by Contributed | Jun 25, 2023 | Technology
This article is contributed. See the original author and article here.
We received some support cases when customers encounter following error “TSQL CRUD has been disallowed via policy for this Azure subscription“ while trying to create or modify of Azure SQL resources through T-SQL.
Cause
This error occurred when Azure Administrator block the T-SQL CRUD operations of Azure SQL resources through T-SQL. This is enforced at the subscription level to block T-SQL commands from affecting SQL resources in any Azure SQL database.
How to enable block T-SQL CRUD
To use this feature “block T-SQL CRUD” operation an Azure user with owner or contributor role is needed, by following the below steps:
- Go to your subscription on Azure portal.
- Select the Preview Features tab.
- Select Block T-SQL CRUD.
- After you select Block T-SQL CRUD, a new window will open, select Register, to register this block with Microsoft.Sql resource provider.

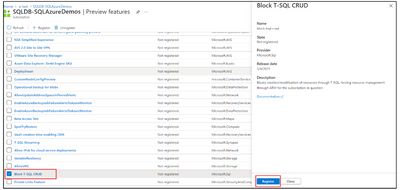
After you register the block of T-SQL CRUD with Microsoft.Sql resource provider, you must re-register the Microsoft.Sql resource provider for the changes to take effect. To re-register the Microsoft.Sql resource provider:
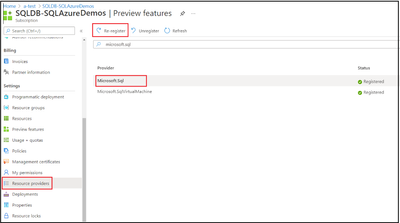
- Go to your subscription on Azure portal.
- Select the Resource Providers tab.
- Search and select Microsoft.Sql resource provider.
- Select Re-register.
Removing Block T-SQL CRUD
To remove the block on T-SQL create or modify operations from your subscription, first unregister the previously registered T-SQL block. Then, re-register the Microsoft.Sql resource provider as shown above for the removal of T-SQL block to take effect.
When to use Block T-SQL CRUD feature
When you are using Azure Policies to enforce organizational standards through ARM templates. Since T-SQL does not adhere to the Azure Policies, a block on T-SQL create or modify operations can be applied. The syntax blocked includes CRUD (create, update, delete) statements for databases in Azure SQL, specifically CREATE DATABASE, ALTER DATABASE, and DROP DATABASE statements.
Blocked statement
- CREATE DATABASE statements
- DROP DATABASE statements
- A subset of ALTER DATABASE statements, as follows:
- ALTER DATABASE … ADD SECONDARY ON SERVER
- ALTER DATABASE … REMOVE SECONDARY ON SERVER
- ALTER DATABASE … FAILOVER
- ALTER DATABASE … MODIFY NAME …
- ALTER DATABASE … MODIFY (MAXSIZE | EDITION | SERVICE_OBJECTIVE …)
- ALTER DATABASE … MODIFY BACKUP_STORAGE_REDUNDANCY …
- ALTER DATABASE … SET ENCRYPTION …
Disclaimer
Please note that the products and options presented in this article are subject to change. This article reflects Block T-SQL CRUD in June 2023. To check for new update or more information please check the below link:
Block T-SQL commands to create or modify Azure SQL resources – Block T-SQL commands to create or modify Azure SQL resources | Microsoft Learn
I hope this article was helpful to you, please feel free to share your feedback in the comments section.
by Contributed | Jun 24, 2023 | Technology
This article is contributed. See the original author and article here.
Azure Portal Admin is a cloud-based management console provided by Microsoft Azure. It is a web-based interface that allows users to manage and monitor their Azure resources and services, configure security settings, and monitor costs. It provides a single, unified view of all Azure resources and services, making it easier to manage and monitor your cloud infrastructure.

Importance of Effective Cloud Management
Effective cloud management is critical for businesses that use cloud computing services. Cloud computing has many benefits, including cost savings, scalability, and flexibility. However, without effective cloud management, these benefits can quickly turn into liabilities. Poorly managed cloud resources can lead to security vulnerabilities, inefficient resource usage, and increased costs.
Overview of the guide
This guide will provide a comprehensive overview of Azure Portal Admin and how to use it for effective cloud management. We will cover everything from setting up your Azure account to managing resources, configuring security, monitoring costs, and best practices for effective cloud management. By the end of this guide, you will have a solid understanding of how to use Azure Portal Admin to manage and monitor your cloud infrastructure effectively.
Setting up Azure Portal Admin
Before you can start using Azure Portal Admin, you need to create an Azure account. You can sign up for a free trial or a paid account, depending on your needs. Once you have an account, you can sign into Azure Portal Admin and start managing your cloud resources.
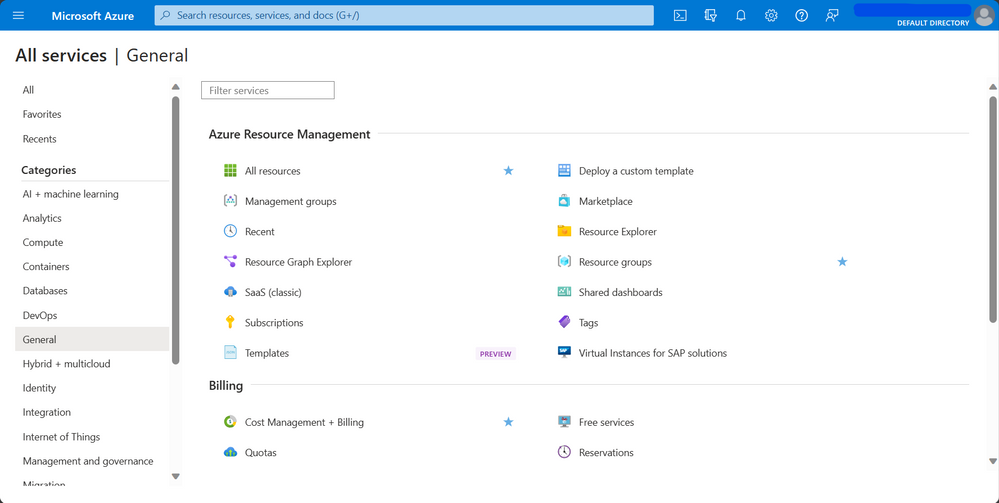
Understanding the Azure Portal Interface
Azure Portal Admin has a web-based interface that provides a single, unified view of all your Azure resources and services. The interface is customizable, allowing you to create dashboards and customize views to suit your needs. You can also use the search bar to quickly find resources and services.
Configuring Azure Services and Resources
Azure Portal Admin allows you to configure and manage a wide range of Azure services and resources, including virtual machines, storage accounts, databases, and more. You can provision and deploy new resources, configure settings, and monitor resource usage.
Managing Access and Permissions
Azure Portal Admin allows you to manage access and permissions for your cloud resources. You can create roles and assign permissions to users and groups, controlling who can access and manage your resources. You can also configure authentication and authorization settings to ensure that only authorized users can access your resources.
In this section, we covered the basics of setting up Azure Portal Admin. By creating an Azure account, understanding the interface, configuring services and resources, and managing access and permissions, you can get started with managing your cloud infrastructure effectively.
Managing Azure Resources
Azure resources are the building blocks of your cloud infrastructure. They include virtual machines, storage accounts, databases, networking resources, and more. Managing Azure resources effectively is critical for ensuring that your cloud infrastructure is running smoothly and efficiently.
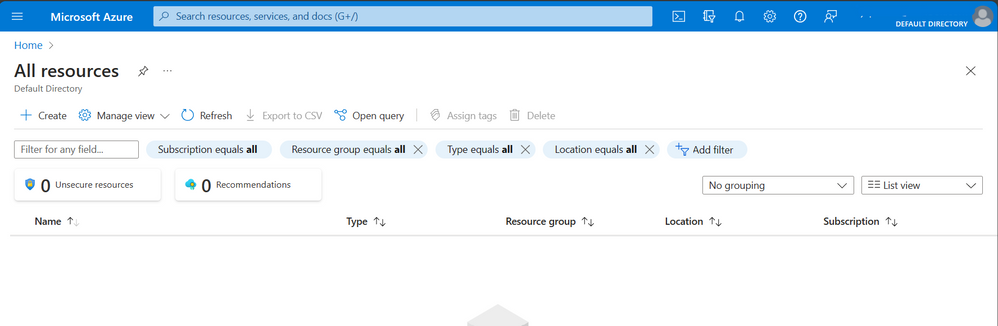
Provisioning and Deploying Azure Resources
Provisioning and deploying Azure resources involves creating and configuring resources to meet your specific needs. Azure Portal Admin provides a simple, user-friendly interface for provisioning and deploying resources. You can choose from a wide range of pre-configured templates or create your own custom templates.
Monitoring and Optimizing Resource Performance
Monitoring resource performance is essential for ensuring that your cloud infrastructure is running efficiently. Azure Portal Admin allows you to monitor resource usages and performance metrics, such as CPU usage, memory usage, and network bandwidth. You can also set up alerts to notify you when resources reach certain thresholds.
Optimizing resource performance involves identifying and addressing performance bottlenecks. Azure Portal Admin provides tools for identifying and resolving performance issues, such as scaling resources, optimizing storage, and tuning database performance.
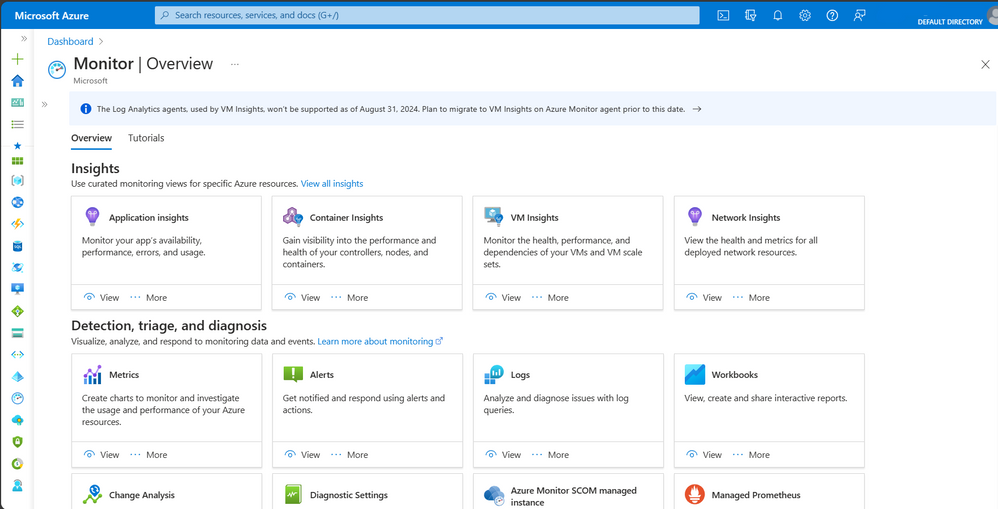
Scaling Azure Resources
Scaling resources involves adjusting resource capacity to meet changing demand. Azure Portal Admin allows you to scale resources up or down, depending on your needs. You can also configure autoscaling to automatically adjust resource capacity based on predefined rules.
In this section, we covered the basics of managing Azure resources. By provisioning and deploying resources, monitoring, and optimizing performance, and scaling resources, you can ensure that your cloud infrastructure is running smoothly and efficiently.
Security and Compliance – Understanding Azure Security
Security is a top concern for businesses using cloud computing services. Azure provides a wide range of security features and tools to help you secure your cloud infrastructure. Azure Portal Admin allows you to configure and manage security settings for your resources and services.
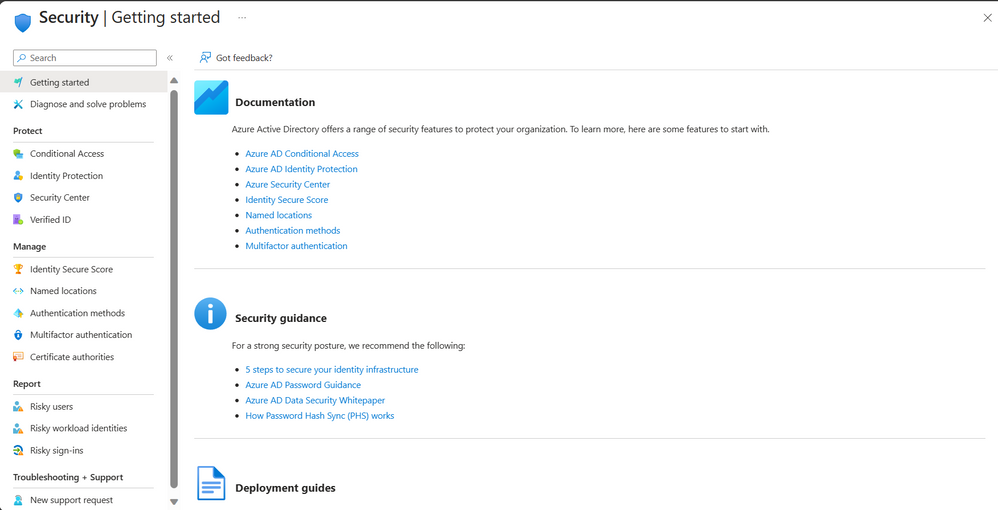
Configuring Azure Security Features
Azure Portal Admin provides a range of security features that you can configure to secure your resources and services. These include network security groups, virtual network security, firewall rules, access control lists, and more. You can also configure identity and access management settings, such as single sign-on and multifactor authentication.
Managing Azure Security Risks
Managing security risks involves identifying and addressing security vulnerabilities and threats. Azure Portal Admin provides tools for identifying and mitigating security risks, such as security centers, threat protection, and vulnerability assessment. You can also configure alerts to notify you when security risks are detected.
Compliance Considerations for Azure
Compliance is a critical consideration for businesses that store and process sensitive data in the cloud. Azure Portal Admin provides tools for ensuring compliance with a range of regulations and standards, such as HIPAA, PCI DSS, and GDPR. You can configure compliance settings and monitor compliance status using Azure Portal Admin.
In this section, we covered the basics of security and compliance in Azure. By understanding Azure security features, configuring security settings, managing security risks, and ensuring compliance, you can secure your cloud infrastructure and protect sensitive data.
Cost Management – Understanding Azure Pricing
Understanding Azure pricing is essential for effective cost management. Azure offers a range of pricing models, such as pay-as-you-go, reserved instances, and spot instances. Azure Portal Admin provides tools for estimating and optimizing costs based on your usage and needs.
Managing Azure Costs
Managing Azure costs involves monitoring and controlling your cloud spending. Azure Portal Admin provides tools for managing costs, such as cost analysis, budget alerts, and cost allocation. You can also use Azure Advisor to identify cost-saving opportunities.
Cost Optimization Strategies
Cost optimization involves reducing costs without sacrificing performance or functionality. Azure Portal Admin provides tools for optimizing costs, such as resource tagging, resource consolidation, and resource deletion. You can also use Azure Cost Management to identify areas where you can reduce costs.
Monitoring and Tracking Azure Spending
Monitoring and tracking your Azure spending is essential for ensuring that you stay within your budget. Azure Portal Admin provides tools for monitoring and tracking spendings, such as cost analysis and spending reports. You can also set up alerts to notify you when you approach or exceed your budget.
In this section, we covered the basics of cost management in Azure. By understanding Azure pricing, managing costs, optimizing costs, and monitoring and tracking spending, you can ensure that you are using Azure in a cost-effective way that aligns with your business needs and goals.
Best Practices for Azure Portal Admin – Tips for effective cloud management
Effective cloud management involves adopting best practices that help you get the most out of your Azure infrastructure. Some tips for effective cloud management include implementing automation, using templates and scripts, monitoring performance and availability, and establishing clear governance policies.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
There are also common mistakes that you should avoid when managing Azure infrastructure. These include:
- Failing to properly configure security settings,
- Not monitoring and optimizing costs,
- Not keeping software and infrastructure up to date, and
- Failing to establish clear governance policies.
Conclusion
In this guide, we covered the basics of Azure Portal Admin and effective cloud management. We explored how to set up Azure Portal Admin, manage Azure resources, ensure security and compliance, manage costs, and adopt best practices for effective cloud management.
Effective cloud management is essential for ensuring that your cloud infrastructure is secure, optimized, and cost-effective. By implementing the strategies and best practices covered in this guide, you can effectively manage your Azure infrastructure and achieve your business goals.
As technology continues to evolve, cloud computing will continue to play an increasingly important role in businesses of all sizes. By mastering Azure Portal Admin and effective cloud management, you can stay ahead of the curve and position your business for success in the digital age. Remember to continue learning and staying up to date with the latest developments in cloud computing, and don’t hesitate to seek out help and resources when needed.
Thank you for reading this comprehensive guide on mastering Azure Portal Admin and effective cloud management. We hope that you found it informative and useful in your journey toward becoming a cloud management expert.
Resources for Ongoing Learning
Learning is an ongoing process, and there are many resources available to help you deepen your knowledge of Azure and cloud computing. Some resources for ongoing learning include:
by Contributed | Jun 22, 2023 | Technology
This article is contributed. See the original author and article here.
Introduction
Azure OpenAI models provide a secure and robust solution for tasks like creating content, summarizing information, and various other applications that involve working with human language. Now you can operate these models in the context of your own data. Try Azure OpenAI Studio today to naturally interact with your data and publish it as an app from from within the studio.
Getting Started
Follow this quickstart tutorial for pre-requisites and setting up your Azure OpenAI environment.
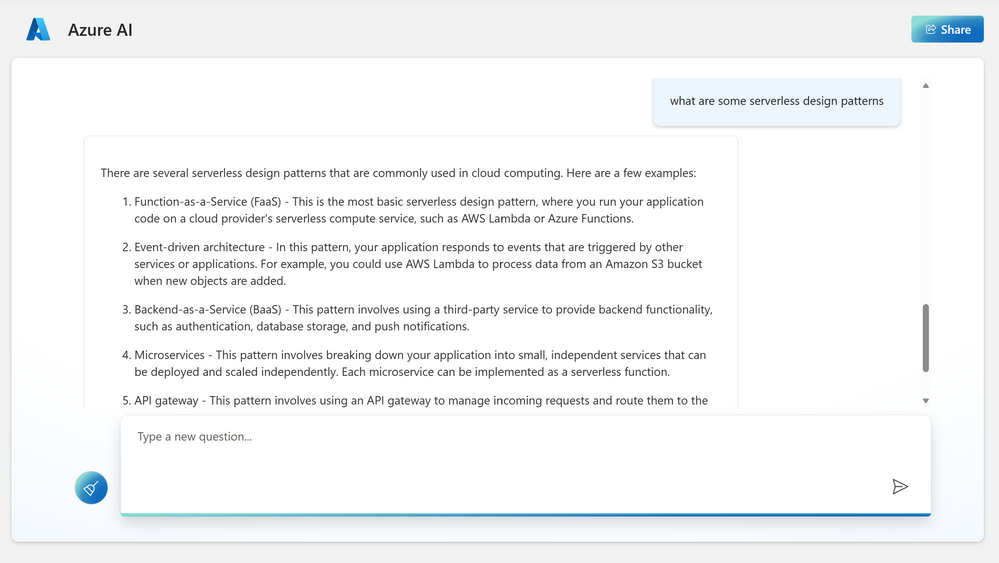
In order to try the capabilities of the Azure OpenAI model on private data, I am uploading an ebook to the Azure OpenAI chat model. This e-book is about “Serverless Apps: Architecture, patterns and Azure Implementation” written by Jeremy Likness and Cecil Phillip. You can download the e-book here
Before uploading own data
Prior to uploading this particular e-book, the model’s response to the question on serverless design patterns is depicted below. While this response is relevant, let’s examine if the model is able to pick up the e-book related content during the next iteration

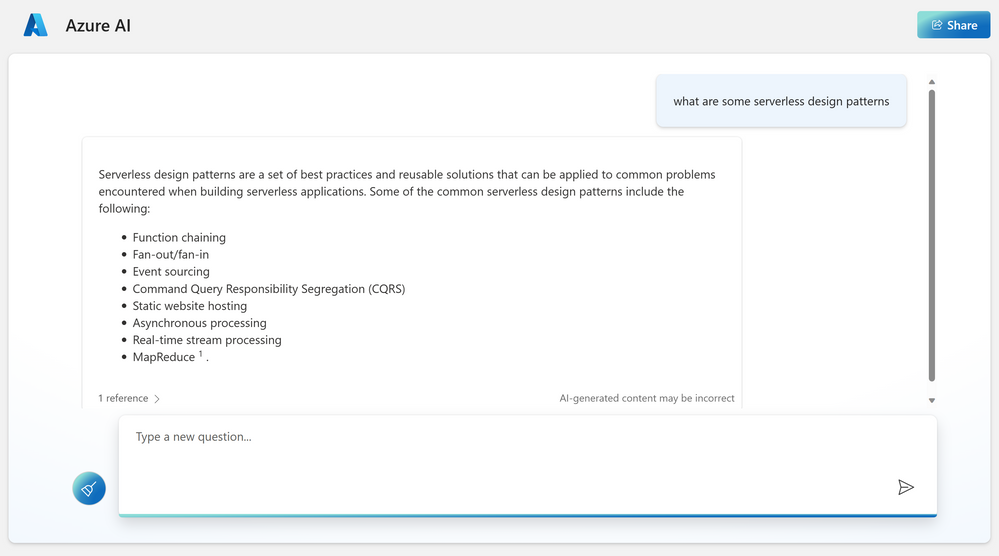
After uploading own data
This e-book has an exclusive section that talks in detail about different design patterns like Scheduling, CQRS, Event based processing etc.

After training the model on this PDF data, I asked a few questions and the following responses were nearly accurate. I also limited the model to only supply the information from the uploaded content. Here’s what I found.
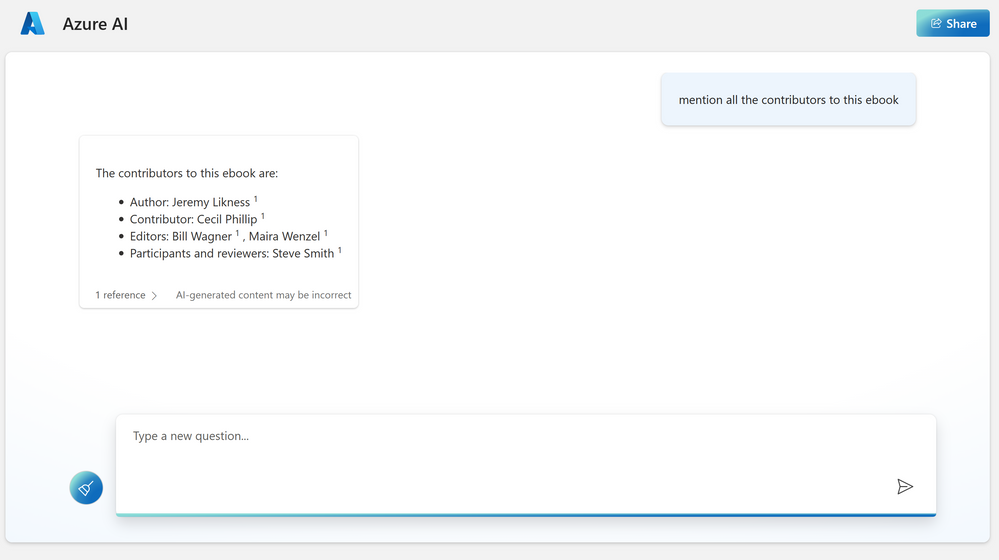
Now when I asked about the contributors to this e-book, it listed everyone right.
Read more
With enterprise data ranging to large volumes in size, it is not practical to supply them in the context of a prompt to these models. Therefore, the setup leverages Azure services to create a repository of your knowledge base and utilize Azure OpenAI models to interact naturally with them.
The Azure OpenAI Service on your own data uses Azure Cognitive Search service in the background to rank and index your custom data and utilizes a storage account to host your content (.txt, .md, .html, .pdf, .docx, .pptx). Your data source is used to help ground the model with specific data. You can select an existing Azure Cognitive Search index, Azure Storage container, or upload local files as the source we will build the grounding data from. Your data is stored securely in your Azure subscription.
We also have another Enterprise GPT demo that allows you to piece all the azure building blocks yourself. An in-depth blog written by Pablo Castro chalks the detail steps here.
Getting started directly from Azure OpenAI studio allows you to iterate on your ideas quickly. At the time of writing this blog, the completions playground allow 23 different use cases that take advantage of different models under Azure OpenAI.
- Summarize issue resolution from conversation
- Summarize key points from financial report (extractive )
- Summarize an article (abstractive)
- Generate product name ideas
- Generate an email
- Generate a product description (bullet points)
- Generate a listicle-style blog
- Generate a job description
- Generate a quiz
- Classify Text
- Classify and detect intent
- Cluster into undefined categories
- Analyze sentiment with aspects
- Extract entities from text
- Parse unstructured data
- Translate text
- Natural Language to SQL
- Natural language to Python
- Explain a SQL query
- Question answering
- Generate insights
- Chain of thought reasoning
- Chatbot
Resources
There are different resources to get you started on Azure OpenAI. Here’s a few:
by Contributed | Jun 21, 2023 | Technology
This article is contributed. See the original author and article here.
Introduction
Did you know that you can use Microsoft Fabric to copy data at scale from on-premises SQL Server to Azure SQL Database or Azure SQL Managed Instance within minutes?
It is often required to copy data from on-premises to Azure SQL database, Azure SQL Managed Instance or to any other data store for data analytics purposes. You may simply want to migrate data from on-premises data sources to Azure Database Services. You will most likely want to be able to do this data movement at scale, with minimal coding and complexity and require an automated and simple approach to handle such scenarios.
In the following example, I am copying 2 tables from an On-premises SQL Server 2019 database to Azure SQL Database using Microsoft Fabric. The entire migration is driven through a metadata table approach, so the copy pipeline is simple and easy to deploy. We have used this approach to copy hundreds of tables from one database to another efficiently. The monitoring UI provides flexibility and convenience to track the progress and rerun the data migration in case of any failures. The entire migration is driven using a database table that holds the information about the tables to copy from the source.
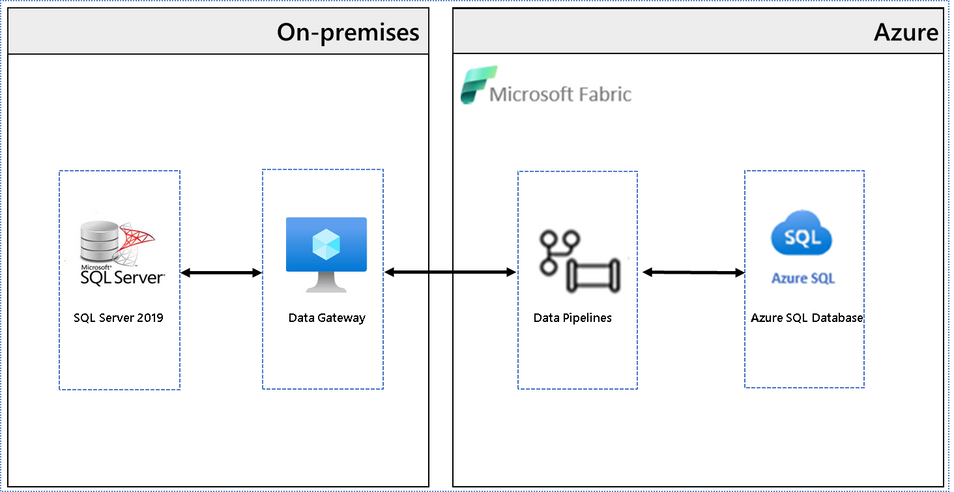
Architecture diagram
This architectural diagram shows the components of the solution from SQL Server on-premises to Microsoft Fabric.

Steps
Install data gateway:
To connect to an on-premises data source from Microsoft Fabric, a data gateway needs to be installed. Use this link to install an on-premises data gateway | Microsoft Learn
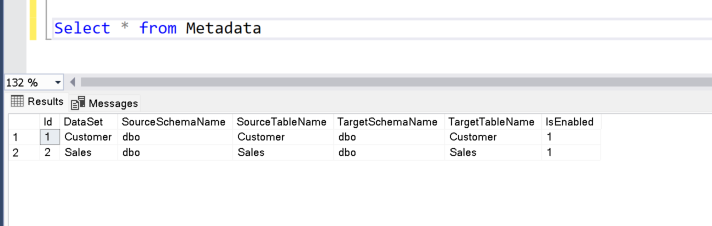
Create a table to hold metadata information:
First, let us create this table in the target Azure SQL Database.
CREATE TABLE [dbo].[Metadata](
[Id] [int] IDENTITY(1,1) NOT NULL,
[DataSet] [nvarchar](255) NULL,
[SourceSchemaName] [nvarchar](255) NULL,
[SourceTableName] [nvarchar](255) NULL,
[TargetSchemaName] [nvarchar](255) NULL,
[TargetTableName] [nvarchar](255) NULL,
[IsEnabled] [bit] NULL
)
I intend to copy two tables – Customer and Sales – from the source to the target. Let us insert these entries into the metadata table. Insert one row per table.
INSERT [dbo].[Metadata] ([DataSet], [SourceSchemaName], [SourceTableName], [TargetSchemaName], [TargetTableName], [IsEnabled]) VALUES (N'Customer', N'dbo', N'Customer', N'dbo', N'Customer', 1);
INSERT [dbo].[Metadata] ([DataSet], [SourceSchemaName], [SourceTableName], [TargetSchemaName], [TargetTableName], [IsEnabled]) VALUES (N'Sales', N'dbo', N'Sales', N'dbo', N'Sales', 1);
Ensure that the table is populated. The data pipelines will use this table to drive the migration.
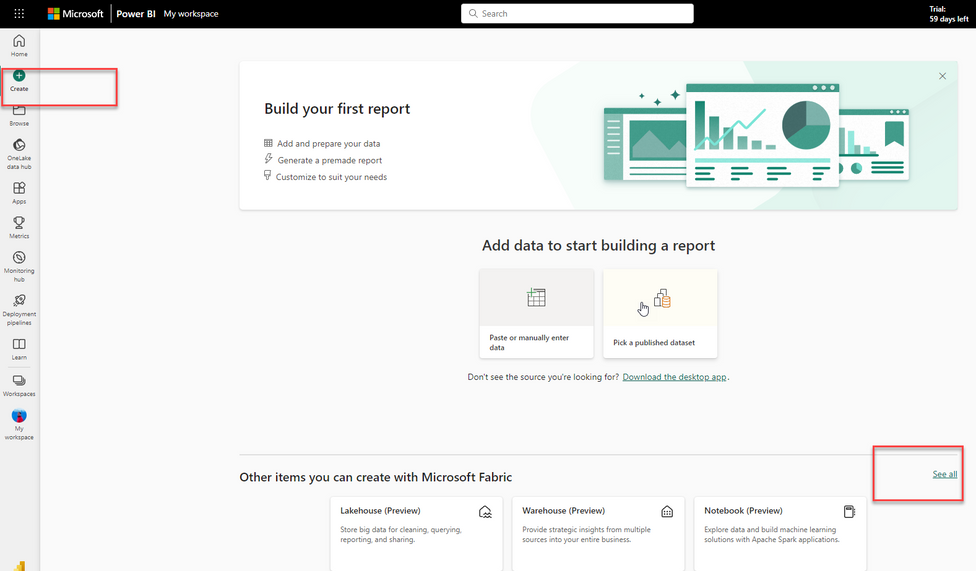
Create Data Pipelines:
Open Microsoft Fabric and click create button to see the items you can create with Microsoft Fabric.
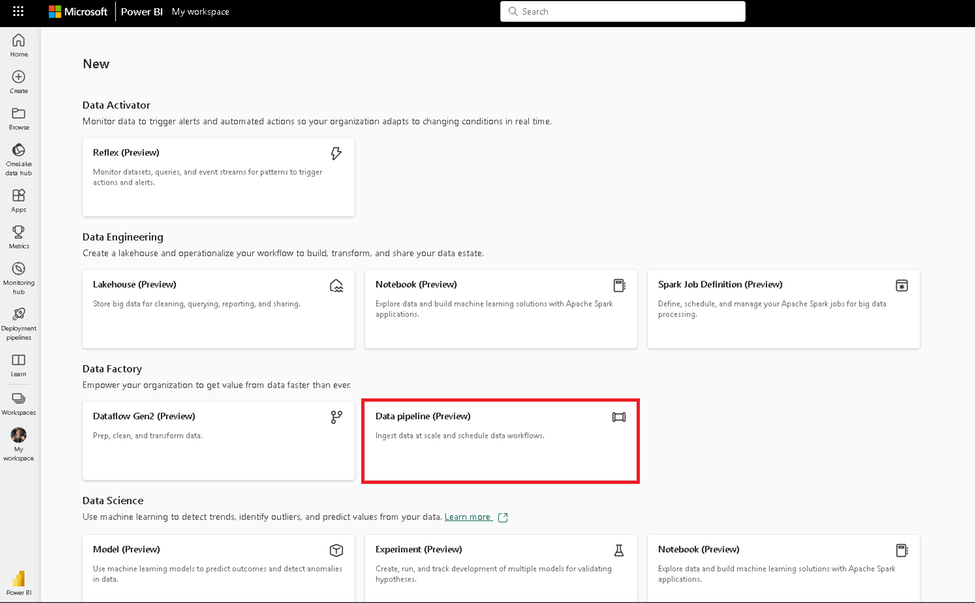
Click on “Data pipeline” to start creating a new data pipeline.
Let us name the pipeline “Copy_Multiple_Tables”.
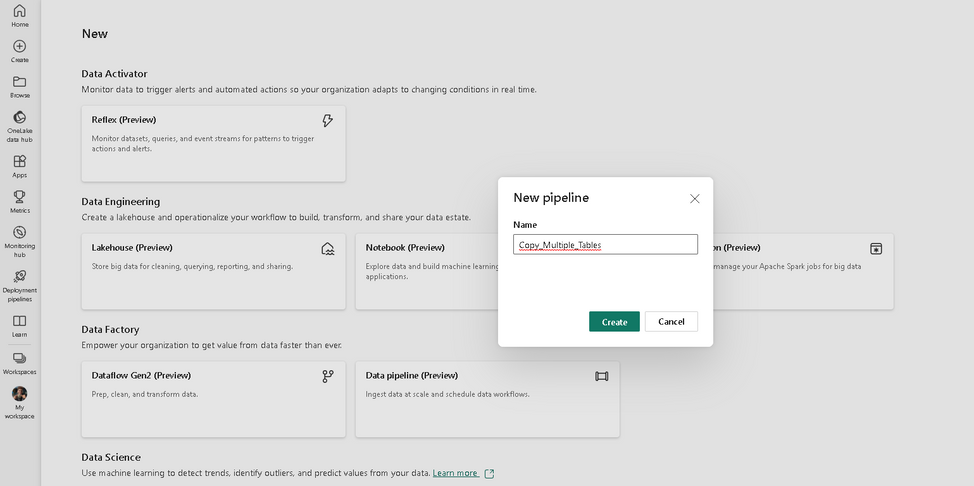
Click on “Add pipeline activity” to add a new activity.
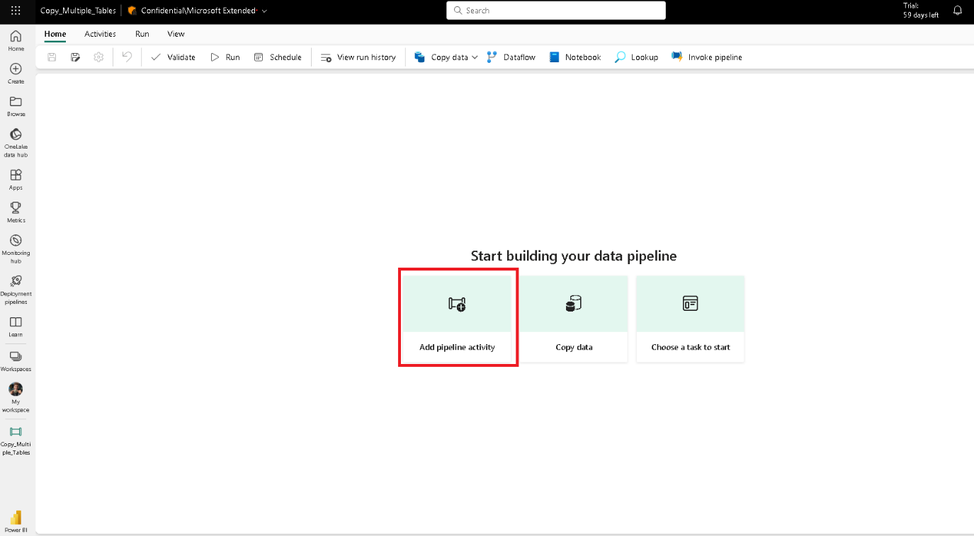
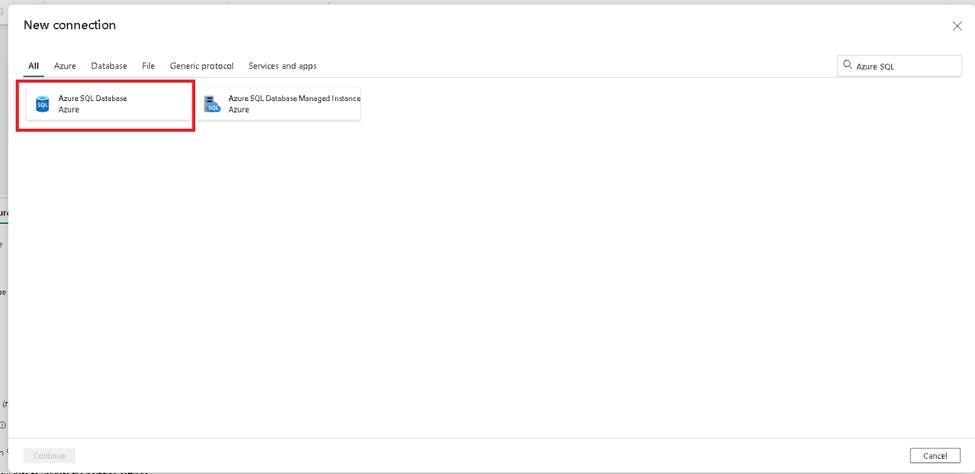
Choose Azure SQL Database from the list. We will create the table to hold metadata in the target.
Ensure that the settings are as shown in the screenshot.
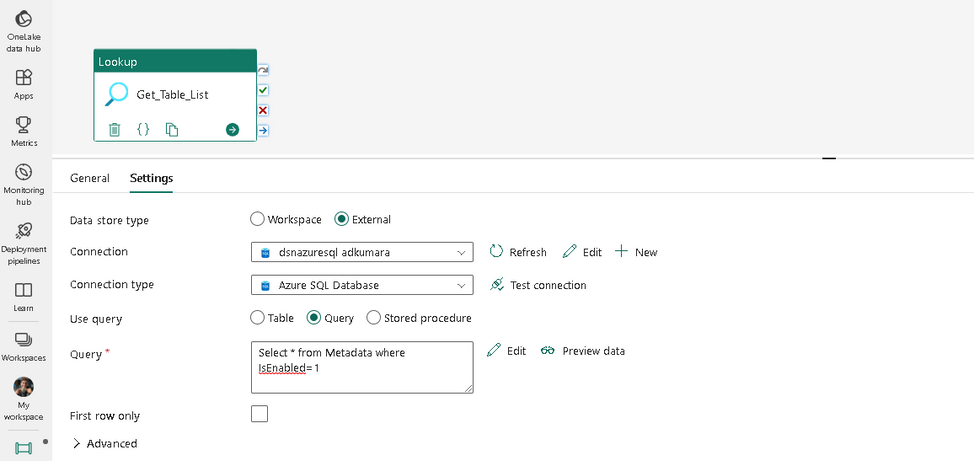
Click the preview data button and check if you can view the data from the table.
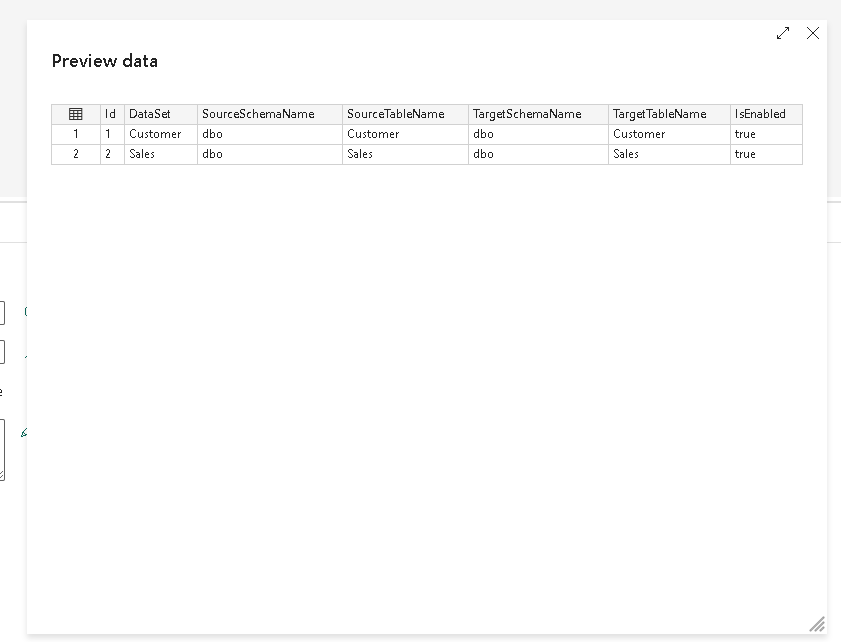
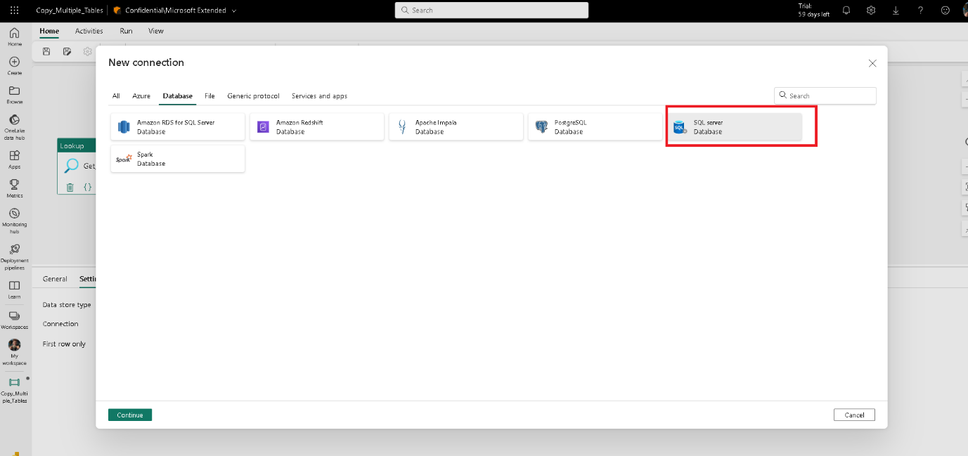
Let us now create a new connection to the source. From the list of available connections, choose SQL Server, as we intend to copy data from SQL Server 2019 on-premises. Ensure that the gateway cluster and connection are already configured and available.
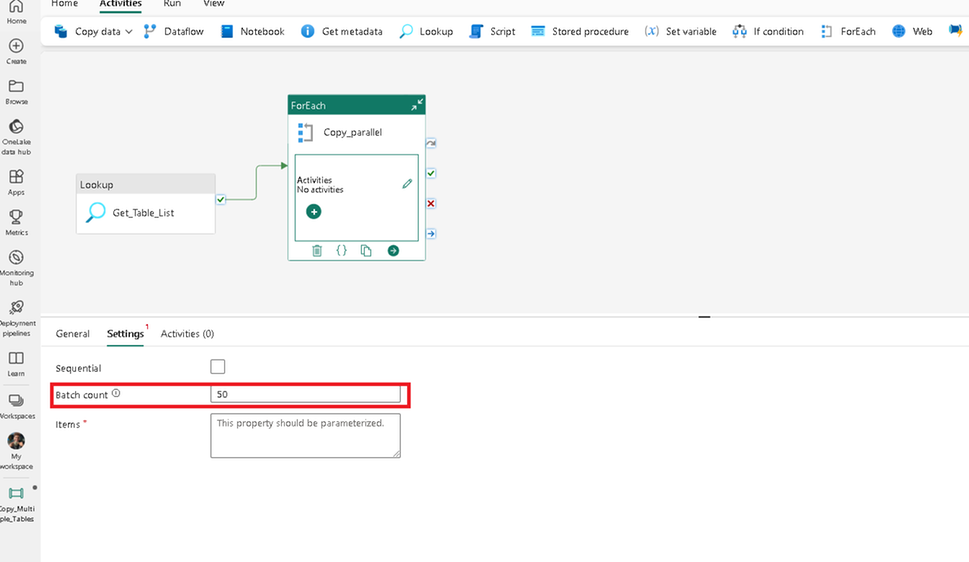
Add a new activity and set the batch count to copy tables in parallel.
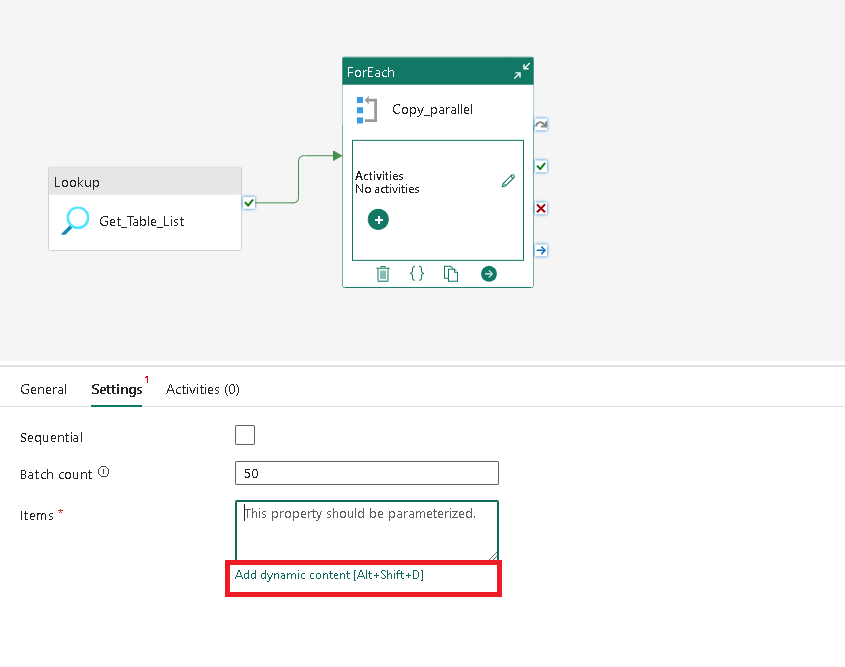
We now need to set the Items property, which is dynamically populated at runtime. To set this click on this button as shown in the screenshot and set the value as:
@activity('Get_Table_List').output.value
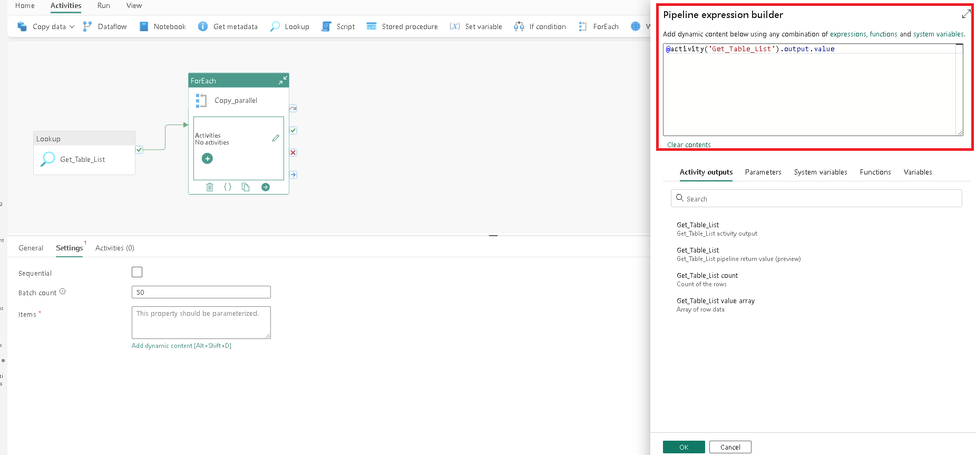
Add a copy activity to the activity container.
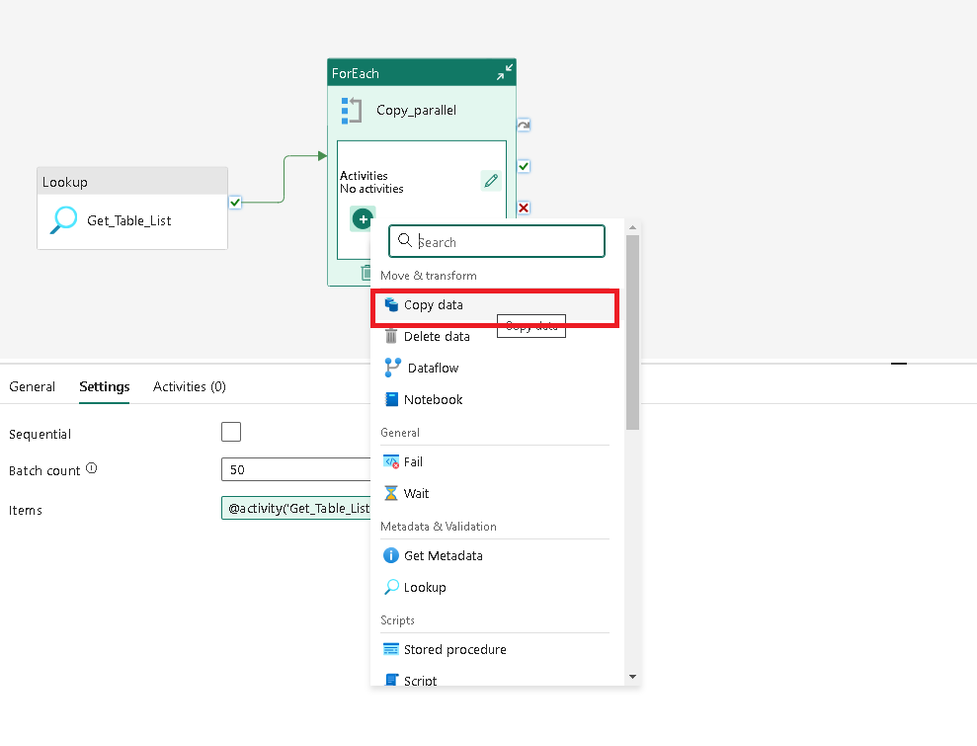
Set the source Table attributes in the copy activity as shown in the screenshot. Click on the edit button and click the “Add dynamic content” button. Ensure that you paste the text only after you click the “Add dynamic content” button, otherwise, the text will not render dynamically during runtime.
Set the Table schema name to:
@item().SourceSchemaName
Set the Table name to:
@item().SourceTableName
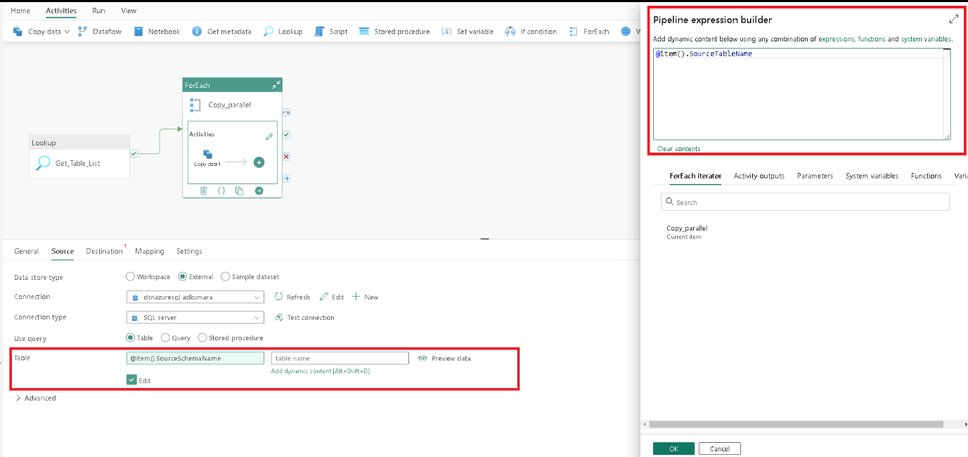
Click on the destination tab and set the destination attributes as in the screenshot.
Set the Table schema name to:
@item().TargetSchemaName
Set the Table name to:
@item().TargetTableName
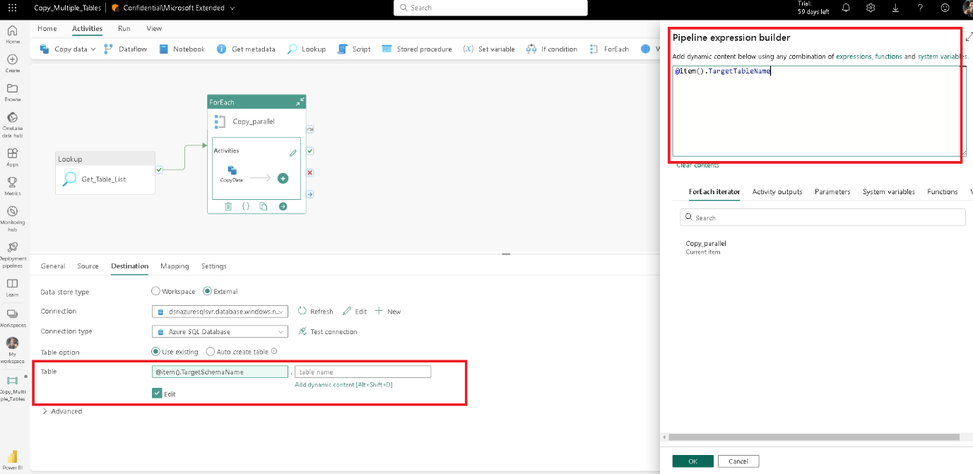
We have configured the pipeline. Now click on save to publish the pipeline.
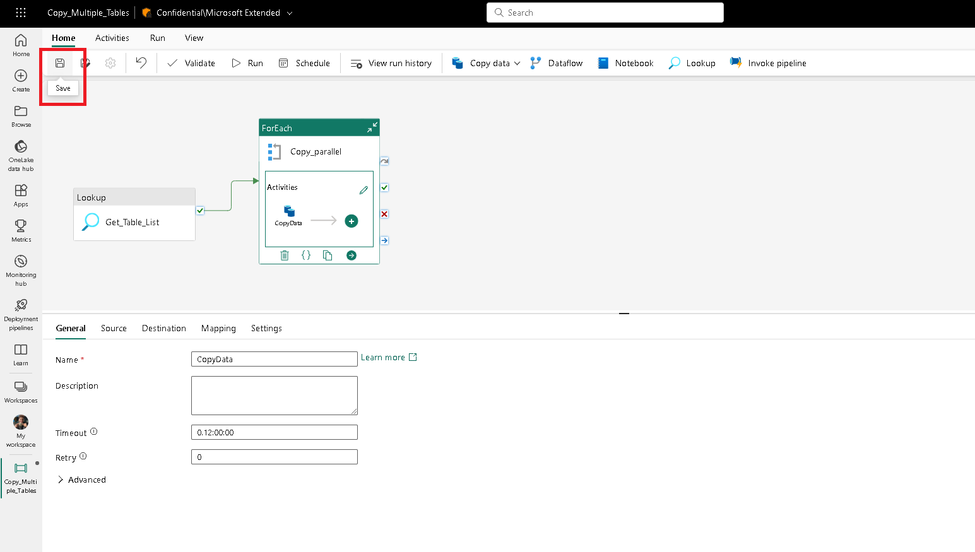
Run pipeline:
Click the Run button from the top menu to execute the pipeline. Ensure the pipeline runs successfully. This will copy both tables from source to target.
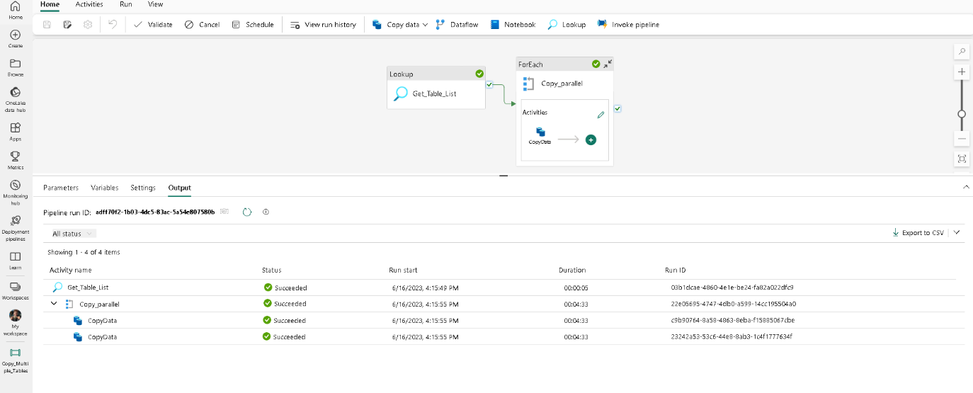
Summary:
In the above example, we have used Microsoft Fabric pipelines to copy data from an on-premises SQL Server 2019 database to Azure SQL Database. You can modify the sink/destination in this pipeline to copy to other sources such as Azure SQL Managed Instance or Azure Database for PostgreSQL. If you are interested in copying data from a mainframe z/OS database, then you will find this blog post from our team also very helpful.
Feedback and suggestions
If you have feedback or suggestions for improving this data migration asset, please contact the Azure Databases SQL Customer Success Engineering Team. Thanks for your support!
Note: For additional information about migrating various source databases to Azure, see the Azure Database Migration Guide.


Recent Comments