by Contributed | Jan 11, 2021 | Technology
This article is contributed. See the original author and article here.
The following is the third on a series of articles by @Ali Youssefi that we will be cross-posting into this Test Community Blog. These articles were first published by Ali in the Dynamics community but since the topic is very related with Testing it makes sense to publish here as well.
If you didn’t get a chance to catch the first one of the series, please have a look here:
Otherwise, please read ahead!
Summary
EasyRepro is an open source framework built upon Selenium allowing automated UI tests to be performed on a specific Dynamics 365 organization. This article will focus on reviewing how EasyRepro works with the Document Object Model otherwise known as the DOM. This will help us understand how we can extend the EasyRepro code for use with custom objects or areas of the platform not included in the framework at this time. We will wrap with a brief look at XPath and referencing elements from the DOM.
Getting Started
If you haven’t already, check out the first article which covers getting familiar with EasyRepro and working with the source code locally. It covers cloning from GitHub to Azure DevOps then from Azure DevOps Git repository to a development machine. and reviews setting up dependencies and test settings to run a simple test. The second article goes into common actions performed by users when interacting with Dynamics 365 and the correlating EasyRepro commands. It wraps with covering common troubleshooting and debugging scenarios.
The EasyRepro framework contains an abundance of commands that should suit most of your needs. However you’ll find that at times either these commands will need to be modified per your customizations or you may need to create your own custom commands for reuse among tests.
Some example scenarios for modifying or creating custom commands may include:
Using an ADFS Redirect Login
Working with custom components and resources
Working with strongly typed entity attributes
Including navigation and functionality not present natively in the framework
These scenarios require an understanding of how EasyRepro interacts with Selenium to simulate user actions in a browser. This article will focus on a typical use case for extension: the Login process. We will describe common Selenium functionality and how to reference elements on the Document Object Model in a way to increase maintainability.
Sample Scenarios for Extending
Working with the Browser Driver
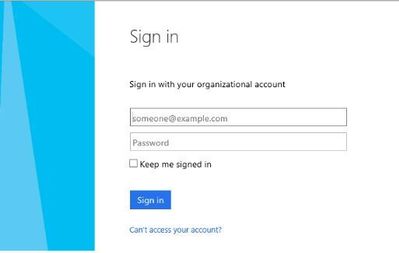
As we discussed earlier, your organization’s login process may have a sign on page that a user will get redirected to once they input their username. This is where we begin our journey into extending the framework and utilizing Selenium.
Typical Single Sign On Page:

Custom method for a Single Sign On Page:
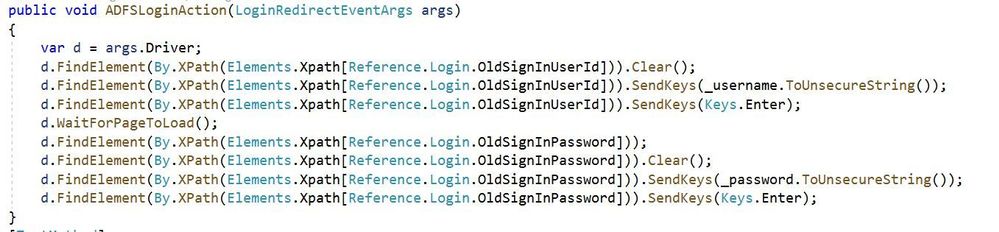
The image above shows a method designed to search through a sign in page DOM for input fields for credentials and submission. You will notice that we are working with the browser driver natively (args.Driver) and using methods not found in the sample EasyRepro unit tests. These include FindElement which is part of Selenium and WaitForPageToLoad which is part of EasyRepro’s extension of Selenium. I’ll touch on these at a high level now.
FindElement
FindElement is part of the Selenium.WebDriver assembly and is used to find an element in the DOM. I’ll cover how to search through the DOM in the next section Extending and Working with XPath but I wanted to take this time to show how we will begin extending unit tests using Selenium natively.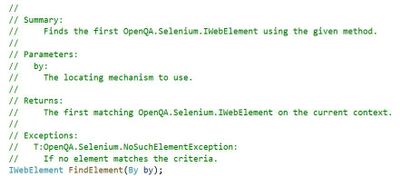
The method returns an IWebElement object that represents the element you want to work with. For instance if you want to work with the username textbox you can use FindElement to locate and return the username textbox. Once returned the framework can interact with it and perform actions such as input text or click.
Reference:
https://www.toolsqa.com/selenium-webdriver/c-sharp/findelement-and-findelements-commands-in-c/
WaitForPageToLoad
WaitForPageToLoad is part of the EasyRepro framework as a Selenium extension. This is key to point out that we are leveraging both EasyRepro and Selenium natively to achieve our desired result to login. This method waits a specific amount of time and checks for the document ready state. The time interval used to check can be adjusted if needed.
SendKeys and Clear
SendKeys is used to send keystrokes to an element on the page. This can be a complete string such as an email or a single keypress. This can be used to send the username and password to your sign in page. It also can be used to send the Enter or Tab keypress to move to the next field or submit.
Clear as it sounds is used to remove any sort of input that may already exist in an element. This is useful if your sign in page attempts to automatically input credentials.
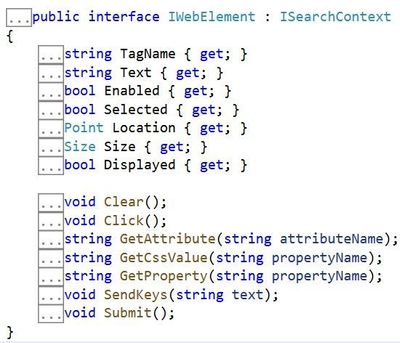
Both of these methods are part of the IWebElement shown above. Other useful properties of IWebElement include Text, Selected and GetAttribute.
Understanding how to extend element references
Considerations need to be made when designing unit tests to help reduce the maintenance work needed if something changes. For instance when referencing custom HTML web resources or even the ADFS Redirect from above, think how a change to an element in the DOM could propagate across some of all of your unit tests. One way to control maintenance is to centralize commonly used references into proxy objects that can hide the underlying mechanics from the test designer. This is exactly how the EasyRepro framework handles references and when extending can leverage the same approach. In this section we will cover the files used by the framework to reference DOM elements and show how to extend them to include references to our custom login page.
The App Element Reference File
The Microsoft.Dynamics365.UIAutomation.Api.UCI project uses the ElementReference.cs file as well as another file called AppElementReference.cs. The ElementReference file looks to have been brought over from the classic interface. What’s unique about each is how they reference elements in the DOM which I’ll cover in the next section. For now let’s focus on reviewing the AppElementReference.cs file which is located in the DTO folder of the Microsoft.Dynamics365.UIAutomation.Api.UCI project.
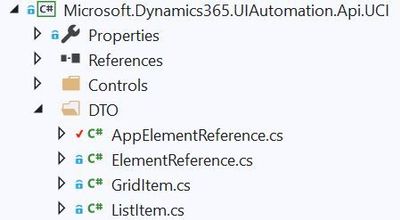
Inside of the AppElementReference file are two objects used by EasyRepro to represent and locate elements: The AppReference and AppElements classes.
The AppReference class
The AppReference class includes sub classes that represent the objects used by EasyRepro, specifically the WebClient object, to connect to DOM elements. This allows the framework to standardize how the search for a particular container or element is performed. Centralizing the reference to the DOM elements will allow the test designer to focus on writing commands against common objects and not specifying the precise location of an element in the DOM.
The AppElement class
The AppElement class is a comma delimited key value pair consisting of the reference object property as a key and the XPath command as the value. The key represents the property name in the class object inside of AppReference while the value is the XPath location of the element in the DOM.
I highly suggest reviewing the AppElement class when extending EasyRepro as it shows recommended ways to locate and reference elements on the DOM. In the next section we will discuss the different ways you can locate elements including XPath.
Referencing elements in the Document Object Model
References to objects generally fall into four patterns:
Resolving via Control Name
Resolving via XPath
Resolving by Element ID
Resolving by CSS Class
In this article we will focus on XPath which is what is primarily used by the EasyRepro framework for the Dynamics 365 platform. However its key to understand each of the approaches for referencing as they can be used for customizations such as web resources, custom controls, etc.
Resolve with Control Name
This will search the DOM for elements with a specific name which is an attribute on the element node. This is not used by EasyRepro to my knowledge. Elements can be found by their name by using By.TagName with the FindElement method.
Resolve with Element ID
This will attempt to find an element by its unique identifier. For instance a textbox on the login form maybe identified as ‘txtUserName’. Assuming this element ID is unique we could search for this particular element by an ID and return an IWebElement representation. An example from the Microsoft.Dynamics365.UIAutomation.Api.UCI project is shown below showing usage with the timeline control.
Definition:

Usage by WebClient:

Elements can be found by their ID by using By.Id with the FindElement method.
Resolve with CSS Class
This allows the ability to search by the CSS class defined on the element. Be aware that this can return multiple elements due to the nature of CSS class. There is no usage of this in EasyRepro but again this could be helpful for customizations. Elements can be found by their CSS class name by using By.Class with the FindElement method.
Resolve with XPath
XPath allows us to work quickly and efficiently to search for a known element or path within the DOM. Key functions include the contains method which allow to search node attributes or values. For instance when you review the DOM of a form you’ll notice attributes such as data-id or static text housed within a span element. Coupling this attribute with the html tag can result in a surprisingly accurate way to locate an element. I suggest leveraging the current element class as well as this link from W3 Schools that goes into the schema of XPath.
Going back to an earlier section let’s review how XPath along with the AppElementReference.cs file can help standardize element location.
Using XPath in the ADFS Redirect Login Method
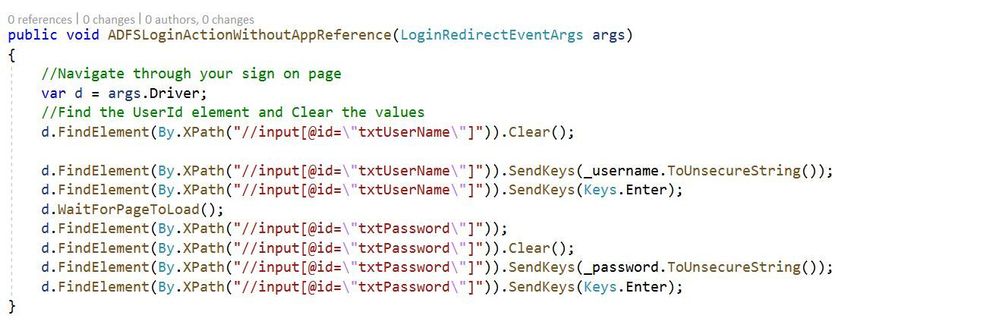
Going back to our original example for the ADFS login method below you’ll see an example of referencing the DOM elements using XPath directly with the Selenium objects driver and By.XPath. Consider the below two images:
Without a static representation of XPath:
Using static classes to represent XPath queries:
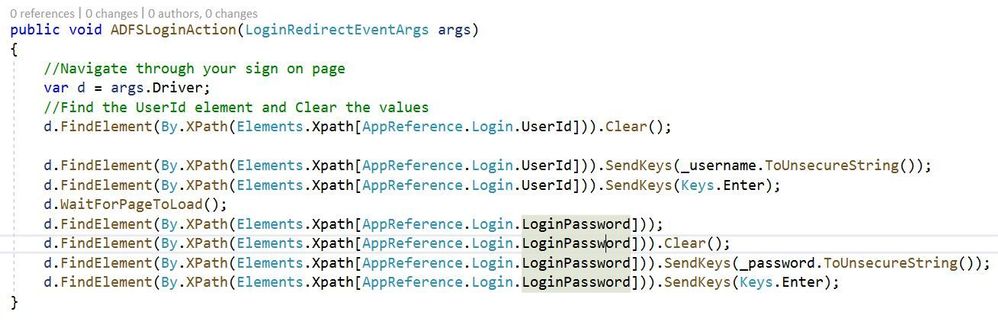
Both of these methods work and perform exactly the same. However the second method provides increased supportability if and when the login page goes through changes. For instance consider if the id of the textbox to input your username changes from txtUserName to txtLoginId. Also what if this txtUserName XPath query is propagated across hundreds or more unit tests?
Creating custom reference objects
Let’s put what we have learned to use by creating a reference to our custom login page. Start by adding a class to the AppReference object and title it AdfsLogin. Inside this class declare string properties that will be used as input for your organization’s login page. Typical inputs include username, password and a submit button. Here is an example:
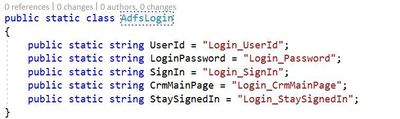
NOTE: While this document demonstrates how to add to the AppElementReference.cs file I would suggest extending this outside of the core files as customizations will have to be merged with any updates from the framework.
Once the static class we want to use in our unit tests has been created we now need to add the XPath references to the AppElement class. Below is an image showing the key value pair discussed in the AppElement section above. The key correlates to the string value of the AdfsLogin class while the value is the XPath directive for our elements.
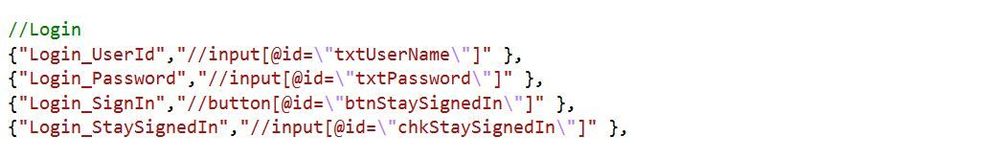
As shown in the image for Login_UserId we are searching the DOM for an input element with the id attribute of ‘txtUserName’. XPath can be used to search for any attribute on the DOM element and can return a single value or multiple depending on what you’re searching for.
Next Steps
Custom Components and Web Resources
PowerApps Control Framework controls and web resources are customizations that represent great options to learn and extend the EasyRepro framework. Try locating the container for the PCF controls and HTML web resources and work towards creating custom objects representing the elements for each as described above.
Conclusion
In this article we discussed reasons why we will may need to extend the EasyRepro framework and some techniques in doing so. We explored working with Selenium objects and creating references to help us when creating unit tests. Finally we put this in an example for working with a ADFS Redirect page on login.
Thank you again for reading! Please let me know in the comments how your journey is going!

by Contributed | Jan 11, 2021 | Technology
This article is contributed. See the original author and article here.
Surface Pro 7+ for Business, the latest generation of the class defining Surface 2-in-1 delivers next level performance and versatility to commercial enterprises and educational institutions.
 Key differences with Surface Pro 7+ for Business:
Key differences with Surface Pro 7+ for Business:
- Removable SSD with options of up to 1 terabyte of storage making it easier for organizations to retain and protect sensitive information.
- Optional LTE Advanced so you can stay connected and receive the latest updates wherever you go.
- Up to 15 hours of battery life (4.5 hours more than Pro 7) plus fast charging that restores battery levels to 80 percent in about an hour.
As a program manager in the commercial engineering group, I’ve been fortunate to learn directly from customers about what matters most when it comes to choosing the best devices for their company and employees. Of course, what stands out as top of mind for almost everyone is ease of device deployment and manageability along with built in, chip to cloud security. So it’s with that lens that I’d like to do a quick tour of our newest Surface 2-in-1, beginning with the different ways you can use the device.
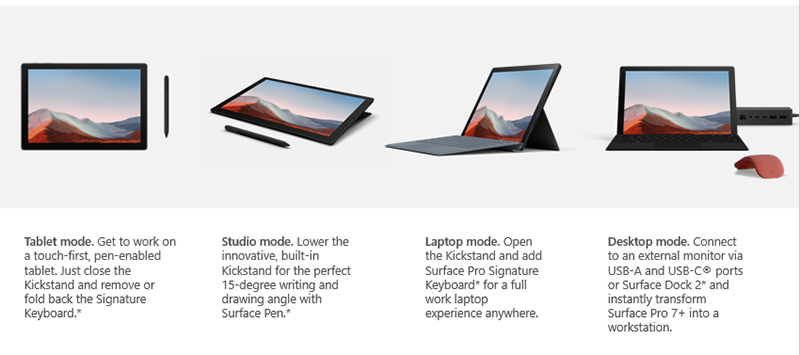
More control with cloud-first device deployment and management
Surface Pro 7+ offers some of the most flexible device management options. Starting with device procurement, before devices are shipped using the Windows Autopilot service Surface Pro 7+ can be placed under management and personalized with required apps and policies, enabling factory direct delivery to your users.
Defense in depth with protection from Microsoft
Every layer is maintained by Microsoft, from the hardened firmware that is adopted from a Microsoft open-source UEFI, to the operating system, through to cloud management. Once devices are up and running, using the Device Firmware Configuration Interface (DFCI), hardware capabilities like built-in cameras, microphones, speakers and radios can be individually disabled at the firmware level using cloud-based policy settings from Intune and Microsoft Endpoint Manager.
Optional LTE Advanced
Of course, a big differentiator for Surface Pro 7+ is the optional LTE Advanced connectivity. Surface Pro 7+ with LTE Advanced is available with the fan-less Core i5 configuration and works with both eSIM and physical nano SIM. Instead of handing out physical SIM cards to your mobile workforce, you can centrally manage calling and network data using eSIM based LTE services.
We’ve now expanded our eSIM ecosystem, giving you more options for geographical coverage. In fact, the eSIM profile in Surface Pro 7+ unlocks access to more mobile operators and services in over 180 countries. Additionally, LTE Advanced can ensure reliable network and internet connections and works in tandem with built-in Wi-Fi 6 capabilities, to avoid dropped video calls and to provide resiliency when Wi-Fi connections aren’t reliable or available. And because Surface Pro 7+ with LTE Advanced is typically always connected, devices can receive updates as soon as they become available.
Inside Surface Pro 7+
Surface Pro 7+ uses the latest 11th gen Intel Core processors more than doubling the performance of the previous generation. And it’s 3.5 times faster than Surface Pro with LTE Advanced from 2017.
Intel 11th Gen “Tiger Lake” processors
With options for Core i3, i5, and i7 processors, Surface Pro 7+ is the first Surface Pro device to offer up to 32 gigabytes of RAM and 1 Terabyte of storage. Of course, Surface Pro 7+ supports Wi-Fi 6 and Bluetooth 5.0. This, combined with the optional LTE Advanced, gives you enhanced connectivity.
Design innovations help boost battery run time
The new thermal design is the most efficient and compact to date. It uses graphite heat spreading, heat pipes and carbon composite materials along with larger vents. Core i7 is designed to minimize fan speed and noise to only the most intensive workloads, while the Core i3 and i5 models are silent and fan-less. We also worked on freeing up internal space by incorporating the same breakthrough technology of Surface Pro X, reducing the thickness of the display. The resulting space advantage went toward increasing the size of the battery. Surface Pro 7+ has the largest battery to date in a Surface Pro with a 50.4-watt hour capacity for improved all-day battery life.
Removable SSD
Surface Pro 7+ provides a removable storage solution that helps commercial organizations comply with specific data retention standards. It also facilitates servicing and repair in the unlikely event of an SSD failure. Enterprise customers no longer need to ship devices back to Microsoft, leaving employees with loaner devices for days.
Retaining proprietary information is made easy with the ability to replace the SSD on-site. Company assets remain in the company with this new option for same unit repair. These offerings include the rSSD and the SSD Door. Purchase of replacement SSDs will be available to commercial customers through authorized resellers beginning with US distribution.

Compatible accessories
Because it uses the same proven design as Pro 7, companies can leverage their investment in compatible Surface Pro accessories like type covers, cases, pens and certified third-party accessories.
Virtual meetings come to life
Support for 1080p Full HD video combined with the dual Studio Microphone array for accurate audio capture makes Surface Pro 7+ ideal for video calls. And, its stereo speakers provide rich sound reproduction using Dolby Atmos®. Capture whiteboard meeting notes and scan documents with the rear-facing 8.0 megapixel HD camera. The high-resolution 12.3” PixelSense™ Display touchscreen features ambient light sensing that automatically adjusts to lighting conditions.
Connect dual 4K monitors
You can easily connect additional monitors using the USB-C port or via the optional Surface Dock 2. The USB ports or Surface Connect can support two external displays with up to 4k resolution, at 60 hertz while working simultaneously with the built-in display, which is great to dock at an office or home office workstation.
Sustainable packaging
Then during shipping, for commercial and bulk shipments, Surface Pro 7+ devices are placed in 23% lighter packaging using device folios. This also makes them easier to distribute broadly, while minimizing waste by using 99% natural fiber-based material, of which 64% is post-consumer recycled materials. And of course, this also makes the devices easier to unpack.
Surface for Business unlocks more value
In summary, Surface Pro 7+ enables businesses and organizations to save time and money with streamlined deployment, modern device management, and built-in, cloud-powered security along with connected experiences from Surface and Microsoft 365. Confidently invest in Surface for today and the future with accessories that are compatible across generations.
To learn more, get a tour from the latest episode of Microsoft Mechanics:

Learn more
For availability and to learn more, see Surface.com.
by Scott Muniz | Jan 11, 2021 | Security, Technology
This article is contributed. See the original author and article here.
| actionpack_gem_for_ruby_on_rails — actionpack_gem_for_ruby_on_rails |
In actionpack gem >= 6.0.0, a possible XSS vulnerability exists when an application is running in development mode allowing an attacker to send or embed (in another page) a specially crafted URL which can allow the attacker to execute JavaScript in the context of the local application. This vulnerability is in the Actionable Exceptions middleware. |
2021-01-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-8264
MISC
MISC |
advanced_webhost_billing_system — advanced_webhost_billing_system
|
Advanced Webhost Billing System 3.7.0 is affected by Cross Site Request Forgery (CSRF) attacks that can delete a contact from the My Additional Contact page. |
2021-01-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-25950
MISC |
asp.net — cute_editor
|
Cute Editor for ASP.NET 6.4 is vulnerable to reflected cross-site scripting (XSS) caused by improper validation of user supplied input. A remote attacker could exploit this vulnerability using a specially crafted URL to execute a script in a victim’s Web browser within the security context of the hosting Web site, once the URL is clicked. An attacker could use this vulnerability to steal the victim’s cookie-based authentication credentials. |
2021-01-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-24903
MISC |
barco — multiple_products
|
Barco TransForm NDN-210 Lite, NDN-210 Pro, NDN-211 Lite, and NDN-211 Pro before 3.8 allows Command Injection (issue 1 of 4). The NDN-210 has a web administration panel which is made available over https. The logon method is basic authentication. There is a command injection issue that will result in unauthenticated remote code execution in the username and password fields of the logon prompt. The NDN-210 is part of Barco TransForm N solution and includes the patch from TransForm N version 3.8 onwards. |
2021-01-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-17500
MISC
CONFIRM
MISC |
barco — transform_n
|
Barco TransForm N before 3.8 allows Command Injection (issue 2 of 4). The NDN-210 has a web administration panel which is made available over https. There is a command injection issue that will allow authenticated users of the administration panel to perform authenticated remote code execution. An issue exists in split_card_cmd.php in which the http parameters xmodules, ymodules and savelocking are not properly handled. The NDN-210 is part of Barco TransForm N solution and includes the patch from TransForm N version 3.8 onwards. |
2021-01-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-17502
MISC
CONFIRM
MISC |
barco — transform_n
|
The NDN-210 has a web administration panel which is made available over https. There is a command injection issue that will allow authenticated users to the administration panel to perform authenticated remote code execution. An issue exists in split_card_cmd.php in which the http parameter “locking” is not properly handled. The NDN-210 is part of Barco TransForm N solution and this vulnerability is patched from TransForm N version 3.8 onwards. |
2021-01-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-17503
MISC
CONFIRM
MISC |
barco — transform_n
|
The NDN-210 has a web administration panel which is made available over https. There is a command injection issue that will allow authenticated users to the administration panel to perform authenticated remote code execution. An issue exists in ngpsystemcmd.php in which the http parameters “x_modules” and “y_modules” are not properly handled. The NDN-210 is part of Barco TransForm N solution and this vulnerability is patched from TransForm N version 3.8 onwards. |
2021-01-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-17504
MISC
CONFIRM
MISC |
bssi — web-sesame
|
A misconfiguration in Web-Sesame 2020.1.1.3375 allows an unauthenticated attacker to download the source code of the application, facilitating its comprehension (code review). Specifically, JavaScript source maps were inadvertently included in the production Webpack configuration. These maps contain sources used to generate the bundle, configuration settings (e.g., API keys), and developers’ comments. |
2021-01-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-29041
MISC
MISC |
buns — buns
|
This affects all versions of package buns. The injection point is located in line 678 in index file lib/index.js in the exported function install(requestedModule). |
2021-01-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-7794
MISC |
cairosvg — cairosvg
|
CairoSVG is a Python (pypi) package. CairoSVG is an SVG converter based on Cairo. In CairoSVG before version 2.5.1, there is a regular expression denial of service (REDoS) vulnerability. When processing SVG files, the python package CairoSVG uses two regular expressions which are vulnerable to Regular Expression Denial of Service (REDoS). If an attacker provides a malicious SVG, it can make cairosvg get stuck processing the file for a very long time. This is fixed in version 2.5.1. See Referenced GitHub advisory for more information. |
2021-01-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-21236
MISC
MISC
CONFIRM
MISC |
| ceph — ceph |
A flaw was found in ceph in versions prior to 16.y.z where ceph stores mgr module passwords in clear text. This can be found by searching the mgr logs for grafana and dashboard, with passwords visible. |
2021-01-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-25678
MISC
MISC |
cisco — jabber
|
Multiple vulnerabilities in Cisco Jabber for Windows, Jabber for MacOS, and Jabber for mobile platforms could allow an attacker to execute arbitrary programs on the underlying operating system (OS) with elevated privileges or gain access to sensitive information. For more information about these vulnerabilities, see the Details section of this advisory. |
2021-01-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-26085
CISCO |
| citrix — secure_mail |
Citrix Secure Mail for Android before 20.11.0 suffers from improper access control allowing unauthenticated access to read limited calendar related data stored within Secure Mail. Note that a malicious app would need to be installed on the Android device or a threat actor would need to execute arbitrary code on the Android device. |
2021-01-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-8275
MISC |
citrix — secure_mail
|
Citrix Secure Mail for Android before 20.11.0 suffers from Improper Control of Generation of Code (‘Code Injection’) by allowing unauthenticated access to read data stored within Secure Mail. Note that a malicious app would need to be installed on the Android device or a threat actor would need to execute arbitrary code on the Android device. |
2021-01-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-8274
MISC |
cockpit — cockpit
|
Cockpit before 0.6.1 allows an attacker to inject custom PHP code and achieve Remote Command Execution via registerCriteriaFunction in lib/MongoLite/Database.php, as demonstrated by values in JSON data to the /auth/check or /auth/requestreset URI. |
2021-01-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-35131
MISC
MISC
MISC |
d-link — dsl-2888a_devices
|
An issue was discovered on D-Link DSL-2888A devices with firmware prior to AU_2.31_V1.1.47ae55. The One Touch application discloses sensitive information, such as the hashed admin login password and the Internet provider connection username and cleartext password, in the application’s response body for a /tmp/var/passwd or /tmp/home/wan_stat URI. |
2021-01-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-24577
MISC
CONFIRM
MISC |
dell — client_and_commerical_consumer_platforms
|
Select Dell Client Commercial and Consumer platforms support a BIOS password reset capability that is designed to assist authorized customers who forget their passwords. Dell is aware of unauthorized password generation tools that can generate BIOS recovery passwords. The tools, which are not authorized by Dell, can be used by a physically present attacker to reset BIOS passwords and BIOS-managed Hard Disk Drive (HDD) passwords. An unauthenticated attacker with physical access to the system could potentially exploit this vulnerability to bypass security restrictions for BIOS Setup configuration, HDD access and BIOS pre-boot authentication. |
2021-01-04 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-5361
MISC |
dell — inspiron_5675_bios
|
Dell Inspiron 5675 BIOS versions prior to 1.4.1 contain a UEFI BIOS RuntimeServices overwrite vulnerability. A local attacker with access to system memory may exploit this vulnerability by overwriting the RuntimeServices structure to execute arbitrary code in System Management Mode (SMM). |
2021-01-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-26186
MISC |
dell — multiple_products
|
Dell EMC Unity, Unity XT, and UnityVSA versions prior to 5.0.4.0.5.012 contains a plain-text password storage vulnerability. A user credentials (including the Unisphere admin privilege user) password is stored in a plain text in a system file. A local authenticated attacker with access to the system files may use the exposed password to gain access with the privileges of the compromised user. |
2021-01-05 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-29489
MISC |
dell — multiple_products
|
Dell EMC Unity, Unity XT, and UnityVSA versions prior to 5.0.4.0.5.012 contain a Denial of Service vulnerability on NAS Servers with NFS exports. A remote authenticated attacker could potentially exploit this vulnerability and cause Denial of Service (Storage Processor Panic) by sending specially crafted UDP requests. |
2021-01-05 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-29490
MISC |
drupal — aes_encryption
|
The AES encryption project 7.x and 8.x for Drupal does not sufficiently prevent attackers from decrypting data, aka SA-CONTRIB-2017-027. NOTE: This project is not covered by Drupal’s security advisory policy. |
2021-01-01 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2017-20001
MISC |
drupal — kcfinder_integration
|
uploader.php in the KCFinder integration project through 2018-06-01 for Drupal mishandles validation, aka SA-CONTRIB-2018-024. NOTE: This project is not covered by Drupal’s security advisory policy. |
2021-01-01 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2018-25002
MISC
MISC
MISC |
eaton — easysoft
|
Eaton’s easySoft software v7.20 and prior are susceptible to file parsing type confusion remote code execution vulnerability. A malicious entity can execute a malicious code or make the application crash by tricking user upload a malformed .E70 file in the application. The vulnerability arises due to improper validation of user data supplied through E70 file which is causing Type Confusion. |
2021-01-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-6656
MISC
MISC
MISC
MISC |
eaton — easysoft
|
The Eaton’s easySoft software v7.20 and prior are susceptible to Out-of-bounds remote code execution vulnerability. A malicious entity can execute a malicious code or make the application crash by tricking user to upload the malformed .E70 file in the application. The vulnerability arises due to improper validation and parsing of the E70 file content by the application. |
2021-01-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-6655
MISC
MISC |
evolucare — ecsimaging
|
** UNSUPPORTED WHEN ASSIGNED ** EVOLUCARE ECSIMAGING (aka ECS Imaging) through 6.21.5 has an OS Command Injection vulnerability via shell metacharacters and an IFS manipulation. The parameter “file” on the webpage /showfile.php can be exploited to gain root access. NOTE: This vulnerability only affects products that are no longer supported by the maintainer. |
2021-01-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-3029
MISC
MISC |
formstone — formstone
|
Formstone <=1.4.16 is vulnerable to a Reflected Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) vulnerability caused by improper validation of user supplied input in the upload-target.php and upload-chunked.php files. A remote attacker could exploit this vulnerability using a specially crafted URL to execute a script in a victim’s Web browser within the security context of the hosting Web site once the URL is clicked or visited. An attacker could use this vulnerability to steal the victim’s cookie-based authentication credentials, force malware execution, user redirection and others. |
2021-01-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-26768
MISC |
foxit — multiple_products
|
The Portable Document Format (PDF) specification does not provide any information regarding the concrete procedure of how to validate signatures. Consequently, a Signature Wrapping vulnerability exists in multiple products. An attacker can use /ByteRange and xref manipulations that are not detected by the signature-validation logic. This affects Foxit Reader before 9.4 and PhantomPDF before 8.3.9 and 9.x before 9.4. It also affects eXpert PDF 12 Ultimate, Expert PDF Reader, Nitro Pro, Nitro Reader, PDF Architect 6, PDF Editor 6 Pro, PDF Experte 9 Ultimate, PDFelement6 Pro, PDF Studio Viewer 2018, PDF Studio Pro, PDF-XChange Editor and Viewer, Perfect PDF 10 Premium, Perfect PDF Reader, Soda PDF, and Soda PDF Desktop. |
2021-01-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2018-18689
MISC
MISC
CONFIRM
MISC |
foxit — multiple_products
|
The Portable Document Format (PDF) specification does not provide any information regarding the concrete procedure of how to validate signatures. Consequently, an Incremental Saving vulnerability exists in multiple products. When an attacker uses the Incremental Saving feature to add pages or annotations, Body Updates are displayed to the user without any action by the signature-validation logic. This affects Foxit Reader before 9.4 and PhantomPDF before 8.3.9 and 9.x before 9.4. It also affects LibreOffice, Master PDF Editor, Nitro Pro, Nitro Reader, Nuance Power PDF Standard, PDF Editor 6 Pro, PDFelement6 Pro, PDF Studio Viewer 2018, PDF Studio Pro, Perfect PDF 10 Premium, and Perfect PDF Reader. |
2021-01-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2018-18688
MISC
MISC
CONFIRM
MISC |
foxit — pdf_activex
|
Foxit PDF ActiveX before 5.5.1 allows remote code execution via command injection because of the lack of a security permission control. |
2021-01-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2018-19418
MISC
CONFIRM |
| google — chrome |
Use after free in WebCodecs in Google Chrome prior to 87.0.4280.66 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. |
2021-01-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-16023
MISC
MISC |
| google — chrome |
Use after free in WebRTC in Google Chrome prior to 87.0.4280.66 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. |
2021-01-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-16026
MISC
MISC |
| google — chrome |
Use after free in safe browsing in Google Chrome prior to 87.0.4280.141 allowed a remote attacker to potentially perform a sandbox escape via a crafted HTML page. |
2021-01-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-21110
MISC
MISC
GENTOO |
| google — chrome |
Insufficient policy enforcement in WebUI in Google Chrome prior to 87.0.4280.141 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to potentially perform a sandbox escape via a crafted Chrome Extension. |
2021-01-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-21111
MISC
MISC
GENTOO |
| google — chrome |
Insufficient data validation in cros-disks in Google Chrome on ChromeOS prior to 87.0.4280.66 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the browser process to bypass noexec restrictions via a malicious file. |
2021-01-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-16035
MISC
MISC |
| google — chrome |
Use after free in clipboard in Google Chrome prior to 87.0.4280.88 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. |
2021-01-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-16037
MISC
MISC |
| google — chrome |
Use after free in audio in Google Chrome prior to 87.0.4280.141 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. |
2021-01-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-21114
MISC
MISC
GENTOO |
| google — chrome |
Use after free in drag and drop in Google Chrome on Linux prior to 87.0.4280.141 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to potentially perform a sandbox escape via a crafted HTML page. |
2021-01-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-21107
MISC
MISC
GENTOO |
| google — chrome |
User after free in safe browsing in Google Chrome prior to 87.0.4280.141 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to potentially perform a sandbox escape via a crafted HTML page. |
2021-01-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-21115
MISC
MISC
GENTOO |
| google — chrome |
Heap buffer overflow in audio in Google Chrome prior to 87.0.4280.141 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. |
2021-01-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-21116
MISC
MISC
GENTOO |
| google — chrome |
Use after free in media in Google Chrome on OS X prior to 87.0.4280.88 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. |
2021-01-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-16038
MISC
MISC |
google — chrome
|
Inappropriate implementation in PDFium in Google Chrome prior to 87.0.4280.66 allowed a remote attacker to bypass navigation restrictions via a crafted PDF file. |
2021-01-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-16029
MISC
MISC |
google — chrome
|
Inappropriate implementation in cookies in Google Chrome prior to 87.0.4280.66 allowed a remote attacker to bypass cookie restrictions via a crafted HTML page. |
2021-01-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-16036
MISC
MISC |
google — chrome
|
Insufficient data validation in sharing in Google Chrome prior to 87.0.4280.66 allowed a remote attacker to spoof the contents of the Omnibox (URL bar) via a crafted HTML page. |
2021-01-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-16032
MISC
MISC |
google — chrome
|
Inappropriate implementation in filesystem in Google Chrome on ChromeOS prior to 87.0.4280.66 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the browser process to bypass noexec restrictions via a malicious file. |
2021-01-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-16019
MISC
MISC |
google — chrome
|
Insufficient data validation in UI in Google Chrome prior to 87.0.4280.66 allowed a remote attacker to spoof the contents of the Omnibox (URL bar) via a crafted HTML page. |
2021-01-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-16031
MISC
MISC |
google — chrome
|
Insufficient data validation in Blink in Google Chrome prior to 87.0.4280.66 allowed a remote attacker to inject arbitrary scripts or HTML (UXSS) via a crafted HTML page. |
2021-01-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-16030
MISC
MISC |
google — chrome
|
Insufficient policy enforcement in developer tools in Google Chrome prior to 87.0.4280.66 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to obtain potentially sensitive information from the user’s disk via a crafted Chrome Extension. |
2021-01-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-16027
MISC
MISC |
google — chrome
|
Heap buffer overflow in WebRTC in Google Chrome prior to 87.0.4280.66 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. |
2021-01-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-16028
MISC
MISC |
google — chrome
|
Insufficient data validation in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 87.0.4280.88 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. |
2021-01-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-16040
MISC
MISC |
google — chrome
|
Use after free in site isolation in Google Chrome prior to 86.0.4240.198 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to potentially perform a sandbox escape via a crafted HTML page. |
2021-01-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-16017
MISC
MISC |
google — chrome
|
Heap buffer overflow in clipboard in Google Chrome prior to 87.0.4280.66 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to potentially perform a sandbox escape via a crafted HTML page. |
2021-01-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-16025
MISC
MISC |
google — chrome
|
Heap buffer overflow in UI in Google Chrome prior to 87.0.4280.66 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to potentially perform a sandbox escape via a crafted HTML page. |
2021-01-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-16024
MISC
MISC |
google — chrome
|
Inappropriate implementation in cryptohome in Google Chrome on ChromeOS prior to 87.0.4280.66 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the browser process to bypass discretionary access control via a malicious file. |
2021-01-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-16020
MISC
MISC |
google — chrome
|
Inappropriate implementation in WebRTC in Google Chrome prior to 87.0.4280.66 allowed a local attacker to bypass policy restrictions via a crafted HTML page. |
2021-01-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-16034
MISC
MISC |
google — chrome
|
Use after free in extensions in Google Chrome prior to 87.0.4280.88 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. |
2021-01-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-16039
MISC
MISC |
google — chrome
|
Use after free in media in Google Chrome prior to 87.0.4280.141 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to potentially perform a sandbox escape via a crafted HTML page. |
2021-01-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-21108
MISC
MISC
GENTOO |
google — chrome
|
Out of bounds read in networking in Google Chrome prior to 87.0.4280.88 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to obtain potentially sensitive information from process memory via a crafted HTML page. |
2021-01-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-16041
MISC
MISC |
google — chrome
|
Uninitialized Use in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 87.0.4280.88 allowed a remote attacker to obtain potentially sensitive information from process memory via a crafted HTML page. |
2021-01-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-16042
MISC
MISC |
google — chrome
|
Insufficient data validation in networking in Google Chrome prior to 87.0.4280.141 allowed a remote attacker to bypass discretionary access control via malicious network traffic. |
2021-01-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-16043
MISC
MISC
GENTOO |
google — chrome
|
Race in image burner in Google Chrome on ChromeOS prior to 87.0.4280.66 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the browser process to perform OS-level privilege escalation via a malicious file. |
2021-01-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-16021
MISC
MISC |
google — chrome
|
Inappropriate implementation in WebUSB in Google Chrome prior to 87.0.4280.66 allowed a remote attacker to spoof security UI via a crafted HTML page. |
2021-01-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-16033
MISC
MISC |
google — chrome
|
Inappropriate implementation in base in Google Chrome prior to 86.0.4240.193 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to potentially perform a sandbox escape via a crafted HTML page. |
2021-01-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-16016
MISC
MISC |
google — chrome
|
Insufficient policy enforcement in networking in Google Chrome prior to 87.0.4280.66 allowed a remote attacker to potentially bypass firewall controls via a crafted HTML page. |
2021-01-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-16022
MISC
MISC |
google — chrome
|
Use after free in PPAPI in Google Chrome prior to 87.0.4280.66 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to potentially perform a sandbox escape via a crafted HTML page. |
2021-01-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-16014
MISC
MISC |
google — chrome
|
Inappropriate implementation in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 86.0.4240.198 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. |
2021-01-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-16013
MISC
MISC |
google — chrome
|
Side-channel information leakage in graphics in Google Chrome prior to 87.0.4280.66 allowed a remote attacker to leak cross-origin data via a crafted HTML page. |
2021-01-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-16012
MISC
MISC |
google — chrome
|
Use after free in payments in Google Chrome prior to 87.0.4280.141 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to potentially perform a sandbox escape via a crafted HTML page. |
2021-01-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-21109
MISC
MISC
GENTOO |
google — chrome
|
Insufficient data validation in WASM in Google Chrome prior to 87.0.4280.66 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. |
2021-01-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-16015
MISC
MISC |
google — chrome
|
Heap buffer overflow in Skia in Google Chrome prior to 87.0.4280.141 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. |
2021-01-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-21113
MISC
MISC
GENTOO |
google — chrome
|
Use after free in Blink in Google Chrome prior to 87.0.4280.141 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. |
2021-01-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-21112
MISC
MISC
GENTOO |
google — chrome
|
Use after free in payments in Google Chrome prior to 87.0.4280.66 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to potentially perform a sandbox escape via a crafted HTML page. |
2021-01-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-16018
MISC
MISC |
google — chrome
|
Use after free in autofill in Google Chrome prior to 87.0.4280.141 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to potentially perform a sandbox escape via a crafted HTML page. |
2021-01-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-21106
MISC
MISC
GENTOO |
ibm — emptoris_contract_management
|
IBM Emptoris Contract Management 10.1.3 is vulnerable to cross-site scripting. This vulnerability allows users to embed arbitrary JavaScript code in the Web UI thus altering the intended functionality potentially leading to credentials disclosure within a trusted session. IBM X-Force ID: 190979. |
2021-01-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-4892
XF
CONFIRM |
ibm — emptoris_contract_management_and_emptoris_spend_analysis
|
IBM Emptoris Contract Management and IBM Emptoris Spend Analysis 10.1.0, 10.1.1, and 10.1.3 could allow a remote attacker to obtain sensitive information when a detailed technical error message is returned in the browser. This information could be used in further attacks against the system. IBM X-Force ID: 190988. |
2021-01-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-4897
XF
CONFIRM
CONFIRM |
ibm — emptoris_sourcing
|
IBM Emptoris Sourcing 10.1.0, 10.1.1, and 10.1.3 is vulnerable to web cache poisoning, caused by improper input validation by modifying HTTP request headers. IBM X-Force ID: 190987. |
2021-01-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-4896
XF
CONFIRM |
ibm — engineering_requirements_quality_assistant_on-premises
|
IBM Engineering Requirements Quality Assistant On-Premises could allow an authenticated user to obtain sensitive information due to improper input validation. IBM X-Force ID: 186282. |
2021-01-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-4667
XF
CONFIRM |
ibm — engineering_requirements_quality_assistant_on-premises
|
IBM Engineering Requirements Quality Assistant On-Premises is vulnerable to cross-site scripting. This vulnerability allows users to embed arbitrary JavaScript code in the Web UI thus altering the intended functionality potentially leading to credentials disclosure within a trusted session. IBM X-Force ID: 186281. |
2021-01-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-4666
XF
CONFIRM |
ibm — engineering_requirements_quality_assistant_on-premises
|
IBM Engineering Requirements Quality Assistant On-Premises is vulnerable to cross-site scripting. This vulnerability allows users to embed arbitrary JavaScript code in the Web UI thus altering the intended functionality potentially leading to credentials disclosure within a trusted session. IBM X-Force ID: 186235. |
2021-01-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-4664
XF
CONFIRM |
ibm — engineering_requirements_quality_assistant_on-premises
|
IBM Engineering Requirements Quality Assistant On-Premises is vulnerable to cross-site scripting. This vulnerability allows users to embed arbitrary JavaScript code in the Web UI thus altering the intended functionality potentially leading to credentials disclosure within a trusted session. IBM X-Force ID: 186234. |
2021-01-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-4663
XF
CONFIRM |
| ibm — jazz_foundation_products |
IBM Jazz Foundation products are vulnerable to cross-site scripting. This vulnerability allows users to embed arbitrary JavaScript code in the Web UI thus altering the intended functionality potentially leading to credentials disclosure within a trusted session. IBM X-Force ID: 188127. |
2021-01-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-4733
XF
CONFIRM |
ibm — jazz_foundation_products
|
IBM Jazz Foundation Products could allow a remote attacker to obtain sensitive information when a detailed technical error message is returned in the browser. This information could be used in further attacks against the system. IBM X-Force ID: 183189. |
2021-01-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-4544
XF
CONFIRM |
ibm — jazz_foundation_products
|
IBM Jazz Foundation Products could allow a remote attacker to obtain sensitive information when a detailed technical error message is returned in the browser. This information could be used in further attacks against the system. IBM X-Force ID: 181862. |
2021-01-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-4487
XF
CONFIRM |
ibm — jazz_foundation_products
|
IBM Jazz Foundation Products are vulnerable to cross-site scripting. This vulnerability allows users to embed arbitrary JavaScript code in the Web UI thus altering the intended functionality potentially leading to credentials disclosure within a trusted session. IBM X-Force ID: 186698. |
2021-01-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-4691
XF
CONFIRM |
ibm — jazz_foundation_products
|
IBM Jazz Foundation products are vulnerable to cross-site scripting. This vulnerability allows users to embed arbitrary JavaScript code in the Web UI thus altering the intended functionality potentially leading to credentials disclosure within a trusted session. IBM X-Force ID: 186790. |
2021-01-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-4697
XF
CONFIRM |
ibm — security_verify_privilege_manager
|
IBM Security Verify Privilege Manager 10.8 is vulnerable to an XML External Entity Injection (XXE) attack when processing XML data. A local attacker could exploit this vulnerability to expose sensitive information or consume memory resources. IBM X-Force ID: 184883. |
2021-01-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-4606
XF
CONFIRM |
ibm — spectrum_protect_plus
|
IBM Spectrum Protect Plus 10.1.0 through 10.1.6 may include sensitive information in its URLs increasing the risk of such information being caputured by an attacker. IBM X-Force ID: 193654. |
2021-01-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-5018
XF
CONFIRM |
ibm — spectrum_protect_plus
|
IBM Spectrum Protect Plus 10.1.0 through 10.1.6 does not invalidate session after a password reset which could allow a local user to impersonate another user on the system. IBM X-Force ID: 193657. |
2021-01-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-5021
XF
CONFIRM |
ibm — spectrum_protect_plus
|
IBM Spectrum Protect Plus 10.1.0 through 10.1.6 is vulnerable to HTTP header injection, caused by improper validation of input by the HOST headers. By sending a specially crafted HTTP request, a remote attacker could exploit this vulnerability to inject HTTP HOST header, which will allow the attacker to conduct various attacks against the vulnerable system, including cross-site scripting, cache poisoning or session hijacking. IBM X-Force ID: 193655. |
2021-01-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-5019
XF
CONFIRM |
ibm — spectrum_protect_plus
|
IBM Spectrum Protect Plus 10.1.0 through 10.1.6 could allow a remote attacker to hijack the clicking action of the victim. By persuading a victim to visit a malicious Web site, a remote attacker could exploit this vulnerability to hijack the victim’s click actions and possibly launch further attacks against the victim. IBM X-Force ID: 193656. |
2021-01-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-5020
XF
CONFIRM |
ibm — spectrum_protect_plus
|
IBM Spectrum Protect Plus 10.1.0 through 10.1.6 may allow a local user to obtain access to information beyond their intended role and permissions. IBM X-Force ID: 193653. |
2021-01-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-5017
XF
CONFIRM |
ibm — spectrum_protect_plus
|
IBM Spectrum Protect Plus 10.1.0 through 10.1.6 may allow unauthenticated and unauthorized access to VDAP proxy which can result in an attacker obtaining information they are not authorized to access. IBM X-Force ID: 193658. |
2021-01-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-5022
XF
CONFIRM |
ibm — websphere_extreme_scale
|
IBM WebSphere eXtreme Scale 8.6.1 stores sensitive information in URL parameters. This may lead to information disclosure if unauthorized parties have access to the URLs via server logs, referrer header or browser history. IBM X-Force ID: 177932. |
2021-01-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-4336
XF
CONFIRM |
innokas — yhtma_oy_vital_signs_monitor
|
Innokas Yhtymä Oy Vital Signs Monitor VC150 prior to Version 1.7.15 HL7 v2.x injection vulnerabilities exist in the affected products that allow physically proximate attackers with a connected barcode reader to inject HL7 v2.x segments into specific HL7 v2.x messages via multiple expected parameters. |
2021-01-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-27260
MISC |
innokas — yhtma_oy_vital_signs_monitor
|
Innokas Yhtymä Oy Vital Signs Monitor VC150 prior to Version 1.7.15 A stored cross-site scripting (XSS) vulnerability exists in the affected products that allow an attacker to inject arbitrary web script or HTML via the filename parameter to multiple update endpoints of the administrative web interface. |
2021-01-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-27262
MISC |
invision_community — ips_community_suite
|
Invision Community IPS Community Suite before 4.5.4.2 allows SQL Injection via the Downloads REST API (the sortDir parameter in a sortBy=popular action to the GETindex() method in applications/downloads/api/files.php). |
2021-01-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-3025
MISC
MISC |
krpano — panorama_viewer
|
The default installation of Krpano Panorama Viewer version <=1.20.8 is prone to Reflected XSS due to insecure XML load in file /viewer/krpano.html, parameter xml. |
2021-01-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-24900
MISC |
krpano — panorama_viewer
|
The default installation of Krpano Panorama Viewer version <=1.20.8 is vulnerable to Reflected XSS due to insecure remote js load in file viewer/krpano.html, parameter plugin[test].url. |
2021-01-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-24901
MISC |
liferay — cms_portal
|
Liferay CMS Portal version 7.1.3 and 7.2.1 have a blind persistent cross-site scripting (XSS) vulnerability in the user name parameter to Calendar. An attacker can insert the malicious payload on the username, lastname or surname fields of its own profile, and the malicious payload will be injected and reflected in the calendar of the user who submitted the payload. An attacker could escalate its privileges in case an admin visits the calendar that injected the payload. |
2021-01-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-25476
MISC
MISC
MISC |
linux — linux_kernel
|
A use after free in the Linux kernel infiniband hfi1 driver in versions prior to 5.10-rc6 was found in the way user calls Ioctl after open dev file and fork. A local user could use this flaw to crash the system. |
2021-01-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-27835
MISC |
marvell — qcconvergeconsole
|
Marvell QConvergeConsole GUI <= 5.5.0.74 is affected by a path traversal vulnerability. The deleteEventLogFile method of the GWTTestServiceImpl class lacks proper validation of a user-supplied path prior to using it in file deletion operations. An authenticated, remote attacker can leverage this vulnerability to delete arbitrary remote files as SYSTEM or root. |
2021-01-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-5804
MISC |
marvell — qcconvergeconsole
|
In Marvell QConvergeConsole GUI <= 5.5.0.74, credentials are stored in cleartext in tomcat-users.xml. OS-level users on the QCC host who are not authorized to use QCC may use the plaintext credentials to login to QCC. |
2021-01-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-5805
MISC |
mdbook — mdbook
|
mdBook is a utility to create modern online books from Markdown files and is written in Rust. In mdBook before version 0.4.5, there is a vulnerability affecting the search feature of mdBook, which could allow an attacker to execute arbitrary JavaScript code on the page. The search feature of mdBook (introduced in version 0.1.4) was affected by a cross site scripting vulnerability that allowed an attacker to execute arbitrary JavaScript code on an user’s browser by tricking the user into typing a malicious search query, or tricking the user into clicking a link to the search page with the malicious search query prefilled. mdBook 0.4.5 fixes the vulnerability by properly escaping the search query. Owners of websites built with mdBook have to upgrade to mdBook 0.4.5 or greater and rebuild their website contents with it. |
2021-01-04 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-26297
MISC
MISC
MISC
CONFIRM
MISC |
mendixsso — mendixsso
|
MendixSSO <= 2.1.1 contains endpoints that make use of the openid handler, which is suffering from a Cross-Site Scripting vulnerability via the URL path. This is caused by the reflection of user-supplied data without appropriate HTML escaping or output encoding. As a result, a JavaScript payload may be injected into the above endpoint causing it to be executed within the context of the victim’s browser. |
2021-01-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-8160
MISC
MISC |
mercusys — mercury_xg18_devices
|
MERCUSYS Mercury X18G 1.0.5 devices allow Directory Traversal via ../ to the UPnP server, as demonstrated by the /../../conf/template/uhttpd.json URI. |
2021-01-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-23242
MISC
MISC
MISC |
mercusys — mercury_xg18_devices
|
MERCUSYS Mercury X18G 1.0.5 devices allow Directory Traversal via ../ in conjunction with a loginLess or login.htm URI (for authentication bypass) to the web server, as demonstrated by the /loginLess/../../etc/passwd URI. |
2021-01-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-23241
MISC
MISC
MISC |
monocms — monocms_blog
|
MonoCMS Blog 1.0 is affected by incorrect access control that can lead to remote arbitrary code execution. At monofiles/category.php:27, user input can be saved to category/[foldername]/index.php causing RCE. |
2021-01-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-28672
MISC |
| mozilla — firefox |
Mozilla developers reported memory safety bugs present in Firefox 83. Some of these bugs showed evidence of memory corruption and we presume that with enough effort some of these could have been exploited to run arbitrary code. This vulnerability affects Firefox < 84. |
2021-01-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-35114
MISC
MISC |
mozilla — firefox
|
When a user typed a URL in the address bar or the search bar and quickly hit the enter key, a website could sometimes capture that event and then redirect the user before navigation occurred to the desired, entered address. To construct a convincing spoof the attacker would have had to guess what the user was typing, perhaps by suggesting it. This vulnerability affects Firefox < 84. |
2021-01-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-26979
MISC
MISC |
mozilla — firefox
|
When a HTTPS pages was embedded in a HTTP page, and there was a service worker registered for the former, the service worker could have intercepted the request for the secure page despite the iframe not being a secure context due to the (insecure) framing. This vulnerability affects Firefox < 84. |
2021-01-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-26976
MISC
MISC |
mozilla — firefox
|
When a malicious application installed on the user’s device broadcast an Intent to Firefox for Android, arbitrary headers could have been specified, leading to attacks such as abusing ambient authority or session fixation. This was resolved by only allowing certain safe-listed headers. *Note: This issue only affected Firefox for Android. Other operating systems are unaffected.*. This vulnerability affects Firefox < 84. |
2021-01-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-26975
MISC
MISC |
mozilla — firefox
|
The lifecycle of IPC Actors allows managed actors to outlive their manager actors; and the former must ensure that they are not attempting to use a dead actor they have a reference to. Such a check was omitted in WebGL, resulting in a use-after-free and a potentially exploitable crash. This vulnerability affects Firefox < 84. |
2021-01-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-26972
MISC
MISC |
mozilla — firefox
|
By attempting to connect a website using an unresponsive port, an attacker could have controlled the content of a tab while the URL bar displayed the original domain. *Note: This issue only affects Firefox for Android. Other operating systems are unaffected.*. This vulnerability affects Firefox < 84. |
2021-01-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-26977
MISC
MISC |
| mozilla — multiple_products |
Mozilla developers reported memory safety bugs present in Firefox 83 and Firefox ESR 78.5. Some of these bugs showed evidence of memory corruption and we presume that with enough effort some of these could have been exploited to run arbitrary code. This vulnerability affects Firefox < 84, Thunderbird < 78.6, and Firefox ESR < 78.6. |
2021-01-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-35113
MISC
MISC
MISC
MISC |
mozilla — multiple_products
|
Certain input to the CSS Sanitizer confused it, resulting in incorrect components being removed. This could have been used as a sanitizer bypass. This vulnerability affects Firefox < 84, Thunderbird < 78.6, and Firefox ESR < 78.6. |
2021-01-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-26973
MISC
MISC
MISC
MISC |
mozilla — multiple_products
|
When an extension with the proxy permission registered to receive <all_urls>, the proxy.onRequest callback was not triggered for view-source URLs. While web content cannot navigate to such URLs, a user opening View Source could have inadvertently leaked their IP address. This vulnerability affects Firefox < 84, Thunderbird < 78.6, and Firefox ESR < 78.6. |
2021-01-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-35111
MISC
MISC
MISC
MISC |
mozilla — multiple_products
|
If a user downloaded a file lacking an extension on Windows, and then “Open”-ed it from the downloads panel, if there was an executable file in the downloads directory with the same name but with an executable extension (such as .bat or .exe) that executable would have been launched instead. *Note: This issue only affected Windows operating systems. Other operating systems are unaffected.*. This vulnerability affects Firefox < 84, Thunderbird < 78.6, and Firefox ESR < 78.6. |
2021-01-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-35112
MISC
MISC
MISC
MISC |
mozilla — multiple_products
|
When flex-basis was used on a table wrapper, a StyleGenericFlexBasis object could have been incorrectly cast to the wrong type. This resulted in a heap user-after-free, memory corruption, and a potentially exploitable crash. This vulnerability affects Firefox < 84, Thunderbird < 78.6, and Firefox ESR < 78.6. |
2021-01-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-26974
MISC
MISC
MISC
MISC |
mozilla — multiple_products
|
Certain blit values provided by the user were not properly constrained leading to a heap buffer overflow on some video drivers. This vulnerability affects Firefox < 84, Thunderbird < 78.6, and Firefox ESR < 78.6. |
2021-01-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-26971
MISC
MISC
MISC
MISC |
mozilla — multiple_products
|
Using techniques that built on the slipstream research, a malicious webpage could have exposed both an internal network’s hosts as well as services running on the user’s local machine. This vulnerability affects Firefox < 84, Thunderbird < 78.6, and Firefox ESR < 78.6. |
2021-01-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-26978
MISC
MISC
MISC
MISC |
multiple_vendors — multiple_2fa_security_keys
|
An electromagnetic-wave side-channel issue was discovered on NXP SmartMX / P5x security microcontrollers and A7x secure authentication microcontrollers, with CryptoLib through v2.9. It allows attackers to extract the ECDSA private key after extensive physical access (and consequently produce a clone). This was demonstrated on the Google Titan Security Key, based on an NXP A7005a chip. Other FIDO U2F security keys are also impacted (Yubico YubiKey Neo and Feitian K9, K13, K21, and K40) as well as several NXP JavaCard smartcards (J3A081, J2A081, J3A041, J3D145_M59, J2D145_M59, J3D120_M60, J3D082_M60, J2D120_M60, J2D082_M60, J3D081_M59, J2D081_M59, J3D081_M61, J2D081_M61, J3D081_M59_DF, J3D081_M61_DF, J3E081_M64, J3E081_M66, J2E081_M64, J3E041_M66, J3E016_M66, J3E016_M64, J3E041_M64, J3E145_M64, J3E120_M65, J3E082_M65, J2E145_M64, J2E120_M65, J2E082_M65, J3E081_M64_DF, J3E081_M66_DF, J3E041_M66_DF, J3E016_M66_DF, J3E041_M64_DF, and J3E016_M64_DF). |
2021-01-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-3011
MISC
MISC |
netapp — element_os
|
Element OS versions prior to 1.8P1 and 12.2 are susceptible to a vulnerability that could allow an unauthenticated remote attacker to perform arbitrary code execution. |
2021-01-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-8584
MISC |
nextcloud — contacts
|
A missing file type check in Nextcloud Contacts 3.3.0 allows a malicious user to upload malicious SVG files to perform cross-site scripting (XSS) attacks. |
2021-01-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-8281
MISC
MISC |
nextcloud — contacts
|
A missing file type check in Nextcloud Contacts 3.4.0 allows a malicious user to upload SVG files as PNG files to perform cross-site scripting (XSS) attacks. |
2021-01-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-8280
MISC
MISC |
| node.js — node.js |
Node.js versions before 10.23.1, 12.20.1, 14.15.4, 15.5.1 are vulnerable to a use-after-free bug in its TLS implementation. When writing to a TLS enabled socket, node::StreamBase::Write calls node::TLSWrap::DoWrite with a freshly allocated WriteWrap object as first argument. If the DoWrite method does not return an error, this object is passed back to the caller as part of a StreamWriteResult structure. This may be exploited to corrupt memory leading to a Denial of Service or potentially other exploits. |
2021-01-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-8265
MISC
FEDORA
MISC
DEBIAN |
node.js — node.js
|
Node.js versions before 10.23.1, 12.20.1, 14.15.4, 15.5.1 allow two copies of a header field in an HTTP request (for example, two Transfer-Encoding header fields). In this case, Node.js identifies the first header field and ignores the second. This can lead to HTTP Request Smuggling. |
2021-01-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-8287
MISC
FEDORA
MISC
DEBIAN |
| nvidia — gpu_display_driver |
NVIDIA GPU Display Driver for Linux, all versions, contains a vulnerability in the kernel mode layer (nvidia.ko) in which it does not completely honor operating system file system permissions to provide GPU device-level isolation, which may lead to denial of service or information disclosure. |
2021-01-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1056
CONFIRM |
nvidia — gpu_display_driver
|
NVIDIA GPU Display Driver for Windows and Linux, all versions, contains a vulnerability in the kernel mode layer (nvlddmkm.sys) handler for DxgkDdiEscape or IOCTL in which user-mode clients can access legacy privileged APIs, which may lead to denial of service, escalation of privileges, and information disclosure. |
2021-01-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1052
CONFIRM |
nvidia — gpu_display_driver
|
NVIDIA GPU Display Driver for Windows and Linux, all versions, contains a vulnerability in the kernel mode layer (nvlddmkm.sys) handler for DxgkDdiEscape or IOCTL in which improper validation of a user pointer may lead to denial of service. |
2021-01-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1053
CONFIRM |
nvidia — gpu_display_driver
|
NVIDIA GPU Display Driver for Windows, all versions, contains a vulnerability in the kernel mode layer (nvlddmkm.sys) handler for DxgkDdiEscape in which the software does not perform or incorrectly performs an authorization check when an actor attempts to access a resource or perform an action, which may lead to denial of service. |
2021-01-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1054
CONFIRM |
nvidia — gpu_display_driver
|
NVIDIA GPU Display Driver for Windows, all versions, contains a vulnerability in the kernel mode layer (nvlddmkm.sys) handler for DxgkDdiEscape in which improper access control may lead to denial of service and information disclosure. |
2021-01-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1055
CONFIRM |
nvidia — gpu_display_driver
|
NVIDIA GPU Display Driver for Windows, all versions, contains a vulnerability in the kernel mode layer (nvlddmkm.sys) handler for DxgkDdiEscape in which an operation is performed which may lead to denial of service or escalation of privileges. |
2021-01-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1051
CONFIRM |
| nvidia — vgpu |
NVIDIA vGPU software contains a vulnerability in the guest kernel mode driver and vGPU plugin, in which an input index is not validated, which may lead to tampering of data or denial of service. This affects vGPU version 8.x (prior to 8.6) and version 11.0 (prior to 11.3). |
2021-01-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1060
CONFIRM |
nvidia — vgpu
|
NVIDIA vGPU software contains a vulnerability in the guest kernel mode driver and vGPU plugin, in which an input data size is not validated, which may lead to tampering of data or denial of service. This affects vGPU version 8.x (prior to 8.6) and version 11.0 (prior to 11.3). |
2021-01-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1058
CONFIRM |
| nvidia — vgpu_manager |
NVIDIA vGPU manager contains a vulnerability in the vGPU plugin, in which input data is not validated, which may lead to tampering of data or denial of service. This affects vGPU version 8.x (prior to 8.6) and version 11.0 (prior to 11.3). |
2021-01-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1065
CONFIRM |
| nvidia — vgpu_manager |
NVIDIA vGPU manager contains a vulnerability in the vGPU plugin, in which an input offset is not validated, which may lead to a buffer overread, which in turn may cause tampering of data, information disclosure, or denial of service. This affects vGPU version 8.x (prior to 8.6) and version 11.0 (prior to 11.3). |
2021-01-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1063
CONFIRM |
| nvidia — vgpu_manager |
NVIDIA vGPU manager contains a vulnerability in the vGPU plugin, in which it obtains a value from an untrusted source, converts this value to a pointer, and dereferences the resulting pointer, which may lead to information disclosure or denial of service. This affects vGPU version 8.x (prior to 8.6) and version 11.0 (prior to 11.3). |
2021-01-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1064
CONFIRM |
nvidia — vgpu_manager
|
NVIDIA vGPU manager contains a vulnerability in the vGPU plugin, in which an input index is not validated, which may lead to integer overflow, which in turn may cause tampering of data, information disclosure, or denial of service. This affects vGPU version 8.x (prior to 8.6) and version 11.0 (prior to 11.3). |
2021-01-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1059
CONFIRM |
nvidia — vgpu_manager
|
NVIDIA vGPU manager contains a vulnerability in the vGPU plugin, in which a race condition may cause the vGPU plugin to continue using a previously validated resource that has since changed, which may lead to denial of service or information disclosure. This affects vGPU version 8.x (prior to 8.6) and version 11.0 (prior to 11.3). |
2021-01-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1061
CONFIRM |
nvidia — vgpu_manager
|
NVIDIA vGPU manager contains a vulnerability in the vGPU plugin, in which input data is not validated, which may lead to unexpected consumption of resources, which in turn may lead to denial of service. This affects vGPU version 8.x (prior to 8.6) and version 11.0 (prior to 11.3). |
2021-01-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1066
CONFIRM |
nvidia — vgpu_manager
|
NVIDIA vGPU manager contains a vulnerability in the vGPU plugin, in which an input data length is not validated, which may lead to tampering of data or denial of service. This affects vGPU version 8.x (prior to 8.6) and version 11.0 (prior to 11.3). |
2021-01-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1062
CONFIRM |
| nvidia — virtual_gpu_manager |
NVIDIA Virtual GPU Manager NVIDIA vGPU manager contains a vulnerability in the vGPU plugin in which it allows guests to allocate some resources for which the guest is not authorized, which may lead to integrity and confidentiality loss, denial of service, or information disclosure. This affects vGPU version 8.x (prior to 8.6) and version 11.0 (prior to 11.3). |
2021-01-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1057
CONFIRM |
pearson — vue_vts_installer
|
The Application Wrapper in Pearson VUE VTS Installer 2.3.1911 has Full Control permissions for Everyone in the “%SYSTEMDRIVE%Pearson VUE” directory, which allows local users to obtain administrative privileges via a Trojan horse application. |
2021-01-04 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-36154
MISC
MISC |
phpfusion — phpfusion
|
login.php in PHPFusion (aka PHP-Fusion) Andromeda 9.x before 2020-12-30 generates error messages that distinguish between incorrect username and incorrect password (i.e., not a single “Incorrect username or password” message in both cases), which might allow enumeration. |
2021-01-03 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-35952
MISC |
phpgurukul — hospital_management_system
|
PHPGURUKUL Hospital Management System V 4.0 does not properly restrict access to admin/dashboard.php, which allows attackers to access all data of users, doctors, patients, change admin password, get appointment history and access all session logs. |
2021-01-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-35745
MISC
MISC
MISC |
portland_labs — concrete5
|
The Express Entries Dashboard in Concrete5 8.5.4 allows stored XSS via the name field of a new data object at an index.php/dashboard/express/entries/view/ URI. |
2021-01-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-3111
MISC
MISC |
pwntools — pwntools
|
This affects the package pwntools before 4.3.1. The shellcraft generator for affected versions of this module are vulnerable to Server-Side Template Injection (SSTI), which can lead to remote code execution. |
2021-01-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-28468
MISC
MISC
MISC |
quixplorer — quixplorer
|
Quixplorer <=2.4.1 is vulnerable to reflected cross-site scripting (XSS) caused by improper validation of user supplied input. A remote attacker could exploit this vulnerability using a specially crafted URL to execute a script in a victim’s Web browser within the security context of the hosting Web site, once the URL is clicked. An attacker could use this vulnerability to steal the victim’s cookie-based authentication credentials. |
2021-01-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-24902
MISC |
red_hat — jbcs_httpd
|
A flaw was found in JBCS httpd in version 2.4.37 SP3, where it uses a back-end worker SSL certificate with the keystore file’s ID is ‘unknown’. The validation of the certificate whether CN and hostname are matching stopped working and allow connecting to the back-end work. The highest threat from this vulnerability is to data integrity. |
2021-01-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-25680
MISC |
| rock_rms — rock_rms |
Rock RMS versions before 8.10 and versions 9.0 through 9.3 fails to properly validate files uploaded in the application. The only protection mechanism is a file-extension blacklist that can be bypassed by adding multiple spaces and periods after the file name. This could allow an attacker to upload ASPX code and gain remote code execution on the application. The application typically runs as LocalSystem as mandated in the installation guide. Patched in versions 8.10 and 9.4. |
2021-01-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2019-18643
MISC |
rock_rms — rock_rms
|
Rock RMS version before 8.6 is vulnerable to account takeover by tampering with the user ID parameter in the profile update feature. The lack of validation and use of sequential user IDs allows any user to change account details of any other user. This vulnerability could be used to change the email address of another account, even the administrator account. Upon changing another account’s email address, performing a password reset to the new email address could allow an attacker to take over any account. |
2021-01-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2019-18642
MISC |
rocket.chat_technologies_corp — rocket.chat
|
An email address enumeration vulnerability exists in the password reset function of Rocket.Chat through 3.7.1. |
2021-01-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-28208
MISC
MLIST
MLIST
MISC
MISC |
rockwell_automation — rslinx_classic
|
A denial-of-service vulnerability exists in the Ethernet/IP server functionality of Rockwell Automation RSLinx Classic 2.57.00.14 CPR 9 SR 3. A specially crafted network request can lead to a denial of service. An attacker can send a sequence of malicious packets to trigger this vulnerability. |
2021-01-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-13573
MISC |
socket.io — engine.io
|
Engine.IO before 4.0.0 allows attackers to cause a denial of service (resource consumption) via a POST request to the long polling transport. |
2021-01-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-36048
MISC
MISC
MISC |
socket.io — socket.io-parser
|
socket.io-parser before 3.4.1 allows attackers to cause a denial of service (memory consumption) via a large packet because a concatenation approach is used. |
2021-01-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-36049
MISC
MISC
MISC |
softmaker — office_textmaker
|
An exploitable signed conversion vulnerability exists in the TextMaker document parsing functionality of SoftMaker Office 2021’s TextMaker application. A specially crafted document can cause the document parser to miscalculate a length used to allocate a buffer, later upon usage of this buffer the application will write outside its bounds resulting in a heap-based memory corruption. An attacker can entice the victim to open a document to trigger this vulnerability. |
2021-01-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-13545
MISC |
softmaker — office_textmaker
|
An exploitable sign extension vulnerability exists in the TextMaker document parsing functionality of SoftMaker Office 2021’s TextMaker application. A specially crafted document can cause the document parser to sign-extend a length used to terminate a loop, which can later result in the loop’s index being used to write outside the bounds of a heap buffer during the reading of file data. An attacker can entice the victim to open a document to trigger this vulnerability. |
2021-01-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-13544
MISC |
sonicwall — netextender
|
SonicWall NetExtender Windows client vulnerable to unquoted service path vulnerability, this allows a local attacker to gain elevated privileges in the host operating system. This vulnerability impact SonicWall NetExtender Windows client version 10.2.300 and earlier. |
2021-01-09 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-5147
CONFIRM |
sonicwall — sma100_apliiance
|
A vulnerability in SonicWall SMA100 appliance allow an authenticated management-user to perform OS command injection using HTTP POST parameters. This vulnerability affected SMA100 Appliance version 10.2.0.2-20sv and earlier. |
2021-01-09 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-5146
CONFIRM |
sourcecodester — restaurant_reservation_system
|
Restaurant Reservation System 1.0 suffers from an authenticated SQL injection vulnerability, which allows a remote, authenticated attacker to execute arbitrary SQL commands via the date parameter in includes/reservation.inc.php. |
2021-01-07 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-26773
MISC
MISC |
spring-boot-actuator-logview — spring-boot-actuator-logview
|
spring-boot-actuator-logview in a library that adds a simple logfile viewer as spring boot actuator endpoint. It is maven package “eu.hinsch:spring-boot-actuator-logview”. In spring-boot-actuator-logview before version 0.2.13 there is a directory traversal vulnerability. The nature of this library is to expose a log file directory via admin (spring boot actuator) HTTP endpoints. Both the filename to view and a base folder (relative to the logging folder root) can be specified via request parameters. While the filename parameter was checked to prevent directory traversal exploits (so that `filename=../somefile` would not work), the base folder parameter was not sufficiently checked, so that `filename=somefile&base=../` could access a file outside the logging base directory). The vulnerability has been patched in release 0.2.13. Any users of 0.2.12 should be able to update without any issues as there are no other changes in that release. There is no workaround to fix the vulnerability other than updating or removing the dependency. However, removing read access of the user the application is run with to any directory not required for running the application can limit the impact. Additionally, access to the logview endpoint can be limited by deploying the application behind a reverse proxy. |
2021-01-05 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-21234
MISC
MISC
CONFIRM
MISC |
tp-link — tl-wr840n_6_eu_devices
|
oal_ipt_addBridgeIsolationRules on TP-Link TL-WR840N 6_EU_0.9.1_4.16 devices allows OS command injection because a raw string entered from the web interface (an IP address field) is used directly for a call to the system library function (for iptables). NOTE: oal_ipt_addBridgeIsolationRules is not the only function that calls util_execSystem. |
2021-01-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-36178
MISC
MISC
MISC |
ts-process-promises — ts-process-promises
|
This affects all versions of package ts-process-promises. The injection point is located in line 45 in main entry of package in lib/process-promises.js. The vulnerability is demonstrated with the following PoC: |
2021-01-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-7784
MISC |
vela — vela
|
Vela is a Pipeline Automation (CI/CD) framework built on Linux container technology written in Golang. In Vela compiler before version 0.6.1 there is a vulnerability which allows exposure of server configuration. It impacts all users of Vela. An attacker can use Sprig’s `env` function to retrieve configuration information, see referenced GHSA for an example. This has been fixed in version 0.6.1. In addition to upgrading, it is recommended to rotate all secrets. |
2021-01-04 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-26294
MISC
CONFIRM
MISC |
veritas — aptare
|
An issue was discovered in Veritas APTARE 10.4 before 10.4P9 and 10.5 before 10.5P3. By default, on Windows systems, users can create directories under C:. A low privileged user can create a directory at the configuration file locations. When the Windows system restarts, a malicious OpenSSL engine could exploit arbitrary code execution as SYSTEM. This gives the attacker administrator access on the system, allowing the attacker (by default) to access all data, access all installed applications, etc. |
2021-01-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-36161
MISC |
veritas — backup_exec
|
An issue was discovered in the server in Veritas Backup Exec through 16.2, 20.6 before hotfix 298543, and 21.1 before hotfix 657517. On start-up, it loads the OpenSSL library from the Installation folder. This library in turn attempts to load the /usr/local/ssl/openssl.cnf configuration file, which may not exist. On Windows systems, this path could translate to <drive>:usrlocalsslopenssl.cnf. A low privileged user can create a :usrlocalsslopenssl.cnf configuration file to load a malicious OpenSSL engine, resulting in arbitrary code execution as SYSTEM when the service starts. This gives the attacker administrator access on the system, allowing the attacker (by default) to access all data, access all installed applications, etc. If the system is also an Active Directory domain controller, then this can affect the entire domain. |
2021-01-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-36167
CERT-VN
MISC |
| veritas — cloudpoint |
An issue was discovered in Veritas CloudPoint before 8.3.0.1+hotfix. The CloudPoint Windows Agent leverages OpenSSL. This OpenSSL library attempts to load the usrlocalsslopenssl.cnf configuration file, which does not exist. By default, on Windows systems users can create directories under <drive>:. A low privileged user can create a <drive>:usrlocalsslopenssl.cnf configuration file to load a malicious OpenSSL engine, which may result in arbitrary code execution. This would give the attacker administrator access on the system, allowing the attacker (by default) to access all data, access all installed applications, etc. |
2021-01-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-36162
MISC |
veritas — desktop_and_laptop_option
|
An issue was discovered in Veritas Desktop and Laptop Option (DLO) before 9.4. On start-up, it loads the OpenSSL library from /ReleaseX64/ssl. This library attempts to load the /ReleaseX64/ssl/openssl.cnf configuration file, which does not exist. By default, on Windows systems, users can create directories under C:. A low privileged user can create a C:/ReleaseX64/ssl/openssl.cnf configuration file to load a malicious OpenSSL engine, resulting in arbitrary code execution as SYSTEM when the service starts. This gives the attacker administrator access on the system, allowing the attacker (by default) to access all data, access all installed applications, etc. This impacts DLO server and client installations. |
2021-01-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-36165
MISC |
veritas — enterprise_vault
|
An issue was discovered in Veritas Enterprise Vault through 14.0. On start-up, it loads the OpenSSL library. The OpenSSL library then attempts to load the openssl.cnf configuration file (which does not exist) at the following locations in both the System drive (typically C:) and the product’s installation drive (typically not C:): Isodeetcsslopenssl.cnf (on SMTP Server) or usersslopenssl.cnf (on other affected components). By default, on Windows systems, users can create directories under C:. A low privileged user can create a openssl.cnf configuration file to load a malicious OpenSSL engine, resulting in arbitrary code execution as SYSTEM when the service starts. This gives the attacker administrator access on the system, allowing the attacker (by default) to access all data, access all installed applications, etc. This vulnerability only affects a server with MTP Server, SMTP Archiving IMAP Server, IMAP Archiving, Vault Cloud Adapter, NetApp File server, or File System Archiving for NetApp as File Server. |
2021-01-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-36164
MISC |
veritas — infoscale
|
An issue was discovered in Veritas InfoScale 7.x through 7.4.2 on Windows, Storage Foundation through 6.1 on Windows, Storage Foundation HA through 6.1 on Windows, and InfoScale Operations Manager (aka VIOM) Windows Management Server 7.x through 7.4.2. On start-up, it loads the OpenSSL library from usrlocalssl. This library attempts to load the usrlocalsslopenssl.cnf configuration file, which may not exist. On Windows systems, this path could translate to <drive>:usrlocalsslopenssl.cnf, where <drive> could be the default Windows installation drive such as C: or the drive where a Veritas product is installed. By default, on Windows systems, users can create directories under any top-level directory. A low privileged user can create a <drive>:usrlocalsslopenssl.cnf configuration file to load a malicious OpenSSL engine, resulting in arbitrary code execution as SYSTEM when the service starts. This gives the attacker administrator access on the system, allowing the attacker (by default) to access all data, access all installed applications, etc. |
2021-01-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-36166
MISC |
veritas — netbackup
|
An issue was discovered in Veritas NetBackup through 8.3.0.1 and OpsCenter through 8.3.0.1. Processes using OpenSSL attempt to load and execute libraries from paths that do not exist by default on the Windows operating system. By default, on Windows systems, users can create directories under the top level of any drive. If a low privileged user creates an affected path with a library that the Veritas product attempts to load, they can execute arbitrary code as SYSTEM or Administrator. This gives the attacker administrator access on the system, allowing the attacker (by default) to access all data, access all installed applications, etc. This vulnerability affects master servers, media servers, clients, and OpsCenter servers on the Windows platform. The system is vulnerable during an install or upgrade and post-install during normal operations. |
2021-01-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-36169
MISC |
veritas — netbackup_and_opscenter
|
An issue was discovered in Veritas NetBackup and OpsCenter through 8.3.0.1. NetBackup processes using Strawberry Perl attempt to load and execute libraries from paths that do not exist by default on the Windows operating system. By default, on Windows systems, users can create directories under C:. If a low privileged user on the Windows system creates an affected path with a library that NetBackup attempts to load, they can execute arbitrary code as SYSTEM or Administrator. This gives the attacker administrator access on the system, allowing the attacker (by default) to access all data, access all installed applications, etc. This affects NetBackup master servers, media servers, clients, and OpsCenter servers on the Windows platform. The system is vulnerable during an install or upgrade on all systems and post-install on Master, Media, and OpsCenter servers during normal operations. |
2021-01-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-36163
MISC |
veritas — resiliency_platform
|
An issue was discovered in Veritas Resiliency Platform 3.4 and 3.5. It leverages OpenSSL on Windows systems when using the Managed Host addon. On start-up, it loads the OpenSSL library. This library may attempt to load the openssl.cnf configuration file, which does not exist. By default, on Windows systems, users can create directories under C:. A low privileged user can create a C:usrlocalsslopenssl.cnf configuration file to load a malicious OpenSSL engine, resulting in arbitrary code execution as SYSTEM when the service starts. This gives the attacker administrator access on the system, allowing the attacker (by default) to access all data, access all installed applications, etc. |
2021-01-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-36168
MISC |
veritas — system_recovery
|
An issue was discovered in Veritas System Recovery before 21.2. On start-up, it loads the OpenSSL library from usrlocalssl. This library attempts to load the from usrlocalsslopenssl.cnf configuration file, which does not exist. By default, on Windows systems, users can create directories under C:. A low privileged user can create a C:usrlocalsslopenssl.cnf configuration file to load a malicious OpenSSL engine, resulting in arbitrary code execution as SYSTEM when the service starts. This gives the attacker administrator access on the system, allowing the attacker (by default) to access all data and installed applications, etc. If the system is also an Active Directory domain controller, then this can affect the entire domain. |
2021-01-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-36160
MISC |
videolan — vlc_media_player
|
A vulnerability in EbmlTypeDispatcher::send in VideoLAN VLC media player 3.0.11 allows attackers to trigger a heap-based buffer overflow via a crafted .mkv file. |
2021-01-08 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-26664
MISC
MISC
MISC |
wolfssl — wolfssl
|
RsaPad_PSS in wolfcrypt/src/rsa.c in wolfSSL before 4.6.0 has an out-of-bounds write for certain relationships between key size and digest size. |
2021-01-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-36177
MISC
MISC
MISC
MISC
MISC |
| wordpress — wordpress |
An issue was discovered in the Divi Builder plugin, Divi theme, and Divi Extra theme before 4.5.3 for WordPress. Authenticated attackers, with contributor-level or above capabilities, can upload arbitrary files, including .php files. This occurs because the check for file extensions is on the client side. |
2021-01-01 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-35945
MISC
MISC |
| wordpress — wordpress |
PHP Object injection vulnerabilities in the Team Showcase plugin before 1.22.16 for WordPress allow remote authenticated attackers to inject arbitrary PHP objects due to insecure unserialization of data supplied in a remotely hosted crafted payload in the source parameter via AJAX. The action must be set to team_import_xml_layouts. |
2021-01-01 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-35939
MISC |
| wordpress — wordpress |
PHP Object injection vulnerabilities in the Post Grid plugin before 2.0.73 for WordPress allow remote authenticated attackers to inject arbitrary PHP objects due to insecure unserialization of data supplied in a remotely hosted crafted payload in the source parameter via AJAX. The action must be set to post_grid_import_xml_layouts. |
2021-01-01 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-35938
MISC |
| wordpress — wordpress |
Stored Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) vulnerabilities in the Post Grid plugin before 2.0.73 for WordPress allow remote authenticated attackers to import layouts including JavaScript supplied via a remotely hosted crafted payload in the source parameter via AJAX. The action must be set to post_grid_import_xml_layouts. |
2021-01-01 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-35936
MISC |
| wordpress — wordpress |
The Advanced Access Manager plugin before 6.6.2 for WordPress allows privilege escalation on profile updates via the aam_user_roles POST parameter if Multiple Role support is enabled. (The mechanism for deciding whether a user was entitled to add a role did not work in various custom-role scenarios.) |
2021-01-01 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-35935
MISC |
| wordpress — wordpress |
A Reflected Authenticated Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) vulnerability in the Newsletter plugin before 6.8.2 for WordPress allows remote attackers to trick a victim into submitting a tnpc_render AJAX request containing either JavaScript in an options parameter, or a base64-encoded JSON string containing JavaScript in the encoded_options parameter. |
2021-01-01 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-35933
MISC |
| wordpress — wordpress |
Stored Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) vulnerabilities in the Team Showcase plugin before 1.22.16 for WordPress allow remote authenticated attackers to import layouts including JavaScript supplied via a remotely hosted crafted payload in the source parameter via AJAX. The action must be set to team_import_xml_layouts. |
2021-01-01 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-35937
MISC |
wordpress — wordpress
|
The iThemes Security (formerly Better WP Security) plugin before 7.7.0 for WordPress does not enforce a new-password requirement for an existing account until the second login occurs. |
2021-01-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-36176
MISC |
wordpress — wordpress
|
An issue was discovered in the Quiz and Survey Master plugin before 7.0.1 for WordPress. It made it possible for unauthenticated attackers to upload arbitrary files and achieve remote code execution. If a quiz question could be answered by uploading a file, only the Content-Type header was checked during the upload, and thus the attacker could use text/plain for a .php file. |
2021-01-01 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-35949
MISC
MISC |
wordpress — wordpress
|
The Advanced Access Manager plugin before 6.6.2 for WordPress displays the unfiltered user object (including all metadata) upon login via the REST API (aam/v1/authenticate or aam/v2/authenticate). This is a security problem if this object stores information that the user is not supposed to have (e.g., custom metadata added by a different plugin). |
2021-01-01 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-35934
MISC |
wordpress — wordpress
|
An issue was discovered in the XCloner Backup and Restore plugin before 4.2.153 for WordPress. It allows CSRF (via almost any endpoint). |
2021-01-01 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-35950
MISC
MISC |
wordpress — wordpress
|
Insecure Deserialization in the Newsletter plugin before 6.8.2 for WordPress allows authenticated remote attackers with minimal privileges (such as subscribers) to use the tpnc_render AJAX action to inject arbitrary PHP objects via the options[inline_edits] parameter. NOTE: exploitability depends on PHP objects that might be present with certain other plugins or themes. |
2021-01-01 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-35932
MISC |
wordpress — wordpress
|
The Elementor Website Builder plugin before 3.0.14 for WordPress does not properly restrict SVG uploads. |
2021-01-06 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-36171
MISC |
wordpress — wordpress
|
An issue was discovered in the XCloner Backup and Restore plugin before 4.2.13 for WordPress. It gave authenticated attackers the ability to modify arbitrary files, including PHP files. Doing so would allow an attacker to achieve remote code execution. The xcloner_restore.php write_file_action could overwrite wp-config.php, for example. Alternatively, an attacker could create an exploit chain to obtain a database dump. |
2021-01-01 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-35948
MISC
MISC |


Recent Comments