by Contributed | Sep 25, 2020 | Azure, Technology, Uncategorized
This article is contributed. See the original author and article here.
The most read paths on LEARN has gotten an update. Check out the new paths here and some description on what each path contains:
Azure Fundamentals part 1: Describe core Azure concepts
- Understand the benefits of cloud computing in Azure and how it can save you time and money
- Explain cloud concepts such as high availability, scalability, elasticity, agility, and disaster recovery
- Describe core Azure architecture components such as subscriptions, management groups, resources and resource groups
- Summarize geographic distribution concepts such as Azure regions, region pairs, and availability zones
Azure Fundamentals part 2: Describe core Azure services
- Understand the breadth of services available in Azure including compute, network, storage, and database
- Identify virtualization services such as Azure Virtual Machines, Azure Container Instances, Azure Kubernetes Service, and Windows Virtual Desktop
- Compare Azure’s database services such as Azure Cosmos DB, Azure SQL, Azure Database for MySQL, Azure Database for PostgreSQL, and Azure’s big data and analysis services
- Examine Azure networking resources such as Virtual Networks, VPN Gateways, and Azure ExpressRoute
- Summarize Azure storage services such Azure Blob Storage, Azure Disk Storage, and Azure File Storage
Azure Fundamentals part 3: Describe core solutions and management tools on Azure
- Choose the correct Azure Artificial Intelligence service to address different kinds of business challenges.
- Choose the best software development process tools and services for a given business scenario.
- Choose the correct cloud monitoring service to address different kinds of business challenges.
- Choose the correct Azure management tool to address different kinds of technical needs and challenges.
- Choose the right serverless computing technology for your business scenario.
- Choose the best Azure IoT service for a given business scenario.
Azure Fundamentals part 4: Describe general security and network security features
-
Having a good security strategy is essential in today’s digital world. Every application and service, whether on-premises or in the cloud, needs to be designed with security in mind. Security needs to happen at the application level, at the data level, and at the network level.
Learn about the various Azure services you can use to help ensure that your cloud resources are safe, secure, and trusted.
Azure Fundamentals part 5: Describe identity, governance, privacy, and compliance features
-
With the rise of remote work, bring your own device (BYOD), mobile applications, and cloud applications, the primary security boundary has shifted from firewalls and physical access controls to identity.
Understanding who is using your systems and what they have permission to do are critical to keeping your data safe from attackers. To stay organized, manage costs, and meet your compliance goals, you need a good cloud governance strategy.
Learn how Azure can help you secure access to cloud resources, what it means to build a cloud governance strategy, and how Azure adheres to common regulatory and compliance standards.
Azure Fundamentals part 6: Describe Azure cost management and service level agreements
-
Migration to the cloud presents new ways to think about your IT expenses. The cloud also removes the burden of supporting IT infrastructure.
As you move to the cloud, you might ask:
- How much will it cost?
- What guarantees does Azure provide around uptime and connectivity?
- How do preview services impact my production applications?
Learn about the factors that influence cost, tools you can use to help estimate and manage your cloud spend, and how Azure’s service-level agreements (SLAs) can impact your application design decisions.
by Contributed | Sep 25, 2020 | Azure, Technology, Uncategorized
This article is contributed. See the original author and article here.
The most read paths on LEARN has gotten an update. Check out the new paths here and some description on what each path contains:
Azure Fundamentals part 1: Describe core Azure concepts
- Understand the benefits of cloud computing in Azure and how it can save you time and money
- Explain cloud concepts such as high availability, scalability, elasticity, agility, and disaster recovery
- Describe core Azure architecture components such as subscriptions, management groups, resources and resource groups
- Summarize geographic distribution concepts such as Azure regions, region pairs, and availability zones
Azure Fundamentals part 2: Describe core Azure services
- Understand the breadth of services available in Azure including compute, network, storage, and database
- Identify virtualization services such as Azure Virtual Machines, Azure Container Instances, Azure Kubernetes Service, and Windows Virtual Desktop
- Compare Azure’s database services such as Azure Cosmos DB, Azure SQL, Azure Database for MySQL, Azure Database for PostgreSQL, and Azure’s big data and analysis services
- Examine Azure networking resources such as Virtual Networks, VPN Gateways, and Azure ExpressRoute
- Summarize Azure storage services such Azure Blob Storage, Azure Disk Storage, and Azure File Storage
Azure Fundamentals part 3: Describe core solutions and management tools on Azure
- Choose the correct Azure Artificial Intelligence service to address different kinds of business challenges.
- Choose the best software development process tools and services for a given business scenario.
- Choose the correct cloud monitoring service to address different kinds of business challenges.
- Choose the correct Azure management tool to address different kinds of technical needs and challenges.
- Choose the right serverless computing technology for your business scenario.
- Choose the best Azure IoT service for a given business scenario.
Azure Fundamentals part 4: Describe general security and network security features
-
Having a good security strategy is essential in today’s digital world. Every application and service, whether on-premises or in the cloud, needs to be designed with security in mind. Security needs to happen at the application level, at the data level, and at the network level.
Learn about the various Azure services you can use to help ensure that your cloud resources are safe, secure, and trusted.
Azure Fundamentals part 5: Describe identity, governance, privacy, and compliance features
-
With the rise of remote work, bring your own device (BYOD), mobile applications, and cloud applications, the primary security boundary has shifted from firewalls and physical access controls to identity.
Understanding who is using your systems and what they have permission to do are critical to keeping your data safe from attackers. To stay organized, manage costs, and meet your compliance goals, you need a good cloud governance strategy.
Learn how Azure can help you secure access to cloud resources, what it means to build a cloud governance strategy, and how Azure adheres to common regulatory and compliance standards.
Azure Fundamentals part 6: Describe Azure cost management and service level agreements
-
Migration to the cloud presents new ways to think about your IT expenses. The cloud also removes the burden of supporting IT infrastructure.
As you move to the cloud, you might ask:
- How much will it cost?
- What guarantees does Azure provide around uptime and connectivity?
- How do preview services impact my production applications?
Learn about the factors that influence cost, tools you can use to help estimate and manage your cloud spend, and how Azure’s service-level agreements (SLAs) can impact your application design decisions.
by Contributed | Sep 25, 2020 | Uncategorized
This article is contributed. See the original author and article here.
This week at Microsoft Ignite we announced the new home site app. The app gives employees a gateway to your organization, starting with the app’s name and icon, which you can customize to reflect the identity of your organization or your intranet. The app’s multi-level navigation lets people find sites across the organization, including portals, teams, communities and applications.
We are happy to see the excitement for this in the community and with our customers. Many of you have asked for additional information. As part of Ignite we have released a new session, on demand, focused on the home site app.
We have also put together an FAQ with the most common questions we have been asked.
Home site app
Q: Can any site be pinned as a Home site app in Teams?
A: Communication sites designated as Home Sites are eligible for pinning in Teams as the Home site app using our default configuration flow.
Q: Where are global navigation links curated?
A: Links for global navigation are managed through the home site, by home site owners, freeing global admins from having to play the role of curator
Q: Can my classic site be pinned in Teams ?
A: Only home sites are eligible to be pinned as the home site app in Teams with our default configuration flow. Home sites must be modern SharePoint communication sites.
Q: What is difference between Home site app and Home page pinned as tab?
A: The home site app provides organizations to pin company branded entry point to their intranet as a top level app in Teams. It provides an immersive site consumption experience, complete with navigation, mega-manus and support for tenant wide search. It also provides quick access to company curated resources, important sites and news similar to those provided by the SharePoint App Bar in the web. Home pages (or any other SharePoint pages) pinned as tabs in Channels provide ways to bring content directly into Team collaboration scenarios, and these pages have navigation and search elements removed to facilitate focus on the page content itself.
Q: Do I need a Home site app for the Global nav to show up in Teams?
A: Yes, the global navigation links are stored in the home site of a tenant, and is required in order for the navigation panel to appear in the home site app in Teams
Q: Can a Team site be a Home site?
A: No. Only communication sites can be made a Home site in a tenant.
We are humbled and honored by the reaction to this upcoming feature and appreciate all the engagement with us. Please, keep your feedback and questions coming.
by Contributed | Sep 25, 2020 | Uncategorized
This article is contributed. See the original author and article here.
This week’s blog roundup brought to you by Excel MVPs Charles Williams, David Abiola, and Yolanda Cuesta
Backward Compatibility of Dynamic Arrays
Charles Williams offers an in-depth discussion of dynamic array backward compatibility
Lookup Values in VBA Userform using XLOOKUP
David Abiola provides a tutorial on using XLOOKUP to look up values in Excel VBA Userform
Crea tu hoja Excel de gastos (Create your Excel expense sheet)
Yolanda Cuesta shows how to create a simple Excel expense sheet to help manage household income and payments
Find this useful and/or have an Excel question? Click the Like button and/or leave a comment below
by Contributed | Sep 25, 2020 | Uncategorized
This article is contributed. See the original author and article here.
HoloLens applications have the power to overlay digital objects on top of the real world. Getting these holograms to look visually accurate comes with its own set of challenges, but how should they sound? This post will cover the audio side of developing for mixed reality, providing some tips and tricks for making your application’s audio more immersive.
Adding audio to your application is an easy way to increase user engagement and confidence. For example, even the simple act of adding a sound to confirm a button click can let the user know when their input has been recognized. Going one step further – enabling spatial audio for that same button click can make the user interface feel like it is coexisting in the same physical room as the user, rather than just some button floating in space. This short video demonstrates these differences (best listened to over headphones for the closest representation of what a user will hear with HoloLens).
To get started, you’ll need to add an audio spatializer plugin to your Unity project. I recommend including the Microsoft Spatializer. This has the added benefit of offloading all spatial audio processing to dedicated hardware on the HoloLens 2, freeing up more CPU for your application’s core business logic. If you’re looking to get started quickly, you can download this plugin directly from the releases tab on Github. If you need to customize the plugin for any reason, you can also build it directly from the repository – it is fully open source.
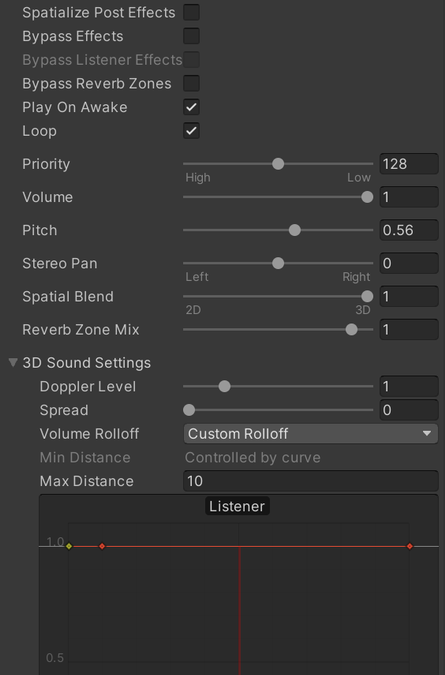
Once you have the plugin added to your Unity project, you can enable spatial audio for an audio source by clicking the Spatialize checkbox and setting the Spatial Blend to 1.0. You’ll also notice that there is a volume roll-off curve. Unity’s default curve may or may not work for your application. For example, we recommend disabling distance attenuation for UI sounds. To do this, flatten the curve out as seen below. Don’t be afraid to experiment with this volume curve! All applications have different requirements, so different curves can be useful.
 Unity Audio Source settings to enable spatial audio and disable distance attenuation
Unity Audio Source settings to enable spatial audio and disable distance attenuation
What about for sounds for more interesting holograms? Spatial audio has the benefit of helping a user distinguish between multiple sound sources playing simultaneously. Instead of a cacophony of sounds, users can enjoy increased ability to locate holograms when spatial sound is enabled, as seen in this video.
One important note about the Microsoft Spatializer – to leverage the hardware acceleration capabilities of the HoloLens 2, the Unity audio mixer functionality is bypassed. If you are accustomed to routing audio sources to different mixer groups to better control volume or effects processing, you’ll need to apply those effects on a per-source basis instead of using the audio mixer. Unity comes with some built-in audio effects, such as EQ filters and reverb. Additionally, some other Unity plugins, such as WebRTC, rely on the audio effect infrastructure to operate properly. If you want to use audio effects in conjunction with the Microsoft Spatializer, make sure to check the “Spatialize Post Effects” checkbox on the audio source, otherwise these components won’t work properly.
A quick note on when not to use spatial audio. Given how easy it is to enable spatial audio, you may be inclined to enable it for all the audio in your application! However, there are cases when this can be distracting. In general, spatial audio works best for things that also have a visual component (i.e. menus, holograms, etc.). For audio-only parts of your application, such as narrators or background music, spatial audio may actually be more of a distraction. Consider disabling spatial audio for these sounds so the user may enjoy them without looking around for some visual cue of where they are coming from.
If you want more information about adding spatial audio to your application, definitely check out the full set of documentation, and try out the spatial audio tutorial. If you’re developing with the Unreal Engine, these same principals apply but there’s a slightly different setup process. You can learn more about using spatial audio in the Unreal Engine here. If you’ve done all this and are ready to explore what else you can do with audio, check out Project Acoustics! It can add an additional layer of immersion to your application by simulating room effects. If you’ve gotten stuck somewhere along the way, let us know in the comments, or feel free to file an issue on the Microsoft Spatializer issues page.
by Contributed | Sep 25, 2020 | Uncategorized
This article is contributed. See the original author and article here.
This week, at Ignite, we announced that the next version of Skype for Business (SfB) Server will be available in the second half of 2021, and will only be available with the purchase of a subscription license. Subscription entitles access to support, product updates, bug and security fixes. We will share additional details around the official name, pricing and availability, later.
The next version of SfB Server will support in-place upgrade from SfB Server 2019 for a period of approximately two years following release. This feature will allow the admin to easily upgrade existing servers running SfB Server 2019 to the subscription-based codebase without needing to add or change servers.
The next version of SfB Server will continue to support side-by-side deployment and migration from earlier versions of SfB, as has been the case over the last few releases, but we have increased the number of versions it can be installed alongside. Customers with Lync Server 2013, SfB Server 2015 or SfB Server 2019 can install the next version of SfB Server into their existing organization.
We highly recommended that customers with existing Lync Server 2013 or SfB Server 2015 deployments and who expect to keep on-premises servers in the future, should start planning and installing SfB Server 2019 today. Once the next version of SfB is released, they will then be able to perform an in-place upgrade to that version, making the move to SfB Server 2019 the last major upgrade they will ever need to do.
We will have more details on this change over the coming months.
-SfB Server Team



Recent Comments