat-certification is not properly configured and it lists all files and directories in the /var/www/rhcert/store/transfer directory through the /rhcert-transfer URL. An unauthorized attacker may use this flaw to gather sensible information. This flaw affects redhat-certification version 7. |
2021-05-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2018-10863
MISC |
resteasy — resteasy
|
A cross-site scripting (XSS) flaw was found in RESTEasy in versions before 3.11.1.Final and before 4.5.3.Final, where it did not properly handle URL encoding when the RESTEASY003870 exception occurs. An attacker could use this flaw to launch a reflected XSS attack. |
2021-05-27 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-10688
MISC
MISC
MISC |
resteasy — resteasy
|
A flaw was found in RESTEasy, where an incorrect response to an HTTP request is provided. This flaw allows an attacker to gain access to privileged information. The highest threat from this vulnerability is to confidentiality and integrity. Versions before resteasy 2.0.0.Alpha3 are affected. |
2021-05-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-25724
MISC |
roomer — roomer
|
Roomer is a discord bot cog (extension) which provides automatic voice channel generation as well as private voice and text channels. A vulnerability has been discovered allowing discord users to get the “manage channel“ permissions in a private VC they have joined. This allowed them to make changes to or delete the voice channel they have taken over. The exploit does not allow access or control to any other channels in the server. Upgrade to version 1.0.1 for a patched version of the cog. As a workaround you may disable private VCs in your guild(server) or unload the roomer cog to render the exploit unusable. |
2021-05-28 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-32646
CONFIRM
MISC |
rsync — rsync
|
A flaw was found in rsync in versions since 3.2.0pre1. Rsync improperly validates certificate with host mismatch vulnerability. A remote, unauthenticated attacker could exploit the flaw by performing a man-in-the-middle attack using a valid certificate for another hostname which could compromise confidentiality and integrity of data transmitted using rsync-ssl. The highest threat from this vulnerability is to data confidentiality and integrity. This flaw affects rsync versions before 3.2.4. |
2021-05-27 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-14387
MISC |
ruby_on_rails — ruby_on_rails
|
A possible information disclosure / unintended method execution vulnerability in Action Pack >= 2.0.0 when using the `redirect_to` or `polymorphic_url`helper with untrusted user input. |
2021-05-27 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-22885
MISC |
runc — runc
|
runc before 1.0.0-rc95 allows a Container Filesystem Breakout via Directory Traversal. To exploit the vulnerability, an attacker must be able to create multiple containers with a fairly specific mount configuration. The problem occurs via a symlink-exchange attack that relies on a race condition. |
2021-05-27 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-30465
CONFIRM
MISC
MISC
FEDORA
FEDORA |
rust — deno
|
Deno is a runtime for JavaScript and TypeScript that uses V8 and is built in Rust. In Deno versions 1.5.0 to 1.10.1, modules that are dynamically imported through `import()` or `new Worker` might have been able to bypass network and file system permission checks when statically importing other modules. The vulnerability has been patched in Deno release 1.10.2. |
2021-05-28 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-32619
CONFIRM |
| rust — please |
please before 0.4 allows a local unprivileged attacker to gain knowledge about the existence of files or directories in privileged locations via the search_path function, the –check option, or the -d option. |
2021-05-27 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-31153
MISC
MISC |
rust — please
|
Failure to normalize the umask in please before 0.4 allows a local attacker to gain full root privileges if they are allowed to execute at least one command. |
2021-05-27 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-31155
MISC
MISC |
rust — please
|
pleaseedit in please before 0.4 uses predictable temporary filenames in /tmp and the target directory. This allows a local attacker to gain full root privileges by staging a symlink attack. |
2021-05-27 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-31154
MISC
MISC |
scada — multiple_products
|
Use of Password Hash with Insufficient Computational Effort vulnerability exists in ClearSCADA (all versions), EcoStruxure Geo SCADA Expert 2019 (all versions), and EcoStruxure Geo SCADA Expert 2020 (V83.7742.1 and prior), which could cause the revealing of account credentials when server database files are available. Exposure of these files to an attacker can make the system vulnerable to password decryption attacks. Note that “.sde” configuration export files do not contain user account password hashes. |
2021-05-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-22741
MISC |
scansnap — manager
|
Untrusted search path vulnerability in the installers of ScanSnap Manager prior to versions V7.0L20 and the Software Download Installer prior to WinSSInst2JP.exe and WinSSInst2iX1500JP.exe allows an attacker to gain privileges and execute arbitrary code with the privilege of the user invoking the installer via a Trojan horse DLL in an unspecified directory. |
2021-05-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-20722
MISC
MISC |
| schneider_electric — homelynk_and_spacelynk |
Information Exposure vulnerability exists in homeLYnk (Wiser For KNX) and spaceLYnk V2.60 and prior which could cause a device to be compromised when it is first configured. |
2021-05-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-22739
MISC |
| schneider_electric — homelynk_and_spacelynk |
Information Exposure vulnerability exists in homeLYnk (Wiser For KNX) and spaceLYnk V2.60 and prior which could cause information to be exposed when an unauthorized file is uploaded. |
2021-05-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-22740
MISC |
| schneider_electric — homelynk_and_spacelynk |
Improper Verification of Cryptographic Signature vulnerability exists inhomeLYnk (Wiser For KNX) and spaceLYnk V2.60 and prior which could allow remote code execution when unauthorized code is copied to the device. |
2021-05-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-22735
MISC |
| schneider_electric — homelynk_and_spacelynk |
Use of a Broken or Risky Cryptographic Algorithm vulnerability exists in homeLYnk (Wiser For KNX) and spaceLYnk V2.60 and prior that could cause unauthorized access when credentials are discovered after a brute force attack. |
2021-05-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-22738
MISC |
| schneider_electric — homelynk_and_spacelynk |
Improper Privilege Management vulnerability exists in homeLYnk (Wiser For KNX) and spaceLYnk V2.60 and prior which could cause shell access when unauthorized code is loaded into the system folder. |
2021-05-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-22733
MISC |
| schneider_electric — homelynk_and_spacelynk |
Improper Limitation of a Pathname to a Restricted Directory (‘Path Traversal’) vulnerability exists in homeLYnk (Wiser For KNX) and spaceLYnk V2.60 and prior which could cause a denial of service when an unauthorized file is uploaded. |
2021-05-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-22736
MISC |
schneider_electric — homelynk_and_spacelynk
|
Improper Privilege Management vulnerability exists in homeLYnk (Wiser For KNX) and spaceLYnk V2.60 and prior which could cause a code execution issue when an attacker loads unauthorized code on the web server. |
2021-05-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-22732
MISC |
schneider_electric — homelynk_and_spacelynk
|
Insufficiently Protected Credentials vulnerability exists in homeLYnk (Wiser For KNX) and spaceLYnk V2.60 and prior that could cause unauthorized access of when credentials are discovered after a brute force attack. |
2021-05-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-22737
MISC |
schneider_electric — homelynk_and_spacelynk
|
Improper Verification of Cryptographic Signature vulnerability exists in homeLYnk (Wiser For KNX) and spaceLYnk V2.60 and prior which could cause remote code execution when an attacker loads unauthorized code. |
2021-05-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-22734
MISC |
seacms — seacms
|
A cross-site scripting (XSS) vulnerability has been discovered in the login page of SeaCMS version 11 which allows an attacker to inject arbitrary web script or HTML. |
2021-05-28 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-26642
MISC |
simantic — multiple_products
|
A vulnerability has been identified in SIMATIC Drive Controller family (All versions < V2.9.2), SIMATIC ET 200SP Open Controller CPU 1515SP PC (incl. SIPLUS variants) (All versions), SIMATIC ET 200SP Open Controller CPU 1515SP PC2 (incl. SIPLUS variants) (All versions), SIMATIC S7-1200 CPU family (incl. SIPLUS variants) (All versions < V4.5.0), SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU family (incl. related ET200 CPUs and SIPLUS variants) (All versions < V2.9.2), SIMATIC S7-1500 Software Controller (All versions), SIMATIC S7-PLCSIM Advanced (All versions < V4.0). Affected devices are vulnerable to a memory protection bypass through a specific operation. A remote unauthenticated attacker with network access to port 102/tcp could potentially write arbitrary data and code to protected memory areas or read sensitive data to launch further attacks. |
2021-05-28 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-15782
CONFIRM |
singularity — singularity
|
### Impact Due to incorrect use of a default URL, `singularity` action commands (`run`/`shell`/`exec`) specifying a container using a `library://` URI will always attempt to retrieve the container from the default remote endpoint (`cloud.sylabs.io`) rather than the configured remote endpoint. An attacker may be able to push a malicious container to the default remote endpoint with a URI that is identical to the URI used by a victim with a non-default remote endpoint, thus executing the malicious container. Only action commands (`run`/`shell`/`exec`) against `library://` URIs are affected. Other commands such as `pull` / `push` respect the configured remote endpoint. ### Patches All users should upgrade to Singularity 3.7.4 or later. ### Workarounds Users who only interact with the default remote endpoint are not affected. Installations with an execution control list configured to restrict execution to containers signed with specific secure keys are not affected. ### For more information General questions about the impact of the advisory can be asked in the: – [SingularityCE Slack Channel](https://singularityce.slack.com) – [SingularityCE Mailing List](https://groups.google.com/g/singularity-ce) Any sensitive security concerns should be directed to: security@sylabs.io See our Security Policy here: https://sylabs.io/security-policy |
2021-05-28 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-32635
CONFIRM |
smallrye — smallrye
|
A flaw was found in SmallRye’s API through version 1.6.1. The API can allow other code running within the application server to potentially obtain the ClassLoader, bypassing any permissions checks that should have been applied. The largest threat from this vulnerability is a threat to data confidentiality. This is fixed in SmallRye 1.6.2 |
2021-05-28 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-1729
MISC |
sonicwall — nsm_on-prem
|
A vulnerability in the SonicWall NSM On-Prem product allows an authenticated attacker to perform OS command injection using a crafted HTTP request. This vulnerability affects NSM On-Prem 2.2.0-R10 and earlier versions. |
2021-05-27 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-20026
CONFIRM |
spice — spice
|
A flaw was found in spice in versions before 0.14.92. A DoS tool might make it easier for remote attackers to cause a denial of service (CPU consumption) by performing many renegotiations within a single connection. |
2021-05-28 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-20201
MISC
MISC |
spring_framework — spring_framework
|
In Spring Framework, versions 5.2.x prior to 5.2.15 and versions 5.3.x prior to 5.3.7, a WebFlux application is vulnerable to a privilege escalation: by (re)creating the temporary storage directory, a locally authenticated malicious user can read or modify files that have been uploaded to the WebFlux application, or overwrite arbitrary files with multipart request data. |
2021-05-27 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-22118
MISC |
| squid — squid |
An issue was discovered in Squid before 4.15 and 5.x before 5.0.6. Due to an input-validation bug, it is vulnerable to a Denial of Service attack (against all clients using the proxy). A client sends an HTTP Range request to trigger this. |
2021-05-27 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-31808
MISC
MISC |
| squid — squid |
An issue was discovered in Squid before 4.15 and 5.x before 5.0.6. Due to incorrect parser validation, it allows a Denial of Service attack against the Cache Manager API. This allows a trusted client to trigger memory leaks that. over time, lead to a Denial of Service via an unspecified short query string. This attack is limited to clients with Cache Manager API access privilege. |
2021-05-27 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-28652
MISC
MISC |
squid — squid
|
Squid before 4.15 and 5.x before 5.0.6 allows remote servers to cause a denial of service (affecting availability to all clients) via an HTTP response. The issue trigger is a header that can be expected to exist in HTTP traffic without any malicious intent by the server. |
2021-05-28 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-33620
MISC
MISC
MISC |
squid — squid
|
An issue was discovered in Squid before 4.15 and 5.x before 5.0.6. Due to a memory-management bug, it is vulnerable to a Denial of Service attack (against all clients using the proxy) via HTTP Range request processing. |
2021-05-27 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-31806
MISC
MISC |
squid — squid
|
An issue was discovered in Squid 4.x before 4.15 and 5.x before 5.0.6. If a remote server sends a certain response header over HTTP or HTTPS, there is a denial of service. This header can plausibly occur in benign network traffic. |
2021-05-27 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-28662
MISC
MISC
MISC |
squid — squid
|
An issue was discovered in Squid before 4.15 and 5.x before 5.0.6. Due to a buffer-management bug, it allows a denial of service. When resolving a request with the urn: scheme, the parser leaks a small amount of memory. However, there is an unspecified attack methodology that can easily trigger a large amount of memory consumption. |
2021-05-27 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-28651
MISC
MISC |
stmicroelectronics — stm32l4_devices
|
STMicroelectronics STM32L4 devices through 2021-03-29 have incorrect physical access control. |
2021-05-21 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-29414
MISC
MISC
MISC |
stmicroelectronics — stm32l4_devices
|
STMicroelectronics STM32L4 devices through 2020-10-19 have incorrect access control. The flash read-out protection (RDP) can be degraded from RDP level 2 (no access via debug interface) to level 1 (limited access via debug interface) by injecting a fault during the boot phase. |
2021-05-21 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-27212
MISC
MISC
MISC |
sync_repl — sync_repl
|
When using a sync_repl client in 389-ds-base, an authenticated attacker can cause a NULL pointer dereference using a specially crafted query, causing a crash. |
2021-05-28 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-3514
MISC |
tableau — rsa_archer
|
The Tableau integration in RSA Archer 6.4 P1 (6.4.0.1) through 6.9 P2 (6.9.0.2) is affected by an insecure credential storage vulnerability. An malicious attacker with access to the Tableau workbook file may obtain access to credential information to use it in further attacks. |
2021-05-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-29253
MISC
CONFIRM |
tableau — rsa_archer
|
RSA Archer before 6.9 SP1 P1 (6.9.1.1) contains a stored XSS vulnerability. A remote authenticated malicious Archer user with access to modify link name fields could potentially exploit this vulnerability to execute code in a victim’s browser. |
2021-05-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-29252
MISC
CONFIRM |
tenancy — tenancy
|
Tenancy multi-tenant is an open source multi-domain controller for the Laravel web framework. In some situations, it is possible to have open redirects where users can be redirected from your site to any other site using a specially crafted URL. This is only the case for installations where the default Hostname Identification is used and the environment uses tenants that have `force_https` set to `true` (default: `false`). Version 5.7.2 contains the relevant patches to fix this bug. Stripping the URL from special characters to prevent specially crafted URL’s from being redirected to. As a work around users can set the `force_https` to every tenant to `false`, however this may degrade connection security. |
2021-05-27 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-32645
CONFIRM
MISC
MISC
MISC |
trend_micro — home_network_security
|
A privilege escalation vulnerability exists in the tdts.ko chrdev_ioctl_handle functionality of Trend Micro, Inc. Home Network Security 6.1.567. A specially crafted ioctl can lead to increased privileges. An attacker can issue an ioctl to trigger this vulnerability. |
2021-05-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-32457
MISC
MISC |
trend_micro — home_network_security
|
A privilege escalation vulnerability exists in the tdts.ko chrdev_ioctl_handle functionality of Trend Micro, Inc. Home Network Security 6.1.567. A specially crafted ioctl can lead to code execution. An attacker can issue an ioctl to trigger this vulnerability. |
2021-05-27 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-32458
MISC
MISC |
trend_micro — home_network_security
|
A hard-coded password vulnerability exists in the SFTP Log Collection Server function of Trend Micro Inc.’s Home Network Security 6.1.567. A specially crafted network request can lead to arbitrary authentication. An attacker can send an unauthenticated message to trigger this vulnerability. |
2021-05-27 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-32459
MISC
MISC |
| triconex — tricon |
Improper Check for Unusual or Exceptional Conditions vulnerability exists in Triconex TCM 4351B installed on Tricon V11.3.x systems that could cause module reset when TCM receives malformed TriStation packets while the write-protect keyswitch is in the program position. |
2021-05-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-22743
MISC |
| triconex — tricon |
Improper Check for Unusual or Exceptional Conditions vulnerability exists in Triconex Model 3009 MP installed on Tricon V11.3.x systems that could cause module reset when TCM receives malformed TriStation packets while the write-protect keyswitch is in the program position. This CVE ID is unique from CVE-2021-22742, CVE-2021-22744, CVE-2021-22745, and CVE-2021-22746. |
2021-05-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-22747
MISC |
| triconex — tricon |
Improper Check for Unusual or Exceptional Conditions vulnerability exists in Triconex Model 3009 MP installed on Tricon V11.3.x systems that could cause module reset when TCM receives malformed TriStation packets while the write-protect keyswitch is in the program position. This CVE ID is unique from CVE-2021-22742, CVE-2021-22744, CVE-2021-22746, and CVE-2021-22747. |
2021-05-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-22745
MISC |
triconex — tricon
|
Improper Check for Unusual or Exceptional Conditions vulnerability exists in Triconex Model 3009 MP installed on Tricon V11.3.x systems that could cause module reset when TCM receives malformed TriStation packets while the write-protect keyswitch is in the program position. This CVE ID is unique from CVE-2021-22742, CVE-2021-22745, CVE-2021-22746, and CVE-2021-22747. |
2021-05-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-22744
MISC |
triconex — tricon
|
Improper Check for Unusual or Exceptional Conditions vulnerability exists in Triconex Model 3009 MP installed on Tricon V11.3.x systems that could cause module reset when TCM receives malformed TriStation packets while the write-protect keyswitch is in the program position. |
2021-05-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-22742
MISC |
triconex — tricon
|
Improper Check for Unusual or Exceptional Conditions vulnerability exists in Triconex Model 3009 MP installed on Tricon V11.3.x systems that could cause module reset when TCM receives malformed TriStation packets while the write-protect keyswitch is in the program position. This CVE ID is unique from CVE-2021-22742, CVE-2021-22744, CVE-2021-22745, and CVE-2021-22747. |
2021-05-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-22746
MISC |
trim-newlines — node.js
|
The trim-newlines package before 3.0.1 and 4.x before 4.0.1 for Node.js has an issue related to regular expression denial-of-service (ReDoS) for the .end() method. |
2021-05-28 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-33623
MISC
CONFIRM |
upx — membuffer
|
An assertion abort was found in upx MemBuffer::alloc() in mem.cpp, in version UPX 4.0.0. The flow allows attackers to cause a denial of service (abort) via a crafted file. |
2021-05-27 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-30501
MISC
MISC
MISC
MISC |
upx — packlinuxelf
|
Null pointer dereference was found in upx PackLinuxElf::canUnpack() in p_lx_elf.cpp,in version UPX 4.0.0. That allow attackers to execute arbitrary code and cause a denial of service via a crafted file. |
2021-05-27 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-30500
MISC
MISC
MISC |
versa — analytics
|
In Versa Analytics, the cron jobs are used for scheduling tasks by executing commands at specific dates and times on the server. If the job is run as the user root, there is a potential privilege escalation vulnerability. In this case, the job runs a script as root that is writable by users who are members of the versa group. |
2021-05-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2018-16497
MISC |
| versa — director |
In Versa Director, the unencrypted backup files stored on the Versa deployment contain credentials stored within configuration files. These credentials are for various application components such as SNMP, and SSL and Trust keystores. |
2021-05-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2018-16498
MISC |
versa — director
|
In Versa Director, the un-authentication request found. |
2021-05-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2018-16496
MISC |
versa — director
|
In Versa Director, the command injection is an attack in which the goal is execution of arbitrary commands on the host operating system via a vulnerable application. Command injection attacks are possible when an application passes unsafe user supplied data (forms, cookies, HTTP headers etc.) to a system shell. In this attack, the attacker-supplied operating system commands are usually executed with the privileges of the vulnerable application. Command injection attacks are possible largely due to insufficient input validation. |
2021-05-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2019-25029
MISC |
versa — multiple_products
|
In Versa Director, Versa Analytics and VOS, Passwords are not hashed using an adaptive cryptographic hash function or key derivation function prior to storage. Popular hashing algorithms based on the Merkle-Damgardconstruction (such as MD5 and SHA-1) alone are insufficient in thwarting password cracking. Attackers can generate and use precomputed hashes for all possible password character combinations (commonly referred to as “rainbow tables”) relatively quickly. The use of adaptive hashing algorithms such asscryptorbcryptor Key-Derivation Functions (i.e.PBKDF2) to hash passwords make generation of such rainbow tables computationally infeasible. |
2021-05-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2019-25030
MISC |
| versa — vos |
In VOS compromised, an attacker at network endpoints can possibly view communications between an unsuspecting user and the service using man-in-the-middle attacks. Usage of unapproved SSH encryption protocols or cipher suites also violates the Data Protection TSR (Technical Security Requirements). |
2021-05-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2018-16499
MISC |
versa — vos
|
In VOS and overly permissive “umask” may allow for authorized users of the server to gain unauthorized access through insecure file permissions that can result in an arbitrary read, write, or execution of newly created files and directories. Insecure umask setting was present throughout the Versa servers. |
2021-05-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2018-16494
MISC |
versa — vos
|
In VOS user session identifier (authentication token) is issued to the browser prior to authentication but is not changed after the user successfully logs into the application. Failing to issue a new session ID following a successful login introduces the possibility for an attacker to set up a trap session on the device the victim is likely to login with. |
2021-05-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2018-16495
MISC |
vfairs — vfairs
|
In vFairs 3.3, any user logged in to a vFairs virtual conference or event can modify any other users profile information to include a cross-site scripting payload. The user data stored by the database includes HTML tags that are intentionally rendered out onto the page, and this can be abused to perform XSS attacks. |
2021-05-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-26680
MISC
MISC |
vfairs — vfairs
|
vFairs 3.3 is affected by Remote Code Execution. Any user logged in to a vFairs virtual conference or event can abuse the functionality to upload a profile picture in order to place a malicious PHP file on the server and gain code execution. |
2021-05-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-26678
MISC
MISC
MISC |
vfairs — vfairs
|
vFairs 3.3 is affected by Insecure Permissions. Any user logged in to a vFairs virtual conference or event can modify any other users profile information or profile picture. After receiving any user’s unique identification number and their own, an HTTP POST request can be made update their profile description or supply a new profile image. This can lead to potential cross-site scripting attacks on any user, or upload malicious PHP webshells as “profile pictures.” The user IDs can be easily determined by other responses from the API for an event or chat room. |
2021-05-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-26679
MISC
MISC
MISC
MISC |
vfairs — vfairs
|
Any user logged in to a vFairs 3.3 virtual conference or event can perform SQL injection with a malicious query to the API. |
2021-05-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-26677
MISC
MISC
MISC |
vmware — workstation
|
VMware Workstation (16.x prior to 16.1.2) and Horizon Client for Windows (5.x prior to 5.5.2) contain out-of-bounds read vulnerability in the Cortado ThinPrint component (TTC Parser). A malicious actor with access to a virtual machine or remote desktop may be able to exploit these issues leading to information disclosure from the TPView process running on the system where Workstation or Horizon Client for Windows is installed. |
2021-05-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-21989
MISC
MISC |
vmware — workstation
|
VMware Workstation (16.x prior to 16.1.2) and Horizon Client for Windows (5.x prior to 5.5.2) contain out-of-bounds read vulnerability in the Cortado ThinPrint component (TTC Parser). A malicious actor with access to a virtual machine or remote desktop may be able to exploit these issues leading to information disclosure from the TPView process running on the system where Workstation or Horizon Client for Windows is installed. |
2021-05-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-21987
MISC
MISC |
vmware — workstation
|
VMware Workstation (16.x prior to 16.1.2) and Horizon Client for Windows (5.x prior to 5.5.2) contain out-of-bounds read vulnerability in the Cortado ThinPrint component (JPEG2000 Parser). A malicious actor with access to a virtual machine or remote desktop may be able to exploit these issues leading to information disclosure from the TPView process running on the system where Workstation or Horizon Client for Windows is installed. |
2021-05-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-21988
MISC
MISC |
volpmonitor — volpmonitor
|
A remote code execution issue was discovered in the web UI of VoIPmonitor before 24.61. When the recheck option is used, the user-supplied SPOOLDIR value (which might contain PHP code) is injected into config/configuration.php. |
2021-05-29 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-30461
MISC |
vsphere — client
|
The vSphere Client (HTML5) contains a remote code execution vulnerability due to lack of input validation in the Virtual SAN Health Check plug-in which is enabled by default in vCenter Server. A malicious actor with network access to port 443 may exploit this issue to execute commands with unrestricted privileges on the underlying operating system that hosts vCenter Server. |
2021-05-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-21985
MISC
MISC |
vsphere — client
|
The vSphere Client (HTML5) contains a vulnerability in a vSphere authentication mechanism for the Virtual SAN Health Check, Site Recovery, vSphere Lifecycle Manager, and VMware Cloud Director Availability plug-ins. A malicious actor with network access to port 443 on vCenter Server may perform actions allowed by the impacted plug-ins without authentication. |
2021-05-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-21986
MISC
MISC |
wordpress — wordpress
|
The Ultimate Member – User Profile, User Registration, Login & Membership Plugin WordPress plugin before 2.1.20 did not properly sanitise, validate or encode the query string when generating a link to edit user’s own profile, leading to an authenticated reflected Cross-Site Scripting issue. Knowledge of the targeted username is required to exploit this, and attackers would then need to make the related logged in user open a malicious link. |
2021-05-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-24306
CONFIRM |
ws — ws
|
ws is an open source WebSocket client and server library for Node.js. A specially crafted value of the `Sec-Websocket-Protocol` header can be used to significantly slow down a ws server. The vulnerability has been fixed in ws@7.4.6 (https://github.com/websockets/ws/commit/00c425ec77993773d823f018f64a5c44e17023ff). In vulnerable versions of ws, the issue can be mitigated by reducing the maximum allowed length of the request headers using the [`–max-http-header-size=size`](https://nodejs.org/api/cli.html#cli_max_http_header_size_size) and/or the [`maxHeaderSize`](https://nodejs.org/api/http.html#http_http_createserver_options_requestlistener) options. |
2021-05-25 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-32640
CONFIRM
MISC |
x.org — x.org
|
LookupCol.c in X.Org X through X11R7.7 and libX11 before 1.7.1 might allow remote attackers to execute arbitrary code. The libX11 XLookupColor request (intended for server-side color lookup) contains a flaw allowing a client to send color-name requests with a name longer than the maximum size allowed by the protocol (and also longer than the maximum packet size for normal-sized packets). The user-controlled data exceeding the maximum size is then interpreted by the server as additional X protocol requests and executed, e.g., to disable X server authorization completely. For example, if the victim encounters malicious terminal control sequences for color codes, then the attacker may be able to take full control of the running graphical session. |
2021-05-27 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-31535
MISC
MISC
MISC
MISC
MISC |
xorg-x11-server — xorg-x11-server
|
A privilege escalation flaw was found in the Xorg-x11-server due to a lack of authentication for X11 clients. This flaw allows an attacker to take control of an X application by impersonating the server it is expecting to connect to. |
2021-05-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-25697
MLIST
MISC
MISC
MLIST
MISC |
xwiki — xwiki
|
### Impact A user without Script or Programming right is able to execute script requiring privileges by editing gadget titles in the dashboard. ### Patches The issue has been patched in XWiki 12.6.7, 12.10.3 and 13.0RC1. ### Workarounds There’s no easy workaround for this issue, it is recommended to upgrade XWiki. ### References https://jira.xwiki.org/browse/XWIKI-17794 ### For more information If you have any questions or comments about this advisory: * Open an issue in [JIRA](https://jira.xwiki.org) * Email us at [XWiki security mailing-list](mailto:security@xwiki.org) |
2021-05-28 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-32621
CONFIRM |
xwiki — xwiki
|
### Impact A user disabled on a wiki using email verification for registration can re-activate himself by using the activation link provided for his registration. ### Patches The problem has been patched in the following versions of XWiki: 11.10.13, 12.6.7, 12.10.2, 13.0. ### Workarounds It’s possible to workaround the issue by resetting the `validkey` property of the disabled XWiki users. This can be done by editing the user profile with object editor. ### References https://jira.xwiki.org/browse/XWIKI-17942 ### For more information If you have any questions or comments about this advisory: * Open an issue in [Jira](http://jira.xwiki.org) * Email us at [Security mailing-list](mailto:security@xwiki.org) |
2021-05-28 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-32620
MISC
CONFIRM |
ytnef — ytnef
|
Multiple directory traversal and buffer overflow vulnerabilities were discovered in yTNEF, and in Evolution’s TNEF parser that is derived from yTNEF. A crafted email could cause these applications to write data in arbitrary locations on the filesystem, crash, or potentially execute arbitrary code when decoding attachments. |
2021-05-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2009-3721
MISC
MISC |
yubico — pam-u2f
|
Yubico pam-u2f before 1.1.1 has a logic issue that, depending on the pam-u2f configuration and the application used, could lead to a local PIN bypass. This issue does not allow user presence (touch) or cryptographic signature verification to be bypassed, so an attacker would still need to physically possess and interact with the YubiKey or another enrolled authenticator. If pam-u2f is configured to require PIN authentication, and the application using pam-u2f allows the user to submit NULL as the PIN, pam-u2f will attempt to perform a FIDO2 authentication without PIN. If this authentication is successful, the PIN requirement is bypassed. |
2021-05-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-31924
MISC
MISC |
| zephyr — zephyr |
Malformed SPI in response for eswifi can corrupt kernel memory. Zephyr versions >= 1.14.2, >= 2.3.0 contain Heap-based Buffer Overflow (CWE-122). For more information, see https://github.com/zephyrproject-rtos/zephyr/security/advisories/GHSA-hx4p-j86p-2mhr |
2021-05-25 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-13600
MISC |
zephyr — zephyr
|
FS: Buffer Overflow when enabling Long File Names in FAT_FS and calling fs_stat. Zephyr versions >= v1.14.2, >= v2.3.0 contain Stack-based Buffer Overflow (CWE-121). For more information, see https://github.com/zephyrproject-rtos/zephyr/security/advisories/GHSA-7fhv-rgxr-x56h |
2021-05-25 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-13598
MISC |
zephyr — zephyr
|
Security problem with settings and littlefs. Zephyr versions >= 1.14.2, >= 2.3.0 contain Incorrect Default Permissions (CWE-276). For more information, see https://github.com/zephyrproject-rtos/zephyr/security/advisories/GHSA-5qhg-j6wc-4f6q |
2021-05-25 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-13599
MISC |
zeromq — zeromq
|
A flaw was found in the ZeroMQ server in versions before 4.3.3. This flaw allows a malicious client to cause a stack buffer overflow on the server by sending crafted topic subscription requests and then unsubscribing. The highest threat from this vulnerability is to confidentiality, integrity, as well as system availability. |
2021-05-28 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-20236
MISC
MISC |
zeromq — zeromq
|
An uncontrolled resource consumption (memory leak) flaw was found in ZeroMQ’s src/xpub.cpp in versions before 4.3.3. This flaw allows a remote unauthenticated attacker to send crafted PUB messages that consume excessive memory if the CURVE/ZAP authentication is disabled on the server, causing a denial of service. The highest threat from this vulnerability is to system availability. |
2021-05-28 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-20237
MISC
MISC |
zettlr — zettlr
|
Cross-site scripting vulnerability in Zettlr from 0.20.0 to 1.8.8 allows an attacker to execute an arbitrary script by loading a file or code snippet containing an invalid iframe into Zettlr. |
2021-05-27 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-20727
MISC
MISC
MISC |

by Contributed | May 29, 2021 | Technology
This article is contributed. See the original author and article here.
It’s been an eventful time for Hyperscale (Citus) lately. If you’re interested in Postgres, distributed databases, and how to handle ever growing needs for your Postgres application or simply use Hyperscale (Citus), keep reading.
Citus is an open source extension to Postgres that enables horizontal scaling of your Postgres database. Citus distributes your Postgres tables, writes, and SQL queries across multiple nodes—parallelizing your workload and enabling you to use the memory, compute, and disk of a multi-node cluster. And Citus is available on Azure: Hyperscale (Citus) is a deployment option in Azure Database for PostgreSQL.
What’s really exciting to me is that we’ve made it easier and cheaper than ever to try and use Hyperscale (Citus). With Basic tier, you can now use Hyperscale (Citus) on a single node, parallelizing your operations and adopting a distributed database model from the very beginning. And you can now try Citus open source with a single docker run command—boom!
And Hyperscale (Citus) can scale to serve some big applications: it’s used to manage public transport in a large European capital, to handle ongoing market analysis in one of the biggest banks in the world, and to power the UK Coronavirus Dashboard. Lots of use cases can benefit from scaling out Postgres.
So what’s new with Hyperscale (Citus)? Lots. In the last month we launched these new features in preview:
- Basic tier: with Basic tier, you can now run Hyperscale (Citus) on a single node for as little as $0.27 USD/hour[1]
- Postgres 12 & Postgres 13: for the latest developments in Postgres
- Citus 10: The latest version of Citus with all the new capabilities—including columnar compression
- Read replicas in the same region for unlimited read scalability
- Managed PgBouncer: so you no longer need to set up and maintain your own PgBouncer anymore
And there’s more! We have also rolled out:
- Custom schedules for maintenance
- Shard rebalancing features in portal
You can go ahead and try the new Hyperscale (Citus) features right now—whether they are still in preview or have already GA’d. This post will walk you through the new features that were recently added to Hyperscale (Citus) and how you can benefit. Ready? Let’s dive in.

What is the new Basic tier for Hyperscale (Citus)?
Some of you gave us feedback that you wanted us to create a smaller Hyperscale (Citus) cluster, to make it easier to get started and to try out Hyperscale (Citus). We heard you loud and clear.
Think about it—20 worker nodes with 64 vCores in each node would give you 1280 vCores with 8TB+ of RAM to run your Postgres database. That is a lot of power. And in many cases, you don’t need it (yet). Or you need something smaller than even a 2-node cluster for development, test, or stage environment.
So in Preview, we are now introducing a Basic tier.
The new Basic tier in Hyperscale (Citus) allows you to shard Postgres on a single node. So that you are “scale-out ready” and can use a distributed data model from the very start, even when you are still running on a single node database. And it’s easy to add workers nodes to your Hyperscale (Citus) basic tier when you need to—when you do, you’re effectively converting your Basic configuration to a Standard tier.
And the configuration with 1 coordinator and 2 or more worker nodes that you used to know is now called “Standard tier”.
Some of you who have been using Citus for a while told us that if you could rewind the clock, you would have started using Citus earlier, even when your Postgres database was smaller. Now you can, by using Basic tier!
And you can select Postgres version of your choice—11, 12, or 13—for your Basic and Standard tiers. Which brings me to my next point.
Postgres 12 and 13
One of the tough challenges a PM faces with a popular cloud database service like Postgres is prioritization. You keep talking to your customers and you feel how much they need this new functionality. And that one. And another one. It is great to see how many customers are asking for so many things—there is definitely a lot of interest in your service! But it also means that some much-needed capabilities will have to wait until our team delivers others. No matter how big (or not) the team is you can’t get it all at the same time.
One of the tradeoffs we previously made for Hyperscale (Citus) was to delay support for the latest Postgres versions. The good news is, now we are catching up and are extremely happy to offer Postgres 12 and Postgres 13 support in Hyperscale (Citus).
With addition of Postgres 12 and Postgres 13, you may ask—how can I upgrade my Hyperscale (Citus) cluster to the latest Postgres version? You can initiate a major Postgres version upgrade for your cluster with few clicks in Azure portal. Upgrade on all nodes in your Hyperscale (Citus) cluster is performed by the service and keeps all configuration, including server group name and connection string, the same.
One of the advantages to have the latest Postgres versions—in addition to the new capabilities in these major Postgres versions—is the ability to use the latest Citus version! Let’s take a closer look at why you could be interested in the latest Citus version.
Almighty Citus 10
OK, maybe not almighty but look at what Citus database team delivered this time!
In case you didn’t know, we have a dedicated team in Azure Data that is working full time on …the open source Citus extension! That’s right. You can run a Citus cluster on your own anywhere if you don’t need any of the advantages provided by a managed database service. No strings attached and we love our Citus open source community. However, many customers would like us, Azure Data, to run their databases for them and take care of updates, security, backups, BCDR, and many other important things that frankly you can spend a lot of time setting up and maintaining as your databases grow. This way you can focus on what matters most to you: your application. And we love to help you with it.
But let’s get back to Citus 10 in Hyperscale (Citus). With Citus 10 support in Hyperscale (Citus), you can:
- Compress your tables to reduce storage cost and speed up your analytical queries using columnar storage.
- Use joins and foreign keys between local PostgreSQL tables and distributed tables.
- Use the new alter table function to change your distribution key, shard count, colocation properties and more.
- And there’s more: More DDL commands supported, better SQL support, and new views to see the state of your cluster with
citus_tables and citus_shards.
Let’s see what these new capabilities are.
Columnar compression with Citus 10
Postgres typically stores data using the heap access method, which is row-based storage. Row-based tables are good for transactional workloads but can cause excessive IO for some analytic queries.
Columnar storage provides another way to store data in a Postgres table, by grouping data by column instead of by row.
So what are some of the benefits of columnar?
- Compression reduces storage requirements.
- Compression reduces IO needed to scan the table.
- Performance: Queries can skip over the columns that they don’t need, further reducing IO.
All of these together mean faster queries and lower costs!
To use the new columnar feature with Hyperscale (Citus), you just need to create tables with the new USING columnar syntax, and you’re ready to go (of course, read the docs, too!).
And finally, you can mix and match columnar and row tables and partitions; you can also mix and match local and distributed columnar tables; and you can use columnar with Basic tier on a single node as well as on a distributed Citus cluster in Standard tier. There are lots more details in Jeff’s “Quickstart” blog posts about using Columnar in Hyperscale (Citus)—as well as using columnar with Citus open source. Oh, and Jeff made a video demo about Citus Columnar too.
Use joins and foreign keys between local and distributed tables
If you have a very large Postgres table and a data-intensive workload (e.g. the frequently-queried part of the table exceeds memory), then the performance gains from distributing the table over multiple nodes with Citus will vastly outweigh any downsides. However, if most of your other Postgres tables are small, then you may not get much of additional benefits by distributing them.
A simple solution for you would be to not distribute the smaller Postgres tables at all!
Because the Citus coordinator is just a regular Postgres server, you can keep some of your tables as local, regular Postgres tables that live on the Citus coordinator. That’s right, you don’t need to distribute all of your tables with Citus.
Here’s an example of how you could organize your database:
- take your large tables and distribute them across a cluster with Citus,
- convert smaller tables that frequently JOIN with distributed tables into reference tables,
- convert smaller tables that have foreign keys from distributed tables into reference tables,
- keep all other tables as local PostgreSQL tables, that stay local to the coordinator.
That way, you can scale out compute, memory, and IO where you need it—and minimize application changes and other trade-offs where you don’t.
To make this model work seamlessly, Citus 10 adds support for 2 important features:
- foreign keys between local Postgres tables and reference tables
- direct joins between local Postgres tables and distributed tables
With these new features, you can use Postgres tables and Citus distributed tables in combination to get the best of both worlds.
Change your distribution key if you need to
When you distribute a table, choosing your distribution column is an important step, since the distribution column determines which constraints you can create, how (fast) you can join tables, and more.
With Citus 10 you can change the distribution column, shard count, and co-location of a distributed table using the new alter_distributed_table function.
Internally, alter_distributed_table reshuffles the data between the worker nodes, which means it is fast and works well on very large tables. For instance, using this capability makes it much easier to experiment with distributing your tables without having to reload your data.
You can also use the function in production (it’s fully transactional!), but you do need to:
(1) make sure that you have enough disk space to store the table several times, and
(2) make sure that your application can tolerate blocking all writes to the table for a while.
Read scalability via read replicas
Some of you might have sizable read needs that are hard to satisfy with just one database. For instance, dozens and hundreds of business analysts across your company might hit your database hard with queries but are not going to write to your database. That is when a Hyperscale (Citus) server group that contains a read replica of the database in addition to the primary Hyperscale (Citus) cluster can help.
You can now create one or more read-only replicas of a Hyperscale (Citus) server group.
Any changes that happen to the original server group get promptly reflected in its read replicas via asynchronous replication, and queries against the read replicas cause no extra load on the original. The replica is a safe place for you to run big report queries.
The replica cluster is distinct from the original and has its own database connection string. You can also change compute configuration separately on each replica. You can create unlimited number of read replicas without performance penalty on the primary cluster.
Managed PgBouncer
Each client connection to PostgreSQL consumes a noticeable amount of resources. To protect resource usage, Hyperscale (Citus) enforces a hard limit of 300 concurrent connections to the coordinator.
What if you require more client connections for some reason? While you can always setup your preferred connection pooler in front of Hyperscale (Citus) coordinator, it requires additional effort to set it up and maintain.
To improve connection scaling, Hyperscale (Citus) now comes with PgBouncer. If your application requires more than 300 connections, change the port in the connection URL from 5432 to 6432. This will connect to PgBouncer rather than directly to the coordinator, allowing up to roughly 2,000 simultaneous connections.
This new Managed PgBouncer capability in Hyperscale (Citus) will give you all the capabilities of your self-managed PgBouncer—combined with managed service benefits such as automatic updates without connection interruption. And if HA is enabled for your Hyperscale (Citus) cluster, managed PgBouncer is going to be highly available too.
More scheduling choices for maintenance windows
Having an up-to-date database engine (Postgres), operating system (Linux), and other service components is one of the big benefits of any managed database service. Updates however come at a price of downtime that is required to apply them to your system.
For a while now, Hyperscale (Citus) has posted notifications about scheduled maintenance events 5 days before the actual update—plus we’ve had a policy of doing maintenance at least 30 days after the last successful update.
Now you have even more control over planned maintenance events: you can define your preferred day of the week and time window on that day when maintenance for your Hyperscale (Citus) cluster should be scheduled. So you now get to choose between 2 different types of scheduling options for each of your Hyperscale (Citus) clusters:
- System managed schedule: The default maintenance scheduling option is to let the system pick a day and a 30-minute time window between 11pm and 7am in the time zone of your Azure region geography.
- Custom maintenance schedule: You can select day of the week and 30-minute time window, e.g. Sunday at 01:00-01:30am, when maintenance events should be scheduled for that cluster.
You will get notifications about scheduled maintenance 5 days in advance regardless of what schedule your cluster is on.
Take advantage of shard rebalancer recommendations & progress monitoring in the Azure portal
When you add a new node to your Hyperscale (Citus) cluster—or when your database has grown and the data distribution across nodes has become uneven—you will want to rebalance your shards. Shard rebalancing is the movement of shards between nodes in your Citus cluster, to make sure your database is spread evenly across all nodes.
Hyperscale (Citus) has had the shard rebalancer as one of its core features from the very beginning. Recently, we’ve added both shard rebalancing recommendations and progress tracking to the Azure portal.
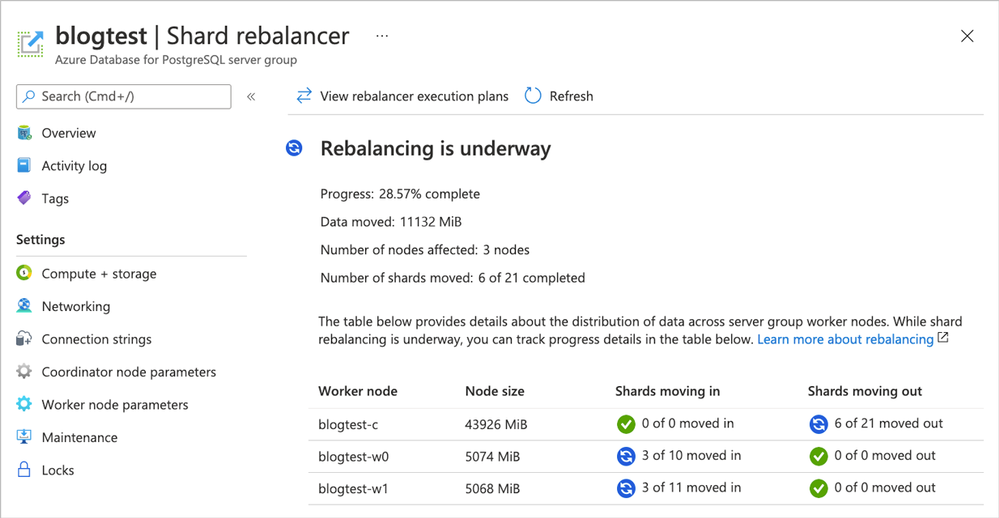 Figure 1. Screenshot of the Azure portal and the Shard rebalancer screen for Hyperscale (Citus).
Figure 1. Screenshot of the Azure portal and the Shard rebalancer screen for Hyperscale (Citus).
Ways to learn more about Hyperscale (Citus) and to try all of these new things
To figure out if Azure Database for PostgreSQL – Hyperscale (Citus) is right for you and your app, here are some ways to roll up your sleeves and get started. Pick what works best for you!
If you need help figuring out whether Hyperscale (Citus) is a good fit for your workload, you can always reach out to us—the team that created Hyperscale (Citus)—via email at Ask AzureDB for PostgreSQL.
Oh, and if you want to stay connected, you can follow our @AzureDBPostgres account on Twitter. Plus, we ship a monthly technical Citus newsletter to our open source community.
Footnotes
- In the East US region on Azure, the cost of a Hyperscale (Citus) Basic tier with 2 vCores, 8 GiB total memory, and 128 GiB of storage on the coordinator node is $0.27/hour or ~$200/month. At $0.27 USD/hour, you can try it for ~8 hours or so and you’ll only pay $2 to $3 USD.↩

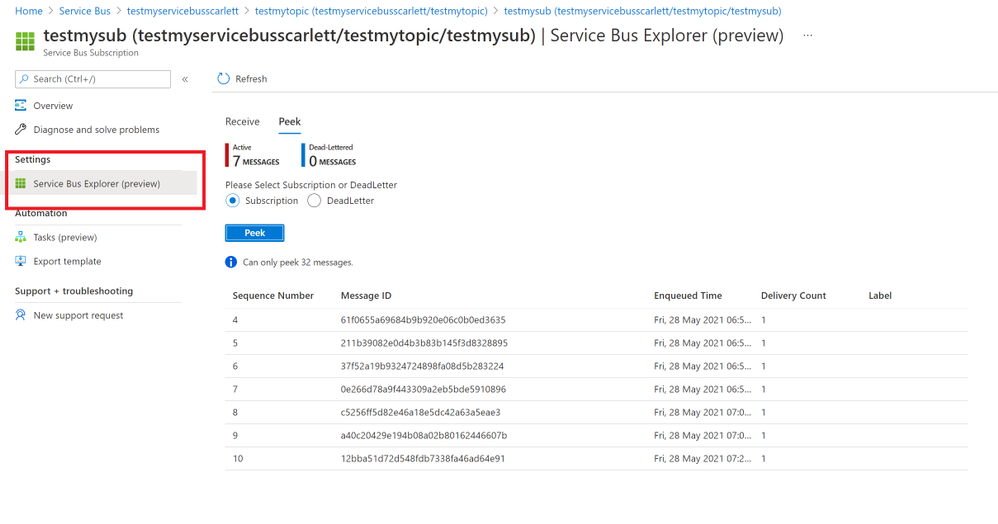
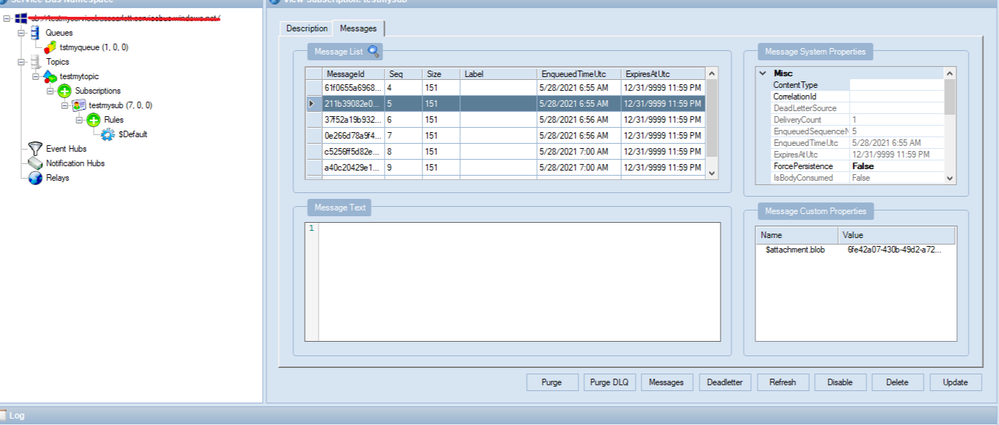
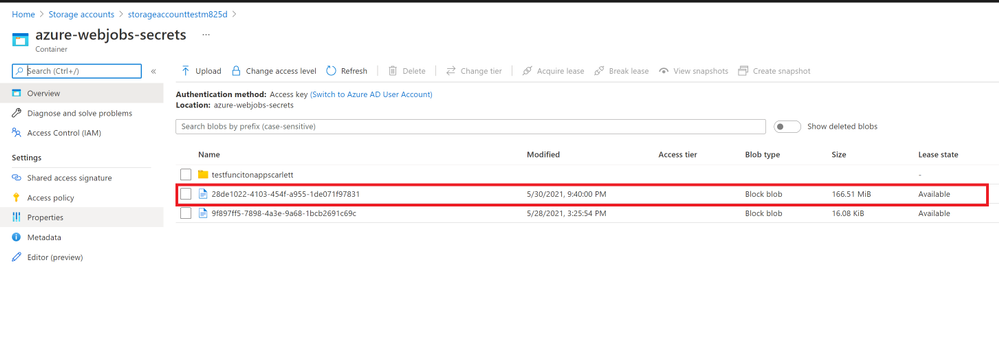





Recent Comments