by Scott Muniz | Aug 12, 2020 | Uncategorized
This article is contributed. See the original author and article here.
The database level health detection failover option introduced on this article
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/sql/database-engine/availability-groups/windows/sql-server-always-on-database-health-detection-failover-option?view=sql-server-ver15
In addition to the existing checks, the new implementation has the following additional checks.
- The new implementation stores and uses a historical snapshot of the database state information to decide if the AG needs to be marked in error state or not. The health check routine caches the database state and associated error information, for the last three executions, which is then compared with the state information from the current execution of the health detection routine. If the same error condition (for the below mentioned error codes) exists in the four consecutive runs of the health detection routine, a failover is initiated. So for example if during the first run, let’s say at 22:00:00 there is an error 823, and the same error conditions exists at the subsequent runs at 22:00:10, 22:00:20 and 22:00:30 then the AG is marked in an error state and the control is passed to the cluster. This implementation is intended to provide safeguards against transient errors and issues which can be fixed by the auto page repair capabilities of the availability groups.
- The new implementation checks for following additional errors. Majority of these errors are indicative of a hardware issues on the server. Please note, that this is not an exhaustive list of errors which could impact the database availability. There is an outstanding item to include error 824 to this list.
If we enable this feature, to make sure AG can failover successfully, we need to change the default failover policy.
The default “max restarts in the specified Period =1 in 1 hour
The default “max failure in the specified Period” =1 in 6 hours
Based on this settings, if the 823 error reported but this error could not be repaired from the secondary replica:
- Detected 823 in 3 generation(30s)
- WFSC got the error state from the AG controller, restarted the AG resource. –DB level error won’t prevent AG resource restart, the restart always works fine.
- The failure count +1, the restart count+1
- If continue detect 823 again—>AG offline. No failover because it reach to “max failure in the specified Period” =1. no more action took.
Recommend setting : “max failure in the specified Period” >=“max restarts in the specified Period+1 at least. Then all restart attempt finished but the issue still is detected, next time failover will trigger.

by Scott Muniz | Aug 12, 2020 | Uncategorized
This article is contributed. See the original author and article here.
2020 has been a challenging year for everyone and good news has been hard to come by ,this is why we are excited to announce that System Center Operations Manager 2019 has come out with Update Rollup 2 to elevate your monitoring spirits!
Update Roll Up 2 for System Center Operations Manager 2019 was released last week and there are some cool new features to explore .This blog will briefly go through these features to get you plugged in and ready to go .
To begin with we have the management pack change tracking supported to finally be able to audit certain changes being done in SCOM. It is a feature that many SCOM users, administrators and customers have been waiting for.
In System Center Operations Manager user roles are defined to determine as to who can potentially change monitoring settings for applications and services through management packs. Various user roles (profiles) are defined to access and perform actions on the monitored objects. There can be multiple users associated with a single user role and these users interact with SCOM to monitor data relevant to their role. A profile is defined on a group of users which impose Role-based security and limit privileges that users have for various aspects of Operations Manager. When multiple users access and change the same object it becomes difficult to track, WHAT changes are done by WHOM and WHEN?
For SCOM customers with large scale environments this exercise can sometimes seem as daunting as looking for a needle in a haystack! With the change tracking feature enabled these time consuming and frustrating activities can be carried out in a matter of minutes .Admin users can now easily identify root causes for issues caused due to changes done by any user in SCOM. Once the changes are identified the admin can choose to undo them if needed.
To overcome this challenge, SCOM 2019 UR2 has enabled Change Tracking by default which tracks and reports all the changes on the management packs and management pack objects. All these changes are logged in Operations Manager Datawarehouse Database and you can generate reports on it.
There are 3 new reports created in SCOM to show these changes. They are present under Reporting -> Microsoft Generic Report library as “Management Pack History”, “Management Pack Objects”, “Overrides Tracking”. These reports have the filtering enabled so you can track and report the changes as per your need. The section below gives an overview of each report:
- Management Pack History
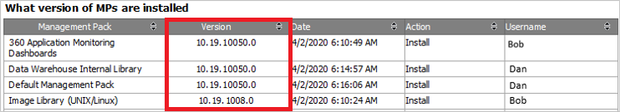
The management pack history report generates the list of all the management packs, which are either imported or deleted on any management server in your management group. You can filter the report by date, action, and username.
You can find an example of how the filters and reports look like below:
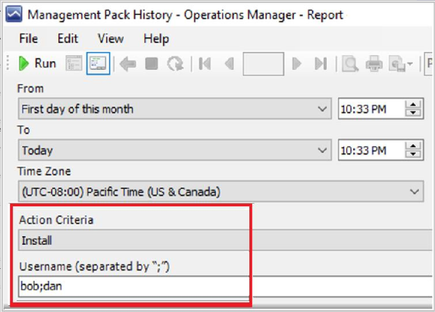
Sample Report:
- Management Pack Objects
This report tracks and generates the list of all management pack objects, which are newly created or deleted from the management server. This report also tracks edits on management pack objects like renaming a group/monitor/rule or adding/deleting a member in the group etc.
You can find an example of how the filters and reports look like below:
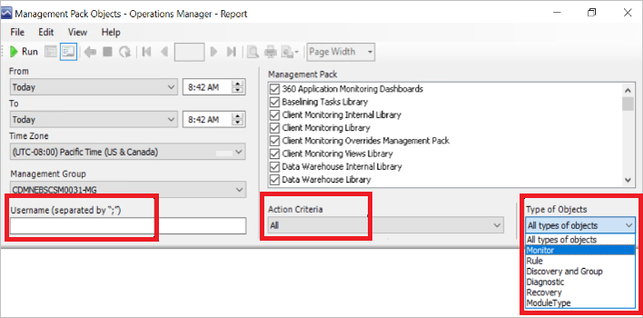
Sample Report:
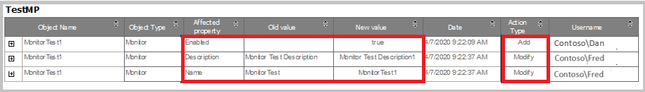
- Overrides Tracking
Overrides are created to tune monitoring. Multiple user roles can create these overrides in Operations Manager. When different users create overrides, it becomes crucial to track and capture the user who made these changes and when.
To view detailed information for every changed parameter, expand each of the rows, the results are grouped by management pack name.
You can find an example of how the filters and reports look like below:
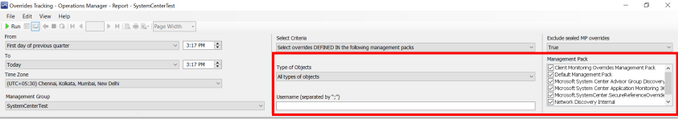
Sample Report:
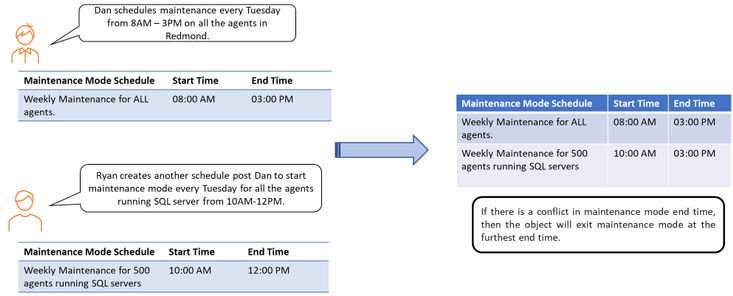
Customers have been asking for enhancements of the schedule maintenance mode feature in SCOM and we have been listening!
As we all know schedule maintenance mode feature was introduced in SCOM 2016 where SCOM admins can choose a time in future to put the machines in maintenance mode. SCOM customers have 1000s of agents monitoring their infrastructure environments. They usually patch these agents in groups at predefined schedules which may or may not be recurring in nature.
Users who are patching the agents are generally different from admin users and conflicting maintenance mode schedules can lead to the undesirable scenario of SCOM generating multiple alerts. Based on feedback received from our customers we have included some enhancement to this critical feature to help customers ensure seamless business continuity.
With 2019 UR2, if there is a conflict in maintenance mode end time, then the object will exit maintenance mode at the furthest end time defined for the object.
Below is an example to illustrate this feature:
Let’s talk about the Web Console!
It has been our continued focus to give customers a consistent user experience in the Web Console. We have now included the Favorite Reports feature and support for folders in the monitoring view of web console in SCOM 2019 as well.
Without Favorite Reports ,running ad-hoc SCOM reports on a regular basis can be time consuming for users going about their day to day tasks ,as it adds the overhead of also launching the Operations Console .But this pain point will now be a thing of the past as Favorite Reports feature is now available in the Web Console as part of SCOM 2019 UR2 .
To further allow efficient organization and easy access to important dashboards and views users can also create folders and place dashboards inside them in SCOM 2019 UR2.
We also continue to invest in enhancing the cross-platform monitoring capabilities of SCOM to cater to the rapidly increasing diverse environments. Operations Manager 2019 UR2 now also supports CentOS 8 under Universal Linux (RPM package).
Here is a list of supported Linux distributions on SCOM 2019 as of UR2:
- Red Hat Enterprise 7 and 8
- Suse Enterprise 12 and 15
- OpenSuse Leap 15
- Debian 8 and 9
- Ubuntu 16.04 and 18.04
- CentOS 6,7 and 8
- Oracle Linux 6 and 7
Silect Dashboards for SCOM
Last but not least the new Silect dashboards for System Center Operations Manager leverage the interactive visualizations and business intelligence capabilities of Power BI to provide you with an in-depth look at the state of your IT infrastructure. View and easily share rich visualizations of the operational state of your IT environment including alert information, management pack activities, details on the state of critical SCOM components and much more. More Information https://www.silect.com/dashboards-for-scom/.
Some of you got the opportunity to try out of the preview of the Update Roll up 2 of SCOM 2019 and the feedback has been very encouraging!!
Additionally, fixes for critical defects continue to be a part of UR2. Find more details at the following link:
KB Article- Update Rollup 2 (UR2) for System Center 2019 Operations Manager.
For the details of features that are released in Update Rollup 2, see the following Microsoft Docs article:
What’s New in System Center Operations Manager 2019 Update Rollup 2
We sincerely hope you enjoy the SCOM 2019 Update Roll up 2. Upgrade Now!
by Scott Muniz | Aug 11, 2020 | Uncategorized
This article is contributed. See the original author and article here.
Update 2006 for Microsoft Endpoint Configuration Manager current branch is now available. Microsoft Endpoint Manager is an integrated solution for managing all your devices. Microsoft brings together Configuration Manager and Intune into a single console called Microsoft Endpoint Manager admin center.
On our minds and we are sure yours too, are the challenges posed with working from home. Previously we have blogged some guidance for these scenarios.
In March, we made the decision to close the Microsoft Redmond campus and ask all of our engineers to work from home for three weeks to help curb the spread of COVID19. At the time, three weeks sounded like a long time – little did we know that 6 months later we would still not set foot on campus. It was certainly an adjustment for everyone – but fortunately the tools and investments that Microsoft made in the name of employee flexibility and empowerment (Cloud identity using Azure Active Directory, Cloud provisioning using AutoPilot, Cloud Management from Microsoft Endpoint Configuration Manager and Intune ) also enabled employees to more easily work from home.
 work from anywhere
work from anywhere
But of course as we were forced to rely on our tools to work remotely 100% of the time, we found opportunities to improve: allowing clients to upgrade on metered networks, making it easier to download content from the cloud instead of a VPN, and simplifying remove provisioning among other things. So, we committed to focusing our ConfigMgr 2006 release on making these improvements and making them available to you.
Look below for the Work from Anywhere tag  to find these features and others.
to find these features and others.
This release is brought to you by team members in Florida, Washington, British Columbia, Massachusetts, Pennsylvania, Maine, North Carolina, Michigan, Utah, California, Georgia, Shanghai and Suzhou China, and ‘Undisclosed’ – and we hope it will help make it easier to continue to manage your devices wherever they may be.
This release includes:
Microsoft Endpoint Manager tenant attach
Import previously created Azure AD application during tenant attach onboarding – During a new onboarding, an administrator can specify a previously created application during onboarding to tenant attach.
Endpoint Analytics
Endpoint Analytics Preview – the Endpoint Analytics preview is available. Endpoint analytics can help identify policies or hardware issues that may be slowing down devices and proactively make changes without disrupting end users or generating a help desk ticket.
Endpoint analytics data collection enabled by default – In 2006, the Enable Endpoint analytics data collection client setting is now enabled by default for tenants attaching for the first time. This setting allows your managed endpoints to send data, such as startup performance insights, to your Configuration Manager site server. This change affects local data collection only. Endpoint analytics data isn’t uploaded to the Microsoft Endpoint Manager admin center until you enable data upload in Configuration Manager. The new default value applies to the default client settings and any custom client settings created after upgrading to version 2006.
Site infrastructure
 VPN boundary type – To simplify managing remote clients, you can now create a new boundary type for VPNs. Previously, you had to create boundaries for VPN clients based on the IP address or subnet. Now when a client sends a location request, it includes additional information about its network configuration. Based on this information, the server determines whether the client is on a VPN.
VPN boundary type – To simplify managing remote clients, you can now create a new boundary type for VPNs. Previously, you had to create boundaries for VPN clients based on the IP address or subnet. Now when a client sends a location request, it includes additional information about its network configuration. Based on this information, the server determines whether the client is on a VPN.
 Management insights to optimize for remote workers – This release adds a new group of management insights, Optimize for remote workers. These insights help you create better experiences for remote workers and reduce load on your infrastructure. The insights in this release primarily focus on VPN:
Management insights to optimize for remote workers – This release adds a new group of management insights, Optimize for remote workers. These insights help you create better experiences for remote workers and reduce load on your infrastructure. The insights in this release primarily focus on VPN:
- Define VPN boundary groups
- Configure VPN connected clients to prefer cloud-based content sources
- Disable peer to peer content sharing for VPN connected clients
 Improved support for Windows Virtual Desktop – The Windows 10 Enterprise multi-session platform is available in the list of supported OS versions on objects with requirement rules or applicability lists.
Improved support for Windows Virtual Desktop – The Windows 10 Enterprise multi-session platform is available in the list of supported OS versions on objects with requirement rules or applicability lists.
 Intranet clients can use a CMG software update point – Intranet clients can now access a CMG software update point when it’s assigned to a boundary group. You can allow intranet devices to scan against a CMG software update point in the following scenarios:
Intranet clients can use a CMG software update point – Intranet clients can now access a CMG software update point when it’s assigned to a boundary group. You can allow intranet devices to scan against a CMG software update point in the following scenarios:
- When an internet machine connects to the VPN, it will continue scanning against the CMG software update point over the internet.
- If the only software update point for the boundary group is the CMG software update point, then all intranet and internet devices will scan against it.
Cloud-attached management
Notification for Azure AD app secret key expiration – If you configure Azure services to cloud-attach your site, the Configuration Manager console now displays notifications for the following circumstances:
- One or more Azure AD app secret keys will expire soon
- One or more Azure AD app secret keys have expired
Use Microsoft Azure China 21Vianet for co-management – You can now select the Azure China Cloud as your Azure environment when enabling co-management.
Real-time management
The following improvements have been made in CMPivot –
- CMPivot from the console and CMPivot standalone have been converged
- Run CMPivot from an individual device or multiple devices without having to select or create a collection
- From CMPivot query results, you can select an individual device or multiple devices then launch a separate CMPivot instance scoped to your selection.
Client management
 Install and upgrade the client on a metered connection –Previously, if the device was connected to a metered network, new clients wouldn’t install. Existing clients only upgraded if you allowed all client communication. Starting in this release, client install and upgrade both work when you set the client setting Client communication on metered internet connections to Allow or Limit. With this setting, you can allow the client to stay current, but still manage the client communication on a metered network.
Install and upgrade the client on a metered connection –Previously, if the device was connected to a metered network, new clients wouldn’t install. Existing clients only upgraded if you allowed all client communication. Starting in this release, client install and upgrade both work when you set the client setting Client communication on metered internet connections to Allow or Limit. With this setting, you can allow the client to stay current, but still manage the client communication on a metered network.
Improvements to managing device restarts – Configuration Manager provides many options to manage device restart notifications. You can now configure the client setting Configuration Manager can force a device to restart to prevent devices from automatically restarting when a deployment requires it. By default, Configuration Manager can still force devices to restart
Application management
 Improvements to available apps via CMG – This release fixes an issue with Software Center and Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) authentication. For a client detected as on the intranet but communicating via the cloud management gateway (CMG), previously Software Center would use Windows authentication. When it tried to get the list of user-available apps, it would fail. It now uses Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) identity for devices joined to Azure AD. These devices can be cloud-joined or hybrid-joined.
Improvements to available apps via CMG – This release fixes an issue with Software Center and Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) authentication. For a client detected as on the intranet but communicating via the cloud management gateway (CMG), previously Software Center would use Windows authentication. When it tried to get the list of user-available apps, it would fail. It now uses Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) identity for devices joined to Azure AD. These devices can be cloud-joined or hybrid-joined.
Microsoft 365 Apps for enterprise – Office 365 ProPlus was renamed to Microsoft 365 Apps for enterprise on April 21, 2020. Starting in version 2006, the following changes have been made:
- The Configuration Manager console has been updated to use the new name. This change also includes update channel names for Microsoft 365 Apps.
- A banner notification was added to the console to notify you if one or more automatic deployment rules reference obsolete channel names in the Title criteria for Microsoft 365 Apps updates.
Operating system deployment
 Task sequence media support for cloud-based content – Task sequence media can now download cloud-based content. Instead of further taxing the WAN to download large OS deployment content, boot media and PXE deployments can now get content from cloud-based sources.
Task sequence media support for cloud-based content – Task sequence media can now download cloud-based content. Instead of further taxing the WAN to download large OS deployment content, boot media and PXE deployments can now get content from cloud-based sources.
 Improvements to task sequences via CMG – This release includes the following improvements to deploy task sequences to devices that communicate via a cloud management gateway (CMG):
Improvements to task sequences via CMG – This release includes the following improvements to deploy task sequences to devices that communicate via a cloud management gateway (CMG):
- Support for OS deployment: With a task sequence that uses a boot image to deploy an OS, you can deploy it to a device that communicates via CMG. The user needs to start the task sequence from Software Center.
- This release fixes the two known issues from Configuration Manager current branch version 2002. You can now run a task sequence on a device that communicates via CMG in the following circumstances:
Improvements to BitLocker task sequence steps
- You can now specify the disk encryption mode on the Enable BitLocker and Pre-provision BitLocker task sequence steps. By default, the steps continue to use the default encryption method for the OS version.
- The Enable BitLocker step also now includes a setting to Skip this step for computers that do not have a TPM or when TPM is not enabled. When you enable this setting, the step logs an error on a device without a TPM or a TPM that doesn’t initialize, and the task sequence continues.
Management insight rules for OS deployment – When the size of the task sequence policy exceeds 32 MB, the client fails to process the large policy. The client then fails to run the task sequence deployment. To help you manage the policy size of task sequences, this release includes the following management insights:
- Large task sequences may contribute to exceeding maximum policy size
- Total policy size for task sequences exceeds policy limit
Improvements to OS deployment – This release includes the following additional improvements to OS deployment:
- Use a task sequence variable to specify the target of the Format and Partition Disk step. This new variable option supports more complex task sequences with dynamic behaviors.
- The Check Readiness step now includes a check to determine if the device uses UEFI. It also includes a new read-only task sequence variable, _TS_CRUEFI.
- If you enable the task sequence progress window to show more detailed progress information, it now doesn’t count enabled steps in a disabled group. This change helps make the progress estimate more precise.
- Previously, during a task sequence to upgrade a device to Windows 10, a command prompt window opened during one of the final Windows configuration phases. The window was on top of the Windows out-of-box experience (OOBE), and users could interact with it to disrupt the upgrade process. Now the SetupCompleteTemplate.cmd and SetupRollbackTemplate.cmd scripts from Configuration Manager include a change to hide this command prompt window.
- Some customers build custom task sequence interfaces using the IProgressUI::ShowMessage method, but it doesn’t return a value for the user’s response. This release adds the IProgressUI::ShowMessageEx method. This new method is similar to the existing method, but also includes a new integer result variable, pResult.
Protection
 CMG support for endpoint protection policies – While the cloud management gateway (CMG) has supported endpoint protection policies, devices required access to on-premises domain controllers. Starting in this release, clients that communicate via a CMG can immediately apply endpoint protection policies without an active connection to Active Directory.
CMG support for endpoint protection policies – While the cloud management gateway (CMG) has supported endpoint protection policies, devices required access to on-premises domain controllers. Starting in this release, clients that communicate via a CMG can immediately apply endpoint protection policies without an active connection to Active Directory.
BitLocker management support for hierarchies – You can now install the BitLocker self-service portal and the administration and monitoring website at the central administration site.
Configuration Manager console
Community hub and GitHub – (First introduced in June 2020)
The IT admin community has developed a wealth of knowledge over the years. Rather than reinventing items like scripts and reports from scratch, we’ve built a Configuration Manager Community hub where you can share with each other. The Community hub fosters creativity by building on others’ work and having other people build on yours. GitHub already has industry-wide processes and tools built for sharing. Now, the Community hub will leverage those tools directly in the Configuration Manager console as foundational pieces for driving this new community. For the initial release, the content made available in the Community hub will be uploaded only by Microsoft.
Notifications from Microsoft
You can now choose to receive notifications from Microsoft in the Configuration Manager console. These notifications help you stay informed about new or updated features, changes to Configuration Manager and attached services, and issues that require action to remediate.
Other updates
For more details and to view the full list of new features in this update, check out our What’s new in version 2006 of Microsoft Endpoint Configuration Manager documentation.
Note: As the update is rolled out globally in the coming weeks, it will be automatically downloaded, and you’ll be notified when it’s ready to install from the “Updates and Servicing” node in your Configuration Manager console. If you can’t wait to try these new features, see these instructions on how to use the PowerShell script to ensure that you are in the first wave of customers getting the update. By running this script, you’ll see the update available in your console right away.
For assistance with the upgrade process, please post your questions in the Site and Client Deployment forum. Send us your Configuration Manager feedback through Send-a-Smile in the Configuration Manager console.
Continue to use our UserVoice page to share and vote on ideas about new features in Configuration Manager.
Thank you,
The Configuration Manager team
Additional resources:
by Scott Muniz | Aug 11, 2020 | Uncategorized
This article is contributed. See the original author and article here.
Did you know that you can utilize Microsoft Endpoint Manager to help manage BitLocker on your Windows devices?
In May of 2019, we announced that we would be adding capabilities to manage Microsoft BitLocker on enterprise Windows devices to both Microsoft Intune and Configuration Manager. We then announced the marriage of Microsoft Intune and Configuration Manager with Microsoft Endpoint Manager.
Here is a quick summary of those announcements and the current status (although I do recommend you read both posts in detail):
- We have added many configuration service providers, or CSPs, to Microsoft Intune to help you turn on, manage, report the status of, and turn off BitLocker encryption, including Trusted Platform Module (TPM) management. In Intune, these CSPs were added in the second half of 2019. We added these capabilities to Configuration Manager starting with a private preview in June 2019, and they are generally available today.
- In November of 2019, we combined our two enterprise management offerings—Microsoft Intune for cloud management and Configuration Manager for on-premises management—into a single offering called Microsoft Endpoint Manager. Today over 200 million devices are managed with Microsoft Endpoint Manager.
Last year, we also announced extended support for Microsoft BitLocker Administration and Monitoring (MBAM). Those of you using MBAM can continue to do so until April 14, 2026. In the meantime, we recommend that you start thinking about migrating your devices to Microsoft Endpoint Manager to manage BitLocker.
Manage BitLocker using Microsoft Intune
Microsoft Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) and Microsoft Intune bring the power of the intelligent cloud to Windows 10 device management, including management capabilities for BitLocker. Some of these capabilities work on Windows 10 Pro, while other capabilities require Windows 10 Enterprise or Education editions.
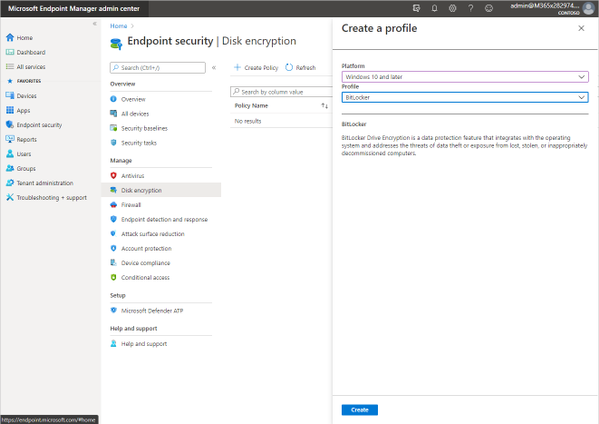
The first step to managing BitLocker using Microsoft Intune is to visit the new Microsoft Endpoint Manager admin center. Select Endpoint security > Disk encryption, and then Create policy. Enter in the Platform and Profile indicated in the screen capture below, and then select Create.
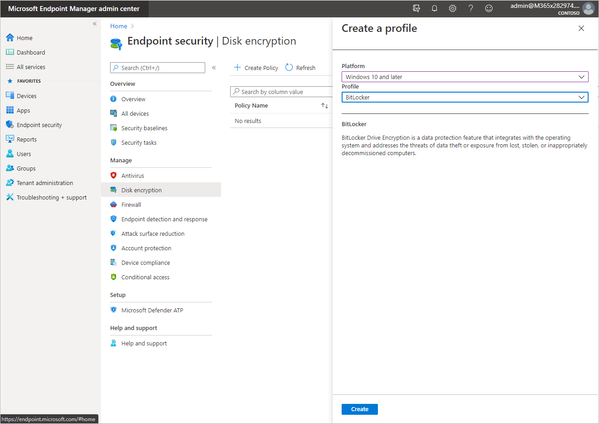 creating a new Microsoft BitLocker policy in Microsoft Endpoint Manager
creating a new Microsoft BitLocker policy in Microsoft Endpoint Manager
Next, enter the basics, such as the name of the policy and an optional description, then move on to Configuration settings. Notice you can search for a specific setting, like “fixed drive policy,” or you can scroll through the settings. Also notice the options offered for key rotation. This setting, which requires Windows 10, version 1909 or later, will change the recovery key when the recovery key is used to unlock a drive.
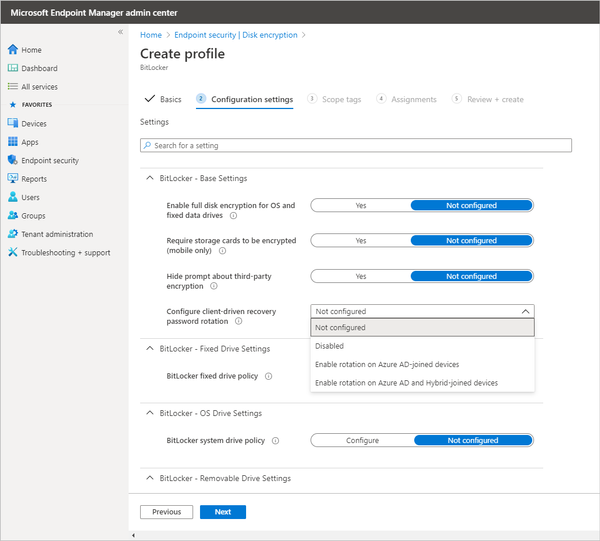 Create an Endpoint Security profile in Microsoft Endpoint Manager
Create an Endpoint Security profile in Microsoft Endpoint Manager
As you enable settings, additional settings may appear. For example, Enabling Fixed drive encryption expands more options: Recovery key file creation and Configure BitLocker recovery key package.
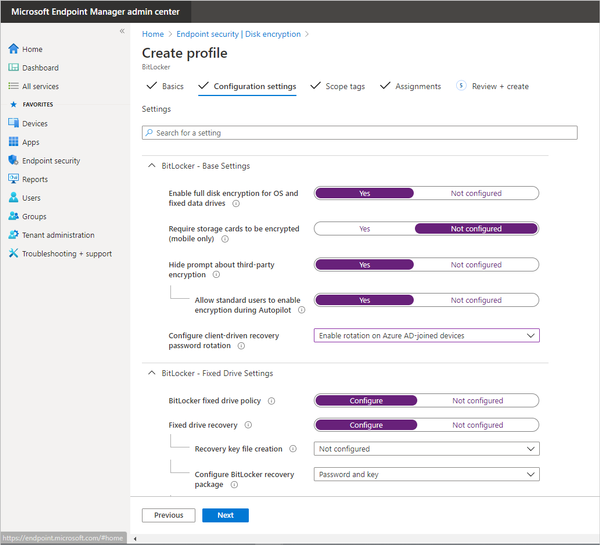 Configuring BitLocker settings in Microsoft Endpoint Manager
Configuring BitLocker settings in Microsoft Endpoint Manager
Finally, add Scope tags, assign the new policy to specific groups of users or devices, and select Create.
The settings that can be configured here include:
- BitLocker – Base Settings
- Enable full disk encryption for OS and fixed data drives
- Require storage cards to be encrypted (mobile only)
- Hide Prompt about third-party encryption
- Configure client-driven recovery password rotation
- BitLocker – Fixed Drive Settings
- BitLocker fixed drive policy
- BitLocker – OS Drive Settings
- BitLocker system drive policy
- BitLocker – Removable Drive Settings
- BitLocker removable drive settings
For more details, see the RequireDeviceEncryptionsection of the BitLocker CSP.
Manage BitLocker using Configuration Manager
For enterprise organizations currently using on-premises management of their endpoint devices, the best approach would be to enable co-management with Microsoft Intune and Configuration Manager, and use the CSPs available in Microsoft Intune. This may not be an option, so we’ve also made BitLocker management available in Configuration Manager current branch, as early as July 2019. When using Configuration Manager, BitLocker management also supports Windows 8.1. And, although Windows 7 is no longer a supported operating system, we are not blocking BitLocker management on Windows 7; however, some settings may not apply to Windows 7 devices. Please review the product support lifecycle page for end of support dates for these operating systems.
When you open the Microsoft Endpoint Configuration Manager console, navigate to Assets and Compliance > Overview > Endpoint Protection > BitLocker Management. From there, you can create a new BitLocker Management Control Policy, where you can specify whether to encrypt the Operating System Drive, and/or Fixed Drives, and/or Removeable Drives, and set Client Management policies.
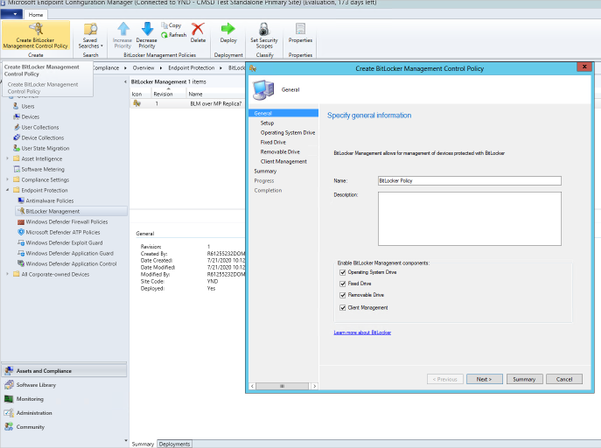 Creating a new BitLocker Management Control Policy to manage BitLocker on the Configuration Manager managed devices
Creating a new BitLocker Management Control Policy to manage BitLocker on the Configuration Manager managed devices
As you select these checkboxes, additional pages will appear in the navigation pane on the left.
Enabling the Drive encryption policy, then allows you to choose the encryption method: AES 128-bit (default), AES 128-bit with Diffuser, AES 256-bit with Diffuser, or AES 256-bit. Enabling the encryption and cypher strength (Windows 10) offers a few more choices: AES-CBC 128-bit, AES-CBC 256-bit, XTS-AES 128-bit, XTS-AES 256-bit. Hovering over a policy displays a message box full of information. For more information about the different encryption and cypher strengths available, see the BitLocker settings reference.
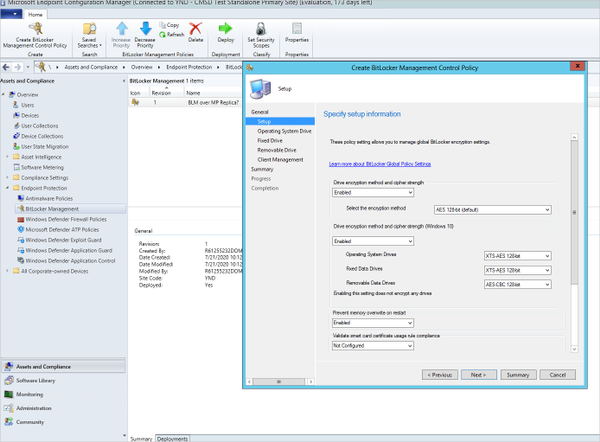 Specifying setup information for the BitLocker Management Control Policy
Specifying setup information for the BitLocker Management Control Policy
All entries listed in the screenshot above are the default once enabled and are not necessarily the recommended settings. Research the different encryption and cypher strengths available before configuring the policy.
The next page brings you to the Operating System Drive, where you can enable settings such as TPM protector, and PIN length. PIN must be between 4-20 characters. You can also configuration settings for Enhanced PINs – that is, PINs that allow upper and lower case letters, numbers, special characters, and spaces, and a password for operating system drives, which likewise allows you to either allow or require password complexity.
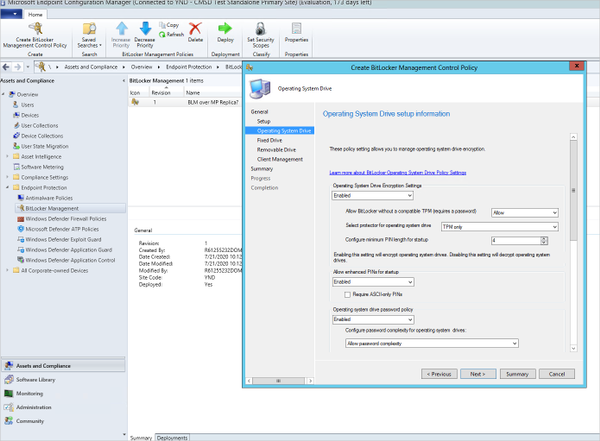 Configuring BitLocker Management Control Policy settings for OS drives
Configuring BitLocker Management Control Policy settings for OS drives
Configuring the settings on the Fixed Drive page allows you to enable fixed drive encryption, as well as specify whether or not fixed drives can be auto-unlocked, deny write access to fixed drives that are not protected by BitLocker, and specify whether or not to install BitLocker To Go on FAT formatted drives.
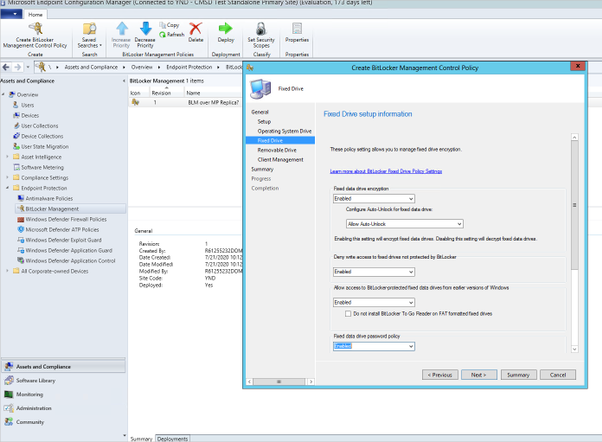 Configuring BitLocker Management Control Policy settings for fixed drives
Configuring BitLocker Management Control Policy settings for fixed drives
The next page allows you to specify the settings which will be applied to removeable drives, such as denying access to those drives which have not been protected with BitLocker, and whether or not these removeable drives should be accessible from earlier versions of Windows.
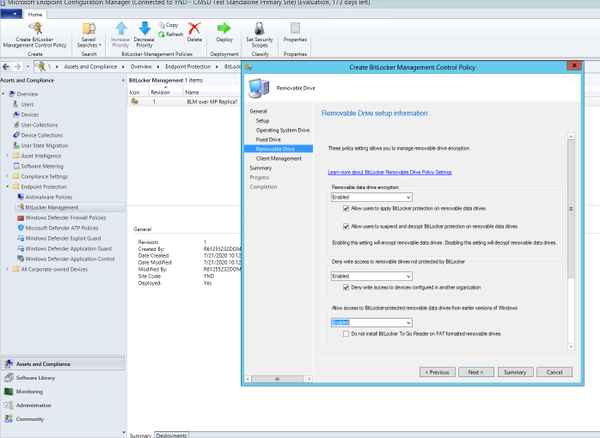 Configuring BitLocker Management Control Policy settings for removable system drives
Configuring BitLocker Management Control Policy settings for removable system drives
Finally, the Client Management policy allows you to manage the key recovery service backup of the BitLocker information, such as Recovery password and key package, or Recovery password only. You can also configure how often the client will check for changes to the BitLocker policy, and a method for users to request and exemption from this policy. These choices are URL, email address, or Phone number.
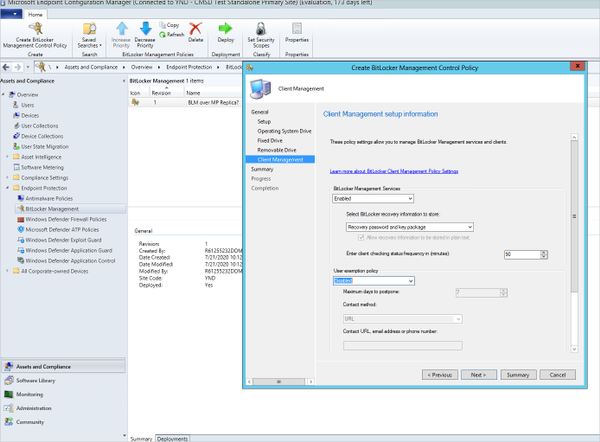 Configuring client management settings for the BitLocker Management Control Policy
Configuring client management settings for the BitLocker Management Control Policy
Once the policy has been created, deploy it to the target Collection.
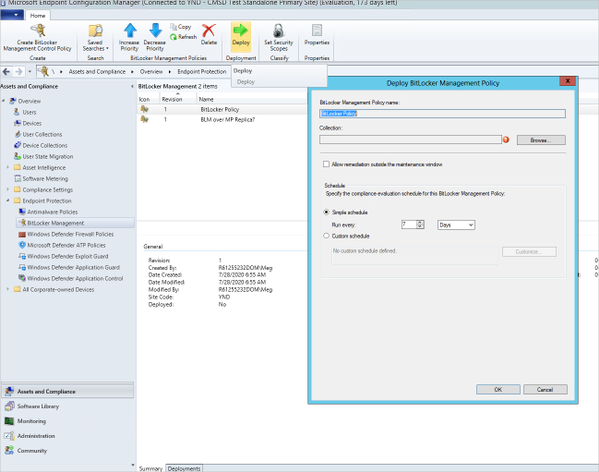 Deploying the new BitLocker Management Control Policy to a target collection in Configuration Manager
Deploying the new BitLocker Management Control Policy to a target collection in Configuration Manager
Once you set the policy, in the Configuration Manager console navigate to Monitoring > Overview > Reporting > Reports. From here you can report on BitLocker compliance in the enterprise.
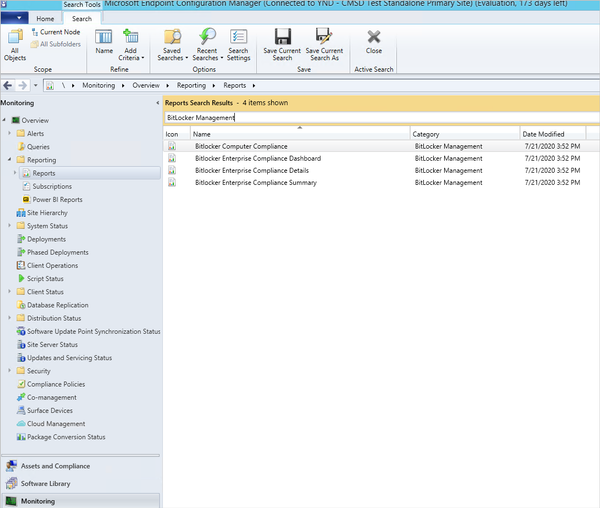 BitLocker reports in Configuration Manager
BitLocker reports in Configuration Manager
Learn more
Whether you are a current MBAM customer or are using a third-party tool to manage BitLocker, Microsoft can help you transition to Microsoft Endpoint Manager, at your pace. Don’t have Endpoint Manager, or need to learn more? Start a free trial or buy a subscription today!
Frequently asked questions
What licenses do I need to manage Microsoft BitLocker?
BitLocker can be enabled and disabled using Microsoft Endpoint Manager on Windows 10 Pro, Enterprise, or Education. However, all other management, such as enforcing a key rotation and compliance reporting require a Microsoft 365 E3/E5 or Windows E3/E5 license.
Can I enable BitLocker while deploying a device with Microsoft Autopilot?
Yes! You can configure the BitLocker policy in Endpoint Manager and link the policy to all devices, including those deployed with Windows Autopilot.
What settings are available for my Windows 7 workstations?
Windows 7 is no longer a supported operating system, and as such we do not test any BitLocker settings on Windows 7 clients. Using Configuration Manager, you can deploy the BitLocker policy to a Collection that contains Windows 7. However, as encryption and cyphers strengthen over time, these new settings may not work on Windows 7 workstations. The settings to enable and disable BitLocker, and a supported strength, should work on Windows 7, but again these are not tested. Our recommendation is that you upgrade to a supported operating system as soon as possible, but we’ll help you keep Windows 7 encrypted and more secure during your migration project.
How can I migrate my clients from using Configuration Manager to using Intune to manage BitLocker policies and compliance?
To migrate the clients to use Intune, enable co-management and set the Endpoint Protection workload to Intune.
Can I migrate from a third- party encryption to Microsoft BitLocker without decrypting the device?
No. If you are using a third-party disk encryption product, you must decrypt the device and then set the Microsoft BitLocker policies. To make this quicker, set the policy to only encrypt used space.
I’m using Microsoft BitLocker but am using a third-party management tool. How can I migrate the recovery key to Microsoft Endpoint Manager?
You can remove the third-party agent, configure the BitLocker policies in Endpoint Manager, and force a key rotation. This will change the recovery key from the key stored on the third-party management tool and upload a new recovery key in Endpoint Manager. You should check with the third-party management tool documentation if the removal of the agent will force a decryption of the drive.
by Scott Muniz | Aug 11, 2020 | Uncategorized
This article is contributed. See the original author and article here.
At Build 2020, we announced the upcoming availability of the Windows CE App Container technology. The technology allows CE applications to run on top of x64 and ARM32 systems using Windows 10 IoT Core Services. I’m happy to announce that this technology is generally available today!!
We’ve previously discussed how this technology works, but one question customers have asked is when they should take this gradual approach and when does it make sense to just move their application natively to Windows 10 IoT.
All roads lead to Windows 10 IoT Enterprise
As we announced at Build 2020, the 2021 long term supported release of Windows 10 IoT Enterprise will combine the best of IoT Core and IoT Enterprise by offering several new features in a smaller footprint on both x64 and ARM64 hardware. Going forward, Windows 10 IoT Enterprise will be the only non-server version of Windows 10 IoT offered.
For devices needing access to the full range of x64 hardware, ARM64 hardware like NXP i.MX8, advanced UX, or have CE applications that can be migrated in one product design iteration, the best option is to move to Windows 10 IoT Enterprise directly. You will be able to begin taking advantage of the features quickly and have the maximum product support lifetime.
Partners in the Early Engineering Access Program can download the latest IoT Enterprise private preview begin development now, and it will be generally available in 2021. Please speak with your Microsoft account manager to join the EEAP program.
Steady progress
For designs that need to leverage ARM32 or have complex CE applications that will require multiple development cycles to migrate, the CE App Container with Windows 10 IoT Core Services offers a solution for gradual migration.
To use the Windows CE App Container, developers place a special ARM32 or x86 Windows Embedded Compact 2013 platform image within their IoT Core system image. They then deploy the resulting Windows 10 IoT Core image on Windows 10 IoT Core compatible hardware. Developers will have access to add functionality, like Azure cloud connectivity or modern peripherals, through the Windows 10 layer and can move portions of the CE application over as well aiming for complete migration before 2029.
With Windows 10 IoT Core Services, you receive licenses for both Windows Embedded Compact 2013 and Windows 10 IoT Core, and the IoT Core OS continue to receive security updates until 2029. And, with capabilities like Device Update Center, OEMs can manage the timing of the OS updates as well as distribute application updates easily.
End of Support is not the end of the road
Finally, for some device builders, they have already created a new modern offering with Windows 10, but not all their customers are ready to upgrade. In these cases, device makers need to continue producing and providing their legacy Windows CE based solutions. This could be because of long term orders, customers needing replacement hardware, etc.
While Windows CE will reach end of extended support in late 2023, Microsoft will allow license sales to continue for Windows Embedded Compact 2013 until 2028. And of course, Windows CE devices can continue to be used indefinitely.
Next Steps
Microsoft has a decades-long history of providing platform technologies and operating systems for device manufacturers and developers to use as part of their embedded solutions. The Windows CE operating system has powered industrial, medical, and a variety of other devices for more than 20 years. With Windows 10 IoT Core Services, Windows 10 IoT Enterprise, and the new Windows CE App Migration technology we’ve developed a path forward to modern operating systems designed for cloud connectivity to enable intelligent workloads. For more information about Windows CE App Migration, please see http://aka.ms/cemigration. For information about the Windows 10 IoT products please see http://www.windowsondevices.com.
by Scott Muniz | Aug 11, 2020 | Uncategorized
This article is contributed. See the original author and article here.
In a recent case, I was asked to help with an FTP error 550 when the FTP client tried to list the files in the FTP site. The user logged on without error but could not see ant files or folders. There was a firewall but the FTP ports being used were open.
So I asked for the FTP logs to find the reason logged. In the FTP logs, we saw 550 1236 38 (status, win32Status, sub status). We know 550 is no such file or directory, I looked up the win32staus 1236 and it is “The network connection was aborted by the local system.” I was not familiar with the FTP sub status, so I opened article 969061, The FTP status codes in IIS 7.0 and later versions to find sub status 38. this is listed: 38 – Client IP on the control channel didn’t match the client IP on the data channel.
Went back to the FTP log and noticed client IP changing once PASV command is run… .7 to .8 and therefore the error.
2020-07-10 21:37:30 n.n.n.7 <User> <server IP> PASV – 227 0 0 7b461e17-7dc0-45f3-b0a5-ccaf36c708ac –
2020-07-10 21:37:30 n.n.n.8 <User> <server IP> 6003 DataChannelOpened – – 0 0 7b461e17-7dc0-45f3-b0a5-ccaf36c708ac –
2020-07-10 21:37:30 n.n.n.8 <User> <server IP> 6003 DataChannelClosed – – 1236 38 7b461e17-7dc0-45f3-b0a5-ccaf36c708ac –
2020-07-10 21:37:30 n.n.n.7 <User> <server IP> 21 LIST – 550 1236 38 7b461e17-7dc0-45f3-b0a5-ccaf36c708ac /
At this point, the firewall engineer mentioned that this was due to the firewall configuration and this behavior could not be changed so the customer ended up using a different firewall product.
This article lists all of the FTP status codes and what they mean…IIS web sites also log sub status…many times the sub status tells us exactly what is wrong without collecting any other data. There are 56 sub statuses listed near the bottom of the page.
https://support.microsoft.com/en-us/help/969061/the-ftp-7-0-status-codes-in-iis-7-0#:~:text=When%20you%20try%20to%20access%20content%20on%20a,the%20exact%20reason%20that%20a%20request%20is%20unsuccessful.
The FTP substatus codes
This section describes the FTP substatus codes that IIS 7.0 uses:
- 0 – Successful operation.
- 1 – Authorization rules denied the access.
- 2 – File system denied the access.
- 3 – File system returned an error.
- 4 – IP restriction rules denied the access.
- 5 – Write access for the root of the virtual directory is forbidden.
- 6 – Short file name check has failed.
- 7 – Short file names are forbidden.
- 8 – Hidden segment was detected in the path based on request filtering rules.
- 9 – Denied Url sequence detected in the path based on request filtering rules.
- 10 – High bit characters detected in the path based on request filtering rules.
- 11 – File extension was denied based on request filtering rules.
- 12 – Path is too long based on request filtering rules.
- 13 – Attempt was made to open object that is not a file or directory.
- 14 – Control channel timed out.
- 15 – Data channel timed out.
- 16 – Control channel timed out based on new connection timeout.
- 17 – Invalid site configuration.
- 18 – Invalid configuration.
- 19 – Maximum connection limit was reached.
- 20 – Data channel was closed by ABOR command from client.
- 21 – Site is being stopped.
- 22 – Data channel was aborted by server due to an error.
- 23 – Data channel was aborted by client.
- 24 – SSL policy requires SSL for data channel.
- 25 – SSL policy requires SSL for control channel.
- 26 – SSL policy requires SSL for credentials.
- 27 – SSL policy denies SSL for data channel.
- 28 – SSL policy denies SSL for data channel.
- 29 – SSL policy denies SSL for credentials.
- 30 – SSL policy denies SSL for commands.
- 31 – SSL certificate was not configured.
- 32 – SSL initialization failed.
- 33 – Home directory lookup failed.
- 34 – Custom authentication call failed.
- 35 – User failed to authenticate.
- 36 – All authentication methods are disabled.
- 37 – Hostname didn’t match any configured ftp site.
- 38 – Client IP on the control channel didn’t match the client IP on the data channel.
- 39 – Maximum file size was exceeded. 40ActiveDirectory Isolation must be combined with basic authentication.
- 41 – An error occurred during the authentication process.
- 42 – Anonymous authentication is not allowed.
- 43 – Protection negotiation failed. PROT command with recognized parameter must precede this command.
- 44 – SSL certificate was not found.
- 45 – Private key was not found for the specified SSL certificate.
- 46 – SSL certificate hash has invalid length.
- 47 – SSL policy requires client certificate.
- 48 – User provided invalid client certificate.
- 49 – SSL policy requires matching client certificate for control and data channel.
- 50 – Data channel timed out due to not meeting the minimum bandwidth requirement.
- 51 – Command filtering rules denied the access.
- 52 – Session disconnected by administrator.
- 53 – Connection error.
- 54 – Session closed because of configuration change.
- 55 – 128-bit encryption is required for SSL connections.






Recent Comments