by Contributed | Dec 14, 2020 | Technology
This article is contributed. See the original author and article here.
This past year has been one of tremendous integration between Microsoft Teams and SharePoint. SharePoint provides rich content services that power files, lists and pages directly inside of Teams. Team members can easily highlight files, organize lists, and design pages – all as powerful tabs in Teams – due to the ease of benefitting more from the connected SharePoint team site.
We’re pleased to announce the following updates within Teams – all powered by SharePoint:
- Updated flow to add Microsoft Teams to your SharePoint team site
- Updated SharePoint tab app
- Updated SharePoint pages tab app
More screenshots, details, and links to documentation below…
Unifying Teams and SharePoint content collaboration
Updated flow to add Microsoft Teams to your SharePoint team site
[roadmap ID: 46990]
We’re pleased to announce that we are making it even easier to bring SharePoint content into Teams, in the same motion of adding Microsoft Teams to your team site, aka #teamify.
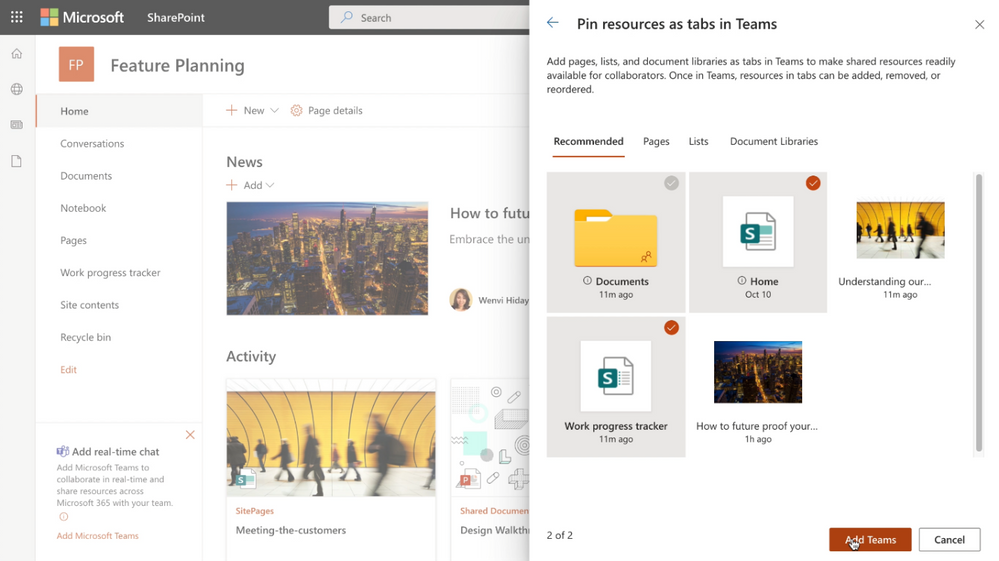
We’ll make it easy to choose lists, libraries and pages that you want to bring into Teams as tabs. When you’ve selected what you need, click the Add Team button to make it happen. By default, your team site home page will be selected, you can change it to suit your needs, and you can fully navigate primary document library from the Files tab – just follow the folder breadcrumbs.
 When adding Microsoft Teams to your SharePoint team site, you can select resources (pages, lists and document libraries) to be added as tabs in the general channel of the newly created Teams team.
When adding Microsoft Teams to your SharePoint team site, you can select resources (pages, lists and document libraries) to be added as tabs in the general channel of the newly created Teams team.
Once in Teams, it is easy to collaborate with the same group directly around the SharePoint content you just brought in. Pick the same list or page (even the team site home page) you were just working on and engage your colleagues with chat side-by-side the list directly in Teams.
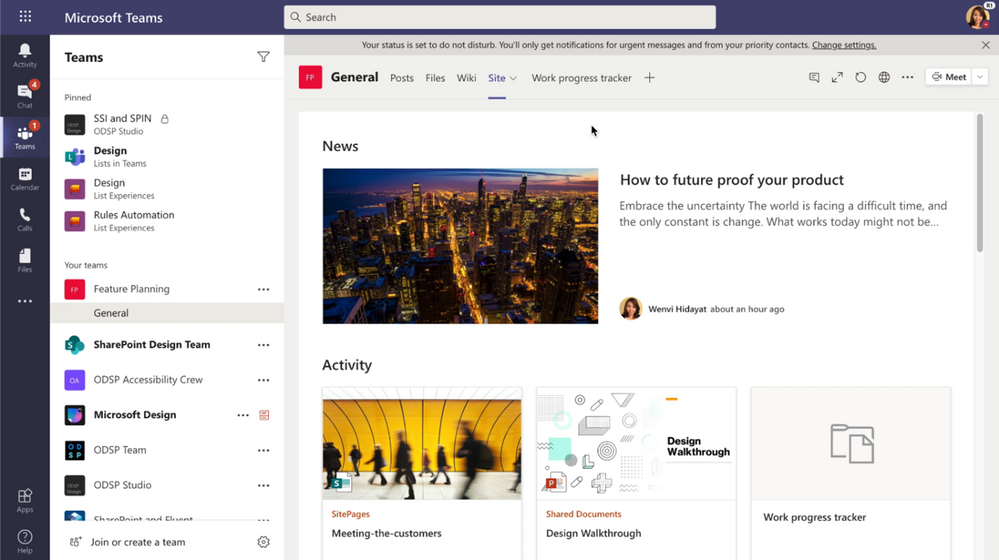
With your content available in Teams, we make it even easier to collaborate and get work done.
Learn more about adding Microsoft Teams to your SharePoint team site.
Updated SharePoint tab app
[roadmap ID: 68860]
We have improved the SharePoint tab experience when adding pages, lists or document libraries to a channel in Teams. It’s easy to select multiple content types from the connected team site, or by providing a link to any other page, list or library to which the user has access.
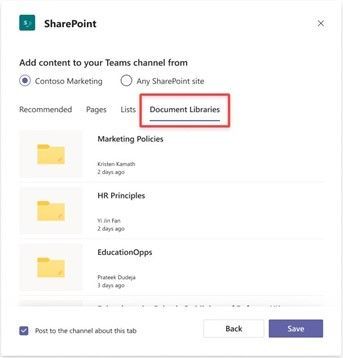 The updated SharePoint tab experience when adding pages, lists or document libraries to a channel in Teams.
The updated SharePoint tab experience when adding pages, lists or document libraries to a channel in Teams.
We have also added a new “Recommended” section in the SharePoint tab to help user easily find the most relevant content from their site to pin in their channels. It’s a one-stop shop for adding various types of existing content that began in SharePoint.
Learn more how to add a SharePoint page, list, or document library as a tab in Teams.
Updated SharePoint pages app
[roadmap ID: 60614]
Using SharePoint pages is a great way to consolidate and share content in the right context using images, Excel, Word and PowerPoint documents, videos, links, Twitter feeds and more – all on the same page. And now you can more easily your pages as tabs in Microsoft Teams.
The updated experience makes it easier to choose pages from the connected SharePoint team site and you can also add a page from any SharePoint site link and then paste the URL of the page, or news post, that you want to add as a tab.
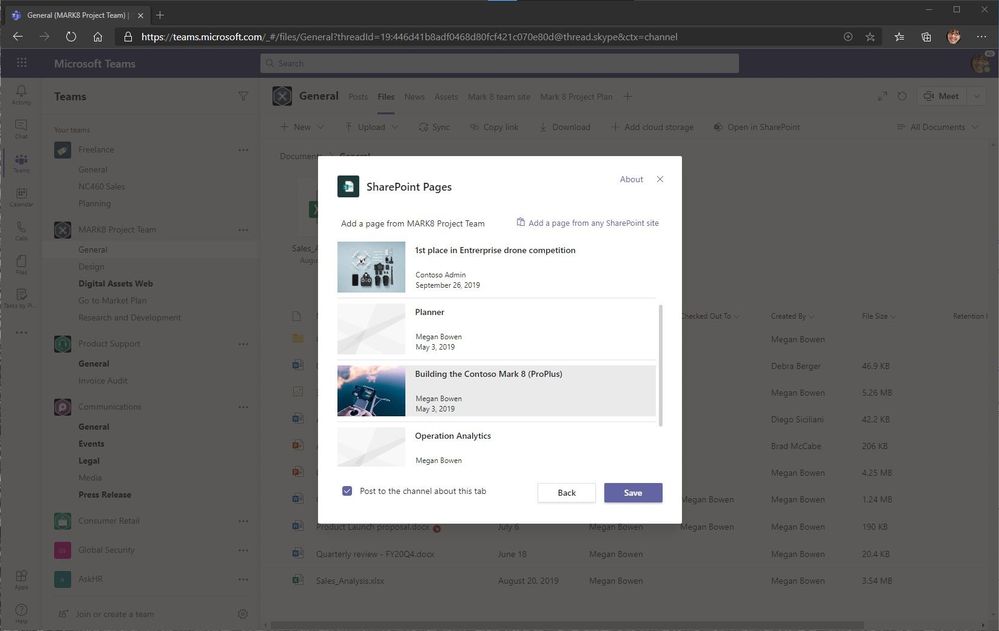 Choose pages from the connected SharePoint team site or add a page from any SharePoint site (via URL).
Choose pages from the connected SharePoint team site or add a page from any SharePoint site (via URL).
SharePoint will validate the SharePoint URL and if you have access to the page. Permissions of the page itself will not change, and if users on the team do not have permission to the tabbed page, they will be shown a page to request access.
Note: When adding content as tabs in Teams, you may notice a few SharePoint-powered apps – here as an FYI and clarity (in quotes is the text that shows in-app). This is an area of investment to ensure you can easily connect content stored in SharePoint in Teams channels:
- “SharePoint”– add existing content from the connected team site or any SharePoint site – including: Recommended content, Pages, Lists and Document libraries.
- “SharePoint Pages”– add a SharePoint page from the connected team site or from any SharePoint site using a URL. (this is the new app mentioned above)
- Microsoft “Lists”– Create a new list for your team or add an existing list from any existing SharePoint site. (more about working with the Lists app in Microsoft Teams)
- “SharePoint lists”– you may see this app if you don’t yet have the new Lists app. It can be used to bring existing lists as a tab in Teams – but not to create a new list.
- SharePoint “Document Library”– add a SharePoint document library from relevant sites or use a SharePoint document library URL to a site or folder.
Learn more about adding SharePoint pages as tabs in Microsoft Teams, plus further info on how to use built-in and custom tabs in Microsoft Teams.
In closing …
When people work together and get things done, there is less confusion between team members and the content they create. This is the design goal behind Microsoft Teams – the hub for teamwork – and the reason why SharePoint is deeply integrated to provide great content experiences and services within the same user interface. And, it’s all backed by world-class security and compliance to meet the needs of every team across your organization.
At Microsoft, our mission is to empower every person and organization on the planet to achieve more. And when you do this together – as a team – it’s teamwork that moves things forward.
Thanks, @Microsoft_Teams_team
 Microsoft Teams plus SharePoint = better together.
Microsoft Teams plus SharePoint = better together.
by Scott Muniz | Dec 14, 2020 | Security, Technology
This article is contributed. See the original author and article here.
| apache — apisix |
In Apache APISIX, the user enabled the Admin API and deleted the Admin API access IP restriction rules. Eventually, the default token is allowed to access APISIX management data. This affects versions 1.2, 1.3, 1.4, 1.5. |
2020-12-07 |
4 |
CVE-2020-13945
CONFIRM |
| apple — icloud |
A use after free issue was addressed with improved memory management. This issue is fixed in watchOS 7.0, iOS 14.0 and iPadOS 14.0, iTunes for Windows 12.10.9, iCloud for Windows 11.5, tvOS 14.0, Safari 14.0. Processing maliciously crafted web content may lead to arbitrary code execution. |
2020-12-08 |
6.8 |
CVE-2020-9947
MISC
MISC
MISC
MISC
MISC
MISC |
| apple — icloud |
A use after free issue was addressed with improved memory management. This issue is fixed in macOS Big Sur 11.0.1, watchOS 7.1, iOS 14.2 and iPadOS 14.2, iCloud for Windows 11.5, Safari 14.0.1, tvOS 14.2, iTunes 12.11 for Windows. Processing maliciously crafted web content may lead to arbitrary code execution. |
2020-12-08 |
6.8 |
CVE-2020-27918
MISC
MISC
MISC
MISC
MISC
MISC
MISC |
| apple — icloud |
This issue was addressed with improved checks. This issue is fixed in macOS Big Sur 11.0.1, watchOS 7.0, iOS 14.0 and iPadOS 14.0, iCloud for Windows 7.21, tvOS 14.0. A remote attacker may be able to cause a denial of service. |
2020-12-08 |
5 |
CVE-2020-9991
MISC
MISC
MISC
MISC
MISC |
| apple — ipad_os |
An issue existed within the path validation logic for symlinks. This issue was addressed with improved path sanitization. This issue is fixed in macOS Big Sur 11.0.1, iOS 14.2 and iPadOS 14.2, tvOS 14.2, watchOS 7.1. A local attacker may be able to elevate their privileges. |
2020-12-08 |
4.6 |
CVE-2020-10003
MISC
MISC
MISC
MISC |
| apple — ipad_os |
An out-of-bounds write was addressed with improved input validation. This issue is fixed in macOS Big Sur 11.0.1, iOS 14.2 and iPadOS 14.2, tvOS 14.2, watchOS 7.1. Processing a maliciously crafted audio file may lead to arbitrary code execution. |
2020-12-08 |
6.8 |
CVE-2020-10017
MISC
MISC
MISC
MISC |
| apple — ipad_os |
A validation issue existed in the entitlement verification. This issue was addressed with improved validation of the process entitlement. This issue is fixed in macOS Big Sur 11.0.1, iOS 14.0 and iPadOS 14.0. A malicious application may be able to determine a user’s open tabs in Safari. |
2020-12-08 |
4.3 |
CVE-2020-9977
MISC
MISC |
| apple — ipad_os |
A logic issue was addressed with improved state management. This issue is fixed in macOS Big Sur 11.0.1, iOS 14.2 and iPadOS 14.2. Opening a maliciously crafted file may lead to unexpected application termination or arbitrary code execution. |
2020-12-08 |
6.8 |
CVE-2020-10004
MISC
MISC |
| apple — ipad_os |
An out-of-bounds read was addressed with improved input validation. This issue is fixed in macOS Big Sur 11.0.1, watchOS 7.0, tvOS 14.0, iOS 14.0 and iPadOS 14.0. An application may be able to execute arbitrary code with kernel privileges. |
2020-12-08 |
6.8 |
CVE-2020-9966
MISC
MISC
MISC
MISC |
| apple — ipad_os |
A use after free issue was addressed with improved memory management. This issue is fixed in macOS Big Sur 11.0.1, iOS 14.0 and iPadOS 14.0. A malicious application may be able to elevate privileges. |
2020-12-08 |
6.8 |
CVE-2020-9996
MISC
MISC |
| apple — ipad_os |
A logic issue was addressed with improved state management. This issue is fixed in macOS Big Sur 11.0.1, iOS 14.2 and iPadOS 14.2, tvOS 14.2, watchOS 7.1. A malicious application may be able to determine kernel memory layout. |
2020-12-08 |
4.3 |
CVE-2020-9974
MISC
MISC
MISC
MISC |
| apple — ipad_os |
A buffer overflow issue was addressed with improved memory handling. This issue is fixed in iOS 14.0 and iPadOS 14.0. Processing a maliciously crafted USD file may lead to unexpected application termination or arbitrary code execution. |
2020-12-08 |
6.8 |
CVE-2020-9972
MISC |
| apple — ipados |
A memory corruption issue was addressed with improved input validation. This issue is fixed in macOS Big Sur 11.0.1, watchOS 7.1, iOS 12.4.9, watchOS 6.2.9, Security Update 2020-006 High Sierra, Security Update 2020-006 Mojave, iOS 14.2 and iPadOS 14.2, watchOS 5.3.9, macOS Catalina 10.15.7 Supplemental Update, macOS Catalina 10.15.7 Update. Processing a maliciously crafted font may lead to arbitrary code execution. |
2020-12-08 |
6.8 |
CVE-2020-27930
MISC
MISC
MISC
MISC
MISC
MISC
MISC
MISC |
| apple — ipados |
A path handling issue was addressed with improved validation. This issue is fixed in macOS Big Sur 11.0.1, iOS 14.2 and iPadOS 14.2, tvOS 14.2, watchOS 7.1. A local attacker may be able to elevate their privileges. |
2020-12-08 |
4.6 |
CVE-2020-10010
MISC
MISC
MISC
MISC |
| apple — ipados |
A buffer overflow issue was addressed with improved memory handling. This issue is fixed in watchOS 7.0, tvOS 14.0, macOS Catalina 10.15.7, Security Update 2020-005 High Sierra, Security Update 2020-005 Mojave, iOS 14.0 and iPadOS 14.0. Playing a malicious audio file may lead to arbitrary code execution. |
2020-12-08 |
6.8 |
CVE-2020-9954
MISC
MISC
MISC
MISC |
| apple — ipados |
An out-of-bounds write issue was addressed with improved bounds checking. This issue is fixed in macOS Big Sur 11.0.1, iOS 14.2 and iPadOS 14.2, tvOS 14.2, watchOS 7.1. Processing a maliciously crafted font file may lead to arbitrary code execution. |
2020-12-08 |
6.8 |
CVE-2020-27927
MISC
MISC
MISC
MISC |
| apple — ipados |
An out-of-bounds read was addressed with improved bounds checking. This issue is fixed in iOS 14.2 and iPadOS 14.2, macOS Catalina 10.15.7, Security Update 2020-005 High Sierra, Security Update 2020-005 Mojave. Processing a maliciously crafted USD file may lead to unexpected application termination or arbitrary code execution. |
2020-12-08 |
6.8 |
CVE-2020-10011
MISC
MISC |
| apple — ipados |
The issue was addressed with improved handling of icon caches. This issue is fixed in macOS Big Sur 11.0.1, iOS 14.0 and iPadOS 14.0. A malicious app may be able to determine the existence of files on the computer. |
2020-12-08 |
4.3 |
CVE-2020-9963
MISC
MISC |
| apple — ipados |
An out-of-bounds read was addressed with improved bounds checking. This issue is fixed in macOS Big Sur 11.0.1, watchOS 7.0, tvOS 14.0, iOS 14.0 and iPadOS 14.0. An application may be able to read restricted memory. |
2020-12-08 |
4.3 |
CVE-2020-9944
MISC
MISC
MISC
MISC |
| apple — ipados |
An out-of-bounds read was addressed with improved bounds checking. This issue is fixed in macOS Big Sur 11.0.1, watchOS 7.0, tvOS 14.0, iOS 14.0 and iPadOS 14.0. A malicious application may be able to read restricted memory. |
2020-12-08 |
4.3 |
CVE-2020-9943
MISC
MISC
MISC
MISC |
| apple — iphone_os |
A logic issue existed in the handling of Group FaceTime calls. The issue was addressed with improved state management. This issue is fixed in iOS 12.4.9. A user may send video in Group FaceTime calls without knowing that they have done so. |
2020-12-08 |
4.3 |
CVE-2020-27929
MISC |
| apple — itunes |
An information disclosure issue was addressed with improved state management. This issue is fixed in macOS Big Sur 11.0.1, watchOS 7.0, iOS 14.0 and iPadOS 14.0, iTunes for Windows 12.10.9, iCloud for Windows 11.5, tvOS 14.0. A remote attacker may be able to leak memory. |
2020-12-08 |
4.3 |
CVE-2020-9849
MISC
MISC
MISC
MISC
MISC
MISC |
| apple — itunes |
A memory corruption issue was addressed with improved state management. This issue is fixed in macOS Big Sur 11.0.1, iTunes for Windows 12.10.9. Processing a maliciously crafted text file may lead to arbitrary code execution. |
2020-12-08 |
6.8 |
CVE-2020-9999
MISC
MISC |
| apple — itunes |
An information disclosure issue existed in the transition of program state. This issue was addressed with improved state handling. This issue is fixed in iTunes 12.11 for Windows. A malicious application may be able to access local users Apple IDs. |
2020-12-08 |
4.3 |
CVE-2020-27895
MISC |
| apple — mac_os |
The issue was addressed with additional user controls. This issue is fixed in macOS Big Sur 11.0.1. Users may be unable to remove metadata indicating where files were downloaded from. |
2020-12-08 |
4.3 |
CVE-2020-27894
MISC |
| apple — mac_os_x |
A logic issue was addressed with improved state management. This issue is fixed in macOS Catalina 10.15.6, Security Update 2020-004 Mojave, Security Update 2020-004 High Sierra. Processing a maliciously crafted email may lead to writing arbitrary files. |
2020-12-08 |
4.3 |
CVE-2020-9922
MISC |
| apple — mac_os_x |
A logic issue was addressed with improved state management. This issue is fixed in macOS Big Sur 11.0.1. A sandboxed process may be able to circumvent sandbox restrictions. |
2020-12-08 |
4.3 |
CVE-2020-10009
MISC |
| apple — mac_os_x |
A path handling issue was addressed with improved validation. This issue is fixed in macOS Big Sur 11.0.1. A remote attacker may be able to modify the file system. |
2020-12-08 |
4.3 |
CVE-2020-27896
MISC |
| apple — mac_os_x |
This issue was addressed with improved entitlements. This issue is fixed in macOS Big Sur 11.0.1. A malicious application may be able to access restricted files. |
2020-12-08 |
4.3 |
CVE-2020-10006
MISC |
| apple — macos |
A parsing issue in the handling of directory paths was addressed with improved path validation. This issue is fixed in macOS Big Sur 11.0.1. A malicious application may be able to break out of its sandbox. |
2020-12-08 |
4.3 |
CVE-2020-10014
MISC |
| apple — macos |
An issue existed in the handling of snapshots. The issue was resolved with improved permissions logic. This issue is fixed in macOS Big Sur 11.0.1. A malicious application may be able to preview files it does not have access to. |
2020-12-08 |
4.3 |
CVE-2020-27900
MISC |
| apple — macos |
An access issue was addressed with improved access restrictions. This issue is fixed in macOS Big Sur 11.0.1. Processing a maliciously crafted document may lead to a cross site scripting attack. |
2020-12-08 |
4.3 |
CVE-2020-10012
MISC |
| apple — macos |
A denial of service issue was addressed with improved state handling. This issue is fixed in macOS Big Sur 11.0.1. An attacker may be able to bypass Managed Frame Protection. |
2020-12-08 |
4.3 |
CVE-2020-27898
MISC |
| apple — safari |
The issue was addressed with improved UI handling. This issue is fixed in watchOS 7.0, Safari 14.0, iOS 14.0 and iPadOS 14.0. Visiting a malicious website may lead to address bar spoofing. |
2020-12-08 |
4.3 |
CVE-2020-9993
MISC
MISC
MISC |
| apple — safari |
An inconsistent user interface issue was addressed with improved state management. This issue is fixed in macOS Big Sur 11.0.1, Safari 13.1.2. Visiting a malicious website may lead to address bar spoofing. |
2020-12-08 |
4.3 |
CVE-2020-9942
MISC
MISC |
| apple — safari |
A spoofing issue existed in the handling of URLs. This issue was addressed with improved input validation. This issue is fixed in macOS Big Sur 11.0.1, Safari 14.0.1. Visiting a malicious website may lead to address bar spoofing. |
2020-12-08 |
4.3 |
CVE-2020-9945
MISC
MISC |
| apple — safari |
An inconsistent user interface issue was addressed with improved state management. This issue is fixed in Safari 14.0. Visiting a malicious website may lead to address bar spoofing. |
2020-12-08 |
4.3 |
CVE-2020-9987
MISC |
| apple — safari |
A use after free issue was addressed with improved memory management. This issue is fixed in watchOS 7.0, tvOS 14.0, Safari 14.0, iOS 14.0 and iPadOS 14.0. Processing maliciously crafted web content may lead to arbitrary code execution. |
2020-12-08 |
6.8 |
CVE-2020-9950
MISC
MISC
MISC
MISC |
| asus — rt-ac88u_firmware |
An information disclosure vulnerability exists in RT-AC88U Download Master before 3.1.0.108. A direct access to /downloadmaster/dm_apply.cgi?action_mode=initial&download_type=General&special_cgi=get_language makes it possible to reach “unknown functionality” in a “known to be easy” manner via an unspecified “public exploit.” |
2020-12-09 |
5 |
CVE-2020-29656
MISC |
| asus — rt-ac88u_firmware |
An injection vulnerability exists in RT-AC88U Download Master before 3.1.0.108. Accessing Main_Login.asp?flag=1&productname=FOOBAR&url=/downloadmaster/task.asp will redirect to the login site, which will show the value of the parameter productname within the title. An attacker might be able to influence the appearance of the login page, aka text injection. |
2020-12-09 |
5 |
CVE-2020-29655
MISC |
| aswf — openexr |
A heap-based buffer overflow vulnerability exists in Academy Software Foundation OpenEXR 2.3.0 in chunkOffsetReconstruction in ImfMultiPartInputFile.cpp that can cause a denial of service via a crafted EXR file. |
2020-12-09 |
4.3 |
CVE-2020-16587
MISC
MISC |
| aswf — openexr |
A Null Pointer Deference issue exists in Academy Software Foundation OpenEXR 2.3.0 in generatePreview in makePreview.cpp that can cause a denial of service via a crafted EXR file. |
2020-12-09 |
4.3 |
CVE-2020-16588
MISC
MISC |
| aswf — openexr |
A head-based buffer overflow exists in Academy Software Foundation OpenEXR 2.3.0 in writeTileData in ImfTiledOutputFile.cpp that can cause a denial of service via a crafted EXR file. |
2020-12-09 |
4.3 |
CVE-2020-16589
MISC
MISC |
| bookstackapp — bookstack |
BookStack is a platform for storing and organising information and documentation. In BookStack before version 0.30.5, a user with permissions to edit a page could set certain image URL’s to manipulate functionality in the exporting system, which would allow them to make server side requests and/or have access to a wider scope of files within the BookStack file storage locations. The issue was addressed in BookStack v0.30.5. As a workaround, page edit permissions could be limited to only those that are trusted until you can upgrade. |
2020-12-09 |
5.5 |
CVE-2020-26260
MISC
MISC
CONFIRM |
| boom-core — risvc-boom |
An issue was discovered in SonicBOOM riscv-boom 3.0.0. For LR, it does not avoid acquiring a reservation in the case where a load translates successfully but still generates an exception. |
2020-12-04 |
4.3 |
CVE-2020-29561
MISC |
| divebook_project — divebook |
The DiveBook plugin 1.1.4 for WordPress is prone to unauthenticated XSS within the filter function (via an arbitrary parameter). |
2020-12-08 |
4.3 |
CVE-2020-14206
MISC
MISC |
| divebook_project — divebook |
The DiveBook plugin 1.1.4 for WordPress is prone to improper access control in the Log Dive form because it fails to perform authorization checks. An attacker may leverage this issue to manipulate the integrity of dive logs. |
2020-12-08 |
5 |
CVE-2020-14205
MISC
MISC |
| divebook_project — divebook |
The DiveBook plugin 1.1.4 for WordPress was prone to a SQL injection within divelog.php, allowing unauthenticated users to retrieve data from the database via the divelog.php filter_diver parameter. |
2020-12-08 |
5 |
CVE-2020-14207
MISC
MISC |
| getkirby — kirby |
Kirby is a CMS. In Kirby CMS (getkirby/cms) before version 3.4.5, and Kirby Panel before version 2.5.14 , an editor with full access to the Kirby Panel can upload a PHP .phar file and execute it on the server. This vulnerability is critical if you might have potential attackers in your group of authenticated Panel users, as they can gain access to the server with such a Phar file. Visitors without Panel access *cannot* use this attack vector. The problem has been patched in Kirby 2.5.14 and Kirby 3.4.5. Please update to one of these or a later version to fix the vulnerability. Note: Kirby 2 reaches end of life on December 31, 2020. We therefore recommend to upgrade your Kirby 2 sites to Kirby 3. If you cannot upgrade, we still recommend to update to Kirby 2.5.14. |
2020-12-08 |
6.5 |
CVE-2020-26255
MISC
MISC
CONFIRM
MISC
MISC
MISC |
| getkirby — kirby |
Kirby is a CMS. In Kirby CMS (getkirby/cms) before version 3.3.6, and Kirby Panel before version 2.5.14 there is a vulnerability in which the admin panel may be accessed if hosted on a .dev domain. In order to protect new installations on public servers that don’t have an admin account for the Panel yet, we block account registration there by default. This is a security feature, which we implemented years ago in Kirby 2. It helps to avoid that you forget registering your first admin account on a public server. In this case – without our security block – someone else might theoretically be able to find your site, find out it’s running on Kirby, find the Panel and then register the account first. It’s an unlikely situation, but it’s still a certain risk. To be able to register the first Panel account on a public server, you have to enforce the installer via a config setting. This helps to push all users to the best practice of registering your first Panel account on your local machine and upload it together with the rest of the site. This installation block implementation in Kirby versions before 3.3.6 still assumed that .dev domains are local domains, which is no longer true. In the meantime, those domains became publicly available. This means that our installation block is no longer working as expected if you use a .dev domain for your Kirby site. Additionally the local installation check may also fail if your site is behind a reverse proxy. You are only affected if you use a .dev domain or your site is behind a reverse proxy and you have not yet registered your first Panel account on the public server and someone finds your site and tries to login at `yourdomain.dev/panel` before you register your first account. You are not affected if you have already created one or multiple Panel accounts (no matter if on a .dev domain or behind a reverse proxy). The problem has been patched in Kirby 3.3.6. Please upgrade to this or a later version to fix the vulnerability. |
2020-12-08 |
4.3 |
CVE-2020-26253
MISC
CONFIRM
MISC
MISC
MISC |
| gnu — binutils |
A use after free issue exists in the Binary File Descriptor (BFD) library (aka libbfd) in GNU Binutils 2.34 in bfd_hash_lookup, as demonstrated in nm-new, that can cause a denial of service via a crafted file. |
2020-12-09 |
4.3 |
CVE-2020-16592
MISC
MISC |
| gnu — binutils |
A Null Pointer Dereference vulnerability exists in the Binary File Descriptor (BFD) library (aka libbfd), as distributed in GNU Binutils 2.34, in scan_unit_for_symbols, as demonstrated in addr2line, that can cause a denial of service via a crafted file. |
2020-12-09 |
4.3 |
CVE-2020-16593
MISC
MISC |
| gnu — binutils |
A Null Pointer Dereference vulnerability exists in the Binary File Descriptor (BFD) library (aka libbfd), as distributed in GNU Binutils 2.34, in debug_get_real_type, as demonstrated in objdump, that can cause a denial of service via a crafted file. |
2020-12-09 |
4.3 |
CVE-2020-16598
MISC
MISC |
| gnu — binutils |
A Null Pointer Dereference vulnerability exists in the Binary File Descriptor (BFD) library (aka libbfd), as distributed in GNU Binutils 2.34, in _bfd_elf_get_symbol_version_string, as demonstrated in nm-new, that can cause a denial of service via a crafted file. |
2020-12-09 |
4.3 |
CVE-2020-16599
MISC
MISC |
| gnu — binutils |
A double free vulnerability exists in the Binary File Descriptor (BFD) (aka libbrd) in GNU Binutils 2.34 in the process_symbol_table, as demonstrated in readelf, via a crafted file. |
2020-12-09 |
4.3 |
CVE-2020-16590
MISC
MISC |
| gnu — binutils |
A Denial of Service vulnerability exists in the Binary File Descriptor (BFD) in GNU Binutils 2.34 due to an invalid read in process_symbol_table, as demonstrated in readeif. |
2020-12-09 |
4.3 |
CVE-2020-16591
MISC
MISC |
| gnu — glibc |
sysdeps/i386/ldbl2mpn.c in the GNU C Library (aka glibc or libc6) before 2.23 on x86 targets has a stack-based buffer overflow if the input to any of the printf family of functions is an 80-bit long double with a non-canonical bit pattern, as seen when passing a x00x04x00x00x00x00x00x00x00x04 value to sprintf. |
2020-12-06 |
5 |
CVE-2020-29573
MISC
MISC |
| gnu — glibc |
The iconv function in the GNU C Library (aka glibc or libc6) 2.30 to 2.32, when converting UCS4 text containing an irreversible character, fails an assertion in the code path and aborts the program, potentially resulting in a denial of service. |
2020-12-04 |
5 |
CVE-2020-29562
MISC |
| huawei — honor_20_pro_firmware |
There is a buffer overflow vulnerability in several Huawei products. The system does not sufficiently validate certain configuration parameter which is passed from user that would cause buffer overflow. The attacker should trick the user into installing and running a malicious application with a high privilege, successful exploit may cause code execution. Affected product include Huawei HONOR 20 PRO, Mate 20, Mate 20 Pro, Mate 20 X, P30, P30 Pro, Hima-L29C, Laya-AL00EP, Princeton-AL10B, Tony-AL00B, Yale-L61A, Yale-TL00B and YaleP-AL10B. |
2020-12-07 |
6.8 |
CVE-2020-9247
MISC |
| ibm — sterling_b2b_integrator |
IBM Sterling B2B Integrator Standard Edition 5.2.0.0 through 5.2.6.5 and 6.0.0.0 through 6.0.3.1 discloses sensitive information to an authenticated user from the dashboard UI which could be used in further attacks against the system. IBM X-Force ID: 172753. |
2020-12-10 |
4 |
CVE-2019-4738
XF
CONFIRM |
| imagemagick — imagemagick |
A flaw was found in ImageMagick in MagickCore/gem-private.h. An attacker who submits a crafted file that is processed by ImageMagick could trigger undefined behavior in the form of values outside the range of type `unsigned char` or division by zero. This would most likely lead to an impact to application availability, but could potentially cause other problems related to undefined behavior. This flaw affects ImageMagick versions prior to 7.0.9-0. |
2020-12-04 |
4.3 |
CVE-2020-27773
MISC |
| imagemagick — imagemagick |
In the CropImage() and CropImageToTiles() routines of MagickCore/transform.c, rounding calculations performed on unconstrained pixel offsets was causing undefined behavior in the form of integer overflow and out-of-range values as reported by UndefinedBehaviorSanitizer. Such issues could cause a negative impact to application availability or other problems related to undefined behavior, in cases where ImageMagick processes untrusted input data. The upstream patch introduces functionality to constrain the pixel offsets and prevent these issues. This flaw affects ImageMagick versions prior to 7.0.9-0. |
2020-12-08 |
4.3 |
CVE-2020-25675
MISC |
| imagemagick — imagemagick |
Due to a missing check for 0 value of `replace_extent`, it is possible for offset `p` to overflow in SubstituteString(), causing potential impact to application availability. This could be triggered by a crafted input file that is processed by ImageMagick. This flaw affects ImageMagick versions prior to 7.0.8-68. |
2020-12-04 |
4.3 |
CVE-2020-27770
MISC |
| imagemagick — imagemagick |
In CatromWeights(), MeshInterpolate(), InterpolatePixelChannel(), InterpolatePixelChannels(), and InterpolatePixelInfo(), which are all functions in /MagickCore/pixel.c, there were multiple unconstrained pixel offset calculations which were being used with the floor() function. These calculations produced undefined behavior in the form of out-of-range and integer overflows, as identified by UndefinedBehaviorSanitizer. These instances of undefined behavior could be triggered by an attacker who is able to supply a crafted input file to be processed by ImageMagick. These issues could impact application availability or potentially cause other problems related to undefined behavior. This flaw affects ImageMagick versions prior to 7.0.9-0. |
2020-12-08 |
4.3 |
CVE-2020-25676
MISC |
| imagemagick — imagemagick |
A flaw was found in ImageMagick in MagickCore/quantum.h. An attacker who submits a crafted file that is processed by ImageMagick could trigger undefined behavior in the form of values outside the range of types `float` and `unsigned char`. This would most likely lead to an impact to application availability, but could potentially cause other problems related to undefined behavior. This flaw affects ImageMagick versions prior to 7.0.9-0. |
2020-12-04 |
4.3 |
CVE-2020-27767
MISC |
| imagemagick — imagemagick |
A flaw was found in ImageMagick in MagickCore/segment.c. An attacker who submits a crafted file that is processed by ImageMagick could trigger undefined behavior in the form of math division by zero. This would most likely lead to an impact to application availability, but could potentially cause other problems related to undefined behavior. This flaw affects ImageMagick versions prior to 7.0.9-0. |
2020-12-04 |
4.3 |
CVE-2020-27765
MISC |
| imagemagick — imagemagick |
A flaw was found in ImageMagick in coders/txt.c. An attacker who submits a crafted file that is processed by ImageMagick could trigger undefined behavior in the form of values outside the range of type `unsigned long long`. This would most likely lead to an impact to application availability, but could potentially cause other problems related to undefined behavior. This flaw affects ImageMagick versions prior to 7.0.8-68. |
2020-12-08 |
4.3 |
CVE-2020-27758
MISC |
| imagemagick — imagemagick |
WriteOnePNGImage() from coders/png.c (the PNG coder) has a for loop with an improper exit condition that can allow an out-of-bounds READ via heap-buffer-overflow. This occurs because it is possible for the colormap to have less than 256 valid values but the loop condition will loop 256 times, attempting to pass invalid colormap data to the event logger. The patch replaces the hardcoded 256 value with a call to MagickMin() to ensure the proper value is used. This could impact application availability when a specially crafted input file is processed by ImageMagick. This flaw affects ImageMagick versions prior to 7.0.8-68. |
2020-12-08 |
4.3 |
CVE-2020-25674
MISC |
| imagemagick — imagemagick |
A flaw was found in ImageMagick in MagickCore/colorspace-private.h and MagickCore/quantum.h. An attacker who submits a crafted file that is processed by ImageMagick could trigger undefined behavior in the form of values outside the range of type `unsigned char` and math division by zero. This would most likely lead to an impact to application availability, but could potentially cause other problems related to undefined behavior. This flaw affects ImageMagick versions prior to 7.0.8-68. |
2020-12-08 |
4.3 |
CVE-2020-27750
MISC |
| imagemagick — imagemagick |
A flaw was found in ImageMagick in MagickCore/quantum-export.c. An attacker who submits a crafted file that is processed by ImageMagick could trigger undefined behavior in the form of values outside the range of type `unsigned long long` as well as a shift exponent that is too large for 64-bit type. This would most likely lead to an impact to application availability, but could potentially cause other problems related to undefined behavior. This flaw affects ImageMagick versions prior to 7.0.9-0. |
2020-12-08 |
4.3 |
CVE-2020-27751
MISC |
| imagemagick — imagemagick |
There are several memory leaks in the MIFF coder in /coders/miff.c due to improper image depth values, which can be triggered by a specially crafted input file. These leaks could potentially lead to an impact to application availability or cause a denial of service. It was originally reported that the issues were in `AcquireMagickMemory()` because that is where LeakSanitizer detected the leaks, but the patch resolves issues in the MIFF coder, which incorrectly handles data being passed to `AcquireMagickMemory()`. This flaw affects ImageMagick versions prior to 7.0.9-0. |
2020-12-08 |
4.3 |
CVE-2020-27753
MISC |
| imagemagick — imagemagick |
In IntensityCompare() of /magick/quantize.c, there are calls to PixelPacketIntensity() which could return overflowed values to the caller when ImageMagick processes a crafted input file. To mitigate this, the patch introduces and uses the ConstrainPixelIntensity() function, which forces the pixel intensities to be within the proper bounds in the event of an overflow. This flaw affects ImageMagick versions prior to 6.9.10-69 and 7.0.8-69. |
2020-12-08 |
4.3 |
CVE-2020-27754
MISC |
| imagemagick — imagemagick |
in SetImageExtent() of /MagickCore/image.c, an incorrect image depth size can cause a memory leak because the code which checks for the proper image depth size does not reset the size in the event there is an invalid size. The patch resets the depth to a proper size before throwing an exception. The memory leak can be triggered by a crafted input file that is processed by ImageMagick and could cause an impact to application reliability, such as denial of service. This flaw affects ImageMagick versions prior to 7.0.9-0. |
2020-12-08 |
4.3 |
CVE-2020-27755
MISC |
| imagemagick — imagemagick |
In ParseMetaGeometry() of MagickCore/geometry.c, image height and width calculations can lead to divide-by-zero conditions which also lead to undefined behavior. This flaw can be triggered by a crafted input file processed by ImageMagick and could impact application availability. The patch uses multiplication in addition to the function `PerceptibleReciprocal()` in order to prevent such divide-by-zero conditions. This flaw affects ImageMagick versions prior to 7.0.9-0. |
2020-12-08 |
4.3 |
CVE-2020-27756
MISC |
| imagemagick — imagemagick |
In RestoreMSCWarning() of /coders/pdf.c there are several areas where calls to GetPixelIndex() could result in values outside the range of representable for the unsigned char type. The patch casts the return value of GetPixelIndex() to ssize_t type to avoid this bug. This undefined behavior could be triggered when ImageMagick processes a crafted pdf file. Red Hat Product Security marked this as Low severity because although it could potentially lead to an impact to application availability, no specific impact was demonstrated in this case. This flaw affects ImageMagick versions prior to 7.0.9-0. |
2020-12-04 |
4.3 |
CVE-2020-27771
MISC |
| imagemagick — imagemagick |
A flaw was found in ImageMagick in coders/bmp.c. An attacker who submits a crafted file that is processed by ImageMagick could trigger undefined behavior in the form of values outside the range of type `unsigned int`. This would most likely lead to an impact to application availability, but could potentially cause other problems related to undefined behavior. This flaw affects ImageMagick versions prior to 7.0.9-0. |
2020-12-04 |
4.3 |
CVE-2020-27772
MISC |
| imagemagick — imagemagick |
TIFFGetProfiles() in /coders/tiff.c calls strstr() which causes a large out-of-bounds read when it searches for `”dc:format=”image/dng”` within `profile` due to improper string handling, when a crafted input file is provided to ImageMagick. The patch uses a StringInfo type instead of a raw C string to remedy this. This could cause an impact to availability of the application. This flaw affects ImageMagick versions prior to 7.0.9-0. |
2020-12-08 |
4.3 |
CVE-2020-25667
MISC |
| imagemagick — imagemagick |
A flaw was found in ImageMagick in MagickCore/statistic.c. An attacker who submits a crafted file that is processed by ImageMagick could trigger undefined behavior in the form of values outside the range of type `unsigned long`. This would most likely lead to an impact to application availability, but could potentially cause other problems related to undefined behavior. This flaw affects ImageMagick versions prior to 7.0.8-69. |
2020-12-04 |
6.8 |
CVE-2020-27766
MISC |
| imagemagick — imagemagick |
A flaw was found in ImageMagick in MagickCore/statistic.c. An attacker who submits a crafted file that is processed by ImageMagick could trigger undefined behavior in the form of values outside the range of type unsigned long. This would most likely lead to an impact to application availability, but could potentially cause other problems related to undefined behavior. This flaw affects ImageMagick versions prior to 7.0.9-0. |
2020-12-04 |
4.3 |
CVE-2020-27776
MISC |
| imagemagick — imagemagick |
A flaw was found in ImageMagick in MagickCore/quantum.h. An attacker who submits a crafted file that is processed by ImageMagick could trigger undefined behavior in the form of values outside the range of type unsigned char. This would most likely lead to an impact to application availability, but could potentially cause other problems related to undefined behavior. This flaw affects ImageMagick versions prior to 7.0.9-0. |
2020-12-04 |
4.3 |
CVE-2020-27775
MISC |
| imagemagick — imagemagick |
In WriteOnePNGImage() of the PNG coder at coders/png.c, an improper call to AcquireVirtualMemory() and memset() allows for an out-of-bounds write later when PopShortPixel() from MagickCore/quantum-private.h is called. The patch fixes the calls by adding 256 to rowbytes. An attacker who is able to supply a specially crafted image could affect availability with a low impact to data integrity. This flaw affects ImageMagick versions prior to 6.9.10-68 and 7.0.8-68. |
2020-12-08 |
5.8 |
CVE-2020-25664
MISC |
| imagemagick — imagemagick |
A flaw was found in ImageMagick in MagickCore/statistic.c. An attacker who submits a crafted file that is processed by ImageMagick could trigger undefined behavior in the form of a too large shift for 64-bit type `ssize_t`. This would most likely lead to an impact to application availability, but could potentially cause other problems related to undefined behavior. This flaw affects ImageMagick versions prior to 7.0.9-0. |
2020-12-04 |
4.3 |
CVE-2020-27774
MISC |
| imagemagick — imagemagick |
A floating point math calculation in ScaleAnyToQuantum() of /MagickCore/quantum-private.h could lead to undefined behavior in the form of a value outside the range of type unsigned long long. The flaw could be triggered by a crafted input file under certain conditions when it is processed by ImageMagick. Red Hat Product Security marked this as Low because although it could potentially lead to an impact to application availability, no specific impact was shown in this case. This flaw affects ImageMagick versions prior to 7.0.8-68. |
2020-12-08 |
4.3 |
CVE-2020-27757
MISC |
| imagemagick — imagemagick |
A call to ConformPixelInfo() in the SetImageAlphaChannel() routine of /MagickCore/channel.c caused a subsequent heap-use-after-free or heap-buffer-overflow READ when GetPixelRed() or GetPixelBlue() was called. This could occur if an attacker is able to submit a malicious image file to be processed by ImageMagick and could lead to denial of service. It likely would not lead to anything further because the memory is used as pixel data and not e.g. a function pointer. This flaw affects ImageMagick versions prior to 7.0.9-0. |
2020-12-08 |
4.3 |
CVE-2020-25663
MISC
MISC
MISC |
| imagemagick — imagemagick |
The PALM image coder at coders/palm.c makes an improper call to AcquireQuantumMemory() in routine WritePALMImage() because it needs to be offset by 256. This can cause a out-of-bounds read later on in the routine. The patch adds 256 to bytes_per_row in the call to AcquireQuantumMemory(). This could cause impact to reliability. This flaw affects ImageMagick versions prior to 7.0.8-68. |
2020-12-08 |
4.3 |
CVE-2020-25665
MISC |
| imagemagick — imagemagick |
There are 4 places in HistogramCompare() in MagickCore/histogram.c where an integer overflow is possible during simple math calculations. This occurs in the rgb values and `count` value for a color. The patch uses casts to `ssize_t` type for these calculations, instead of `int`. This flaw could impact application reliability in the event that ImageMagick processes a crafted input file. This flaw affects ImageMagick versions prior to 7.0.9-0. |
2020-12-08 |
4.3 |
CVE-2020-25666
MISC |
| imagemagick — imagemagick |
A flaw was found in ImageMagick in MagickCore/quantum-private.h. An attacker who submits a crafted file that is processed by ImageMagick could trigger a heap buffer overflow. This would most likely lead to an impact to application availability, but could potentially lead to an impact to data integrity as well. This flaw affects ImageMagick versions prior to 7.0.9-0. |
2020-12-08 |
5.8 |
CVE-2020-27752
MISC |
| infolific — ultimate_category_excluder |
The ultimate-category-excluder plugin before 1.2 for WordPress allows ultimate-category-excluder.php CSRF. |
2020-12-11 |
6.8 |
CVE-2020-35135
MISC
MISC |
| inspur — nf8480m5_firmware |
Inspur NF5266M5 through 3.21.2 and other server M5 devices allow remote code execution via administrator privileges. The Baseboard Management Controller (BMC) program of INSPUR server is weak in checking the firmware and lacks the signature verification mechanism, the attacker who obtains the administrator’s rights can control the BMC by inserting malicious code into the firmware program and bypassing the current verification mechanism to upgrade the BMC. |
2020-12-07 |
6.5 |
CVE-2020-26122
MISC
CONFIRM |
| intland — codebeamer_application_lifecycle_management |
An issue was discovered in Intland codeBeamer ALM 10.x through 10.1.SP4. The ReqIF XML data, used by the codebeamer ALM application to import projects, is parsed by insecurely configured software components, which can be abused for XML External Entity Attacks. |
2020-12-07 |
4.3 |
CVE-2020-26513
MISC
MISC |
| jerryscript — jerryscript |
In JerryScript 2.3.0, there is an out-of-bounds read in main_print_unhandled_exception in the main-utils.c file. |
2020-12-09 |
6.4 |
CVE-2020-29657
MISC |
| kaspersky — anti-ransomware_tool |
The installer of Kaspersky Anti-Ransomware Tool (KART) prior to KART 4.0 Patch C was vulnerable to a DLL hijacking attack that allowed an attacker to elevate privileges during installation process. |
2020-12-04 |
6.9 |
CVE-2020-28950
MISC
MISC |
| libpng — pngcheck |
A flaw was found in the check_chunk_name() function of pngcheck-2.4.0. An attacker able to pass a malicious file to be processed by pngcheck could cause a temporary denial of service, posing a low risk to application availability. |
2020-12-08 |
4.3 |
CVE-2020-27818
MISC
MISC
MISC
MISC
MISC
MISC
CONFIRM |
| matrix — synapse |
Matrix is an ecosystem for open federated Instant Messaging and VoIP. Synapse is a reference “homeserver” implementation of Matrix. A malicious or poorly-implemented homeserver can inject malformed events into a room by specifying a different room id in the path of a `/send_join`, `/send_leave`, `/invite` or `/exchange_third_party_invite` request. This can lead to a denial of service in which future events will not be correctly sent to other servers over federation. This affects any server which accepts federation requests from untrusted servers. The Matrix Synapse reference implementation before version 1.23.1 the implementation is vulnerable to this injection attack. Issue is fixed in version 1.23.1. As a workaround homeserver administrators could limit access to the federation API to trusted servers (for example via `federation_domain_whitelist`). |
2020-12-09 |
4 |
CVE-2020-26257
MISC
MISC
MISC
CONFIRM |
| mcafee — virusscan_enterprise |
Incorrect Permission Assignment for Critical Resource vulnerability in McAfee VirusScan Enterprise (VSE) prior to 8.8 Patch 16 allows local administrators to bypass local security protection through VSE not correctly integrating with Windows Defender Application Control via careful manipulation of the Code Integrity checks. |
2020-12-09 |
4.6 |
CVE-2020-7337
CONFIRM |
| microsoft — 365_apps |
, aka ‘Microsoft Outlook Information Disclosure Vulnerability’. |
2020-12-10 |
5 |
CVE-2020-17119
MISC
MISC |
| microsoft — 365_apps |
, aka ‘Microsoft Excel Security Feature Bypass Vulnerability’. |
2020-12-10 |
6 |
CVE-2020-17130
MISC |
| microsoft — azure_devops_server |
, aka ‘Azure DevOps Server Spoofing Vulnerability’. |
2020-12-10 |
4.9 |
CVE-2020-17135
MISC |
| microsoft — azure_sdk_for_java |
, aka ‘Azure SDK for Java Security Feature Bypass Vulnerability’. |
2020-12-10 |
6.4 |
CVE-2020-16971
MISC |
| microsoft — dynamics_365 |
, aka ‘Microsoft Dynamics 365 for Finance and Operations (on-premises) Remote Code Execution Vulnerability’. This CVE ID is unique from CVE-2020-17158. |
2020-12-10 |
6.5 |
CVE-2020-17152
MISC |
| microsoft — dynamics_365 |
, aka ‘Microsoft Dynamics 365 for Finance and Operations (on-premises) Remote Code Execution Vulnerability’. This CVE ID is unique from CVE-2020-17152. |
2020-12-10 |
6.5 |
CVE-2020-17158
MISC |
| microsoft — dynamics_nav |
, aka ‘Microsoft Dynamics Business Central/NAV Information Disclosure’. |
2020-12-10 |
4 |
CVE-2020-17133
MISC |
| microsoft — edge |
, aka ‘Microsoft Edge for Android Spoofing Vulnerability’. |
2020-12-10 |
5.8 |
CVE-2020-17153
MISC |
| microsoft — exchange_server |
, aka ‘Microsoft Exchange Remote Code Execution Vulnerability’. This CVE ID is unique from CVE-2020-17117, CVE-2020-17132, CVE-2020-17141, CVE-2020-17144. |
2020-12-10 |
6.5 |
CVE-2020-17142
MISC |
| microsoft — exchange_server |
, aka ‘Microsoft Exchange Remote Code Execution Vulnerability’. This CVE ID is unique from CVE-2020-17117, CVE-2020-17132, CVE-2020-17141, CVE-2020-17142. |
2020-12-10 |
6 |
CVE-2020-17144
MISC |
| microsoft — exchange_server |
, aka ‘Microsoft Exchange Remote Code Execution Vulnerability’. This CVE ID is unique from CVE-2020-17117, CVE-2020-17141, CVE-2020-17142, CVE-2020-17144. |
2020-12-10 |
6.5 |
CVE-2020-17132
MISC |
| microsoft — exchange_server |
, aka ‘Microsoft Exchange Information Disclosure Vulnerability’. |
2020-12-10 |
6.5 |
CVE-2020-17143
MISC |
| microsoft — exchange_server |
, aka ‘Microsoft Exchange Remote Code Execution Vulnerability’. This CVE ID is unique from CVE-2020-17117, CVE-2020-17132, CVE-2020-17142, CVE-2020-17144. |
2020-12-10 |
6 |
CVE-2020-17141
MISC |
| microsoft — sharepoint_foundation |
, aka ‘Microsoft SharePoint Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability’. |
2020-12-10 |
6 |
CVE-2020-17089
MISC |
| microsoft — sharepoint_foundation |
, aka ‘Microsoft SharePoint Remote Code Execution Vulnerability’. This CVE ID is unique from CVE-2020-17118. |
2020-12-10 |
6.5 |
CVE-2020-17121
MISC |
| microsoft — sharepoint_foundation |
, aka ‘Microsoft SharePoint Spoofing Vulnerability’. |
2020-12-10 |
6 |
CVE-2020-17115
MISC |
| microsoft — sharepoint_foundation |
, aka ‘Microsoft SharePoint Information Disclosure Vulnerability’. |
2020-12-10 |
4 |
CVE-2020-17120
MISC |
| microsoft — team_foundation_server |
, aka ‘Azure DevOps Server and Team Foundation Services Spoofing Vulnerability’. |
2020-12-10 |
4.9 |
CVE-2020-17145
MISC |
| microsoft — visual_studio_2017 |
, aka ‘Visual Studio Remote Code Execution Vulnerability’. |
2020-12-10 |
6.8 |
CVE-2020-17156
MISC |
| microsoft — visual_studio_code |
, aka ‘Visual Studio Code Remote Code Execution Vulnerability’. |
2020-12-10 |
6.8 |
CVE-2020-17150
MISC |
| microsoft — visual_studio_code |
, aka ‘Visual Studio Code Java Extension Pack Remote Code Execution Vulnerability’. |
2020-12-10 |
6.8 |
CVE-2020-17159
MISC |
| microsoft — visual_studio_code |
, aka ‘Visual Studio Code Remote Development Extension Remote Code Execution Vulnerability’. |
2020-12-10 |
6.8 |
CVE-2020-17148
MISC |
| microsoft — windows_10 |
, aka ‘Windows Digital Media Receiver Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability’. |
2020-12-10 |
4.6 |
CVE-2020-17097
MISC |
| microsoft — windows_10 |
, aka ‘Windows Lock Screen Security Feature Bypass Vulnerability’. |
2020-12-10 |
4.6 |
CVE-2020-17099
MISC |
| microsoft — windows_10 |
, aka ‘Windows Cloud Files Mini Filter Driver Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability’. This CVE ID is unique from CVE-2020-17103, CVE-2020-17136. |
2020-12-10 |
4.6 |
CVE-2020-17134
MISC |
| microsoft — windows_10 |
, aka ‘Windows SMB Information Disclosure Vulnerability’. |
2020-12-10 |
4 |
CVE-2020-17140
MISC |
| microsoft — windows_10 |
, aka ‘DirectX Graphics Kernel Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability’. |
2020-12-10 |
4.6 |
CVE-2020-17137
MISC |
| microsoft — windows_10 |
, aka ‘Windows Overlay Filter Security Feature Bypass Vulnerability’. |
2020-12-10 |
4.6 |
CVE-2020-17139
MISC |
| microsoft — windows_10 |
, aka ‘Windows Cloud Files Mini Filter Driver Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability’. This CVE ID is unique from CVE-2020-17103, CVE-2020-17134. |
2020-12-10 |
4.6 |
CVE-2020-17136
MISC |
| microsoft — windows_server_2012 |
, aka ‘Kerberos Security Feature Bypass Vulnerability’. |
2020-12-10 |
4 |
CVE-2020-16996
MISC |
| misp — misp |
app/View/Elements/genericElements/SingleViews/Fields/genericField.ctp in MISP 2.4.135 has XSS via the authkey comment field. |
2020-12-06 |
4.3 |
CVE-2020-29572
MISC |
| mitsubishielectric — gt2107-wtbd_firmware |
Out-of-bounds read issue in GT21 model of GOT2000 series (GT2107-WTBD all versions, GT2107-WTSD all versions, GT2104-RTBD all versions, GT2104-PMBD all versions, and GT2103-PMBD all versions), GS21 model of GOT series (GS2110-WTBD all versions and GS2107-WTBD all versions), and Tension Controller LE7-40GU-L all versions allows a remote attacker to cause a denial-of-service (DoS) condition by sending a specially crafted packet. As a result, deterioration of communication performance or a denial-of-service (DoS) condition of the TCP communication functions of the products may occur. |
2020-12-04 |
5 |
CVE-2020-5675
MISC
MISC
MISC |
| moodle — moodle |
A vulnerability was found in Moodle where users with “Log in as” capability in a course context (typically, course managers) may gain access to some site administration capabilities by “logging in as” a System manager. This affects 3.9 to 3.9.1, 3.8 to 3.8.4, 3.7 to 3.7.7, 3.5 to 3.5.13 and earlier unsupported versions. This is fixed in 3.9.2, 3.8.5, 3.7.8 and 3.5.14. |
2020-12-08 |
6.5 |
CVE-2020-25629
CONFIRM |
| moodle — moodle |
A vulnerability was found in Moodle where the decompressed size of zip files was not checked against available user quota before unzipping them, which could lead to a denial of service risk. This affects versions 3.9 to 3.9.1, 3.8 to 3.8.4, 3.7 to 3.7.7, 3.5 to 3.5.13 and earlier unsupported versions. Fixed in 3.9.2, 3.8.5, 3.7.8 and 3.5.14. |
2020-12-08 |
5 |
CVE-2020-25630
CONFIRM |
| moodle — moodle |
A vulnerability was found in Moodle 3.9 to 3.9.1, 3.8 to 3.8.4 and 3.7 to 3.7.7 where it was possible to include JavaScript in a book’s chapter title, which was not escaped on the “Add new chapter” page. This is fixed in 3.9.2, 3.8.5 and 3.7.8. |
2020-12-08 |
4.3 |
CVE-2020-25631
CONFIRM |
| moodle — moodle |
The moodlenetprofile user profile field required extra sanitizing to prevent a stored XSS risk. This affects versions 3.9 to 3.9.1. Fixed in 3.9.2. |
2020-12-09 |
4.3 |
CVE-2020-25627
CONFIRM |
| moodle — moodle |
The filter in the tag manager required extra sanitizing to prevent a reflected XSS risk. This affects 3.9 to 3.9.1, 3.8 to 3.8.4, 3.7 to 3.7.7, 3.5 to 3.5.13 and earlier unsupported versions. Fixed in 3.9.2, 3.8.5, 3.7.8 and 3.5.14. |
2020-12-08 |
4.3 |
CVE-2020-25628
MISC
CONFIRM |
| mozilla — firefox |
Searching for a single word from the address bar caused an mDNS request to be sent on the local network searching for a hostname consisting of that string; resulting in an information leak. *Note: This issue only affected Windows operating systems. Other operating systems are unaffected.*. This vulnerability affects Firefox < 83, Firefox ESR < 78.5, and Thunderbird < 78.5. |
2020-12-09 |
4.3 |
CVE-2020-26966
MISC
CONFIRM
CONFIRM
CONFIRM |
| mozilla — firefox |
Some websites have a feature “Show Password” where clicking a button will change a password field into a textbook field, revealing the typed password. If, when using a software keyboard that remembers user input, a user typed their password and used that feature, the type of the password field was changed, resulting in a keyboard layout change and the possibility for the software keyboard to remember the typed password. This vulnerability affects Firefox < 83, Firefox ESR < 78.5, and Thunderbird < 78.5. |
2020-12-09 |
4.3 |
CVE-2020-26965
MISC
CONFIRM
CONFIRM
CONFIRM |
| mozilla — firefox |
OneCRL was non-functional in the new Firefox for Android due to a missing service initialization. This could result in a failure to enforce some certificate revocations. *Note: This issue only affected Firefox for Android. Other operating systems are unaffected.*. This vulnerability affects Firefox < 83. |
2020-12-09 |
4.3 |
CVE-2020-26957
MISC
CONFIRM |
| mozilla — firefox |
Repeated calls to the history and location interfaces could have been used to hang the browser. This was addressed by introducing rate-limiting to these API calls. This vulnerability affects Firefox < 83. |
2020-12-09 |
4.3 |
CVE-2020-26963
MISC
CONFIRM |
| mozilla — firefox |
Cross-origin iframes that contained a login form could have been recognized by the login autofill service, and populated. This could have been used in clickjacking attacks, as well as be read across partitions in dynamic first party isolation. This vulnerability affects Firefox < 83. |
2020-12-09 |
4.3 |
CVE-2020-26962
MISC
CONFIRM |
| mozilla — firefox |
When DNS over HTTPS is in use, it intentionally filters RFC1918 and related IP ranges from the responses as these do not make sense coming from a DoH resolver. However when an IPv4 address was mapped through IPv6, these addresses were erroneously let through, leading to a potential DNS Rebinding attack. This vulnerability affects Firefox < 83, Firefox ESR < 78.5, and Thunderbird < 78.5. |
2020-12-09 |
4.3 |
CVE-2020-26961
MISC
CONFIRM
CONFIRM
CONFIRM |
| mozilla — firefox |
Firefox did not block execution of scripts with incorrect MIME types when the response was intercepted and cached through a ServiceWorker. This could lead to a cross-site script inclusion vulnerability, or a Content Security Policy bypass. This vulnerability affects Firefox < 83, Firefox ESR < 78.5, and Thunderbird < 78.5. |
2020-12-09 |
4.3 |
CVE-2020-26958
MISC
CONFIRM
CONFIRM
CONFIRM |
| mozilla — firefox |
In some cases, removing HTML elements during sanitization would keep existing SVG event handlers and therefore lead to XSS. This vulnerability affects Firefox < 83, Firefox ESR < 78.5, and Thunderbird < 78.5. |
2020-12-09 |
4.3 |
CVE-2020-26956
MISC
CONFIRM
CONFIRM
CONFIRM |
| mozilla — firefox |
When a user downloaded a file in Firefox for Android, if a cookie is set, it would have been re-sent during a subsequent file download operation on the same domain, regardless of whether the original and subsequent request were in private and non-private browsing modes. *Note: This issue only affected Firefox for Android. Other operating systems are unaffected.*. This vulnerability affects Firefox < 83. |
2020-12-09 |
4.3 |
CVE-2020-26955
MISC
CONFIRM |
| mozilla — firefox |
When accepting a malicious intent from other installed apps, Firefox for Android accepted manifests from arbitrary file paths and allowed declaring webapp manifests for other origins. This could be used to gain fullscreen access for UI spoofing and could also lead to cross-origin attacks on targeted websites. *Note: This issue only affected Firefox for Android. Other operating systems are unaffected.*. This vulnerability affects Firefox < 83. |
2020-12-09 |
4.3 |
CVE-2020-26954
MISC
CONFIRM |
| mozilla — firefox |
It was possible to cause the browser to enter fullscreen mode without displaying the security UI; thus making it possible to attempt a phishing attack or otherwise confuse the user. This vulnerability affects Firefox < 83, Firefox ESR < 78.5, and Thunderbird < 78.5. |
2020-12-09 |
4.3 |
CVE-2020-26953
MISC
CONFIRM
CONFIRM
CONFIRM |
| mozilla — firefox |
A parsing and event loading mismatch in Firefox’s SVG code could have allowed load events to fire, even after sanitization. An attacker already capable of exploiting an XSS vulnerability in privileged internal pages could have used this attack to bypass our built-in sanitizer. This vulnerability affects Firefox < 83, Firefox ESR < 78.5, and Thunderbird < 78.5. |
2020-12-09 |
4.3 |
CVE-2020-26951
MISC
CONFIRM
CONFIRM
CONFIRM |
| mozilla — firefox |
During browser shutdown, reference decrementing could have occured on a previously freed object, resulting in a use-after-free, memory corruption, and a potentially exploitable crash. This vulnerability affects Firefox < 83, Firefox ESR < 78.5, and Thunderbird < 78.5. |
2020-12-09 |
6.8 |
CVE-2020-26959
MISC
CONFIRM
CONFIRM
CONFIRM |
| mozilla — firefox |
When listening for page changes with a Mutation Observer, a malicious web page could confuse Firefox Screenshots into interacting with elements other than those that it injected into the page. This would lead to internal errors and unexpected behavior in the Screenshots code. This vulnerability affects Firefox < 83. |
2020-12-09 |
4.3 |
CVE-2020-26967
MISC
CONFIRM |
| mozilla — firefox |
If the Remote Debugging via USB feature was enabled in Firefox for Android on an Android version prior to Android 6.0, untrusted apps could have connected to the feature and operated with the privileges of the browser to read and interact with web content. The feature was implemented as a unix domain socket, protected by the Android SELinux policy; however, SELinux was not enforced for versions prior to 6.0. This was fixed by removing the Remote Debugging via USB feature from affected devices. *Note: This issue only affected Firefox for Android. Other operating systems are unaffected.*. This vulnerability affects Firefox < 83. |
2020-12-09 |
4 |
CVE-2020-26964
MISC
CONFIRM |
| omniauth-apple_project — omniauth-apple |
omniauth-apple is the OmniAuth strategy for “Sign In with Apple” (RubyGem omniauth-apple). In omniauth-apple before version 1.0.1 attackers can fake their email address during authentication. This vulnerability impacts applications using the omniauth-apple strategy of OmniAuth and using the info.email field of OmniAuth’s Auth Hash Schema for any kind of identification. The value of this field may be set to any value of the attacker’s choice including email addresses of other users. Applications not using info.email for identification but are instead using the uid field are not impacted in the same manner. Note, these applications may still be negatively affected if the value of info.email is being used for other purposes. Applications using affected versions of omniauth-apple are advised to upgrade to omniauth-apple version 1.0.1 or later. |
2020-12-08 |
5 |
CVE-2020-26254
MISC
MISC
CONFIRM |
| online_examination_system_project — online_examination_system |
Cross-site scripting (XSS) vulnerability in Online Examination System 1.0 via the w parameter to index.php. |
2020-12-09 |
4.3 |
CVE-2020-29258
MISC |
| online_examination_system_project — online_examination_system |
Cross-site scripting (XSS) vulnerability in Online Examination System 1.0 via the q parameter to feedback.php. |
2020-12-09 |
4.3 |
CVE-2020-29257
MISC |
| online_examination_system_project — online_examination_system |
Cross-site scripting (XSS) vulnerability in Online Examination System 1.0 via the subject or feedback parameter to feedback.php. |
2020-12-09 |
4.3 |
CVE-2020-29259
MISC |
| openldap — openldap |
A NULL pointer dereference was found in OpenLDAP server and was fixed in openldap 2.4.55, during a request for renaming RDNs. An unauthenticated attacker could remotely crash the slapd process by sending a specially crafted request, causing a Denial of Service. |
2020-12-08 |
5 |
CVE-2020-25692
CONFIRM |
| openssl — openssl |
The X.509 GeneralName type is a generic type for representing different types of names. One of those name types is known as EDIPartyName. OpenSSL provides a function GENERAL_NAME_cmp which compares different instances of a GENERAL_NAME to see if they are equal or not. This function behaves incorrectly when both GENERAL_NAMEs contain an EDIPARTYNAME. A NULL pointer dereference and a crash may occur leading to a possible denial of service attack. OpenSSL itself uses the GENERAL_NAME_cmp function for two purposes: 1) Comparing CRL distribution point names between an available CRL and a CRL distribution point embedded in an X509 certificate 2) When verifying that a timestamp response token signer matches the timestamp authority name (exposed via the API functions TS_RESP_verify_response and TS_RESP_verify_token) If an attacker can control both items being compared then that attacker could trigger a crash. For example if the attacker can trick a client or server into checking a malicious certificate against a malicious CRL then this may occur. Note that some applications automatically download CRLs based on a URL embedded in a certificate. This checking happens prior to the signatures on the certificate and CRL being verified. OpenSSL’s s_server, s_client and verify tools have support for the “-crl_download” option which implements automatic CRL downloading and this attack has been demonstrated to work against those tools. Note that an unrelated bug means that affected versions of OpenSSL cannot parse or construct correct encodings of EDIPARTYNAME. However it is possible to construct a malformed EDIPARTYNAME that OpenSSL’s parser will accept and hence trigger this attack. All OpenSSL 1.1.1 and 1.0.2 versions are affected by this issue. Other OpenSSL releases are out of support and have not been checked. Fixed in OpenSSL 1.1.1i (Affected 1.1.1-1.1.1h). Fixed in OpenSSL 1.0.2x (Affected 1.0.2-1.0.2w). |
2020-12-08 |
5 |
CVE-2020-1971
CONFIRM
CONFIRM
FREEBSD
DEBIAN
CONFIRM |
| openstack — horizon |
An issue was discovered in OpenStack Horizon before 15.3.2, 16.x before 16.2.1, 17.x and 18.x before 18.3.3, 18.4.x, and 18.5.x. There is a lack of validation of the “next” parameter, which would allow someone to supply a malicious URL in Horizon that can cause an automatic redirect to the provided malicious URL. |
2020-12-04 |
5.8 |
CVE-2020-29565
MLIST
MISC
MISC
MISC
CONFIRM |
| os4ed — opensis |
OpenSIS Community Edition before 7.5 is affected by a cross-site scripting (XSS) vulnerability in SideForStudent.php via the modname parameter. |
2020-12-04 |
4.3 |
CVE-2020-27409
MISC
MISC
MISC |
| os4ed — opensis |
OpenSIS Community Edition through 7.6 is affected by incorrect access controls for the file ResetUserInfo.php that allow an unauthenticated attacker to change the password of arbitrary users. |
2020-12-04 |
5 |
CVE-2020-27408
MISC
MISC |
| plummac — ik-401_firmware |
An improper webserver configuration on Plum IK-401 devices with firmware before 1.02 allows an attacker (with network access to the device) to obtain the configuration file, including hashed credential data. Successful exploitation could allow access to hashed credential data with a single unauthenticated GET request. |
2020-12-08 |
5 |
CVE-2020-28946
MISC
MISC |
| processmaker — processmaker |
SQL injection vulnerability exists in the handling of sort parameters in ProcessMaker 3.4.11. A specially crafted HTTP request can cause an SQL injection. The reportTables_Ajax and clientSetupAjax pages are vulnerable to SQL injection in the sort parameter.An attacker can make an authenticated HTTP request to trigger these vulnerabilities. |
2020-12-10 |
6.5 |
CVE-2020-13526
MISC |
| pytest — py |
A denial of service via regular expression in the py.path.svnwc component of py (aka python-py) through 1.9.0 could be used by attackers to cause a compute-time denial of service attack by supplying malicious input to the blame functionality. |
2020-12-09 |
5 |
CVE-2020-29651
MISC
MISC
MISC |
| qnap — multimedia_console |
This cross-site scripting vulnerability in Multimedia Console allows remote attackers to inject malicious code. QANP have already fixed this vulnerability in Multimedia Console 1.1.5 and later. |
2020-12-10 |
4.3 |
CVE-2020-2493
CONFIRM |
| qnap — music_station |
This cross-site scripting vulnerability in Music Station allows remote attackers to inject malicious code. QANP have already fixed this vulnerability in the following versions of Music Station. QuTS hero h4.5.1: Music Station 5.3.13 and later QTS 4.5.1: Music Station 5.3.12 and later QTS 4.4.3: Music Station 5.3.12 and later |
2020-12-10 |
4.3 |
CVE-2020-2494
CONFIRM |
| qnap — photo_station |
This cross-site scripting vulnerability in Photo Station allows remote attackers to inject malicious code. QANP We have already fixed this vulnerability in the following versions of Photo Station. QTS 4.5.1: Photo Station 6.0.12 and later QTS 4.4.3: Photo Station 6.0.12 and later QTS 4.3.6: Photo Station 5.7.12 and later QTS 4.3.4: Photo Station 5.7.13 and later QTS 4.3.3: Photo Station 5.4.10 and later QTS 4.2.6: Photo Station 5.2.11 and later |
2020-12-10 |
4.3 |
CVE-2020-2491
CONFIRM |
| qnap — quts_hero |
If exploited, this cross-site scripting vulnerability could allow remote attackers to inject malicious code in File Station. QANP have already fixed these vulnerabilities in the following versions of QTS and QuTS hero. QuTS hero h4.5.1.1472 build 20201031 and later QTS 4.5.1.1456 build 20201015 and later QTS 4.4.3.1354 build 20200702 and later QTS 4.3.6.1333 build 20200608 and later QTS 4.3.4.1368 build 20200703 and later QTS 4.3.3.1315 build 20200611 and later QTS 4.2.6 build 20200611 and later |
2020-12-10 |
4.3 |
CVE-2020-2496
CONFIRM |
| qnap — quts_hero |
If exploited, this cross-site scripting vulnerability could allow remote attackers to inject malicious code in System Connection Logs. QANP have already fixed these vulnerabilities in the following versions of QTS and QuTS hero. QuTS hero h4.5.1.1472 build 20201031 and later QTS 4.5.1.1456 build 20201015 and later QTS 4.4.3.1354 build 20200702 and later QTS 4.3.6.1333 build 20200608 and later QTS 4.3.4.1368 build 20200703 and later QTS 4.3.3.1315 build 20200611 and later QTS 4.2.6 build 20200611 and later |
2020-12-10 |
4.3 |
CVE-2020-2497
CONFIRM |
| qnap — quts_hero |
If exploited, this cross-site scripting vulnerability could allow remote attackers to inject malicious code in certificate configuration. QANP have already fixed these vulnerabilities in the following versions of QTS and QuTS hero. QuTS hero h4.5.1.1472 build 20201031 and later QTS 4.5.1.1456 build 20201015 and later QTS 4.4.3.1354 build 20200702 and later QTS 4.3.6.1333 build 20200608 and later QTS 4.3.4.1368 build 20200703 and later QTS 4.3.3.1315 build 20200611 and later QTS 4.2.6 build 20200611 and later |
2020-12-10 |
4.3 |
CVE-2020-2498
CONFIRM |
| qnap — quts_hero |
If exploited, this cross-site scripting vulnerability could allow remote attackers to inject malicious code in File Station. QANP have already fixed these vulnerabilities in the following versions of QTS and QuTS hero. QuTS hero h4.5.1.1472 build 20201031 and later QTS 4.5.1.1456 build 20201015 and later QTS 4.4.3.1354 build 20200702 and later QTS 4.3.6.1333 build 20200608 and later QTS 4.3.4.1368 build 20200703 and later QTS 4.3.3.1315 build 20200611 and later QTS 4.2.6 build 20200611 and later |
2020-12-10 |
4.3 |
CVE-2020-2495
CONFIRM |
| react-adal_project — react-adal |
This affects all versions of package react-adal. It is possible for a specially crafted JWT token and request URL can cause the nonce, session and refresh values to be incorrectly validated, causing the application to treat an attacker-generated JWT token as authentic. The logical defect is caused by how the nonce, session and refresh values are stored in the browser local storage or session storage. Each key is automatically appended by ||. When the received nonce and session keys are generated, the list of values is stored in the browser storage, separated by ||, with || always appended to the end of the list. Since || will always be the last 2 characters of the stored values, an empty string (“”) will always be in the list of the valid values. Therefore, if an empty session parameter is provided in the callback URL, and a specially-crafted JWT token contains an nonce value of “” (empty string), then adal.js will consider the JWT token as authentic. |
2020-12-09 |
5 |
CVE-2020-7787
MISC
MISC |
| sap — businessobjects_business_intelligence_platform |
SAP BusinessObjects BI Platform (Crystal Report), versions – 4.1, 4.2, 4.3, does not sufficiently validate uploaded XML entities during crystal report generation due to missing XML validation, An attacker with basic privileges can inject some arbitrary XML entities leading to internal file disclosure, internal directories disclosure, Server-Side Request Forgery (SSRF) and denial-of-service (DoS). |
2020-12-09 |
5.5 |
CVE-2020-26831
MISC
MISC |
| sap — disclosure_management |
SAP Disclosure Management, version – 10.1, provides capabilities for authorized users to upload and download content of specific file type. In some file types it is possible to enter formulas which can call external applications or execute scripts. The execution of a payload (script) on target machine could be used to steal and modify the data available in the spreadsheet |
2020-12-09 |
5.5 |
CVE-2020-26828
MISC
MISC |
| sap — hana_database |
SAP HANA Database, version – 2.0, does not correctly validate the username when performing SAML bearer token-based user authentication. It is possible to manipulate a valid existing SAML bearer token to authenticate as a user whose name is identical to the truncated username for whom the SAML bearer token was issued. |
2020-12-09 |
5.5 |
CVE-2020-26834
MISC
MISC |
| sap — netweaver_as_abap |
SAP NetWeaver AS ABAP, versions – 740, 750, 751, 752, 753, 754 , does not sufficiently encode URL which allows an attacker to input malicious java script in the URL which could be executed in the browser resulting in Reflected Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) vulnerability. |
2020-12-09 |
4.3 |
CVE-2020-26835
MISC
MISC |
| sap — solution_manager |
SAP Solution Manager 7.2 (User Experience Monitoring), version – 7.2, allows an authenticated user to upload a malicious script that can exploit an existing path traversal vulnerability to compromise confidentiality exposing elements of the file system, partially compromise integrity allowing the modification of some configurations and partially compromise availability by making certain services unavailable. |
2020-12-09 |
6.5 |
CVE-2020-26837
MISC
MISC |
| sap — solution_manager |
SAP Solution Manager 7.2 (User Experience Monitoring), version – 7.2, does not perform necessary authorization checks for an authenticated user. Due to inadequate access control, a network attacker authenticated as a regular user can use operations which should be restricted to administrators. These operations can be used to Change the User Experience Monitoring configuration, obtain details about the configured SAP Solution Manager agents, Deploy a malicious User Experience Monitoring script. |
2020-12-09 |
5.5 |
CVE-2020-26830
MISC
MISC |
| sap — solution_manager |
SAP Solution Manager (Trace Analysis), version – 720, allows for misuse of a parameter in the application URL leading to Open Redirect vulnerability, an attacker can enter a link to malicious site which could trick the user to enter credentials or download malicious software, as a parameter in the application URL and share it with the end user who could potentially become a victim of the attack. |
2020-12-09 |
5.8 |
CVE-2020-26836
MISC
MISC |
| seeddms — seeddms |
Cross-site scripting (XSS) exists in SeedDMS 6.0.13 via the folderid parameter to views/bootstrap/class.DropFolderChooser.php. |
2020-12-07 |
4.3 |
CVE-2020-28727
MISC
CONFIRM
MISC |
| snapcraft_project — snapcraft |
In some conditions, a snap package built by snapcraft includes the current directory in LD_LIBRARY_PATH, allowing a malicious snap to gain code execution within the context of another snap if both plug the home interface or similar. This issue affects snapcraft versions prior to 4.4.4, prior to 2.43.1+16.04.1, and prior to 2.43.1+18.04.1. |
2020-12-04 |
4.4 |
CVE-2020-27348
MISC
MISC
MISC |
| systransoft — pure_neural_server |
API calls in the Translation API feature in Systran Pure Neural Server before 9.7.0 allow a threat actor to use the Systran Pure Neural Server as a Denial-of-Service proxy by sending a large amount of translation requests to a destination host on any given TCP port regardless of whether a web service is running on the destination port. |
2020-12-08 |
5 |
CVE-2020-29540
MISC
MISC |
| txjia — imcat |
imcat 5.2 allows an authenticated file upload and consequently remote code execution via the picture functionality. |
2020-12-09 |
6.5 |
CVE-2020-23520
MISC |
| zx2c4 — password-store |
pass through 1.7.3 has a possibility of using a password for an unintended resource. For exploitation to occur, the user must do a git pull, decrypt a password, and log into a remote service with the password. If an attacker controls the central Git server or one of the other members’ machines, and also controls one of the services already in the password store, they can rename one of the password files in the Git repository to something else: pass doesn’t correctly verify that the content of a file matches the filename, so a user might be tricked into decrypting the wrong password and sending that to a service that the attacker controls. NOTE: for environments in which this threat model is of concern, signing commits can be a solution. |
2020-12-09 |
5 |
CVE-2020-28086
MISC |
When adding Microsoft Teams to your SharePoint team site, you can select resources (pages, lists and document libraries) to be added as tabs in the general channel of the newly created Teams team.
The updated SharePoint tab experience when adding pages, lists or document libraries to a channel in Teams.
Choose pages from the connected SharePoint team site or add a page from any SharePoint site (via URL).
Microsoft Teams plus SharePoint = better together.





Recent Comments