
by Contributed | Apr 14, 2023 | Technology
This article is contributed. See the original author and article here.

Migrating databases. When your databases anchor applications, employees, and customers, migration plunks a big rock in the pond that is your business, creating lasting ripples. Ripples that force thoughtful, coordinated action across business units to prevent outages. Add moving to the cloud into the equation and the potential tide of complications rises.
In the past, undertaking migration often required you to refactor your databases to make them compatible with cloud database servers. Security policies needed thorough analysis and updating for cloud models. Factor in potential downtimes, and migration once loomed as a labor-intensive hit to business productivity. This made migrating an on-premises SQL Server to the cloud an ROI evaluation against the once heavy-lift tradeoffs required by moving to the cloud.
Azure SQL Managed Instance eliminates these tradeoffs with the broadest SQL Server engine compatibility offering available. Because of the compatibility level, Azure SQL Managed Instance doesn’t require you to compromise much, if anything, to deploy SQL Server within a fully managed aPlatform as a Service (PaaS) environment. Because the SQL Server 2022 Enterprise Edition and Azure SQL Managed Instance engines are almost one hundred percent identical, making it possible to migrate both ways. You don’t need to refactor databases or risk negative performance impacts to migrate to Azure SQL Managed Instance. Azure SQL Managed Instance is also compatible with earlier SQL Server editions.
Additionally, the storage engine format alignment between Azure SQL Managed Instance and SQL Server 2022 provides an easy way to copy or move databases from Azure SQL Managed Instance to a SQL Server 2022 instance. A back up from Azure SQL Managed Instance can be restored on SQL Server 2022. The standalone SQL Server can be hosted on-premises, on virtual machines in Azure, or in other clouds. This puts you in control of your data, ensuring data mobility regardless of SQL Server location.
Compatibility between the Azure SQL Managed Instance and SQL Server 2022 engines extends to the database engine settings and the database settings. As with the standalone version of SQL Server, with Azure SQL Managed Instance, you decide what server configuration best serves your business needs. To get started with Azure SQL Managed Instance, you choose the performance tier, service tier, and the reserved compute, along with data and backup storage options, that make the most sense for your applications and your data.
Since Azure SQL Managed Instance is built on the latest SQL Server engine, it’s always up to date with the latest features and functionality, including online operations, automatic plan corrections, and other enterprise performance enhancements. A comparison of the available features is explained in Feature comparison: Azure SQL Managed Instance versus SQL Server.
Azure SQL Managed Instance offers two performance tiers:
- General purpose - for applications with typical performance, I/O latency requirements, and built-in High Availability (HA).
- Business Critical - for applications requiring low I/O latency and higher HA requirements. It provides two non-readable secondaries and one readable secondary along with the readable/writable primary replica. The readable secondary allows you to distribute reporting workloads off your primary.
Once you’re running on Azure SQL Managed Instance, changing your service tier (CPU vCores or reserved storage changes) occurs online and incurs little to no downtime. To optimize performance of transaction processing, data ingestion, data load, and transient data, leverage In-Memory OLTP, available in the Business Critical tier.
Migrate from your on-premises SQL Server to Azure SQL Managed Instance with ease. Leverage the fully automated Azure Data Migration Service or set up an Azure SQL Managed Instance link. The link feature uses an expanded version of distributed availability groups to extend your on-prem SQL Server availability group to Azure SQL Managed Instance safely, replicating data in near real-time. With Azure SQL Managed Instance link feature, you can migrate, test, and then perform a simple, controlled fail-over.
While Azure SQL Managed Instance provides nearly one hundred percent compatibility with SQL Server, you will notice some changes in the transition from SQL Server standalone editions. These differences are based on architectural dissimilarities. Certain SQL features (audits, for instance) operate in a fashion that optimizes cloud architecture. Cloud architecture is designed to maximize resource utilization and minimize costs while ensuring high levels of availability, reliability, and security. Azure architecture leverages resource sharing while guaranteeing security and isolation. This resource sharing provides you with a flexible environment that can scale rapidly in response to customer needs. Because high availability is built into Azure SQL Managed Instance, it cannot be configured or controlled by users as it can be in SQL Server 2022.
Explore the differences between SQL Server 2022 Enterprise Edition and Azure SQL Managed Instance.
What’s more, Azure SQL Managed Instance is backed by Intel® Xeon® Scalable processors, ensuring that your environment is performant and secure from the silicon layer. With 8 to 40 powerful cores and a wide range of frequency, feature, and power levels Intel® Xeon® Scalable processors are a part of an end-to-end solution for your data.
Come delve into Azure SQL Server Managed Instance. The depth and breadth of SQL engine compatibility provides you with a safe, simple, full-featured, and flexible migration path. Azure SQL Managed Instance puts you in complete control of your data, your databases, your performance, and your business. Microsoft’s continued commitment to improvement means you can take advantage of the benefits of the cloud with Azure SQL Managed Instance and modernize your on-premises SQL Server databases.
Dive deeper into the benefits of migrating to Azure SQL Managed Instance. Check out the on-demand recording: https://www.mssqltips.com/sql-server-video/932/modernize-your-apps-with-azure-sql-managed-instance/Modernize Your Apps with Azure SQL Managed Instance.
by Contributed | Apr 13, 2023 | Technology
This article is contributed. See the original author and article here.
Modern applications require the capability to retrieve modified data from a database in real time to operate effectively. Usually, developers need to create a customized tracking mechanism in their applications, utilizing triggers, timestamp columns, and supplementary tables, to identify changes in data. The development of such applications typically requires significant effort and can result in schema updates resulting in considerable performance overhead.
Real-time data processing is a crucial aspect of nearly every modern data warehouse project. However, one of the biggest hurdles to overcome in real-time processing solutions is the ability to ingest efficiently and effectively, process, and store messages in real-time, particularly when dealing with high volumes of data. To ensure optimal performance, processing must be conducted in a manner that does not interfere with the ingestion pipeline. In addition to non-blocking processing, the data store must be capable of handling high-volume writes. Further challenges such as the ability to quickly act on the data, generating real-time alerts or business needs where dashboard that needs to be updated in real-time or near real-time. In many cases, the source systems utilize traditional relational database engines, such as MySQL, that do not offer event-based interfaces.
In this series of blog posts, we will introduce an alternative solution that utilizes an open-source tool Debezium to perform Change Data Capture (CDC) from Azure Database for MySQL – Flexible Server with Apache Kafka writes these changes to the Azure Event Hub, Azure Stream Analytics perform real time analytics on the data stream and then write to Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2 for long-term storage and further analysis using Azure Synapse serverless SQL pools and provide insights through Power BI.
Azure Database for MySQL – Flexible Server is a cloud-based solution that provides a fully managed MySQL database service. This service is built on top of Azure’s infrastructure and offers greater flexibility. MySQL uses binary log (binlog) to record all the transactions in the order in which they are committed on the database. This includes changes to table schemas as well as changes to the rows in the tables. MySQL uses binlog mainly for purposes of replication and recovery.
Debezium is a powerful CDC (Change Data Capture) tool that is built on top of Kafka Connect. It is designed to stream the binlog, produces change events for row-level INSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE operations in real-time from MySQL into Kafka topics, leveraging the capabilities of Kafka Connect. This allows users to efficiently query only the changes from the last synchronization and upload those changes to the cloud. After this data is stored in Azure Data Lake storage, it can be processed using Azure Synapse Serverless SQL Pools. Business users can then monitor, analyse, and visualize the data using Power BI.
Solution overview
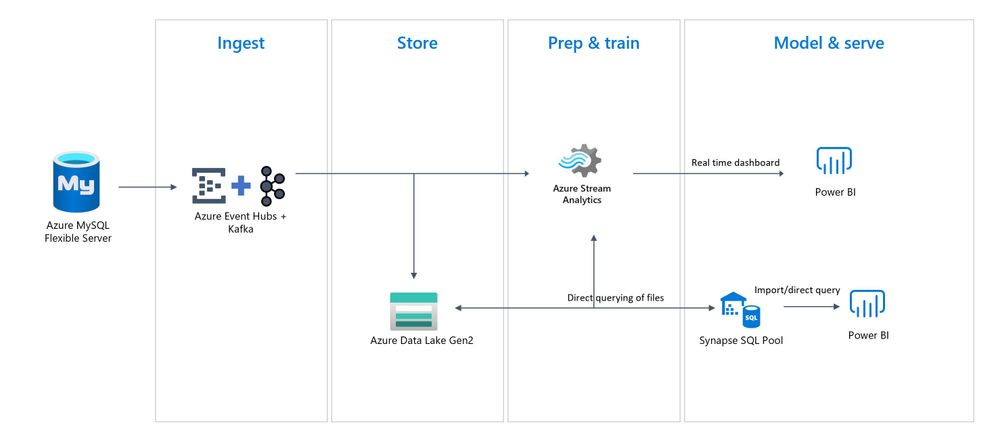
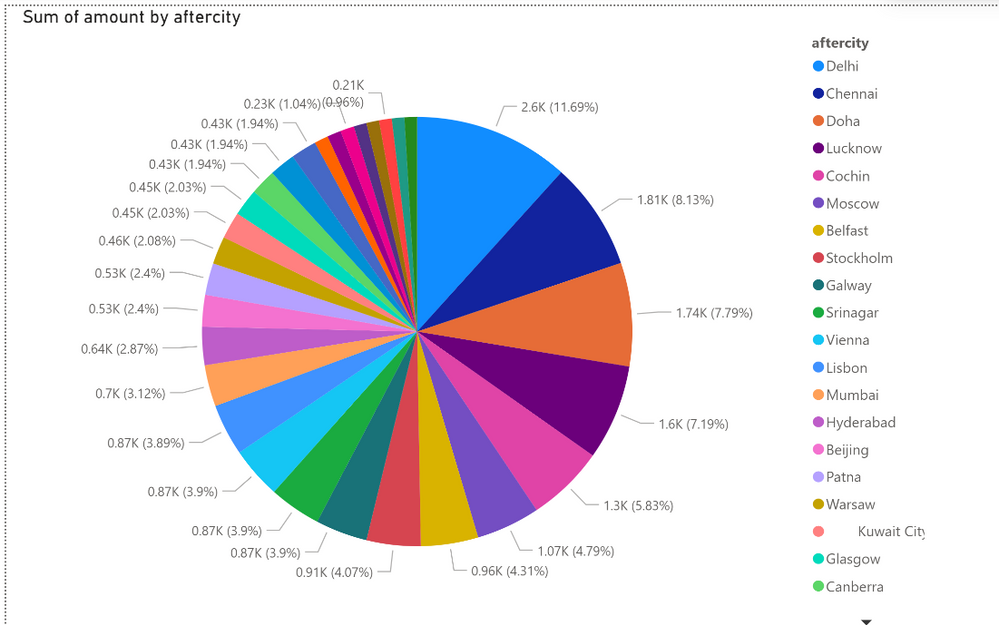
This solution entails ingesting MySQL data changes from the binary logs and converting the changed rows into JSON messages, which are subsequently sent to Azure Event Hub. After the messages are received by the Event Hub, an Azure Stream Analytics (ASA) Job distributes the changes into multiple outputs, as shown in the following diagram.

End-to-end serverless streaming platform with Azure Event Hubs for data ingestion
Components and Services involved
In this blog post, following are the services used for streaming the changes from Azure Database for MySQL to Power BI.
- A Microsoft Azure account
- An Azure Database for MySQL Flexible server
- A Virtual Machine running Linux version 20.04
- Kafka release (version 1.1.1, Scala version 2.11), available from kafka.apache.org
- Debezium 1.6.2
- An Event Hubs namespace
- Azure Stream Analytics
- Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2
- Azure Synapse Serverless SQL pools
- A Power BI workspace
Dataflow
The following steps outline the process to set up the components involved in this architecture to stream data in real time from the source Azure Database for MySQL flexible Server.
- Provisioning and configuring Azure Database for MYSQL- Flexible Server & a Virtual Machine
- Configure and run Kafka Connect with a Debezium MySQL connector
- Reading CDC Messages Downstream from Azure Event Hub and capture data in an Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2 account in Parquet format
- Create External Table with Azure Synapse Serverless SQL Pool
- Use Serverless SQL pool with Power BI Desktop & create a report.
- Build real-time dashboard with Power BI dataset produced from Stream Analytics
Each of the above steps is outlined in detail in the upcoming sections.
Prerequisites
Provisioning and configuring Azure Database for MYSQL- Flexible Server & a Virtual Machine
It is important to create an Azure Database for MySQL Flexible Server instance and a Virtual Machine as outlined below before proceeding to the next step. To do so, perform the following steps:
- Create an instance of Azure Database for MySQL – Flexible Server
- Under server parameters blade, configure binlog_expire_logs_seconds parameter, as per your requirements (e.g.: 86400 seconds for 24Hrs) on the server to make sure that binlogs are not purged quickly. For more information, see How to Configure server parameters.
- Under the same server parameter blade, also configure and set binlog_row_image parameter to a value of FULL.
- Use a command line client or download and install MySQL Workbench or another third-party MySQL client tool to connect to the Azure Database for MySQL Flexible Server.
- Create an Azure VM in the same resource group running Linux version 20.04.
- Maintain enough disk space on the Azure VM to copy binary logs remotely.
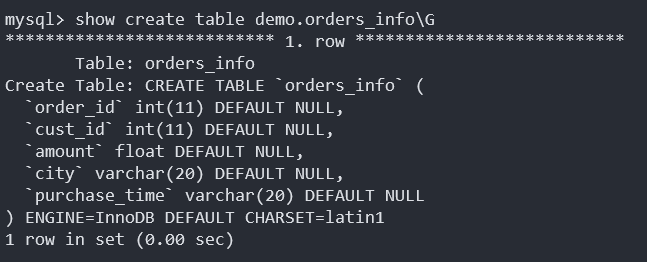
- For this example, the “orders_info” table has been created in Azure Database for MySQL Flexible Server
Configure and run Kafka Connect with a Debezium MySQL connector
To track row-level changes in response to insert, update and delete operations in database tables, Change Data Capture (CDC) is a technique that you use to track these changes, Debezium is a distributed platform that provides a set of Kafka Connect connectors that can convert these changes into event streams and send those events to Apache Kafka.
To set up Debezium & Kafka on a Linux Virtual Machine follow the steps outlined in: CDC in Azure Database for MySQL – Flexible Server using Kafka, Debezium, and Azure Event Hubs – Microsoft Community Hub
Reading CDC Messages Downstream from Event Hub and capture data in an Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2 account in Parquet format
Azure Event Hubs is a fully managed Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS) Data streaming and Event Ingestion platform, capable of processing millions of events per second. Event Hubs can process, and store events, data, or telemetry produced by distributed software and devices. Data sent to an event hub can be transformed and stored by using any real-time analytics provider or batching/storage adapters. Azure Events Hubs provides an Apache Kafka endpoint on an event hub, which enables users to connect to the event hub using the Kafka protocol.
Configure a job to capture data
Use the following steps to configure a Stream Analytics job to capture data in Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2.
- In the Azure portal, navigate to your event hub.
- Select the event hub created for the “orders_info” table.
- Select Features > Process Data, and then select Start on the Capture data to ADLS Gen2 in Parquet format card.
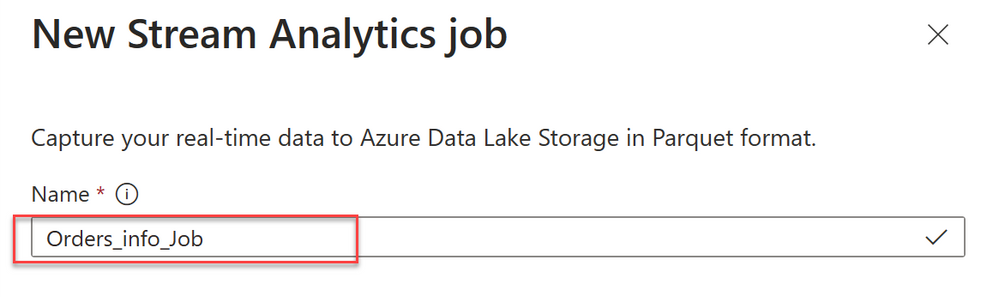
3. Enter a name to identify your Stream Analytics job. Select Create.

4. Specify the Serialization type of your data in the Event Hubs and the Authentication method that the job will use to connect to Event Hubs. Then select Connect.
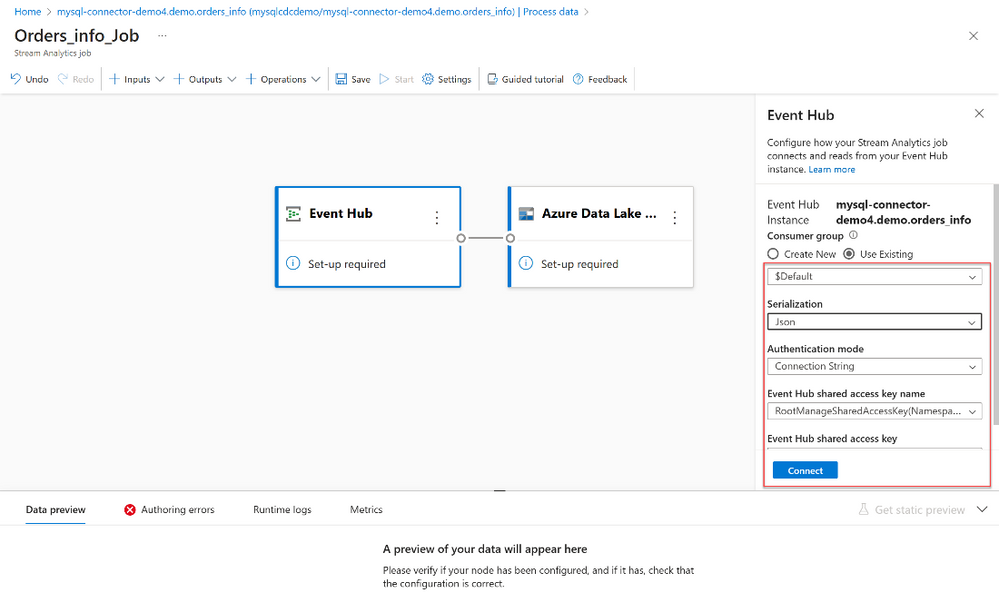
5. Then the connection is established successfully, you’ll see:
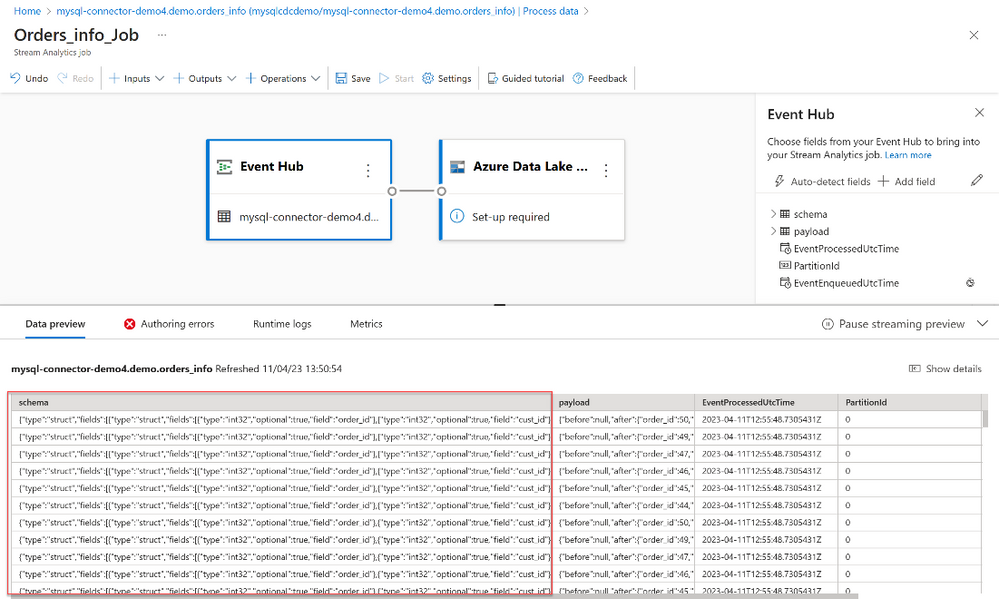
- Fields that are present in the input data. You can choose Add field or you can select the three dots symbol next to a field to optionally remove, rename, or change its name.
- A live sample of incoming data in the Data preview table under the diagram view. It refreshes periodically. You can select Pause streaming preview to view a static view of the sample input.
- Select the Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2 tile to edit the configuration.
- On the Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2 configuration page, follow these steps:
a. Select the subscription, storage account name and container from the drop-down menu.
b. After the subscription is selected, the authentication method and storage account key should be automatically filled in.
c. For streaming blobs, the directory path pattern is expected to be a dynamic value. It’s required for the date to be a part of the file path for the blob – referenced as {date}. To learn about custom path patterns, see to Azure Stream Analytics custom blob output partitioning.
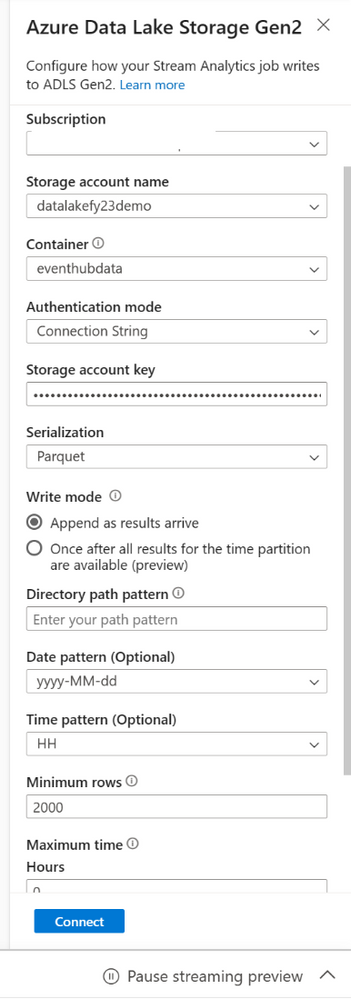
d. Select Connect
- When the connection is established, you’ll see fields that are present in the output data.
- Select Save on the command bar to save your configuration.
- On the Stream Analytics job page, under the Job Topology heading, select Query to open the Query editor window.
- To test your query with incoming data, select Test query.
- After the events are sampled for the selected time range, they appear in the Input preview tab.
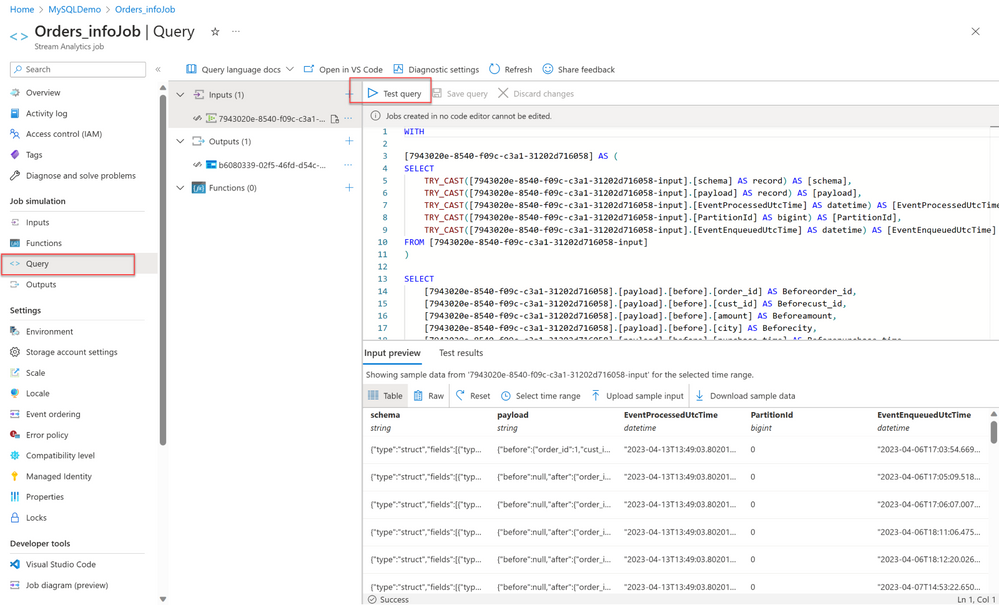
- Stop the job before you make any changes to the query for any desired output. In many cases, your analysis doesn’t need all the columns from the input stream. You can use a query to project a smaller set of returned fields than in the pass-through query.
- When you make changes to your query, select Save query to test the new query logic. This allows you to iteratively modify your query and test it again to see how the output changes.
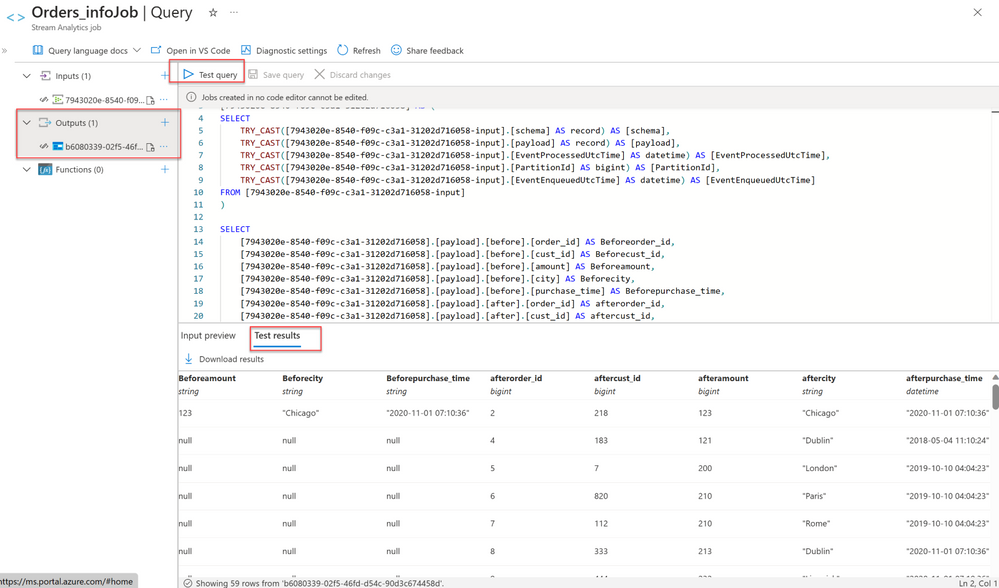
- After you verify the results, you’re ready to Start the job.
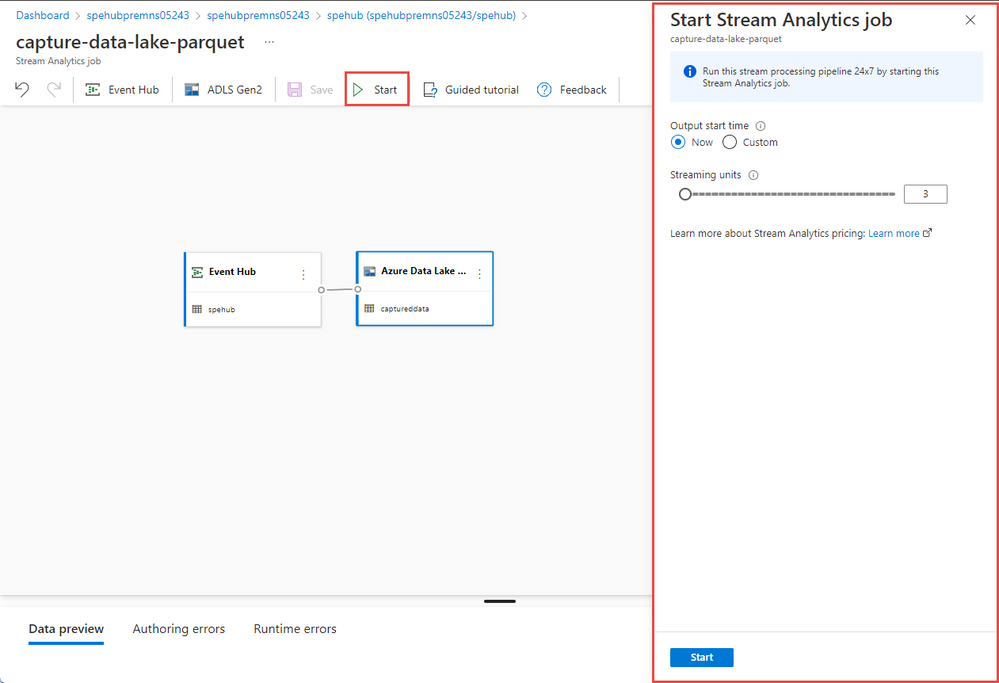
- Select Start on the command bar to start the streaming flow to capture data. Then in the Start Stream Analytics job window:
- Choose the output start time.
- Select the number of Streaming Units (SU) that the job runs with. SU represents the computing resources that are allocated to execute a Stream Analytics job. For more information, see Streaming Units in Azure Stream Analytics.
- In the Choose Output data error handling list, select the behavior you want when the output of the job fails due to data error. Select Retry to have the job retry until it writes successfully or select another option.
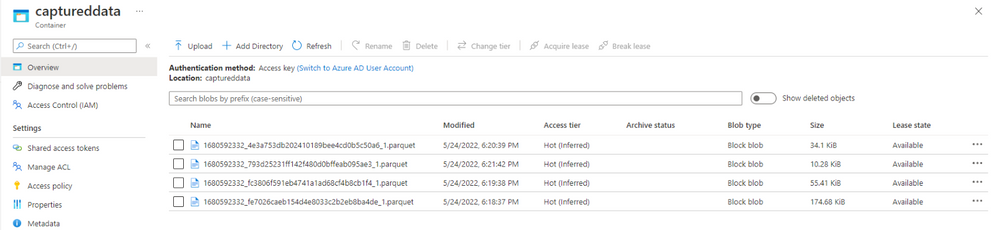
- verify that the Parquet files are generated in the Azure Data Lake Storage container.
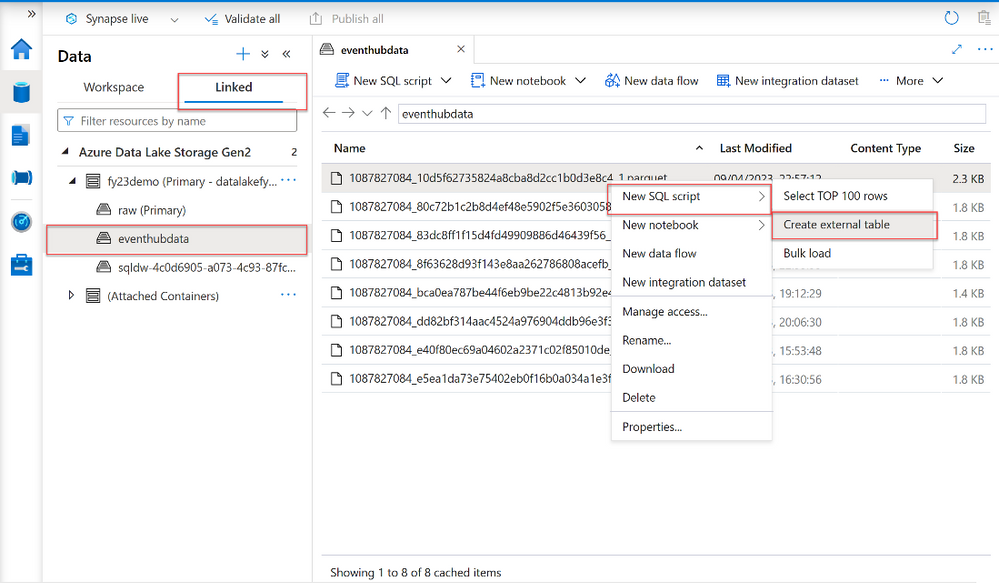
Create External Table with Azure Synapse Serverless SQL Pool
- Navigate to Azure Synapse Analytics Workspace. Select Data -> Linked -> Navigate to the ADLS gen 2 (folder path)
- Select the file that you would like to create the external table from and right click -> New SQL Script -> Create External table
3. In the New External Table, change Max string length to 250 and continue
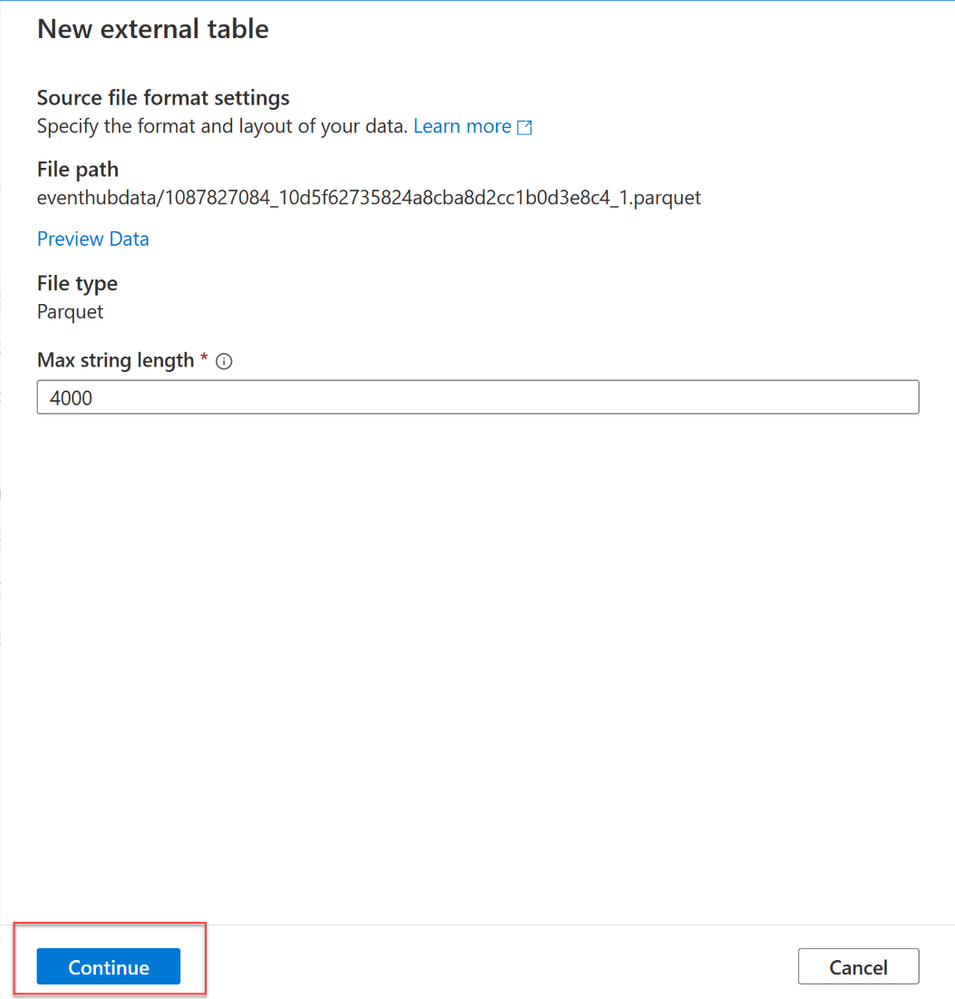
4. A dialog window will open. Select or create new database and provide database table name and select Open script
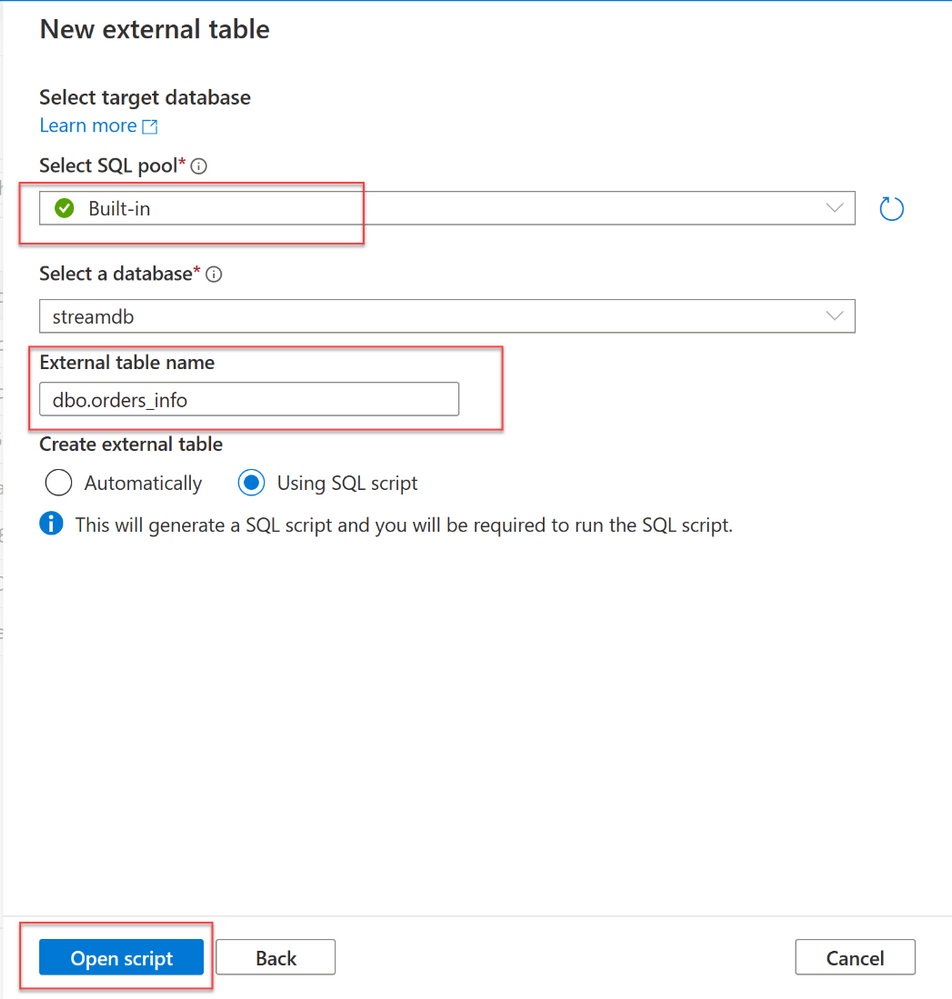
5. A new SQL Script opens, and you run the script against the database, and it will create a new External table.
6. Making a pointer to a specific file. You can only point to folder not the files too
7. Point to enriched folder in Data Lake Storage
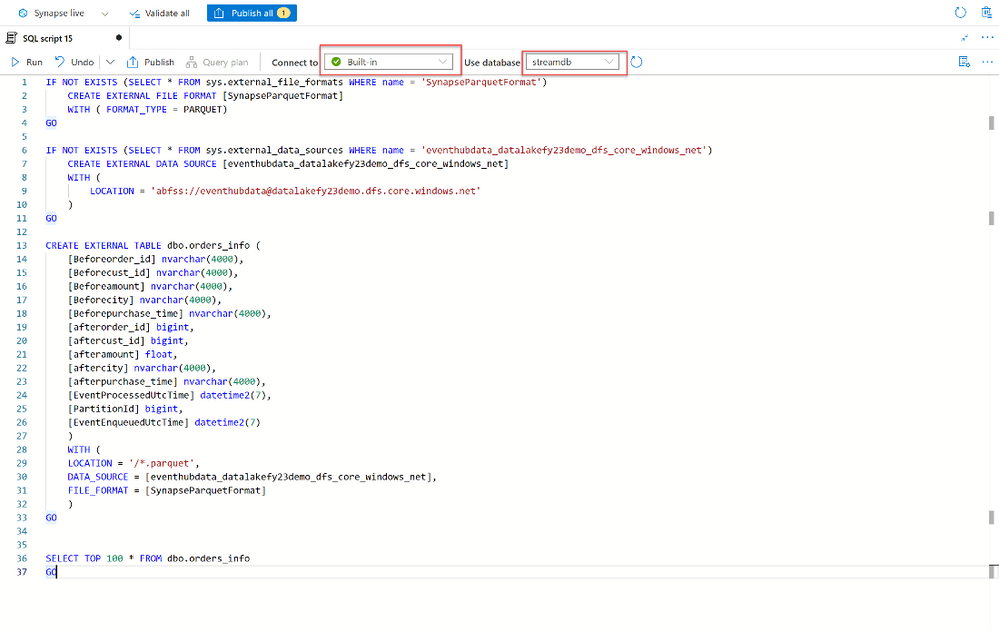
8. Save all the work by clicking Publish All
9. Verify the external table created in Data -> Workspace -> SQL Database
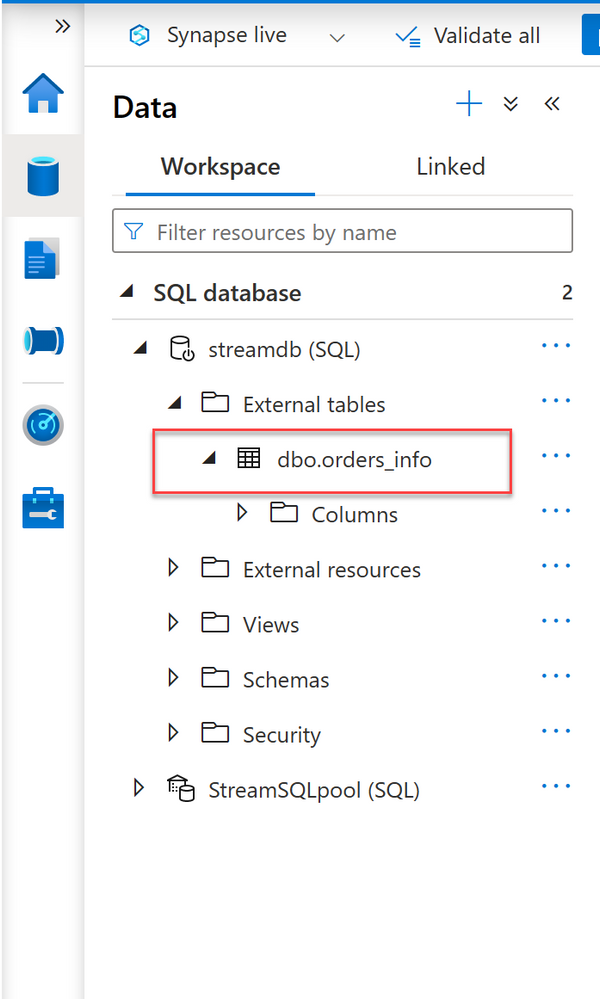
External tables encapsulate access to files making the querying experience almost identical to querying local relational data stored in user tables. Once the external table is created, you can query it just like any other table:
SELECT TOP 100 * FROM dbo.orders_info
GO
SELECT COUNT(*) FROM dbo.orders_info
GO
10. END
Use serverless SQL pool with Power BI Desktop & create a report
- Navigate to Azure Synapse Analytics Workspace. Starting from Synapse Studio, click Manage.
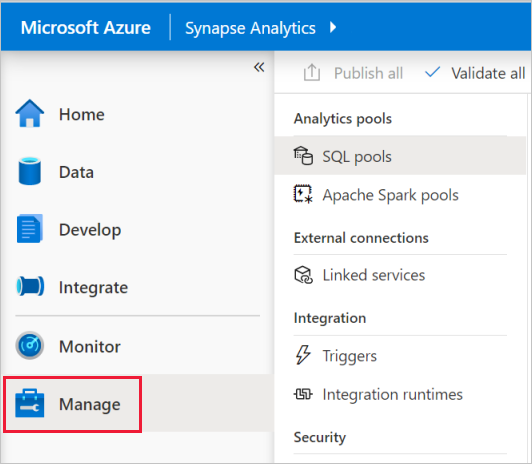
2. Under External Connections, click Linked services. Click + New. Click Power BI and click Continue.
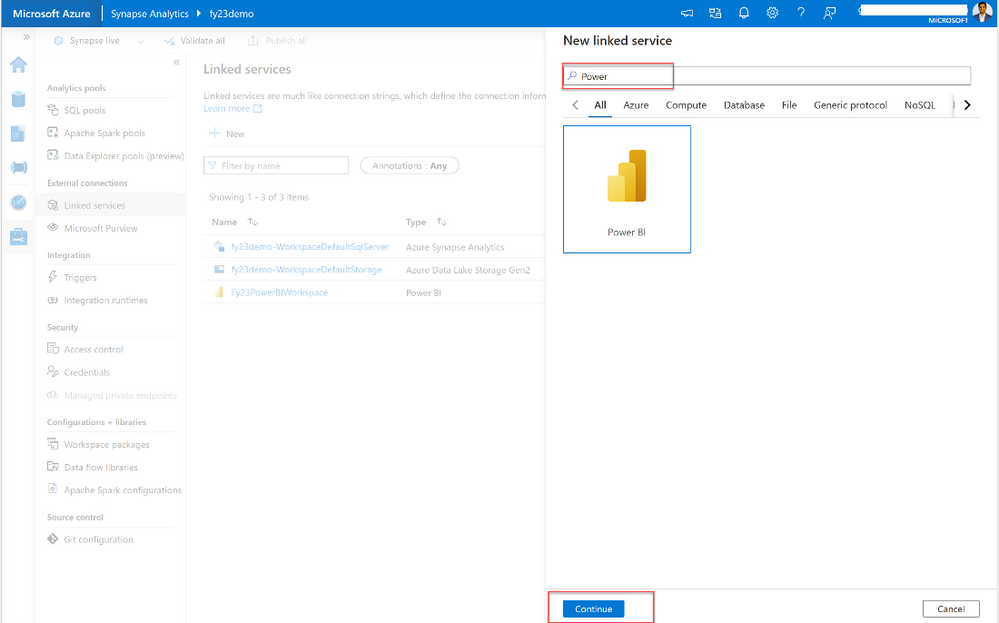
3. Enter a name for the linked service and select an existing workspace which you want to use to publish. Provide any name in the “Name” field. Then you will see Power BI linked connection with the name.
4. Click Create.
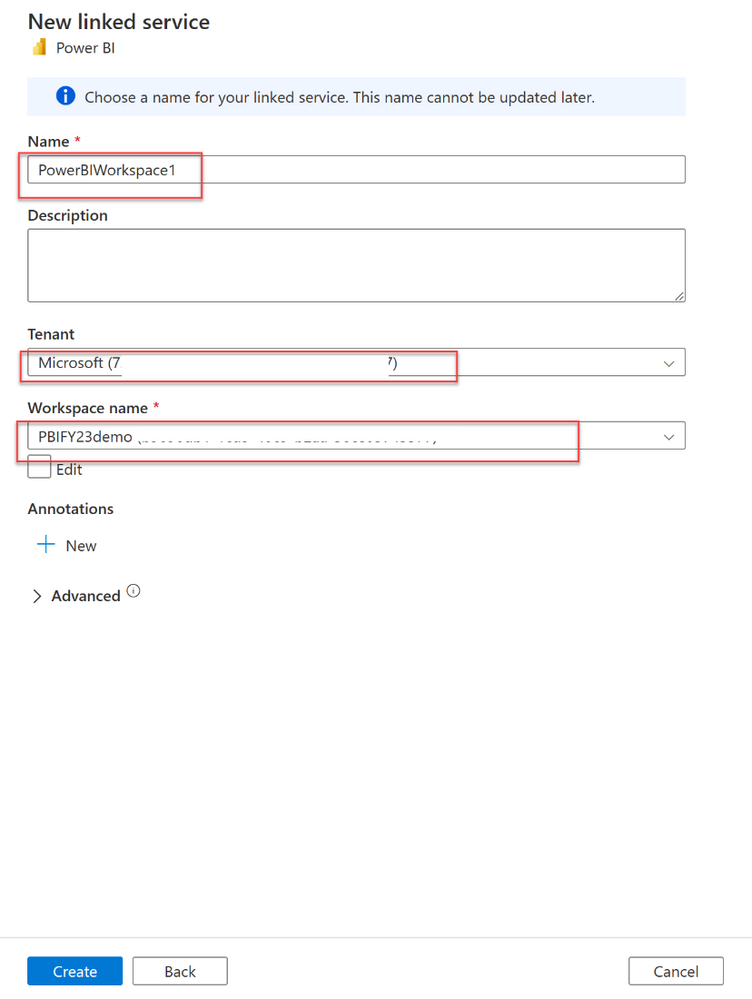
5. View Power BI workspace in Synapse Studio
- After your workspaces are linked, you can browse your Power BI datasets, edit/create new Power BI Reports from Synapse Studio.
- Navigate to develop hub. Create Power BI linked service will be here.
- Expand Power BI and the workspace you wish to use.
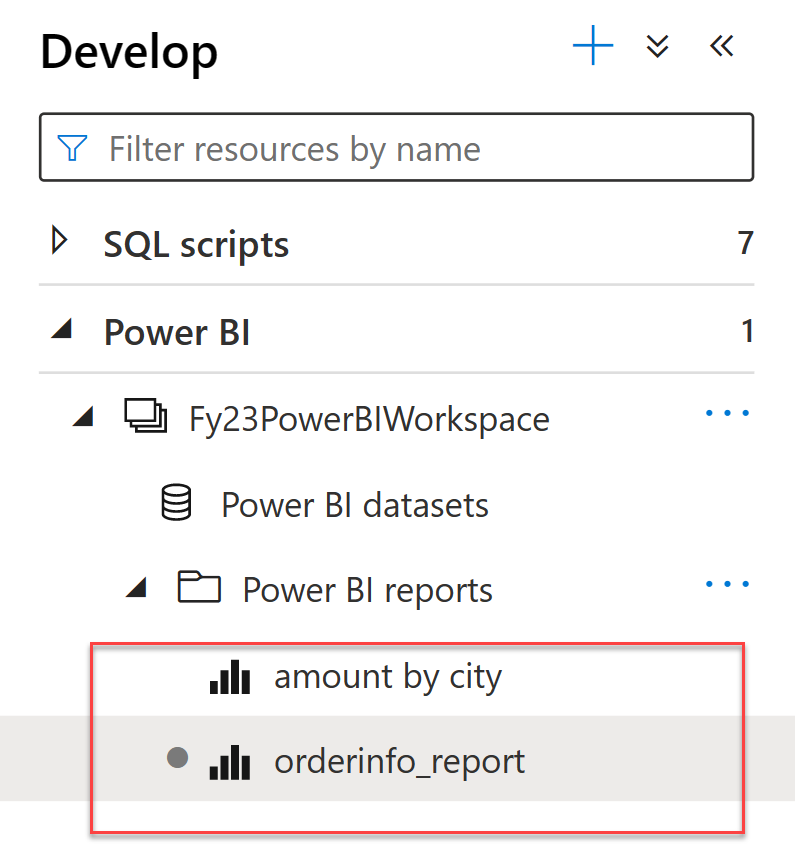
6. New reports can be created clicking + at the top of the Develop tab. Existing reports can be edited by clicking on the report name. Any saved changes will be written back to the Power BI workspace.
Summary
Overall, Debezium, Kafka Connect, Azure Event Hubs, Azure Data Lake Storage, Azure Stream Analytics, Synapse SQL Serverless, and Power BI work together to create a comprehensive, end-to-end data integration, analysis, and visualization solution that can handle real-time data streams from databases, store them in a scalable and cost-effective manner, and provide insights through a powerful BI tool.
To learn more about the services used in this post, check out the following resources:
by Contributed | Apr 12, 2023 | Technology
This article is contributed. See the original author and article here.
As a result of the March 1st order from the Government of Egypt, Daylight Saving Time (DST) in the Arab Republic of Egypt will resume from the last Friday of April. Hence, clocks will be set forward by an hour at 12:00 AM on April 28, 2023.
The April 2023 Monthly quality update for Windows includes the following time zone update for Egypt:
- Clocks will be set forward by an hour at 12:00 a.m. on April 28, 2023, for the Egypt time zone.
Here are the KB article numbers that contain the Egypt DST fix for different versions of Windows:
For Microsoft’s official policy on DST and time zone changes, please see Daylight saving time help and support. For information on how to update Windows to use the latest global time zone rules, see How to configure daylight saving time for Microsoft Windows operating systems.
by Contributed | Apr 12, 2023 | Business, Hybrid Work, Microsoft 365, Technology
This article is contributed. See the original author and article here.
This week at the HIMSS Global Health Conference and Exhibition (HIMSS23), we’re thrilled to be showcasing tailored frontline solutions designed to transform patient care with virtual visits, empower care team collaboration, streamline the clinician experience, and strengthen security and compliance.
The post Discover healthcare innovation from Microsoft Teams at HIMSS23 appeared first on Microsoft 365 Blog.
Brought to you by Dr. Ware, Microsoft Office 365 Silver Partner, Charleston SC.


Recent Comments