by Contributed | Aug 22, 2021 | Technology
This article is contributed. See the original author and article here.
On SQL Server, there is a database setting called parameterization.
parameterization has two values, Simple (the default) or Forced.
I will share here some details and examples to simplify the concept of parameterization, and try to describe how it impacts Database performance:
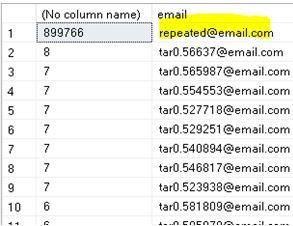
In my scenario, the distribution of the data is not even on column email of my example table infotbl, when I execute the Query below it shows that the value repeated@email.com is repeated in 899766 rows (of 1 million rows table), while the other values are repeated maximum 8 times only:
select email , count(*) from infotbl group by email order by count(*) desc

First, I created an index on the email column using below statement:
create index ix_emailsender on infotbl (email)
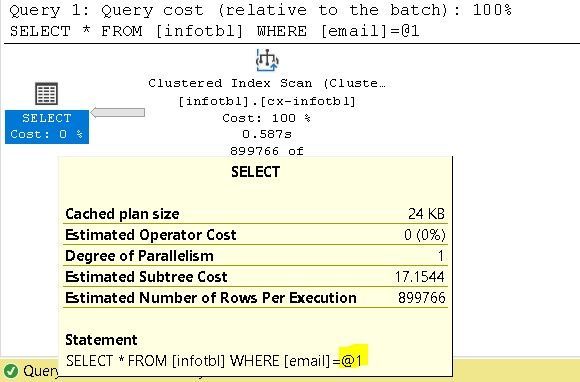
Logically, the Query Optimizer will choose index seek for all values except for repeated@email.com, it will choose a Clustered Index scan instead.
For example, if I execute the following two queries, both will have a different execution plan:
select * from infotbl where email = 'tar0.554553@email.com'
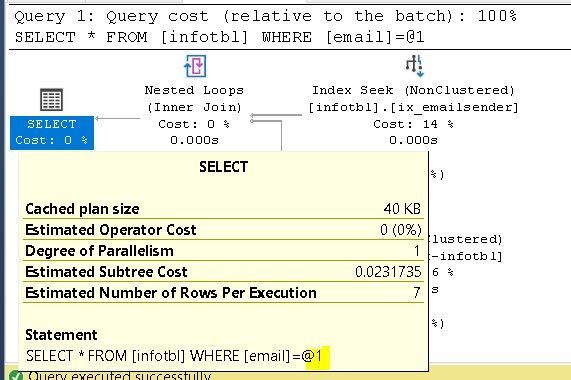
select * from infotbl where email = 'repeated@email.com'
How to check the density of an index ?
By running show_statistics console command as the following:
dbcc show_statistics (infotbl, ix_emailsender)
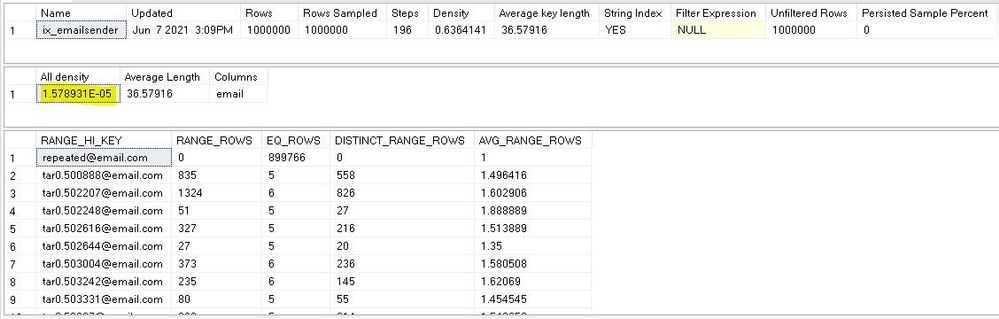
All density in the result above is 1 / distinct values , it is same as the result of the query:
select 1/convert(decimal(30,20),count(distinct email)) from infotbl;
Parameterization Forced:
If I repeat the same queries but after changing the parameterization to Forced, first by running the Alter database:
ALTER DATABASE [mydatabase] SET PARAMETERIZATION FORCED WITH NO_WAIT
--I may need to free the procedure cache by running :
dbcc freeproccache()
Now, I executed the Queries again, first:
select * from infotbl where email = 'repeated@email.com'

Then if I run the second Query, the Query optimizer will use the reserved execution plan “that has been created by Query 1”:
select * from infotbl where email = 'tar0.554553@email.com'
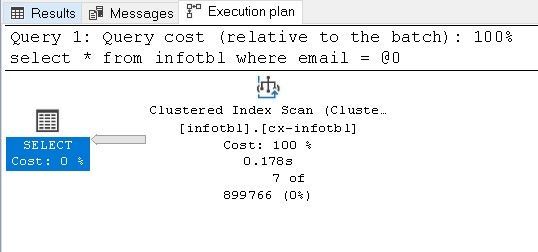
Then all other executions will be slower than expected, because there will be always an Index Scan every time whatever the size of result is and the selectivity of the search value.
Other Disadvantage of Forced parameterization, the Filtered Index:
If I create a filtered index on the ModifiedOn column, as an example when all Application’s important queries and Reports are accessing only data of 2021.
Filtered Index script:
create index IX_createdon on infotbl (createdon) include (email) where createdon => '1-1-2021'
With Simple parametrization, all Queries that search for values in 2021 range, will use index Seek:
select email from infotbl where createdon = '2021-06-08 11:00:22.513'

And others are as below example, will use Clustered index scan instead:
select email from infotbl where createdon = '2020-06-09 15:02:02.280'

Now if I set Parametrization Forced again and execute the same two Queries, I will have the same execution plan, as below:
select email from infotbl where createdon = '2021-06-08 11:00:22.513'

If you view the Execution Plan’s XML, you will find the Waring UnmatchedIndexes=”true” as the following :
<QueryPlan DegreeOfParallelism="1" CachedPlanSize="24" CompileTime="1" CompileCPU="1" CompileMemory="200">
<UnmatchedIndexes>
<Parameterization>
<Object Database="[tarasheedb]" Schema="[dbo]" Table="[infotbl]" Index="[IX_createdon]" />
</Parameterization>
</UnmatchedIndexes>
<Warnings UnmatchedIndexes="true" />
This is because the Query Optimizer cannot use the Filtered index when the parametrization is Forced.
What is the good thing in Parameterization forced option?
The following script will show the execution plans of my Select Queries:
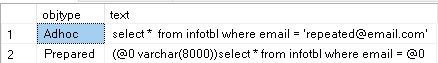
SELECT objtype, text
FROM sys.dm_exec_cached_plans
CROSS APPLY sys.dm_exec_sql_text(plan_handle)
WHERE text like '%select * from infotbl where email%' and not (text like '%SELECT objtype, text %')
With parameterization Forced, Only one Adhoc Execution plan exists in the plan cache, and the prepared execution plan that will be reused every time the query executed “again”, this will save the time of recompiling overhead every time, and decreases the size of the Procedure cache.
by Scott Muniz | Aug 21, 2021 | Security, Technology
This article is contributed. See the original author and article here.
CISA warns users to remain on alert for malicious cyber activity targeting potential disaster victims and charitable donors following a hurricane. Fraudulent emails—often containing malicious links or attachments—are common after major natural disasters. Exercise caution in handling emails with hurricane-related subject lines, attachments, or hyperlinks. In addition, be wary of social media pleas, texts, or door-to-door solicitations relating to severe weather events.
To avoid becoming victims of malicious activity, users and administrators should review the following resources and take preventative measures.
If you believe you have been a victim of cybercrime, file a complaint with the Federal Bureau of Investigation’s Internet Crime Complaint Center (IC3) at www.ic3.gov.
by Contributed | Aug 20, 2021 | Technology
This article is contributed. See the original author and article here.
What is Page cannot be displayed?
There are certain scenarios in which when we try to browse a site hosted on IIS server, we end up getting Page cannot be displayed (PCBD) . There are several reasons for which we will eventually get PCBD , some of the reasons are :
- Network related problems
- Improper bindings on IIS
- Improper certificates on IIS
- Incorrect settings on Http.Sys
In most of the scenarios the request doesn’t even reach to the IIS layer and fails before that . Here is a nice article explaining about layers of service that a request has to travel: https://techcommunity.microsoft.com/t5/iis-support-blog/iis-services-http-sys-w3svc-was-w3wp-oh-my/ba-p/287856
Generally, a PCBD error looks like below:

This blog will focus on list of steps which are going to be useful for troubleshooting these kinds of scenarios .Here, I have created a Flow chart:
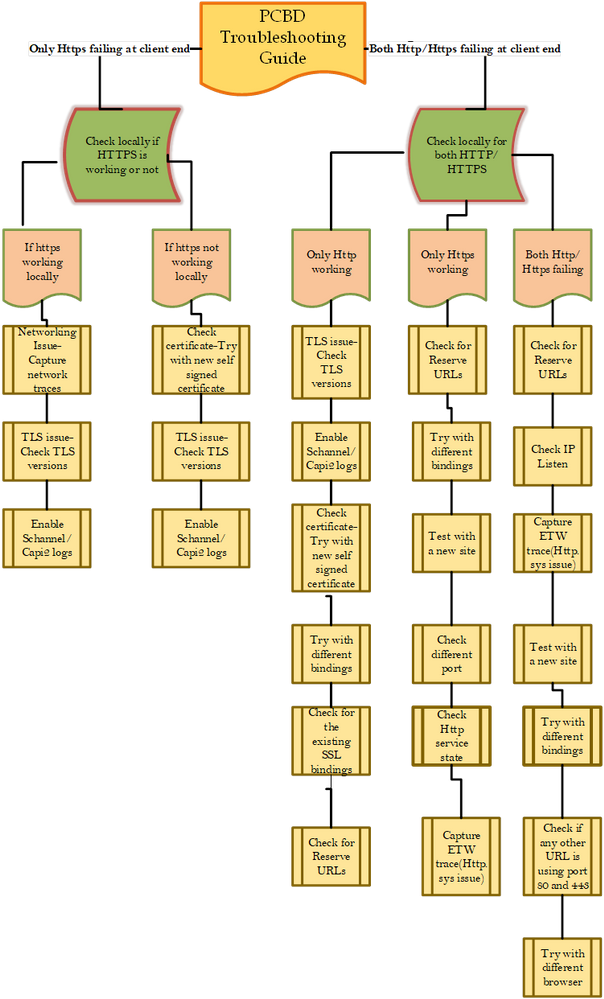
There are several steps in the flow chart which require data collection , just listing a few of them here:
Steps for capturing Schnannel logs and Capi2 logs :
Schannel Logs:
- Start Registry Editor. To do this, click Start, click Run, type regedt32, and then click OK.
- Locate the following key in the registry:
- HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESystemCurrentControlSetControlSecurityProvidersSCHANNEL
- On the Edit menu, click Add Value, and then add the following registry value:
- Value Name: EventLogging
- Data Type: REG_DWORD
- Note After you add this property, you must give it a value. See the table in the “Logging options” section to obtain the appropriate value for the kind of events that you want to log.
- Exit Registry Editor.
- Click Start, click Shut Down, click to select Restart, and then click OK to restart the computer. (Logging does not take effect until after you restart the computer).
Logging options:
The default value for Schannel event logging is 0x0000 in Windows NT Server 4.0, which means that no Schannel events are logged. In Windows 2000 Server and Windows XP Professional, this value is set to 0x0001, which means that error messages are logged. Additionally, you can log multiple events by specifying the hexadecimal value that equates to the logging options that you want. For example, to log error messages (0x0001) and warnings (0x0002), set the value to 0x0003.
Value Description
0x0000 Do not log
0x0001 Log error messages
0x0002 Log warnings
0x0004 Log informational and success events
From https://support.microsoft.com/en-in/help/260729/how-to-enable-schannel-event-logging-in-iis
Capi2 Logs :
The CryptoAPI 2.0 Diagnostics is a feature available on Windows Server 2008+ that supports the trouble shooting of issues concerned with, for example: Certificate Chain Validation Certificate Store Operations Signature Verification
This article describes how to enable the CAPI2 Diagnostic, but for an in depth review of the capability, check here.
Enable CAPI2 logging by opening the Event Viewer and navigating to the Event Viewer (Local)Applications and Services LogsMicrosoftWindowsCAPI2 directory and expand it. You should see a view named Operational as illustrated in Figure 1.
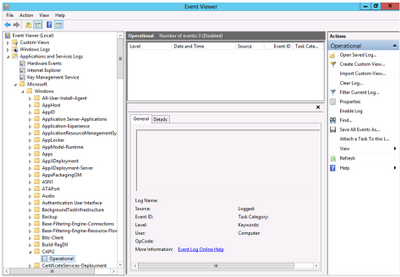
Figure 1, CAPI2 Diagnostics in Event Viewer
Next, right-click on the Operational view and click the Enable Log menu item as shown in Figure 2.
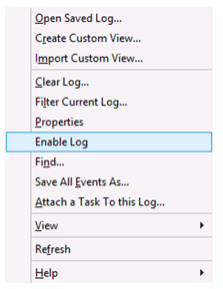
Figure 2, Enable CAPI2 Event Logging
Once enabled, any warnings or errors are logged into the viewer. Reproduce the problem you are experiencing and check if the issue is logged.
Command for checking Reserved URLs:
netsh http show urlacl
The above command lists DACLs (discretionary access control list ) for the specified reserved URL or all reserved URLs.
Command for checking Http.sys Service State:
netsh http show ServiceState
The above command shows snapshot of Http service .
Command for checking the IP Listen:
netsh http show iplisten
The above command lists all IP addresses in the IP listen list. The IP listen list is used to scope the list of addresses to which the HTTP service binds. “0.0.0.0” means any IPv4 address and “::” means any IPv6 address
Capturing Network trace –
To capture Network trace using Netmon tool…please check out this link : https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/client-management/troubleshoot-tcpip-netmon
Steps for capturing Http.sys ETW trace:
Capture a Perfview trace with IIS ETW providers. You can download Perfview from : https://github.com/microsoft/perfview/releases/tag/P2.0.71
Before starting the Pervfiew trace just run this command in admin command prompt (this captures http.sys traces), also start the other traces:
netsh trace start capture=yes overwrite=yes maxsize=2048 tracefile=c:minio_http.etl provider={DD5EF90A-6398-47A4-AD34-4DCECDEF795F} keywords=0xffffffffffffffff level=0xff provider={20F61733-57F1-4127-9F48-4AB7A9308AE2} keywords=0xffffffffffffffff level=0xff provider="Microsoft-Windows-HttpLog" keywords=0xffffffffffffffff level=0xff provider="Microsoft-Windows-HttpService" keywords=0xffffffffffffffff level=0xff provider="Microsoft-Windows-HttpEvent" keywords=0xffffffffffffffff level=0xff provider="Microsoft-Windows-Http-SQM-Provider" keywords=0xffffffffffffffff level=0xff
Make some 5-6 requests from client (http requests not https).. Once they fail, stop all of them, then run the below command to stop the command
netsh trace stop
This netsh trace will be saved on C drive with the name “minio_http.etl”..
Hope this one helps you.
Happy troubleshooting !!! :smiling_face_with_smiling_eyes:

by Scott Muniz | Aug 20, 2021 | Security
This article was originally posted by the FTC. See the original article here.
More and more places are requiring proof that you’ve had a COVID-19 vaccine or have recently tested negative before giving you access. Scammers see this as an opportunity to profit by selling fake verification tools or products, like fake vaccination cards, certificates, and test results.
Our advice:
- Know that buying fake vaccine cards, making your own, or filling in blank cards with false information is illegal and could get you fined, or even land you in jail.
- Don’t share personal information with people you don’t know. Scammers will turn the tables and sell your data or use it to commit identity theft.
- The only legitimate way to get proof that you’re vaccinated — or that you test negative — is to GET vaccinated or to TEST negative. If you lose that proof, check with your state health department or the place you got vaccinated to find out how you might be able to get a replacement.
If you spot a fake vaccine card, report it to the Office of the Inspector General of the Department of Health and Human Services at 1-800-HHS-TIPS or oig.hhs.gov, or file a complaint with the FBI’s Internet Crime Complaint Center.
You can also file a report with the FTC at ReportFraud.ftc.gov. Your report can make a difference. We use reports like yours to investigate, bring law enforcement cases, and alert people about what frauds to be on the lookout for so they can protect themselves, their friends, and family.
To learn more about COVID-related scams, visit ftc.gov.coronavirus/scams and subscribe to consumer alerts from the FTC to get updates delivered right to your email inbox.
Brought to you by Dr. Ware, Microsoft Office 365 Silver Partner, Charleston SC.



















Recent Comments