by Contributed | May 24, 2022 | Technology
This article is contributed. See the original author and article here.
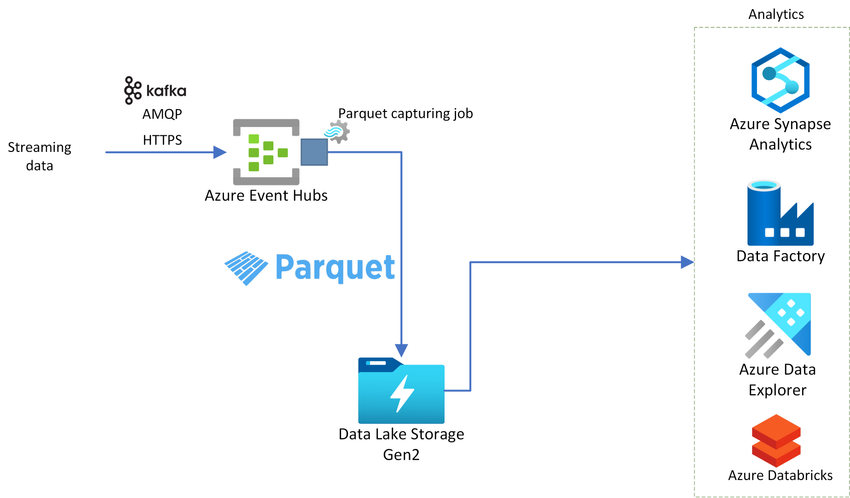
Azure Event Hubs enables you to stream millions of events per second from any source using Kafka, AMQP or HTTPS protocols. Using Event Hubs capture feature, you can load real-time streaming data to data lakes, warehouses, and other storage services, so that they can be processed or analyzed by analytics services.
Today we are excited to announce the preview of Apache Parquet capturing support in Azure Event Hubs.
Why Apache Parquet for big data analytics?
Apache Parquet is column-oriented storage format that is designed for efficient data storage and retrieval. It’s open source and is not tied to any processing framework, data model or programming language. Parquet is ideal for storing any kind of big data and is built to support efficient compression and encoding schemes.
Capture streaming data in Parquet format using Event Hubs
Using Azure Event Hubs, no code editor for event processing, you can automatically capture streaming data in an Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2 account in Parquet format. The no code editor allows you to easily develop an Azure Stream Analytics job without writing a single line of code.

Once data is captured, any analytics service of your choice can process or analyze Parquet data.
Get Started Today
by Contributed | May 23, 2022 | Technology
This article is contributed. See the original author and article here.
Data loss prevention is a major concern with all customers who would like to have granular control over their data and how it gets exported from their databases on Azure.
The steps below guide on how Outbound Firewall Rules can be leveraged to improve the security posture and ensure data gets exported only to approved Azure Storage accounts. All other Azure Storage accounts are treated as unapproved unless explicitly whitelisted.
The steps below use Azure APIs and Powershell cmdlets to implement the lockdown and enable OFRs.
Pre-requisites:
1. Valid Service Principal based Azure Active Directory (AAD) token for authentication of requests.
2. Latest version of Azure Powershell cmdlets
To enable Restrict Outbound Network Access and add/create OFRs using APIs
1. Check the current OFR configuration of the SQL Server using a GET request on
https://management.azure.com/subscriptions/{{subId}}/resourceGroups/{{sqlRg}}/providers/Microsoft.Sql/servers/{{sqlServer}}?api-version=2021-02-01-preview
where
{{subId}} = Subscription ID
{{sqlRg}} = Resource Group hosting the SQL server
{{sqlServer}} = name of the SQL server
It should show that the restrictOutboundNetworkAccess is disabled.
2. Create two storage accounts on Azure Storage. Example:
– auditallowstorage
– auditdenystorage
3. Export database to both storage accounts. The export should be successful for both accounts.
4. Issue a PUT request to Enable RestrictOutboundNetworkAccess on the SQL server using SQL API
https://management.azure.com/subscriptions/{{subId}}/resourceGroups/{{sqlRg}}/providers/Microsoft.Sql/servers/{{sqlServer}}?api-version=2021-02-01-preview
with JSON body as
{ "properties" :
{"restrictOutboundNetworkAccess": "Enabled"},
"location": "<sql_server_region>"
}
where
{{subId}} = Subscription ID
{{sqlRg}} = Resource Group hosting the SQL server
{{sqlServer}} = name of the SQL server
<server_region> = region where the SQL server is hosted
5. Verify that the restrictOutboundNetworkAccess property is now set to Enabled by issuing a GET request on
https://management.azure.com/subscriptions/{{subId}}/resourceGroups/{{sqlRg}}/providers/Microsoft.Sql/servers/{{sqlServer}}/outboundfirewallrules?api-version=2021-02-01-preview
where
{{subId}} = Subscription ID
{{sqlRg}} = Resource Group hosting the SQL server
{{sqlServer}} = name of the SQL server
It should show that the provisioned state is “ready” for restrictOutboundNetworkAccess
6. Ensure that there is no existing Outbound Firewall Rule in place using this Powershell command:
Get-AzSqlServerOutboundFirewallRule -ServerName <sql_server_name> -ResourceGroupName <resource_group_name>
where
<resource_group_name> = Resource Group hosting the SQL server
<sql_server_name> = name of the SQL server
7. Export database again to both of the storage accounts (auditallowstorage and auditdenystorage). This should fail.
8. Create OFR only for storage account auditallowstorage using this PUT request:
https://management.azure.com/subscriptions/{{subId}}/resourceGroups/{{sqlRg}}/providers/Microsoft.Sql/servers/{{sqlServer}}/outboundfirewallrules/{{saName}}.blob.core.windows.net?api-version=2021-02-01-preview
where
{{subId}} = Subscription ID
{{sqlRg}} = Resource Group hosting the SQL server
{{sqlServer}} = name of the SQL server
{{saName}} = Storage Account name for which OFR is created. In this case, its auditallowstorage
9. Verify that OFR was successfully created for storage account using this Powershell command:
Get-AzSqlServerOutboundFirewallRule -ServerName <sql_server_name> -ResourceGroupName <resource_group_name>
where
<resource_group_name> = Resource Group hosting the SQL server
<sql_server_name> = name of the SQL server
It should show the list of the allowed FQDN (Fully Qualified Domain Name). In this case, its auditallowstorage.
10. Export database to storage account auditallowstorage. This should be successful.
11. Export database to storage account auditdenystorage should still fail.
To disable Restrict Outbound Network Access and remove OFRs
1. Remove all Outbound Firewall Rules:
Remove-AzSqlServerOutboundFirewallRule -ServerName <sql_server_name> -ResourceGroupName <resource_group_name> -AllowedFQDN <sa_name>.blob.core.windows.net
where
<resource_group_name> = Resource Group hosting the SQL server
<sql_server_name> = name of the SQL server
<sa_name> = Storage Account Name
2. Issue a PUT request to disable RestrictOutboundNetworkAccess on the SQL server using SQL API
https://management.azure.com/subscriptions/{{subId}}/resourceGroups/{{sqlRg}}/providers/Microsoft.Sql/servers/{{sqlServer}}?api-version=2021-02-01-preview
with JSON body as
{ "properties" :
{"restrictOutboundNetworkAccess": "Disabled"},
"location": "<sql_server_region>"
}
where
{{subId}} = Subscription ID
{{sqlRg}} = Resource Group hosting the SQL server
{{sqlServer}} = name of the SQL server
<server_region> = region where the SQL server is hosted
3. Verify that the restrictOutboundNetworkAccess property is disabled on the SQL server by issuing the following GET request on
https://management.azure.com/subscriptions/{{subId}}/resourceGroups/{{sqlRg}}/providers/Microsoft.Sql/servers/{{sqlServer}}?api-version=2021-02-01-preview
where
{{subId}} = Subscription ID
{{sqlRg}} = Resource Group hosting the SQL server
{{sqlServer}} = name of the SQL server
To enable Restrict Outbound Network Access and add/create OFRs using Powershell
1. Execute the following command to enable restrictOutboundNetworkAccess property on the SQL server:
Set-AzSqlServer -ServerName <server_name> -ResourceGroupName <resource_group> -RestrictOutboundNetworkAccess "Enabled"
where
<server_name> = name of the SQL server
<resource_group> = name of the resource group
2. Check the current list of Outbound Firewall Rules on the SQL server:
Get-AzSqlServerOutboundFirewallRule -ServerName <server_name> -ResourceGroupName <resource_group>
where
<server_name> = name of the SQL server
<resource_group> = name of the resource group
3. Export database again to both of the storage accounts (auditallowstorage and auditdenystorage). This should fail.
4. Add a new Outbound Firewall Rule on the server using the command:
New-AzSqlServerOutboundFirewallRule -ServerName <server_name> -ResourceGroupName <resource_group> -AllowedFQDN <sa_name>.blob.core.windows.net
where
<resource_group> = Resource Group hosting the SQL server
<server_name> = name of the SQL server
<sa_name> = Storage Account Name
5. List the OFRs on the server using the following command:
Get-AzSqlServerOutboundFirewallRule -ServerName <server_name> -ResourceGroupName <resource_group>
6. Export database to storage account auditallowstorage. This should be successful
7. Export database to storage auditdenystorage should still fail.
Hope this was useful folks! Feel free to get in touch :)

by Contributed | May 20, 2022 | Technology
This article is contributed. See the original author and article here.

If you’re not already familiar with Mixed Reality Toolkit (MRTK), it’s an open-source project led by Microsoft that provides UX building blocks for MR and VR applications. The experiences you build with MRTK can run on any device that supports the OpenXR runtime such as HoloLens and Meta Quest. We’ve heard from the community that they love the richness of the MRTK UI controls and that it reduces development time, especially for apps that need to run on multiple platforms. Components for hand and eye tracking, inputs, solvers, diagnostic tools, scene management, and more can help you to build experiences that look great with less effort.
We’re excited to share the next release of this powerful toolkit, MRTK3 Public Preview, at Mixed Reality Dev Days on June 8-9. With MRTK3, you’ll have the option of a lighter-weight solution which allows you to select only the components of the toolkit you need. The release also includes a new interaction system, new theming and databinding features, Unity canvas support, and an updated design language that can help you refresh your app’s look and add polish. Additionally, native OpenXR support makes it even easier to target multiple devices such as HoloLens, Meta Quest, Windows Mixed Reality, and future OpenXR-supported devices.
Be the first to learn about MRTK3 at a free event, online or in-person
Join us June 8th and 9th via livestream or at the Microsoft Campus in Redmond, WA. Either way, you’ll learn about MRTK3 directly from the engineers who are building the latest features. Catch deep technical sessions, provide feedback to the team, and ask your questions live.
By attending in-person, you’ll have access to even more goodness.
- Network with the Microsoft team and other developers.
- Catch a fireside chat or panel discussion
- Get expanded session content covering:
- How to build applications with C# and OpenXR using StereoKit, a code-first, open-source library for cross-platform development.
- Introduction to Babylon.js and how easy it is to bring mixed reality to the web.
- Recently released HoloLens features like Moving Platform Mode
Participate in the online hackathon
Mixed Reality Dev Days also marks the kickoff of a month-long online hackathon where you can compete for prizes while getting hands on with MRTK3 public preview or StereoKit. Join a team or build a solo project with access to expert support.
Learn more about Mixed Reality Dev Days and sign up now.
We look forward to connecting with you soon!
Mixed Reality Dev Days Team
by Contributed | May 20, 2022 | Technology
This article is contributed. See the original author and article here.
The Data Science Virtual Machine (DSVM) is a powerful data science development environment where you can perform data exploration and modeling tasks. The environment comes already built and bundled with several popular data analytics and data science tools that make it easy to get started without spending 20 min to 1 hour deploying a suitable infrastructure.
A new learning experience for R developers
Also, we are delighted to announce some exciting new updates which makes R a 1st Class developer experience for learners on DSVMs and on Learn Sandboxes on MS Learn. Starting from April 2022, the DSVM offering has been enriched by DSVM for Windows 2019 v. 22.04.21, DSVM for Ubuntu 20.04 and Ubuntu 18.04 v. 22.04.27, which provide an updated R environment including the following R libraries: Cluster, Devtools Factoextra, GlueHere, Ottr, Paletteer, Patchwork, Plotly, Rmd2jupyter, Scales, Statip, Summarytools, Tidyverse, Tidymodels and Testthat.
Getting started with R on DSVMs : a guided tutorial
But how you can start using R on DSVMs in your course or lab to perform data science tasks? Let’s go through all the steps you’ll need to create a DSVM on Azure and run a R Jupyter notebook.
1. First of all, you’ll need an Azure subscription. You have not one yet, have a look on how to sign up for a free trial or to the offers dedicated to your students.
2. Sign in to the Azure Portal and search for “data science virtual machine”. Choose one of the resulting offerings by clicking on it. For this tutorial we will use Data Science Virtual Machine – Ubuntu 20.04.

3. Choose a resource group and the name of the VM you want to create as well as the Azure subscription on which the machine will be billed. Select the datacenter region closest to your physical location and, for quicker set up, select “Password” as authentication type. Then specify the username and password you’ll use to login into your virtual machine.
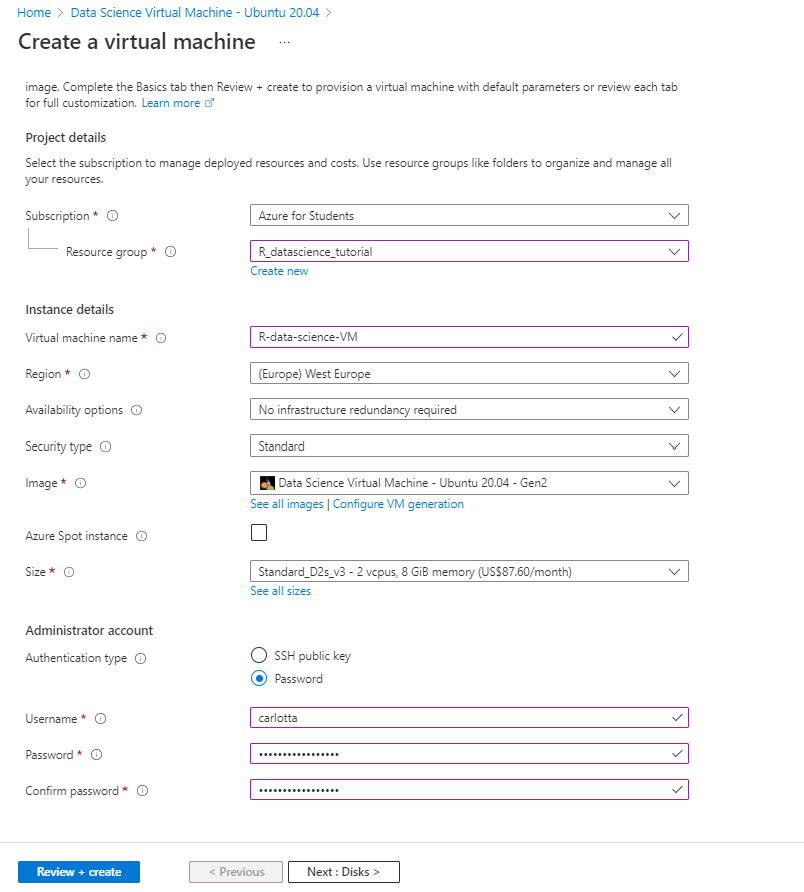
Click on Review + create and wait until the deploy is succesfully completed.
4. There are different ways to access your DSVM. One of these is Jupyter Hub, a multiuser Jupyter server. To connect, open a web browser from your local machine and navigate to https://your-vm-ip:8000, replacing “your-vm-ip” with the IP address you can find in the overview section of your resource.
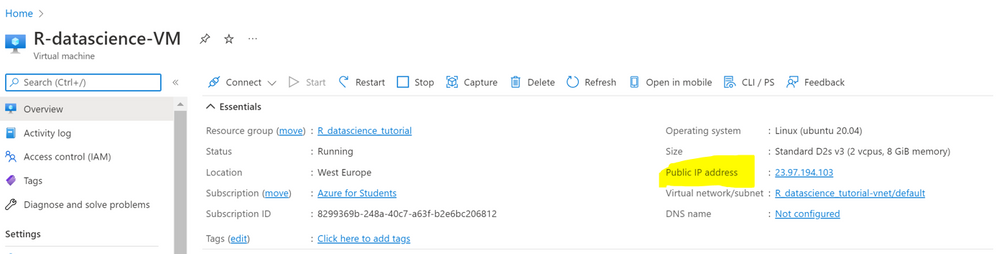
5. At this point, you can sign in using the credentials you specified at the creation of the resource.
6. You’re now ready to start coding in R. You may browse the many sample notebooks that are available or you can create a new notebook by clicking on the R kernel button.
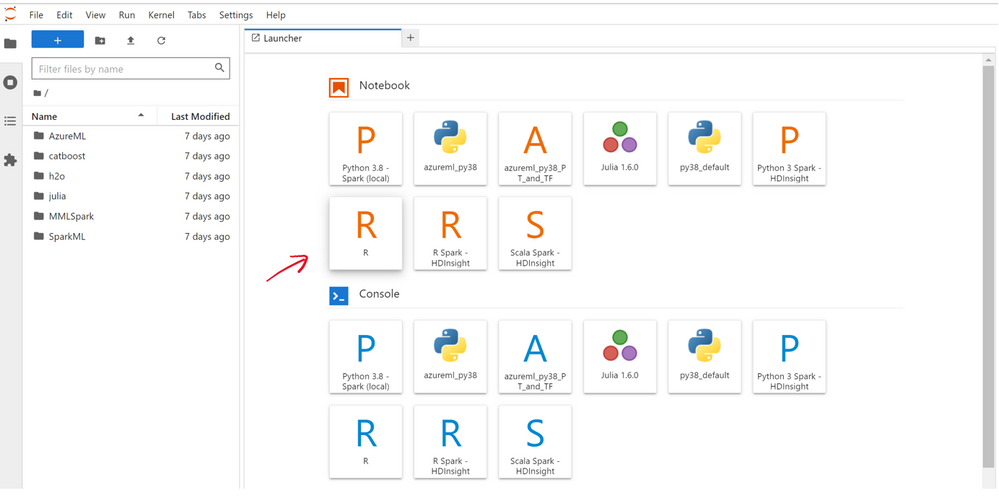
If you want to get more R code examples on data analysis and machine learning you can have a look to the exercise units of this MS Learn path: Create machine learning models with R and tidymodels .
7. Remember to shut down your machine when you are not using it.
Note that if you are an educator and you want to use DSVMs for you R course, you have the chance to choose if providing all your students with a single DSVM, by sharing the credentials within the class or to provide every student with a single DSVM, finding the right trade-off for you among costs and flexibility.
Keep on learning
The example above covers only one of the possible functionalities enabled by DSVMs. You can also open a session in an interactive R console or coding within RStudio, which is pre-installed in the VM. In addition, you can leverage on other Azure services for data storage and modeling and you can share code with your team by using GitHub and the pre-installed Git clients: Git Bash and Git GUI. Find out more guidance on the DSVM documentation.


Recent Comments