by Scott Muniz | Dec 22, 2021 | Security, Technology
This article is contributed. See the original author and article here.
The Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA), the Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI), National Security Agency (NSA), Australian Cyber Security Centre (ACSC), Canadian Centre for Cyber Security (CCCS), the Computer Emergency Response Team New Zealand (CERT NZ), the New Zealand National Cyber Security Centre (NZ NCSC), and the United Kingdom’s National Cyber Security Centre (NCSC-UK) are releasing this joint Cybersecurity Advisory (CSA) to provide mitigation guidance on addressing vulnerabilities in Apache’s Log4j software library: CVE-2021-44228 (known as “Log4Shell”), CVE-2021-45046, and CVE-2021-45105. Sophisticated cyber threat actors are actively scanning networks to potentially exploit Log4Shell, CVE-2021-45046, and CVE-2021-45105 in vulnerable systems. According to public reporting, Log4Shell and CVE-2021-45046 are being actively exploited.
CISA, in collaboration with industry members of CISA’s Joint Cyber Defense Collaborative (JCDC), previously published guidance on Log4Shell for vendors and affected organizations in which CISA recommended that affected organizations immediately apply appropriate patches (or apply workarounds if unable to upgrade), conduct a security review, and report compromises to CISA or the FBI. CISA also issued an Emergency Directive directing U.S. federal civilian executive branch (FCEB) agencies to immediately mitigate Log4j vulnerabilities in solution stacks that accept data from the internet. This joint CSA expands on the previously published guidance by detailing steps that vendors and organizations with IT and/or cloud assets should take to reduce the risk posed by these vulnerabilities.
These steps include:
- Identifying assets affected by Log4Shell and other Log4j-related vulnerabilities,
- Upgrading Log4j assets and affected products to the latest version as soon as patches are available and remaining alert to vendor software updates, and
- Initiating hunt and incident response procedures to detect possible Log4Shell exploitation.
This CSA also provides guidance for affected organizations with operational technology (OT)/industrial control systems (ICS) assets.
Log4j is a Java-based logging library used in a variety of consumer and enterprise services, websites, applications, and OT products. These vulnerabilities, especially Log4Shell, are severe—Apache has rated Log4Shell and CVE-2021-45046 as critical and CVE-2021-45105 as high on the Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS). These vulnerabilities are likely to be exploited over an extended period. CISA, the FBI, NSA, ACSC, CCCS, CERT NZ, NZ NCSC, and NCSC-UK strongly urge all organizations to apply the recommendations in the Mitigations section.
CISA, the FBI, NSA, ACSC, CCCS, CERT NZ, NZ NCSC, and NCSC-UK encourage leaders of organizations to review NCSC-UK’s blog post, Log4j vulnerability: what should boards be asking?, for information on Log4Shell’s possible impact on their organization as well as response recommendations.
Note: this is an evolving situation, and new vulnerabilities are being discovered. CISA, the FBI, NSA, ACSC, CCCS, CERT NZ, NZ NCSC, and NCSC-UK will update this CSA as we learn more about this exploitation and have further guidance to impart.
Click here for a PDF version of this report.
Disclaimer
The information in this report is being provided “as is” for informational purposes only. CISA, the FBI, NSA, ACSC, CCCS, CERT NZ, NZ NCSC, and NCSC-UK do not endorse any commercial product or service, including any subjects of analysis. Any reference to specific commercial products, processes, or services by service mark, trademark, manufacturer, or otherwise, does not constitute or imply endorsement, recommendation, or favoring by CISA, the FBI, NSA, ACSC, CCCS, CERT NZ, NZ NCSC, or NCSC-UK.
Log4Shell
Log4Shell, disclosed on December 10, 2021, is a remote code execution (RCE) vulnerability affecting Apache’s Log4j library, versions 2.0-beta9 to 2.14.1. The vulnerability exists in the action the Java Naming and Directory Interface (JNDI) takes to resolve variables. Affected versions of Log4j contain JNDI features—such as message lookup substitution—that do not protect against adversary-controlled Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP), Domain Name System (DNS), and other JNDI-related endpoints.
An adversary can exploit Log4Shell by submitting a specially crafted request to a vulnerable system that causes that system to execute arbitrary code. The request allows the adversary to take full control over the system. The adversary can then steal information, launch ransomware, or conduct other malicious activity.
CVE-2021-45046
CVE-2021-45046, disclosed on December 13, 2021, enables a remote attacker to cause RCE, a denial-of-service (DoS) condition, or other effects in certain non-default configurations. This vulnerability affects all versions of Log4j from 2.0-beta9 through 2.12.1 and 2.13.0 through 2.15.0. In response, Apache released Log4j version 2.16.0 (Java 8).
CVE-2021- 45105
CVE-2021-45105, disclosed on December 16, 2021, enables a remote attacker to cause a DoS condition or other effects in certain non-default configurations. According to Apache, when the logging configuration uses a non-default Pattern Layout with a Context Lookup (for example, $${ctx:loginId}), attackers with control over Thread Context Map (MDC) input data can craft malicious input data that contains a recursive lookup, resulting in a StackOverflowError that will terminate the process. In response, Apache released Log4j version 2.17.0 (Java 8).
Impact
Log4Shell and CVE-2021-45046—rated as critical vulnerabilities by Apache—are severe because Java is used extensively across IT and OT platforms, they are easy to exploit, and applying mitigations is resource intensive. Log4Shell is especially critical because it allows malicious actors to remotely run code on vulnerable networks and take full control of systems.
According to public reporting, exploitation of Log4Shell began on or around December 1, 2021, and a proof-of-concept exploit is publicly available for this vulnerability. The FBI has observed attempted exploitation and widespread scanning of the Log4j vulnerability to gain access to networks to deploy cryptomining and botnet malware. The FBI assesses this vulnerability may be exploited by sophisticated cyber threat actors and incorporated into existing cyber criminal schemes that are looking to adopt increasingly sophisticated obfuscation techniques. According to public reporting, CVE-2021-45046 is being actively exploited as well.
CISA, the FBI, NSA, ACSC, CCCS, CERT NZ, NZ NCSC, and NCSC-UK assess that exploitation of these vulnerabilities, especially Log4Shell, is likely to increase and continue over an extended period. Given the severity of the vulnerabilities and likely increased exploitation, CISA, the FBI, NSA, ACSC, CCCS, CERT NZ, NZ NCSC, and NCSC-UK strongly urge all organizations to apply the recommendations in the Mitigations section to identify, mitigate, and update affected assets.
For more information on these vulnerabilities, see the Apache Log4j Security Vulnerabilities webpage.
Vendors
CISA, the FBI, NSA, ACSC, CCCS, CERT NZ, NZ NCSC, and NCSC-UK encourage vendors to:
- Immediately identify, mitigate, and update affected products that use Log4j to the latest patched version.
- For environments using Java 8 or later, upgrade to Log4j version 2.17.0 (released December 17, 2021) or newer.
- For environments using Java 7, upgrade to Log4j version 2.12.3 (released December 21, 2021). Note: Java 7 is currently end of life and organizations should upgrade to Java 8.
- Inform your end users of products that contain these vulnerabilities and strongly urge them to prioritize software updates. CISA, the FBI, NSA, ACSC, CCCS, CERT NZ, NZ NCSC, and NCSC-UK strongly recommend vendors take steps to ensure messaging on software updates reaches the widest possible audience (for example, avoid placing relevant information behind paywalls). Note: CISA is actively maintaining a GitHub page and repository with patch information for products known to be affected by Log4Shell. CISA has also notified ICS vendors that may be affected and has asked them to confirm any assets affected by Log4Shell and to apply available mitigations.
Affected Organizations with IT and Cloud Assets
CISA, the FBI, NSA, ACSC, CCCS, CERT NZ, NZ NCSC, and NCSC-UK recommend that affected organizations take the following steps to patch these vulnerabilities in their IT and cloud assets and initiate threat hunting to detect possible compromise. Organizations with OT/ICS environments should review the Organizations with OT/ICS Assets section for additional guidance. Note: this guidance includes resources that may or may not be possible for all organizations. CISA, the FBI, NSA, ACSC, CCCS, CERT NZ, NZ NCSC, and NCSC-UK recommend that organizations apply the mitigations listed in this advisory to the extent allowed by their environments.
1. Identify vulnerable assets in your environment.
Knowing where Log4j and other affected products exist in your environment is key for protecting your networks.
- Inventory all assets that make use of the Log4j Java library. According to public reporting, adversaries are patching and mitigating assets they compromise to retain control of assets. To avoid missing such defense evasion, organizations should carefully track assets under investigation.
- Assume all versions of Java and Log4j are vulnerable and include them in the inventory.
- Ensure the inventory includes all assets, including cloud assets, regardless of function, operating system, or make. Ensure the inventory includes the following information about each asset
- Software versions
- Timestamps of when last updated and by whom
- User accounts on the asset with their privilege level
- Location of asset in your enterprise topology
- Identify the inventoried assets that are likely vulnerable.
- Use CISA’s GitHub repository and CERT/CC’s CVE-2021-44228_scanner to identify assets vulnerable to Log4Shell.
Additional resources for detecting vulnerable instances of Log4j are identified below. CISA, the FBI, NSA, ACSC, CCCS, CERT NZ, NZ NCSC, and NCSC-UK will update the sources for detection rules as we obtain them. Note: due to the urgency to share this information, CISA, the FBI, NSA, ACSC, CCCS, CERT NZ, NZ NCSC, and NCSC-UK have not yet validated this content.
- To identify server applications that may be affected by Log4Shell and CVE-2021-45046, see TrendMicro: Log4J Vulnerability Tester.
- For a list of hashes to help determine if a Java application is running a vulnerable version of Log4j, see:
- For PowerShell to detect vulnerable instances, see:
- For guidance on using Canary Token to test for callback, see Thinkst Canary’s Twitter thread on using Canary Tokens.
- For guidance on using Burpsuite Pro to scan, see:
- For guidance on using NetMap’s Nmap Scripting Engine (NSE), see Divertor’s GitHub page: nse-log4shell.
- See Florian Roth’s GitHub page, Fenrir 0.9.0 – Log4Shell Release, for guidance on using Roth’s Fenrir tool to detect vulnerable instances.
2. Mitigate known and suspected vulnerable assets in your environment.
A. Treat known and suspected vulnerable assets as compromised. These assets should be isolated until they are mitigated and verified (step 2.D). The method of isolation that you should use depends on the criticality of the asset. Possible isolation methods include:
- Physically removing the asset from the network (e.g., unplug the network cable);
- Moving the asset to a “jail VLAN” with heightened monitoring and security;
- Blocking at the network layer (a switch or some other device);
- Implementing a firewall (including web application firewall) with strict port control and logging; or
- Restricting the asset’s communication, especially to the internet and the rest of the enterprise network.
B. Patch Log4j and other affected products to the latest version.
- See the Apache Log4j Security Vulnerabilities webpage (as of December 22, 2021, the latest Log4j version is 2.17.0 for Java 8 and 2.12.3 for Java 7). Note: patching or updating Java is not enough, you must upgrade the Log4j library itself.
- For other affected products, see CISA’s GitHub page.
Note: if your organization is unable to immediately identify and patch vulnerable instances of Log4j, apply appropriate workarounds. CISA, the FBI, NSA, ACSC, CCCS, CERT NZ, NZ NCSC, and NCSC-UK recommend using vendor-provided mitigations when available. Due to the rapidly evolving situation, these workarounds should not be considered permanent fixes and organizations should apply the appropriate patch as soon as it is made available. Additional mitigations are identified below; however, organizations should use these mitigations at their own risk as they may be incomplete, temporary, or cause harmful effects, such as application instability, a DoS condition, or log evasion.
- Remove the
Jndilookup.class from the class path. [1]
- Ensure that older versions unable or waiting to be upgraded are configured so that the library configuration
log4j2.formatMsgNoLookups is set to TRUE. Note: this mitigation is a quick response for initially identified vulnerable configurations along with patch deployment.
- Delete or rename
Jndilookup.class. Note: removal of the JndiManager will cause the JndiContextSelector and JMSAppender to no longer function). [2]
- Apply a hot patch.
C. Keep an inventory of known and suspected vulnerable assets and what is done with them throughout this process. It is important to track patching because malicious cyber actors may compromise an asset and then patch it to protect their operations. Organizations should keep a meticulous record of vulnerable assets they have patched to identify whether a threat actor may have patched an asset.
D. Verify the mitigation has worked, if possible.
- Scan the patched/mitigated asset with the tools and methods listed in step 1.B. Use more than one method to verify the mitigation was successfully applied.
- Monitor the asset closely.
- Remain alert to changes from vendors for the software on the asset. Additionally, see CISA’s GitHub page for known affected products and patch information. CISA will continually update the repository as vendors release patches.
3. Initiate hunt and incident response procedures. Given the widespread exploitation of this vulnerability, CISA, the FBI, NSA, ACSC, CCCS, CERT NZ, NZ NCSC, and NCSC-UK encourage all organizations to assume their assets that use Log4j may have been compromised and initiate hunt procedures.
A. Hunt for signs of exploitation and compromise.
- Treat assets that use Log4j as suspect and conduct vigorous forensic investigation of those assets.
- Inspect and monitor accounts across your enterprise that exist on or connect to assets that use Log4j.
- Inspect changes to configurations made since December 1, 2021, and verify they were intended, especially on assets that use Log4j.
- Use CISA’s GitHub page to detect possible exploitation or compromise.
Additional resources to detect possible exploitation or compromise are identified below. Note: due to the urgency to share this information, CISA, the FBI, NSA, ACSC, CCCS, CERT NZ, NZ NCSC, and NCSC-UK have not yet validated this content.
B. If compromise is detected, organizations should:
- Initiate incident response procedures. See the joint advisory from ACSC, CCCS, NZ NCSC, CERT NZ, NCSC-UK, and CISA on Technical Approaches to Uncovering and Remediating Malicious Activity for guidance on hunting or investigating a network, and for common mistakes in incident handling. CISA, the FBI, NSA, ACSC, CCCS, CERT NZ, NZ NCSC, and NCSC-UK encourage organizations to see CISA’s Federal Government Cybersecurity Incident and Vulnerability Response Playbooks. Although tailored to U.S. FCEB agencies, these playbooks provide operational procedures for planning and conducting cybersecurity incident and vulnerability response activities and detail each step for both incident and vulnerability response.
- Consider reporting compromises immediately to applicable cybersecurity authorities. Organizations are encouraged to be as thorough as possible by including information such as IP addresses/domains used to exploit your infrastructure, exploited applications/servers, administrators contact information, and the start and end dates of the attack.
- U.S. organizations should report compromises to CISA and the FBI.
- Australian organizations can visit cyber.gov.au or call 1300 292 371 (1300 CYBER 1) to report cybersecurity incidents.
- Canadian organizations can report incidents by emailing CCCS at contact@cyber.gc.ca.
- New Zealand organizations can visit NCSC.govt.nz to report incidents.
- UK organizations can report a significant cyber security incident at ncsc.gov.uk/report-an-incident (monitored 24 hrs) or, for urgent assistance, call 03000 200 973.
4. Evaluate and apply other mitigations.
A. Remain alert to changes from vendors for the software on the asset, and immediately apply updates to assets when notified by a vendor that their product has a patch for this vulnerability. Additionally, see CISA’s GitHub repository for known affected products and patch information. CISA will continually update the repository as vendors release patches.
B. Continue to monitor Log4J assets closely. Continually use signatures and indicators of compromise that may indicate exploitation.
- See the exploitation and detection resources listed in step 3.A.(4).
- Be aware that there are many ways to obfuscate the exploit string. Do not depend on one detection method to work all the time.
C. Continue to monitor the Apache Log4j Security Vulnerabilities webpage for new updates. Note: as this is an evolving situation and new vulnerabilities in Log4J are being discovered, organizations should ensure their Apache Log4j is up to date. Identify the software your enterprise uses and stay on top of updates as these may be superseded by other updates and fixes.
D. Block specific outbound Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) and User Datagram Protocol (UDP) network traffic.
- Outbound LDAP: for most networks, LDAP is used internally, but it is rare for LDAP requests to be routed outside a network. Organizations should block outbound LDAP or use an allowlist for outbound LDAP to known good destinations. Note: this may be difficult to detect on certain ports without a firewall that does application layer filtering.
- Remote Method Invocation (RMI): for most networks, RMI is either unused or used for internal sources. Organizations should block outbound RMI or use an allowlist for outbound RMI to known good destinations.
- Outbound DNS: organizations using enterprise DNS resolution can block outbound DNS from sources other than identified DNS resolvers. At a minimum, blocking direct outbound DNS from web application servers configured to use enterprise DNS resolution will mitigate the risks to those systems.
Note: blocking attacker internet IP addresses during this event is difficult due to the high volume of scanning from non-malicious researchers and vendors. The false positives on IP addresses are high. Organizations should focus on looking for signs of successful exploitation and not scans.
Affected Organizations with OT/ICS Assets
Due to the pervasiveness of the Apache Log4j software library—and the integration of the library in operational products—CISA, the FBI, NSA, ACSC, CCCS, CERT NZ, NZ NCSC, and NCSC-UK strongly recommend that OT asset owners and operators review their operational architecture and enumerate the vulnerability status against current product alerts and advisories. If a product does not have a security advisory specifically addressing the status of the vulnerability, treat it with additional protections. CISA, the FBI, NSA, ACSC, CCCS, CERT NZ, NZ NCSC, and NCSC-UK urge patching or deployment of mitigations to reduce the risk of the threat of these vulnerabilities.
Note: CISA, the FBI, NSA, ACSC, CCCS, CERT NZ, NZ NCSC, and NCSC-UK recommend prioritizing patching IT devices, especially those with internet connectivity. Affected internet-facing devices as well as laptops, desktops, and tablets are especially susceptible to exploitation of these vulnerabilities. OT/ICS devices—if segmented appropriately from the IT environment—do not face the internet and, as such, have a smaller attack surface to this vulnerability. Exploitation of IT devices may affect OT/ICS devices if there is insufficient network segmentation that prevents lateral movement.
CISA, the FBI, NSA, ACSC, CCCS, CERT NZ, NZ NCSC, and NCSC-UK recommend that OT/ICS asset owner/operators take the following guidance into consideration:
- Review operational architecture and enumerate the vulnerability against current product alerts and advisories. If products do not have a security advisory specifically addressing their status of the vulnerability, it is recommended to treat these devices with additional protections.
- Implement the steps listed in the previous section to identify and isolate vulnerable assets in the OT/ICS environment. Understand what type of products in the OT environment would be affected. Many OT/ICS-specific products incorporate vulnerable versions of the Log4j library.
- Use a risk-informed decision-making process to apply the latest version of hotfixes or patches to affected devices as soon as is operationally feasible. If patches cannot be applied, mitigations provided by the product’s manufacturer or reseller should be deployed. Note: CISA, the FBI, NSA, ACSC, CCCS, CERT NZ, NZ NCSC, and NCSC-UK recommend, as quality assurance, that users test the update in a test development environment that reflects their production environment prior to installation.
- Minimize network exposure for all control system devices and/or systems, and ensure they are not accessible from the internet.
- Locate control system networks and remote devices behind firewalls and isolate them from the business network.
When remote access is required, use secure methods such as virtual private networks (VPNs), recognizing VPNs may have vulnerabilities and should be updated to the most current version available. Also recognize that a VPN is only as secure as its connected devices.
CISA, the FBI, NSA, ACSC, CCCS, CERT NZ, NZ NCSC, and NCSC-UK also remind organizations to perform proper impact analysis and risk assessment prior to deploying defensive measures.
CISA also provides a section for control systems security recommended practices on the ICS webpage on cisa.gov. Several recommended practices are available for reading and download, including Improving Industrial Control Systems Cybersecurity with Defense-in-Depth Strategies.
Additional mitigation guidance and recommended practices are publicly available on the ICS webpage on cisa.gov in the Technical Information Paper, ICS-TIP-12-146-01B–Targeted Cyber Intrusion Detection and Mitigation Strategies.
Organizations observing any suspected malicious activity should follow their established internal procedures and consider reporting compromises immediately.
- U.S. organizations should report compromises to CISA and the FBI.
- Australian organizations can visit cyber.gov.au or call 1300 292 371 (1300 CYBER 1) to report cybersecurity incidents.
- Canadian organizations can report incidents by emailing CCCS at contact@cyber.gc.ca.
- New Zealand organizations can visit NCSC.govt.nz to report incidents.
- UK organizations can report a significant cyber security incident at ncsc.gov.uk/report-an-incident (monitored 24 hrs) or, for urgent assistance, call 03000 200 973.
Resources
For more information, resources, and general guidance, including resources and mitigation guidance from industry members of JCDC, see CISA’s webpage Apache Log4j Vulnerability Guidance. Note: due to the prominent and ever evolving nature of this vulnerability, there are multiple unverified published guidance documents that are geared towards Log4j vulnerabilities. CISA, the FBI, NSA, ACSC, CCCS, CERT NZ, NZ NCSC, and NCSC-UK encourage all organizations to verify information with trusted sources, such CISA, the FBI, NSA, ACSC, CCCS, CERT NZ, NZ NCSC, NCSC-UK vendors.
by Scott Muniz | Dec 21, 2021 | Security, Technology
This article is contributed. See the original author and article here.
N/A — N/A
|
pep_sock_accept in net/phonet/pep.c in the Linux kernel through 5.15.8 has a refcount leak. |
2021-12-16 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-45095
MISC
MISC |
addons-ssh — addons-ssh
|
** DISPUTED ** The addon.stdin service in addon-ssh (aka Home Assistant Community Add-on: SSH & Web Terminal) before 10.0.0 has an attack surface that requires social engineering. NOTE: the vendor does not agree that this is a vulnerability; however, addon.stdin was removed as a defense-in-depth measure against complex social engineering situations. |
2021-12-16 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-45099
MISC
MISC |
ajaxsoundstudio — ajaxsoundstudio
|
Buffer Overflow Vulnerability exists in ajaxsoundstudio.com n Pyo < 1.03 in the Server_debug function, which allows remote attackers to conduct DoS attacks by deliberately passing on an overlong audio file name. |
2021-12-17 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-41499
MISC |
alac_decoder — alac_decoder
|
In alac decoder, there is a possible out of bounds read due to an incorrect bounds check. This could lead to local information disclosure with no additional execution privileges needed. User interaction is not needed for exploitation. Patch ID: ALPS06064258; Issue ID: ALPS06064237. |
2021-12-17 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-0674
MISC |
anchor — cms
|
Cross Site Scripting (XSS) vulnerability exits in Anchor CMS <=0.12.7 in posts.php. Attackers can use the posts column to upload the title and content containing malicious code to achieve the purpose of obtaining the administrator cookie, thereby achieving other malicious operations. |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-44116
MISC |
anonaddy — anonaddy
|
A Broken or Risky Cryptographic Algorithm exists in AnonAddy 0.8.5 via VerificationController.php. |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-42216
MISC
MISC
MISC |
apache — log4j2
|
Apache Log4j2 versions 2.0-alpha1 through 2.16.0 (excluding 2.12.3) did not protect from uncontrolled recursion from self-referential lookups. This allows an attacker with control over Thread Context Map data to cause a denial of service when a crafted string is interpreted. This issue was fixed in Log4j 2.17.0 and 2.12.3. |
2021-12-18 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-45105
MISC
CONFIRM
MLIST
DEBIAN
MISC
CISCO |
apache — nifi
|
In the TransformXML processor of Apache NiFi before 1.15.1 an authenticated user could configure an XSLT file which, if it included malicious external entity calls, may reveal sensitive information. |
2021-12-17 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-44145
MISC
MLIST |
apache — sling_commons_messaging_mail
|
Apache Sling Commons Messaging Mail provides a simple layer on top of JavaMail/Jakarta Mail for OSGi to send mails via SMTPS. To reduce the risk of “man in the middle” attacks additional server identity checks must be performed when accessing mail servers. For compatibility reasons these additional checks are disabled by default in JavaMail/Jakarta Mail. The SimpleMailService in Apache Sling Commons Messaging Mail 1.0 lacks an option to enable these checks for the shared mail session. A user could enable these checks nevertheless by accessing the session via the message created by SimpleMessageBuilder and setting the property mail.smtps.ssl.checkserveridentity to true. Apache Sling Commons Messaging Mail 2.0 adds support for enabling server identity checks and these checks are enabled by default. – https://javaee.github.io/javamail/docs/SSLNOTES.txt – https://javaee.github.io/javamail/docs/api/com/sun/mail/smtp/package-summary.html – https://github.com/eclipse-ee4j/mail/issues/429 |
2021-12-14 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-44549
MISC |
apple — ios
|
GGLocker iOS application, contains an insecure data storage of the password hash value which results in an authentication bypass. |
2021-12-16 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-3179
MISC
MISC
MISC |
apple — ios
|
An URL Address bar spoofing vulnerability was discovered in Safe Browser for iOS. When user clicks on a specially crafted a malicious URL, if user does not carefully pay attention to url, user may be tricked to think content may be coming from a valid domain, while it comes from another. This is performed by using a very long username part of the url so that user cannot see the domain name. A remote attacker can leverage this to perform url address bar spoofing attack. The fix is, browser no longer shows the user name part in address bar. |
2021-12-16 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-40835
MISC
MISC |
apusys — apusys
|
In apusys, there is a possible out of bounds write due to a missing bounds check. This could lead to local escalation of privilege with System execution privileges needed. User interaction is not needed for exploitation. Patch ID: ALPS05672107; Issue ID: ALPS05670549. |
2021-12-17 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-0897
MISC |
apusys — apusys
|
In apusys, there is a possible out of bounds write due to a missing bounds check. This could lead to local escalation of privilege with System execution privileges needed. User interaction is not needed for exploitation. Patch ID: ALPS05672107; Issue ID: ALPS05656488. |
2021-12-17 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-0903
MISC |
apusys — apusys
|
In apusys, there is a possible out of bounds read due to an incorrect bounds check. This could lead to local information disclosure with System execution privileges needed. User interaction is not needed for exploitation. Patch ID: ALPS05672107; Issue ID: ALPS05656484. |
2021-12-17 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-0902
MISC |
apusys — apusys
|
In apusys, there is a possible memory corruption due to a missing bounds check. This could lead to local escalation of privilege with System execution privileges needed. User interaction is not needed for exploitation. Patch ID: ALPS05672107; Issue ID: ALPS05664618. |
2021-12-17 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-0901
MISC |
apusys — apusys
|
In apusys, there is a possible out of bounds read due to an incorrect bounds check. This could lead to local information disclosure with System execution privileges needed. User interaction is not needed for exploitation. Patch ID: ALPS05672107; Issue ID: ALPS05672055. |
2021-12-17 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-0900
MISC |
apusys — apusys
|
In apusys, there is a possible memory corruption due to a use after free. This could lead to local escalation of privilege with System execution privileges needed. User interaction is not needed for exploitation. Patch ID: ALPS05672107; Issue ID: ALPS05672059. |
2021-12-17 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-0899
MISC |
apusys — apusys
|
In apusys, there is a possible memory corruption due to a use after free. This could lead to local escalation of privilege with System execution privileges needed. User interaction is not needed for exploitation. Patch ID: ALPS05672107; Issue ID: ALPS05672071. |
2021-12-17 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-0898
MISC |
apusys — apusys
|
In apusys, there is a possible out of bounds write due to a missing bounds check. This could lead to local escalation of privilege with System execution privileges needed. User interaction is not needed for exploitation. Patch ID: ALPS05672107; Issue ID: ALPS05722511. |
2021-12-17 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-0678
MISC |
apusys — apusys
|
In apusys, there is a possible memory corruption due to a missing bounds check. This could lead to local escalation of privilege with System execution privileges needed. User interaction is not needed for exploitation. Patch ID: ALPS05672107; Issue ID: ALPS05687781. |
2021-12-17 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-0679
MISC |
apusys — apusys
|
In apusys, there is a possible memory corruption due to a use after free. This could lead to local escalation of privilege with System execution privileges needed. User interaction is not needed for exploitation. Patch ID: ALPS05672107; Issue ID: ALPS05687474. |
2021-12-17 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-0893
MISC |
apusys — apusys
|
In apusys, there is a possible out of bounds write due to a missing bounds check. This could lead to local escalation of privilege with System execution privileges needed. User interaction is not needed for exploitation. Patch ID: ALPS05672107; Issue ID: ALPS05672038. |
2021-12-17 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-0894
MISC |
apusys — apusys
|
In apusys, there is a possible out of bounds write due to a missing bounds check. This could lead to local escalation of privilege with System execution privileges needed. User interaction is not needed for exploitation. Patch ID: ALPS05672107; Issue ID: ALPS05672003. |
2021-12-17 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-0895
MISC |
apusys — apusys
|
In apusys, there is a possible out of bounds write due to a missing bounds check. This could lead to local escalation of privilege with System execution privileges needed. User interaction is not needed for exploitation. Patch ID: ALPS05672107; Issue ID: ALPS05671206. |
2021-12-17 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-0896
MISC |
atomix — atomix
|
An issue in Atomix v3.1.5 allows attackers to cause a denial of service (DoS) via false link event messages sent to a master ONOS node. |
2021-12-16 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-35213
MISC |
atomix — atomix
|
An issue in Atomix v3.1.5 allows a malicious Atomix node to remove states of ONOS storage via abuse of primitive operations. |
2021-12-16 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-35214
MISC |
atomix — atomix
|
An issue in Atomix v3.1.5 allows unauthorized Atomix nodes to join a target cluster via providing configuration information. |
2021-12-16 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-35209
MISC |
atomix — atomix
|
A vulnerability in Atomix v3.1.5 allows attackers to cause a denial of service (DoS) via a Raft session flooding attack using Raft OpenSessionRequest messages. |
2021-12-16 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-35210
MISC |
atomix — atomix
|
An issue in Atomix v3.1.5 allows unauthorized Atomix nodes to become the lead node in a target cluster via manipulation of the variable terms in RaftContext. |
2021-12-16 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-35211
MISC |
atomix — atomix
|
An issue in Atomix v3.1.5 allows attackers to access sensitive information when a malicious Atomix node queries distributed variable primitives which contain the entire primitive lists that ONOS nodes use to share important states. |
2021-12-16 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-35215
MISC |
atomix — atomix
|
An issue in Atomix v3.1.5 allows attackers to cause a denial of service (DoS) via false member down event messages. |
2021-12-16 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-35216
MISC |
audio_aurisys_hal — audio_aurisys_hal
|
In Audio Aurisys HAL, there is a possible permission bypass due to a missing permission check. This could lead to local escalation of privilege with no additional execution privileges needed. User interaction is not needed for exploitation. Patch ID: ALPS05977326; Issue ID: ALPS05977326. |
2021-12-17 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-0673
MISC |
auth0 — auth0
|
The Auth0 Next.js SDK is a library for implementing user authentication in Next.js applications. Versions before 1.6.2 do not filter out certain returnTo parameter values from the login url, which expose the application to an open redirect vulnerability. Users are advised to upgrade as soon as possible. There are no known workarounds for this issue. |
2021-12-16 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-43812
MISC
CONFIRM |
bitdefender — endpoint_security_tools
|
A Server-Side Request Forgery (SSRF) vulnerability in the EPPUpdateService component of Bitdefender Endpoint Security Tools allows an attacker to proxy requests to the relay server. This issue affects: Bitdefender Bitdefender GravityZone versions prior to 3.3.8.272 |
2021-12-16 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-3959
MISC |
bitdefender — gravityzone
|
Improper Limitation of a Pathname to a Restricted Directory (‘Path Traversal’) vulnerability in the UpdateServer component of Bitdefender GravityZone allows an attacker to execute arbitrary code on vulnerable instances. This issue affects Bitdefender GravityZone versions prior to 3.3.8.272 |
2021-12-16 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-3960
MISC |
bookstack — bookstack
|
bookstack is vulnerable to Improper Access Control |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-4119
MISC
CONFIRM |
| bus_pass_management_system — bus_pass_management_system |
In Bus Pass Management System v1.0, Directory Listing/Browsing is enabled on the web server which allows an attacker to view the sensitive files of the application, for example: Any file which contains sensitive information of the user or server. |
2021-12-16 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-44315
MISC
MISC |
|
bus_pass_management_system — bus_pass_management_system
|
In Bus Pass Management System v1.0, parameters ‘pagedes’ and `About Us` are affected with a Stored Cross-site scripting vulnerability. |
2021-12-16 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-44317
MISC
MISC |
catfish — catfish
|
Cross Site Scripting (XSS) vulnerability exists in Catfish <=6.3.0 via a Google search in url:/catfishcms/index.php/admin/Index/addmenu.htmland then the .html file on the website that uses this editor (the file suffix is allowed). |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-45018
MISC |
catfish — catfish
|
Cross Site Request Forgery (CSRF) vulnerability exits in Catfish <=6.1.* when you upload an html file containing CSRF on the website that uses a google editor; you can specify the menu url address as your malicious url address in the Add Menu column. |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-45017
MISC |
cbioportal — cbioportal
|
A regular expression denial of service (ReDoS) vulnerability exits in cbioportal 3.6.21 and older via a POST request to /ProteinArraySignificanceTest.json. |
2021-12-16 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-38244
MISC
MISC |
ccu_driver — ccu_driver
|
In ccu driver, there is a possible out of bounds read due to an integer overflow. This could lead to local information disclosure with System execution privileges needed. User interaction is not needed for exploitation. Patch ID: ALPS05827154; Issue ID: ALPS05827154. |
2021-12-17 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-0677
MISC |
convos-chat — convos-chat
|
A Stored Cross Site Scripting (XSS) issue exists in Convos-Chat before 6.32. |
2021-12-17 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-42584
MISC
MISC
MISC |
cvxopt — cvxopt
|
Incomplete string comparison vulnerability exits in cvxopt.org cvxop <= 1.2.6 in APIs (cvxopt.cholmod.diag, cvxopt.cholmod.getfactor, cvxopt.cholmod.solve, cvxopt.cholmod.spsolve), which allows attackers to conduct Denial of Service attacks by construct fake Capsule objects. |
2021-12-17 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-41500
MISC |
discourse — discourse
|
discourse-footnote is a library providing footnotes for posts in Discourse. ### Impact When posting an inline footnote wrapped in `<a>` tags (e.g. `<a>^[footnote]</a>`, the resulting rendered HTML would include a nested `<a>`, which is stripped by Nokogiri because it is not valid. This then caused a javascript error on topic pages because we were looking for an `<a>` element inside the footnote reference span and getting its ID, and because it did not exist we got a null reference error in javascript. Users are advised to update to version 0.2. As a workaround editing offending posts from the rails console or the database console for self-hosters, or disabling the plugin in the admin panel can mitigate this issue. |
2021-12-14 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-43827
MISC
CONFIRM |
dojo — dojo
|
All versions of package dojo are vulnerable to Prototype Pollution via the setObject function. |
2021-12-17 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-23450
CONFIRM
CONFIRM
CONFIRM
CONFIRM
CONFIRM
CONFIRM |
dojo — dojo
|
All versions of package http-server-node are vulnerable to Directory Traversal via use of –path-as-is. |
2021-12-17 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-23797
CONFIRM |
elabftw — elabftw
|
eLabFTW is an electronic lab notebook manager for research teams. In versions prior to 4.2.0 there is a vulnerability which allows any authenticated user to gain access to arbitrary accounts by setting a specially crafted email address. This vulnerability impacts all instances that have not set an explicit email domain name allowlist. Note that whereas neither administrators nor targeted users are notified of a change, an attacker will need to control an account. The default settings require administrators to validate newly created accounts. The problem has been patched. Users should upgrade to at least version 4.2.0. For users unable to upgrade enabling an email domain allow list (from Sysconfig panel, Security tab) will completely resolve the issue. |
2021-12-16 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-43833
CONFIRM
MISC |
elabftw — elabftw
|
eLabFTW is an electronic lab notebook manager for research teams. In versions prior to 4.2.0 there is a vulnerability which allows an attacker to authenticate as an existing user, if that user was created using a single sign-on authentication option such as LDAP or SAML. It impacts instances where LDAP or SAML is used for authentication instead of the (default) local password mechanism. Users should upgrade to at least version 4.2.0. |
2021-12-16 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-43834
MISC
CONFIRM |
fatpipe_network — fatpipe_warp_ipvpn_and_mpvpn_software
|
A missing authorization vulnerability in the web management interface of FatPipe WARP, IPVPN, and MPVPN software prior to versions 10.1.2r60p91 and 10.2.2r42 allows an authenticated, remote attacker with read-only privileges to create an account with administrative privileges. Older versions of FatPipe software may also be vulnerable. This does not appear to be a CSRF vulnerability. The FatPipe advisory identifier for this vulnerability is FPSA005. |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-27859
CONFIRM
MISC
MISC |
fatpipe_network — fatpipe_warp_ipvpn_and_mpvpn_software
|
A missing authorization vulnerability in the web management interface of FatPipe WARP, IPVPN, and MPVPN software prior to versions 10.1.2r60p91 and 10.2.2r42 allows a remote attacker to access at least the URL “/fpui/jsp/index.jsp” leading to unknown impact, presumably some violation of confidentiality. Older versions of FatPipe software may also be vulnerable. The FatPipe advisory identifier for this vulnerability is FPSA004. |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-27858
CONFIRM
MISC
MISC |
fatpipe_network — fatpipe_warp_ipvpn_and_mpvpn_software
|
A missing authorization vulnerability in the web management interface of FatPipe WARP, IPVPN, and MPVPN software prior to versions 10.1.2r60p91 and 10.2.2r42 allows a remote, unauthenticated attacker to download a configuration archive. The attacker needs to know or correctly guess the hostname of the target system since the hostname is used as part of the configuration archive file name. Older versions of FatPipe software may also be vulnerable. The FatPipe advisory identifier for this vulnerability is FPSA003. |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-27857
MISC
CONFIRM
MISC |
fatpipe_network — fatpipe_warp_ipvpn_and_mpvpn_software
|
FatPipe WARP, IPVPN, and MPVPN software prior to versions 10.1.2r60p91 and 10.2.2r42 includes an account named “cmuser” that has administrative privileges and no password. Older versions of FatPipe software may also be vulnerable. The FatPipe advisory identifier for this vulnerability is FPSA002. |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-27856
MISC
CONFIRM
MISC |
fatpipe_network — fatpipe_warp_ipvpn_and_mpvpn_software
|
FatPipe WARP, IPVPN, and MPVPN software prior to versions 10.1.2r60p91 and 10.2.2r42 allows a remote, authenticated attacker with read-only privileges to grant themselves administrative privileges. Older versions of FatPipe software may also be vulnerable. The FatPipe advisory identifier for this vulnerability is FPSA001. |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-27855
MISC
MISC
CONFIRM |
fiberhome — onu_gpon_an5506
|
FiberHome ONU GPON AN5506-04-F RP2617 is affected by an OS command injection vulnerability. This vulnerability allows the attacker, once logged in, to send commands to the operating system as the root user via the ping diagnostic tool, bypassing the IP address field, and concatenating OS commands with a semicolon. |
2021-12-16 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-42912
MISC
MISC
MISC |
fortiguard — forticlientems
|
A combination of a use of hard-coded cryptographic key vulnerability [CWE-321] in FortiClientEMS 7.0.1 and below, 6.4.6 and below and an improper certificate validation vulnerability [CWE-297] in FortiClientWindows, FortiClientLinux and FortiClientMac 7.0.1 and below, 6.4.6 and below may allow an unauthenticated and network adjacent attacker to perform a man-in-the-middle attack between the EMS and the FCT via the telemetry protocol. |
2021-12-16 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-41028
CONFIRM |
ftpshell — ftpshell
|
A buffer overflow vulnerability in the Virtual Path Mapping component of FTPShell v6.83 allows attackers to cause a denial of service (DoS). |
2021-12-17 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-18077
MISC |
galette — galette
|
Galette is a membership management web application built for non profit organizations and released under GPLv3. Versions prior to 0.9.6 are subject to SQL injection attacks by users with “member” privilege. Users are advised to upgrade to version 0.9.6 as soon as possible. There are no known workarounds. |
2021-12-16 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-41262
MISC
CONFIRM |
galette — galette
|
Galette is a membership management web application built for non profit organizations and released under GPLv3. Versions prior to 0.9.6 are subject to stored cross site scripting attacks via the preferences footer. The preference footer can only be altered by a site admin. This issue has been resolved in the 0.9.6 release and all users are advised to upgrade. There are no known workarounds. |
2021-12-16 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-41261
CONFIRM
MISC |
galette — galette
|
Galette is a membership management web application built for non profit organizations and released under GPLv3. Versions prior to 0.9.6 do not check for Cross Site Request Forgery attacks. All users are advised to upgrade to 0.9.6 as soon as possible. There are no known workarounds for this issue. |
2021-12-16 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-41260
CONFIRM
MISC |
geniezone_driver — geniezone_driver
|
In geniezone driver, there is a possible out of bounds read due to an incorrect bounds check. This could lead to local information disclosure with System execution privileges needed. User interaction is not needed for exploitation. Patch ID: ALPS05863009; Issue ID: ALPS05863009. |
2021-12-17 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-0676
MISC |
gnu — binutils
|
stab_xcoff_builtin_type in stabs.c in GNU Binutils through 2.37 allows attackers to cause a denial of service (heap-based buffer overflow) or possibly have unspecified other impact, as demonstrated by an out-of-bounds write. NOTE: this issue exists because of an incorrect fix for CVE-2018-12699. |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-45078
MISC
MISC |
google — android
|
In dsi_panel_debugfs_read_cmdset of dsi_panel.c, there is a possible disclosure of freed kernel heap memory due to a use after free. This could lead to local information disclosure with System execution privileges needed. User interaction is not needed for exploitation.Product: AndroidVersions: Android kernelAndroid ID: A-187851056References: N/A |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1042
MISC |
google — android
|
In gadget_dev_desc_UDC_show of configfs.c, there is a possible disclosure of kernel heap memory due to a race condition. This could lead to local information disclosure with System execution privileges needed. User interaction is not needed for exploitation.Product: AndroidVersions: Android kernelAndroid ID: A-160822094References: Upstream kernel |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-39648
MISC |
google — android
|
In adjustStreamVolume of AudioService.java, there is a possible way for unprivileged app to change audio stream volume due to a confused deputy. This could lead to local escalation of privilege with no additional execution privileges needed. User interaction is not needed for exploitation.Product: AndroidVersions: Android-12Android ID: A-189857506 |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1003
MISC |
google — android
|
In WT_Interpolate of eas_wtengine.c, there is a possible out of bounds read due to a missing bounds check. This could lead to remote information disclosure with no additional execution privileges needed. User interaction is not needed for exploitation.Product: AndroidVersions: Android-12Android ID: A-194533433 |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1002
MISC |
google — android
|
In PVInitVideoEncoder of mp4enc_api.cpp, there is a possible out of bounds read due to a heap buffer overflow. This could lead to local information disclosure with no additional execution privileges needed. User interaction is not needed for exploitation.Product: AndroidVersions: Android-12Android ID: A-190435883 |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1001
MISC |
google — android
|
In quota_proc_write of xt_quota2.c, there is a possible way to read kernel memory due to uninitialized data. This could lead to local information disclosure with System execution privileges needed. User interaction is not needed for exploitation.Product: AndroidVersions: Android kernelAndroid ID: A-196046570References: Upstream kernel |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-0961
MISC |
google — android
|
In do_ipt_get_ctl and do_ipt_set_ctl of ip_tables.c, there is a possible way to leak kernel information due to uninitialized data. This could lead to local information disclosure with system execution privileges needed. User interaction is not needed for exploitation.Product: AndroidVersions: Android kernelAndroid ID: A-120612905References: Upstream kernel |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-39636
MISC |
google — android
|
In CreateDeviceInfo of trusty_remote_provisioning_context.cpp, there is a possible out of bounds read due to a missing bounds check. This could lead to local information disclosure with System execution privileges needed. User interaction is not needed for exploitation.Product: AndroidVersions: Android kernelAndroid ID: A-193579873References: N/A |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-39637
MISC |
google — android
|
In periodic_io_work_func of lwis_periodic_io.c, there is a possible out of bounds write due to a use after free. This could lead to local escalation of privilege with System execution privileges needed. User interaction is not needed for exploitation.Product: AndroidVersions: Android kernelAndroid ID: A-195607566References: N/A |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-39638
MISC |
google — android
|
In TBD of fvp.c, there is a possible way to glitch CPU behavior due to a missing permission check. This could lead to local escalation of privilege with physical access to device internals with no additional execution privileges needed. User interaction is not needed for exploitation.Product: AndroidVersions: Android kernelAndroid ID: A-198291476References: N/A |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-39639
MISC |
google — android
|
In __dwc3_gadget_ep0_queue of ep0.c, there is a possible out of bounds write due to improper locking. This could lead to local escalation of privilege with no additional execution privileges needed. User interaction is not needed for exploitation.Product: AndroidVersions: Android kernelAndroid ID: A-157294279References: N/A |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-39640
MISC |
google — android
|
Product: AndroidVersions: Android kernelAndroid ID: A-126949257References: N/A |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-39641
MISC |
google — android
|
In synchronous_process_io_entries of lwis_ioctl.c, there is a possible out of bounds write due to a race condition. This could lead to local escalation of privilege with System execution privileges needed. User interaction is not needed for exploitation.Product: AndroidVersions: Android kernelAndroid ID: A-195731663References: N/A |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-39642
MISC |
google — android
|
In ic_startRetrieveEntryValue of acropora/app/identity/ic.c, there is a possible bypass of defense-in-depth due to missing validation of the return value. This could lead to local escalation of privilege with System execution privileges needed. User interaction is not needed for exploitation.Product: AndroidVersions: Android kernelAndroid ID: A-195573629References: N/A |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-39643
MISC |
google — android
|
In mon_smc_load_sp of gs101-sc/plat/samsung/exynos/soc/exynos9845/smc_booting.S, there is a possible reinitialization of TEE due to improper locking. This could lead to local information disclosure with System execution privileges needed. User interaction is not needed for exploitation.Product: AndroidVersions: Android kernelAndroid ID: A-198713939References: N/A |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-39647
MISC |
google — android
|
In regmap_exit of regmap.c, there is a possible use-after-free due to improper locking. This could lead to local escalation of privilege in the kernel with System execution privileges needed. User interaction is not needed for exploitation.Product: AndroidVersions: Android kernelAndroid ID: A-174049006References: N/A |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-39649
MISC |
google — android
|
In TBD of TBD, there is a possible downgrade attack due to under utilized anti-rollback protections. This could lead to local information disclosure with no additional execution privileges needed. User interaction is not needed for exploitation.Product: AndroidVersions: Android kernelAndroid ID: A-194697257References: N/A |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1043
MISC |
google — android
|
In (TBD) of (TBD), there is a possible out of bounds write due to a missing bounds check. This could lead to local escalation of privilege with System execution privileges needed. User interaction is not needed for exploitation.Product: AndroidVersions: Android kernelAndroid ID: A-169763055References: N/A |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-39650
MISC |
google — android
|
In TBD of TBD, there is a possible way to access PIN protected settings bypassing PIN confirmation due to a missing permission check. This could lead to local escalation of privilege with no additional execution privileges needed. User interaction is not needed for exploitation.Product: AndroidVersions: Android kernelAndroid ID: A-193438173References: N/A |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-39651
MISC |
google — android
|
In sec_ts_parsing_cmds of (TBD), there is a possible out of bounds write due to an incorrect bounds check. This could lead to local escalation of privilege with System execution privileges needed. User interaction is not needed for exploitation.Product: AndroidVersions: Android kernelAndroid ID: A-194499021References: N/A |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-39652
MISC |
google — android
|
In (TBD) of (TBD), there is a possible way to boot with a hidden debug policy due to a missing warning to the user. This could lead to local escalation of privilege after preparing the device, hiding the warning, and passing the phone to a new user, with no additional execution privileges needed. User interaction is not needed for exploitation.Product: AndroidVersions: Android kernelAndroid ID: A-193443223References: N/A |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-39653
MISC |
google — android
|
Product: AndroidVersions: Android kernelAndroid ID: A-192641593References: N/A |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-39655
MISC |
google — android
|
In __configfs_open_file of file.c, there is a possible use-after-free due to improper locking. This could lead to local escalation of privilege in the kernel with System execution privileges needed. User interaction is not needed for exploitation.Product: AndroidVersions: Android kernelAndroid ID: A-174049066References: Upstream kernel |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-39656
MISC |
google — android
|
In ufshcd_eh_device_reset_handler of ufshcd.c, there is a possible out of bounds read due to a missing bounds check. This could lead to local information disclosure with System execution privileges needed. User interaction is not needed for exploitation.Product: AndroidVersions: Android kernelAndroid ID: A-194696049References: Upstream kernel |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-39657
MISC |
google — android
|
In update of km_compat.cpp, there is a possible loss of potentially sensitive data due to a logic error in the code. This could lead to local denial of service with User execution privileges needed. User interaction is not needed for exploitation.Product: AndroidVersions: Android-11 Android-12Android ID: A-200041882 |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-0958
MISC |
google — android
|
In NfcTag::discoverTechnologies (activation) of NfcTag.cpp, there is a possible out of bounds write due to an incorrect bounds check. This could lead to remote escalation of privilege with no additionalSystem execution privileges needed. User interaction is not needed for exploitation.Product: AndroidVersions: Android-11 Android-12Android ID: A-189942532 |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-0956
MISC |
google — android
|
In pf_write_buf of FuseDaemon.cpp, there is possible memory corruption due to a race condition. This could lead to local escalation of privilege with no additional execution privileges needed. User interaction is not needed for exploitation.Product: AndroidVersions: Android-11Android ID: A-192085766 |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-0955
MISC |
google — android
|
In ResolverActivity, there is a possible user interaction bypass due to a tapjacking/overlay attack. This could lead to local escalation of privilege with User execution privileges needed. User interaction is needed for exploitation.Product: AndroidVersions: Android-10 Android-11Android ID: A-143559931 |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-0954
MISC |
google — android
|
In setOnClickActivityIntent of SearchWidgetProvider.java, there is a possible way to access contacts and history bookmarks without permission due to an unsafe PendingIntent. This could lead to local escalation of privilege with User execution privileges needed. User interaction is not needed for exploitation.Product: AndroidVersions: Android-10 Android-11 Android-12 Android-9Android ID: A-184046278 |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-0953
MISC |
google — android
|
In WT_InterpolateNoLoop of eas_wtengine.c, there is a possible out of bounds read due to an incorrect bounds check. This could lead to remote information disclosure with no additional execution privileges needed. User interaction is needed for exploitation.Product: AndroidVersions: Android-10 Android-11 Android-9Android ID: A-190286685 |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-0650
MISC |
google — android
|
In getConfiguredNetworks of WifiServiceImpl.java, there is a possible way to determine whether an app is installed, without query permissions, due to a missing permission check. This could lead to local escalation of privilege with no additional execution privileges needed. User interaction is not needed for exploitation.Product: AndroidVersions: Android-12Android ID: A-197749180 |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1004
MISC |
google — android
|
In getDeviceIdWithFeature of PhoneInterfaceManager.java, there is a possible way to determine whether an app is installed, without query permissions, due to side channel information disclosure. This could lead to local information disclosure with no additional execution privileges needed. User interaction is not needed for exploitation.Product: AndroidVersions: Android-12Android ID: A-186530889 |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1005
MISC |
google — android
|
In several functions of DatabaseManager.java, there is a possible leak of Bluetooth MAC addresses due to log information disclosure. This could lead to local information disclosure with System execution privileges needed. User interaction is not needed for exploitation.Product: AndroidVersions: Android-12Android ID: A-183961974 |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1006
MISC |
google — android
|
In checkExistsAndEnforceCannotModifyImmutablyRestrictedPermission of PermissionManagerService.java, there is a possible way to determine whether an app is installed, without query permissions, due to side channel information disclosure. This could lead to local information disclosure with no additional execution privileges needed. User interaction is not needed for exploitation.Product: AndroidVersions: Android-12Android ID: A-186404356 |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1013
MISC |
google — android
|
In eicOpsDecryptAes128Gcm of acropora/app/identity/identity_support.c, there is a possible out of bounds write due to a missing bounds check. This could lead to local escalation of privilege with no additional execution privileges needed. User interaction is not needed for exploitation.Product: AndroidVersions: Android kernelAndroid ID: A-195570681References: N/A |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1044
MISC |
google — android
|
Product: AndroidVersions: Android kernelAndroid ID: A-195580473References: N/A |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1045
MISC |
google — android
|
In (TBD) of (TBD), there is a possible out of bounds read due to memory corruption. This could lead to local information disclosure with no additional execution privileges needed. User interaction is not needed for exploitation.Product: AndroidVersions: Android kernelAndroid ID: A-182950799References: N/A |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1041
MISC |
google — android
|
In valid_ipc_dram_addr of cm_access_control.c, there is a possible out of bounds read due to an integer overflow. This could lead to local information disclosure with System execution privileges needed. User interaction is not needed for exploitation.Product: AndroidVersions: Android kernelAndroid ID: A-197966306References: N/A |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1047
MISC |
google — android
|
In ep_loop_check_proc of eventpoll.c, there is a possible way to corrupt memory due to a use after free. This could lead to local escalation of privilege with no additional execution privileges needed. User interaction is not needed for exploitation.Product: AndroidVersions: Android kernelAndroid ID: A-204573007References: Upstream kernel |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1048
MISC |
google — android
|
In onCreate of BluetoothPairingSelectionFragment.java, there is a possible EoP due to a tapjacking/overlay attack. This could lead to local escalation of privilege with no additional execution privileges needed. User interaction is needed for exploitation.Product: AndroidVersions: Android-10 Android-11 Android-12 Android-9Android ID: A-182810085 |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1040
MISC |
google — android
|
In NotificationAccessActivity of AndroidManifest.xml, there is a possible EoP due to a tapjacking/overlay attack. This could lead to local escalation of privilege with no additional execution privileges needed. User interaction is needed for exploitation.Product: AndroidVersions: Android-10 Android-11 Android-12 Android-9Android ID: A-182808318 |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1039
MISC |
google — android
|
In getLine1NumberForDisplay of PhoneInterfaceManager.java, there is apossible way to determine whether an app is installed, without querypermissions due to a missing permission check. This could lead to localinformation disclosure with no additional execution privileges needed. Userinteraction is not needed for exploitation.Product: AndroidVersions: Android-12Android ID: A-193441322 |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1034
MISC |
google — android
|
In getMimeGroup of PackageManagerService.java, there is a possible way to determine whether an app is installed, without query permissions, due to side channel information disclosure. This could lead to local information disclosure with no additional execution privileges needed. User interaction is not needed for exploitation.Product: AndroidVersions: Android-12Android ID: A-184745603 |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1032
MISC |
google — android
|
In cancelNotificationsFromListener of NotificationManagerService.java, there is a possible way to determine whether an app is installed, without query permissions, due to side channel information disclosure. This could lead to local information disclosure with no additional execution privileges needed. User interaction is not needed for exploitation.Product: AndroidVersions: Android-12Android ID: A-194697004 |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1031
MISC |
google — android
|
In getMeidForSlot of PhoneInterfaceManager.java, there is a possible way to determine whether an app is installed, without query permissions, due to side channel information disclosure. This could lead to local information disclosure with no additional execution privileges needed. User interaction is not needed for exploitation.Product: AndroidVersions: Android-12Android ID: A-186530496 |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1015
MISC |
google — android
|
In getNetworkTypeForSubscriber of PhoneInterfaceManager.java, there is a possible way to determine whether an app is installed, without query permissions, due to side channel information disclosure. This could lead to local information disclosure with no additional execution privileges needed. User interaction is not needed for exploitation.Product: AndroidVersions: Android-12Android ID: A-186776740 |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1014
MISC |
google — android
|
In AdapterService and GattService definition of AndroidManifest.xml, there is a possible way to disable bluetooth connection due to a missing permission check. This could lead to local escalation of privilege with no additional execution privileges needed. User interaction is needed for exploitation.Product: AndroidVersions: Android-12Android ID: A-182583850 |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1017
MISC |
google — android
|
In onResume of NotificationAccessDetails.java, there is a possible way to determine whether an app is installed, without query permissions, due to side channel information disclosure. This could lead to local information disclosure with no additional execution privileges needed. User interaction is not needed for exploitation.Product: AndroidVersions: Android-12Android ID: A-195412179 |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1012
MISC |
google — android
|
In setApplicationCategoryHint of PackageManagerService.java, there is a possible way to determine whether an app is installed, without query permissions, due to side channel information disclosure. This could lead to local information disclosure with no additional execution privileges needed. User interaction is not needed for exploitation.Product: AndroidVersions: Android-12Android ID: A-189858128 |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1009
MISC |
google — android
|
In btu_hcif_process_event of btu_hcif.cc, there is a possible out of bounds read due to an incorrect bounds check. This could lead to local information disclosure with System execution privileges needed. User interaction is not needed for exploitation.Product: AndroidVersions: Android-12Android ID: A-167759047 |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1007
MISC |
google — android
|
In setPackageStoppedState of PackageManagerService.java, there is a missing permission check. This could lead to local information disclosure with no additional execution privileges needed. User interaction is not needed for exploitation.Product: AndroidVersions: Android-12Android ID: A-188219307 |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1011
MISC |
google — android
|
In addSubInfo of SubscriptionController.java, there is a possible way to force the user to make a factory reset due to a logic error in the code. This could lead to local denial of service with System execution privileges needed. User interaction is not needed for exploitation.Product: AndroidVersions: Android-12Android ID: A-197327688 |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1008
MISC |
google — android
|
In lwis_dpm_update_clock of lwis_device_dpm.c, there is a possible out of bounds read due to an incorrect bounds check. This could lead to local information disclosure with System execution privileges needed. User interaction is not needed for exploitation.Product: AndroidVersions: Android kernelAndroid ID: A-195609074References: N/A |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1046
MISC |
google — android
|
In getSigningKeySet of PackageManagerService.java, there is a missing permission check. This could lead to local information disclosure with no additional execution privileges needed. User interaction is not needed for exploitation.Product: AndroidVersions: Android-12Android ID: A-189857801 |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1010
MISC |
gradio — gradio
|
Gradio is an open source framework for building interactive machine learning models and demos. In versions prior to 2.5.0 there is a vulnerability that affects anyone who creates and publicly shares Gradio interfaces. File paths are not restricted and users who receive a Gradio link can access any files on the host computer if they know the file names or file paths. This is limited only by the host operating system. Paths are opened in read only mode. The problem has been patched in gradio 2.5.0. |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-43831
MISC
CONFIRM |
hashicorp — vault_and_vault_enterprise
|
In HashiCorp Vault and Vault Enterprise before 1.7.7, 1.8.x before 1.8.6, and 1.9.x before 1.9.1, clusters using the Integrated Storage backend allowed an authenticated user (with write permissions to a kv secrets engine) to cause a panic and denial of service of the storage backend. The earliest affected version is 1.4.0. |
2021-12-17 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-45042
MISC
MISC |
hillrom — welch_allyn_cardio_products
|
The impacted products, when configured to use SSO, are affected by an improper authentication vulnerability. This vulnerability allows the application to accept manual entry of any active directory (AD) account provisioned in the application without supplying a password, resulting in access to the application as the supplied AD account, with all associated privileges. |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-43935
MISC |
htcondor — htcondor
|
An issue was discovered in HTCondor 9.0.x before 9.0.4 and 9.1.x before 9.1.2. When authenticating to an HTCondor daemon using a SciToken, a user may be granted authorizations beyond what the token should allow. |
2021-12-16 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-45102
MISC |
htcondor — htcondor
|
An issue was discovered in HTCondor before 8.8.15, 9.0.x before 9.0.4, and 9.1.x before 9.1.2. Using standard command-line tools, a user with only READ access to an HTCondor SchedD or Collector daemon can discover secrets that could allow them to control other users’ jobs and/or read their data. |
2021-12-16 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-45101
MISC |
ibm — bmc_firmware
|
BMC firmware (IBM Power System S821LC Server (8001-12C) OP825.50) configuration changed to allow an authenticated user to open an insecure communication channel which could allow an attacker to obtain sensitive information using man in the middle techniques. IBM X-Force ID: 205267. |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-29847
CONFIRM
XF |
ibm — business_automation_workflow
|
IBM Business Automation Workflow 18.0, 19.0, 20,0 and 21.0 and IBM Business Process Manager 8.5 and 8.6 are vulnerable to cross-site scripting. This vulnerability allows users to embed arbitrary JavaScript code in the Web UI thus altering the intended functionality potentially leading to credentials disclosure within a trusted session. IBM X-Force ID: 209165. |
2021-12-17 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-38883
CONFIRM
XF |
irfanview — irfanview
|
IrfanView 4.54 allows a user-mode write access violation starting at FORMATS!ReadXPM_W+0x0000000000000531. |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-23545
MISC
MISC
MISC |
ivanti — workspace_control
|
Ivanti Workspace Control before 10.4.50.0 allows attackers to degrade integrity. |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2019-19138
MISC
MISC |
jflyfox — jfinal_cms
|
JFinal_cms 5.1.0 is vulnerable to regex injection that may lead to Denial of Service. |
2021-12-16 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-37262
MISC |
jsx-slack — jsx-slack
|
jsx-slack is a library for building JSON objects for Slack Block Kit surfaces from JSX. In versions prior to 4.5.1 users are vulnerable to a regular expression denial-of-service (ReDoS) attack. If attacker can put a lot of JSX elements into `<blockquote>` tag, an internal regular expression for escaping characters may consume an excessive amount of computing resources. jsx-slack v4.5.1 has patched to a regex for escaping blockquote characters. Users are advised to upgrade as soon as possible. |
2021-12-17 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-43838
MISC
CONFIRM |
knime — knime
|
KNIME Server before 4.12.6 and 4.13.x before 4.13.4 (when installed in unattended mode) keeps the administrator’s password in a file without appropriate file access controls, allowing all local users to read its content. |
2021-12-16 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-45097
MISC |
knime — knime
|
KNIME Analytics Platform before 4.5.0 is vulnerable to XXE (external XML entity injection) via a crafted workflow file (.knwf), aka AP-17730. |
2021-12-16 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-45096
MISC
MISC
MISC |
ksmbd — ksmbd
|
The ksmbd server through 3.4.2, as used in the Linux kernel through 5.15.8, sometimes communicates in cleartext even though encryption has been enabled. This occurs because it sets the SMB2_GLOBAL_CAP_ENCRYPTION flag when using the SMB 3.1.1 protocol, which is a violation of the SMB protocol specification. When Windows 10 detects this protocol violation, it disables encryption. |
2021-12-16 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-45100
MISC
MISC
MISC |
laravel-filemanager — laravel-filemanager
|
This affects the package unisharp/laravel-filemanager from 0.0.0. The upload() function does not sufficiently validate the file type when uploading. An attacker may be able to reproduce the following steps: – Install a package with a web Laravel application. – Navigate to the Upload window – Upload an image file, then capture the request – Edit the request contents with a malicious file (webshell) – Enter the path of file uploaded on URL – Remote Code Execution **Note: Prevention for bad extensions can be done by using a whitelist in the config file(lfm.php). Corresponding document can be found in the [here](https://unisharp.github.io/laravel-filemanager/configfolder-categories). |
2021-12-17 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-23814
CONFIRM
CONFIRM |
lattelatte — lattelatte
|
This affects the package latte/latte before 2.10.6. There is a way to bypass allowFunctions that will affect the security of the application. When the template is set to allow/disallow the use of certain functions, adding control characters (x00-x08) after the function will bypass these restrictions. |
2021-12-17 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-23803
CONFIRM
CONFIRM
CONFIRM |
limesurvey — limesurvey
|
Cross-site scripting (XSS) vulnerability in /application/controller/admin/theme.php in LimeSurvey 3.6.2+180406 allows remote attackers to inject arbitrary web script or HTML via the changes_cp parameter to the index.php/admin/themes/sa/templatesavechanges URI. |
2021-12-14 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2018-10228
MISC |
listary — listary
|
An issue was discovered in Listary through 6. An attacker can create a .pipeListary.listaryService named pipe and wait for a privileged user to open a session on the Listary installed host. Listary will automatically access the named pipe and the attacker will be able to duplicate the victim’s token to impersonate him. This exploit is valid in certain Windows versions (Microsoft has patched the issue in later Windows 10 builds). |
2021-12-14 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-41065
MISC
MISC |
listary — listary
|
An issue was discovered in Listary through 6. When Listary is configured as admin, Listary will not ask for permissions again if a user tries to access files on the system from Listary itself (it will bypass UAC protection; there is no privilege validation of the current user that runs via Listary). |
2021-12-14 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-41066
MISC
MISC |
livehelperchat — livehelperchat
|
livehelperchat is vulnerable to Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF) |
2021-12-18 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-4131
CONFIRM
MISC |
livehelperchat — livehelperchat
|
livehelperchat is vulnerable to Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF) |
2021-12-16 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-4123
MISC
CONFIRM |
livehelperchat — livehelperchat
|
livehelperchat is vulnerable to Improper Neutralization of Input During Web Page Generation (‘Cross-site Scripting’) |
2021-12-17 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-4132
CONFIRM
MISC |
logback — logback
|
In logback version 1.2.7 and prior versions, an attacker with the required privileges to edit configurations files could craft a malicious configuration allowing to execute arbitrary code loaded from LDAP servers. |
2021-12-16 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-42550
MISC
MISC
CONFIRM |
matrix — libolm
|
The olm_session_describe function in Matrix libolm before 3.2.7 is vulnerable to a buffer overflow. The Olm session object represents a cryptographic channel between two parties. Therefore, its state is partially controllable by the remote party of the channel. Attackers can construct a crafted sequence of messages to manipulate the state of the receiver’s session in such a way that, for some buffer sizes, a buffer overflow happens on a call to olm_session_describe. Furthermore, safe buffer sizes were undocumented. The overflow content is partially controllable by the attacker and limited to ASCII spaces and digits. The known affected products are Element Web And SchildiChat Web. |
2021-12-14 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-44538
MISC
MISC |
mattermost — mattermost
|
Mattermost 6.0 and earlier fails to sufficiently validate parameters during post creation, which allows authenticated attackers to cause a client-side crash of the web application via a maliciously crafted post. |
2021-12-17 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-37863
MISC
MISC |
mattermost — mattermost
|
Mattermost 6.0 and earlier fails to sufficiently validate the email address during registration, which allows attackers to trick users into signing up using attacker-controlled email addresses via crafted invitation token. |
2021-12-17 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-37862
MISC
MISC |
mediawiki — mediawiki
|
An issue was discovered in MediaWiki before 1.35.5, 1.36.x before 1.36.3, and 1.37.x before 1.37.1. It is possible to use action=mcrundo followed by action=mcrrestore to replace the content of any arbitrary page (that the user doesn’t have edit rights for). This applies to any public wiki, or a private wiki that has at least one page set in $wgWhitelistRead. |
2021-12-17 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-44857
CONFIRM
MISC |
mediawiki — mediawiki
|
An issue was discovered in MediaWiki before 1.35.5, 1.36.x before 1.36.3, and 1.37.x before 1.37.1. By using an action=rollback query, attackers can view private wiki contents. |
2021-12-17 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-45038
CONFIRM
MISC |
meetecho — janus-gateway
|
janus-gateway is vulnerable to Improper Neutralization of Input During Web Page Generation (‘Cross-site Scripting’) |
2021-12-16 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-4124
CONFIRM
MISC |
message_bus — message_bus
|
message_bus is a messaging bus for Ruby processes and web clients. In versions prior to 3.3.7 users who deployed message bus with diagnostics features enabled (default off) are vulnerable to a path traversal bug, which could lead to disclosure of secret information on a machine if an unintended user were to gain access to the diagnostic route. The impact is also greater if there is no proxy for your web application as the number of steps up the directories is not bounded. For deployments which uses a proxy, the impact varies. For example, If a request goes through a proxy like Nginx with `merge_slashes` enabled, the number of steps up the directories that can be read is limited to 3 levels. This issue has been patched in version 3.3.7. Users unable to upgrade should ensure that MessageBus::Diagnostics is disabled. |
2021-12-17 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-43840
CONFIRM
MISC |
microsoft — 4k_wireless_display_adapter
|
Microsoft 4K Wireless Display Adapter Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-43899
MISC |
microsoft — appx
|
Windows AppX Installer Spoofing Vulnerability |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-43890
MISC |
microsoft — asp.net_core_and_visual_studio
|
ASP.NET Core and Visual Studio Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-43877
MISC |
microsoft — biztalk_esb_toolkit
|
Microsoft BizTalk ESB Toolkit Spoofing Vulnerability |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-43892
MISC |
microsoft — bot_framework_sdk
|
Bot Framework SDK Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-43225
MISC |
microsoft — defender
|
Microsoft Defender for IoT Remote Code Execution Vulnerability This CVE ID is unique from CVE-2021-41365, CVE-2021-42310, CVE-2021-42311, CVE-2021-42313, CVE-2021-42314, CVE-2021-42315, CVE-2021-43882. |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-43889
MISC |
microsoft — defender
|
Microsoft Defender for IoT Remote Code Execution Vulnerability This CVE ID is unique from CVE-2021-41365, CVE-2021-42310, CVE-2021-42313, CVE-2021-42314, CVE-2021-42315, CVE-2021-43882, CVE-2021-43889. |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-42311
MISC |
microsoft — defender
|
Microsoft Defender for IoT Information Disclosure Vulnerability |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-43888
MISC |
microsoft — defender
|
Microsoft Defender for IoT Remote Code Execution Vulnerability This CVE ID is unique from CVE-2021-42310, CVE-2021-42311, CVE-2021-42313, CVE-2021-42314, CVE-2021-42315, CVE-2021-43882, CVE-2021-43889. |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-41365
MISC |
microsoft — defender
|
Microsoft Defender for IoT Remote Code Execution Vulnerability This CVE ID is unique from CVE-2021-41365, CVE-2021-42310, CVE-2021-42311, CVE-2021-42313, CVE-2021-42314, CVE-2021-42315, CVE-2021-43889. |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-43882
MISC |
microsoft — defender
|
Microsoft Defender for IOT Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-42312
MISC |
microsoft — defender
|
Microsoft Defender for IoT Remote Code Execution Vulnerability This CVE ID is unique from CVE-2021-41365, CVE-2021-42311, CVE-2021-42313, CVE-2021-42314, CVE-2021-42315, CVE-2021-43882, CVE-2021-43889. |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-42310
MISC |
microsoft — defender
|
Microsoft Defender for IoT Remote Code Execution Vulnerability This CVE ID is unique from CVE-2021-41365, CVE-2021-42310, CVE-2021-42311, CVE-2021-42314, CVE-2021-42315, CVE-2021-43882, CVE-2021-43889. |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-42313
MISC |
microsoft — defender
|
Microsoft Defender for IoT Remote Code Execution Vulnerability This CVE ID is unique from CVE-2021-41365, CVE-2021-42310, CVE-2021-42311, CVE-2021-42313, CVE-2021-42315, CVE-2021-43882, CVE-2021-43889. |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-42314
MISC |
microsoft — defender
|
Microsoft Defender for IoT Remote Code Execution Vulnerability This CVE ID is unique from CVE-2021-41365, CVE-2021-42310, CVE-2021-42311, CVE-2021-42313, CVE-2021-42314, CVE-2021-43882, CVE-2021-43889. |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-42315
MISC |
microsoft — excel
|
Microsoft Excel Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-43256
MISC |
microsoft — jet_red_database_engine_and_access_connectivity_engine
|
Microsoft Jet Red Database Engine and Access Connectivity Engine Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-42293
MISC |
microsoft — nfts
|
NTFS Set Short Name Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-43240
MISC |
microsoft — office
|
Visual Basic for Applications Information Disclosure Vulnerability |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-42295
MISC |
microsoft — office
|
Microsoft Office Trust Center Spoofing Vulnerability |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-43255
MISC |
microsoft — office
|
Microsoft Office Graphics Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-43875
MISC |
microsoft — office
|
Microsoft Office app Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-43905
MISC |
microsoft — powershell
|
Microsoft PowerShell Spoofing Vulnerability |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-43896
MISC |
microsoft — sharepoint
|
Microsoft SharePoint Server Remote Code Execution Vulnerability This CVE ID is unique from CVE-2021-42309. |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-42294
MISC |
microsoft — sharepoint
|
Microsoft SharePoint Server Remote Code Execution Vulnerability This CVE ID is unique from CVE-2021-42294. |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-42309
MISC |
microsoft — sharepoint
|
Microsoft SharePoint Server Spoofing Vulnerability This CVE ID is unique from CVE-2021-43242. |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-42320
MISC |
microsoft — sharepoint_server
|
Microsoft SharePoint Server Spoofing Vulnerability This CVE ID is unique from CVE-2021-42320. |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-43242
MISC |
microsoft — storage_spaces_controller
|
Storage Spaces Controller Information Disclosure Vulnerability This CVE ID is unique from CVE-2021-43235. |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-43227
MISC |
microsoft — visual_studio
|
Visual Studio Code Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-43891
MISC |
microsoft — visual_studio
|
Visual Studio Code WSL Extension Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-43907
MISC |
microsoft — visual_studio
|
Visual Studio Code Spoofing Vulnerability |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-43908
MISC |
microsoft — vp9_video_extensions
|
VP9 Video Extensions Information Disclosure Vulnerability |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-43243
MISC |
| microsoft — windows |
Remote Desktop Client Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-43233
MISC |
microsoft — windows
|
Windows Kernel Information Disclosure Vulnerability |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-43244
MISC |
microsoft — windows
|
Windows TCP/IP Driver Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-43247
MISC |
microsoft — windows
|
Windows Installer Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-43883
MISC |
microsoft — windows
|
Windows Recovery Environment Agent Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-43239
MISC |
microsoft — windows
|
Windows Remote Access Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-43238
MISC |
microsoft — windows
|
Windows Setup Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-43237
MISC |
microsoft — windows
|
Microsoft Message Queuing Information Disclosure Vulnerability This CVE ID is unique from CVE-2021-43222. |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-43236
MISC |
microsoft — windows
|
Windows Fax Service Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-43234
MISC |
microsoft — windows
|
Windows Event Tracing Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-43232
MISC |
microsoft — windows
|
Windows NTFS Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability This CVE ID is unique from CVE-2021-43229, CVE-2021-43230. |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-43231
MISC |
microsoft — windows
|
Windows NTFS Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability This CVE ID is unique from CVE-2021-43229, CVE-2021-43231. |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-43230
MISC |
microsoft — windows
|
A vulnerability was discovered in the Keybase Client for Windows before version 5.6.0 when a user executed the “keybase git lfs-config” command on the command-line. In versions prior to 5.6.0, a malicious actor with write access to a user’s Git repository could leverage this vulnerability to potentially execute arbitrary Windows commands on a user’s local system. |
2021-12-14 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-34426
MISC |
microsoft — windows
|
Windows NTFS Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability This CVE ID is unique from CVE-2021-43230, CVE-2021-43231. |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-43229
MISC |
microsoft — windows
|
SymCrypt Denial of Service Vulnerability |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-43228
MISC |
microsoft — windows
|
Windows Common Log File System Driver Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability This CVE ID is unique from CVE-2021-43207. |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-43226
MISC |
microsoft — windows
|
Windows Common Log File System Driver Information Disclosure Vulnerability |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-43224
MISC |
microsoft — windows
|
Windows Remote Access Connection Manager Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-43223
MISC |
microsoft — windows
|
Microsoft Message Queuing Information Disclosure Vulnerability This CVE ID is unique from CVE-2021-43236. |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-43222
MISC |
microsoft — windows
|
DirectX Graphics Kernel File Denial of Service Vulnerability |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-43219
MISC |
microsoft — windows
|
Windows Encrypting File System (EFS) Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-43217
MISC |
microsoft — windows
|
Windows Media Center Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-40441
MISC |
microsoft — windows
|
Microsoft Local Security Authority Server (lsasrv) Information Disclosure Vulnerability |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-43216
MISC |
microsoft — windows
|
iSNS Server Memory Corruption Vulnerability Can Lead to Remote Code Execution |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-43215
MISC |
microsoft — windows
|
Web Media Extensions Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-43214
MISC |
microsoft — windows
|
Windows Common Log File System Driver Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability This CVE ID is unique from CVE-2021-43226. |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-43207
MISC |
microsoft — windows
|
Windows Print Spooler Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-41333
MISC |
microsoft — windows_device_management
|
Windows Mobile Device Management Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-43880
MISC |
microsoft — windows_digital_media_receiver
|
Windows Digital Media Receiver Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-43248
MISC |
microsoft — windows_digital_tv_tuner
|
Windows Digital TV Tuner Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-43245
MISC |
microsoft — windows_encrypting_file_system
|
Windows Encrypting File System (EFS) Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-43893
MISC |
microsoft — windows_hyper-v
|
Windows Hyper-V Denial of Service Vulnerability |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-43246
MISC |
mitsubishi_electric — gx_works2
|
Improper Handling of Length Parameter Inconsistency vulnerability in Mitsubishi Electric GX Works2 versions 1.606G and prior allows a remote unauthenticated attacker to cause a DoS condition in GX Works2 by getting GX Works2 to read a tampered program file from a Mitsubishi Electric PLC by sending malicious crafted packets to tamper with the program file. |
2021-12-17 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-20608
MISC
MISC
MISC |
mitsubishi_electric — gx_works2_melsoft_navigator_and_ezsocket
|
Out-of-bounds Read vulnerability in Mitsubishi Electric GX Works2 versions 1.606G and prior, MELSOFT Navigator all versions and EZSocket all versions allows an attacker to cause a DoS condition in the software by getting a user to open malicious project file specially crafted by an attacker. |
2021-12-17 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-20606
MISC
MISC
MISC |
mitsubishi_electric — gx_works2_melsoft_navigator_and_ezsocket
|
Integer Underflow vulnerability in Mitsubishi Electric GX Works2 versions 1.606G and prior, MELSOFT Navigator all versions and EZSocket all versions allows an attacker to cause a DoS condition in the software by getting a user to open malicious project file specially crafted by an attacker. |
2021-12-17 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-20607
MISC
MISC
MISC |
mongodb — mongodb_servier
|
An attacker with basic CRUD permissions on a replicated collection can run the applyOps command with specially malformed oplog entries, resulting in a potential denial of service on secondaries. This issue affects MongoDB Server v4.0 versions prior to 4.0.25; MongoDB Server v4.2 versions prior to 4.2.14; MongoDB Server v4.4 versions prior to 4.4.6. |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-20330
MISC |
motorola_solutions — avigilon_devices
|
Certain Motorola Solutions Avigilon devices allow XSS in the administrative UI. This affects T200/201 before 4.10.0.68; T290 before 4.4.0.80; T008 before 2.2.0.86; T205 before 4.12.0.62; T204 before 3.28.0.166; and T100, T101, T102, and T103 before 2.6.0.180. |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-38701
CONFIRM
MISC |
numpy — numpy
|
Null Pointer Dereference vulnerability exists in numpy.sort in NumPy < and 1.19 in the PyArray_DescrNew function due to missing return-value validation, which allows attackers to conduct DoS attacks by repetitively creating sort arrays. |
2021-12-17 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-41495
MISC |
numpy — numpy
|
Buffer overflow in the array_from_pyobj function of fortranobject.c in NumPy < 1.19, which allows attackers to conduct a Denial of Service attacks by carefully constructing an array with negative values. |
2021-12-17 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-41496
MISC |
numpy — numpy
|
Incomplete string comparison in the numpy.core component in NumPy1.9.x, which allows attackers to fail the APIs via constructing specific string objects. |
2021-12-17 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-34141
MISC |
numpy — numpy
|
A Buffer Overflow vulnerability exists in NumPy 1.9.x in the PyArray_NewFromDescr_int function of ctors.c when specifying arrays of large dimensions (over 32) from Python code, which could let a malicious user cause a Denial of Service. |
2021-12-17 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-33430
MISC |
opencast — opencast
|
Opencast is an Open Source Lecture Capture & Video Management for Education. Opencast versions prior to 9.10 allow HTTP method spoofing, allowing to change the assumed HTTP method via URL parameter. This allows attackers to turn HTTP GET requests into PUT requests or an HTTP form to send DELETE requests. This bypasses restrictions otherwise put on these types of requests and aids in cross-site request forgery (CSRF) attacks, which would otherwise not be possible. The vulnerability allows attackers to craft links or forms which may change the server state. This issue is fixed in Opencast 9.10 and 10.0. You can mitigate the problem by setting the `SameSite=Strict` attribute for your cookies. If this is a viable option for you depends on your integrations. We strongly recommend updating in any case. |
2021-12-14 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-43807
CONFIRM
MISC
MISC |
opencast — opencast
|
Opencast is an Open Source Lecture Capture & Video Management for Education. Opencast before version 9.10 or 10.6 allows references to local file URLs in ingested media packages, allowing attackers to include local files from Opencast’s host machines and making them available via the web interface. Before Opencast 9.10 and 10.6, Opencast would open and include local files during ingests. Attackers could exploit this to include most local files the process has read access to, extracting secrets from the host machine. An attacker would need to have the privileges required to add new media to exploit this. But these are often widely given. The issue has been fixed in Opencast 10.6 and 11.0. You can mitigate this issue by narrowing down the read access Opencast has to files on the file system using UNIX permissions or mandatory access control systems like SELinux. This cannot prevent access to files Opencast needs to read though and we highly recommend updating. |
2021-12-14 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-43821
CONFIRM
MISC
MISC
MISC |
openemr — openemr
|
An authenticated SQL injection issue in the calendar search function of OpenEMR 6.0.0 before patch 3 allows an attacker to read data from all tables of the database via the parameter provider_id, as demonstrated by the /interface/main/calendar/index.php?module=PostCalendar&func=search URI. |
2021-12-17 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-41843
MISC
MISC
MISC
FULLDISC |
openssl — libssl
|
Internally libssl in OpenSSL calls X509_verify_cert() on the client side to verify a certificate supplied by a server. That function may return a negative return value to indicate an internal error (for example out of memory). Such a negative return value is mishandled by OpenSSL and will cause an IO function (such as SSL_connect() or SSL_do_handshake()) to not indicate success and a subsequent call to SSL_get_error() to return the value SSL_ERROR_WANT_RETRY_VERIFY. This return value is only supposed to be returned by OpenSSL if the application has previously called SSL_CTX_set_cert_verify_callback(). Since most applications do not do this the SSL_ERROR_WANT_RETRY_VERIFY return value from SSL_get_error() will be totally unexpected and applications may not behave correctly as a result. The exact behaviour will depend on the application but it could result in crashes, infinite loops or other similar incorrect responses. This issue is made more serious in combination with a separate bug in OpenSSL 3.0 that will cause X509_verify_cert() to indicate an internal error when processing a certificate chain. This will occur where a certificate does not include the Subject Alternative Name extension but where a Certificate Authority has enforced name constraints. This issue can occur even with valid chains. By combining the two issues an attacker could induce incorrect, application dependent behaviour. Fixed in OpenSSL 3.0.1 (Affected 3.0.0). |
2021-12-14 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-4044
CONFIRM
CONFIRM |
opf — openproject
|
OpenProject is a web-based project management software. OpenProject versions >= 12.0.0 are vulnerable to a SQL injection in the budgets module. For authenticated users with the “Edit budgets” permission, the request to reassign work packages to another budget unsufficiently sanitizes user input in the `reassign_to_id` parameter. The vulnerability has been fixed in version 12.0.4. Versions prior to 12.0.0 are not affected. If you’re upgrading from an older version, ensure you are upgrading to at least version 12.0.4. If you are unable to upgrade in a timely fashion, the following patch can be applied: https://github.com/opf/openproject/pull/9983.patch |
2021-12-14 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-43830
MISC
MISC
MISC
CONFIRM |
owncast — owncast
|
Owncast is an open source, self-hosted live video streaming and chat server. In affected versions inline scripts are executed when Javascript is parsed via a paste action. This issue is patched in 0.0.9 by blocking unsafe-inline Content Security Policy and specifying the script-src. The worker-src is required to be set to blob for the video player. |
2021-12-14 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-39183
CONFIRM |
parallels — remote_application_server
|
Parallels Remote Application Server (RAS) allows a local attacker to retrieve certain profile password in clear text format by uploading a previously stored cyphered file by Parallels RAS. The confidentiality, availability and integrity of the information of the user could be compromised if an attacker is able to recover the profile password. |
2021-12-17 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-8968
CONFIRM |
peopledoc– vault-cli
|
vault-cli is a configurable command-line interface tool (and python library) to interact with Hashicorp Vault. In versions before 3.0.0 vault-cli features the ability for rendering templated values. When a secret starts with the prefix `!template!`, vault-cli interprets the rest of the contents of the secret as a Jinja2 template. Jinja2 is a powerful templating engine and is not designed to safely render arbitrary templates. An attacker controlling a jinja2 template rendered on a machine can trigger arbitrary code, making this a Remote Code Execution (RCE) risk. If the content of the vault can be completely trusted, then this is not a problem. Otherwise, if your threat model includes cases where an attacker can manipulate a secret value read from the vault using vault-cli, then this vulnerability may impact you. In 3.0.0, the code related to interpreting vault templated secrets has been removed entirely. Users are advised to upgrade as soon as possible. For users unable to upgrade a workaround does exist. Using the environment variable `VAULT_CLI_RENDER=false` or the flag `–no-render` (placed between `vault-cli` and the subcommand, e.g. `vault-cli –no-render get-all`) or adding `render: false` to the vault-cli configuration yaml file disables rendering and removes the vulnerability. Using the python library, you can use: `vault_cli.get_client(render=False)` when creating your client to get a client that will not render templated secrets and thus operates securely. |
2021-12-16 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-43837
MISC
MISC
CONFIRM |
phpgurukul — phpgurukul
|
Cross Site Request Forgery (CSRF) vulnerability in Change-password.php in phpgurukul user management system in php using stored procedure V1.0, allows attackers to change the password to an arbitrary account. |
2021-12-16 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-26800
MISC
MISC |
pyo_&it — pyo_&it
|
Buffer overflow in ajaxsoundstudio.com Pyo < and 1.03 in the Server_jack_init function. which allows attackers to conduct Denial of Service attacks by arbitrary constructing a overlong server name. |
2021-12-17 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-41498
MISC |
rapid7 — insight_agent
|
Rapid7 Insight Agent, versions 3.0.1 to 3.1.2.34, suffer from a local privilege escalation due to an uncontrolled DLL search path. Specifically, when Insight Agent versions 3.0.1 to 3.1.2.34 start, the Python interpreter attempts to load python3.dll at “C:DLLspython3.dll,” which normally is writable by locally authenticated users. Because of this, a malicious local user could use Insight Agent’s startup conditions to elevate to SYSTEM privileges. This issue was fixed in Rapid7 Insight Agent 3.1.2.35. This vulnerability is a regression of CVE-2019-5629. |
2021-12-14 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-4007
MISC
CONFIRM |
| rare-technologies — bounter |
Null pointer reference in CMS_Conservative_increment_obj in RaRe-Technologies bounter version 1.01 and 1.10, allows attackers to conduct Denial of Service attacks by inputting a huge width of hash bucket. |
2021-12-17 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-41497
MISC |
rizinorg — rizin
|
Rizin is a UNIX-like reverse engineering framework and command-line toolset. In versions up to and including 0.3.1 there is a heap-based out of bounds write in parse_die() when reversing an AMD64 ELF binary with DWARF debug info. When a malicious AMD64 ELF binary is opened by a victim user, Rizin may crash or execute unintended actions. No workaround are known and users are advised to upgrade. |
2021-12-13 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-43814
MISC
CONFIRM
MISC |
sap — grc_access_control
|
SAP GRC Access Control – versions V1100_700, V1100_731, V1200_750, does not perform necessary authorization checks for an authenticated user, which could lead to escalation of privileges. |
2021-12-14 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-44233
MISC
MISC |
sap — saf-t_framework_transaction_saftn_g
|
SAF-T Framework Transaction SAFTN_G allows an attacker to exploit insufficient validation of path information provided by normal user, leading to full server directory access. The attacker can see the whole filesystem structure but cannot overwrite, delete, or corrupt arbitrary files on the server. |
2021-12-14 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-44232
MISC
MISC |
seafile — seafile
|
Seafile is an open source cloud storage system. A sync token is used in Seafile file syncing protocol to authorize access to library data. To improve performance, the token is cached in memory in seaf-server. Upon receiving a token from sync client or SeaDrive client, the server checks whether the token exist in the cache. However, if the token exists in cache, the server doesn’t check whether it’s associated with the specific library in the URL. This vulnerability makes it possible to use any valid sync token to access data from any **known** library. Note that the attacker has to first find out the ID of a library which it has no access to. The library ID is a random UUID, which is not possible to be guessed. There are no workarounds for this issue. |
2021-12-14 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-43820
CONFIRM
MISC |
securitashome — home_alarm_system
|
An RF replay attack vulnerability in the SecuritasHome home alarm system, version HPGW-G 0.0.2.23F BG_U-ITR-F1-BD_BL.A30.20181117, allows an attacker to trigger arbitrary system functionality by replaying previously recorded signals. This lets an adversary, among other things, disarm an armed system. |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-40170
MISC
CONFIRM |
securitashome — home_alarm_system
|
The absence of notifications regarding an ongoing RF jamming attack in the SecuritasHome home alarm system, version HPGW-G 0.0.2.23F BG_U-ITR-F1-BD_BL.A30.20181117, allows an attacker to block legitimate traffic while not alerting the owner of the system. |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-40171
MISC
MISC |
semcms — semcms
|
A vulnerability in /include/web_check.php of SEMCMS v3.8 allows attackers to reset the Administrator account’s password. |
2021-12-17 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-18078
MISC |
semcms — semcms
|
The checkuser function of SEMCMS 3.8 was discovered to contain a vulnerability which allows attackers to obtain the password in plaintext through a SQL query. |
2021-12-17 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-18081
MISC |
sick — sopas_et
|
SICK SOPAS ET before version 4.8.0 allows attackers to manipulate the command line arguments to pass in any value to the Emulator executable. |
2021-12-17 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-32499
MISC |
sick — sopas_et
|
SICK SOPAS ET before version 4.8.0 allows attackers to manipulate the pathname of the emulator and use path traversal to run an arbitrary executable located on the host system. When the user starts the emulator from SOPAS ET the corresponding executable will be started instead of the emulator |
2021-12-17 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-32498
MISC |
sick — sopas_et
|
SICK SOPAS ET before version 4.8.0 allows attackers to wrap any executable file into an SDD and provide this to a SOPAS ET user. When a user starts the emulator the executable is run without further checks. |
2021-12-17 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-32497
MISC |
siemens — modelsim_simulation_and_questa_simulation
|
A vulnerability has been identified in ModelSim Simulation (All versions), Questa Simulation (All versions). The RSA white-box implementation in affected applications insufficiently protects the built-in private keys that are required to decrypt electronic intellectual property (IP) data in accordance with the IEEE 1735 recommended practice. This could allow a sophisticated attacker to discover the keys, bypassing the protection intended by the IEEE 1735 recommended practice. |
2021-12-14 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-42023
CONFIRM |
siemens — simcenter_star-ccm+_viewer
|
A vulnerability has been identified in Simcenter STAR-CCM+ Viewer (All versions < 2021.3.1). The starview+.exe application lacks proper validation of user-supplied data when parsing scene files. This could result in an out of bounds write past the end of an allocated structure. An attacker could leverage this vulnerability to execute code in the context of the current process. |
2021-12-14 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-42024
CONFIRM |
siemens — sinumerik_edge
|
A vulnerability has been identified in SINUMERIK Edge (All versions < V3.2). The affected software does not properly validate the server certificate when initiating a TLS connection. This could allow an attacker to spoof a trusted entity by interfering in the communication path between the client and the intended server. |
2021-12-14 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-42027
CONFIRM |
snipe-it — snipe-it
|
snipe-it is vulnerable to Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF) |
2021-12-18 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-4130
CONFIRM
MISC |
snipe-it — snipe-it
|
snipe-it is vulnerable to Improper Neutralization of Input During Web Page Generation (‘Cross-site Scripting’) |
2021-12-14 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-4108
MISC
CONFIRM |
sourcecodester_vehice_service_management_system — sourcecodester_vehice_service_management_system
|
Cross Site Scripting (XSS) vulnerability exists in Sourcecodester Vehicle Service Management System 1.0 via the Owner fullname parameter in a Send Service Request in vehicle_service. |
2021-12-16 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-41962
MISC |
stackstorm — stackstorm
|
In StackStorm versions prior to 3.6.0, the jinja interpreter was not run in sandbox mode and thus allows execution of unsafe system commands. Jinja does not enable sandboxed mode by default due to backwards compatibility. Stackstorm now sets sandboxed mode for jinja by default. |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-44657
MISC
MISC
MISC
MISC |
sulu — sulu
|
Sulu is an open-source PHP content management system based on the Symfony framework. In affected versions an attacker can read arbitrary local files via a PHP file include. In a default configuration this also leads to remote code execution. The problem is patched with the Versions 1.6.44, 2.2.18, 2.3.8, 2.4.0. For users unable to upgrade overwrite the service `sulu_route.generator.expression_token_provider` and wrap the translator before passing it to the expression language. |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-43836
CONFIRM
MISC |
sulu — sulu
|
Sulu is an open-source PHP content management system based on the Symfony framework. In affected versions Sulu users who have access to any subset of the admin UI are able to elevate their privilege. Over the API it was possible for them to give themselves permissions to areas which they did not already had. This issue was introduced in 2.0.0-RC1 with the new ProfileController putAction. The versions have been patched in 2.2.18, 2.3.8 and 2.4.0. For users unable to upgrade the only known workaround is to apply a patch to the ProfileController manually. |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-43835
CONFIRM
MISC |
suricata — suricata
|
An issue was discovered in Suricata before 6.0.4. It is possible to bypass/evade any HTTP-based signature by faking an RST TCP packet with random TCP options of the md5header from the client side. After the three-way handshake, it’s possible to inject an RST ACK with a random TCP md5header option. Then, the client can send an HTTP GET request with a forbidden URL. The server will ignore the RST ACK and send the response HTTP packet for the client’s request. These packets will not trigger a Suricata reject action. |
2021-12-16 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-45098
MISC
MISC
MISC
MISC |
suse — longhorn
|
A Improper Access Control vulnerability in SUSE Longhorn allows any workload in the cluster to execute any binary present in the image on the host without authentication. This issue affects: SUSE Longhorn longhorn versions prior to 1.1.3; longhorn versions prior to 1.2.3. |
2021-12-17 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-36779
CONFIRM
CONFIRM |
suse — longhorn
|
A Improper Access Control vulnerability in longhorn of SUSE Longhorn allows attackers to connect to a longhorn-engine replica instance granting it the ability to read and write data to and from a replica that they should not have access to. This issue affects: SUSE Longhorn longhorn versions prior to 1.1.3; longhorn versions prior to 1.2.3v. |
2021-12-17 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-36780
CONFIRM
CONFIRM |
tcman_gim — tcman_gim
|
TCMAN GIM is vulnerable to a lack of authorization in all available webservice methods listed in /PC/WebService.asmx. The exploitation of this vulnerability might allow a remote attacker to obtain information. |
2021-12-17 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-40851
CONFIRM |
tcman_gim — tcman_gim
|
TCMAN GIM does not perform an authorization check when trying to access determined resources. A remote attacker could exploit this vulnerability to access URL that require privileges without having them. The exploitation of this vulnerability might allow a remote attacker to obtain sensible information. |
2021-12-17 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-40853
CONFIRM |
tcman_gim — tcman_gim
|
TCMAN GIM is vulnerable to a SQL injection vulnerability inside several available webservice methods in /PC/WebService.asmx. |
2021-12-17 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-40850
CONFIRM |
tcman_gim — tcman_gim
|
TCMAN GIM is affected by an open redirect vulnerability. This vulnerability allows the redirection of user navigation to pages controlled by the attacker. The exploitation of this vulnerability might allow a remote attacker to obtain information. |
2021-12-17 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-40852
CONFIRM |
teeworlds — teeworlds
|
Teeworlds up to and including 0.7.5 is vulnerable to Buffer Overflow. A map parser does not validate m_Channels value coming from a map file, leading to a buffer overflow. A malicious server may offer a specially crafted map that will overwrite client’s stack causing denial of service or code execution. |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-43518
MISC
MISC |
thinfinity — virtualui
|
Thinfinity VirtualUI before 3.0 has functionality in /lab.html reachable by default that could allow IFRAME injection via the vpath parameter. |
2021-12-16 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-45092
MISC |
thinkphp5 — thinkphp5
|
SQL Injection vulnerability exists in ThinkPHP5 5.0.x <=5.1.22 via the parseOrder function in Builder.php. |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-44350
MISC |
tibco_software_inc — spotfire_server
|
The Spotfire Server component of TIBCO Software Inc.’s TIBCO Spotfire Server, TIBCO Spotfire Server, and TIBCO Spotfire Server contains a difficult to exploit vulnerability that allows malicious custom API clients with network access to execute internal API operations outside of the scope of those granted to it. A successful attack using this vulnerability requires human interaction from a person other than the attacker. Affected releases are TIBCO Software Inc.’s TIBCO Spotfire Server: versions 10.10.6 and below, TIBCO Spotfire Server: versions 11.0.0, 11.1.0, 11.2.0, 11.3.0, 11.4.0, and 11.4.1, and TIBCO Spotfire Server: versions 11.5.0 and 11.6.0. |
2021-12-14 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-43051
CONFIRM
CONFIRM |
tp-link — tp-link
|
An HTTP/1.1 misconfiguration in web interface of TP-Link AX10v1 before V1_211117 could allow an attacker to send a specially crafted HTTP/0.9 packet that could cause a cache poisoning attack. |
2021-12-17 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-41451
MISC
MISC
MISC |
trend_micro — maximum_security
|
A link following denial-of-service (DoS) vulnerability in the Trend Micro Security (Consumer) 2021 familiy of products could allow an attacker to abuse the PC Health Checkup feature of the product to create symlinks that would allow modification of files which could lead to a denial-of-service. |
2021-12-16 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-44023
MISC
MISC |
tuleap — tuleap
|
Tuleap is a Libre and Open Source tool for end to end traceability of application and system developments. In affected versions Tuleap does not sanitize properly user settings when constructing the SQL query to browse and search commits in the CVS repositories. A authenticated malicious user with read access to a CVS repository could execute arbitrary SQL queries. Tuleap instances without an active CVS repositories are not impacted. The following versions contain the fix: Tuleap Community Edition 13.2.99.155, Tuleap Enterprise Edition 13.1-7, and Tuleap Enterprise Edition 13.2-6. |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-43806
CONFIRM
MISC
MISC
MISC |
tuleap — tuleap
|
Tuleap is a Libre and Open Source tool for end to end traceability of application and system developments. This is a follow up to GHSA-887w-pv2r-x8pm/CVE-2021-41276, the initial fix was incomplete. Tuleap does not sanitize properly the search filter built from the ldap_id attribute of a user during the daily synchronization. A malicious user could force accounts to be suspended or take over another account by forcing the update of the ldap_uid attribute. Note that the malicious user either need to have site administrator capability on the Tuleap instance or be an LDAP operator with the capability to create/modify account. The Tuleap instance needs to have the LDAP plugin activated and enabled for this issue to be exploitable. The following versions contain the fix: Tuleap Community Edition 13.2.99.83, Tuleap Enterprise Edition 13.1-6, and Tuleap Enterprise Edition 13.2-4. |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-43782
MISC
CONFIRM
MISC
MISC
MISC |
tuleap — tuleap
|
Tuleap is a Libre and Open Source tool for end to end traceability of application and system developments. In affected versions Tuleap does not sanitize properly the search filter built from the ldap_id attribute of a user during the daily synchronization. A malicious user could force accounts to be suspended or take over another account by forcing the update of the ldap_uid attribute. Note that the malicious user either need to have site administrator capability on the Tuleap instance or be an LDAP operator with the capability to create/modify account. The Tuleap instance needs to have the LDAP plugin activated and enabled for this issue to be exploitable. This issue has been patched in Tuleap Community Edition 13.2.99.31, Tuleap Enterprise Edition 13.1-5, and Tuleap Enterprise Edition 13.2-3. |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-41276
CONFIRM
MISC
MISC
MISC |
uipath_app_studio — uipath_app_studio
|
An issue was discovered in UiPath App Studio 21.4.4. There is a persistent XSS vulnerability in the file-upload functionality for uploading icons when attempting to create new Apps. An attacker with minimal privileges in the application can build their own App and upload a malicious file containing an XSS payload, by uploading an arbitrary file and modifying the MIME type in a subsequent HTTP request. This then allows the file to be stored and retrieved from the server by other users in the same organization. |
2021-12-14 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-44043
MISC
MISC |
uipath_assistant — uipath_assistant
|
UiPath Assistant 21.4.4 will load and execute attacker controlled data from the file path supplied to the –dev-widget argument of the URI handler for uipath-assistant://. This allows an attacker to execute code on a victim’s machine or capture NTLM credentials by supplying a networked or WebDAV file path. |
2021-12-14 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-44041
MISC
MISC |
uipath_assistant — uipath_assistant
|
An issue was discovered in UiPath Assistant 21.4.4. User-controlled data supplied to the –process-start argument of the URI handler for uipath-assistant:// is not correctly encoded, resulting in attacker-controlled content being injected into the error message displayed (when the injected content does not match an existing process). A determined attacker could leverage this to execute JavaScript in the context of the Electron application. |
2021-12-14 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-44042
MISC
MISC |
vaultcli — vaultcli
|
Storage Spaces Controller Information Disclosure Vulnerability This CVE ID is unique from CVE-2021-43227. |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-43235
MISC |
vmware — workspace_one_uem_console
|
VMware Workspace ONE UEM console 20.0.8 prior to 20.0.8.37, 20.11.0 prior to 20.11.0.40, 21.2.0 prior to 21.2.0.27, and 21.5.0 prior to 21.5.0.37 contain an SSRF vulnerability. This issue may allow a malicious actor with network access to UEM to send their requests without authentication and to gain access to sensitive information. |
2021-12-17 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-22054
MISC |
|
wechat-php-sdk — wechat-php-sdk
|
Wechat-php-sdk v1.10.2 is affected by a Cross Site Scripting (XSS) vulnerability in Wechat.php. |
2021-12-17 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-43678
MISC
MISC |
wolters_kluwer — teammate_am
|
Wolters Kluwer TeamMate AM 12.4 Update 1 mishandles attachment uploads, such that an authenticated user may download and execute malicious files. |
2021-12-17 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-44035
MISC
MISC |
wordpress — wordpress
|
Unauthenticated Arbitrary Options Update vulnerability leading to full website compromise discovered in Image Hover Effects Ultimate (versions <= 9.6.1) WordPress plugin. |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-36888
CONFIRM
CONFIRM |
xorg — xserver
|
A flaw was found in xorg-x11-server in versions before 21.1.2 and before 1.20.14. An out-of-bounds access can occur in the SProcXFixesCreatePointerBarrier function. The highest threat from this vulnerability is to data confidentiality and integrity as well as system availability. |
2021-12-17 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-4009
MISC
MISC
FEDORA
FEDORA |
xorg — xserver
|
A flaw was found in xorg-x11-server in versions before 21.1.2 and before 1.20.14. An out-of-bounds access can occur in the SProcScreenSaverSuspend function. The highest threat from this vulnerability is to data confidentiality and integrity as well as system availability. |
2021-12-17 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-4010
MISC
MISC
FEDORA
FEDORA |
xorg — xserver
|
A flaw was found in xorg-x11-server in versions before 21.1.2 and before 1.20.14. An out-of-bounds access can occur in the SProcRenderCompositeGlyphs function. The highest threat from this vulnerability is to data confidentiality and integrity as well as system availability. |
2021-12-17 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-4008
MISC
MISC
FEDORA
FEDORA |
xorg — xserver
|
A flaw was found in xorg-x11-server in versions before 21.1.2 and before 1.20.14. An out-of-bounds access can occur in the SwapCreateRegister function. The highest threat from this vulnerability is to data confidentiality and integrity as well as system availability. |
2021-12-17 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-4011
MISC
MISC
FEDORA
FEDORA |
yetiforcecrm — yetiforcecrm
|
yetiforcecrm is vulnerable to Improper Neutralization of Input During Web Page Generation (‘Cross-site Scripting’) |
2021-12-16 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-4121
MISC
CONFIRM |
zimbra — zimbra_collaboration
|
An issue in /domain/service/.ewell-known/caldav of Zimbra Collaboration 8.8.12 allows attackers to redirect users to any arbitrary website of their choosing. |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-18985
MISC |
zimbra — zimbra_collaboration
|
A reflected cross-site scripting (XSS) vulnerability in the zimbraAdmin/public/secureRequest.jsp component of Zimbra Collaboration 8.8.12 allows unauthenticated attackers to execute arbitrary web scripts or HTML via a host header injection. |
2021-12-15 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-18984
MISC |
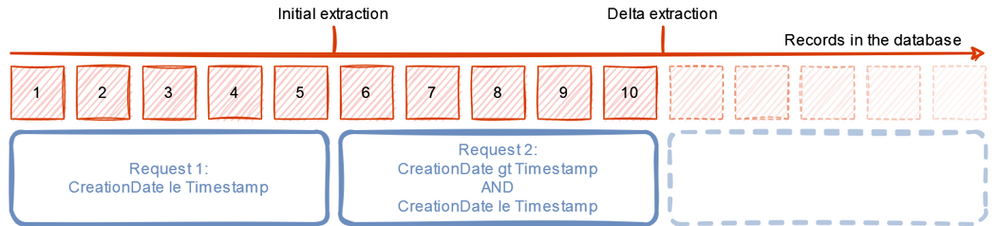
by Contributed | Dec 18, 2021 | Technology
This article is contributed. See the original author and article here.
Before implementing data extraction from SAP systems please always verify your licensing agreement. |
After five episodes of going through basic data extraction scenarios, we finally can deep dive into a more advanced topic. I already explained how crucial is extraction optimization. The created Synapse Pipeline can use client-side paging to chunk a large request into several smaller ones. In the last episode, we focused on data filtering to copy only the required information. Both solutions improve the performance and reliability of the extraction, but a full data copy is not always an answer. It is not uncommon to have millions or even billions of records in the largest tables. A daily extraction job to copy everything is pretty much impossible in such scenarios. It would take too much time and cause performance challenges on SAP application servers. Multiple extractions every day could cause even more problems.
So what can we do to ensure our data in the lake is almost up-to-date? The solution, at least in theory, is quite simple. We should only extract new and changed records in the system. Such an approach highly limits the amount of data to process, which decreases the duration of the copy job and it allows more frequent updates.
INTRODUCTION TO DELTA EXTRACTION
A post about processing only new and changed data, also known as a delta or incremental extraction, was the most requested by you. I received multiple comments and even private messages asking to provide some guidance in this area. OData services have some great features to support delta extraction. That’s one of the reasons why, despite my concerns about using OData protocol for large amounts of data, I decided to write the whole blog series.
As always, please let me start with a short introduction. Extracting only changed and new information is not a new topic. Whenever we work with a large dataset, processing only a subset of information guarantees better performance and reliability. Having to copy only a couple hundred records instead of millions always makes a difference. The main problem is, however, how to select the right data.
As always, there is no single solution. Which is the right one depends on your requirements and technical possibilities. One of the most common approaches uses the date and time of last change to identify new and changed records since the last extraction. Another way of ensuring we have updated data is using triggers to record and send changes after they occur. The second approach is quite common in real-time data replication scenarios.

An important point of consideration is which system defines which are new and changed information. Using the client software, which in our case is Azure Synapse, gives us full control over what we request and copy. At the same time, we are limited to what is available at the source. If the OData service doesn’t expose a field with the timestamp of the last update, it will be nearly impossible to track changes. And unfortunately, that’s a common problem. Always work closely with your functional experts as they may know a solution. Depending on the use case, you may be able to use other fields as well – for example, posting or document date. You could also try finding another data source as it may contain a date to support delta extraction. To be honest, it doesn’t even have to be a date – using a posting period can also give good results. Of course, the number of records to process each time will be larger, but still, it is just a tiny piece of all data stored in the database. One of the common misconceptions is that you always have to fetch only new and updated records. That’s not true – you can always copy more records (for example, extract documents from the current month) and then use processing in Synapse to consolidate multiple extracts. While not perfect, such a solution often helps when the information about the last changes is unavailable.
The SAP system can also help us in identifying delta changes. It offers a set of data extractors and CDS views that out-of-the-box manages delta information, and they expose us only the data we need. That’s quite handy, as we can use pre-built processes instead of designing a pipeline to compare timestamps. Under the hood, they also often use the information about the last change. But in newer SAP releases, they also utilize the SLT framework to track changes.
While asking the SAP system to manage delta information is tempting, I would like to show you both scenarios. Therefore I will cover the delta extraction in two blog posts. In today’s episode, I’ll show you how to extract changes using timestamps stored in the metadata store. You already know how to implement filtering, so we will use that knowledge today. The solution we’ll design today is just one of many. As I mentioned earlier, there are many field types you could use. It may happen that the pipeline we create today requires some further tweaks to fulfil your use case. But I’m sure you’ll have enough knowledge to make the necessary changes on your own.
DELTA EXTRACTION USING TIMESTAMP
With OData services, we can use a wide range of query parameters to limit the data we receive. Last week I published a blog about filtering, that allows us to only extract information for a particular company code or sales organization. We can use the same approach to limit the data based on a timestamp field – ideally containing information about last changes, but creation date or posting date can also be useful.
Let’s take the API_SALES_ORDER_SRV as an example, as we worked with that service previously. The entity set A_SalesOrder exposes us Sales Order header information. It contains CreationDate field which holds the timestamp of when was the document initially created as well as the LastChangeDateTime which provides information about last changes. While that’s not always the case for other OData services, the LastChangeDateTime field is updated even if the document was just created and never edited.
In today’s post, I’ll show you what changes are required to deal with similar OData services. But there are other OData services, like the API_BUSINESS_PARTNER, that require further adjustment. Let’s take a look at a sample payload:
This OData service makes things difficult. There is no single field for the timestamp, and the last update date and time are stored in two separate fields. That makes things slightly more complex – instead of filtering using a single value, we need to use two of them. If you’d like to use the pipeline to work with such OData services, you’ll have to make additional changes on your own.
In theory, there is also a field ETag that looks useful. But in fact, this field is used to manage editing concurrency, and some SAP cloud products already prohibit filtering using the ETag value.
There is also the third type of OData service, which doesn’t expose any form of date or time information. An infamous example is the A_SalesOrderItem in the API_SALES_ORDER. If you have to process sales order line items, it’s better to find another data source, like an extractor or CDS views – next week, I will describe how to use them.
But to be fully honest with you – there are two possible workarounds. After extracting header information, you could create a list of processed sales order numbers, which then becomes a filter when selecting line items. The second potential workaround, which is not available in Synapse so far, is using the $expand query parameter. It asks SAP to include additional information in the response, like the partner information or… line items. I’ll keep an eye on new features in Synapse Pipelines, and I let you know when this parameter is fully supported.
Before we make changes to the pipeline, let’s think about how the delta extraction should work. We need three additional parameters – the first one to mark we want to use delta extraction with the OData source. In the second and third parameters, we will keep the timestamp information together with the field name where it can be found in the OData source.
During the runtime, the pipeline should initially send a request to the service to retrieve the high watermark, which is the timestamp of the last change. We can do this by using Lookup activity and a couple of query parameters. The Copy Data activity will then only process orders, with the timestamp being between the value stored in the metadata store and read from the OData service. Once the extraction finishes, we have to update the metadata store with the new high watermark.
Initially, I considered implementing the above changes to the same child pipeline we’ve used so far, but finally, I decided to create a separate one to increase visibility. All OData services where the delta extraction is not required will still use the old pipeline. I will add a Switch activity in the master pipeline, that based on the value read from the metadata store, will trigger the original or delta-enabled pipeline.
IMPLEMENTATION
Let’s start making the required changes by modifying the metadata store. We need three additional fields:
- ExtractionType – which can take Full or Delta values
- Watermark – to store the timestamp value
- WatermarkField – to store the field name of the timestamp, for example, LastChangeDateTime
I have also updated my list of OData services to include two that we can consider for delta extraction (sales orders and products) and two without a timestamp field we could use.
OData service
|
Entity
|
ExtractionType
|
WatermarkField
|
API_SALES_ORDER_SRV
|
A_SalesOrder
|
Delta
|
LastChangeDateTime
|
API_BUSINESS_PARTNER
|
A_BusinessPartner
|
Full
|
|
API_COMPANYCODE_SRV
|
A_CompanyCode
|
Full
|
|
API_PRODUCT_SRV
|
A_Product
|
Delta
|
LastChangeDateTime
|

Having new fields defined in the metadata store allows us to focus now on the pipeline. Open Synapse Studio and clone the existing child pipeline. Then define two parameters: Watermark and WatermarkField. As the ExtractionType property will only be used in the metadata pipeline, we don’t have to define it here.
Now we have to modify the metadata pipeline, that it triggers the correct processing depending on the content of the ExtractionType field. Open it, and enter the ForEach loop. Add the Switch activity and reference the ExtractionType in the Expression field to evaluate which pipeline to run. Then add a new Case with the value “Delta”.
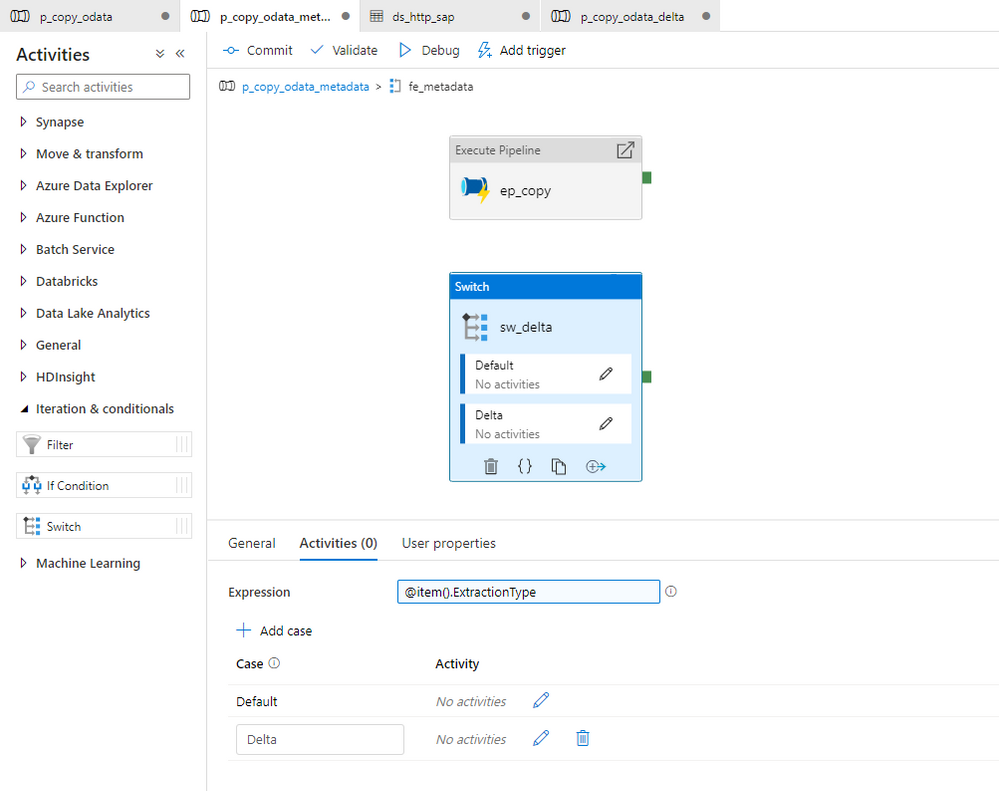
The Switch activity executes the expression and maps the outcome to one of Case groups. If it can’t find a match it will process the Default group.
Move the existing Execute Pipeline activity to the default group. You don’t have to make any changes to the list of parameters.
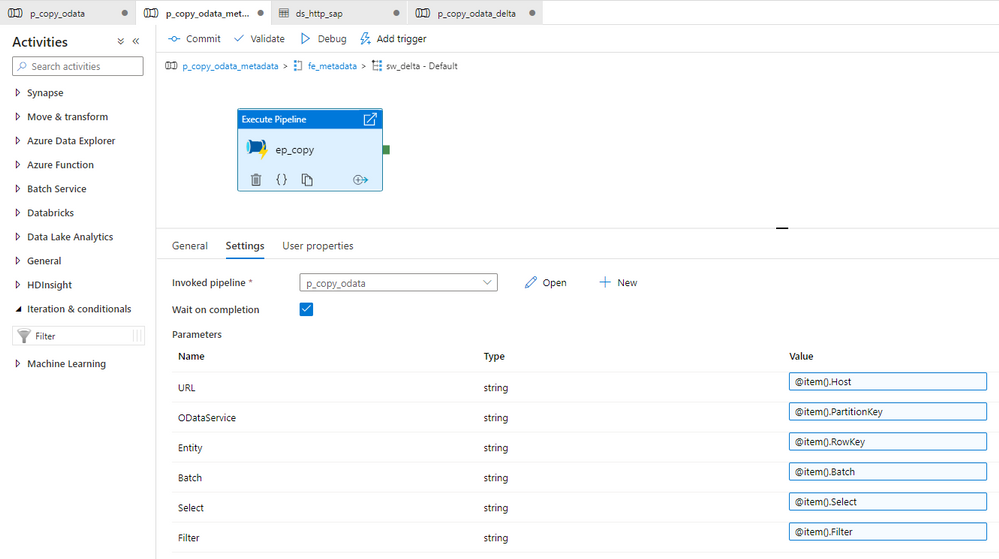
Expand the delta group and add a new Execture Pipeline activity that triggers the delta-enabled pipeline. Set the Invoked pipeline and expand the existing list of parameters with Watermark and WatermarkField.
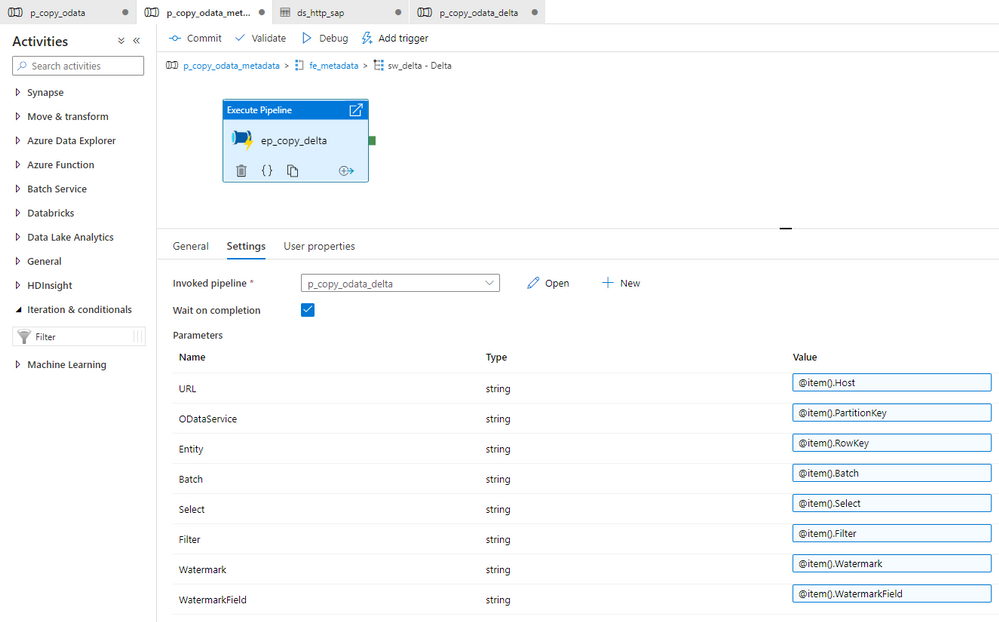
With the above changes, the Switch activity triggers the correct pipeline based on the value stored in the ExtractionType field. We can now proceed with the required improvements to the delta-enabled pipeline.
I want to keep the existing functionality that allows using the client-side paging as well as filtering out unnecessary data. While delta extraction reduces the amount of data in subsequent runs, we still have to ensure robust processing of the initial data extraction that copies all records. We have to update all expressions, and keeping the existing functionality means some of them can get quite lengthy.
Let’s start with an easy change. Before we check the number of records, we have to read the high watermark figure from the OData service to correctly pass the filtering to all subsequent activities. Add a new Lookup activity and reference the OData dataset. Provide the following expressions:
ODataURL: @concat(pipeline().parameters.URL, pipeline().parameters.ODataService, '/')
Entity: @pipeline().parameters.Entity
In the query field, we provide the selection criteria. To read the latest timestamp, I’m sorting the whole dataset using the $orderby parameter. We also have to maintain all filtering rules defined in the metadata store. I came up with the following query:
@if(empty(pipeline().parameters.Filter), concat('?$select=', pipeline().parameters.WatermarkField, '&$top=1&$orderby=', pipeline().parameters.WatermarkField, ' desc'), concat('?$filter=', pipeline().parameters.Filter, '&$select=', pipeline().parameters.WatermarkField, '&$top=1&$orderby=', pipeline().parameters.WatermarkField, ' desc'))
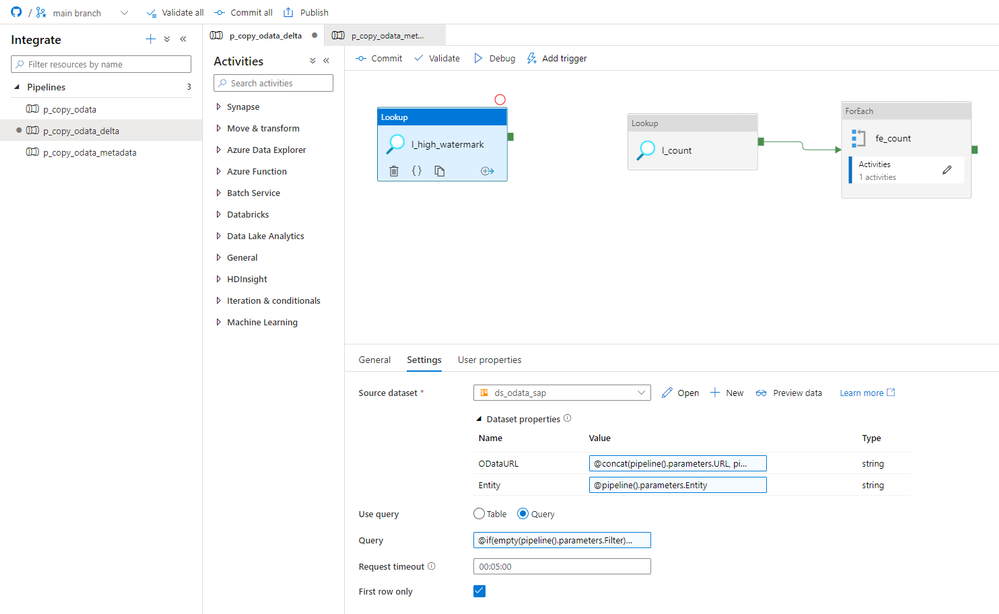
To make the timestamp value easily accessible, I decided to assign it to a variable. We haven’t used any variables so far. They are very similar to parameters, but unlike them, we can modify variables values during the runtime. Which perfectly suits our case.
In the pipeline settings, open the Variables tab and create a new one of type String.
Add the Set Variable activity and create a connection from the lookup. To read the value from the output of the previous action I’m using the following query:
@activity('l_high_watermark').output.firstRow[pipeline().parameters.WatermarkField]
As the timestamp field name is not static, but instead we read it from the metadata store, I’m using square brackets to reference it as part of the expressions (that’s quite a cool feature of ADF).
Having the high watermark value assigned to a variable, we can modify the Lookup responsible for reading the record count. We need to add functionality to count only records between the last replication and the high watermark value stored in the variable. We also have to keep in mind, that during the initial replication, the Watermark field in the metadata store is empty – which adds a little bit of complexity. I use the following expression:
@if(empty(pipeline().parameters.Filter), concat('?$filter=', if(empty(pipeline().parameters.Watermark), '', concat(pipeline().parameters.WatermarkField, ' gt datetimeoffset''', formatDateTime(pipeline().parameters.Watermark, 'yyyy-MM-ddThh:ss:sZ'), ''' and ')), pipeline().parameters.WatermarkField, ' le datetimeoffset''', formatDateTime(variables('v_watermark'), 'yyyy-MM-ddThh:ss:sZ'),''''), concat('?$filter=', pipeline().parameters.Filter, if(empty(pipeline().parameters.Watermark), '', concat(' and ', pipeline().parameters.WatermarkField, ' gt datetimeoffset''', formatDateTime(pipeline().parameters.Watermark, 'yyyy-MM-ddThh:ss:sZ'))), ''' and ', pipeline().parameters.WatermarkField, ' le datetimeoffset''', formatDateTime(variables('v_watermark'), 'yyyy-MM-ddThh:ss:sZ'),''''))
Now it’s time to edit the query in the Copy Activity. I had to admit I was a bit scared of this one, as there are quite a few cases. We may or may not have filters or selection defined. It may be the first extraction, where we only have to pass the high watermark, or it may be a subsequent one that requires both timestamps. Finally, after a while, I wrote the following expression that I think addresses all cases.
@concat('$top=',pipeline().parameters.Batch, '&$skip=',string(mul(int(item()), int(pipeline().parameters.Batch))), if(empty(pipeline().parameters.Filter), concat('&$filter=', if(empty(pipeline().parameters.Watermark), '', concat(pipeline().parameters.WatermarkField, ' gt datetimeoffset''', formatDateTime(pipeline().parameters.Watermark, 'yyyy-MM-ddThh:ss:sZ'),'''', ' and ')), pipeline().parameters.WatermarkField, ' le datetimeoffset''', formatDateTime(variables('v_watermark'), 'yyyy-MM-ddThh:ss:sZ'),''''), concat('&$filter=', pipeline().parameters.Filter, if(empty(pipeline().parameters.Watermark), '', concat(' and ', pipeline().parameters.WatermarkField, ' gt datetimeoffset''', formatDateTime(pipeline().parameters.Watermark, 'yyyy-MM-ddThh:ss:sZ'),'''')), ' and ', pipeline().parameters.WatermarkField, ' le datetimeoffset''', formatDateTime(variables('v_watermark'), 'yyyy-MM-ddThh:ss:sZ'),'''')), if(empty(pipeline().parameters.Select), '', concat('&$select=',pipeline().parameters.Select)))
Great! We’re pretty much done!
We just have to update the metadata store with the high watermark value read from the OData service. I will use the Copy Data activity to do it.
The source and sink stores should refer to the same metadata table dataset, which we use to read content from the store. I will use a query to select the entry to edit based on the OData service name and the Entity.
@concat('PartitionKey eq ''', pipeline().parameters.ODataService, ''' and RowKey eq ''', pipeline().parameters.Entity, '''')
Then, in the Additional Columns I define the high watermark value, which we will map to the target column.
@variables('v_watermark')
Set the Insert Type to Merge on the Sink tab. That’s important – if you leave it to Replace, the whole entry in the table will be recreated, which means we’ll lose part of the data. Change the fields Partition Key Value Selection and Row Key Value Selection to PartitionKey and RowKey respectively.
Open the Mapping tab. The goal here is to reference the PartitionKey and RowKey fields to define the record that requires updating and then use the Additional Column HighWatermark to update the destination field Watermark.
That’s it! We can start testing!
EXECUTION AND MONITORING
To verify the pipeline works fine, I will run two tests. In the first one, as the watermark value for all OData services is empty, I’m expecting to see all data landing in the lake. Then I’ll edit a couple of sales orders that should be extracted in the second run. I won’t make any changes to materials.
3.. 2.. 1.. Go!
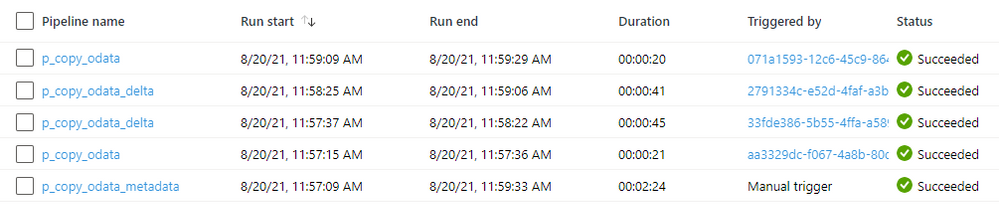
Green status is always good. Let’s check the number of records extracted.
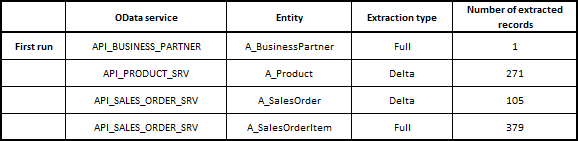
So that looks good. I use tight filtering on the Business Partner which explains why only a single record was processed. A quick look at the metadata table and I can see that the watermark field was updated correctly:
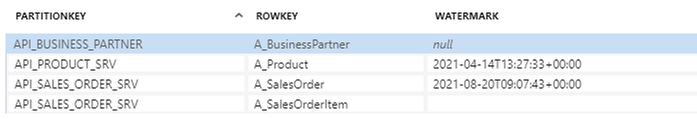
Now I’m going to edit a couple of sales orders and then I’ll trigger the pipeline. Let’s see how many records we extract.
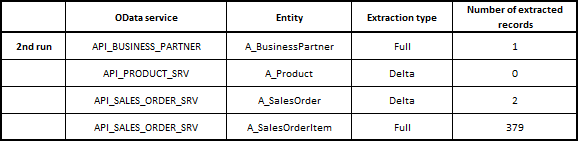
It worked well. Let’s look at the metadata store table:
The high watermark for the Entity A_SalesOrder was updated with the last change timestamp. So everything works correctly.
As always I hope you enjoyed this episode! I showed you how you can implement the delta extraction for OData services using Synapse Pipelines and metadata store to identify records that require processing. It’s not a perfect solution. We need to have the timestamp information and heavy scripting is required. But it works. In the next episode, I’ll show you how to convince your SAP system to manage the delta for you – which is much better approach!




Recent Comments