
by Contributed | Apr 5, 2024 | Technology
This article is contributed. See the original author and article here.

O Global AI Bootcamp é um evento gratuito e anual que é realizada em diferentes cidades espalhadas pelo mundo inteiro com o intuito de promover, ensinar e discutir sobre:
- Inteligência Artificial
- OpenAI
- Azure OpenAI
- LLM’s
- LangChain
- RAG
- Chatbots
- E, muito mais!
O evento é organizado pela comunidade Global AI Community e é realizado em parceria com diversas empresas e organizações locais. E, gostaria de trazer aqui uma grande novidade à toda Comunidade Técnica do Rio de Janeiro!
Em 2024, o Global AI Bootcamp será realizado no Rio de Janeiro! E, será um evento presencial e gratuito. Contará com:
- Palestras
- Workshops
- Laboratórios
- Debates
Ementa do Evento
Vamos agora falar um pouco sobre o que será abordado no evento:
Agenda
- 09:00 – Keynote – Global AI Bootcamp (Abertura)
- 09:05 – Main Talk – Glaucia Lemos: Como Fazer uma Aplicação com Copilot e IA Generativa?
- 10:05 – Coffee Break
- 10:30 – Workshop 1 Rafael Cruz – Staff Engineer no Itaú: Iteragindo com os modelos da OpenAI
- 11:40 – Break
- 13:00 – Painel – Desmistificando a área de Inteligência Artificial no mundo da Tecnologia –
- 14:00- Finalização
Local do Evento
O evento será realizado na Faculdade Ibmec da Barra da Tijuca, localizada na Avenida Armando Lombardi, 940 – Barra da Tijuca, Rio de Janeiro – RJ.
Então, vamos resumir as informações:
- Data: 19 de Abril de 2024
- Horário: 09:00 às 14:00
- Local: Faculdade Ibmec da Barra da Tijuca
- Endereço: Avenida Armando Lombardi, 940 – Barra da Tijuca, Rio de Janeiro – RJ
Inscrições
As inscrições para o evento já estão abertas e as vagas são limitadas. Então, clique na imagem abaixo e garanta já a sua vaga!

As inscrições pelo site oficial do evento é extremamente importante para àqueles que participarão. Pois se você decidir fazer um dos workshops que serão administrados, será gerado uma chave para fazer uso dos recursos da OpenAI de graça!
Material de Apoio para quem já se inscreveu!
Se você já se inscreveu no evento, acessem agora mesmo o material de apoio. Pois, será muito importante para ajudar a vocês a se prepararem para o evento:
Conclusão
A área de Inteligência Artificial é uma das áreas que mais estão em grande ascensão no mercado de tecnologia nos dias de hoje. E, eventos como o Global AI Bootcamp são essenciais para aprendermos e discutirmos sobre essas novas tecnologias e seus impactos em nossas vidas, seja pessoal e principalmente profissional!
Assim sendo, não percam a oportunidade de participar desse grande evento que será realizado no Rio de Janeiro em 2024. E, espero encontrar vocês por lá!
Até a próxima!

by Contributed | Apr 5, 2024 | Technology
This article is contributed. See the original author and article here.
 Imagen “reto”.
Imagen “reto”.
¡Regístrate al VS Code Day Skills Challenge! Ya sea que estes comenzando o buscando cambiar tu carrera, este programa está diseñado para que conozcas VS Code y GitHub Copilot en diferentes áreas profesionales como Ciencia de Datos, Inteligencia Artificial y Desarrollo Web. Con lecciones fáciles de seguir, ejercicios prácticos y talleres en vivo, aprende las novedades en VS Code. ¡Regístrate ahora y descubre el mundo de oportunidades que te ofrece VS Code en: https://aka.ms/VSCodeDayChallenge!
VS Code Day es nuestro evento anual en el cual aprenderás a mejorar tu proceso de programación con las novedades y grandes características de VS Code! Este año, estamos muy emocionados ya que tendremos sesiones enfocadas en la Inteligencia Artificial y escucharás al equipo de VS Code y a expertos de la industria hablar sobre temas como GitHub Copilot, la creación e implementación de aplicaciones de IA generativa en la nube, la mejora de la experiencia de programación en C# y ¡mucho más!
Si estás empezando en el mundo de programación o si eres un programador con experiencia, ¡acompáñanos este 24 de abril de 2024 para conocer más sobre este super editor de código gratuito que te permite programar cualquier cosa! 

 Imagen de “Reconocimientos”
Imagen de “Reconocimientos”
Al completar los 11 módulos de este reto, podrás obtener un reconocimiento (badge) digital en tu perfil de Microsoft Learn por haber finalizado esta experiencia. ¡Mantente al tanto de más información en redes sociales y en este blog – te compartiremos más sobre los eventos de este #VSCodeDay!
NOTA IMPORTANTE: Tu reconocimiento (badge) digital se agregará a tu perfil de Microsoft Learn en el plazo de 1 semana a partir de la fecha de finalización del desafío. ¡Descubre en este tutorial como puedes compartir tus badges en LinkedIn!
 Imagen “Preguntas frecuentes”
Imagen “Preguntas frecuentes”
- ¿Cuándo inicia y finaliza este reto? Inicia el 24 de abril 2024 y finaliza el 17 de mayo del 2024.
- ¿Cuánta experiencia necesito? Solo conocimientos básicos de programación.
- ¿Cuánto tiempo debo dedicarle al día? Está diseñado para que vayas aprendiendo conforme a tus necesidades y tiempo disponible, recuerda que tienes que completarlo hasta el 17 de mayo.
- Prerrequisitos: Ninguno.
- ¿Tiene costo alguno? No tiene costo
 Imagen de “Charlas y talleres en vivo”
Imagen de “Charlas y talleres en vivo”
¡Prepárate para conocer las novedades de VS Code con nuestra serie de charlas y talleres en vivo! Estarán llenas de consejos, trucos y ejercicios prácticos para ayudarles con sus proyectos personales y profesionales. Ya sea que estas comenzando o buscando mejorar tus habilidades, este es un evento imperdible para cualquier persona interesada en programación.
¡Para registrarte a todas estas charlas del #VSCodeDay ingresa a la siguiente página web (aka.ms/VSCodeDay)! Inicia el 24 de Abril desde las 11 am hasta las 6 pm (GMT-6)*.
*Horario Ciudad de México
Evento |
Ponente |
Redes Sociales |
Keynote: View Source: What gets into VS Code and why |
Burke Holland |
@burkehollan |
JavaScript developers: Build fast and have fun with VS Code and Azure AI CLI
|
Natalia Venditto |
@anfibiacreativa |
Generating Synthetic Datasets with GitHub Copilot |
Alfredo Deza |
Alfredo Deza on LinkedIn |
Real-World Development with VS Code and C# |
Scott Hanselman + Leslie Richardson |
@shanselman +@lyrichardson01 |
Building a RAG-powered AI chat app with Python and VS Code |
Pamela Fox |
@pamelafox |
Beyond the Editor: Tips to get the Most out of GitHub Copilot |
Kedasha Kerr |
@itsthatladydev
|
LangChain Examples with Azure OpenAI Service + VS Code |
Rishab Kumar |
@rishabincloud |
AI Made Clear: Practical AI Coding Sessions in VS Code |
Bruno Capuano |
@elbruno |
Asking Copilot about your workspace |
Matt Bierner |
@mattbierner |
 Imagen “Comparte tu experiencia”
Imagen “Comparte tu experiencia”
Si anteriormente has utilizado VS Code, por favor, cuéntanos en los comentarios tu experiencia: tus extensiones favoritas, que te han parecido las charlas del evento e incluso si es la primera vez que has escuchado sobre VS Code!
 ¡Nos fascinaría escuchar tus historias o anécdotas favoritas/divertidas de las veces que has programado en VS Code!
¡Nos fascinaría escuchar tus historias o anécdotas favoritas/divertidas de las veces que has programado en VS Code!
 Etiquétanos en redes sociales usando el siguiente hashtag: #VSCodeDayCSC
Etiquétanos en redes sociales usando el siguiente hashtag: #VSCodeDayCSC

by Contributed | Apr 4, 2024 | Technology
This article is contributed. See the original author and article here.
 Healthcare and Life Sciences (HLS) is a demanding and complex field that requires constant innovation, collaboration, and communication. HLS professionals often have to deal with large amounts of data, information, and documentation, which can be overwhelming and time-consuming. Moreover, the COVID-19 pandemic has added more pressure and stress to the already challenging work environment, leading to increased risks of burnout and mental fatigue.
Healthcare and Life Sciences (HLS) is a demanding and complex field that requires constant innovation, collaboration, and communication. HLS professionals often have to deal with large amounts of data, information, and documentation, which can be overwhelming and time-consuming. Moreover, the COVID-19 pandemic has added more pressure and stress to the already challenging work environment, leading to increased risks of burnout and mental fatigue.
How can HLS professionals cope with these challenges and improve their productivity and well-being? One possible solution is to leverage the power of AI and use Copilot, a tool that helps you write better code faster. Copilot is a smart assistant that can assist with email overload, summarize information from various sources, generate documentation, and more. Copilot also integrates with other applications like Teams, Word, Outlook, and more, creating a seamless workflow that can enhance your efficiency and creativity.
Check out the ever-growing repository of Use case workflow leveraging the power of Copilot.
* Note: all examples are demonstrations for educational purposes only and not intended to be used as production. No warranty or support is stated or implied.
Provider Examples:
Payor Examples:
Pharma Examples
Medical Devices Examples:
by Contributed | Apr 3, 2024 | Technology
This article is contributed. See the original author and article here.
Last updated 4/3/2024 to include v2 Tiers features.
Authors: Faisal Mustafa, Ben Gimblett, Jose Moreno, Srini Padala, and Fernando Mejia.
There are different options when it comes to integrating your API Management with your Azure Virtual Network (VNet) which are important to understand. These options will depend on your network perimeter access requirements and the available tiers and features in Azure API Management.
This blog post aims to guide you through the different options available on both the classic tiers and v2 tiers of Azure API Management, to help you decide which choice works best for your requirements.
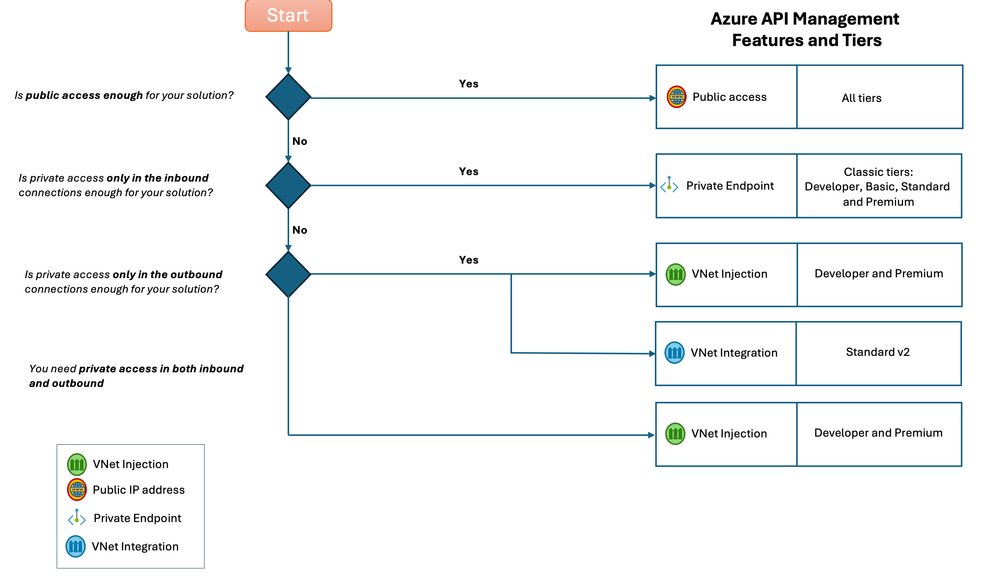
TL; DR

Decision tree describing how to choose the right Azure API Management tier based on networking scenarios.
Here is the relevant documentation to implement these tiers and features:
- Tiers
- Networking Features
Background
Before we jump into the options and differences it’s worth taking a step back to understand more about how Azure Platform as a Service products (PaaS) work regarding networking. If you need a refresher and so we don’t repeat ourselves here, we’d ask the reader to spend a few minutes over at Jose’s excellent “Cloudtrooper blog” and his deep dive post on all things “PaaS networking”. We’ll use some of the same labels and terms in this post for consistency Taxonomy of Azure PaaS service access – Cloudtrooper.
What is API Management, what tiers are available and why does it matter in relation to networking?
The first thing to remember is that the API Management API Gateway is a Layer 7 (in OSI model terms) HTTP Proxy. Keeping this in mind helps a lot when you think about the networking options available through the different tiers. In simple terms:
An HTTP proxy terminates HTTP connections from any client going to a set of [backend] servers and establishes new HTTP connections to those servers. For most API Management Gateway use cases the resource would reside close to the [backend] servers its facades (usually in the same Azure region).
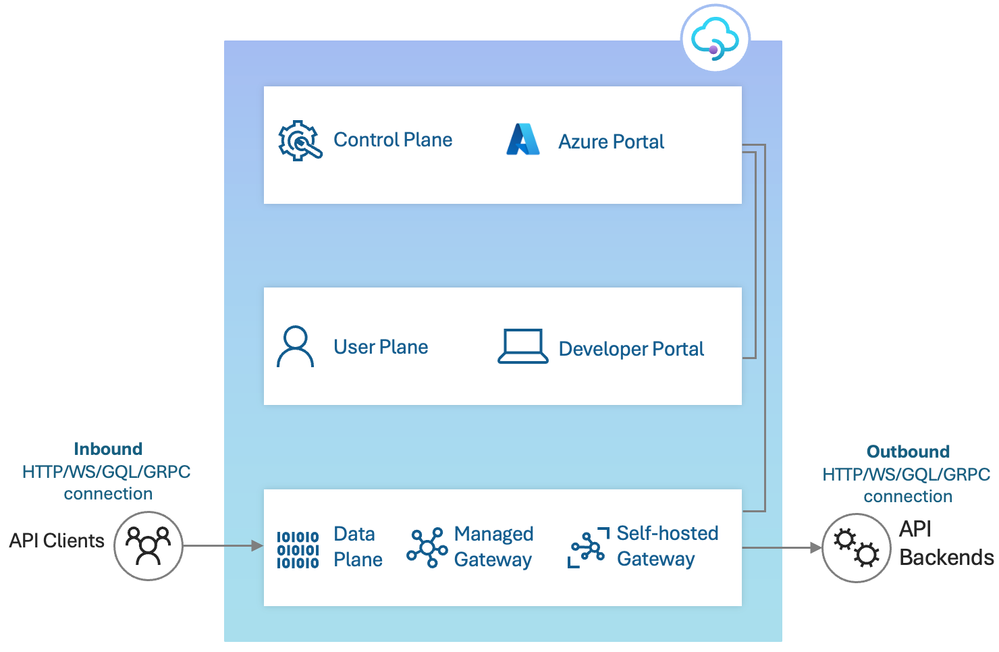
Diagram describing all the components included in Azure API Management, and the difference between inbound and outbound sections.
Why does this matter? When we talk about the available networking-options we talk about features which relate to the initial client connection to API Management(inbound) OR features relating to the connection from API Management to the API backends(outbound). From now on, we will call them inbound and outbound connections, and there are different options/features for each type.
Regarding Azure API Management tiers we will rely in the following categories:
- Consumption tier, the tier that exposes serverless properties.
- Classic tiers, this category refers to the Developer, Basic, Standard and Premium tiers.
- V2 tiers, this category refers to the Basic v2 and Standard v2.
Networking scenarios
Let’s jump right in. To make it easier to navigate and for you to get the information you need to make the right decisions for your use case, lets summarize by the applicable use-cases, we’ll list the tiers where the functionality is available and add any applicable notes.
I have no specific networking requirements and just want to keep things simple.
Supported tiers: Consumption, Classic tiers, and V2 tiers.
Of course, there’s more to implementing a workload with API Management than just networking features and still a lot of choice when it comes to an API Management tier that fits your workload and scale requirements. But if you are ok with having inbound and outbound connections going through the Azure Backbone or Public Internet, any tier of Azure API Management can help you with this scenario. Of course, we recommend securing your endpoints using Authentication/Authorization mechanisms like subscription keys, certificates, and Oauth2/OIDC.
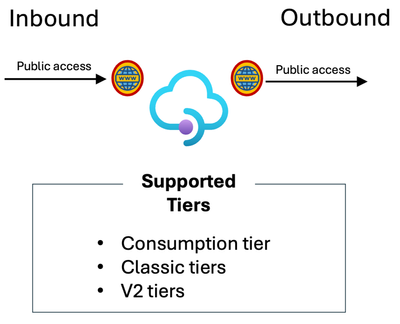
Diagram describing what tiers of Azure API Management allow public access for inbound and outbound.
I have a requirement to connect privately to API Management for one or more of my Client Applications
Option 1: Consider deploying a Private Endpoint into API Management.
Supported tiers: Classic tiers.
“Private endpoints allow you to access services privately within your virtual network, avoiding exposure over the public internet.” (Thanks Microsoft co-pilot).
Deploying a Private Endpoint for inbound connectivity is a good option to support secure client connections into API Management. Remember, in this context the Private Endpoint you deploy for API Management creates an alternative network path into your API MANAGEMENT service instance; it’s about facilitating inbound communication (the client connecting to API Management), and it is “one way only” meaning it doesn’t help for scenarios where you also want to connect privately to your backends.
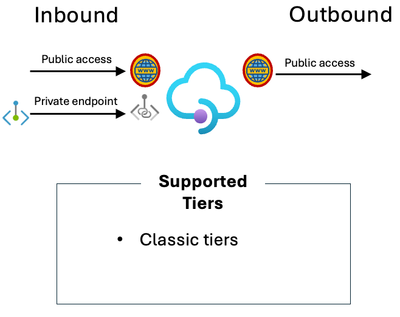
Diagram describing what tiers of Azure API Management allow public access and private endpoint for inbound.
Note: Whilst it’s supported to use Private Endpoints in the Premium or Developer tiers – the service must not have been added to a Virtual Network (VNET). This makes private endpoints and the “VNET Injection” capability supported by Premium and Developer mutually exclusive. The Basic and Standard tiers can’t be added to a Virtual Network.
Option 2: Consider adding your API Management to your VNet.
Supported tiers: Developer tier and Premium tier.
Developer and Premium are the only tiers where you can deploy the service into your virtual network – what we sometimes refer to as “VNet injection” – and allows you to set the inbound as public or private.
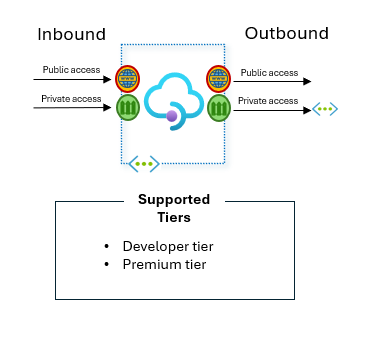
Diagram describing what tiers of Azure API Management allow private access for both inbound and outbound.
As far as the Developer Tier is concerned, this is NOT meant for production use and no workloads showed be deployed on this Developer Tier.
The API backends I want to reach from API Management are private.
Supported tiers: Developer tier, Premium tier, and Standard v2 tier.
For the classic tiers Developer and Premium, as we mentioned before you can deploy the service into your virtual network. This could be in “internal” (private) or external mode.
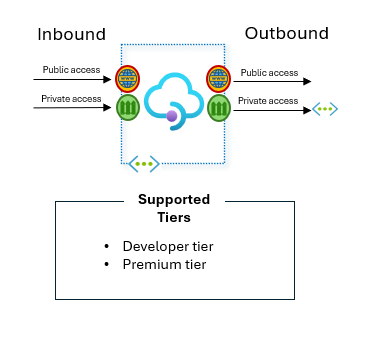
Diagram describing what tiers of Azure API Management allow private access for both inbound and outbound.
For the v2 tiers, Standard v2, allows you to rely on a feature called “VNet Integration” (please not the difference between VNet Integration and VNet injection) which allows API Management to “see” into your network and access services through a private IP in the connected Virtual Network, or in peered / connected network(s).
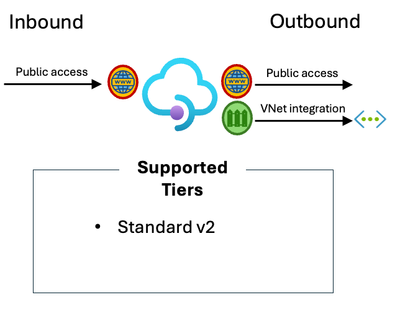
Diagram describing what tiers of Azure API Management allow private access for outbound using VNet integration.
I need to connect to API Management privately as well as reach private backends with no public access.
Supported tiers: Developer tier and Premium tier.
Add API Management Premium or Developer to your Virtual Network. The best practice would be to set the mode to “internal” – meaning inbound connectivity is via a private IP, via an internal load balancer.
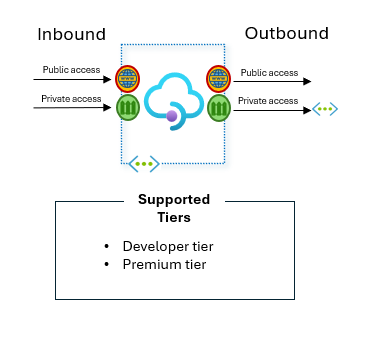
Diagram describing what tiers of Azure API Management allow private access for both inbound and outbound.
This allows you to keep all API’s private/internal but offers the option of later placing a Reverse Proxy in front of API Management (for example Azure Application Gateway) to electively open access to any private APIs you want to make publicly accessible.
A last word about IP Addresses…
It’s something that relates to networking and is oft asked, so it would be remiss of us not to add a few lines summarizing the behavior and NAT (network address translation) for the different deployment modes:
Inbound
- By default, inbound is via a public IP address assigned to the service.
- This changes if you opt into using a Private Endpoint (for any of the tiers supporting this feature). Always remember to explicitly turn off the public ingress if you deploy a private endpoint instead and no longer require it.
- This also changes if you deploy the Premium (or Developer) tier, added to your Virtual Network (“VNet-injected”), and set the mode to “internal”. In this mode, although a public IP is still deployed for control plane traffic, all data plane traffic will go through the private IP (Internal load balancer endpoint) which is provided in this mode.
Outbound
- By default, outbound traffic is via the public IP(s) assigned to the service.
- This changes for Premium (or Developer) tiers when the service is added to your Virtual Network (irrespective of the inbound mode being public or private). In this case
- For internal traffic leaving API Management – for example API Management reaching to a backend service hosted on a downstream VM within the network – there is no SNAT (source network address translation). If the next hop is an NVA (network virtual appliance/firewall) any rules for the source should use the subnet prefix, not individually mapped IPs.
- External bound traffic breaking out (non RFC1918) is SNAT to the single-tenant (dedicated) public IP assigned. This includes traffic to other PaaS services via a public endpoint (although you should note the traffic in this instance stays on the Azure backbone).
- For Standard V2 using “VNet integration”
- NAT for internal traffic is the same.
- External bound traffic breaking out is SNAT to one of the hosting stamps shared public IPs. If you want control over the outbound IP, use an Azure NAT Gateway on the subnet or route via an NVA (network virtual appliance, or firewall). Same note as above applies for PaaS-to-PaaS traffic via Public IPs.
Note for v2 tiers: API MANAGEMENT control plane and its own dependency traffic is not seen on the customers network, which is an enhancement from the GA tiers, and simplifies scenarios requiring force-tunnelling / firewall integration.
by Contributed | Apr 2, 2024 | Technology
This article is contributed. See the original author and article here.
Microsoft is excited to participate in Embedded World, April 9-11, 2024 in Nuremberg, Germany, the leading international fair for embedded systems. This event showcases the latest innovations and trends in the field. From hardware and software to tools and services, this event brings together experts and industry leaders from around the globe to share their knowledge and insights. In this blog, we will give you a sneak peek at Microsoft’s presence at the event, including highlights on key topics, and what to expect from Embedded World.
Makers of embedded devices will be interested in Azure Private MEC (Multi-access Edge Compute) for several reasons:
- Low Latency and Edge Compute: Azure private MEC provides low-latency and high-bandwidth connectivity combined with highly available edge computing services, for IoT and other edge devices, enabling real-time data processing and decision-making.
- Scalability: Azure private MEC allows makers of embedded devices to easily scale their solutions, adding new devices and capabilities as needed.
- Security: Azure private MEC provides a secure and isolated environment for processing sensitive data, reducing the risk of data breaches and cyber-attacks.
- Device Density: Azure private MEC can support a high density of devices on a manufacturing floor, allowing for seamless connectivity and communication between numerous devices.
Connect with us in Hall 5 Stand 353
Visit us at our booth in Hall 5 to explore our innovative demos and experiences, connect with product and partner experts on featured products, and meet one-on-one with Microsoft leaders.
Microsoft invites attendees to join the following sessions where they will discover more about Azure private MEC and how private 5G is unlocking industry transformation. This is a great opportunity to get practical guidance on how to prepare your organization for innovation and growth, including learning on tools and frameworks to determine when, where, and how to focus on specific use cases emerging across industries today.
Understanding the ROI of a 5G-enabled factory April 9 | 12:00 pm
Intelligent factories leverage advanced technologies and automation to optimize manufacturing processes and enhance overall efficiency. These factories integrate various technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, Internet of Things (IoT), robotics, and data analytics to create a connected and intelligent production environment.
Hand on Lab with Azure Private 5G Core April 10 | 4:00 pm
April 11 | 1:30 pm
Register for a deep dive session in our Microsoft Learning Center, located across from the Microsoft booth (#5-469) where we will explore:
- Azure private MEC solutions and their use in different industry verticals.
- Why build applications and devices supporting the private MEC platforms.
- Opportunity for growth with 5G and private MEC
Learn more about Azure private MEC
- Whether you’re an enterprise , looking to leverage our solutions, a developer eager to create network-aware applications, or an application ISV seeking to collaborate with Microsoft on MEC solutions, we invite you complete this form to get contacted by a member of the private MEC team.
- To learn how Microsoft is helping organizations embrace 5G with modern connected applications, sign up for news and updates delivered to your inbox.


Recent Comments