North Korean Malicious Cyber Activity: AppleJeus
This article is contributed. See the original author and article here.
This article is contributed. See the original author and article here.
This article is contributed. See the original author and article here.
The North Korean government has used multiple versions of AppleJeus since the malware was initially discovered in 2018. This section outlines seven of the versions below. The MARs listed above provide further technical details of these versions. Initially, HIDDEN COBRA actors used websites that appeared to host legitimate cryptocurrency trading platforms to infect victims with AppleJeus; however, these actors are now also using other initial infection vectors, such as phishing, social networking, and social engineering techniques, to get users to download the malware.
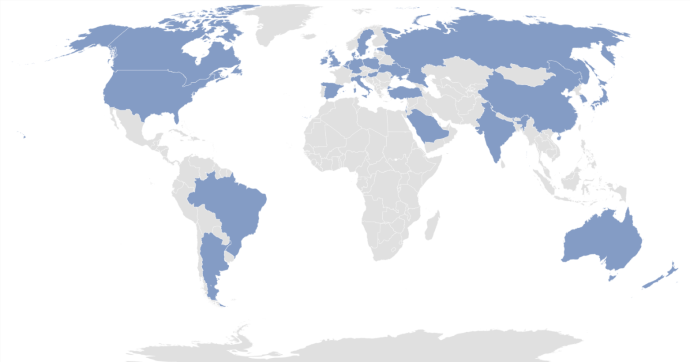
HIDDEN COBRA actors have targeted institutions with AppleJeus malware in several sectors, including energy, finance, government, industry, technology, and telecommunications. Since January 2020, the threat actors have targeted these sectors in the following countries: Argentina, Australia, Belgium, Brazil, Canada, China, Denmark, Estonia, Germany, Hong Kong, Hungary, India, Ireland, Israel, Italy, Japan, Luxembourg, Malta, the Netherlands, New Zealand, Poland, Russia, Saudi Arabia, Singapore, Slovenia, South Korea, Spain, Sweden, Turkey, the United Kingdom, Ukraine, and the United States (figure 1).

Figure 1: Countries targeted with AppleJeus by HIDDEN COBRA threat actors since 2020
The version numbers used for headings in this document correspond to the order the AppleJeus campaigns were identified in open source or through other investigative means. These versions may or may not be in the correct order to develop or deploy the AppleJeus campaigns.
In August 2018, open-source reporting disclosed information about a trojanized version of a legitimate cryptocurrency trading application on an undisclosed victim’s computer. The malicious program, known as Celas Trade Pro, was a modified version of the benign Q.T. Bitcoin Trader application. This incident led to the victim company being infected with a Remote Administration Tool (RAT) known as FALLCHILL, which was attributed to North Korea (HIDDEN COBRA) by the U.S. Government. FALLCHILL is a fully functional RAT with multiple commands that the adversary can issue from a command and control (C2) server to infected systems via various proxies. FALLCHILL typically infects a system as a file dropped by other HIDDEN COBRA malware (Develop Capabilities: Malware [T1587.001]). Because of this, additional HIDDEN COBRA malware may be present on systems compromised with FALLCHILL.[4]
Further research revealed that a phishing email from a Celas LLC company (Phishing: Spearphishing Link [T1566.002]) recommended the trojanized cryptocurrency trading application to victims. The email provided a link to the Celas’ website, celasllc[.]com (Acquire Infrastructure: Domain [T1583.001]), where the victim could download a Windows or macOS version of the trojanized application.
The celasllc[.]com domain resolved to the following Internet Protocol (IP) addresses from May 29, 2018, to January 23, 2021.
45.199.63[.]220107.187.66[.]103145.249.106[.]19175.29.32[.]160185.142.236[.]213185.181.104[.]82198.251.83[.]27208.91.197[.]46209.99.64[.]18The celasllc[.]com domain had a valid Sectigo (previously known as Comodo) Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) certificate (Obtain Capabilities: Digital Certificates [T1588.004]). The SSL certificate was “Domain Control Validated,” a weak security verification level that does not require validation of the owner’s identity or the actual business’s existence.
The Windows version of the malicious Celas Trade Pro application is an MSI Installer (.msi). The MSI Installer installation package comprises a software component and an application programming interface (API) that Microsoft uses for the installation, maintenance, and removal of software. The installer looks legitimate and is signed by a valid Sectigo certificate that was purchased by the same user as the SSL certificate for celasllc[.]com (Obtain Capabilities: Code Signing Certificates [T1588.003]). The MSI Installer asks the victim for administrative privileges to run (User Execution: Malicious File [T1204.002]).
Once permission is granted, the threat actor is able to run the program with elevated privileges (Abuse Elevation Control Mechanism [T1548]) and MSI executes the following actions.
CelasTradePro.exe in folder C:Program Files (x86)CelasTradeProUpdater.exe in folder C:Program Files (x86)CelasTradeProUpdater.exe with the CheckUpdate parametersThe CelasTradePro.exe program asks for the user’s exchange and loads a legitimate-looking cryptocurrency trading platform—very similar to the benign Q.T. Bitcoin Trader—that exhibits no signs of malicious activity.
The Updater.exe program has the same program icon as CelasTradePro.exe. When run, it checks for the CheckUpdate parameter, collects the victim’s host information (System Owner/User Discovery [T1033]), encrypts the collected information with a hardcoded XOR encryption, and sends information to a C2 website (Exfiltration Over C2 Channel [T1041]).
The macOS version of the malicious application is a DMG Installer that has a disk image format that Apple commonly uses to distribute software over the internet. The installer looks legitimate and has a valid digital signature from Sectigo (Obtain Capabilities: Digital Certificates [T1588.004]). It has very similar functionality to the Windows version. The installer executes the following actions.
CelasTradePro in folder /Applications/CelasTradePro.app/Contents/MacOS/Updater in folder /Applications/CelasTradePro.app/Contents/MacOSpostinstall script
.com.celastradepro.plist to folder LaunchDaemonsUpdater with the CheckUpdate parameterCelasTradePro asks for the user’s exchange and loads a legitimate-looking cryptocurrency trading platform—very similar to the benign Q.T. Bitcoin Trader—that exhibits no signs of malicious activity.
Updater checks for the CheckUpdate parameter and, when found, it collects the victim’s host information (System Owner/User Discovery [T1033]), encrypts the collected information with a hardcoded XOR key before exfiltration, and sends the encrypted information to a C2 website (Exfiltration Over C2 Channel [T1041]). This process helps the adversary obtain persistence on a victim’s network.
The postinstall script is a sequence of instructions that runs after successfully installing an application (Command and Scripting Interpreter: AppleScript [T1059.002]). This script moves property list (plist) file .com.celastradepro.plist from the installer package to the LaunchDaemons folder (Scheduled Task/Job: Launchd [T1053.004]). The leading “.” makes it unlisted in the Finder app or default Terminal directory listing (Hide Artifacts: Hidden Files and Directories [T1564.001]). Once in the folder, this property list (plist) file will launch the Updater program with the CheckUpdate parameter on system load as Root for every user. Because the LaunchDaemon will not run automatically after the plist file is moved, the postinstall script launches the Updater program with the CheckUpdate parameter and runs it in the background (Create or Modify System Process: Launch Daemon [T1543.004]).
After a cybersecurity company published a report detailing the above programs and their malicious extras, the website was no longer accessible. Since this site was the C2 server, the payload cannot be confirmed. The cybersecurity company that published the report states the payload was an encrypted and obfuscated binary (Obfuscated Files or Information [T1027]), which eventually drops FALLCHILL onto the machine and installs it as a service (Create or Modify System Process: Windows Service [T1543.003]). FALLCHILL malware uses an RC4 encryption algorithm with a 16-byte key to protect its communications (Encrypted Channel: Symmetric Cryptography [T1573.001]). The key employed in these versions has also been used in a previous version of FALLCHILL.[5][6]
For more details on AppleJeus Version 1: Celas Trade Pro, see MAR-10322463-1.v1.
In October 2019, a cybersecurity company identified a new version of the AppleJeus malware—JMT Trading—thanks to its many similarities to the original AppleJeus malware. Again, the malware was in the form of a cryptocurrency trading application, which a legitimate-looking company, called JMT Trading, marketed and distributed on their website, jmttrading[.]org (Acquire Infrastructure: Domain [T1583.001]). This website contained a “Download from GitHub” button, which linked to JMT Trading’s GitHub page (Acquire Infrastructure: Web Services [T1583.006]), where Windows and macOS X versions of the JMT Trader application were available for download (Develop Capabilities: Malware [T1587.001]). The GitHub page also included .zip and tar.gz files containing the source code.
The jmttrading[.]org domain resolved to the following IP addresses from October 15, 2016, to January 22, 2021.
45.33.2[.]7945.33.23[.]18345.56.79[.]2345.79.19[.]19696.126.123[.]244146.112.61[.]107184.168.221[.]40184.168.221[.]57198.187.29[.]20198.54.117[.]197198.54.117[.]198198.54.117[.]199198.54.117[.]200198.58.118[.]167The jmttrading[.]org domain had a valid Sectigo SSL certificate (Obtain Capabilities: Digital Certificates [T1588.004]). The SSL certificate was “Domain Control Validated,” a weak security verification level that does not require validation of the owner’s identity or the actual business’s existence. The current SSL certificate was issued by Let’s Encrypt.
The Windows version of the malicious cryptocurrency application is an MSI Installer. The installer looks legitimate and has a valid digital signature from Sectigo (Obtain Capabilities: Digital Certificates [T1588.004]). The signature was signed with a code signing certificate purchased by the same user as the SSL certificate for jmttrading[.]org (Obtain Capabilities: Code Signing Certificates [T1588.003]). The MSI Installer asks the victim for administrative privileges to run (User Execution: Malicious File [T1204.002]).
Once permission is granted, the MSI executes the following actions.
JMTTrader.exe in folder C:Program Files (x86)JMTTraderCrashReporter.exe in folder C:Users<username>AppDataRoamingJMTTraderCrashReporter.exe with the Maintain parameterThe JMTTrader.exe program asks for the user’s exchange and loads a legitimate-looking cryptocurrency trading platform—very similar to CelasTradePro.exe and the benign Q.T. Bitcoin Trader—that exhibits no signs of malicious activity.
The program CrashReporter.exe is heavily obfuscated with the ADVObfuscation library, renamed “snowman” (Obfuscated Files or Information [T1027]). When run, it checks for the Maintain parameter and collects the victim’s host information (System Owner/User Discovery [T1033]), encrypts the collected information with a hardcoded XOR key before exfiltration, and sends the encrypted information to a C2 website (Exfiltration Over C2 Channel [T1041]). The program also creates a scheduled SYSTEM task, named JMTCrashReporter, which runs CrashReporter.exe with the Maintain parameter at any user’s login (Scheduled Task/Job: Scheduled Task [T1053.005]).
The macOS version of the malicious application is a DMG Installer. The installer looks legitimate and has very similar functionality to the Windows version, but it does not have a digital certificate and will warn the user of that before installation. The installer executes the following actions.
JMTTrader in folder /Applications/JMTTrader.app/Contents/MacOS/.CrashReporter in folder /Applications/JMTTrader.app/Contents/Resources/
postinstall script
.com.jmttrading.plist to folder LaunchDaemonsplistCrashReporter with the Maintain parameter.CrashReporter to folder /Library/JMTTrader/CrashReporter.CrashReporter executableThe JMTTrader program asks for the user’s exchange and loads a legitimate-looking cryptocurrency trading platform—very similar to CelasTradePro and the benign Q.T. Bitcoin Trader—that exhibits no signs of malicious activity.
The CrashReporter program checks for the Maintain parameter and is not obfuscated. This lack of obfuscation makes it easier to determine the program’s functionality in detail. When it finds the Maintain parameter, it collects the victim’s host information (System Owner/User Discovery [T1033]), encrypts the collected information with a hardcoded XOR key before exfiltration, and sends the encrypted information to a C2 website (Exfiltration Over C2 Channel [T1041]).
The postinstall script has similar functionality to the one used by CelasTradePro, but it has a few additional features (Command and Scripting Interpreter: AppleScript [T1059.002]). It moves the property list (plist) file .com.jmttrading.plist from the Installer package to the LaunchDaemons folder (Scheduled Task/Job: Launchd [T1053.004]), but also changes the file permissions on the plist file. Once in the folder, this property list (plist) file will launch the CrashReporter program with the Maintain parameter on system load as Root for every user. Also, the postinstall script moves the .CrashReporter program to a new location /Library/JMTTrader/CrashReporter and makes it executable. Because the LaunchDaemon will not run automatically after the plist file is moved, the postinstall script launches CrashReporter with the Maintain parameter and runs it in the background (Create or Modify System Process: Launch Daemon [T1543.004]).
Soon after the cybersecurity company tweeted about JMT Trader on October 11, 2019, the files on GitHub were updated to clean, non-malicious installers. Then on October 13, 2019, a different cybersecurity company published an article detailing the macOS X JMT Trader, and soon after, the C2 beastgoc[.]com website went offline. There is not a confirmed sample of the payload to analyze at this point.
For more details on AppleJeus Version 2: JMT Trading, see MAR-10322463-2.v1.
In December 2019, another version of the AppleJeus malware was identified on Twitter by a cybersecurity company based on many similarities to the original AppleJeus malware. Again, the malware was in the form of a cryptocurrency trading application, which was marketed and distributed by a legitimate-looking company, called Union Crypto, on their website, unioncrypto[.]vip (Acquire Infrastructure: Domain [T1583.001]). Although this website is no longer available, a cybersecurity researcher discovered a download link, https://www.unioncrypto[.]vip/download/W6c2dq8By7luMhCmya2v97YeN, recorded on VirusTotal for the macOS X version of UnionCryptoTrader. In contrast, open-source reporting stated that the Windows version might have been downloaded via instant messaging service Telegram, as it was found in a “Telegram Downloads” folder on an unnamed victim.[7]
The unioncrypto[.]vip domain resolved to the following IP addresses from June 5, 2019, to July 15, 2020.
104.168.167[.]16198.54.117[.]197198.54.117[.]198198.54.117[.]199198.54.117[.]200The domain unioncrypto[.]vip had a valid Sectigo SSL certificate (Obtain Capabilities: Digital Certificates [T1588.004]). The SSL certificate was “Domain Control Validated,” a weak security verification level that does not require validation of the owner’s identity or the actual business’s existence.
The Windows version of the malicious cryptocurrency application is a Windows executable (.exe) (User Execution: Malicious File [T1204.002]), which acts as an installer that extracts a temporary MSI Installer.
The Windows program executes the following actions.
UnionCryptoTrader.msi to folder C:Users<username>AppDataLocalTemp{82E4B719-90F74BD1-9CF1-56CD777E0C42}UnionCryptoUpdater.msi
UnionCryptoTrader.exe in folder C:Program FilesUnionCryptoTraderUnionCryptoUpdater.exe in folder C:Users<username>AppDataLocalUnionCryptoTraderUnionCryptoUpdater.msiUnionCryptoUpdater.exeThe program UnionCryptoTrader.exe loads a legitimate-looking cryptocurrency arbitrage application—defined as “the simultaneous buying and selling of securities, currency, or commodities in different markets or in derivative forms to take advantage of differing prices for the same asset”—which exhibits no signs of malicious activity. This application is very similar to another cryptocurrency arbitrage application known as Blackbird Bitcoin Arbitrage.[8]
The program UnionCryptoUpdater.exe first installs itself as a service (Create or Modify System Process: Windows Service [T1543.003]), which will automatically start when any user logs on (Boot or Logon Autostart Execution [T1547]). The service is installed with a description stating it “Automatically installs updates for Union Crypto Trader.” When launched, it collects the victim’s host information (System Owner/User Discovery [T1033]), combines the information in a string that is MD5 hashed and stored in the auth_signature variable before exfiltration, and sends it to a C2 website (Exfiltration Over C2 Channel [T1041]).
The macOS version of the malicious application is a DMG Installer. The installer looks legitimate and has very similar functionality to the Windows version, but it does not have a digital certificate and will warn the user of that before installation. The installer executes the following actions.
UnionCryptoTrader in folder /Applications/UnionCryptoTrader.app/Contents/MacOS/.unioncryptoupdater in folder /Applications/UnionCryptoTrader.app/Contents/Resources/
postinstall script
.vip.unioncrypto.plist to folder LaunchDaemonsplist to Rootunioncryptoupdater.unioncryptoupdater to folder /Library/UnionCrypto/unioncryptoupdater.unioncryptoupdater executableThe UnionCryptoTrader program loads a legitimate-looking cryptocurrency arbitrage application, which exhibits no signs of malicious activity. The application is very similar to another cryptocurrency arbitrage application known as Blackbird Bitcoin Arbitrage.
The .unioncryptoupdater program is signed ad-hoc, meaning it is not signed with a valid code-signing identity. When launched, it collects the victim’s host information (System Owner/User Discovery [T1033]), combines the information in a string that is MD5 hashed and stored in the auth_signature variable before exfiltration, and sends it to a C2 website (Exfiltration Over C2 Channel [T1041]).
The postinstall script has similar functionality to the one used by JMT Trading (Command and Scripting Interpreter: AppleScript [T1059.002]). It moves the property list (plist) file .vip.unioncrypto.plist from the Installer package to the LaunchDaemons folder (Scheduled Task/Job: Launchd [T1053.004]), but also changes the file permissions on the plist file to Root. Once in the folder, this property list (plist) file will launch the .unioncryptoupdater on system load as Root for every user. The postinstall script moves the .unioncryptoupdater program to a new location /Library/UnionCrypto/unioncryptoupdater and makes it executable. Because the LaunchDaemon will not run automatically after the plist file is moved, the postinstall script launches .unioncryptoupdater and runs it in the background (Create or Modify System Process: Launch Daemon [T1543.004]).
The payload for the Windows malware is a Windows Dynamic-Link-Library. UnionCryptoUpdater.exe does not immediately download the stage 2 malware but instead downloads it after a time specified by the C2 server. This delay could be implemented to prevent researchers from directly obtaining the stage 2 malware.
The macOS X malware’s payload could not be downloaded, as the C2 server is no longer accessible. Additionally, none of the open-source reporting for this sample contained copies of the macOS X payload. The macOS X payload is likely similar in functionality to the Windows stage 2 detailed above.
For more details on AppleJeus Version 3: Union Crypto, see MAR-10322463-3.v1.
In each AppleJeus version, there are hardcoded values used for encryption or to create a signature when combined with the time (table 1).
Table 1: AppleJeus hardcoded values and uses
| AppleJeus Version | Value | Use |
|---|---|---|
| 1: Celas Trade Pro | Moz&Wie;#t/6T!2y | XOR encryption to send data |
| 1: Celas Trade Pro | W29ab@ad%Df324V$Yd | RC4 decryption |
| 2: JMT Trader Windows | X,%`PMk–Jj8s+6=15:20:11 | XOR encryption to send data |
| 2: JMT Trader OSX | X,%`PMk–Jj8s+6=x02 | XOR encryption to send data |
| 3: Union Crypto Trader | 12GWAPCT1F0I1S14 | Combined with time for signature |
The Union Crypto Trader and Celas LLC (XOR) values are 16 bytes in length. For JMT Trader, the first 16 bytes of the Windows and macOS X values are identical, and the additional bytes are in a time format for the Windows sample. The structure of a 16-byte value combined with the time is also used in Union Crypto Trader to create the auth_signature.
As mentioned, FALLCHILL was reported as the final payload for Celas Trade Pro. All FALLCHILL samples use 16-byte hardcoded RC4 keys for sending data, similar to the 16-byte keys in the AppleJeus samples.
All three AppleJeus samples are bundled with modified copies of legitimate cryptocurrency applications and can be used as originally designed to trade cryptocurrency. Both Celas LLC and JMT Trader modified the same cryptocurrency application, Q.T. Bitcoin Trader; Union Crypto Trader modified the Blackbird Bitcoin Arbitrage application.
The macOS X samples of all three AppleJeus versions contain postinstall scripts with similar logic. The Celas LLC postinstall script only moves the plist file to a new location and launches Updater with the CheckUpdate parameter in the background. The JMT Trader and Union Crypto Trader also perform these actions and have identical functionality. The additional actions performed by both postinstall scripts are to change the file permissions on the plist, make a new directory in the /Library folder, move CrashReporter or UnionCryptoUpdater to the newly created folder, and make them executable.
The plist files for all three AppleJeus files have identical functionality. They only differ in the files’ names and one default comment that was not removed from the Celas LLC plist. As the logic and functionality of the postinstall scripts and plist files are almost identical, the LaunchDaemons created also function the same.
They will all launch the secondary executable as Root on system load for every user.
On March 13, 2020, a new version of the AppleJeus malware was identified. The malware was marketed and distributed by a legitimate-looking company, called Kupay Wallet, on their website kupaywallet[.]com (Acquire Infrastructure: Domain [T1583.001]).
The domain www.kupaywallet[.]com resolved to IP address 104.200.67[.]96 from March 20, 2020, to January 16, 2021. CrownCloud US, LLC controlled the IP address (autonomous system number [ASN] 8100), and is located in New York, NY.
The domain www.kupaywallet[.]com had a valid Sectigo SSL certificate (Obtain Capabilities: Digital Certificates [T1588.004]). The SSL certificate was “Domain Control Validated,” a weak security verification level that does not require validation of the owner’s identity or the actual business’s existence.
The Windows version of the malicious cryptocurrency application is an MSI Installer. The MSI executes the following actions.
Kupay.exe in folder C:Program Files (x86)KupayKupayUpgrade.exe in folder C:Users<username>AppDataRoamingKupaySupportKupayUpgrade.exeThe program Kupay.exe loads a legitimate-looking cryptocurrency wallet platform, which exhibits no signs of malicious activity and is very similar to an open-source platform known as Copay, distributed by Atlanta-based company BitPay.
The program KupayUpgrade.exe first installs itself as a service (Create or Modify System Process: Windows Service [T1543.003]), which will automatically start when any user logs on (Boot or Logon Autostart Execution [T1547]). The service is installed with a description stating it is an “Automatic Kupay Upgrade.” When launched, it collects the victim’s host information (System Owner/User Discovery [T1033]), combines the information in strings before exfiltration, and sends it to a C2 website (Exfiltration Over C2 Channel [T1041]).
The macOS version of the malicious application is a DMG Installer. The installer looks legitimate and has very similar functionality to the Windows version, but it does not have a digital certificate and will warn the user of that before installation. The installer executes the following actions.
Kupay in folder /Applications/Kupay.app/Contents/MacOS/kupay_upgrade in folder /Applications/Kupay.app/Contents/MacOS/postinstall script
KupayDaemon folder in /Library/Application Support folderkupay_upgrade to the new foldercom.kupay.pkg.wallet.plist to folder /Library/LaunchDaemons/launchctl load to load the plist without a restartkupay_upgrade in the backgroundKupay is likely a copy of an open-source cryptocurrency wallet application, loads a legitimate-looking wallet program (fully functional), and its functionality is identical to the Windows Kupay.exe program.
The kupay_upgrade program calls its function CheckUpdate (which contains most of the logic functionality of the malware) and sends a POST to the C2 server with a connection named “Kupay Wallet 9.0.1 (Check Update Osx)” (Application Layer Protocol: Web Protocols [T1071.001]). If the C2 server returns a file, it is decoded and written to the victim’s folder /private/tmp/kupay_update with permissions set by the command chmod 700 (only the user can read, write, and execute) (Command and Scripting Interpreter [T1059]). Stage 2 is then launched, and the malware, kupay_upgrade, returns to sleeping and checking in with the C2 server at predetermined intervals (Application Layer Protocol: Web Protocols [T1071.001]).
The postinstall script has similar functionality to other AppleJeus scripts (Command and Scripting Interpreter: AppleScript [T1059.002]). It creates the KupayDaemon folder in /Library/Application Support folder and then moves kupay_upgrade to the new folder. It moves the property list (plist) file com.kupay.pkg.wallet.plist from the Installer package to the /Library/LaunchDaemons/ folder (Scheduled Task/Job: Launchd [T1053.004]). The script runs the command launchctl load to load the plist without a restart (Command and Scripting Interpreter [T1059]). But, since the LaunchDaemon will not run automatically after the plist file is moved, the postinstall script launches kupay_upgrade and runs it in the background (Create or Modify System Process: Launch Daemon [T1543.004]).
The Windows malware’s payload could not be downloaded since the C2 server is no longer accessible. Additionally, none of the open-source reporting for this sample contained copies of the payload. The Windows payload is likely similar in functionality to the macOS X stage 2 detailed below.
The stage 2 payload for the macOS X malware was decoded and analyzed. The stage 2 malware has a variety of functionalities. Most importantly, it checks in with a C2 and, after connecting to the C2, can send or receive a payload, read and write files, execute commands via the terminal, etc.
For more details on AppleJeus Version 4: Kupay Wallet, see MAR-10322463-4.v1.
In early 2020, another version of the AppleJeus malware was identified. This time the malware was marketed and distributed by a legitimate-looking company called CoinGoTrade on their website coingotrade[.]com (Acquire Infrastructure: Domain [T1583.001]).
The domain CoinGoTrade[.]com resolved to IP address 198.54.114[.]175 from February 28, 2020, to January 23, 2021. The IP address is controlled by NameCheap Inc. (ASN 22612) and is located in Atlanta, GA. This IP address is in the same ASN for Dorusio[.]com and Ants2Whale[.]com.
The domain CoinGoTrade[.]com had a valid Sectigo SSL certificate (Obtain Capabilities: Digital Certificates [T1588.004]). The SSL certificate was “Domain Control Validated,” a weak security verification level that does not require validation of the owner’s identity or the actual business’s existence.
The Windows version of the malicious application is an MSI Installer. The installer appears to be legitimate and will execute the following actions.
CoinGoTrade.exe in folder C:Program Files (x86)CoinGoTradeCoinGoTradeUpdate.exe in folder C:Users<username>AppDataRoamingCoinGoTradeSupportCoinGoTradeUpdate.exeCoinGoTrade.exe loads a legitimate-looking cryptocurrency wallet platform with no signs of malicious activity and is a copy of an open-source cryptocurrency application.
CoinGoTradeUpdate.exe first installs itself as a service (Create or Modify System Process: Windows Service [T1543.003]), which will automatically start when any user logs on (Boot or Logon Autostart Execution [T1547]). The service is installed with a description stating it is an “Automatic CoinGoTrade Upgrade.” When launched, it collects the victim’s host information (System Owner/User Discovery [T1033]), combines the information in strings before exfiltration, and sends it to a C2 website (Exfiltration Over C2 Channel [T1041]).
The macOS version of the malicious application is a DMG Installer. The installer looks legitimate and has very similar functionality to the Windows version, but it does not have a digital certificate and will warn the user of that before installation. The installer executes the following actions.
CoinGoTrade in folder /Applications/CoinGoTrade.app/Contents/MacOS/CoinGoTradeUpgradeDaemon in folder /Applications/CoinGoTrade.app/Contents/MacOS/postinstall script
CoinGoTradeService folder in /Library/Application Support folderCoinGoTradeUpgradeDaemon to the new foldercom.coingotrade.pkg.product.plist to folder /Library/LaunchDaemons/CoinGoTradeUpgradeDaemon in the backgroundThe CoinGoTrade program is likely a copy of an open-source cryptocurrency wallet application and loads a legitimate-looking, fully functional wallet program).
The CoinGoTradeUpgradeDaemon program calls its function CheckUpdate (which contains most of the logic functionality of the malware) and sends a POST to the C2 server with a connection named “CoinGoTrade 1.0 (Check Update Osx)” (Application Layer Protocol: Web Protocols [T1071.001]). If the C2 server returns a file, it is decoded and written to the victim’s folder /private/tmp/updatecoingotrade with permissions set by the command chmod 700 (only the user can read, write, and execute) (Command and Scripting Interpreter [T1059]). Stage 2 is then launched, and the malware, CoinGoTradeUpgradeDaemon, returns to sleeping and checking in with the C2 server at predetermined intervals (Application Layer Protocol: Web Protocols [T1071.001]).
The postinstall script has similar functionality to the other scripts (Command and Scripting Interpreter: AppleScript [T1059.002]) and installs CoinGoTrade and CoinGoTradeUpgradeDaemon in folder /Applications/CoinGoTrade.app/Contents/MacOS/. It moves the property list (plist) file com.coingotrade.pkg.product.plist to the /Library/LaunchDaemons/ folder (Scheduled Task/Job: Launchd [T1053.004]). Because the LaunchDaemon will not run automatically after the plist file is moved, the postinstall script launches CoinGoTradeUpgradeDaemon and runs it in the background (Create or Modify System Process: Launch Daemon [T1543.004]).
The Windows malware’s payload could not be downloaded because the C2 server is no longer accessible. Additionally, none of the open-source reporting for this sample contained copies of the payload. The Windows payload is likely similar in functionality to the macOS X stage 2 detailed below.
The stage 2 payload for the macOS X malware was no longer available from the specified download URL. Still, a file was submitted to VirusTotal by the same user on the same date as the macOS X CoinGoTradeUpgradeDaemon. These clues suggest that the submitted file may be related to the macOS X version of the malware and the downloaded payload.
The file prtspool is a 64-bit Mach-O executable with a large variety of features that have all been confirmed as functionality. The file has three C2 URLs hardcoded into the file and communicates to these with HTTP POST multipart-form data boundary string. Like other HIDDEN COBRA malware, prtspool uses format strings to store data collected about the system and sends it to the C2s.
For more details on AppleJeus Version 5: CoinGoTrade, see MAR-10322463-5.v1.
In March 2020, an additional version of the AppleJeus malware was identified. This time the malware was marketed and distributed by a legitimate-looking company called Dorusio on their website, dorusio[.]com (Acquire Infrastructure: Domain [T1583.001]). Researchers collected samples for Windows and macOS X versions of the Dorusio Wallet (Develop Capabilities: Malware [T1587.001]). As of at least early 2020, the actual download links result in 404 errors. The download page has release notes with version revisions claiming to start with version 1.0.0, released on April 15, 2019.
The domain dorusio[.]com resolved to IP address 198.54.115[.]51 from March 30, 2020 to January 23, 2021. The IP address is controlled by NameCheap Inc. (ASN 22612) and is located in Atlanta, GA. This IP address is in the same ASN for CoinGoTrade[.]com and Ants2Whale[.]com.
The domain dorusio[.]com had a valid Sectigo SSL certificate (Obtain Capabilities: Digital Certificates [T1588.004]). The SSL certificate was “Domain Control Validated,” a weak security verification level that does not require validation of the owner’s identity or the actual business’s existence.
The Windows version of the malicious application is an MSI Installer. The installer appears to be legitimate and will install the following two programs.
Dorusio.exe in folder C:Program Files (x86)DorusioDorusioUpgrade.exe in folder C:Users<username>AppDataRoamingDorusioSupportDorusioUpgrade.exeThe program, Dorusio.exe, loads a legitimate-looking cryptocurrency wallet platform with no signs of malicious activity and is a copy of an open-source cryptocurrency application.
The program DorusioUpgrade.exe first installs itself as a service (Create or Modify System Process: Windows Service [T1543.003]), which will automatically start when any user logs on (Boot or Logon Autostart Execution [T1547]). The service is installed with a description stating it “Automatic Dorusio Upgrade.” When launched, it collects the victim’s host information (System Owner/User Discovery [T1033]), combines the information in strings before exfiltration, and sends it to a C2 website (Exfiltration Over C2 Channel [T1041]).
The macOS version of the malicious application is a DMG Installer. The installer looks legitimate and has very similar functionality to the Windows version, but it does not have a digital certificate and will warn the user of that before installation. The installer executes the following actions.
Dorusio in folder /Applications/Dorusio.app/Contents/MacOS/Dorusio_upgrade in folder /Applications/Dorusio.app/Contents/MacOS/postinstall script
DorusioDaemon folder in /Library/Application Support folderDorusio_upgrade to the new foldercom.dorusio.pkg.wallet.plist to folder /Library/LaunchDaemons/Dorusio_upgrade in the backgroundThe Dorusio program is likely a copy of an open-source cryptocurrency wallet application and loads a legitimate-looking wallet program (fully functional). Aside from the Dorusio logo and two new services, the wallet appears to be the same as the Kupay Wallet. This application seems to be a modification of the open-source cryptocurrency wallet Copay distributed by Atlanta-based company BitPay.
The Dorusio_upgrade program calls its function CheckUpdate (which contains most of the logic functionality of the malware) and sends a POST to the C2 server with a connection named “Dorusio Wallet 2.1.0 (Check Update Osx)” (Application Layer Protocol: Web Protocols [T1071.001]). If the C2 server returns a file, it is decoded and written to the victim’s folder /private/tmp/Dorusio_update with permissions set by the command chmod 700 (only the user can read, write, and execute) (Command and Scripting Interpreter [T1059]). Stage 2 is then launched, and the malware, Dorusio_upgrade, returns to sleeping and checking in with the C2 server at predetermined intervals (Application Layer Protocol: Web Protocols [T1071.001]).
The postinstall script has similar functionality to other AppleJeus scripts (Command and Scripting Interpreter: AppleScript [T1059.002]). It creates the DorusioDaemon folder in /Library/Application Support folder and then moves Dorusio_upgrade to the new folder. It moves the property list (plist) file com.dorusio.pkg.wallet.plist from the Installer package to the /Library/LaunchDaemons/ folder (Scheduled Task/Job: Launchd [T1053.004]). Because the LaunchDaemon will not run automatically after the plist file is moved, the postinstall script launches Dorusio_upgrade and runs it in the background (Create or Modify System Process: Launch Daemon [T1543.004]).
Neither the payload for the Windows nor macOS X malware could be downloaded; the C2 server is no longer accessible. The payloads are likely similar in functionality to the macOS X stage 2 from CoinGoTrade and Kupay Wallet, or the Windows stage 2 from Union Crypto.
For more details on AppleJeus Version 6: Dorusio, see MAR-10322463-6.v1.
If a user attempts to install the Kupay Wallet, CoinGoTrade, and Dorusio applications on the same system, they will encounter installation conflicts.
If Kupay Wallet is already installed on a system and the user tries to install CoinGoTrade or Dorusio:
If CoinGoTrade is already installed on a system and the user attempts to install Kupay Wallet:
Kupay.exe will be installed in the C:Program Files (x86)CoinGoTrade folder.CoinGoTrade files will be deleted.C:Users<username>AppDataRoamingCoinGoTradeSupport will remain installed.KupayUpgrade.exe is installed in the new folder C:Users<username>AppDataRoamingKupaySupport.If Dorusio is already installed on a system and the user attempts to install Kupay Wallet:
Kupay.exe will be installed in the C:Program Files (x86)Dorusio folder.Dorusio.exe files will be deleted.C:Users<username>AppDataRoamingDorusioSupport will remain installed.KupayUpgrade.exe is installed in the new folder C:Users<username>AppDataRoamingKupaySupport.In late 2020, a new version of AppleJeus was identified called “Ants2Whale.” The site for this version of AppleJeus is ants2whale[.]com (Acquire Infrastructure: Domain [T1583.001]). The website shows a legitimate-looking cryptocurrency company and application. The website contains multiple spelling and grammar mistakes indicating the creator may not have English as a first language. The website states that to download Ants2Whale, a user must contact the administrator, as their product is a “premium package” (Develop Capabilities: Malware [T1587.001]).
The domain ants2whale[.]com resolved to IP address 198.54.114[.]237 from September 23, 2020, to January 22, 2021. The IP address is controlled by NameCheap, Inc. (ASN 22612) and is located in Atlanta, GA. This IP address is in the same ASN for CoinGoTrade[.]com and Dorusio[.]com.
The domain ants2whale[.]com had a valid Sectigo SSL certificate (Obtain Capabilities: Digital Certificates [T1588.004]). The SSL certificate was “Domain Control Validated,” a weak security verification level that does not require validation of the owner’s identity or the actual business’s existence.
As of late 2020, the Windows program was not available on VirusTotal. It is likely very similar to the macOS X version detailed below.
The macOS version of the malicious application is a DMG Installer. The installer looks legitimate and has very similar functionality to the Windows version, but it does not have a digital certificate and will warn the user of that before installation. The installer executes the following actions.
Ants2Whale in folder /Applications/Ants2whale.app/Contents/MacOS/Ants2whaleAnts2WhaleHelper in folder /Library/Application Support/Ants2WhaleSupport/postinstall script
com.Ants2whale.pkg.wallet.plist to folder /Library/LaunchDaemons/Ants2WhaleHelper in the backgroundThe Ants2Whale and Ants2WhaleHelper programs and the postinstall script function almost identically to previous versions of AppleJeus and will not be discussed in depth in this advisory.
For more details on AppleJeus Version 7: Ants2Whale, see MAR-10322463-7.v1.
Figure 2 and table 2 provide summaries of the MITRE ATT&CK techniques observed.
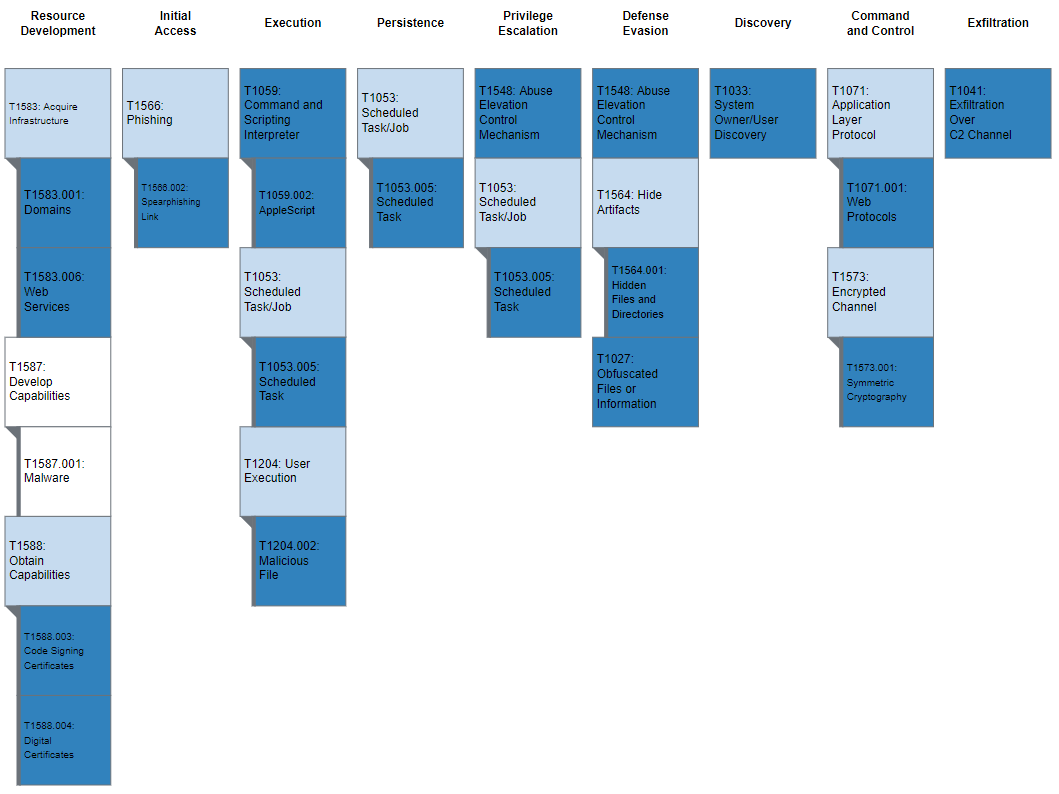
Figure 2: MITRE ATT&CK enterprise techniques used by AppleJeus
Table 2: MITRE ATT&CK techniques observed
This article is contributed. See the original author and article here.
This report is provided “as is” for informational purposes only. The Department of Homeland Security (DHS) does not provide any warranties of any kind regarding any information contained herein. The DHS does not endorse any commercial product or service referenced in this bulletin or otherwise.
This document is marked TLP:WHITE–Disclosure is not limited. Sources may use TLP:WHITE when information carries minimal or no foreseeable risk of misuse, in accordance with applicable rules and procedures for public release. Subject to standard copyright rules, TLP:WHITE information may be distributed without restriction. For more information on the Traffic Light Protocol (TLP), see http://www.us-cert.gov/tlp.
This Malware Analysis Report (MAR) is the result of analytic efforts among the Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI), the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA), and the Department of Treasury (Treasury) to highlight the cyber threat to cryptocurrency posed by North Korea, formally known as the Democratic People’s Republic of Korea (DPRK), and provide mitigation recommendations. Working with U.S. government partners, FBI, CISA, and Treasury assess that Lazarus Group—which these agencies attribute to North Korean state-sponsored advanced persistent threat (APT) actors—is targeting individuals and companies, including cryptocurrency exchanges and financial service companies, through the dissemination of cryptocurrency trading applications that have been modified to include malware that facilitates theft of cryptocurrency.
This MAR highlights this cyber threat posed by North Korea and provides detailed indicators of compromise (IOCs) used by the North Korean government. The U.S. Government refers to malicious cyber activity by the North Korean government as HIDDEN COBRA. For more information on other versions of AppleJeus and recommended steps to mitigate this threat, see Joint Cybersecurity Advisory AA21-048A: AppleJeus: Analysis of North Korea’s Cryptocurrency Malware at https://www.us-cert.cisa.gov/ncas/alerts/AA21-048A.
There have been multiple versions of AppleJeus malware discovered since its initial discovery in August 2018. In most versions, the malware appears to be from a legitimate-looking cryptocurrency trading company and website, whereby an unsuspecting individual downloads a third-party application from a website that appears legitimate.
The U.S. Government has identified AppleJeus malware version—Ants2Whale—and associated IOCs used by the North Korean government in AppleJeus operations.
Ants2Whale, discovered in October 2020, is a legitimate-looking cryptocurrency trading software that is marketed and distributed by a company and website—Ants2Whale and ants2whale[.]com, respectively—that appear legitimate. Some information has been redacted from this report to preserve victim anonymity.
For a downloadable copy of IOCs, see: MAR-10322463-7.v1.stix.
bb430087484c1f4587c54efc75681eb60cf70956ef2a999a75ce7b563b8bd694 (Ants2WhaleHelper)
d5ac680e14b013e0624470da7f46e84809d00b59a7544f6a42b110cf0e29254e (Ants2Whale)
[Redacted] (Ants2Whale.dmg)
ants2whale.com
qnalytica.com
45.147.231.77
downloaderloader
| Name | Ants2Whale.dmg |
|---|---|
| Size | [Redacted] bytes |
| Type | zlib compressed data |
| MD5 | [Redacted] |
| SHA1 | [Redacted] |
| SHA256 | [Redacted] |
| SHA512 | [Redacted] |
| ssdeep | [Redacted] |
| Entropy | [Redacted] |
| Avira | OSX/Agent.denpi |
|---|---|
| Ikarus | OSX.Agent |
| Zillya! | Downloader.Agent.OSX.390 |
No matches found.
No matches found.
| [Redacted] | Downloaded_By | ants2whale.com |
| [Redacted] | Contains | d5ac680e14b013e0624470da7f46e84809d00b59a7544f6a42b110cf0e29254e |
| [Redacted] | Contains | bb430087484c1f4587c54efc75681eb60cf70956ef2a999a75ce7b563b8bd694 |
This OSX program from the Ants2Whale site is an Apple DMG installer. The OSX program does not have a digital signature and will warn the user of that before installation. As all previous versions of AppleJeus, the Ants2Whale installer appears to be legitimate and installs “Ants2Whale”(D5AC680E14B013E0624470DA7F46E84809D00B59A7544F6A42B110CF0E29254E) in the “/Applications/Ants2whale.app/Contents/MacOS/Ants2whale” folder and a program named Ants2WhaleHelper (BB430087484C1F4587C54EFC75681EB60CF70956EF2A999A75CE7B563B8BD694) also in the “/Library/Application Support/Ants2WhaleSupport/” folder.
Similar to all previous OSX AppleJeus variants, there is a postinstall script and a plist file which creates a LaunchDaemon to automatically run the Ants2WhaleHelper program.
| ants2whale.com | Downloaded | [Redacted] |
The website appears to show a legitimate cryptocurrency company and application, though it does contain multiple spelling and grammar mistakes indicating the creator may not have English as a first language. The website states that in order to download, a user must contact the administrator as their product is “premium package.”
The domain ants2whale.com had a legitimately signed Sectigo Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) certificate, which was “Domain Control Validated” just as all previous AppleJeus domain certificates. The certificate was is valid from 09/21/2020 – 09/21/2021.
The domain is registered with NameCheap at the IP address 198.54.114.237 with ASN 22612. This IP is on the same ASN as the CoinGoTrade (AppleJeus variant 5 and Dorusio IP addresses (AppleJeus variant 6).
Figure 1 – Screenshot the ants2whale.com site.
Figure 2 – Screenshot of how to download Ants2Whale.
trojan
| Name | Ants2Whale |
|---|---|
| Size | 77856 bytes |
| Type | Mach-O 64-bit x86_64 executable, flags:<NOUNDEFS|DYLDLINK|TWOLEVEL|PIE> |
| MD5 | 022298cf16c0c44d7b01b5de2cf84023 |
| SHA1 | 939ec41183bbe1f4fb65c924323543ee91a35dbf |
| SHA256 | d5ac680e14b013e0624470da7f46e84809d00b59a7544f6a42b110cf0e29254e |
| SHA512 | bda62d09606bbf5a0ee17dac06f1f3cfc77919f98e5fc14bd50b4f41f794df521aeced7b0f2a769a89498b7a6cd69be37689dab1652c3c16e7a8b1295c245ffa |
| ssdeep | 768:jPoXPdCyI4jB5nvjILkTSF3TSFi5UeSj0OfpZDkm+UjnAT9vSs:cXPdLI6XbIOem0EpZDX+Ujnc9v3 |
| Entropy | 4.361681 |
No matches found.
No matches found.
No matches found.
| d5ac680e14… | Contained_Within | [Redacted] |
| d5ac680e14… | Connected_To | 45.147.231.77 |
This OSX sample was contained within Apple DMG installer “Ants2Whale.dmg.” Ants2Whale is likely a copy of an open source cryptocurrency wallet application. When ran it loads a legitimate looking program which is fully functional and is very similar to the AppleJeus variant 5 “CoinGoTrade” application. Similar to CoinGoTrade there are references to “CryptoMex” in the Ants2Whale application.
Similarly to the CoinGoTrade application, the strings from Ants2Whale reveal the C2 hxxp[:]//45.147.231.77:3000. Investigation revealed the IP address 45.147.231.77 was hosted at Combahton GMH.
Figure 3 – Screenshot of the “Ants2Whale” application.
command-and-control
Queried whois.ripe.net with “-B 45.147.231.77″…
% Information related to ‘45.147.228.0 – 45.147.231.255’
% Abuse contact for ‘45.147.228.0 – 45.147.231.255’ is ‘abuse@combahton.net’
inetnum: 45.147.228.0 – 45.147.231.255
netname: DE-COMBAHTON4-20190902
country: DE
org: ORG-CG252-RIPE
admin-c: JH29913-RIPE
tech-c: JH29913-RIPE
status: ALLOCATED PA
mnt-by: mnt-de-combahton4-1
mnt-by: RIPE-NCC-HM-MNT
mnt-lower: mnt-de-combahton4-1
mnt-routes: mnt-de-combahton4-1
created: 2019-09-02T09:46:42Z
last-modified: 2019-09-02T09:46:42Z
source: RIPE
organisation: ORG-CG252-RIPE
org-name: combahton GmbH
country: DE
org-type: LIR
address: Mitterfeld 47
address: 85419
address: Mauern
address: GERMANY
e-mail: decombahton4@combahton.net
admin-c: JH29913-RIPE
tech-c: JH29913-RIPE
abuse-c: AR55171-RIPE
mnt-ref: mnt-de-combahton4-1
mnt-by: RIPE-NCC-HM-MNT
mnt-by: mnt-de-combahton4-1
created: 2019-08-30T08:08:51Z
last-modified: 2020-12-16T13:30:44Z
source: RIPE
phone: +4987642589890
person: Joseph Hofmann
address: Mitterfeld 47
address: 85419
address: Mauern
address: GERMANY
phone: +4987642589890
nic-hdl: JH29913-RIPE
mnt-by: mnt-de-combahton4-1
created: 2019-08-30T08:08:51Z
last-modified: 2019-08-30T08:08:51Z
source: RIPE
% Information related to ‘45.147.228.0/22AS30823’
route: 45.147.228.0/22
origin: AS30823
mnt-by: mnt-de-combahton4-1
created: 2019-09-02T09:57:36Z
last-modified: 2019-09-02T09:57:36Z
source: RIPE
| 45.147.231.77 | Connected_From | d5ac680e14b013e0624470da7f46e84809d00b59a7544f6a42b110cf0e29254e |
The C2 for Ants2Whale (D5AC680E14B013E0624470DA7F46E84809D00B59A7544F6A42B110CF0E29254E).
downloaderloadertrojan
| Name | Ants2WhaleHelper |
|---|---|
| Size | 69104 bytes |
| Type | Mach-O 64-bit x86_64 executable, flags:<NOUNDEFS|DYLDLINK|TWOLEVEL|BINDS_TO_WEAK|PIE> |
| MD5 | d4d1bcdfb67ee30303f30137db752b94 |
| SHA1 | 34e134d614a0d5b0e4d94d63336aa8b898b0b104 |
| SHA256 | bb430087484c1f4587c54efc75681eb60cf70956ef2a999a75ce7b563b8bd694 |
| SHA512 | eb9b518f95658c605b1bb3a548d7bfe630f9bff93b1f84919476377f9aabcd187db28ead9bc504ffd5c982a3985d12708888505f3d70fa5eaa046c5ebf567c31 |
| ssdeep | 1536:W1mJaIKMXBmyIZFED2enSoTVIV/3MpJy5T:XagpIsjnPTV03MpJy5T |
| Entropy | 4.831788 |
| Avira | OSX/Dldr.NukeSped.efijh |
|---|---|
| BitDefender | Trojan.MAC.Generic.105439 |
| ESET | a variant of OSX/TrojanDownloader.NukeSped.B trojan |
| Emsisoft | Trojan.MAC.Generic.105439 (B) |
| Ikarus | Trojan-Downloader.OSX.Nukesped |
| Lavasoft | Trojan.MAC.Generic.105439 |
| McAfee | OSX/Nukesped.h |
| Quick Heal | MacOS.Trojan.40149.GC |
| Symantec | OSX.Trojan.Gen |
| Zillya! | Downloader.NukeSped.OSX.13 |
No matches found.
No matches found.
| bb43008748… | Contained_Within | [Redacted] |
| bb43008748… | Connected_To | qnalytica.com |
This OSX sample was contained within Apple DMG installer “Ants2Whale.dmg.” Ants2WhaleHelper is similar to variants of AppleJeus. The Ants2WhaleHelper program contains the custom C++ “Barbeque” class for network communication as seen in the unioncryptoupater program. The C2 for this program is hxxps[:]//www[.]qnalytica.com/wp-rss.php.
command-and-control
Whois for qnalytica.com had the following information:
Registrar: ENOM INC
Creation Date: 2020-08-11
Registrar Registration Expiration Date: 2021-08-11
| qnalytica.com | Connected_From | bb430087484c1f4587c54efc75681eb60cf70956ef2a999a75ce7b563b8bd694 |
The domain qnalytica.com has a legitimately signed SSL certificate from cPanel. cPanel is a hosting platform and certificate authority which is a reseller for Sectigo. The domain is registered with NameCheap at the IP address 194.36.191.196 with ASN 60117.
| [Redacted] | Downloaded_By | ants2whale.com |
| [Redacted] | Contains | d5ac680e14b013e0624470da7f46e84809d00b59a7544f6a42b110cf0e29254e |
| [Redacted] | Contains | bb430087484c1f4587c54efc75681eb60cf70956ef2a999a75ce7b563b8bd694 |
| ants2whale.com | Downloaded | [Redacted] |
| d5ac680e14… | Contained_Within | [Redacted] |
| d5ac680e14… | Connected_To | 45.147.231.77 |
| 45.147.231.77 | Connected_From | d5ac680e14b013e0624470da7f46e84809d00b59a7544f6a42b110cf0e29254e |
| bb43008748… | Contained_Within | [Redacted] |
| bb43008748… | Connected_To | qnalytica.com |
| qnalytica.com | Connected_From | bb430087484c1f4587c54efc75681eb60cf70956ef2a999a75ce7b563b8bd694 |
CISA recommends that users and administrators consider using the following best practices to strengthen the security posture of their organization’s systems. Any configuration changes should be reviewed by system owners and administrators prior to implementation to avoid unwanted impacts.
Additional information on malware incident prevention and handling can be found in National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) Special Publication 800-83, “Guide to Malware Incident Prevention & Handling for Desktops and Laptops”.
CISA continuously strives to improve its products and services. You can help by answering a very short series of questions about this product at the following URL: https://us.cert.cisa.gov/forms/feedback/
What is a MIFR? A Malware Initial Findings Report (MIFR) is intended to provide organizations with malware analysis in a timely manner. In most instances this report will provide initial indicators for computer and network defense. To request additional analysis, please contact CISA and provide information regarding the level of desired analysis.
What is a MAR? A Malware Analysis Report (MAR) is intended to provide organizations with more detailed malware analysis acquired via manual reverse engineering. To request additional analysis, please contact CISA and provide information regarding the level of desired analysis.
Can I edit this document? This document is not to be edited in any way by recipients. All comments or questions related to this document should be directed to the CISA at 1-888-282-0870 or CISA Service Desk.
Can I submit malware to CISA? Malware samples can be submitted via three methods:
CISA encourages you to report any suspicious activity, including cybersecurity incidents, possible malicious code, software vulnerabilities, and phishing-related scams. Reporting forms can be found on CISA’s homepage at www.cisa.gov.
This article is contributed. See the original author and article here.
This report is provided “as is” for informational purposes only. The Department of Homeland Security (DHS) does not provide any warranties of any kind regarding any information contained herein. The DHS does not endorse any commercial product or service referenced in this bulletin or otherwise.
This document is marked TLP:WHITE–Disclosure is not limited. Sources may use TLP:WHITE when information carries minimal or no foreseeable risk of misuse, in accordance with applicable rules and procedures for public release. Subject to standard copyright rules, TLP:WHITE information may be distributed without restriction. For more information on the Traffic Light Protocol (TLP), see http://www.us-cert.gov/tlp.
This Malware Analysis Report (MAR) is the result of analytic efforts among the Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI), the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA), and the Department of Treasury (Treasury) to highlight the cyber threat to cryptocurrency posed by North Korea, formally known as the Democratic People’s Republic of Korea (DPRK), and provide mitigation recommendations. Working with U.S. government partners, FBI, CISA, and Treasury assess that Lazarus Group—which these agencies attribute to North Korean state-sponsored advanced persistent threat (APT) actors—is targeting individuals and companies, including cryptocurrency exchanges and financial service companies, through the dissemination of cryptocurrency trading applications that have been modified to include malware that facilitates theft of cryptocurrency.
This MAR highlights this cyber threat posed by North Korea and provides detailed indicators of compromise (IOCs) used by the North Korean government. The U.S. Government refers to malicious cyber activity by the North Korean government as HIDDEN COBRA. For more information on other versions of AppleJeus and recommended steps to mitigate this threat, see Joint Cybersecurity Advisory AA21-048A: AppleJeus: Analysis of North Korea’s Cryptocurrency Malware at https://www.us-cert.cisa.gov/ncas/alerts/AA21-048A.
There have been multiple versions of AppleJeus malware discovered since its initial discovery in August 2018. In most versions, the malware appears to be from a legitimate-looking cryptocurrency trading company and website, whereby an unsuspecting individual downloads a third-party application from a website that appears legitimate.
The U.S. Government has identified AppleJeus malware version—Dorusio—and associated IOCs used by the North Korean government in AppleJeus operations. Some information has been redacted from this report to preserve victim anonymity.
Dorusio, discovered in March 2020, is a legitimate-looking cryptocurrency trading software that is marketed and distributed by a company and website— Dorusio Wallet and dorusio[.]com, respectively—that appear legitimate. There are Windows and OSX versions of Dorusio Wallet. As of at least early 2020, the actual download links result in 404 errors. The download page has release notes with version revisions claiming to start with Version 1.0.0, which was released on April 15, 2019.
For a downloadable copy of IOCs, see: MAR-10322463-6.v1.stix.
[Redacted] (dorusio_osx_v2.1.0.dmg)
21afaceee5fab15948a5a724222c948ad17cad181bf514a680267abcce186831 (DorusioUpgrade.exe)
[Redacted] (dorusio_win_v2.1.0.msi)
78b56a1385f2a92f3c9404f71731088646aac6c2c84cc19a449976272dab418f (Dorusio.exe)
a0c461c94ba9f1573c7253666d218b3343d24bfa5d8ef270ee9bc74b7856e492 (Dorusio)
dcb232409c799f6ddfe4bc0566161c2d0b372db6095a0018e6059e34c2b79c61 (dorusio_upgrade)
dorusio.com
droppertrojan
| Name | dorusio_win_v2.1.0.msi |
|---|---|
| Size | 141426176 bytes |
| Type | Composite Document File V2 Document, Little Endian, Os: Windows, Version 10.0, MSI Installer, Security: 0, Code page: 1252, Number of Words: 2, Subject: Dorusio, Author: Dorusio Service Ltd, Name of Creating Application: Advanced Installer 14.5.2 build 83143, Template: ;1033, Comments: This installer database contains the logic and data required to install Dorusio., Title: Installation Database, Keywords: Installer, MSI, Database, Number of Pages: 200 |
| MD5 | [Redacted] |
| SHA1 | [Redacted] |
| SHA256 | [Redacted] |
| SHA512 | [Redacted] |
| ssdeep | [Redacted] |
| Entropy | [Redacted] |
No matches found.
No matches found.
No matches found.
| [Redacted] | Downloaded_By | dorusio.com |
| [Redacted] | Contains | 78b56a1385f2a92f3c9404f71731088646aac6c2c84cc19a449976272dab418f |
| [Redacted] | Contains | 21afaceee5fab15948a5a724222c948ad17cad181bf514a680267abcce186831 |
This Windows program from the Dorusio Wallet site is a Windows MSI Installer. This installer appears to be legitimate and will install “Dorusio.exe” (78b56a1385f2a92f3c9404f71731088646aac6c2c84cc19a449976272dab418f) in the “C:Program Files (x86)Dorusio” folder. It will also install “DorusioUpgrade.exe” (21afaceee5fab15948a5a724222c948ad17cad181bf514a680267abcce186831) in the “C:Users<username>AppDataRoamingDorusioSupport” folder. Immediately after installation, the installer launches “DorusioUpgrade.exe.” During installation, a Dorusio folder containing the “Dorusio.exe” application is added to the start menu.
Figure 1 – Screenshot of the Dorusio Wallet installation.
command-and-control
Whois for dorusio.com had the following information:
Registrar: NAMECHEAP INC
Creation Date: 2020-03-30
Registrar Registration Expiration Date: 2021-03-30
| dorusio.com | Connected_From | dcb232409c799f6ddfe4bc0566161c2d0b372db6095a0018e6059e34c2b79c61 |
| dorusio.com | Downloaded | [Redacted] |
| dorusio.com | Downloaded | [Redacted] |
The domain “dorusio.com” had a legitimately signed Sectigo SSL certificate, which was “Domain Control Validated” similar to the domain certificates for previous AppleJeus domain certificates. Investigation revealed the point of contact listed for verification was support[@]dorusio.com. No other contact information was available as the administrative or technical contact for the domain.
The domain is registered with NameCheap at the IP address 198.54.115.51 with ASN 22612. This IP is on the same ASN as the AppleJeus version 5 “CoinGoTrade” IP address.
Figure 2 – Screenshot of the Dorusio site.
Figure 3 – Screenshot of the Dorusio download page.
trojan
| Name | Dorusio.exe |
|---|---|
| Size | 97682432 bytes |
| Type | PE32+ executable (GUI) x86-64, for MS Windows |
| MD5 | 6c36c8efe2ec2b12f343537d214f45e8 |
| SHA1 | 69eb27395e8f23b592547b69fbaf19ad03d6a89a |
| SHA256 | 78b56a1385f2a92f3c9404f71731088646aac6c2c84cc19a449976272dab418f |
| SHA512 | e9e72322983315d7a99e104b0a36e6301b7c78b3e93fc33c03e2e74ea1d5423b852a23a87a8ecaadf33f73ceb03b306d953b197a13542ae436c6b039ec1c00a7 |
| ssdeep | 1572864:odJvugr82jf19dUM/1T8+1VJRukUhkmG:odhg6Pm |
| Entropy | 6.674758 |
No matches found.
No matches found.
| 97 | 1b60a6d35c872102f535ae6a3d7669fb7d55c43dc7e73354423fdcca01a955d6 |
|---|
| Compile Date | 2019-12-16 00:00:00-05:00 |
|---|---|
| Import Hash | bb1d46df79ee2045d0bc2529cf6c7458 |
| Company Name | BitPay |
| File Description | Dorusio |
| Internal Name | Dorusio |
| Legal Copyright | Copyright © 2020 BitPay |
| Product Name | Dorusio |
| Product Version | 2.1.0.0 |
| MD5 | Name | Raw Size | Entropy |
|---|---|---|---|
| f62420692d3492b34a0696beb92d52dc | header | 1024 | 2.991122 |
| 36430f041d87935dcb34adde2e7d625d | .text | 78234112 | 6.471421 |
| ee7e02e8e2958ff79f25c8fd8b7d33e5 | .rdata | 15596032 | 6.376243 |
| 65c59271f5c2bab26a7d0838e9f04bcf | .data | 262144 | 3.484705 |
| 00406f1d9355757d80cbf48242fdf344 | .pdata | 2768896 | 6.805097 |
| 6a6a225bfe091e65d3f82654179fbc50 | .00cfg | 512 | 0.195869 |
| 786f587a97128c401be15c90fe059b72 | .rodata | 6144 | 4.219562 |
| 9efa43af7b1faae15ffbd428d0485819 | .tls | 512 | 0.136464 |
| 60d3ea61d541c9be2e845d2787fb9574 | CPADinfo | 512 | 0.122276 |
| bf619eac0cdf3f68d496ea9344137e8b | prot | 512 | 0.000000 |
| fb5463e289f28642cc816a9010f32981 | .rsrc | 102912 | 4.766115 |
| fb3216031225fdb1902888e247009d0c | .reloc | 709120 | 5.476445 |
| Microsoft Visual C++ 8.0 (DLL) |
| 78b56a1385… | Contained_Within | [Redacted] |
This file is a 64-bit Windows executable contained within the Windows MSI Installer “dorusio_win_v2.1.0.msi.” When executed, “Dorusio.exe” loads a legitimate looking cryptocurrency wallet application with no signs of malicious activity. Aside from the “Dorusio” logo and two new services, the wallet appears to be the same as the AppleJeus version 4 “Kupay wallet.”
This application appears to be a modification of the opensource cryptocurrency wallet Copay, which is distributed by Atlanta based company BitPay. According to the website “bitpay.com,” “BitPay builds powerful, enterprise-grade tools for crypto acceptance and spending”.
In addition to application appearance being similar, a DNS request for “bitpay.com” is always sent out immediately after a DNS request for “dorusio.com” and the company listed for “Dorusio” is Bitpay.
In addition, the GitHub “Commit Hash” listed in the “Dorusio” application “638b2b1” is to a branch of Copay found at hxxps[:]//github.com/flean/copay-1.
Figure 4 – Screenshot of the Dorusio application.
Figure 5 – Screenshot of the “Dorusio.exe” file information.
trojan
| Name | DorusioUpgrade.exe |
|---|---|
| Size | 115712 bytes |
| Type | PE32+ executable (GUI) x86-64, for MS Windows |
| MD5 | 0f39312e8eb5702647664e9ae8502ceb |
| SHA1 | 7e64fb8ec24361406ed685719d8dedc7920791d5 |
| SHA256 | 21afaceee5fab15948a5a724222c948ad17cad181bf514a680267abcce186831 |
| SHA512 | 3362ef6d9c24814972c9b59f2e0b57b2c3acdb4d1dd8cd5a240359bf73ae953116ef9b8d217a817ce985ca22b3bcfe01c1085b5e707a36e93a7fae36f94bfc31 |
| ssdeep | 3072:LHOKVwaew2/vN5z3bwe+F6s3yvMBhKBrF:TjwaewcPz3Me+33UF |
| Entropy | 6.126094 |
| Ahnlab | Trojan/Win64.FakeCoinTrader |
|---|---|
| Avira | TR/NukeSped.xmawj |
| BitDefender | Trojan.GenericKD.34182499 |
| Cyren | W64/Trojan.ACZK-7741 |
| ESET | a variant of Win64/NukeSped.DE trojan |
| Emsisoft | Trojan.GenericKD.34182499 (B) |
| Ikarus | Trojan.Win64.Nukesped |
| K7 | Trojan ( 00569b451 ) |
| Lavasoft | Trojan.GenericKD.34182499 |
| NetGate | Trojan.Win32.Malware |
| Symantec | Trojan.Gen.MBT |
| TACHYON | Trojan/W64.APosT.115712.B |
| VirusBlokAda | Trojan.APosT |
| Zillya! | Trojan.NukeSped.Win64.104 |
No matches found.
No matches found.
| Compile Date | 2020-03-30 02:52:41-04:00 |
|---|---|
| Import Hash | 565005404f00b7def4499142ade5e3dd |
| MD5 | Name | Raw Size | Entropy |
|---|---|---|---|
| 7ad599057f9d62e659ad5265b6bf8c8e | header | 1024 | 2.724023 |
| 7b2cea9046657ec66f103b9b3f53453d | .text | 65536 | 6.457037 |
| 59a79bcabee5542c73040a87b4be2d4e | .rdata | 39936 | 5.085609 |
| dbf3b39f579f6cafbdf3960f0a87f5f9 | .data | 2560 | 1.851526 |
| a6f84d98a061c4cd7874a78606fff84f | .pdata | 4096 | 4.924567 |
| 9c5adf56a571e84dc0c7329a768be170 | .gfids | 512 | 1.326857 |
| c7e574f00528a7e39d594132f836e2ca | .reloc | 2048 | 4.763069 |
| Microsoft Visual C++ 8.0 (DLL) |
| 21afaceee5… | Contained_Within | [Redacted] |
This file is a 64-bit Windows executable contained within the Windows MSI Installer “dorusio_win_v2.1.0.msi.” When executed, “DorusioUpgrade.exe” first installs itself as a service, which will automatically start when any user logs on. The service is installed with a description of “Automatic Dorusio Upgrade.”
After installing the service, “DorusioUpgrade.exe” has similar behavior to the upgrade components of Kupay Wallet (AppleJeus variant 4) and CoinGoTrade (AppleJeus variant 5). On startup, “DorusioUpgrade.exe” allocates memory in order to later write a file. After allocating the memory and storing the hardcoded string “Latest” in a variable, the program attempts to open a network connection. The connection is named “Dorusio Wallet 2.1.0 (Check Update Windows)”, likely to avoid suspicion from a user.
Similar to previous AppleJeus variants, “DorusioUpgrade.exe” collects some basic information from the system as well as a timestamp and places them in hard-coded format strings. Specifically, the timestamp is placed into a format string “ver=%d×tamp=%lu” where ver is set as the 201000, possibly referring to the Dorusio Wallet version previously mentioned (Figure 5).
This basic information and hard-coded strings are sent via a POST to the command and control (C2) “dorusio.com/dorusio_update.php.” If the POST is successful (i.e. returns an HTTP response status code of 200) but fails any of multiple different checks, “DorusioUpgrade.exe” will sleep for two minutes and then regenerate the timestamp and contact the C2 again.
After receiving the payload from the C2, the program writes the payload to memory and executes the payload.
The payload could not be downloaded as the C2 server dorusio.com/dorusio_update.php is no longer accessible. In addition, the sample was not identified in open source reporting for this sample.
Figure 6 – Screenshot of the format string and version.
droppertrojan
| Name | dorusio_osx_v2.1.0.dmg |
|---|---|
| Size | [Redacted] bytes |
| Type | zlib compressed data |
| MD5 | [Redacted] |
| SHA1 | [Redacted] |
| SHA256 | [Redacted] |
| SHA512 | [Redacted] |
| ssdeep | [Redacted] |
| Entropy | [Redacted] |
No matches found.
No matches found.
No matches found.
| [Redacted] | Downloaded_By | dorusio.com |
This OSX program from the Dorusio Wallet site is an Apple DMG installer. The OSX program does not has a digital signature and will warn the user of that before installation. As all previous versions of AppleJeus, the Dorusio Wallet installer appears to be legitimate, and installs both “Dorusio” (a0c461c94ba9f1573c7253666d218b3343d24bfa5d8ef270ee9bc74b7856e492) in the “/Applications/Dorusio.app/Contents/MacOS/” folder and a program named “dorusio_upgrade” (dcb232409c799f6ddfe4bc0566161c2d0b372db6095a0018e6059e34c2b79c61) also in the “/Applications/Dorusio.app/Contents/MacOS/” folder. The installer contains a postinstall script (Figure 7).
The postinstall script is identical in functionality to the postinstall scripts from previous AppleJeus variants and is identical to the CoinGoTrade (version 5) postinstall script. The postinstall script creates a “DorusioDaemon” folder in the OSX “/Library/Application Support” folder and moves “dorusio_upgrade” to it. The “Application Support” folder contains both system and third-party support files which are necessary for program operation. Typically, the subfolders have names matching those of the actual applications. At installation, Dorusio placed the plist file (com.dorusio.pkg.wallet.plist) in “/Library/LaunchDaemons/.”
As the LaunchDaemon will not be run immediately after the plist file is moved, the postinstall script then launches the dorusio_upgrade program in the background.
Figure 7 – Screenshot of the postinstall script.
Figure 8 – Screenshot of “com.dorusio.pkg.wallet.plist.”
trojan
| Name | Dorusio |
|---|---|
| Size | 186044 bytes |
| Type | Mach-O 64-bit x86_64 executable, flags:<NOUNDEFS|DYLDLINK|TWOLEVEL|PIE> |
| MD5 | 4a43bafb4af0a038a7f430417bcc1b6e |
| SHA1 | 438243575764a5e856951126674f72f20b2a0d6f |
| SHA256 | a0c461c94ba9f1573c7253666d218b3343d24bfa5d8ef270ee9bc74b7856e492 |
| SHA512 | 51d37b27f390bc7f124f2cb8efb2b9c940d7a0c21b0912d06634f7f6af46a35e3221d25945bcad4b39748699ba8a33b17c350a480560e5c5cc09dffa84c54df0 |
| ssdeep | 3072:RiD/8kxClwjnLFycZ+xzknUapR+Nghc1VeY1HhNGKBqzoJGUNKFsJuMuixQdf:RiDUSyQnLFycZ+a8yhUVeY1LngzofKFF |
| Entropy | 6.083001 |
No matches found.
No matches found.
No matches found.
This OSX sample was contained within Apple DMG installer “dorusio_osx_v2.1.0.dmg.” Similar to the Windows version, “Dorusio” is likely a copy of Copay from BitPay and is almost identical to the AppleJeus variant 4 OSX “Kupay” program.
trojan
| Name | dorusio_upgrade |
|---|---|
| Size | 33312 bytes |
| Type | Mach-O 64-bit x86_64 executable, flags:<NOUNDEFS|DYLDLINK|TWOLEVEL|PIE> |
| MD5 | d620c699a5b1828aca699b5aee77e5e6 |
| SHA1 | e769a810389f931b748bbe80742c427126c063a4 |
| SHA256 | dcb232409c799f6ddfe4bc0566161c2d0b372db6095a0018e6059e34c2b79c61 |
| SHA512 | 7bd98454d2a3fdd9d541dd0547c1f6a690b02b24495ce58324dd6377730f85a22f217173e178253dd8def989106702e87f7fa57223dde011439ed90db148eb18 |
| ssdeep | 192:fHck6do21hhIymPTzTQxkqMd+K2uk7DLOJ4eL:fHcNqghDmPTzTE |
| Entropy | 1.688205 |
| ESET | a variant of OSX/NukeSped.F trojan |
|---|
No matches found.
No matches found.
| dcb232409c… | Connected_To | dorusio.com |
This OSX sample was contained within Apple DMG installer “dorusio_osx_v2.1.0.dmg.” The program “dorusio_upgrade” is similar to AppleJeus variant 4 OSX sample “kupay_upgrade” and AppleJeus variant 5 OSX sample “CoinGoTradeUpgradeDaemon.”When executed, “dorusio_upgrade” immediately sleeps for five seconds then tests to see if the hard-coded value stored in “isReady” is a 0 or a 1. If it is a 0, the program sleeps again, and if it is a 1, the function “CheckUpdate” is called. This function contains most of the logic functionality of the malware. “CheckUpdate” sends a POST to the C2 hxxps[:]//dorusio.com/dorusio_update.php with a connection named “Dorusio Wallet 2.1.0 (Check Update Osx).
Just as the Kupay and CoinGoTrade malware, the timestamp is placed into a format string “ver=%d×tamp=%ld” where ver is set as the 20100, possibly referring to the Dorusio Wallet version previously mentioned.
If the C2 server returns a file, it is decoded and written to /private/tmp/dorusio_update,” with permissions by the command “chmod 700” (only the user can read, write, and execute). The stage2 (/private/tmp/dorusio_update) is then launched and the malware dorusio_upgrade returns to sleeping and checking in with the C2.
The payload could not be downloaded as the C2 server dorusio.com/dorusio_update.php is no longer accessible. In addition, the sample was not identified in open source reporting for this sample.
Figure 9 – Screenshot of the C2 loaded into the variable.
| [Redacted] | Downloaded_By | dorusio.com |
| [Redacted] | Contains | 78b56a1385f2a92f3c9404f71731088646aac6c2c84cc19a449976272dab418f |
| [Redacted] | Contains | 21afaceee5fab15948a5a724222c948ad17cad181bf514a680267abcce186831 |
| dorusio.com | Connected_From | dcb232409c799f6ddfe4bc0566161c2d0b372db6095a0018e6059e34c2b79c61 |
| dorusio.com | Downloaded | [Redacted] |
| dorusio.com | Downloaded | [Redacted] |
| 78b56a1385… | Contained_Within | [Redacted] |
| 21afaceee5… | Contained_Within | [Redacted] |
| [Redacted] | Downloaded_By | dorusio.com |
| dcb232409c… | Connected_To | dorusio.com |
CISA recommends that users and administrators consider using the following best practices to strengthen the security posture of their organization’s systems. Any configuration changes should be reviewed by system owners and administrators prior to implementation to avoid unwanted impacts.
Additional information on malware incident prevention and handling can be found in National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) Special Publication 800-83, “Guide to Malware Incident Prevention & Handling for Desktops and Laptops”.
CISA continuously strives to improve its products and services. You can help by answering a very short series of questions about this product at the following URL: https://us-cert.cisa.gov/forms/feedback/
What is a MIFR? A Malware Initial Findings Report (MIFR) is intended to provide organizations with malware analysis in a timely manner. In most instances this report will provide initial indicators for computer and network defense. To request additional analysis, please contact CISA and provide information regarding the level of desired analysis.
What is a MAR? A Malware Analysis Report (MAR) is intended to provide organizations with more detailed malware analysis acquired via manual reverse engineering. To request additional analysis, please contact CISA and provide information regarding the level of desired analysis.
Can I edit this document? This document is not to be edited in any way by recipients. All comments or questions related to this document should be directed to the CISA at 1-888-282-0870 or CISA Service Desk.
Can I submit malware to CISA? Malware samples can be submitted via three methods:
CISA encourages you to report any suspicious activity, including cybersecurity incidents, possible malicious code, software vulnerabilities, and phishing-related scams. Reporting forms can be found on CISA’s homepage at www.cisa.gov.
This article is contributed. See the original author and article here.
This report is provided “as is” for informational purposes only. The Department of Homeland Security (DHS) does not provide any warranties of any kind regarding any information contained herein. The DHS does not endorse any commercial product or service referenced in this bulletin or otherwise.
This document is marked TLP:WHITE–Disclosure is not limited. Sources may use TLP:WHITE when information carries minimal or no foreseeable risk of misuse, in accordance with applicable rules and procedures for public release. Subject to standard copyright rules, TLP:WHITE information may be distributed without restriction. For more information on the Traffic Light Protocol (TLP), see http://www.us-cert.gov/tlp.
This Malware Analysis Report (MAR) is the result of analytic efforts among the Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI), the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA), and the Department of Treasury (Treasury) to highlight the cyber threat to cryptocurrency posed by North Korea, formally known as the Democratic People’s Republic of Korea (DPRK), and provide mitigation recommendations. Working with U.S. government partners, FBI, CISA, and Treasury assess that Lazarus Group—which these agencies attribute to North Korean state-sponsored advanced persistent threat (APT) actors—is targeting individuals and companies, including cryptocurrency exchanges and financial service companies, through the dissemination of cryptocurrency trading applications that have been modified to include malware that facilitates theft of cryptocurrency.
This MAR highlights this cyber threat posed by North Korea and provides detailed indicators of compromise (IOCs) used by the North Korean government. The U.S. Government refers to malicious cyber activity by the North Korean government as HIDDEN COBRA. For more information on other versions of AppleJeus and recommended steps to mitigate this threat, see Joint Cybersecurity Advisory AA21-048A: AppleJeus: Analysis of North Korea’s Cryptocurrency Malware at https://www.us-cert.cisa.gov/ncas/alerts/AA21-048A.
There have been multiple versions of AppleJeus malware discovered since its initial discovery in August 2018. In most versions, the malware appears to be from a legitimate-looking cryptocurrency trading company and website, whereby an unsuspecting individual downloads a third-party application from a website that appears legitimate.
The U.S. Government has identified AppleJeus malware version—CoinGoTrade—and associated IOCs used by the North Korean government in AppleJeus operations.
CoinGoTrade discovered in October 2020, is a legitimate-looking cryptocurrency trading software that is marketed and distributed by a company and website—CoinGoTrade and coingotrade[.]com, respectively—that appear legitimate. Some information has been redacted from this report to preserve victim anonymity.
For a downloadable copy of IOCs, see: MAR-10322463-5.v1.stix.
326d7836d580c08cf4b5e587434f6e5011ebf2284bbf3e7c083a8f41dac36ddd (CoinGoTradeUpgradeDaemon)
[Redacted] (CoinGoTrade.msi)
3e5442440aea07229a1bf6ca2fdf78c5e2e5eaac312a325ccb49d45da14f97f4 (CoinGoTrade.exe)
527792dfab79f026eaa6930d2109c93e816ed31826dba0338a9223db71aced18 (CoinGo_Trade)
572a124f5665be68eaa472590f3ba75bf34b0ea2942b5fcbfd3e74654202dd09 (CoinGoTradeUpdate.exe)
5e40d106977017b1ed235419b1e59ff090e1f43ac57da1bb5d80d66ae53b1df8 (prtspool)
[Redacted] (CoinGoTrade.dmg)
airbseeker.com
coingotrade.com
globalkeystroke.com
woodmate.it
23.152.0.101
dropper
| Name | CoinGoTrade.msi |
|---|---|
| Size | [Redacted] bytes |
| Type | Composite Document File V2 Document, Little Endian, Os: Windows, Version 10.0, MSI Installer, Security: 0, Code page: 1252, Number of Words: 2, Subject: CoinGoTrade, Author: CoinGoTrade, Name of Creating Application: Advanced Installer 14.5.2 build 83143, Template: ;1033, Comments: This installer database contains the logic and data required to install CoinGoTrade., Title: Installation Database, Keywords: Installer, MSI, Database, Number of Pages: 200 |
| MD5 | [Redacted] |
| SHA1 | [Redacted] |
| SHA256 | [Redacted] |
| SHA512 | [Redacted] |
| ssdeep | [Redacted] |
| Entropy | [Redacted] |
| Avira | TR/NukeSped.lyfhd |
|---|
No matches found.
No matches found.
| [Redacted] | Downloaded_By | coingotrade.com |
| [Redacted] | Contains | 3e5442440aea07229a1bf6ca2fdf78c5e2e5eaac312a325ccb49d45da14f97f4 |
| [Redacted] | Contains | 572a124f5665be68eaa472590f3ba75bf34b0ea2942b5fcbfd3e74654202dd09 |
This Windows program from the CoinGoTrade site is a Windows MSI Installer. The installer appears to be legitimate and will install “CoinGoTrade.exe” (3e5442440aea07229a1bf6ca2fdf78c5e2e5eaac312a325ccb49d45da14f97f4) in the “C:Program Files (x86)CoinGoTrade” folder. It will also install “CoinGoTradeUpdate.exe” (572a124f5665be68eaa472590f3ba75bf34b0ea2942b5fcbfd3e74654202dd09) in the “C:Users<username>AppDataRoamingCoinGoTradeSupport” folder. Immediately after installation, the installer launches “CoinGoTradeUpdate.exe.” During installation, a “CoinGoTrade” folder containing the “CoinGoTrade.exe” application is added to the start menu.
Figure 1 – Screenshot of “CoinGoTrade” installation.
Whois for coingotrade.com had the following information:
Registrar: NAMECHEAP INC
Creation Date: 2020-02-28
Registrar Registration Expiration Date: 2021-02-28
| coingotrade.com | Downloaded | [Redacted] |
| coingotrade.com | Connected_From | 572a124f5665be68eaa472590f3ba75bf34b0ea2942b5fcbfd3e74654202dd09 |
| coingotrade.com | Downloaded | [Redacted] |
The domain “coingotrade.com” had a legitimately signed Sectigo Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) certificate, which was “Domain Control Validated,” similar to the domain certificates for previous AppleJeus variants. Investigation revealed the point of contact listed for verification was support[@]coingotrade.com. No other contact information was available as the administrative or technical contact for the coingotrade.com domain.
The domain is registered with NameCheap at the IP address 198.54.114.175 with ASN 22612.
Investigation revealed the IP address 198.54.114.175 was hosted at NameCheap, but no records were available at the time of writing.
Figure 2 – Screenshot of the “CoinGoTrade” website.
trojan
| Name | CoinGoTrade.exe |
|---|---|
| Size | 166912 bytes |
| Type | PE32 executable (GUI) Intel 80386 Mono/.Net assembly, for MS Windows |
| MD5 | 88de31ad947927004ab56ab1e855fd64 |
| SHA1 | 1d1f9f3ee8329c3f3033222a46c7a311f259a359 |
| SHA256 | 3e5442440aea07229a1bf6ca2fdf78c5e2e5eaac312a325ccb49d45da14f97f4 |
| SHA512 | 6e8391afc19ddfb841b79cc9b697fcd162d3a94a79976d3525476475d6fbe684ce9f2ba3a433cd725a51a71f6f74635a109914ff14252fac7e167a095ff1a890 |
| ssdeep | 3072:ssXh1ExFDi8z4C3Ssi5jCxe7IDYQFNY7BGMDK49eQ:sZRul5rLK4s |
| Entropy | 4.402659 |
| Ahnlab | Trojan/Win32.FakeCoinTrader |
|---|---|
| BitDefender | Gen:Variant.MSILHeracles.2293 |
| ESET | a variant of MSIL/Agent.TYJ trojan |
| Emsisoft | Gen:Variant.MSILHeracles.2293 (B) |
| Lavasoft | Gen:Variant.MSILHeracles.2293 |
No matches found.
No matches found.
| Compile Date | 2020-03-17 04:55:13-04:00 |
|---|---|
| Import Hash | f34d5f2d4577ed6d9ceec516c1f5a744 |
| File Description | CryptoMex |
| Internal Name | CoinGoTrade.exe |
| Legal Copyright | Copyright © 2020 |
| Original Filename | CoinGoTrade.exe |
| Product Name | CryptoMex |
| Product Version | 1.0.0.0 |
| MD5 | Name | Raw Size | Entropy |
|---|---|---|---|
| ebb11bbea122a2fc761dff1d05defdb0 | header | 512 | 2.714333 |
| b0d3ef9b5a227d092cf27c40c028d82d | .text | 40960 | 4.785436 |
| 35d28033f1f2359f265d8f406fc2c620 | .rsrc | 124928 | 4.154855 |
| 9d7ce3b9440143a341b9232fc0cb38ce | .reloc | 512 | 0.081539 |
| Microsoft Visual C# v7.0 / Basic .NET |
| 3e5442440a… | Contained_Within | [Redacted] |
| 3e5442440a… | Connected_To | 23.152.0.101 |
This file is a 32-bit Windows executable contained within the Windows MSI Installer “CoinGoTrade.msi.” When executed, “CoinGoTrade.exe” loads a legitimate looking cryptocurrency wallet application with no signs of malicious activity. The strings for “CoinGoTrade.exe” contain the command and control (C2) “hxxp[:]//23.152.0.101:8080/ which was also identified in the MacOS CoinGo_Trade (527792dfab79f026eaa6930d2109c93e816ed31826dba0338a9223db71aced18) and the Kupay Wallet Stage 2 from AppleJeus version 4. In addition, a build path is present in the strings “U:workCryptoMexteobotteobotobjReleaseCoinGoTrade.pdb” and the file properties description also states “CryptoMex.” CryptoMex is likely an open source cryptocurrency application which was copied in order to create this application.
Figure 3 – Screenshot of “CryptoMex” listed in CoinGoTrade.exe” properties.
command-and-control
Queried whois.arin.net with “n 23.152.0.101″…
NetRange: 23.152.0.0 – 23.152.0.255
CIDR: 23.152.0.0/24
NetName: CROWNCLOUD-V6V4
NetHandle: NET-23-152-0-0-1
Parent: NET23 (NET-23-0-0-0-0)
NetType: Direct Allocation
OriginAS: AS8100
Organization: Crowncloud US LLC (CUL-34)
RegDate: 2015-11-23
Updated: 2015-11-23
Comment: IPs in this block are statically assigned, please report any abuse to admin@crowncloud.us
Ref: https://rdap.arin.net/registry/ip/23.152.0.0
OrgName: Crowncloud US LLC
OrgId: CUL-34
Address: 530 W 6th St
Address: C/O Cid 4573 Quadranet Inc. Ste 901
City: Los Angeles
StateProv: CA
PostalCode: 90014-1207
Country: US
RegDate: 2014-07-25
Updated: 2017-10-10
Ref: https://rdap.arin.net/registry/entity/CUL-34
OrgTechHandle: CROWN9-ARIN
OrgTechName: Crowncloud Support
OrgTechPhone: +1-940-867-4072
OrgTechEmail: admin@crowncloud.us
OrgTechRef: https://rdap.arin.net/registry/entity/CROWN9-ARIN
OrgAbuseHandle: CROWN9-ARIN
OrgAbuseName: Crowncloud Support
OrgAbusePhone: +1-940-867-4072
OrgAbuseEmail: admin@crowncloud.us
OrgAbuseRef: https://rdap.arin.net/registry/entity/CROWN9-ARIN
| 23.152.0.101 | Connected_From | 3e5442440aea07229a1bf6ca2fdf78c5e2e5eaac312a325ccb49d45da14f97f4 |
| 23.152.0.101 | Connected_From | 527792dfab79f026eaa6930d2109c93e816ed31826dba0338a9223db71aced18 |
This IP address is the C2 for “CoinGoTrade.exe” and “CoinGo_Trade.”
trojan
| Name | CoinGoTradeUpdate.exe |
|---|---|
| Size | 115712 bytes |
| Type | PE32+ executable (GUI) x86-64, for MS Windows |
| MD5 | 149a696472d4a189f5896336ab16cc34 |
| SHA1 | decb43141699e43a1d27dc2db063e0020f9f33aa |
| SHA256 | 572a124f5665be68eaa472590f3ba75bf34b0ea2942b5fcbfd3e74654202dd09 |
| SHA512 | 32081f04a1b4a9540aad81a2a20c00c81ade40624dd446babebeb7230bb84025ba59516fab1388aad3fbf6842811ef2d8d6f0978950442c320edcd2bd8380847 |
| ssdeep | 3072:FHAqeXaeHx9pdpqw6IQIsMF6s3yv7pHOBo:FWXaeHxrvB6X9M33 |
| Entropy | 6.128250 |
| Ahnlab | Trojan/Win64.FakeCoinTrader |
|---|---|
| Avira | TR/NukeSped.ooibk |
| ESET | a variant of Win64/NukeSped.CR trojan |
| Ikarus | Trojan.Win64.Nukesped |
| K7 | Trojan ( 00567f291 ) |
| Symantec | Trojan.Gen.2 |
| TACHYON | Trojan/W64.APosT.115712 |
| Zillya! | Trojan.APosT.Win32.1433 |
No matches found.
| 94 | fc1aafd2ed190fa523e60c3d22b6f7ca049d97fc41c9a2fe987576d6b5e81d6d |
|---|
| Compile Date | 2020-03-17 21:02:52-04:00 |
|---|---|
| Import Hash | 565005404f00b7def4499142ade5e3dd |
| MD5 | Name | Raw Size | Entropy |
|---|---|---|---|
| d959d6ecb853f993046f81f109f7a5a9 | header | 1024 | 2.714314 |
| e350351a05606da16418a7f01436cd7d | .text | 65536 | 6.455927 |
| 5889779ac56e5fa9aa8123921d9ba943 | .rdata | 39936 | 5.084443 |
| dbf3b39f579f6cafbdf3960f0a87f5f9 | .data | 2560 | 1.851526 |
| 9b5c53415d33ef775d744a48f71fcd18 | .pdata | 4096 | 4.957426 |
| 90e2eb1b90616d039eca5e2627ea1134 | .gfids | 512 | 1.320519 |
| 3f1861d2a0b1dc2d1329c9d2b3353924 | .reloc | 2048 | 4.762609 |
| Microsoft Visual C++ 8.0 (DLL) |
| 572a124f56… | Contained_Within | [Redacted] |
| 572a124f56… | Connected_To | coingotrade.com |
This file is a 32-bit Windows executable contained within the Windows MSI Installer “CoinGoTrade.msi.” When executed, CoinGoTradeUpdate.exe will installs itself as a service, which will automatically start when any user logs on. The service is installed with the description of “Automatic CoinGoTrade Upgrade.”
After installing the service, “CoinGoTradeUpdate.exe” has similar behavior to the updater component for AppleJeus version 4 “Kupay Wallet.” On startup “CoinGoUpdate.exe” allocates memory to write a file. After allocating the memory and storing the hard-coded string “Latest” in a variable, the program attempts to open a network connection. The connection is named “CoinGoTrade 1.0 (Check Update Windows),” which is likely to avoid suspicion from a user.
Similarly, to previous AppleJeus variants, “CoinGoTradeUpdate.exe” collects some basic information from the system as well as a timestamp, and places the collected information in hard-coded format strings. Specifically, the timestamp is placed into a format string “ver=%d×tamp=%lu” where “ver” is set as the 1000, possibly referring to the CoinGoTrade version previously mentioned. This basic information and hard-coded strings are sent via a POST to the C2 “coingotrade.com/update_coingotrade.php.” If the POST is successful (i.e. returns an HTTP response status code of 200) but fails any of multiple different checks, “CoinGoTradeUpdate.exe” will sleep for two minutes and then regenerate the timestamp and contact the C2 again.
After receiving the payload from the C2, the program writes the payload to memory and executes the payload.
The payload for the Windows malware could not be downloaded, as the C2 server “coingotrade.com/coingotrade_update.php” was no longer accessible. In addition, the sample was not identified in open source reporting for this sample. The Windows payload is likely similar in functionality to “prtspool” (5e40d106977017b1ed235419b1e59ff090e1f43ac57da1bb5d80d66ae53b1df8) the OSX stage 2 sample.
Figure 4 – Screenshot of the format string and version.
droppertrojan
| Name | CoinGoTrade.dmg |
|---|---|
| Size | [Redacted] bytes |
| Type | zlib compressed data |
| MD5 | [Redacted] |
| SHA1 | [Redacted] |
| SHA256 | [Redacted] |
| SHA512 | [Redacted] |
| ssdeep | [Redacted] |
| Entropy | [Redacted] |
No matches found.
No matches found.
No matches found.
| [Redacted] | Downloaded_By | coingotrade.com |
| [Redacted] | Contains | 527792dfab79f026eaa6930d2109c93e816ed31826dba0338a9223db71aced18 |
| [Redacted] | Contains | 326d7836d580c08cf4b5e587434f6e5011ebf2284bbf3e7c083a8f41dac36ddd |
This OSX program from the CoinGoTrade site is an Apple DMG installer. The installer was hosted at hxxps[:]//coingotrade.com/[GUID]. The [GUID] is a unique file that is crafted for a specific victim and is being withheld to preserve the identity of the intended recipient. The OSX program is an Apple DMG installer with the file name CoinGoTrade.dmg.
The OSX program does not have a digital signature and will warn the user of that before installation. As all previous versions of AppleJeus, the CoinGoTrade installer appears to be legitimate and installs both “CoinGo_Trade” (527792dfab79f026eaa6930d2109c93e816ed31826dba0338a9223db71aced18) in the “/Applications/CoinGoTrade.app/Contents/MacOS/” folder and a program named “CoinGoTradeUpgradeDaemon” (326d7836d580c08cf4b5e587434f6e5011ebf2284bbf3e7c083a8f41dac36ddd) also in the “/Applications/CoinGoTrade.app/Contents/MacOS/” folder. The installer contains a postinstall script (Figure 5).
The postinstall script is identical in functionality to the postinstall scripts from previous AppleJeus variants and is identical to the AppleJeus variant 4 “Kupay” postinstall script without the “launchctl” command. The postinstall script creates a “CoinGoTradeService” folder in the OSX “/Library/Application Support” folder and moves “CoinGoTradeUpgradeDaemon” to it. The “Application Support” folder contains both system and third-party support files which are necessary for program operation. Typically, the subfolders have names matching those of the actual applications. At installation, CoinGoTrade placed the plist file (com.coingotrade.pkg.product.plist) in “/Library/LaunchDaemons/.”
As the LaunchDaemon will not be run immediately after the plist file is moved, the postinstall script then launches the “CoinGoTradeUpgradeDaemon” program in the background.
Figure 5 – Screenshot of the postinstall script.
Figure 6 – Screenshot of “com.coingotrade.pkg.product.plist.”
trojan
| Name | CoinGo_Trade |
|---|---|
| Size | 49536 bytes |
| Type | Mach-O 64-bit x86_64 executable, flags:<NOUNDEFS|DYLDLINK|TWOLEVEL|PIE> |
| MD5 | 7a73178c682d1a61b2f1c61ae558b608 |
| SHA1 | 358f4c8575c82f45340886f282d41ca0560cfa6e |
| SHA256 | 527792dfab79f026eaa6930d2109c93e816ed31826dba0338a9223db71aced18 |
| SHA512 | bb044103c9d2abd04b06a7bae31215302e8310ef5e815ee15025b430b9ea230c7246c96769b2f03a614e1d196ab9bbdf9d3b49980d1b282f58d3823b510ce990 |
| ssdeep | 384:O6XCYcjaTtLXN8KzIBAsyDfpBkSp6nHYYAZvamQ5nT:O6XZnRNnzICsyuHYrBxgn |
| Entropy | 3.472034 |
No matches found.
No matches found.
No matches found.
| 527792dfab… | Contained_Within | [Redacted] |
| 527792dfab… | Connected_To | 23.152.0.101 |
This OSX sample was contained within Apple DMG installer “CoinGoTrade.dmg.” “CoinGo _Trade” is likely a copy of an open source cryptocurrency application. The strings for “CoinGo_Trade” contain the C2 hxxp[:]//23.152.0.101:8080, which is also found in the Windows CoinGoTrade.exe (3e5442440aea07229a1bf6ca2fdf78c5e2e5eaac312a325ccb49d45da14f97f4) and the Kupay Wallet Stage 2 from AppleJeus version 4.
backdoortrojan
| Name | CoinGoTradeUpgradeDaemon |
|---|---|
| Size | 33312 bytes |
| Type | Mach-O 64-bit x86_64 executable, flags:<NOUNDEFS|DYLDLINK|TWOLEVEL|PIE> |
| MD5 | 0d195513534855e613bd7a29243565ab |
| SHA1 | 80923c208c2c821ed99e1ed8f50bd549598a210c |
| SHA256 | 326d7836d580c08cf4b5e587434f6e5011ebf2284bbf3e7c083a8f41dac36ddd |
| SHA512 | d4c822252c03523a3e37edf314caa5142be230e2c34e3f5b648a944b88632e6e74af41bc9c8661c608fdff19822c590f6f98d41dc524385be3092af42936f30f |
| ssdeep | 192:fWkPKt21UIIymPTTDO/kqMd+K2uk6aLc4eL:fWIogUKmPTT8 |
| Entropy | 1.690330 |
| Ahnlab | Trojan/OSX64.FakeCoinTrader.33313 |
|---|---|
| Antiy | Trojan/Mac.NukeSped |
| Avira | OSX/NukeSped.ifaaj |
| BitDefender | Gen:Variant.Trojan.MAC.Lazarus.4 |
| ClamAV | Osx.Malware.Agent-8010705-0 |
| ESET | a variant of OSX/NukeSped.F trojan |
| Emsisoft | Gen:Variant.Trojan.MAC.Lazarus.4 (B) |
| Ikarus | Trojan.OSX.Nukesped |
| Lavasoft | Gen:Variant.Trojan.MAC.Lazarus.4 |
| McAfee | OSX/Lazarus.c |
| Microsoft Security Essentials | Trojan:MacOS/NukeSped.D!MTB |
| Quick Heal | Mac.Backdoor.38173.GC |
| Sophos | OSX/NukeSped-AG |
| Symantec | OSX.Trojan.Gen |
| TrendMicro | TROJ_FR.84D8D3BE |
| TrendMicro House Call | TROJ_FR.84D8D3BE |
| Zillya! | Trojan.NukeSped.OSX.7 |
No matches found.
No matches found.
| 326d7836d5… | Contained_Within | [Redacted] |
This OSX sample was contained within Apple DMG installer “CoinGoTrade.dmg.” “CoinGoTradeUpgradeDaemon” is similar to “kupay_upgrade” from AppleJeus version 4. When executed, “CoinGoTradeUpgradeDaemon” will immediately sleep for five seconds and then test to see if the hard-coded value stored in “isReady” is a 0 or a 1. If it is a 0, the program sleeps again and if it is a 1, the function “CheckUpdate” is called. This function contains most of the logic functionality of the malware. “CheckUpdate” sends a POST to the C2 hxxps[:]//coingotrade.com/update_coingotrade.php with a connection named “CoinGoTrade 1.0 (Check Update Osx).
If the C2 server returns a file, it is decoded and written to “/private/tmp/updatecoingotrade” and the permissions are set with the command “chmod” 700 (only the user can read, write, and execute). The stage 2 malware (/private/tmp/updatecoingotrade) is then launched and the malware “CoinGoTradeUpgradeDaemon” returns to sleeping and checking in with the C2 server.
The stage 2 payload for CoinGoTrade was no longer available from the specified download URL, however, there was a file “prtspool” (5e40d106977017b1ed235419b1e59ff090e1f43ac57da1bb5d80d66ae53b1df8) submitted to VirusTotal by the same user on the same date as “CoinGoTradeUpgradeDaemon.” This suggests the submitted file may be related to the OSX malware and could be the downloaded payload. Analysis by Crowdstrike showed the file has the same encryption algorithm and initial key values as a Lazarus Group implant known as HOPLIGHT or MANUSCRYPT.
Figure 7 – Screenshot of the C2 loaded into variable.
Figure 8 – Screenshot of the format string.
backdoortrojan
| Name | prtspool |
|---|---|
| Size | 57376 bytes |
| Type | Mach-O 64-bit x86_64 executable, flags:<NOUNDEFS|DYLDLINK|TWOLEVEL|BINDS_TO_WEAK|PIE> |
| MD5 | 451c23709ecd5a8461ad060f6346930c |
| SHA1 | 58b0516d28bd7218b1908fb266b8fe7582e22a5f |
| SHA256 | 5e40d106977017b1ed235419b1e59ff090e1f43ac57da1bb5d80d66ae53b1df8 |
| SHA512 | 80961db270b9f15cff4b0443be79b253e0f98304990fceda03cd2b25393b0e483eacc553e7b33d20da23e3317fafc7b41f93c4a9da863b99c8f5d3c642d036c8 |
| ssdeep | 768:qQS5bSXXUkVSpVM0ZJflKprXYgICxdAvV/hQJx62:gbGkjZ7KbICY/hQJx6 |
| Entropy | 4.259743 |
| Antiy | Trojan[Backdoor]/OSX.NukeSped |
|---|---|
| Avira | OSX/NukeSped.vhsxo |
| BitDefender | Trojan.MAC.Generic.12195 |
| ClamAV | Osx.Malware.Agent-8019494-0 |
| ESET | a variant of OSX/NukeSped.E trojan |
| Emsisoft | Trojan.MAC.Generic.12195 (B) |
| Ikarus | Trojan.OSX.Nukesped |
| Lavasoft | Trojan.MAC.Generic.12195 |
| McAfee | OSX/Nukesped.e |
| Quick Heal | Mac.Backdoor.38173.GC |
| Sophos | OSX/NukeSped-AF |
| Symantec | OSX.Trojan.Gen |
| TrendMicro | TROJ_FR.84D8D3BE |
| TrendMicro House Call | TROJ_FR.84D8D3BE |
| Zillya! | Trojan.NukeSped.OSX.14 |
No matches found.
No matches found.
| 5e40d10697… | Connected_To | airbseeker.com |
| 5e40d10697… | Connected_To | globalkeystroke.com |
| 5e40d10697… | Connected_To | woodmate.it |
This file is a OSX samples that was likely the payload for the sample “CoinGoTradeUpgradeDaemon.”This file “prtspool” is a 64-bit MACHO executable with the following capabilities:
–Begin capabilities–
Perform a heart-beat check in with the current C2
Sleep for the specified number of minutes
Ensure a copy of the current configuration data is written to the file on disk
Delete the configuration file and exit the implant.
Upload the current in memory configuration data.
Download a new configuration, overwrite the current in memory configuration and write the data to the file /private/etc/krb5d.conf
Perform a secure delete or file wipe the specified file by overwriting it with all zeros before deleting it from the system.
Download a file from the C2 and write it to the specified path.
Upload a file from the specified file to the C2 server.
Execute the specified command on the OS shell, pipe the output to a temporary file, and upload it to the C2.
Execute the specified process.
List the files and directories in the specified path.
Perform a TCP connection to the specified IP address and port and report the status back to the C2.
Set the current working directory to the specified path.
–End capabilities–
The file has three C2 URLs hard-coded into the file. In communicating with these servers, the file uses an HTTP POST with multipart-form data boundary string “–N9dLfqxHNUUw8qaUPqggVTpX.” Similar to other Lazarus malware, “prtspool” uses format strings to store data collected about the system and sends it to the C2s.
–Begin C2 URLs–
hxxps[:]//airbseeker.com/rediret.php
hxxps[:]//globalkeystroke.com/pockbackx.php
hxxps[:]//www[.]woodmate.it/administrator/help/en-GB/bins/tags/taghelper.php.
–End C2 URLs–
command-and-control
Whois for airbseeker.com had the following information:
Registrar: NAMECHEAP INC
Created: 2020-03-03
Expires: 2021-03-03
| airbseeker.com | Connected_From | 5e40d106977017b1ed235419b1e59ff090e1f43ac57da1bb5d80d66ae53b1df8 |
The domain “airbseeker.com” has a legitimately signed Sectigo SSL certificate, which was “Domain Control Validated.” The domain was at the IP address 68.65.122.160 with ASN 22612.
command-and-control
Whois for globalkeystroke.com had the following information:
Registrar: NAMECHEAP INC
Created: 2019-11-11
Expires: 2020-11-11
| globalkeystroke.com | Connected_From | 5e40d106977017b1ed235419b1e59ff090e1f43ac57da1bb5d80d66ae53b1df8 |
The domain “globalkeystroke.com” has a legitimately signed Sectigo SSL certificate, which was “Domain Control Validated.” Investigation revealed the point of contact listed for verification was admin[@]globalkeystroke.com. No other contact information was available as the administrative or technical contact for the globalkeystroke.com domain.
The domain is registered with NameCheap at the IP address 68.65.122.160 with ASN 22612. The IP address of 185.228.83.129 belongs to Access2.it Group B.v. ISP of the Netherlands. Whois information for the IP revealed the network name as belonging to CrownCloud of Australia.
On October 11, 2019, the IP address 185.228.83.129 was hosting the domain dev.jmttrading.org according to PassiveDNS. JMT Trading was the second variant of the AppleJeus malware.
command-and-control
Whois for woodmate.it had the following information:
Registrar: REGISTRYGATE GMBH
Created: 2014-05-07
Expires: 2020-05-07
| woodmate.it | Connected_From | 5e40d106977017b1ed235419b1e59ff090e1f43ac57da1bb5d80d66ae53b1df8 |
The domain “woodmate.it” has a legitimately signed Let’s Encrypt certificate. Let’s Encrypt is a nonprofit Certificate Authority which provides free and automated TLS/SSL certificates for anyone running their software. They do not perform any identity validation.
The domain is registered with RegistryGate GMBH of Germany at the IP address 85.13.146.113 with ASN 34788.
The IP address 85.13.146.113 is hosted by Neue Medien Muennich Gmbh of Germany.
| [Redacted] | Downloaded_By | coingotrade.com |
| [Redacted] | Contains | 3e5442440aea07229a1bf6ca2fdf78c5e2e5eaac312a325ccb49d45da14f97f4 |
| [Redacted] | Contains | 572a124f5665be68eaa472590f3ba75bf34b0ea2942b5fcbfd3e74654202dd09 |
| coingotrade.com | Downloaded | [Redacted] |
| coingotrade.com | Connected_From | 572a124f5665be68eaa472590f3ba75bf34b0ea2942b5fcbfd3e74654202dd09 |
| coingotrade.com | Downloaded | [Redacted] |
| 3e5442440a… | Contained_Within | [Redacted] |
| 3e5442440a… | Connected_To | 23.152.0.101 |
| 23.152.0.101 | Connected_From | 3e5442440aea07229a1bf6ca2fdf78c5e2e5eaac312a325ccb49d45da14f97f4 |
| 23.152.0.101 | Connected_From | 527792dfab79f026eaa6930d2109c93e816ed31826dba0338a9223db71aced18 |
| 572a124f56… | Contained_Within | [Redacted] |
| 572a124f56… | Connected_To | coingotrade.com |
| [Redacted] | Downloaded_By | coingotrade.com |
| [Redacted] | Contains | 527792dfab79f026eaa6930d2109c93e816ed31826dba0338a9223db71aced18 |
| [Redacted] | Contains | 326d7836d580c08cf4b5e587434f6e5011ebf2284bbf3e7c083a8f41dac36ddd |
| 527792dfab… | Contained_Within | [Redacted] |
| 527792dfab… | Connected_To | 23.152.0.101 |
| 326d7836d5… | Contained_Within | [Redacted] |
| 5e40d10697… | Connected_To | airbseeker.com |
| 5e40d10697… | Connected_To | globalkeystroke.com |
| 5e40d10697… | Connected_To | woodmate.it |
| airbseeker.com | Connected_From | 5e40d106977017b1ed235419b1e59ff090e1f43ac57da1bb5d80d66ae53b1df8 |
| globalkeystroke.com | Connected_From | 5e40d106977017b1ed235419b1e59ff090e1f43ac57da1bb5d80d66ae53b1df8 |
| woodmate.it | Connected_From | 5e40d106977017b1ed235419b1e59ff090e1f43ac57da1bb5d80d66ae53b1df8 |
CISA recommends that users and administrators consider using the following best practices to strengthen the security posture of their organization’s systems. Any configuration changes should be reviewed by system owners and administrators prior to implementation to avoid unwanted impacts.
Additional information on malware incident prevention and handling can be found in National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) Special Publication 800-83, “Guide to Malware Incident Prevention & Handling for Desktops and Laptops”.
CISA continuously strives to improve its products and services. You can help by answering a very short series of questions about this product at the following URL: https://us-cert.cisa.gov/forms/feedback/
What is a MIFR? A Malware Initial Findings Report (MIFR) is intended to provide organizations with malware analysis in a timely manner. In most instances this report will provide initial indicators for computer and network defense. To request additional analysis, please contact CISA and provide information regarding the level of desired analysis.
What is a MAR? A Malware Analysis Report (MAR) is intended to provide organizations with more detailed malware analysis acquired via manual reverse engineering. To request additional analysis, please contact CISA and provide information regarding the level of desired analysis.
Can I edit this document? This document is not to be edited in any way by recipients. All comments or questions related to this document should be directed to the CISA at 1-888-282-0870 or CISA Service Desk.
Can I submit malware to CISA? Malware samples can be submitted via three methods:
CISA encourages you to report any suspicious activity, including cybersecurity incidents, possible malicious code, software vulnerabilities, and phishing-related scams. Reporting forms can be found on CISA’s homepage at www.cisa.gov.
Recent Comments